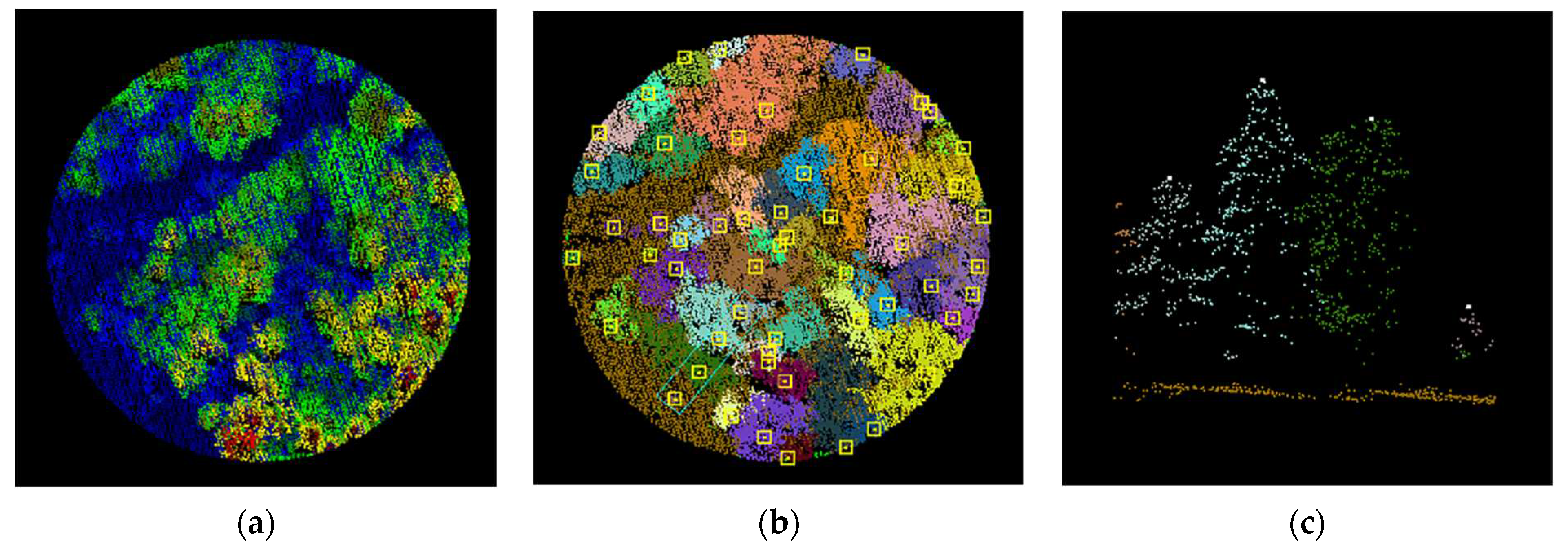
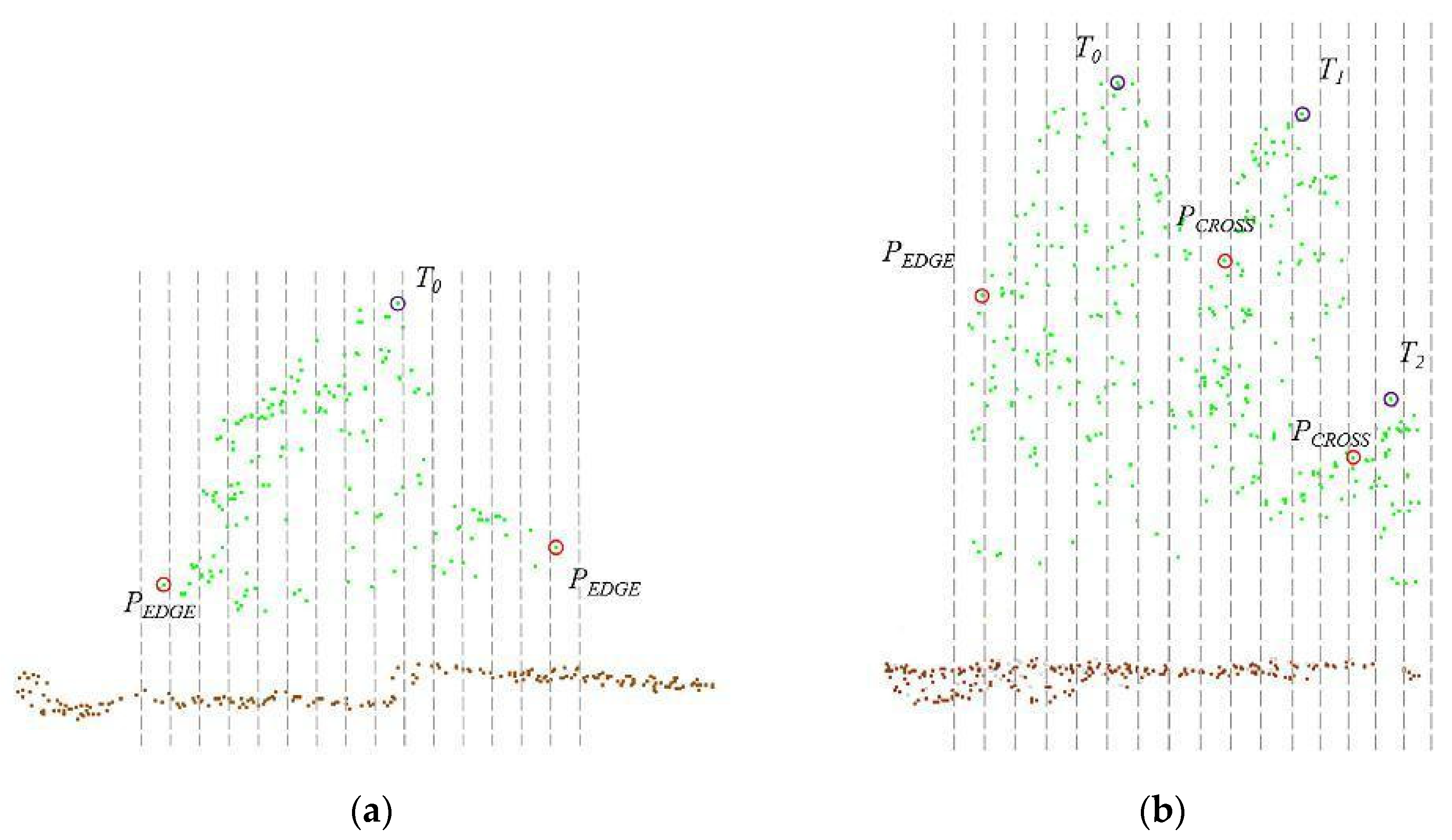
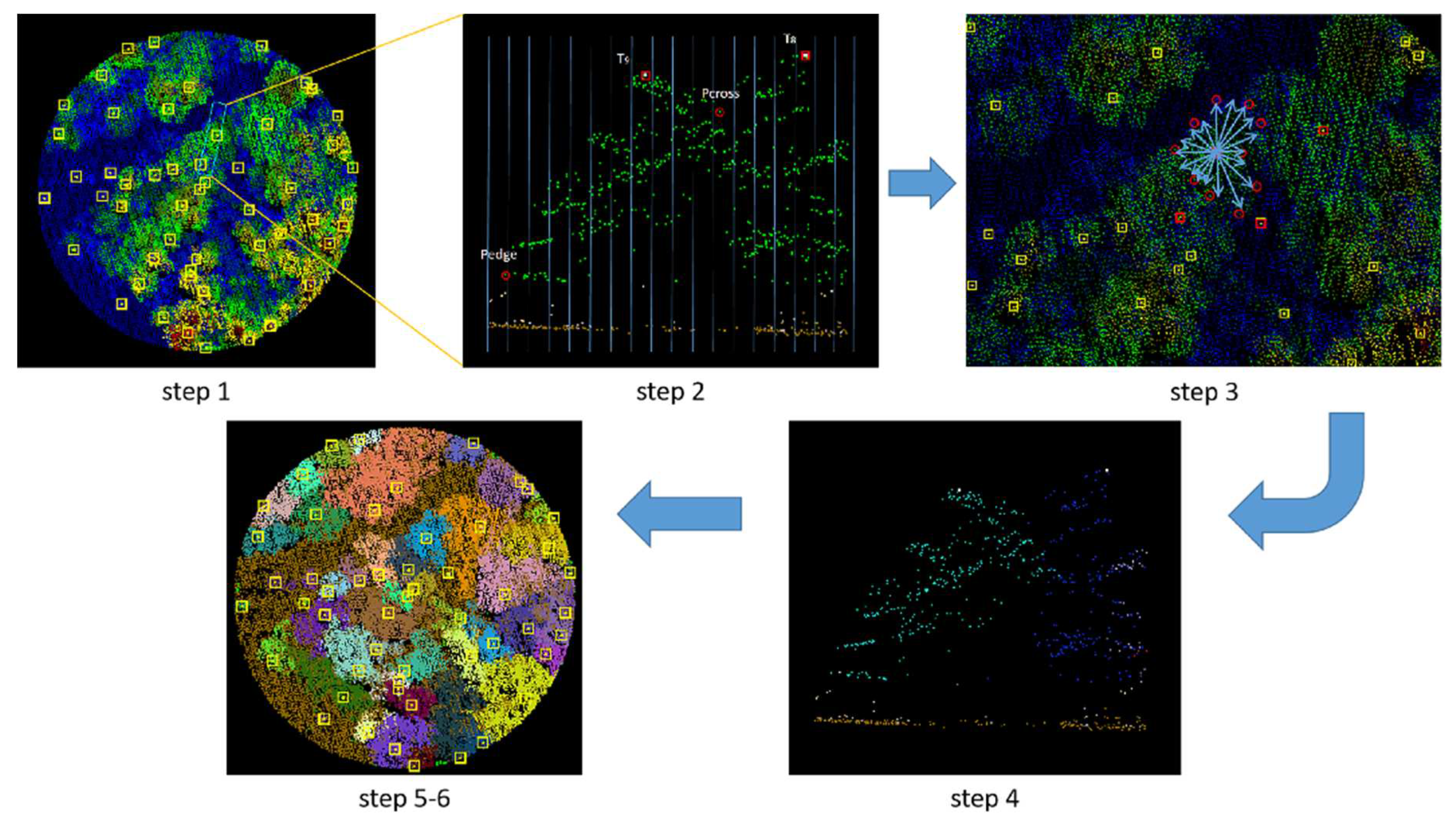
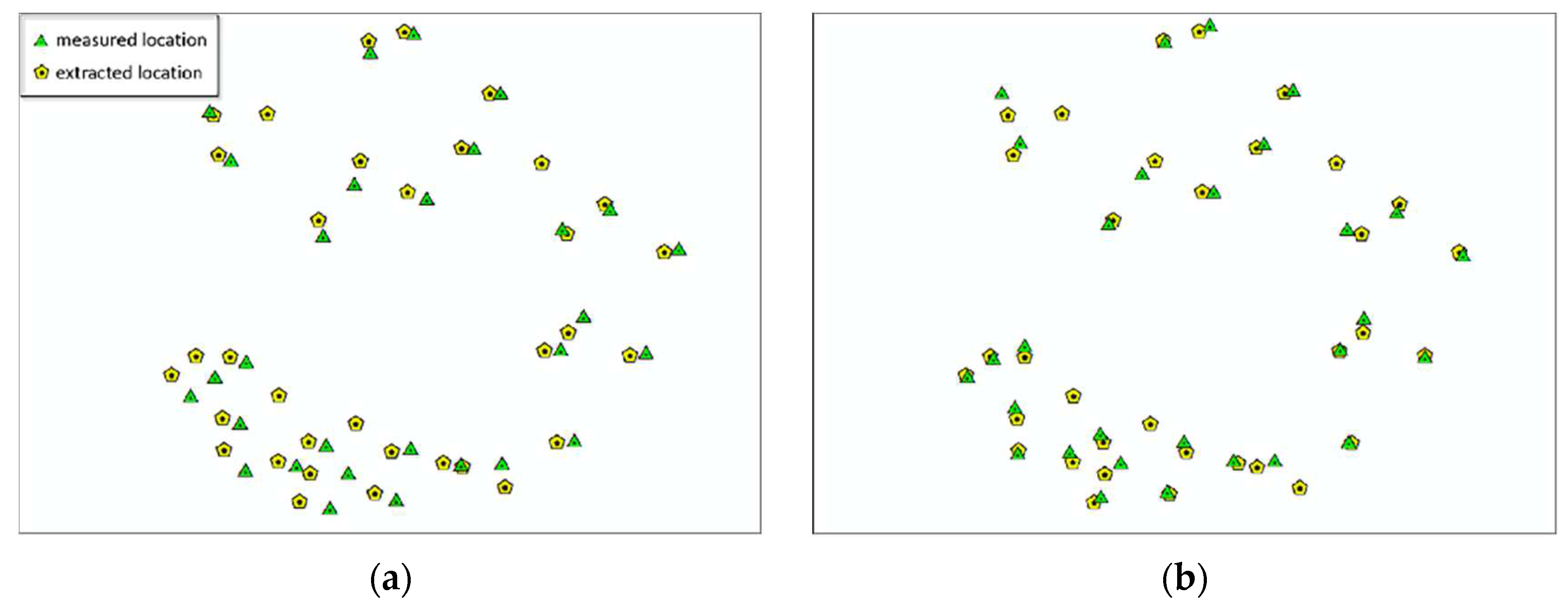
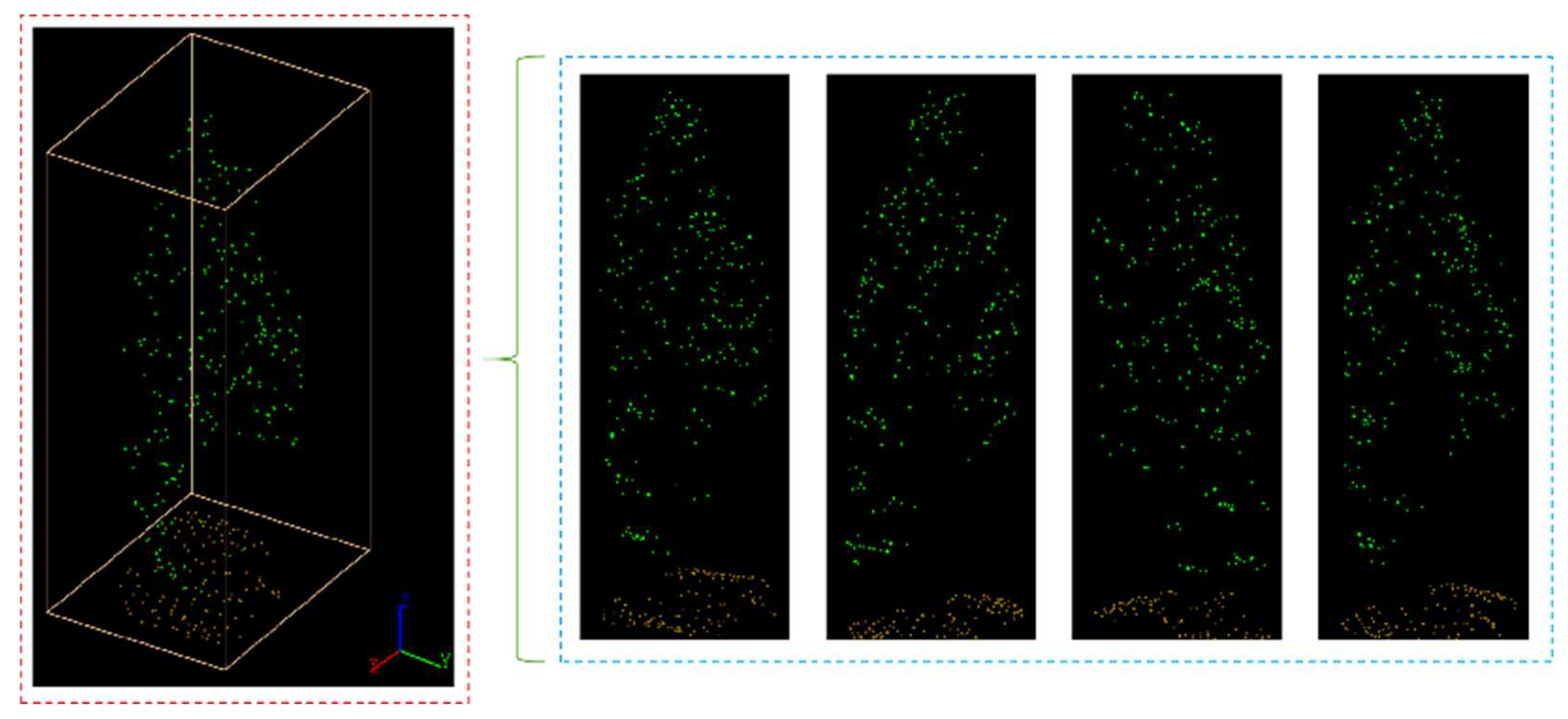
1. Introduction
Forests are the largest carbon reservoir and ecosystem on land, providing not only vital ecological services but also enormous economic benefits in the process of human development [
1]. The acquisition of forestry parameters, such as tree height, crown width, species, and biomass, etc., is critical in the process of investigation and monitoring. The monitoring of forest resources is to provide an effective scientific methodology for off-ground density estimation, change trend analysis, forest growth detection, harvest prediction and so on [2-4]. Traditional forest resource monitoring is usually time-consuming and labor-intensive due to manual field collection, which is unsuitable for large-scale research. In addition, the information accuracy for parameters such as tree height and crown width collected by hand demonstrate a high margin of error; therefore, it is necessary to explore a new and reliable forest survey method to meet the current needs of forestry production and ecological construction [
5]. Since the characteristics of remote sensing technology include wide monitoring range, quick data acquisition, and low cost, it is theoretical and practical to apply it to the extraction of forestry parameters in large areas.
