1. Introduction
Cheminformatics is a relatively recent discipline of information technology that focuses on chemical data gathering, storage, analysis, and reorganization. Small molecule formulae, structures, characteristics, spectra, and activities (biological or industrial) are typical examples of chemical data of interest. Cheminformatics began as a tool to aid in the drug discovery and development process, but it is now playing an increasingly essential role in many fields of biology, chemistry, and biochemistry. [
1]
The identification of hits is the first and most important stage in small-molecule drug discovery [
2]. The computer development of virtual chemical libraries to be utilized in various virtual screening procedures is one strategy to increasing the chance of identifying new hit chemicals. As a result, numerous academics are generating new de novo chemical libraries and "make-on-demand" libraries using various in silico methodologies. [
3]
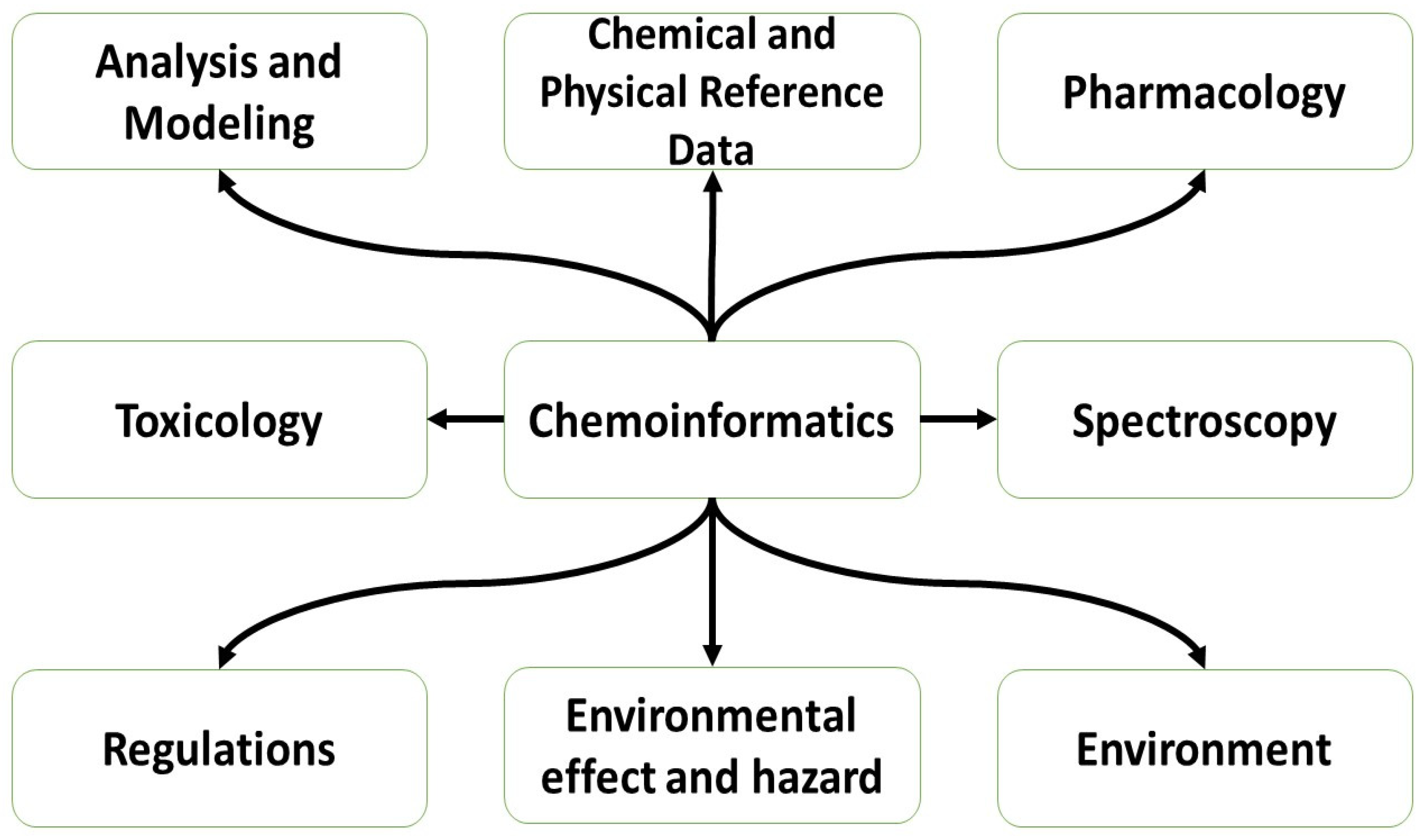
Figure 1.
Chemoinformatics applications [
4].
Figure 1.
Chemoinformatics applications [
4].
