Submitted:
27 April 2023
Posted:
28 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Pre-registration
2.2. Sample
2.3. Risk assessment instruments
2.4. MRI acquisition and preprocessing
2.5. Measured variables
2.6. Quality control and data exclusion
2.7. Statistical Analysis
2.8. Machine learning analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographics
3.2. Statistical Analysis
3.3. Machine learning analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Inclusion and exclusion criteria for the three recruitment pathways.
Appendix B. Bash shell script in a virtual Linux environment at the high-performance computing (ZIH) prompting a parallel preprocessing of the subcortical segmentation procedure.
Appendix C. MATLAB script for calculating the FDR of the explorative analysis.
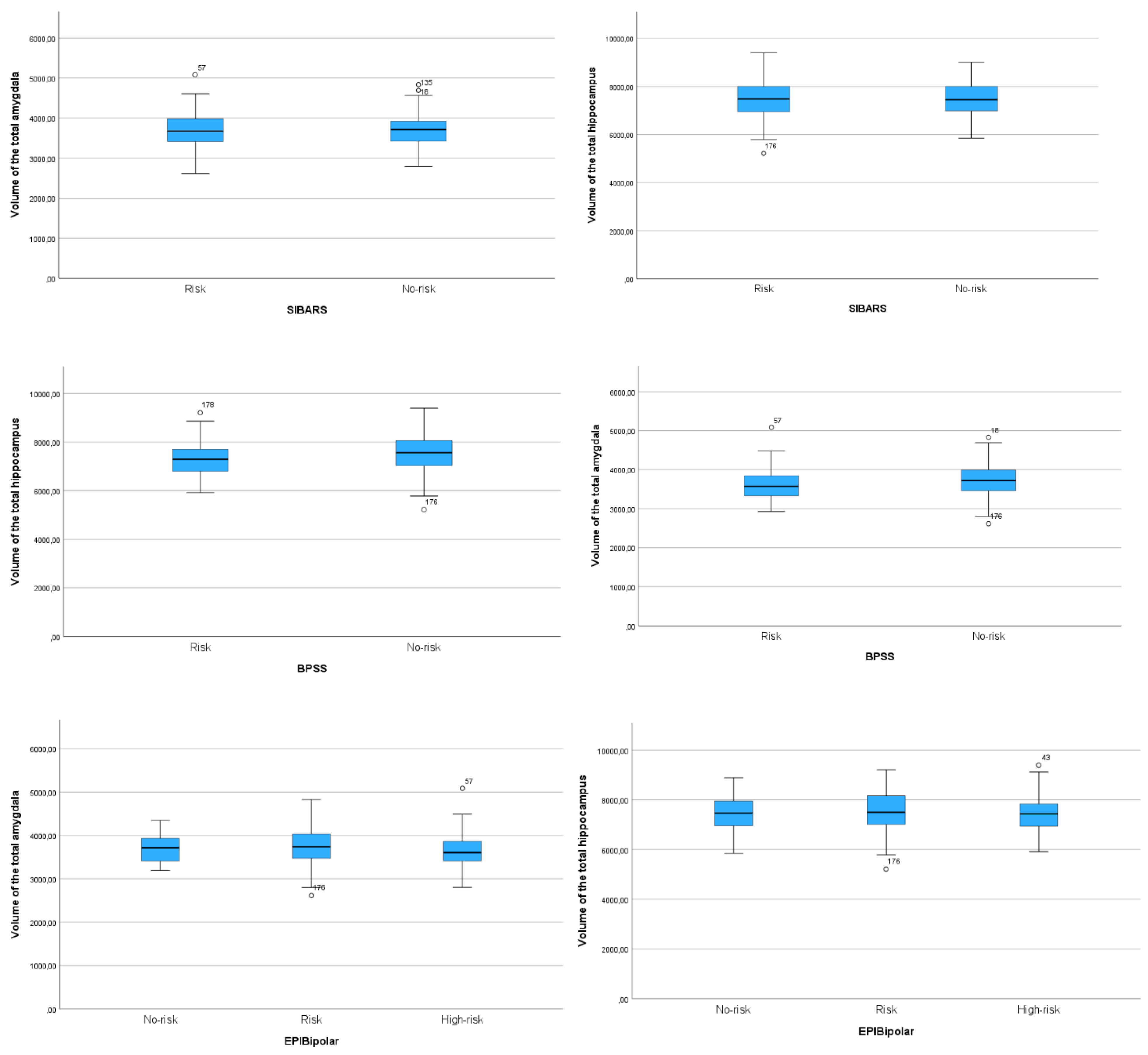
Appendix D. Boxplot diagrams comparing the volumes of the total hippocampus and of the total amygdala for all three risk assessment tools.