Passive optical remote sensing such as multispectral remote sensing, hyperspectral remote sensing, and high-resolution remote sensing have been widely used for estimating forest parameters with notable progress and outcomes. The spectral information of passive optical remote sensing data from visible to near-infrared reflects the physical structure parameters of the forest, and the forestry parameters such as vegetation index and texture information can then be the derived. Ouma used semi-variance functions on QuickBird images to investigate the relationship between forest biomass and spectral variables in Kenya [
6]. Marshall & Thenkabail compared the response of hyperspectral data EO-1 Hyperion and multispectral data on biomass generation, determining that hyperspectral data was superior [
7]. Mohammadi et al. developed a model for forest stock estimation in northern Iraq using Landsat ETM+ data [
8]. Franklin et al. estimated the depression of spruce using Thematic Mapper (TM) data with an accuracy of 80% [
9]. According to the findings of the preceding studies, passive optical remote sensing data are mostly used to invert the horizontal structural parameters of forests and are rarely utilized to estimate the vertical structure (e.g., tree height) of forests. This is mainly attributed to the low signal penetration of optical remote sensing data, which makes obtaining information in the vertical direction challenging. However, some researchers, such as Brown et al. [
10], have tried to use high resolution overlapping stereo images to achieve canopy height estimation, but the elevation accuracy of the under-tree surface still cannot meet sufficiency requirements.
Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) as the active remote sensing technology has the ability to penetrate forest vegetation canopies and observe the ground in all weather conditions. SAR can also interact with treetops and trunks to gather the vertical structure of forests. Cloude & Papathanassiou used polarization coherence tomography to reconstruct low-frequency three-dimensional (3D) images and provided a method for optimal interferometric baseline selection to estimate forest vertical structure [
11]. Blomberg et al. used L-band SAR data from Argentina’s observation satellite SAOCOM to accurately invert forest biomass in northern Europe [
12]. Matasci et al. approximated the above-ground biomass of forests with root-mean-square deviation (RMSD) error of less than 20% using European Space Agency (ESA) P-band radar data [
13]. Although SAR is sensitive to forest vertical structure, backscatter signal saturation often occurs when the forest biomass is large. For example, Luckman et al. used JERS-1 SAR data to estimate tropical forest biomass and discovered that the backscatter coefficient saturated when the biomass reached 6 kg/m
2, affecting the accuracy of forest biomass estimation [
14].
Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) has advantages such as high angle resolution, distance resolution, and anti-interference ability, which make it possible to gather high precision 3D surface information while avoiding signal saturation in high biomass areas [
15]. Particularly in the field of forestry survey application, LiDAR has significant advantages over other remote sensing technologies with respect to forest height measurement and vertical structure acquisition in forest stands. LiDAR can provide highly accurate horizontal and vertical information of forests depending on the sampling method and configuration, but the optical sensors can only be used to provide detailed information on the horizontal distribution of forests. Therefore, this study will use airborne LiDAR data to identify the critical indicators of the forest resources present in the sample area.
The basis for estimating forestry parameters is accurate segmentation of tree point clouds. Tree crown segmentation methods based on LiDAR data are mainly divided into the following two categories: raster-based tree segmentation and direct point cloud-based tree segmentation. By interpolating the 3D point cloud, the raster-based tree segmentation firstly develops a digital surface model (DSM) and a canopy height model (CHM) by normalizing the tree height. Then, based on the height undulations in the CHM, local maximum [16, 17] or variable windows [18, 19] are used to search for local maximum as initial treetop locations, and finally, edge detection or feature extraction methods are employed to identify tree canopies. Watershed segmentation algorithms [20, 21, 22] and flow tracking algorithms [
23] are two examples of raster-based tree segmentation algorithms. The CHM-based segmentation method is quick and effective, but it can identify the wrong segment and omit details. Moreover, the segmentation accuracy is directly influenced by the CHM resolution, and CHM only represents canopy surface information without describing the canopy’s vertical structure. With the development of LiDAR technology, the density and accuracy of point clouds have rapidly developed, and many researchers directly use the point cloud data to segment the tree crowns [24, 25]. Wang et al. first proposed voxel segmentation of raw point cloud data with the vertical canopy structure of the forest, dividing the canopy areas of different heights based on the elevation distribution within the voxels and performing tree segmentation [
26]. Morsdorf et al. used local maxima search as seed points for k-mean clustering of 3D point clouds [
27]. Li et al. proposed a top-to-bottom area growth algorithm relying on the relative distance between trees, and this method achieved 90% segmentation accuracy for coniferous forests, but the applicability was not transferrable to dense forest areas with overlapping canopies [
28]. Compared with the traditional raster-based tree segmentation method, the direct segment processing of point cloud data can more accurately reflect the 3D structure of trees. Unfortunately, the majority of segmentation studies on tree segmentation using LiDAR data prefer low-density stands, and most of them are not ideal for complex forest environments with overlapping canopies and a variety of tree species. Additionally, the single segmentation method is not universal and is challenging to apply to trees of different scales. To get good canopy segmentation for further tree species classification and parameter extraction, this paper adopts a rotating profile segmentation method to obtain all possible seed points as initial treetop and finds canopy edges by analyzing the trend of profile point clouds.
For the study of tree species classification and identification based on LiDAR data, Holmgren & Persson used a supervised classification method to distinguish Norway spruce and Scots pine with 95% accuracy [
29]. Othmani et al. used terrestrial laser scanning (TLS) data to distinguish five tree species using wavelet transform with an overall accuracy of 88% [
30]. Lin & Hyyppä used a support vector machine approach to classify the tree species by extracting point cloud distribution, crown-internal and tree-external features, and achieved an overall accuracy is 85% [
31]. Kim et al. extracted canopy structure parameters for tree species classification using leaf-on and leaf-off LiDAR data in the growing and deciduous seasons; the results indicated that tree species identification from both data was superior to single season data [
32]. In addition, some other scholars have made full use of point cloud intensity information and introduced it into tree species classification studies, such as Ørka et al. who combined structural and intensity features to classify Norway spruce and birch, and their results proved that the classification accuracy was better than using structural or intensity features alone [
33]. The primary benefit of LiDAR intensity is related to the reflectance of surface features; there are several intensity-related confounding variables, such as parameters connected to the feature’s environment, the sensor hardware system, and the data gathering geometry [
34]. As a result, algorithmic parametric models based on intensity information are usually limited to a single location. As demonstrated above, accurate canopy structure information is the most reliable feature for tree species classification. In this paper, a machine learning method is utilized to learn the shape of canopy profiles of known tree species in sample plots for learning, and finally to design the tree species identification model. The method is suitable for most tree species with different shapes and can be widely used in most forest survey situations.
LiDAR has been successfully applied in forestry parameter extraction for a long time. Solodukhin et al. used LiDAR point cloud data for tree height extraction, and the RMSE between their estimated tree height and photogrammetry results was 14 cm [
35]. The parameters that can be directly obtained from the segmented tree crowns are generated from the LiDAR data. Information such as tree height and crown width or height can be easily obtained, but the crown width diameter at breast height (DBH) and tree species cannot be directly obtained. Although LiDAR data cannot directly estimate the diameter at breast height of forest trees, some existing studies use measured data to establish relationships and indirectly infer tree diameter at breast height parameters from LiDAR data. For example, Shrestha & Wynne estimated the diameter at breast height of trees in urban areas of central Oklahoma, USA, using the Optech ALTM 2050 system with an R
2 of 0.89 [
36]. As parameters derived from LiDAR coordinate information, canopy structure parameters are widely used in forest biomass inversion. They are usually calculated from the vegetation echoes after elevation normalization, including 25%, 50%, 75% percentile height, maximum tree height, mean tree height, and forest canopy height. Bortolot & Wynne established a regression analysis based on the 25%, 50% and 75% percentile height and biomass, and obtained correlation coefficients between predicted and actual measurements ranging from 0.59 to 0.82, with RMSE ranging from 13.6 to 140.4 t/ha [
37]. Wang et al. estimated aboveground biomass based on an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) LiDAR system and the results showed that the mean height of trees was the most reasonable parameter to predict aboveground biomass [
38]. Several researchers have recognized the importance of LiDAR intensity data and applied it to biomass inversion, such as García et al. who estimated biomass in a Mediterranean forest in central Spain using height parameters derived from airborne LiDAR point cloud data and distance-corrected intensity parameters; consequently, their results showed that intensity correction could improve the accuracy of forest biomass estimation [
39]. Numerous research studies have demonstrated that parameter estimation considering tree species classifications is more accurate. Donoghue et al. discovered that LiDAR-based tree height and biomass estimation algorithms for coniferous forests were not applicable to mixed forests [
40]. Jin et al. introduced tree species as a dummy variable into the regression model when point cloud feature regression modeling was performed to estimate the stocking volume using the peak forest site in Guangxi, with an elevated coefficient of determination R² of the model estimation results [
41]. Pang & Li divided temperate forests in the Xiaoxing’an Mountains into coniferous, broadleaf, and mixed forests for biomass inversion, and the findings revealed that differentiated biomass modeling can further improve biomass estimation accuracy [
42]. Therefore, in this paper we will use existing tree species to verify and update the wrong tree species information in the sample plots, as well as correct the above-ground biomass at breast height, storage volume, and other parameters of trees in the sample plots based on the accurate tree species information.
