1. Introduction
"Water expansion, dehydration contraction" is the primary expansion and contraction characteristics of expansive soil, and it is also a significant cause of engineering diseases such as uneven deformation, structural instability, building cracking, road bridge structure damage, etc [
1]. In the early 1970s, more than ten landslides occurred in the construction of the Taocha diversion canal in the Nanyang area because of crossing the expansive soil layer, and even landslides occurred on the gentle slope of 1:6, which caused special attention of engineers [
2,
3]. After a lot of research, it is found that the method of retaining reinforcement can effectively solve the problem of expansive soil gentle slope sliding, but it also dramatically costs the project cost and delays the construction period [
4]. Shallow surface collapse or low-level overlying load subgrade strength attenuation is a characteristic problem faced by engineering construction in expansive soil areas [5-6]. In this case, studying how to improve the diseased soil effectively is essential. Many achievements have been made in the mechanism, treatment methods, and prediction measures of expansive soil diseases. The traditional expansive soil improvement method is effective, but there are also many shortcomings. Such as adding lime [
7], iron tailings sand [
8], fly ash [
9], machine-made sand [
10], and other materials can improve the strength of soil, but the brittle failure of the improved soil becomes more significant, the improvement effect is questionable, and the resulting environmental pollution problem is also severe, which runs counter to the low-carbon environmental protection concept proposed by social development. Therefore, it is necessary to change the single and non-environmental improvement method in the past and to seek a composite and green expansive soil improvement method.
In recent years, lignin fiber and its derivatives have gradually become the first choice in improving unique soil engineering as a new soil modifier. They have many advantages, such as large reserves, cheap and easy to obtain, better improvement effect than traditional modifiers, and no secondary pollution to the environment during use [
11,
12]. Alazigha used lignosulfonate to treat expansive soil and found that its expansibility was weakened, showing non-brittle failure, and lignosulfonate could significantly improve the strength and consolidation of soil samples under freeze-thaw / dry-wet cycle conditions. Under the same dosage, the improvement effect of lignosulfonate is better than that of cement, lime, and other improved substances [
13]. Wu et al. studied calcium lignosulfonate-modified expansive soil's macroscopic mechanical properties and microstructure characteristics. The results show that the addition of calcium lignosulfonate can increase the condensation ability of soil, reduce the existence of pores, and increase the unconfined compressive strength [
14]. Chavali et al. studied the treatment of expansive soil with lignosulfonate. The results showed that the negative charge on the surface of the improved soil was reduced, and the microstructure of the polymer chain was formed. The amount of modifier was related to the particle size of the soil [
15]. Wang et al. used lignin to improve expansive soil. Cemented substances were produced in the pores of the improved expansive soil. The soil was denser, and the strength was improved. There was no new material formation before and after soil improvement, which belonged to physical improvement [
16]. Fan Kewei et al. modified expansive soil with lignin fiber and comprehensively analyzed its modification mechanism through triaxial shear strength and electron microscope scanning experimental results. Under freeze-thaw cycles, the shear strength of the improved soil is enhanced, and its enhancement principle is similar to that of reinforced soil. Based on this, the concept of ' quasi-cohesion ' is proposed. Lignin fiber can well inhibit the dislocation and rearrangement between soil particles and enhance the ability to resist freeze-thaw cycles [
17].