Appendix E. LME results for the explorative analysis of all twelve hippocampal subfields and nine nuclei of the amygdala for all three risk assessment tools.
| BPSS-P | BARS | EPIbipolar | |
| Hipoocampal subfields | |||
| CA1 | F(1, 258.392) = 0.015, p = 0. 984 | F(1, 253.719) = 0.418, p = 0.998 | F(2, 261.014) = 1.423 , p = 0.581 |
| CA2/3 | F(1, 257.737) = 0.057, p = 0. 984 | F(1, 253.306) = 0.226, p = 0.998 | F(2, 260.560) = 0.531, p = 0.877 |
| CA4 | F(1, 256.403) = 0.002, p = 0. 984 | F(1, 252.530) = 0.133, p = 0.998 | F(2, 260.047) = 0.210, p = 0.896 |
| Molecular layer | F(1, 257.835) = 0.016, p = 0. 984 | F(1, 253.161) = 0.942, p = 0.998 | F(2, 260.538) = 1.143, p = 0.611 |
| GC ML DG | F(1, 256.400) = 0.044, p = 0. 984 | F(1, 252.529) = 0.115, p = 0.998 | F(2, 260.057) = 0.224, p = 0.896 |
| Hippocampal tail | F(1, 257.433) = 1.866, p = 0. 908 | F(1, 255.414) = 0.075, p = 0.998 | F(2, 262.303) = 1.186, p = 0.611 |
| Subiculum | F(1, 258.919) = 0.094, p = 0. 984 | F(1, 253.869) = 0.574, p = 0.998 | F(2, 261.239) = 0.712, p = 0.795 |
| Presubiculum | F(1, 258.126) = 0.146, p = 0. 984 | F(1, 252.960) = 0.994, p = 0.998 | F(2, 260.245) = 0.425, p = 0.877 |
| Parasubiculum | F(1, 252.592) = 0.131, p = 0. 984 | F(1, 254.835) = 0.095, p = 0.998 | F(2, 260.532) = 0.962, p = 0.672 |
| Fimbria | F(1, 238.399) = 0.184, p = 0. 984 | F(1, 256.843) = 0.844, p = 0.998 | F(2, 262.917) = 0.024, p = 0.976 |
| Hippocampal fissure | F(1, 258.786) = 2.610, p = 0. 749 | F(1, 254.065) = 0.001, p = 0.998 | F(2, 261.224) = 0.397, p = 0.877 |
| HATA | F(1, 259) = 1.138, p = 0. 984 | F(1, 254.478) = 0.000, p = 0.998 | F(2, 261.619) = 1.397, p = 0.581 |
| Nuclei of the amygdala | |||
| Cortical ncl. | F(1, 247.747) = 4.766, p = 0. 315 | F(1, 256.286) = 0.498, p = 0.998 | F(2, 262.740) = 2.239, p = 0.452 |
| Medial ncl. | F(1, 231.662) = 13.706, p = 0.0056** | F(1, 256.062) = 0.091, p = 0.998 | F(2, 262.792) = 0.089, p = 0.961 |
| Basal ncl. | F(1, 257.337) = 0.016, p = 0. 984 | F(1, 255.524) = 0.010, p = 0.998 | F(2, 262.493) = 2.233, p = 0.452 |
| Central ncl. | F(1, 259) = 0.500, p = 0. 984 | F(1, 257) = 0.014, p = 0.998 | F(2, 265) = 0.342, p = 0.877 |
| Lateral ncl. | F(1, 252.575) = 1.096, p = 0. 984 | F(1, 255.551) = 0.970, p = 0.998 | F(2, 262.244) = 4.214, p = 0.336 |
| Accessory basal ncl. | F(1, 249.097) = 0.004, p = 0. 984 | F(1, 256.320) = 0.003, p = 0.998 | F(2, 263.123) = 2.586, p = 0.452 |
| AAA | F(1, 233.022) = 0.000, p = 0. 984 | F(1, 256.675) = 0.648, p = 0.998 | F(2, 263.346) = 2.066, p = 0.452 |
| Corticoamygdaloid transition area | F(1, 247.829) = 0.009, p = 0. 984 | F(1, 255.937) = 0.010, p = 0.998 | F(2, 262.786) = 1.497, p = 0.581 |
| Paralaminar ncl. | F(1, 256.680) = 0.095, p = 0. 984 | F(1, 255.558) = 0.020, p = 0.998 | F(2, 262.455) = 2.375, p = 0.452 |
References
- Merikangas, K.R.; Jin, R.; He, J.-P.; Kessler, R.C.; Lee, S.; Sampson, N.A.; Viana, M.C.; Andrade, L.H.; Hu, C.; Karam, E.G.; et al. Prevalence and Correlates of Bipolar Spectrum Disorder in the World Mental Health Survey Initiative. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2011, 68, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Hu, C.; Ren, Z.; Bai, L.; Gao, F.; Lyu, J. Trends in the Incidence and DALYs of Bipolar Disorder at Global, Regional, and National Levels: Results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Journal of Psychiatric Research 2020, 125, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drancourt, N.; Etain, B.; Lajnef, M.; Henry, C.; Raust, A.; Cochet, B.; Mathieu, F.; Gard, S.; MBailara, K.; Zanouy, L. Duration of Untreated Bipolar Disorder: Missed Opportunities on the Long Road to Optimal Treatment. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 2013, 127, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller-Oerlinghausen, B.; Berghöfer, A.; Bauer, M. Bipolar Disorder. The Lancet 2002, 359, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keramatian, K.; Chakrabarty, T.; Saraf, G.; Yatham, L. Transitioning to Bipolar Disorder: A Systematic Review of Prospective High-Risk Studies. Current Opinion in Psychiatry. [CrossRef]