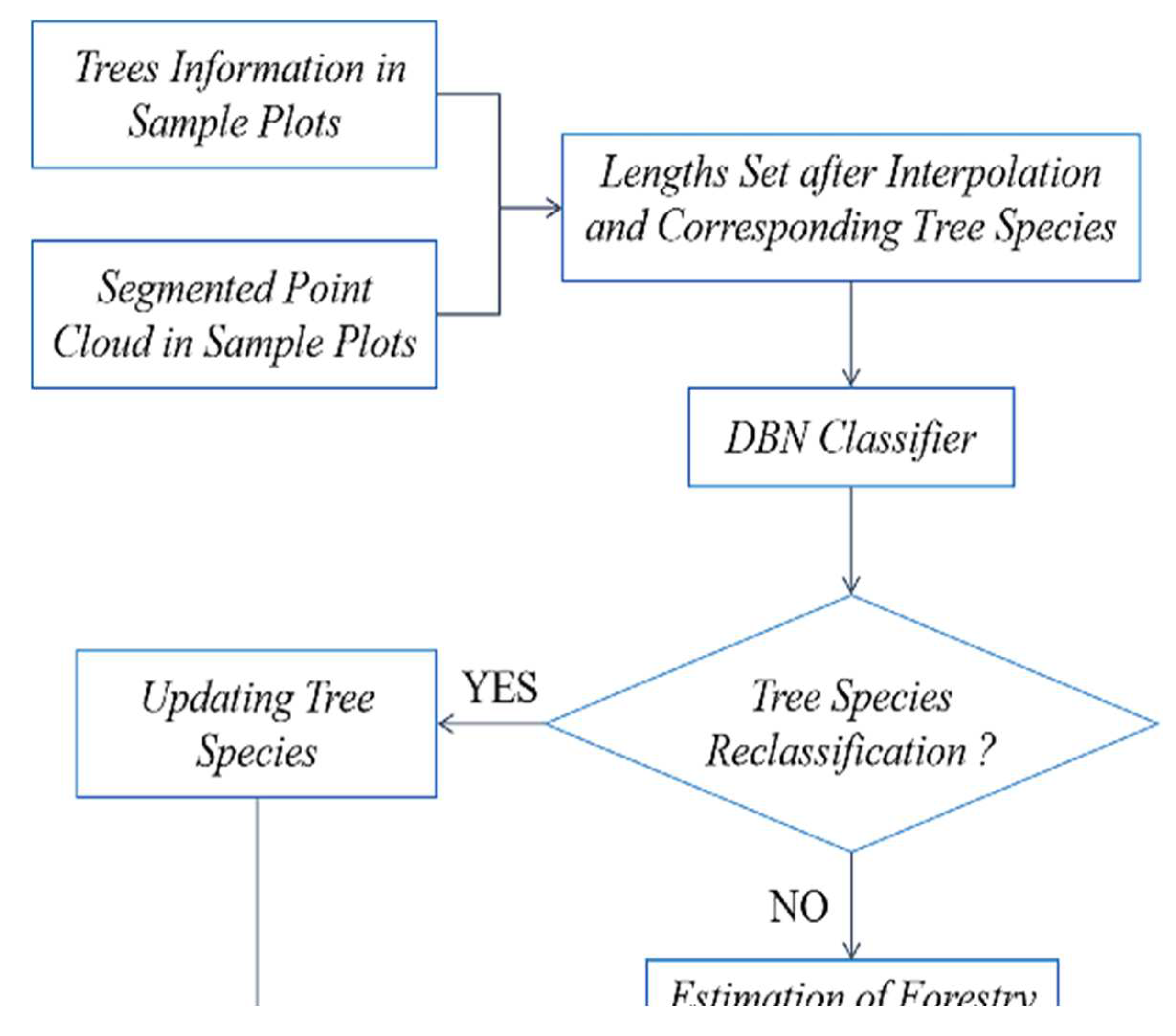
In summary, this paper focuses on the urgent needs of the current forestry survey by using LiDAR point cloud data, which has high-precision horizontal and vertical structure information, to verify and update the error information of manually collected sample plots. The paper addresses the following issues: (1) To solve the segmentation problem of staggered canopies for the complex growing condition of the northeastern primeval forest, the rotating profile segmentation method is used to obtain the canopy edge points and obtain the segmentation point cloud. (2) Since the spectrum information of tree species varies with seasons and growth phases, it is difficult to obtain multi-hyperspectral remote sensing data with LiDAR in most circumstances. This paper will focus on the classification of tree species by using the geometric structure information of tree canopies based on the segmented point cloud. However, the structure of individual tree species is very different, so this paper attempts to use the segmentation of the shape of the canopy section; that is, the 3D information is converted into two-dimensional (2D) information, and then the intercepted line segments of the section are used to change the 2D shape into a one-dimensional (1D) interpolation vector by determining the change trend of the line segments. Based on the 1D vector, the deep belief network (DBN) method is used to establish the tree species recognition model and update the sample tree species error information by combining the sample tree species information. (3) Finally, forestry parameters (diameter at breast height, above-ground biomass and storage volume) are estimated and updated based on the updated tree species information by achieving the extraction of forestry survey parameters based on LiDAR point cloud data and validating the superiority of LiDAR data in forestry parameter extraction for its application in forest resource surveying.
This paper is organized as follows:
Section 1 discusses the significance and advantages of LiDAR point cloud data in forestry resource surveying, as well as the current status and limitations of research on tree segmentation, tree species classification, and forestry parameter extraction based on LiDAR data, which leads to the method of checking and updating the incorrect information of manually collected sample plots based on LiDAR data proposed in this paper.
Section 2 includes an overview of the study area’s location and characteristics, as well as an introduction to the experimental data gathering methods and characteristics (including measured sample data and LiDAR point cloud data). It also describes the paper’s research methods and processes, such as point cloud data pre-processing, the tree segmentation method for rotating profiles, tree species classification based on segmented point clouds, and estimation and update of forestry parameters.
Section 3 contains the results of tree canopy segmentation, species identification, and parameter extraction, while
Section 4 has a full analysis and explanation of the findings. Section 6 outlines the approach’s merits and drawbacks and provides an analysis and outlook on future research works.
3. Results
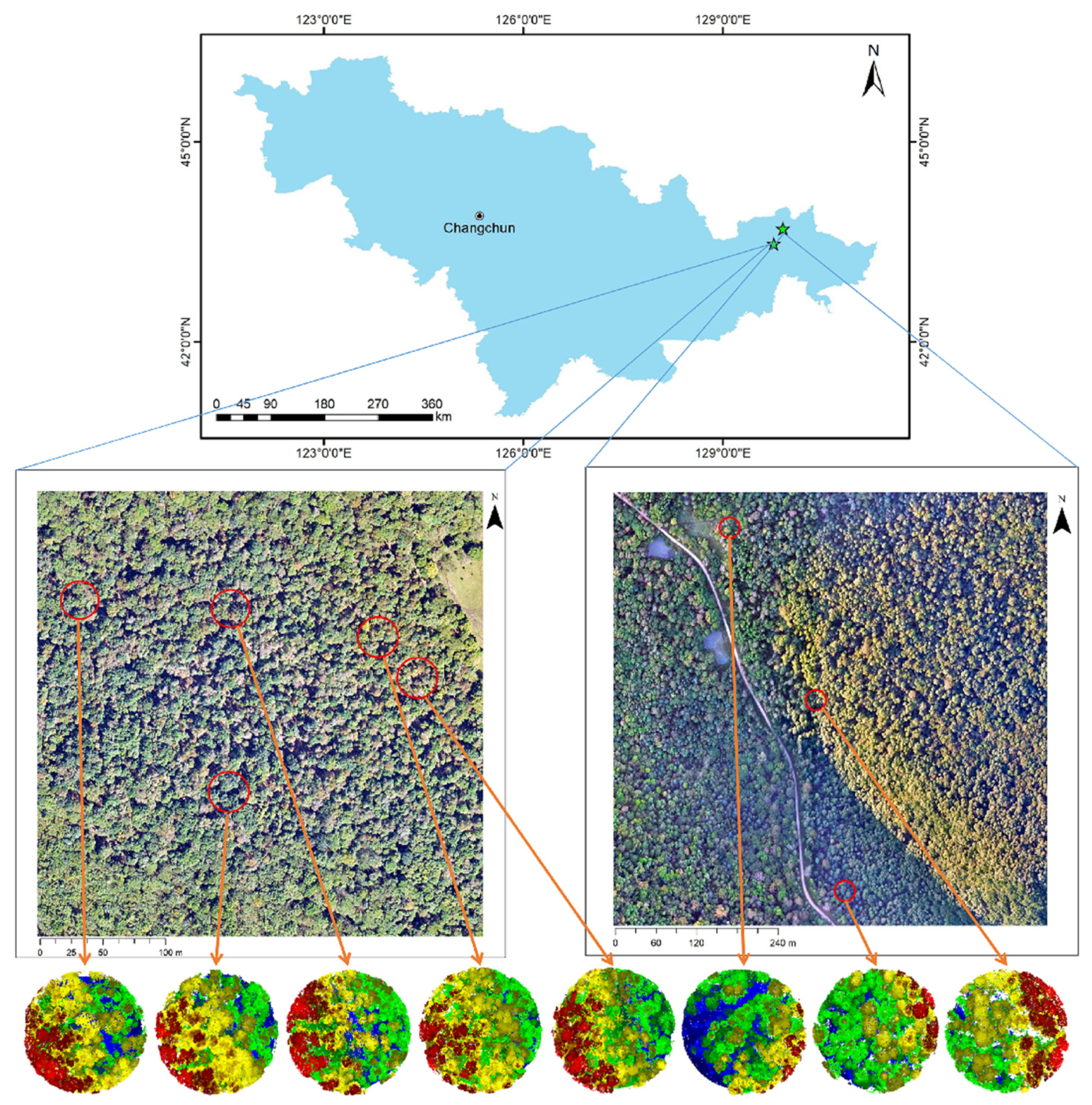
Eight sample plots, totaling 318 trees, were chosen from the Northeast Tiger and Leopard National Park to test the plot verification and update method proposed in this paper. The accuracy of the results from the LiDAR data is compared using the outfield-confirmed data.