In general, virtual libraries address the requirement to increase compound quality in order to effectively discover promising compounds. In this context, the size, structural complexity, and variety of virtual libraries are important factors in boosting the likelihood of a successful drug discovery and development outcome. Another key feature of creating virtual libraries is that the chemicals discovered have some originality and, most importantly, are synthetically viable. This technique is especially appealing for developing libraries for complex and emerging drug targets. [
5]
There are several methods for creating a virtual chemical compound. For example, employing a known reaction schema and readily available chemicals, de novo-based design, morphing/transformation, or painting a molecular graph. [
6]
Both metabolism and conveyance are important factors in determining a molecule's bioavailability and biological activity. Structured and high-quality experimental data kept in an appropriate container, such as a relational database, promote straightforward computer processing and hence allows computational analyses to effectively infer high-quality information/knowledge. Metrabase, an integrated cheminformatics and bioinformatics resource including curated data on human transport and metabolism of chemical substances, is an example of a database. Its major components consist of around 11,500 interaction records involving almost 3,500 small molecule substrates and modulators of transport proteins, as well as cytochrome P450 enzymes, which are now to a much lesser extent. [
7]
2. Materials and Methods
The following sources were considered in the current review: randomized controlled trials, controlled non-randomized clinical trials, retrospective and prospective comparative cohort studies, case studies, reviews, and systematic reviews.
A search strategy was constructed using medical subject headings (MeSH). The MeSH terms of chemoinformatics, bioinformatics, antimicrobial medications, and Egypt were used to systemically search PubMed, and MEDLINE databases. Only studies in the English language were included. All relevant publications from 2018 to 2023 were included. No limits regarding study design were set on the search. Duplicate studies were removed from our study pool. All included studies were scanned against inclusion and exclusion criteria. Our inclusion criteria primarily focused on published literature that assessed the recent advances of bio- and chemoinformatics in Egypt.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemoinformatics and New Tetracycline Analogue
Antimicrobial resistance to existing antibiotics indicates a critical global crossroads. [
8] Unfortunately, widespread antibiotic use has resulted in the emergence of multi-drug resistance pathogenic organisms and a reduction in the efficacy of many of our most potent antibiotics. [
9] In addition, we have recognized various harmful consequences of antibiotics, most notably the rising prevalence of Clostridium difficile inflammatory bowel disease. [
10]
Mechanism of bacterial resistance to tetracycline antibiotic includes mutations within the ribosome binding site or the acquisition of mobile genetic elements containing tetracycline-specific resistance genes. [
11]
Tetracycline serves as bacteriostatic against a wide range of microorganisms, including gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria, chlamydiae, mycoplasmas, and rickettsiae. [
12] They inhibit protein synthesis by binding to the 30S ribosomal subunit and preventing aminoacyl transfer RNA (tRNA) from accessing the acceptor site on the ribosome. [
13]