- Hajek, T.; Cullis, J.; Novak, T.; Kopecek, M.; Blagdon, R.; Propper, L.; Stopkova, P.; Duffy, A.; Hoschl, C.; Uher, R.; et al. Brain Structural Signature of Familial Predisposition for Bipolar Disorder: Replicable Evidence For Involvement of the Right Inferior Frontal Gyrus. Biological Psychiatry 2013, 73, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerner, B. Genetics of Bipolar Disorder. Appl Clin Genet 2014, 7, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafeman, D.M.; Merranko, J.; Goldstein, T.R.; Axelson, D.; Goldstein, B.I.; Monk, K.; Hickey, M.B.; Sakolsky, D.; Diler, R.; Iyengar, S.; et al. Assessment of a Person-Level Risk Calculator to Predict New-Onset Bipolar Spectrum Disorder in Youth at Familial Risk. JAMA Psychiatry 2017, 74, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, R.M.; Altshuler, L.L.; Kupka, R.; McElroy, S.L.; Frye, M.A.; Rowe, M.; Grunze, H.; Suppes, T.; Keck, P.E.; Leverich, G.S.; et al. Multigenerational Transmission of Liability to Psychiatric Illness in Offspring of Parents with Bipolar Disorder. Bipolar Disord 2018, 20, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusar-Poli, P.; De Micheli, A.; Rocchetti, M.; Cappucciati, M.; Ramella-Cravaro, V.; Rutigliano, G.; Bonoldi, I.; McGuire, P.; Falkenberg, I. Semistructured Interview for Bipolar at Risk States (SIBARS). Psychiatry Research 2018, 264, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leopold, K.; Ritter, P.; Correll, C.U.; Marx, C.; Özgürdal, S.; Juckel, G.; Bauer, M.; Pfennig, A. Risk Constellations Prior to the Development of Bipolar Disorders: Rationale of a New Risk Assessment Tool. Journal of affective disorders 2012, 136, 1000–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correll, C.U.; Olvet, D.M.; Auther, A.M.; Hauser, M.; Kishimoto, T.; Carrión, R.E.; Snyder, S.; Cornblatt, B.A. The Bipolar Prodrome Symptom Interview and Scale–Prospective (BPSS-P): Description and Validation in a Psychiatric Sample and Healthy Controls. Bipolar disorders 2014, 16, 505–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, D.B.; Falkai, P.; Koutsouleris, N. Machine Learning Approaches for Clinical Psychology and Psychiatry. Annu Rev Clin Psychol 2018, 14, 91–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsouleris, N.; Dwyer, D.B.; Degenhardt, F.; Maj, C.; Urquijo-Castro, M.F.; Sanfelici, R.; Popovic, D.; Oeztuerk, O.; Haas, S.S.; Weiske, J.; et al. Multimodal Machine Learning Workflows for Prediction of Psychosis in Patients With Clinical High-Risk Syndromes and Recent-Onset Depression. JAMA Psychiatry 2021, 78, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnone, D.; Cavanagh, J.; Gerber, D.; Lawrie, S.M.; Ebmeier, K.P.; McIntosh, A.M. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Studies in Bipolar Disorder and Schizophrenia: Meta-Analysis. The British Journal of Psychiatry 2009, 195, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibar, D.P.; Westlye, L.T.; Doan, N.T.; Jahanshad, N.; Cheung, J.W.; Ching, C.R.K.; Versace, A.; Bilderbeck, A.C.; Uhlmann, A.; Mwangi, B.; et al. Cortical Abnormalities in Bipolar Disorder: An MRI Analysis of 6503 Individuals from the ENIGMA Bipolar Disorder Working Group. Mol Psychiatry 2018, 23, 932–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibar, D.P.; Westlye, L.T.; van Erp, T.G.M.; Rasmussen, J.; Leonardo, C.D.; Faskowitz, J.; Haukvik, U.K.; Hartberg, C.B.; Doan, N.T.; Agartz, I.; et al. Subcortical Volumetric Abnormalities in Bipolar Disorder. Mol Psychiatry 2016, 21, 1710–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haukvik, U.K.; Gurholt, T.P.; Nerland, S.; Elvsåshagen, T.; Akudjedu, T.N.; Alda, M.; Alnæs, D.; Alonso-Lana, S.; Bauer, J.; Baune, B.T. In Vivo Hippocampal Subfield Volumes in Bipolar Disorder—A Mega-analysis from The Enhancing