3.1. Ground Point Extraction
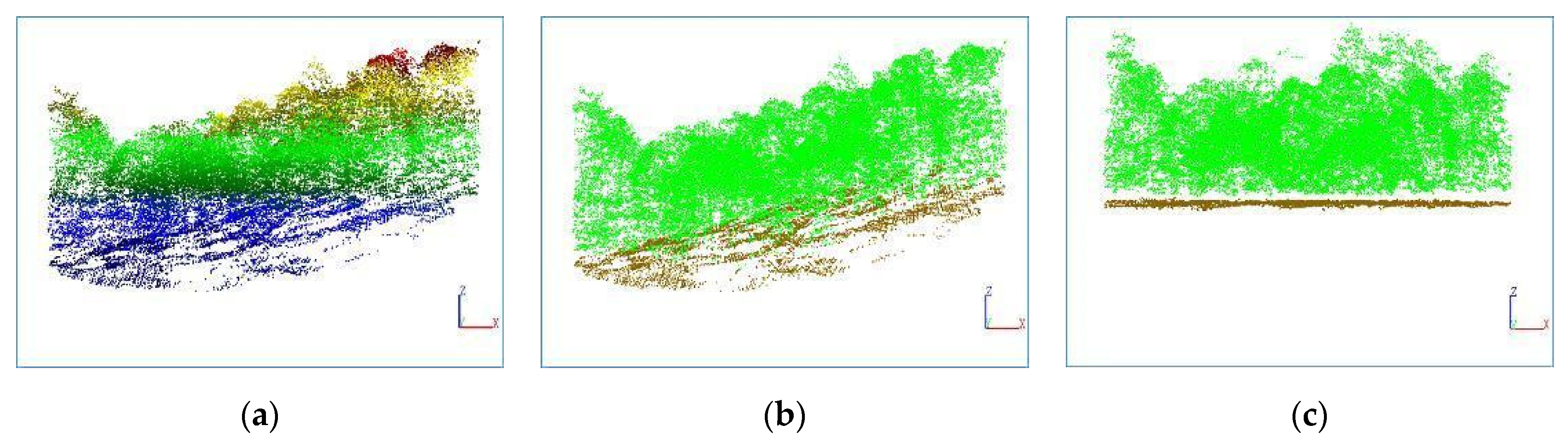
This article uses a PTD algorithm to separate ground points and non-ground points in point cloud data. The eight plots used in this study have diverse terrain conditions, including flat areas, slopes and other situations. To evaluate the accuracy, the following indicators are used:
Separation accuracy: the ratio of correctly classified points to the total number of points in plot;
Type I error: non-ground points classified as ground points after separation;
Type II error: ground points classified as non-ground points after separation.
The ground point separation accuracy of the eight study plots is shown in
Table 7.
As shown in
Table 7, the separation accuracy for each plot is above 95%, indicating that the PTD algorithm has achieved excellent results, and is suitable for various ground conditions. Considering the high separation accuracy, the separated ground points can be used for DEM generation to achieve normalization of point cloud data.
3.2. Tree Segmentation
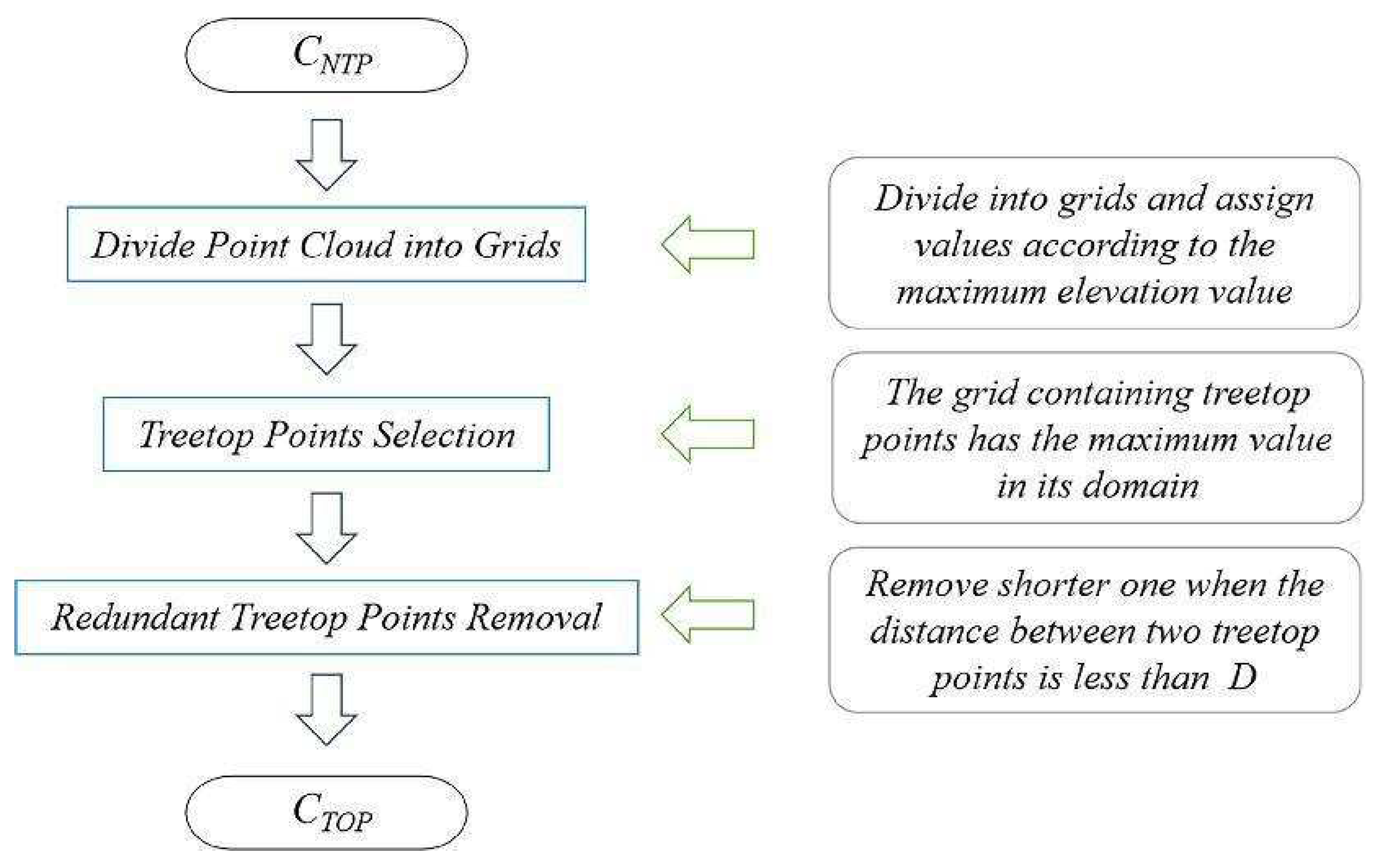
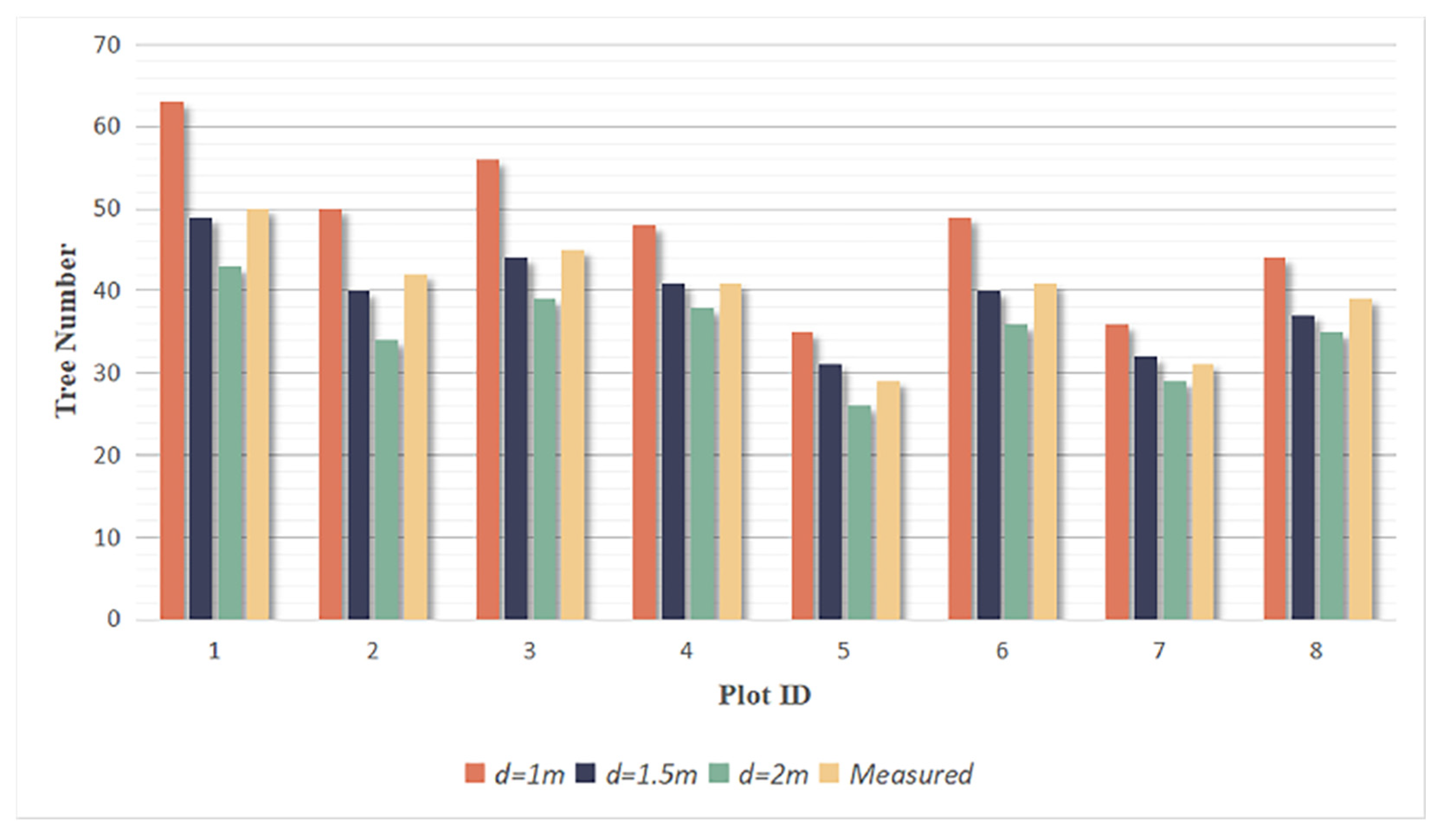
By setting the grid size d, the initial position of trees can be obtained. Using rotating profiles with an angular step of θ, segmented canopies can be generated while optimizing the tree positions. The initial positions are the basis for subsequent treetop points acquisition and final segmentation. Therefore, in order to obtain more accurate initial positions, it is necessary to set a more appropriate grid size. The setting of d is based on the size of the tree canopy in the sample plots, which is concentrated in the range of 2-4 meters in diameter. The value of d should be close to the radius of the tree canopy to ensure that the positions of the trees can be identified to the greatest extent possible. In the experiment, d is set to 1m, 1.5m and 2m to segment the eight sample plots.