A research project was done in Egypt to design new antimicrobial tetracycline analogues and assess their in-vitro antibacterial properties. The in vitro antibacterial activity of a new tetracycline analogue generated semi-synthetically from Streptomyces species was investigated to determine the minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of growth of several harmful bacteria in Egypt. [
14]
Tetracycline was purified using aqueous two-phase systems made up of cholinium-based salts and polyethylene glycol, and then modified using chemoinformatics. The chemo-informatics approach was used to create tetracycline analogue B (iodocycline). This was accomplished by chemically modifying 6-deoxytetracycline at the C7 position with a strong electron-drawing anion such as Iodide anion (I-). Iodination was used to create aromatic iodocycline. The findings showed that iodocycline was more active as a bacteriostatic antibacterial agent than tetracycline. Moreover, it caused less bacterial resistance. In comparison to the chloramphenicol prototype antibiotic, tetracycline analogue B has MICs of less than 10 micrograms/ml for bacterial growth, indicating its potent antibacterial action. [
14]
3.2. Bioinformatics and Heart Disease Classification
For decades, heart disease, has been regarded as the main cause of mortality globally. According to the World Health Organization, 17.9 million people died as a result of heart disease in 2016. [
15] The death rate from heart disease can be lowered if the condition is detected early and warned of its presence. As a result, developing a method to enhance heart disease prediction and categorization is critical. Data mining technologies have been investigated in recent decades to enhance prediction processes in the medical area, where datasets have become available. [
16]
The practice of discovering hidden patterns, information, and anomalies in massive data sets is known as data mining. It is regarded as the central component of the Knowledge Discovery in Database (KDD) process, which includes a number of phases such as data preparation, data selection, data transformation, and data mining, which includes tasks such as prediction, classification, and clustering. [
17,
18]
A quantitative study conducted in Menofia University in Egypt reveals that using the ensemble model in conjunction with brute force as a feature selection strategy results in a top accuracy of 97.8% for heart disease classification. The suggested stacking model has demonstrated to be efficient and outperforms existing techniques in the categorization of cardiac disorders. [
19]
3.3. Bioinformatics and Diagnosis of COVID-19
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has placed many people's lives and health at danger. It has caused confusion in the global population's public life. As the number of cases increases, all countries are running out of resources to detect COVID-19. This needs the employment of a COVID-19 detection approach that is easily accessible, low-cost, and automated. [
20]
Due to the prevalent availability of radiology imaging equipment in hospitals, radiography-based detection methods offer a feasible solution for COVID-19 testing kit shortages. In recent years, machine and deep learning have become basic topics in artificial intelligence. [
21]
Deep learning techniques for COVID-19 detection and classification on an automated basis are being widely investigated. [
22] As a result, deep learning has emerged as a critical component of automated clinical decision-making. [
23]
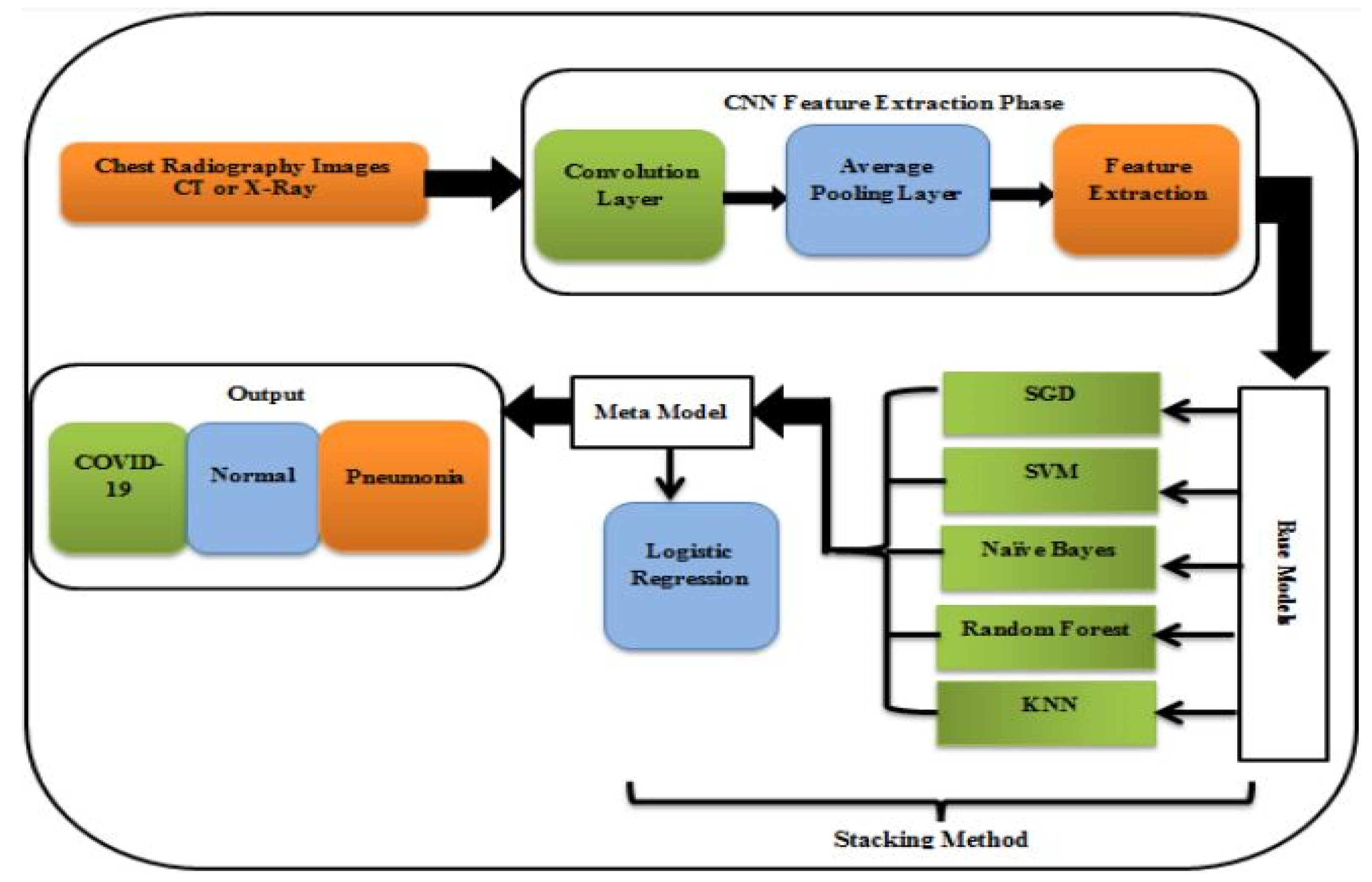
A study for the diagnosis of COVID-19 using Chest CT and Xray images provided multi-classifiers rather than a single classifier layered in an ensemble stacking manner. On two types of datasets, X-ray pictures and CT images, the findings showed a quantitative evaluation of the suggested ensemble stacking technique with percentages approaching 99%. [
24]
Figure 2.
Model for COVID-19 detection [
24].
Figure 2.
Model for COVID-19 detection [
24].