Neuro Imaging Genetics through Meta-Analysis Bipolar Disorder Working Group. Human brain mapping 2022, 43, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haukvik, U.K.; Westlye, L.T.; Mørch-Johnsen, L.; Jørgensen, K.N.; Lange, E.H.; Dale, A.M.; Melle, I.; Andreassen, O.A.; Agartz, I. In Vivo Hippocampal Subfield Volumes in Schizophrenia and Bipolar Disorder. Biological psychiatry 2015, 77, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, I.; Gardin, T.M.; Tandon, N.; Eack, S.; Francis, A.N.; Seidman, L.J.; Clementz, B.; Pearlson, G.D.; Sweeney, J.A.; Tamminga, C.A. Medial Temporal Lobe Structures and Hippocampal Subfields in Psychotic Disorders: Findings from the Bipolar-Schizophrenia Network on Intermediate Phenotypes (B-SNIP) Study. JAMA psychiatry 2014, 71, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, A.S. Cortical-Subcortical Interactions in Depression: From Animal Models to Human Psychopathology. Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience 2016, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolenko, V.N.; Oganesyan, M.V.; Rizaeva, N.A.; Kudryashova, V.A.; Nikitina, A.T.; Pavliv, M.P.; Shchedrina, M.A.; Giller, D.B.; Bulygin, K.V.; Sinelnikov, M.Y. Amygdala: Neuroanatomical and Morphophysiological Features in Terms of Neurological and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Brain Sciences 2020, 10, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, C.; Nerland, S.; de Lange, A.-M.G.; Wortinger, L.A.; Hilland, E.; Andreassen, O.A.; Jørgensen, K.N.; Agartz, I. In Vivo Amygdala Nuclei Volumes in Schizophrenia and Bipolar Disorders. Schizophr Bull 2021, 47, 1431–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielau, H.; Trübner, K.; Krell, D.; Agelink, M.W.; Bernstein, H.-G.; Stauch, R.; Mawrin, C.; Danos, P.; Gerhard, L.; Bogerts, B. Volume Deficits of Subcortical Nuclei in Mood Disorders. European archives of psychiatry and clinical neuroscience 2005, 255, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luders, E.; Thompson, P.M.; Kurth, F.; Hong, J.-Y.; Phillips, O.R.; Wang, Y.; Gutman, B.A.; Chou, Y.-Y.; Narr, K.L.; Toga, A.W. Global and Regional Alterations of Hippocampal Anatomy in Long-term Meditation Practitioners. Human brain mapping 2013, 34, 3369–3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sani, G.; Simonetti, A.; Janiri, D.; Banaj, N.; Ambrosi, E.; De Rossi, P.; Ciullo, V.; Arciniegas, D.B.; Piras, F.; Spalletta, G. Association between Duration of Lithium Exposure and Hippocampus/Amygdala Volumes in Type I Bipolar Disorder. Journal of Affective Disorders 2018, 232, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roeder, S.S.; Burkardt, P.; Rost, F.; Rode, J.; Brusch, L.; Coras, R.; Englund, E.; Håkansson, K.; Possnert, G.; Salehpour, M.; et al. Evidence for Postnatal Neurogenesis in the Human Amygdala. Commun Biol 2022, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orru, G.; Pettersson-Yeo, W.; Marquand, A.F.; Sartori, G.; Mechelli, A. Using Support Vector Machine to Identify Imaging Biomarkers of Neurological and Psychiatric Disease: A Critical Review. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews 2012, 36, 1140–1152. [Google Scholar]
- Mikolas, P.; Marxen, M.; Riedel, P.; Bröckel, K.; Martini, J.; Huth, F.; Berndt, C.; Vogelbacher, C.; Jansesn, A.; Kircher, T.; et al. Prediction of Estimated Risk for Bipolar Disorder Using Machine Learning and Structural MRI Features; In Review. 