Figure 16.
The number of trees segmented from each sample plot.
Figure 16.
The number of trees segmented from each sample plot.
Due to the complexity of natural forest conditions, overlapping canopies can cause short trees to be mistaken as parts of tall trees, resulting in multiple trees being recognized as one tree. Additionally, some trees are divided into multiple trees because of their large canopy or complex shape. These discrepancies cause under-segmentation and over-segmentation in the segmentation results. To evaluate the correct segmentation, under-segmentation and over-segmentation of each plot under different grid sizes d, recall, precision and F-score [
48] are used as indicators to verify and evaluate the accuracy of individual tree segmentation (
Equations 16,
17 &
18). The results are shown in
Table 8.
where
r,
p&
F: recall, precision and F-score
TP: number of correctly segmented trees
FN: number of under-segmented trees
FP: number of over-segmented trees
Table 8.
The TP, FN and FP of different grid sizes d.
Table 8.
The TP, FN and FP of different grid sizes d.
| Plot ID |
Real
Number
|
d= 1 m |
d= 1.5 m |
d= 2 m |
| TP |
FN |
FP |
TP |
FN |
FP |
TP |
FN |
FP |
| 1 |
50 |
49 |
1 |
14 |
47 |
3 |
2 |
42 |
8 |
1 |
| 2 |
42 |
41 |
1 |
9 |
40 |
2 |
0 |
34 |
8 |
0 |
| 3 |
45 |
45 |
0 |
11 |
44 |
1 |
0 |
39 |
6 |
0 |
| 4 |
41 |
41 |
0 |
7 |
40 |
1 |
1 |
37 |
4 |
1 |
| 5 |
29 |
29 |
0 |
6 |
29 |
0 |
2 |
25 |
4 |
1 |
| 6 |
41 |
41 |
0 |
8 |
40 |
1 |
0 |
36 |
5 |
0 |
| 7 |
31 |
31 |
0 |
5 |
31 |
0 |
1 |
29 |
2 |
0 |
| 8 |
39 |
39 |
0 |
5 |
37 |
2 |
0 |
35 |
4 |
0 |
| All |
318 |
316 |
2 |
65 |
308 |
10 |
6 |
277 |
41 |
3 |
Among the three selected grid sizes, when
d=1.5m, the total number of under-segmented and over-segmented trees is the lowest. The number of correctly segmented trees is similar to the actual number of trees in each plot, with a total of 308 correctly segmented trees, which was close to the total actual number of 318 trees. The recall, precision and F-score are calculated in
Table 9, and the F-scores for all eight plots exceed 0.95 when
d=1.5m, with the highest overall F-score of 0.976 in three grid sizes, indicating that the rotational profile algorithm achieves good segmentation results. Therefore, the part of the correctly segmented trees with
d=1.5m was selected for subsequent species identification and parameters extraction.
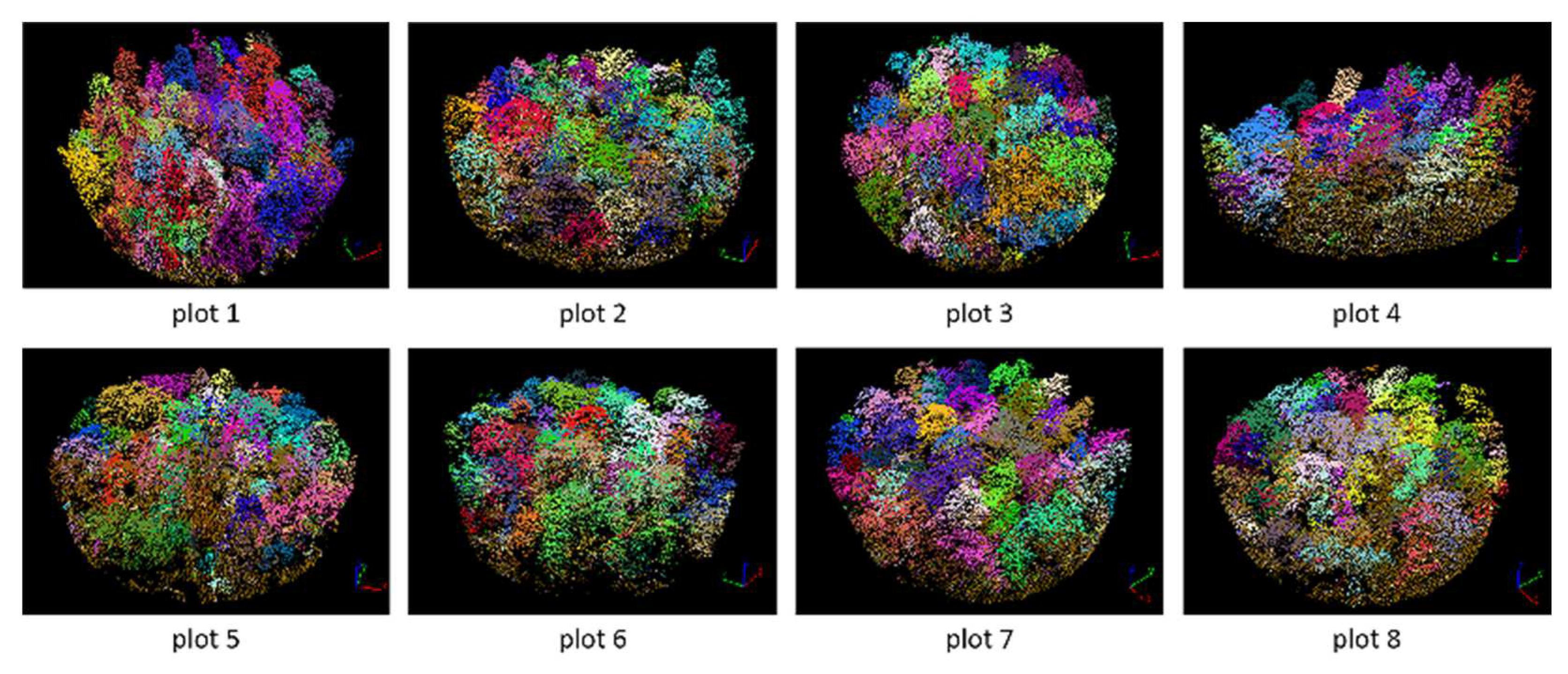
Figure 17.