3.4. Bio- and Cheminformatics in Nose-to-brain Formulation Targeting Meningitis
Meningitis is a potentially fatal infection or inflammation of the meninges caused by a wide range of infectious pathogens. [
25] Viruses contribute for up to half of all cases, whereas fungi (usually cryptococci) account for less than 10% of all cases. [
26]
Bacterial meningitis is the most serious type of this illness. The etiologic agents that cause bacterial meningitis differ by age group. The majority of infections in newborns are caused by group B Streptococcus agalactiae, Escherichia coli, and Listeria monocytogenes. Although Haemophilus (H.) influenzae has been linked to bacterial meningitis in people of all ages, it is most common in children under the age of five. Despite the availability of antibiotics, acute bacterial meningitis is a major cause of morbidity and mortality. Survivors are at risk of long-term repercussions such as brain damage, hearing loss, and learning impairments. [
27]
Bio- and chemoinformatics methods were used to compare antimicrobial medications to choose an effective nose-to-brain formulation targeting meningitis by leveraging differences in the drugs' primary structural, topological, and electronic characteristics. Cephalosporin antibiotics cefotaxime and ceftriaxone were compared at three levels, which are formulation, biopharmaceutical, and therapeutic level. The formulation level includes comparing the loading in gelatin and tripalmitin matrices as bases for the formation of nanoparticulate systems. The biopharmaceutical level includes the interaction with mucin and the P-gp efflux pumps. The therapeutic level includes the interaction with S. pneumoniae bacterial receptors. All-atom molecular dynamics simulations were carried out using the GROMACS v4.6.5 software programme. Results showed that ceftriaxone has a higher affinity for the biopharmaceutical and therapeutic macromolecules studied than cefotaxime. [
28]
Cefotaxime and ceftriaxone docked successfully on mucin, P-gp efflux pump, and S. pneumoniae PBP1a and 2b, however, ceftriaxone had a stronger affinity for the P-gp efflux pump proteins and docked more successfully on mucin. On the gelatin and tripalmitin matrices, ceftriaxone showed decreased out-of-matrix diffusion and increased trapping. As a result, compared to cefotaxime equivalents, Ceftriaxone gelatin nanospheres or tripalmitin solid lipid nanoparticles may represent a more practical and efficient nose-to-brain formulation targeting meningitis. [
28]
3.5. Cheminformatics Application in Phytochemistry
Natural products are thought to be a promising source of antifibrotic medicines, however finding and isolating bioactive molecule(s) remains difficult. The good news is that various computational approaches have emerged in this subject to save time and effort.[
29]
Eucalyptus globulus Labill. is an evergreen tree of the Myrtaceae family that is grown all over the world. Several Eucalyptus species are planted as line plantings in Egypt and utilized for shade, building timbers, poles and fuelwood. The bark is one of the most important byproducts in the Eucalyptus business. Eucalyptus bark is thought to be an excellent source of phenolic chemicals with a variety of biological activity. [
30,
31]
Polyphenols have a variety of uses in the cosmetics, food, and pharmaceutical sectors. This group of chemicals has been shown to have antioxidant, antimicrobial, antidiabetic, anti-inflammatory, antihyperlipidemic, hepatoprotective, nephroprotective, cardioprotective, and anticancer properties. [
32]
A research work conducted in Egypt used numerous cheminformatics tools to investigate the chemical and biological properties of the bark of Eucalyptus globulus grown in Egypt. Sirius software was used to process liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry chemical profiling and forecast precise molecular formulas, chemical classifications, and structures with the use of web databases. As a result, 37 compounds were tentatively identified, with 15 of them being reported for the first time from this species. In addition, the Bio-Transformer tool was successfully used for an in silico virtual analysis of these chemicals' human metabolism, and 1960 distinct products were created via various metabolic pathways. [
29]
Moreover, an electronic library of the discovered chemicals and metabolites was created and docked in silico against eight distinct protein targets implicated in the fibrosis process of the liver. The findings suggest that the extract may have a hepatoprotective impact via many pathways and that the metabolites have higher binding affinities to the relevant enzymes than their parent chemicals. The extract had high cytotoxic activity against the liver cancer cell lines HEPG2 and HUH-7, and its absorption was improved by nano-formulation, as demonstrated by the ex vivo everted gut sac technique. [
29]
3.6. Chemoinformatics Targeting Cancer Cell Therapy
Carcinogenesis is a complicated process involving the interplay of various elements that results in a change in normal cell behaviour and the transformation of the cell into a cancerous state. [
33]
The best way to fight cancer is to thoroughly examine the different functions of the interacting components in the tumor microenvironment, as this analysis could lead to a better understanding of this unfavorable cell transformation and, as a result, the identification of potential molecular targets for early prognosis and antitumor drug discovery. [
34]
Epithelial cell transforming 2 (ECT2) is a putative oncogene that has been linked to the advancement of numerous human malignancies in recent investigations. Despite the increased interest in ECT2 in oncology-related papers, no comprehensive investigation has been conducted to combine and integrate the expression and oncogenic behavior of ECT2 in a panel of human malignancies. Using numerous databases, it was discovered that ECT2 might be used as a prognostic and immunological biomarker in a variety of human malignancies. Moreover, chemoinformatics was used to look for possible ECT2 inhibitors that might eventually be used as anticancer medicines. A study findings discovered that ECT2 was upregulated as mRNA and protein levels in a variety of human tumors, allowing for increased filtration of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC) and decreased the level of natural killer T (NKT) cells, resulting in a poor prognosis survival. Furthermore, the study looked for medicines that could both inhibit ECT2 and function as anticancer agents. [
35]
3.7. Bio- and Cheminformatics in Nose-to-brain Formulation for Treatment of Alzheimer Disease
Delivering drugs to the brain for the treatment of severe CNS illnesses like Alzheimer's has been a significant issue for pharmaceutical formulation research and development. This is due to the numerous defensive systems that defend the brain and present extremely difficult barriers for most medications to cross from the blood circulation to the brain extracellular matrix and reach the brain cells. Most notably, the blood-brain barrier (BBB) continues to be the primary defensive mechanism. [