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Garg, A.; Mago, V. Role of Machine Learning in Medical Research: A Survey. Computer Science Review 2021, 40, 100370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfennig, A.; Leopold, K.; Martini, J.; Boehme, A.; Lambert, M.; Stamm, T.; Bermpohl, F.; Reif, A.; Kittel-Schneider, S.; Juckel, G. Improving Early Recognition and Intervention in People at Increased Risk for the Development of Bipolar Disorder: Study Protocol of a Prospective-Longitudinal, Naturalistic Cohort Study (Early-BipoLife). International Journal of Bipolar Disorders 2020, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, P.S.; Bermpohl, F.; Gruber, O.; Hautzinger, M.; Jansen, A.; Juckel, G.; Kircher, T.; Lambert, M.; Mulert, C.; Pfennig, A. Aims and Structure of the German Research Consortium BipoLife for the Study of Bipolar Disorder. International journal of bipolar disorders 2016, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, R.C.; Berglund, P.; Demler, O.; Jin, R.; Merikangas, K.R.; Walters, E.E. Lifetime Prevalence and Age-of-Onset Distributions of DSM-IV Disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2005, 62, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfennig, A.; Jabs, B.; Pfeiffer, S.; Weikert, B.; Leopold, K.; Bauer, M. Health care service experiences of bipolar patients in Germany survey prior to the introduction of the S3 Guideline for diagnostics and treatment of bipolar disorders. Nervenheilkunde 2011, 30, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, M.; Bock, T.; Naber, D.; Löwe, B.; Schulte-Markwort, M.; Schäfer, I.; Gumz, A.; Degkwitz, P.; Schulte, B.; König, H.; et al. Die psychische Gesundheit von Kindern, Jugendlichen und jungen Erwachsenen – Teil 1: Häufigkeit, Störungspersistenz, Belastungsfaktoren, Service-Inanspruchnahme und Behandlungsverzögerung mit Konsequenzen. Fortschr Neurol Psychiatr 2013, 81, 614–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikolas, P.; Bröckel, K.; Vogelbacher, C.; Müller, D.K.; Marxen, M.; Berndt, C.; Sauer, C.; Jung, S.; Fröhner, J.H.; Fallgatter, A.J.; et al. Individuals at Increased Risk for Development of Bipolar Disorder Display Structural Alterations Similar to People with Manifest Disease. Transl Psychiatry 2021, 11, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogelbacher, C.; Sommer, J.; Schuster, V.; Bopp, M.H.; Falkenberg, I.; Ritter, P.S.; Bermpohl, F.; Hindi Attar, C.; Rauer, L.; Einenkel, K.E. The German Research Consortium for the Study of Bipolar Disorder (BipoLife): A Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study Protocol. International journal of bipolar disorders 2021, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischl, B.; Salat, D.H.; Kouwe, A.J.W. van der; Makris, N.; Ségonne, F.; Quinn, B.T.; Dale, A.M. Sequence-Independent Segmentation of Magnetic Resonance Images. NeuroImage 2004, 23, S69–S84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischl, B.; Sereno, M.I.; Tootell, R.B.H.; Dale, A.M. High-Resolution Intersubject Averaging and a Coordinate System for the Cortical Surface. Human Brain Mapping 1999, 8, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, J.E.; Augustinack, J.C.; Nguyen, K.; Player, C.M.; Player, A.; Wright, M.; Roy, N.; Frosch, M.P.; McKee, A.C.; Wald, L.L. A Computational Atlas of the Hippocampal Formation Using Ex Vivo, Ultra-High Resolution MRI: Application to Adaptive Segmentation of in Vivo MRI. Neuroimage 2015, 115, 117–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saygin, Z.M.; Kliemann, D.; Iglesias, J.E.; van der Kouwe, A.J.; Boyd, E.; Reuter, M.; Stevens, A.; Van Leemput, K.; McKee, A.; Frosch, M.P. High-Resolution Magnetic Resonance Imaging Reveals Nuclei of the Human Amygdala: Manual Segmentation to Automatic Atlas. Neuroimage 2017, 155, 370–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, J.E.; Van Leemput, K.; Augustinack, J.; Insausti, R.; Fischl, B.; Reuter, M.; Initiative, A.D.N. Bayesian Longitudinal Segmentation of Hippocampal Substructures in Brain MRI Using Subject-Specific Atlases. Neuroimage 2016, 141, 542–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Leemput, K.; Bakkour, A.; Benner, T.; Wiggins, G.; Wald, L.L.; Augustinack, J.; Dickerson, B.C.; Golland, P.; Fischl, B. Automated Segmentation of Hippocampal Subfields from Ultra-High Resolution in Vivo MRI. Hippocampus 2009, 19, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sämann, P.G.; Iglesias, J.E.; Gutman, B.; Grotegerd, D.; Leenings, R.; Flint, C.; Dannlowski, U.; Clarke-Rubright, E.K.; Morey, R.A.; Erp, T.G.M.; et al. FREESURFER ‐based Segmentation of Hippocampal Subfields: A Review of Methods and Applications, with a Novel Quality Control Procedure for ENIGMA Studies and Other Collaborative Efforts. Human Brain Mapping 2022, 43, 207–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesli, N.; van der Meer, D.; Rokicki, J.; Storvestre, G.; Røsæg, C.; Jensen, A.; Hjell, G.; Bell, C.; Fischer-Vieler, T.; Tesli, M.; et al. Hippocampal Subfield and Amygdala Nuclei Volumes in Schizophrenia Patients with a History of Violence. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 2020, 270, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yücel, M.; Lorenzetti, V.; Suo, C.; Zalesky, A.; Fornito, A.; Takagi, M.J.; Lubman, D.I.; Solowij, N. Hippocampal Harms, Protection and Recovery Following Regular Cannabis Use. Transl Psychiatry 2016, 6, e710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tozzi, L.; Garczarek, L.; Janowitz, D.; Stein, D.J.; Wittfeld, K.; Dobrowolny, H.; Lagopoulos, J.; Hatton, S.N.; Hickie, I.B.; Carballedo, A.; et al. Interactive Impact of Childhood Maltreatment, Depression, and Age on Cortical Brain Structure: Mega-Analytic Findings from a Large Multi-Site Cohort. Psychol Med 2020, 50, 1020–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikolas, P.; Tozzi, L.; Doolin, K.; Farrell, C.; O’Keane, V.; Frodl, T. Effects of Early Life Adversity and FKBP5 Genotype on Hippocampal Subfields Volume in Major Depression. Journal of Affective Disorders 2019, 252, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twait, E.L.; Blom, K.; Koek, H.L.; Zwartbol, M.H.T.; Ghaznawi, R.; Hendrikse, J.; Gerritsen, L.; Geerlings, M.I. ; UCC SMART Study Group Psychosocial Factors and Hippocampal Subfields: The Medea-7T Study. Hum Brain Mapp 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozzi, L.; Farrell, C.; Booij, L.; Doolin, K.; Nemoda, Z.; Szyf, M.; Pomares, F.B.; Chiarella, J.; O’Keane, V.; Frodl, T. Epigenetic Changes of FKBP5 as a Link Connecting Genetic and Environmental Risk Factors with Structural and Functional Brain Changes in Major Depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 2018, 43, 1138–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klinitzke, G.; Romppel, M.; Häuser, W.; Brähler, E.; Glaesmer, H. The German Version of the Childhood Trauma Questionnaire (CTQ): Psychometric Characteristics in a Representative Sample of the General Population. Psychotherapie, Psychosomatik, Medizinische Psychologie 2011, 62, 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Esteban, O.; Birman, D.; Schaer, M.; Koyejo, O.O.; Poldrack, R.A.; Gorgolewski, K.J. MRIQC: Advancing the Automatic Prediction of Image Quality in MRI from Unseen Sites. PloS one 2017, 12, e0184661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fjell, A.M.; Westlye, L.T.; Grydeland, H.; Amlien, I.; Espeseth, T.; Reinvang, I.; Raz, N.; Holland, D.; Dale, A.M.; Walhovd, K.B. Critical Ages in the Life Course of the Adult Brain: Nonlinear Subcortical Aging. Neurobiology of Aging 2013, 34, 2239–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Eijk, L.; Hansell, N.K.; Strike, L.T.; Couvy-Duchesne, B.; de Zubicaray, G.I.; Thompson, P.M.; McMahon, K.L.; Zietsch, B.P.; Wright, M.J. Region-Specific Sex Differences in the Hippocampus. NeuroImage 2020, 215, 116781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. Journal of the Royal statistical society: series B (Methodological) 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes; Nunes, A. ; Schnack, H.G.; Ching, C.R.K.; Agartz, I.; Akudjedu, T.N.; Alda, M.; Alnæs, D.; Alonso-Lana, S.; Bauer, J.; et al. Using Structural MRI to Identify Bipolar Disorders – 13 Site Machine Learning Study in 3020 Individuals from the ENIGMA Bipolar Disorders Working Group. Mol Psychiatry 2020, 25, 2130–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ching, C.R.K.; Hibar, D.P.; Gurholt, T.P.; Nunes, A.; Thomopoulos, S.I.; Abé, C.; Agartz, I.; Brouwer, R.M.; Cannon, D.M.; Zwarte, S.M.C.; et al. What We Learn about Bipolar Disorder from Large-scale Neuroimaging: Findings and Future Directions from the ENIGMA Bipolar Disorder Working Group. Hum Brain Mapp, 2509; .8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemm, S.; Blankertz, B.; Dickhaus, T.; Müller, K.