This paper proposes a composite improvement method based on the above research results. That is, lignin and its derivatives (calcium lignosulfonate) are used to improve the expansive target soil. A series of laboratory tests, such as liquid plastic limit, free expansion rate, unconfined compressive strength test, low stress direct shear test, and water stability test, is carried out to compare and analyze the effect before and after improvement with the change of dosage. Comparative analysis of the effect before and after improvement varies with the dosage, combined with the study of the development of microscopic characteristics, the compound improvement mechanism, and sample failure characteristics are obtained. The research content of this paper can provide theoretical guidance for soil engineering treatment of diseases in expansive soil areas.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Testing material
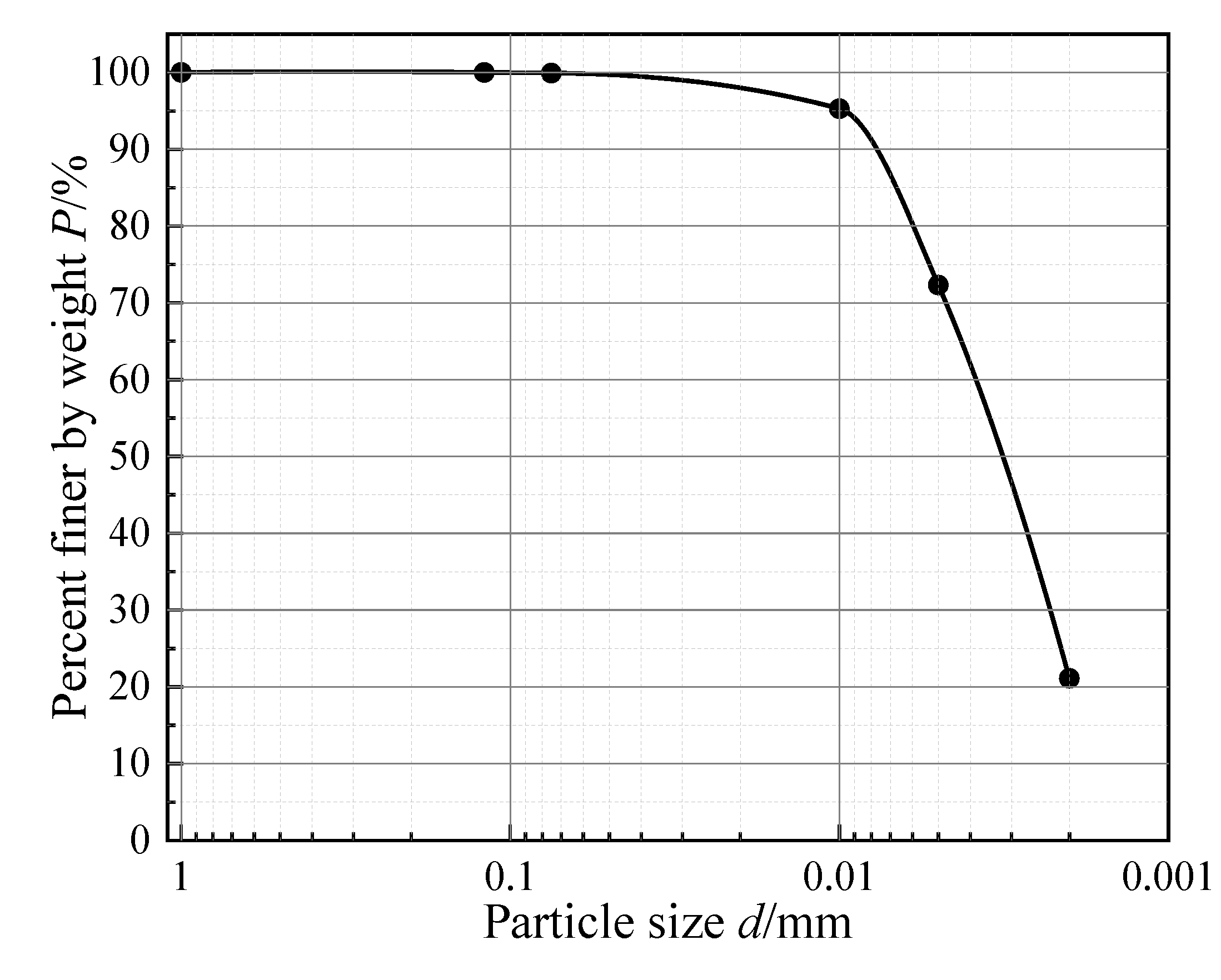
The expansive soil used in the test is taken from a construction site in Mengzi City, Yunnan Province. The sampling depth is 2-3m, it is grayish yellow, the surface is smooth, the texture is complex, the impurities are removed, the air is dried and ground, and the basic physical properties of the soil samples are shown in
Table 1 and
Figure 1. The free expansion rate of the soil sample is 50%. According to the Technical Code for Buildings in Expansive Soil Regions (GB50112-2013) [
18], the soil sample is weakly expansive.