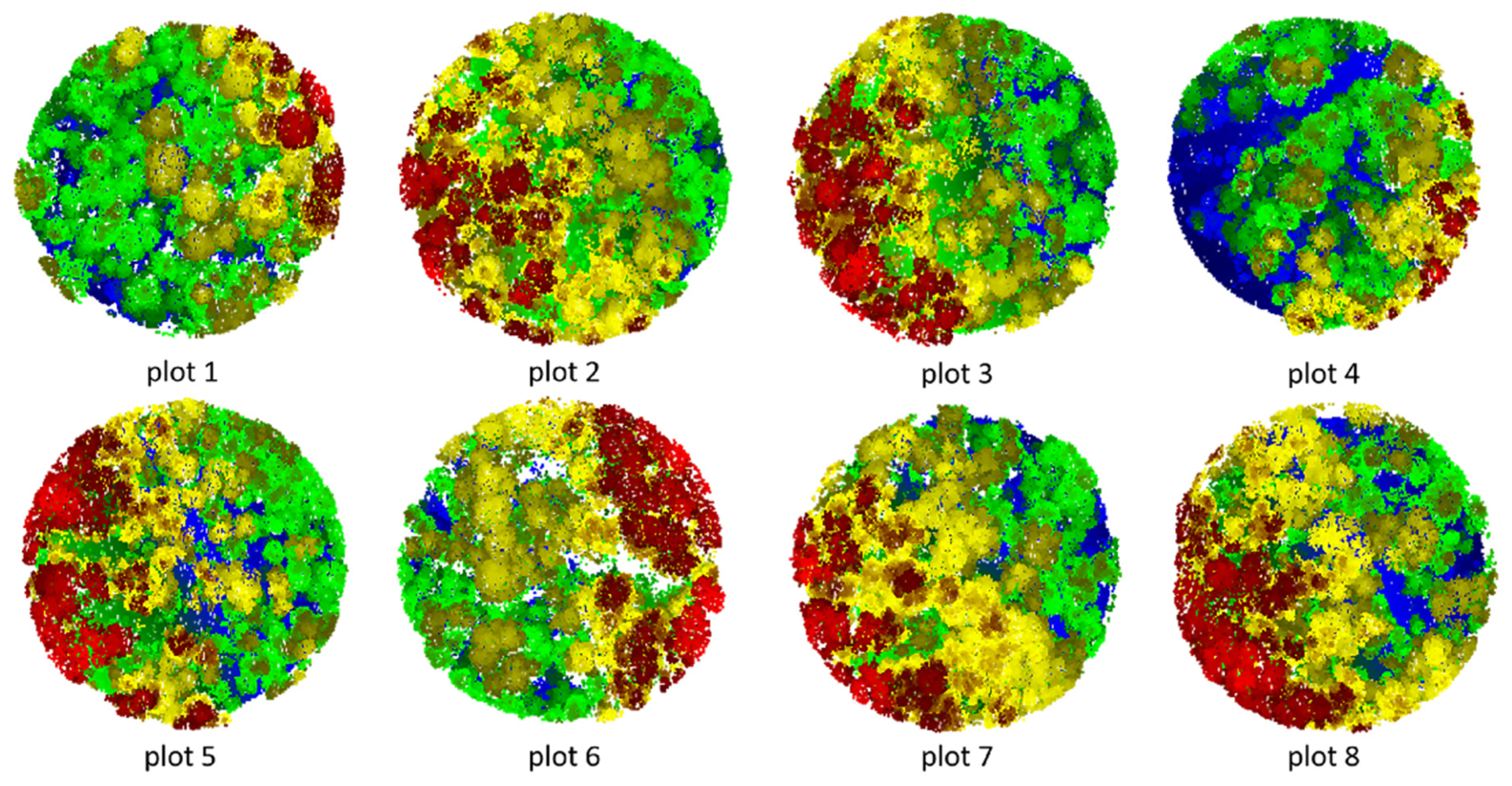
Segmented point cloud of each plot.
Figure 17.
Segmented point cloud of each plot.
3.3. Plots Matching and Tree Species Identification
The main purpose of plot matching is to solve the problem of positional differences between measured data and point cloud. To this end, this paper proposes the concept of matching degree and uses dominant trees for plot matching. However, due to the complexity of the actual situation, it is difficult to achieve complete consistency between the two datasets. Therefore, the deviation of the position of each tree is statistically collected and the deviation values are calculated, as shown in
Table 10. Plot matching is considered complete when the matching degrees of the eight plots are greater than 90% and the deviation values are less than the threshold of 8m.
Based on the plots matching, accurate tree positions can be obtained. In forest surveys, the trees species information in sample plots is mostly accurate. This paper utilizes species information from sample plots to identify and extract individual erroneous tree species information, thereby providing correct species information for obtaining accurate forestry parameters in subsequent forestry surveys.
This article successfully converts the classification problem of 3D point clouds into 1D feature vector classification. It also effectively preserves the detailed characteristic information, fully utilizing spatial structural information to summarize the geometric morphology of each tree, thus achieving tree species identification, classification and updating. The main tree species in the plots include pine, oak, birch, elm, poplar, maple and other species. Several typical profiles are selected as training samples to obtain the morphological structure and parameters of each species.
Table 10 shows that when the sample size of a certain tree species is insufficient, more data can be obtained by selecting profiles in multiple directions.
The trained model is applied to achieve classification. To evaluate the classification performance, the correct rate is defined as the ratio of the number of successfully classified trees to the number of misclassified trees. The method proposed is used to update the tree species information of the trees in eight plots, and the results are shown in
Table 11. Including "Others", which is a collection of trees with extremely low numbers, the overall correct rate reaches 90.9%, providing a reliable tree species classification method and model for forest surveys.
The details are listed in the form of a confusion matrix in
Table 13, which can more accurately indicate the error correction information for each tree species.
Table 12 and
Table 13 show that most tree species can be corrected with 100% accuracy, and the few misclassified tree species are due to different degrees of damage to the tree canopy or inaccurate profile structural information caused by being close to adjacent trees during segmentation. Overall, using LiDAR data to correct tree species information is a reliable method with high accuracy, suitable for classifying most normally growing tree species.
Table 12.
Accuracy of the tree identification.
Table 12.
Accuracy of the tree identification.
| Tree Species |
Correct Classification |
Type Ⅰ Error 1
|
Type Ⅱ Error 2
|
Corrected Tree Number |
Correct Rate |
Overall Correct Rate |
| Pine |
39 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
100% |
90.9% |
| Oak |
25 |
0 |
2 |
2 |
100% |
| Birch |
14 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
100% |
| Elm |
17 |
2 |
1 |
3 |
100% |
| Linden |
107 |
7 |
0 |
6 |
85.7% |
| Poplar |
18 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
100% |
| Maple |
45 |
0 |
3 |
2 |
66.7% |
| Others |
32 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
100% |
Table 13.
Confusion matrix of tree species misinformation correction.
Table 13.
Confusion matrix of tree species misinformation correction.
| |
Collected |
Pine |
Oak |
Birch |
Elm |
Linden |
Polar |
Maple |
Others |
CR 1 |
| True |
|
| Pine |
39 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
100% |
| Oak |
0 |
25 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
100% |
| Birch |
0 |
0 |
14 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
100% |
| Elm |
1 |
0 |
0 |
17 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
100% |
| Linden |
1 |
2 |
1 |
0 |
107 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
87.5% |
| Poplar |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
18 |
1 |
0 |
100% |
| Maple |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
45 |
0 |
66.7% |
| Others |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
32 |
100% |
3.4. Forestry Parameters Extraction
After tree species identification and updating, information is taken from the major tree species’ segmented point cloud, and is utilized to estimate forestry parameters. Linear regressions are performed between the measured forestry parameters and the estimated parameters.
Figure 18.