-R. Introduction to Machine Learning for Brain Imaging. NeuroImage 2011, 56, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chawla, N.V.; Bowyer, K.W.; Hall, L.O.; Kegelmeyer, W.P. SMOTE: Synthetic Minority Over-Sampling Technique. jair 2002, 16, 321–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumberg, H.P.; Kaufman, J.; Martin, A.; Whiteman, R.; Zhang, J.H.; Gore, J.C.; Charney, D.S.; Krystal, J.H.; Peterson, B.S. Amygdala and Hippocampal Volumes in Adolescents and Adults with Bipolar Disorder. Archives of general psychiatry 2003, 60, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattarinussi, G.; Di Giorgio, A.; Wolf, R.C.; Balestrieri, M.; Sambataro, F. Neural Signatures of the Risk for Bipolar Disorder: A Meta-analysis of Structural and Functional Neuroimaging Studies. Bipolar Disord 2019, 21, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, F.; Mitchell, T.; Botvinick, M. Machine Learning Classifiers and FMRI: A Tutorial Overview. Neuroimage 2009, 45, S199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claude, L.; Houenou, J.; Duchesnay, E.; Favre, P. Will Machine Learning Applied to Neuroimaging in Bipolar Disorder Help the Clinician? A Critical Review and Methodological Suggestions. Bipolar Disord 2020, 22, 334–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwenhuis, M.; van Haren, N.E.M.; Hulshoff Pol, H.E.; Cahn, W.; Kahn, R.S.; Schnack, H.G. Classification of Schizophrenia Patients and Healthy Controls from Structural MRI Scans in Two Large Independent Samples. NeuroImage 2012, 61, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupien, S.J.; Juster, R.-P.; Raymond, C.; Marin, M.-F. The Effects of Chronic Stress on the Human Brain: From Neurotoxicity, to Vulnerability, to Opportunity. Front Neuroendocrinol 2018, 49, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logtenberg, E.; Overbeek, M.F.; Pasman, J.A.; Abdellaoui, A.; Luijten, M.; van Holst, R.J.; Vink, J.M.; Denys, D.; Medland, S.E.; Verweij, K.J.H.; et al. Investigating the Causal Nature of the Relationship of Subcortical Brain Volume with Smoking and Alcohol Use. Br J Psychiatry 2022, 221, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Videbech, P. Hippocampal Volume and Depression: A Meta-Analysis of MRI Studies. American Journal of Psychiatry 2004, 161, 1957–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayano, F.; Nakamura, M.; Asami, T.; Uehara, K.; Yoshida, T.; Roppongi, T.; Otsuka, T.; Inoue, T.; Hirayasu, Y. Smaller Amygdala Is Associated with Anxiety in Patients with Panic Disorder. Psychiatry and clinical neurosciences 2009, 63, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sala, M.; Perez, J.; Soloff, P.; Di Nemi, S.U.; Caverzasi, E.; Soares, J.C.; Brambilla, P. Stress and Hippocampal Abnormalities in Psychiatric Disorders. European Neuropsychopharmacology 2004, 14, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Main output | Hippocampal subfields | Nuclei of the amygdala |
|---|---|---|
| Hippocampus (total volume) Amygdala (total volume) Intracranial volume (ICV) |
Hippocampal tail Subiculum Hippocampal fissure Presubiculum Parasubiculum Molecular Layer Granule cell layer of the dentate gyrus (GC ML DG) CA1 CA2/3 CA4 Fimbria Hippocampal amygdala transition area (HATA) |
Lateral nucleus Basal nucleus Central nucleus Medial nucleus Cortical nucleus Accessory basal nucleus Paralaminar nucleus Corticoamygdaloid transition area Anterior amygdaloid area |
| Risk assessment instrument | BPSS-P (N = 264) | BARS (N = 262) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Risk criterion fulfilled | No | Yes | Test | No | Yes | Test |