36]
As a result, while directing medications to the brain poses a significant obstacle in the treatment of many CNS illnesses, a novel route of administration looked to be promising in tackling this problem. This is known as 'Nose-to-Brain' targeting. Recent investigations have shown that if the medication is delivered intranasally, a part of it can skip the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and enter the brain directly. This occurs via the olfactory and trigeminal nerve systems. [
37]
A research work proposes a novel approach to evaluating two bio-similar natural compounds, curcumin and bisdemethoxycurcumin (BDMC), in order to identify a possible nose-to-brain treatment for Alzheimer's disease. The comparison found that curcumin outperformed BDMC. Five novel analogues were also proposed, with diethoxybisdemethoxycurcumin being chosen as the best compound. This study proposed the virtual use of bio/chemo informatics tools as a dependable and cost-effective alternative to the time-consuming and resource-intensive wet-lab testing. [
38]
3.8. Bio- and Cheminformatics in Identification of novel Pyrazole and Benzimidazole based derivatives as penicillin-binding protein 2a (PBP2a) inhibitors
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA's) extensive resistance to the lactam class is linked to the features of the major component of this resistance mechanism, the "acquired" penicillin-binding protein 2a (PBP2a), which has an innate lower sensitivity to β-lactam inactivation. Its lower affinity is due to its preference for a closed active-site conformation, which is governed by allostery. [
39] PBP2a may cross-link the cell wall even in the presence of β-lactam antibiotics, whereas the other four native PBPs are inhibited. [
40]
A research work included ten pyrazole and benzimidazole-based compounds that were developed, synthesized, and tested as anti-MRSA drugs. These compounds were tested for antibacterial activity against two strains of Staphylococcus aureus: methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) ATTC6538 and MRSA USA300. The findings revealed that three of the compounds examined showed modest bactericidal efficacy against MSSA, MRSA, and vancomycin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (VRSA). Docking of these compounds into the allosteric region of PBP2a revealed binding patterns similar to the lead quinazolinone PBP2a inhibitors, indicating a similar mechanism of action. The current analysis identifies a viable candidate for further development as a possible PBP2a inhibitor against MRSA infection. [
41]
3.9. Bioinformatics and genomic correlation with clinical information and Disease state
Obesity research is very important for Egyptians since their country has one of the highest obesity rates. [
42] According to a 2016 survey, more than 30% of the Egyptian population is obese, with over half of all females (46%) fat, which is about double the scale of the problem among Egyptian males (22%). [
43] The majority of Egyptian women (66%) are overweight; in fact, Egyptian women of reproductive age had a 2.21 kg/m2 increase in BMI in just 10 years. [
44]
A recent PCR-based analysis concluded that the LEPR Gln223Arg, UCP2 G 866 A, and INSR exon 17 polymorphisms are associated with obesity in Egyptians, and that several of the risk variations are gender biased. [
45]
It was previously released two personal Egyptian whole genomes, and here nine female whole genome sequences with clinical information have been added to increase the genetic repository of Egyptian personal genomes. The results of research work conducted in 2021 that used an Illumina short-read sequencer-based investigation of the entire genomes of nine Egyptian women from various areas were presented. It was discovered that 12 SNPs were shared by the majority of the participants related to obesity and were concordant with their clinical diagnostic using 30x sequencing coverage. In addition, results showed that the mtDNA mutation A4282G is present in all of the samples and is linked to chronic progressive external ophthalmoplegia (CPEO). [
46]
3.10. Bioinformatics and Multiple Drug Resistant Escherichia coli (E. coli) isolation from Pediatric Cancer patients
Escherichia coli is the most common cause of bloodstream and urinary tract infections globally. A steady growth in E. coli antibiotic resistance affects medical institutions worldwide by creating difficult-to-treat infections in patients. [
47] Multiple Drug Resistance (MDR) genetic patterns are widely found in mobile elements like as transposons, integrons, and plasmids. These components can be passed on from foodborne pathogens to human pathogens, hence boosting their pathogenicity. [
48] With the advent of next generation sequencing technology (NGS), it is now possible to efficiently characterize bacterial infections as well as identify virulence factors and antibiotic resistance genes. [
49]
NGS has been a widely used technology for studying the evolutionary connections of MDR E. coli strains from various geographical locations. It may be able to predict resistance characteristics from genomic sequences by analyzing genetic differences in different E. coli plasmids collected from various sources. [
50]
Infection with multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli (MDR) poses a serious risk to vulnerable paediatric cancer patients. Quinolones and aminoglycoside resistance was observed in 21 carbapenem-resistant E. coli (CRE) isolates. The Illumina next-generation sequencing platform for plasmid shot-gun sequencing and data analysis with bioinformatics pipeline was used. All beta-lactams, carbapenems, aminoglycosides, and quinolones were shown to be resistant among the isolates. The highest represented genes among the 32 antimicrobial resistance genes discovered that exceeded the study threshold coverage were aph(6)-Id, sul2, aph(3′′)-Ib, aph(3′)-Ia, sul1, dfrA12, TEM-220, and NDM-11. Antibiotic efflux, antibiotic inactivation, antibiotic target replacements, and antibiotic target change were among the resistance mechanisms used by isolates. Diverse insertion sequences, including IS26, were found in sequenced isolates, indicating dynamic reshuffling of the plasmids harbored. The majority of the isolates had plasmids from different bacterial species, suggesting a probable horizontal gene transfer. Only two isolates had virulence factors associated with the iroA gene cluster, which was detected in only one of them. Outside of the context of nosocomial infections in hospitalized patients, our findings suggest a transfer of resistance genes and plasmids between species. [
51]
Table 1.
Summarized Information about Chemo/Bioinformatics Applications in Egypt.
Table 1.