Lignin fiber is produced by Langfang Tianya Energy Saving Technology Co., Ltd. Lignin is fibrous, gray-white, neutral, insoluble in water, non-polluting to the environment, and has good hydrophilicity. It is prepared by chemical treatment of natural wood. The treatment temperature is as high as 260°C. It has strong chemical stability and corrosion resistance, as shown in
Figure 2 (a). Calcium lignosulfonate used in the experiment was from Guangzhou Yicheng Chemical Co., Ltd. Calcium lignosulfonate is a brownish-yellow powder easily soluble in water and has good stability. It has strong dispersibility, cohesiveness, and chelation. It can be used as a water reducer in engineering, as shown in
Figure 2 (b).
2.2. Test scheme and test method
2.2.1. Test scheme
After the sample soil is taken back, it is dried, and the impurities are picked out and put into the mortar to grind into powder, passed through 0.5mm and 2mm sieves, respectively. Calcium lignosulphonate was sieved through a 0.5 mm sieve and mixed with 1 %, 2 %, 3 %, and 4 % of the amount of water in a beaker to dissolve it fully. Add it to the dried soil passing through the 0.5 mm sieve and stir to conduct liquid-plastic limit and free expansion rate tests; the same amount of incorporation was weighed and added to the 2mm sieve, thoroughly mixed with the optimal water content, and placed in a closed container for 24 hours to soak the water into the soil thoroughly. The improved soil was weighed according to the maximum dry density standard and placed in the ring cutter and the unconfined compression specimen mold. Join multiple times. Each layer was roughened with a soil cutter so that no fault occurred after the specimen was made. The height of the ring knife sample is 20 mm, and the diameter is 61.8mm. The direct shear test and water stability test are carried out. The unconfined compressive strength test was carried out on the sample with a height of 80 mm and a diameter of 39.1mm. According to the existing literature Fan, more than 2 % of lignin will agglomerate in expansive soil, which will affect its integrity and reduce the strength of the soil [
17]. Therefore, the 0-2% range is selected to add to the plain soil. The calcium lignosulfonate content with good physical and mechanical properties was combined with 0.5%, 1%, 1.5%, and 2% lignin fibers for composite improvement. The specific sample improvement was incorporated into the design ratio, as shown in
Table 2, and the sample was prepared by a single improvement method. Each test was completed according to the 'standard for geotechnical test methods [
19] or building technical specifications for expansive soil areas' (GB50112-2013).
2.2.2. Test method
The unconfined compressive strength test was carried out using the YYW-2 strain-controlled unconfined compressive instrument produced by Nanjing Soil Instrument Factory. The loading rate was 2.4 mm/min.
In the direct shear test, the stress condition is set to low everyday stress, achieved by the sandbag equivalent substitution method. The downward vertical normal pressure is set to 15, 25, 35, and 50kPa, a total of 4 levels. The test instrument is a ZJ type of strain-controlled direct shear apparatus produced by Nanjing Soil Instrument Factory, and the hand wheel speed is 4r/min.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was used to observe the microstructure characteristics of the soil. The test instrument was TESCAN MIRALMS, produced by TESCAN Trading Co., Ltd. When preparing the sample, the cross-section of the model that needs to be observed is selected first, and the complete section is cut and put into the freezer for freeze-drying, and then the vacuum and gold spraying operations are carried out. After that, it is taken out and observed under the electron microscope. The magnification of the scanning electron microscope is 1000 times.