| N (%) | 205 (77.7) | 59 (22.3) | n/a | 74 (28.2) | 188 (71.8) | |
| Female (%) | 93 (45.4) | 34 (57.6) | χ2 = 2.759, p = .097 | 35 (47.3) | 91 (48.4) | χ2 = .026, p = .872 |
| Age (SD) | 24.88 (4.2) | 24.54 (4.7) |
t = -.532, df = 262, p = .595 |
24.39 (3.7) | 25.03 (4.6) |
t = 1.075, df = 260, p = .283 |
| Education high school (%) | 165 (80.5) | 41 (69.5) | χ2 = 3.232, p = .072 | 62 (83.8) | 142 (75.5) | χ2 = 2.098, p = .148 |
| Recruitment pathway | ||||||
| Early recognition (%) | 91 (44.4) | 20 (33.9) |
χ2 = 2.076, p = .354 |
35 (47.3) | 77 (41.0) | |
| Depression (%) | 87 (42.4) | 30 (50.8) | 23 (31.1) | 91 (48.4) | χ2 = 8.823, p = .012* | |
| ADHD (%) | 27 (13.2) | 9 (15.3) | 16 (21.6) | 20 (10.6) | ||
| Psychiatric Medication | ||||||
| Yes (%) | 111 (54.1) | 39 (66.1) | χ2 = 2.669, p = .102 | 34 (45.9) | 115 (61.2) | χ2 = 5.018, p = .025* |
| Substance Use | ||||||
Smoking status
|
97 (47.3) 94 (45.9) 14 (6.8) |
20 (33.9) 31 (52.5) 8 (13.6) |
χ2 = 4.784, p = .091 | 42 (56.8) 27 (36.5) 5 (6.8) |
74 (39.4) 95 (50.5) 19 (10.1) |
χ2 = 6.529, p = .038* |
Cannabis present
|
147 (71.7) 17 (8.3) 12 (5.9) 15 (7.3) 14 (6.8) |
45 (76.3) 3 (5.1) 2 (3.4) 2 (3.4) 7 (11.9) |
χ2 = 3.836, p = .429 | 61 (82.4) 4 (5.4) 3 (4.1) 3 (4.1) 3 (4.1) |
129 (68.6) 16 (8.5) 11 (5.9) 14 (7.4) 18 (9.6) |
χ2 = 5.350, p = .253 |
Cannabis lifetime
|
84 (41.0) 46 (22.4) 9 (4.4) 24 (11.7) 42 (20.5) |
23 (39.0) 11 (18.6) 2 (3.4) 6 (10.2) 17 (28.8) |
χ2 = 1.977, p = .740 | 38 (51.4) 16 (21.6) 2 (2.7) 7 (9.5) 11 (14.9) |
68 (36.2) 40 (21.3) 9 (4.8) 24 (12.8) 47 (25.0) |
χ2 = 6.532, p = .163 |
| Risk assessment instrument | EPIbipolar (N = 271) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| isk criterion fulfilled | No-risk | Low-risk | High-risk | Test | |
| N (%) | 30 (11.1) | 136 (50.2) | 105 (38.7) | n/a | |
| Female (%) | 10 (33.3) | 62 (45.6) | 57 (54.3) | χ2 = 4.550, p = .103 | |
| Age (SD) | 24.13 (3.03) | 25.40 (4.61) | 25.02 (4.34) | F = .570, df = 2, p = .566 | |
| Education high school (%) | 24 (80.0) | 107 (78.7) | 81 (77.1) | χ2 = .144, p = .931 | |
| Recruitment pathway | |||||
| Early recognition (%) | 14 (46.7) | 50 (36.8) | 51 (48.6) | χ2 = 23.707, p < .001** | |
| Depression (%) | 5 (16.7) | 72 (52.9) | 43 (41.0) | ||
| ADHD (%) | 11 (36.7) | 14 (10.3) | 11 (10.5) | ||
| Psychiatric Medication | |||||
| Yes (%) | 11 (36.7) | 87 (64.0) | 57 (54.3) | χ2 = 8.077, p = .018* | |
| Substance Use | |||||
Smoking status
|
16 (53.3) 9 (30.0) 5 (16.7) |
64 (47.1) 64 (47.1) 8 (5.9) |
38 (36.2) 56 (53.3) 11 (10.5) |
χ2 = 8.771, p = .067 | |
Cannabis present
|
25 (83.3) 1 (3.3) 0 (0.0) 2 (6.7) 2 (6.7) |
96 (70.6) 11 (8.1) 8 (5.9) 8 (5.9) 13 (9.6) |
76 (72.4) 10 (9.5) 6 (5.7) 7 (6.7) 6 (5.7) |
χ2 = 4.647, p = .795 | |
Cannabis lifetime
|
14 (46.7) 8 (26.7) 0 (0.0) 3 (10.0) 5 (16.7) |
52 (38.2) 29 (21.3) 6 (4.4) 17 (12.5) 32 (23.5) |
44 (41.9) 21 (20.0) 5 (4.8) 11 (10.5) 24 (22.9) |
χ2 = 3.173, p = .923 | |
| Cohen’s kappa (%) | Balanced accuracy (%) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 95% CI | 95% CI | 95% CI | 95% CI | |||||||||
| lower | upper | lower | upper | lower | upper | lower | upper | |||||
| BPSS-P | ||||||||||||
| 10-fold | .275 | .149 | .401 | 66.9 | 59.2 | 74.6 | 63.0 | 49.7 | 76.3 | 63.0 | 49.7 | 76.3 |
| Leave-one-site-out | .197 | .033 | .361 | 61.9 | 52.0 | 71.9 | 45.0 | 17.7 | 72.2 | 78.9 | 60.2 | 97.7 |
| BARS | ||||||||||||
| 10-fold | -.001 | -.132 | .129 | 49.2 | 41.9 | 56.5 | 56.2 | 44.2 | 68.3 | 42.1 | 35.7 | 48.5 |
| Leave-one-site-out | -.000 | -.103 | .103 | 48.2 | 40.1 | 56.2 | 53.8 | 41.9 | 65.7 | 42.5 | 30.7 | 54.4 |
| EPIbipolar | ||||||||||||
| 10-fold | -.049 | -.143 | .045 | 45.0 | 35.3 | 54.8 | 66.8 | 58.0 | 75.5 | 23.3 | 7.2 | 39.4 |
| Leave-one-site-out | -.027 | -.203 | .148 | 46.2 | 35.6 | 56.8 | 62.4 | 44.4 | 80.5 | 30.0 | 15.2 | 44.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