Summarized Information about Chemo/Bioinformatics Applications in Egypt.
| Reference |
Informatics used |
Application |
Outcome |
| [14] |
Chemoinformatics |
Antibiotic discovery |
Tetracycline analogue B (iodocycline).
More active than tetracycline and less bacterial resistant. |
| [19] |
Bioinformatics |
Disease Classification |
The ensemble model in conjunction with brute force as a feature selection strategy results in a top accuracy of 97.8% for heart disease classification |
| [24] |
Bioinformatics |
Disease Diagnosis |
On two types of datasets, X-ray pictures and CT images, the findings showed a quantitative evaluation of covid-19 of the suggested ensemble stacking technique with percentages approaching 99% |
| [28] |
Chemo/
Bio-informatics |
Special formulation for meningitis |
Ceftriaxone gelatin nanospheres or tripalmitin solid lipid nanoparticles showed more practical and efficient nose-to-brain formulation targeting meningitis over cefotaxime |
| [29] |
Chemoinformatics |
Phytochemistry therapeutic discovery |
Extract of Eucalyptus globulus bark had high cytotoxic activity against the liver cancer cell lines HEPG2 and HUH-7, and its absorption was improved by nanoformulation |
| [35] |
Chemoinformatics |
Targeting Cancer Cells |
ECT2 showed to upregulate as mRNA and protein levels in a variety of human tumors, allowing for increased filtration of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC) and decreased the level of natural killer T (NKT) cells, resulting in a poor prognosis survival. The investigation looked for medicines that could both inhibit ECT2 and function as anticancer agents |
| [38] |
Chemo/
Bio-informatics |
Special formulation for Alzheimer disease |
Curcumin outperformed bisdemethoxycurcumin (BDMC) in a nose-to-brain formulation for treatment of Alzheimer disease |
| [41] |
Chemo/
Bio-informatics |
Testing Antibacterial activity against Resistant microorganisms |
Three pyrazole and benzimidazole-based compounds examined showed modest bactericidal efficacy against MSSA, MRSA, and vancomycin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (VRSA) |
| [46] |
Bioinformatics |
Genomic correlation with disease state |
It was discovered that 12 SNPs were shared by the majority of the participants related to obesity and were concordant with their clinical diagnostic. In addition, results showed that the mtDNA mutation A4282G is present in all of the samples and is linked to chronic progressive external ophthalmoplegia (CPEO). |
| [51] |
Bioinformatics |
Multidrug-resistant organism identification |
The highest represented genes among the 32 antimicrobial resistance genes discovered in cancer pediatric patients that exceeded the study threshold coverage were aph(6)-Id, sul2, aph(3′′)-Ib, aph(3′)-Ia, sul1, dfrA12, TEM-220, and NDM-11.
Suggesting a horizontal transfer of resistance genes and plasmids between species in the context of nosocomial infections. |
4. Conclusions
It seems that in the last five years chemo- and bioinformatics showed different advances in Egyptian research studies. The outcomes include several benefits in drug discovery, disease diagnosis and classification, special pharmaceutical formulations for minorities and Alzheimer disease, and phytochemistry therapeutic discovery. Another benefits in pharmaceutical research include, targeted cancer cell therapy, and identification of novel molecules for antimicrobial resistance, genomic correlation with disease state, and multidrug-resistant organism identification.
5. Recommendations
Extending the application of cheminformatics in drug discovery, clinical pharmacy settings, and formulation of targeted dosage forms for special diseases.
6. Limitations
No broad use of chemoinformatics in drug discovery and formulation of novel dosage forms
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.A.S.; writing—original draft preparation, E.M.S, M.A.E and S.A.R; writing—review and editing, M.A.E and A.S.M; supervision, N.A.S and A.S.M; project administration, N.A.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Drug Research Center (DRC), Egypt for their effort in writing, and editing the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wishart DS. Introduction to cheminformatics. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2007 Jun;Chapter 14:Unit 14.1. PMID: 18428788. [CrossRef]
- Yan XC, Sanders JM, Gao Y-D, Tudor M, Haidle AM, Klein DJ et al (2020) Augmenting hit identification by virtual screening techniques in small molecule drug discovery. J Chem Inf Model. [CrossRef]
- Walters WP, Patrick WW (2019) Virtual chemical libraries. J Med Chem. [CrossRef]
- B.Firdaus Begam, J. Satheesh Kumar, A Study on Cheminformatics and its Applications on Modern Drug Discovery, Procedia Engineering, Volume 38, 2012, Pages 1264-1275. [CrossRef]
- Saldívar-González, F.I., Huerta-García, C.S. & Medina-Franco, J.L. Chemoinformatics-based enumeration of chemical libraries: a tutorial. J Cheminform 12, 64 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Pitt WR, Kroeplien B (2013) Exploring virtual scaffold spaces. In: Brown N (ed) Methods and Principles in Medicinal Chemistry. Wiley, London, pp 83–104.
- Mak L, Marcus D, Howlett A, Yarova G, Duchateau G, Klaffke W, Bender A, Glen RC. Metrabase: a cheminformatics and bioinformatics database for small molecule transporter data analysis and (Q)SAR modeling. J Cheminform. 2015 Jun 23;7:31. PMID: 26106450; PMCID: PMC4477067. [CrossRef]
- Parveen Kumar. Kumar, Clark's clinical medicine; 2020.p.774-811.