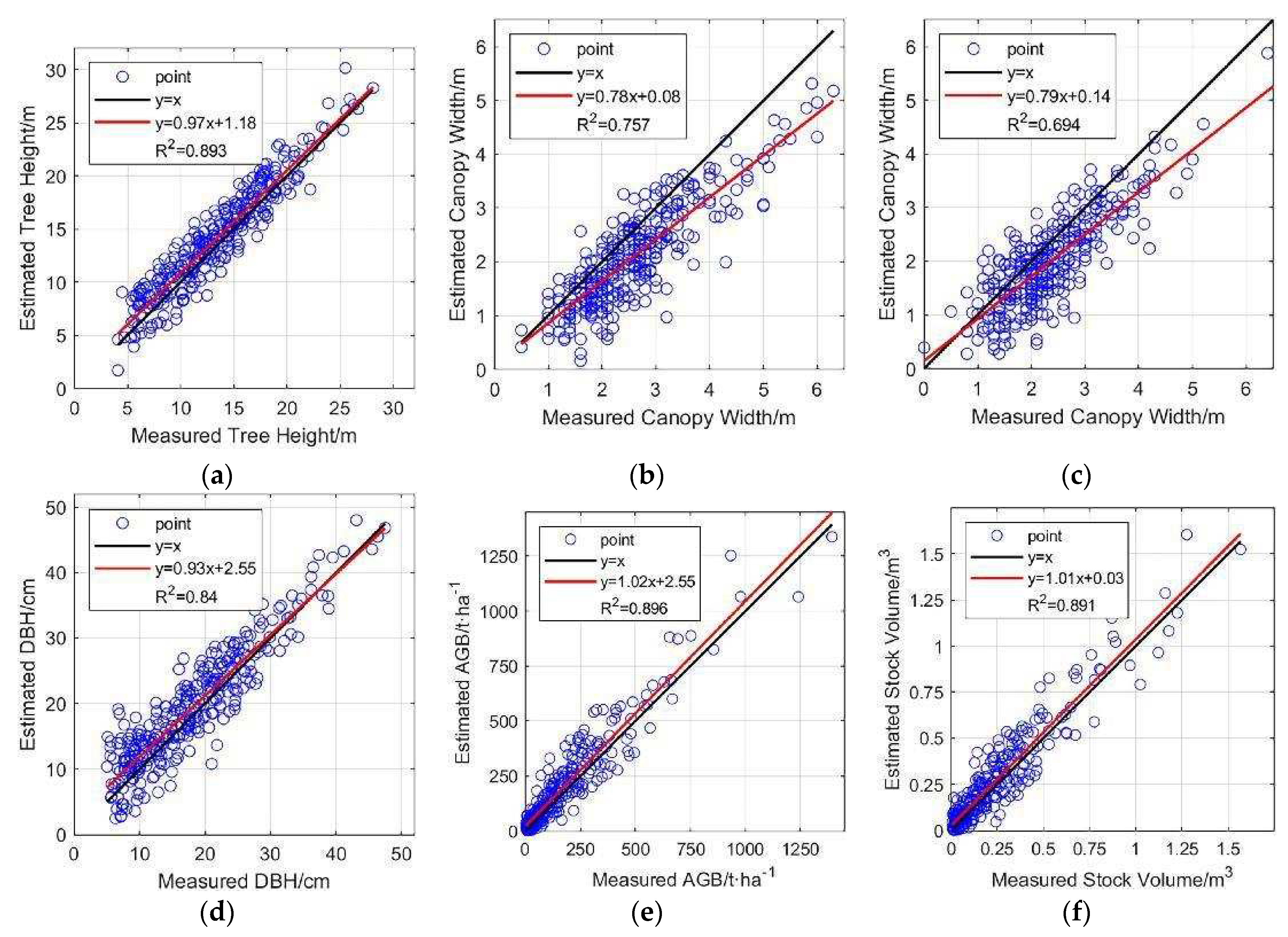
Linear regression plots of six parameters. Red lines are linear regression lines. (a) Tree height; (b) East-west canopy width; (c) North-south canopy width; (d) DBH; (e) AGB; (f) Stock volume.
Figure 18.
Linear regression plots of six parameters. Red lines are linear regression lines. (a) Tree height; (b) East-west canopy width; (c) North-south canopy width; (d) DBH; (e) AGB; (f) Stock volume.
To quantitatively describe the estimation results of each parameter, the coefficient of determination (
R2), the mean absolute error (
MAE) and the root mean square error (
RMSE) are chosen to evaluate the estimation accuracy (
Table 14).
where
: the measured value. (1
≤ i ≤ n,
n is the number of measured values)
: the estimated value
: average of measured values
Table 14.
Estimation accuracy of forestry parameters.
Table 14.
Estimation accuracy of forestry parameters.
| Parameters |
Tree Height |
Canopy Width |
DBH |
AGB |
Stock Volume |
| East-West |
North-South |
| R2 |
0.893 |
0.757 |
0.694 |
0.840 |
0.896 |
0.891 |
| RMSE |
1.793 |
0.719 |
0.638 |
3.735 |
70.914 |
0.090 |
| MAE |
1.465 |
0.575 |
0.511 |
3.015 |
48.875 |
0.066 |
The estimation results of four forestry parameters, namely, tree height, DBH, AGB, and stock volume, show strong consistency with the measured values, with R2 exceeding 0.8. Tree height shows higher consistency in the range of 20-30 m, and in the range of 5-20 m, the estimated tree heights are slightly higher than the measured heights in general, which was similarly reflected in the estimation of DBH. The accuracy of canopy width estimation is relatively lower (R2=0.757 for east-west and R2=0.694 for north-south), and the estimated values are smaller than the measured values in general. This also confirms that the use of LiDAR data is expected to become a powerful tool for future forestry surveys, significantly reducing human involvement and achieving rapid and accurate acquisition of large-scale forest parameters.
4. Discussion
4.1. Tree Segmentation
Among the three tested grid sizes d, the best segmentation performance is achieved when d=1.5m, with precision, recall and F-score of 0.969, 0.981 and 0.975, respectively.
The eight sample plots utilized in this paper are situated in the natural forest of northeast China, characterized by complex and diverse tree growth. Processing point cloud data directly provides a better representation of the 3D structure of trees than raster-based tree segmentation methods. Compared to traditional tree segmentation algorithms, such as watershed algorithm, the rotation profile algorithm can be applied to complex forest areas with overlapping canopies and diverse tree species; it is universal and can segment trees of different scales.
The results of tree segmentation are closely related to the grid size d. When d=1m, the maximum number of trees are segmented, but the computational cost increases. Moreover, the redundant part in initial treetop points also increases, resulting in 65 over-segmented trees, requiring a lot of effort to exclude in practical work. This also leads to the incompleteness of correctly segmented canopies, which affects the subsequent tree species identification and parameters extraction. However, if the value of d is set too large to 2m, some short trees will be missed, and multiple trees with distances less than 2m will be directly merged into one tree. The selection of the optimal value is related to point cloud density, canopy size and shape.
The results of tree segmentation essentially depend on the point cloud density and forest growth conditions. Some small trees and closely spaced trees will inevitably be ignored, resulting in multiple trees being recognized as one after segmentation. When a tree is too large or the canopy shape is incomplete, it is easily segmented into multiple trees. Based on the selected initial treetop points, the method in this paper avoids the under-segmentation and over-segmentation of tree canopies by seeking profiles in multiple directions. Meanwhile, trees located within the high tree canopy range are identified as redundant parts of high trees and merged to further improve the accuracy of segmentation.
4.2. Tree Species Identification
Unlike plantation forest, overlapping phenomenon exists between the canopies of trees in natural forest areas in Northeast China. Therefore, the canopy point cloud obtained by tree segmentation is incomplete and cannot accurately reflect the tree structure information. This is an important example of the limits to the application of LiDAR data in natural forest areas.
Presently, deep learning methods for 3D data are not perfect, and most algorithms are not highly reliable. Therefore, this paper utilizes the profile information of the segmented point cloud of tree canopies, extracts the geometric variation of canopy profile by using parallel lines, and converts it into a 1D vector. The profiles that have no contact with other canopies are used to train the DBN classifier. Usually, a tree can obtain multiple profiles that satisfy the conditions, and all these profiles will be applied in the training, which increases the number of training samples, and learns the canopy structure information from multiple directions. The DBN model will also identify by multiple profiles to solve the dilemma of sparse samples, thus increasing the accuracy of the tree classification model and improving the accuracy and reliability of tree species correction (the overall correct rate is 90.9%). The canopy profiles are not directly applied to the classification. Instead, interpolated equidistant canopy lengths are used as feature vectors and input into the DBN model. This method reduces the computational burden while preserving the profile features, and effectively eliminates the random errors caused by semi-random scattered point clouds.
The method used in this paper relies entirely on the geometric shape of the tree canopy and does not involve any spectral information. Therefore, if the tree canopy of a tree is damaged naturally or artificially, or if the tree canopies are too close to each other, it will affect the reliability of the geometric shape of the section. This can cause the tree species classification model to be unable to identify incorrect tree species information or to classify tree species information incorrectly. For example, in this experiment the elm and maple both show a combination of triangular and rectangular shapes in their sections, making them more prone to misclassification. However, as the spectral characteristics of the leaves and flowering periods of elm and maple are quite distinct, in future studies, we will try to integrate spectral information based on the distribution characteristics of tree species in the study area to achieve high precision tree species classification.
4.3. Forestry Parameters Extraction
Given that the known species of trees, tree height, canopy width, DBH, AGB and stock volume can be estimated, the estimated values show strong consistency with the measured values.
The accuracy of forestry parameter estimation depends largely on the result of tree segmentation; for example, canopy width is directly determined by the size of the segmented canopy. The study area belongs to natural forest, where canopy overlap is more significant compared to artificial forest, resulting in segmented tree canopies being smaller than the actual situation and leading to an estimated canopy width which is smaller than the actual measured value. This is more obvious for taller trees. Therefore, although both are direct parameters, the accuracy of canopy width estimation is lower than that of tree height (R² of tree height is 0.893, while that of east-west canopy width is 0.757 and north-south canopy width is 0.694).
Indirect forest parameters such as AGB use tree height and DBH as independent variables in estimation equations, and DBH estimation also uses tree height as input. Therefore, the accuracy of tree height is particularly important for the estimation of indirect forest parameters. Tree height has higher consistency within the range of 20-30m, while in the range of 5-20m, the estimated tree height is slightly higher than the measured tree height on average, which is caused by the uneven height distribution and overlapping of trees in natural forest. Correspondingly, in the estimation of DBH, which uses tree height as the only input, the estimated values of larger trees have higher consistency with the measured values (usually larger diameter corresponds to higher tree height), and the estimated values of smaller trees are slightly higher than the measured values. As for AGB and stock volume, they are obtained by substituting tree height and DBH into the estimation equations, and their accuracy (AGB R²=0.896, stock volume R²=0.891) is very close to that of tree height and DBH (tree height R²=0.893, DBH R²=0.840).