- Olson James. Clinical pharmacology made ridiculously simple; 2020; 12:93-109.
- Levinson Warren. Review of medical microbiology and immunology; 2021; 9:211-244.
- Metting Patricia J. Physiology; 2019; 14:437-505.
- B Oliva, G Gordon, P Mcnicholas, G Ellestad and I Chopra (2012). Evidence that tetracycline analogs whose primary target is not the bacterial ribosome cause lysis of Escherichia coli. Journal of antimicrobial agents and chemotherapy,36(5):913-919. [CrossRef]
- Alexey Aleksandrov, Thomas Simonson (2009). Molecular mechanics models for tetracycline analogs. Journal of computational chemistry. 30 (2):55-234. [CrossRef]
- Kassab M. Development of novel antimicrobial tetracycline analog b (iodocycline) by chemo-informatics. Ain Shams Medical Journal, Vol. 73, No., 4, December, 2022. ISSN: 2735-3540. [CrossRef]
- (WHO), W. H. (2017). Cardiovascular diseases (CDs) – Key Facts. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovasculardiseases-(cvds).
- Srinivas, K., Rani, B.K., Govrdhan, A., 2010a. Applications of data mining techniques in healthcare and prediction of heart attacks. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Eng. (IJCSE) 2(02), 250–25562.
- Shafenoor Amin M, Kia Chiam Y, Dewi Varathan K. Identification of significant features and data mining techniques in predicting heart disease. Telematics Inf. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Ekta Maini, Bondu Venkateswarlu, Baljeet Maini, Dheeraj Marwaha. Machine learning–based heart disease prediction system for Indian population: An exploratory study done in South India, 2021, ISSN 0377- 1237. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed El Sheikh; Nader Mahmoud; Arabi Elsayed Keshk. "Heart Disease Classification Based on Hybrid Ensemble Stacking Technique". IJCI. International Journal of Computers and Information, 8, 2, 2021, 1-8. [CrossRef]
- W. U. O. COVID-19, 2020. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases /novel-coronavirus-2019.
- D. Das, K.C. Santosh, U. Pal, Truncated inception net: COVID-19 outbreak screening using chest X-rays, Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. (2020). [CrossRef]
- P. Rajpurkar, J. Irvin, K. Zhu, B. Yang, H. Mehta, T. Duan, D. Ding, A. Bagul, C. Langlotz, K. Shpanskaya, et al., Chexnet: Radiologist-level pneumonia detection on chest x-rays with deep learning, arXiv preprint arXiv:1711.05225 (2017). [CrossRef]
- Butt C, Gill J, Chun D, Babu BA. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Deep learning system to screen coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia. Appl Intell (Dordr). 2023;53(4):4874. [CrossRef]
- Esraa Fady Dawod; Nader Mahmoud; Ashraf Elsisi. "Hybrid approach for COVID-19 detection from chest radiography". IJCI. International Journal of Computers and Information, 8, 2, 2021, 71-76. [CrossRef]
- Troendle M, Pettigrew A. A systematic review of cases of meningitis in the absence of cerebrospinal fluid pleocytosis on lumbar puncture. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019;19:692. [CrossRef]
- Griffiths MJ, McGill F, Solomon T. Management of acute meningitis. Clin. Med. (Lond.) 2018;18:164–169. [CrossRef]
- Oordt-Speets AM, Bolijn R, van Hoorn RC, Bhavsar A, Kyaw MH. Global etiology of bacterial meningitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2018;13:e0198772. [CrossRef]
- Hathout RM, Abdelhamid SG, El-Housseiny GS, Metwally AA. Comparing cefotaxime and ceftriaxone in combating meningitis through nose-to-brain delivery using bio/chemoinformatics tools. Sci Rep. 2020 Dec 4;10(1):21250. PMID: 33277611; PMCID: PMC7718871. [CrossRef]
- Nematallah KA, Elmekkawy S, Abdollah MRA, Elmazar MM, Abdel-Sattar E, Meselhy MR. Cheminformatics Application in the Phytochemical and Biological Study of Eucalyptus globulus L. Bark as a Potential Hepatoprotective Drug. ACS Omega. 2022 Feb 24;7(9):7945-7956. PMID: 35284740; PMCID: PMC8908522. [CrossRef]
- Hayat U.; Jilani M. I.; Rehman R.; Nadeem F. A Review on Eucalyptus globulus: A New Perspective in Therapeutics. Int. J. Chem. Biol. Sci. 2015, 8, 85–91.
- Mota M. I. F. D.; Pinto P. C. O. R.; Novo C. C.; Sousa G. D. A.; Guerreiro O. R. F. D. N.; Guerra Â. D. C. R.; Duarte M. F. P.; Rodrigues A. E. Eucalyptus globulus bark as A source of polyphenolic compounds with biological activity. O Papel 2013, 74, 57–64.
- Romano B.; Pagano E.; Montanaro V.; Fortunato A. L.; Milic N.; Borrelli F. Novel insights into the pharmacology of flavonoids. Phytother. Res. 2013, 27, 1588–1596. [CrossRef]
- Gharib, A.F.; Eldeen, M.A.; Khalifa, A.S.; Elsawy, W.H.; Eed, E.M.; Askary, A. El; Eid, R.A.; Soltan, M.A.; Raafat, N. Assessment of Glutathione Peroxidase-1 ( GPX1 ) Gene Expression as a Specific Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 2285. [CrossRef]
- Zabady, S.; Mahran, N.; Soltan, M.A.; Eldeen, M.A.; Eid, R.A.; Albogami, S.; Fayad, E.; Matboli, M.; Habib, E.K.; Hasanin, A.H.; et al. Cyanidin-3-Glucoside Modulates hsa_circ_0001345/miRNA106b/ATG16L1 Axis Expression as a Potential Protective Mechanism against Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022, 44, 1677–1687. [CrossRef]
- Soltan, M.A.; Eldeen, M.A.; Sajer, B.H.; Abdelhameed, R.F.A.; Al-Salmi, F.A.; Fayad, E.; Jafri, I.; Ahmed, H.E.M.; Eid, R.A.; Hassan, H.M.; et al. Integration of Chemoinformatics and Multi-Omics Analysis Defines ECT2 as a Potential Target for Cancer Drug Therapy. Biology 2023, 12, 613. [CrossRef]
- Roney C, Kulkarni P, Arora V, Antich P, Bonte F, Wu A, Mallikarjuana NN, Manohar S, Liang HF, Kulkarni AR, et al. 2005. Targeted nanoparticles for drug delivery through the blood-brain barrier for Alzheimer’s disease. J Control Release. 108:193–214. [CrossRef]
- Wu H, Hu K, Jiang X. 2008. From nose to brain: understanding transport capacity and transport rate of drugs. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 5:1159–1168. [CrossRef]
- Hathout RM, El-Ahmady SH, Metwally AA. Curcumin or bisdemethoxycurcumin for nose-to-brain treatment of Alzheimer disease? A bio/chemo-informatics case study. Nat Prod Res. 2018 Dec;32(24):2873-2881. PMID: 29022380. [CrossRef]
- C. Fuda, M. Suvorov, S. B. Vakulenko, S. Mobashery, The basis for resistance to betalactam antibiotics by penicillin-binding protein 2a of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 40802–40806. [CrossRef]
- M. G. Pinho, H. de Lencastre, A. Tomasz, An acquired and a native penicillin-binding protein cooperate in building the cell wall of drugresistant staphylococci, Proc Natl Acad Sci 2001; 98:10886–10891. [CrossRef]
- Shalaby MW, Dokla EM, Serya RA, Abouzid KA, 2019. Identification of novel pyrazole and benzimidazole based derivatives as PBP2a inhibitors: Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation. Arch Pharm Sci ASU 3(2): 228-245. [CrossRef]
- Ng M, Fleming T, Robinson M, Thomson B, Graetz N, Margono C, Mullany EC, et al. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2014 Aug 30;384(9945):766-81. [CrossRef]
- Alebshehy, R., Shuaib, N., Mbako, J., Barffo, D., Nuotol, R. (2016). Determinant Analysis of Obesity among Adult Females in Egypt. The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine, 65(1), 662-669. [CrossRef]
- Austin AM, Hill AG, Fawzi WW. Maternal obesity trends in Egypt 1995-2005. Matern Child Nutr. 2013 Apr;9(2):167-79. [CrossRef]
- Hassan NE, El-Masry SA, Zarouk W, El Banna RA, Mosaad RM, Al-Tohamy M, Salamah AR. Obesity phenotype in relation to gene polymorphism among samples of Egyptian children and their mothers. Genes Dis. 2017 Dec 18;5(2):150-157. [CrossRef]
- ElHefnawi M, Hegazy E, Elfiky A, Jeon Y, Jeon S, Bhak J, Mohamed Metwally F, Sugano S, Horiuchi T, Kazumi A, Blazyte A. Complete genome sequence and bioinformatics analysis of nine Egyptian females with clinical information from different geographic regions in Egypt. Gene. 2021 Feb 15;769:145237. [CrossRef]
- Sengupta S, Chattopadhyay MK, Grossart HP. The multifaceted roles of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance in nature. Front Microbiol. 2013 Mar 12;4:47. [CrossRef]
- Fricke WF, Welch TJ, McDermott PF, Mammel MK, LeClerc JE, White DG, Cebula TA, Ravel J. Comparative genomics of the IncA/C multidrug resistance plasmid family. J Bacteriol. 2009 Aug;191(15):4750-7. [CrossRef]
- Sabat AJ, Budimir A, Nashev D, Sá-Leão R, van Dijl Jm, Laurent F, Grundmann H, Friedrich AW; ESCMID Study Group of Epidemiological Markers (ESGEM). Overview of molecular typing methods for outbreak detection and epidemiological surveillance. Euro Surveill. 2013 Jan 24;18(4):20380. [CrossRef]
- Stoesser N, Batty EM, Eyre DW, Morgan M, Wyllie DH, Del Ojo Elias C, Johnson JR, Walker AS, Peto TE, Crook DW. Predicting antimicrobial susceptibilities for Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates using whole genomic sequence data. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2013 Oct;68(10):2234-44. [CrossRef]
- Hassan R, Tantawy M, Gouda NA, Elzayat MG, Gabra S, Nabih A, Diab AA, El-Hadidi M, Bakry U, Shoeb MR, Elanany M, Shalaby L, Sayed AA. Genotypic characterization of multiple drug resistant Escherichia coli isolates from a pediatric cancer hospital in Egypt. Sci Rep. 2020 Mar 5;10(1):4165. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).