3. Test result analysis
3.1. Changes in physical properties
3.1.1. Liquid plastic limit test
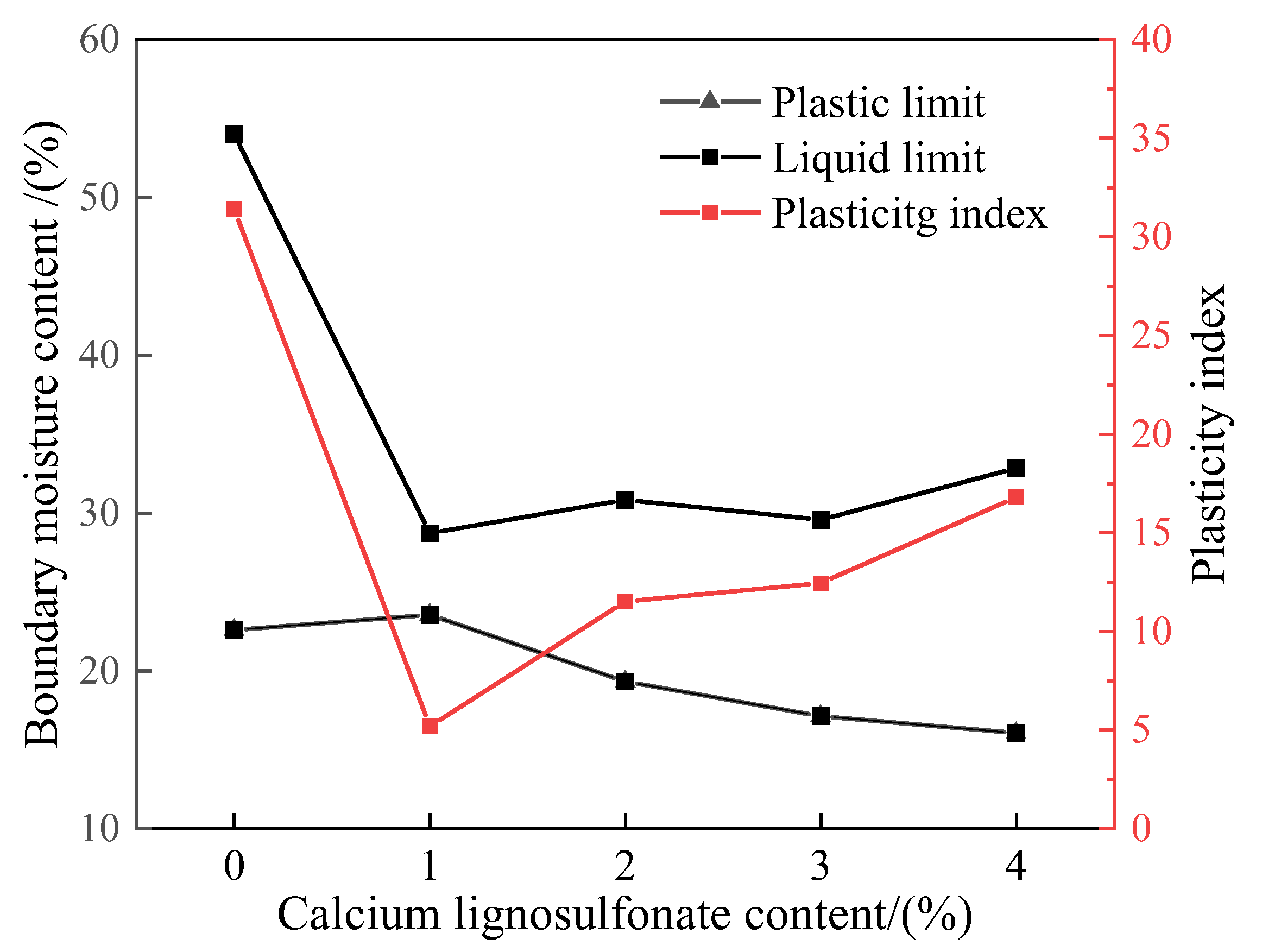
As shown in
Figure 3, the expansive soil's liquid limit and plasticity index decreased significantly after adding calcium lignosulfonate, reaching the lowest values of 28.72 and 5.18 when the content was 1%, respectively, with a decrease of 46.82% and 83.52%. When the mixing amount is greater than 1%, it shows an increasing trend, and the boundary water content in the improved soil increases, but the increase rate is slow. For the plastic limit of improved soil, the maximum value is 23.54 when mixed with 1% Calcium lignosulfonate, which is 4.25% higher than that of plain expansive soil. And after adding calcium lignosulfonate, the moisture content of the improved soil is significantly lower than that of plain expansive soil, which is mainly related to the properties of calcium lignosulfonate itself, and it is often used as a water-reducing agent in actual engineering applications [
16].
3.1.2. Free expansion rate test
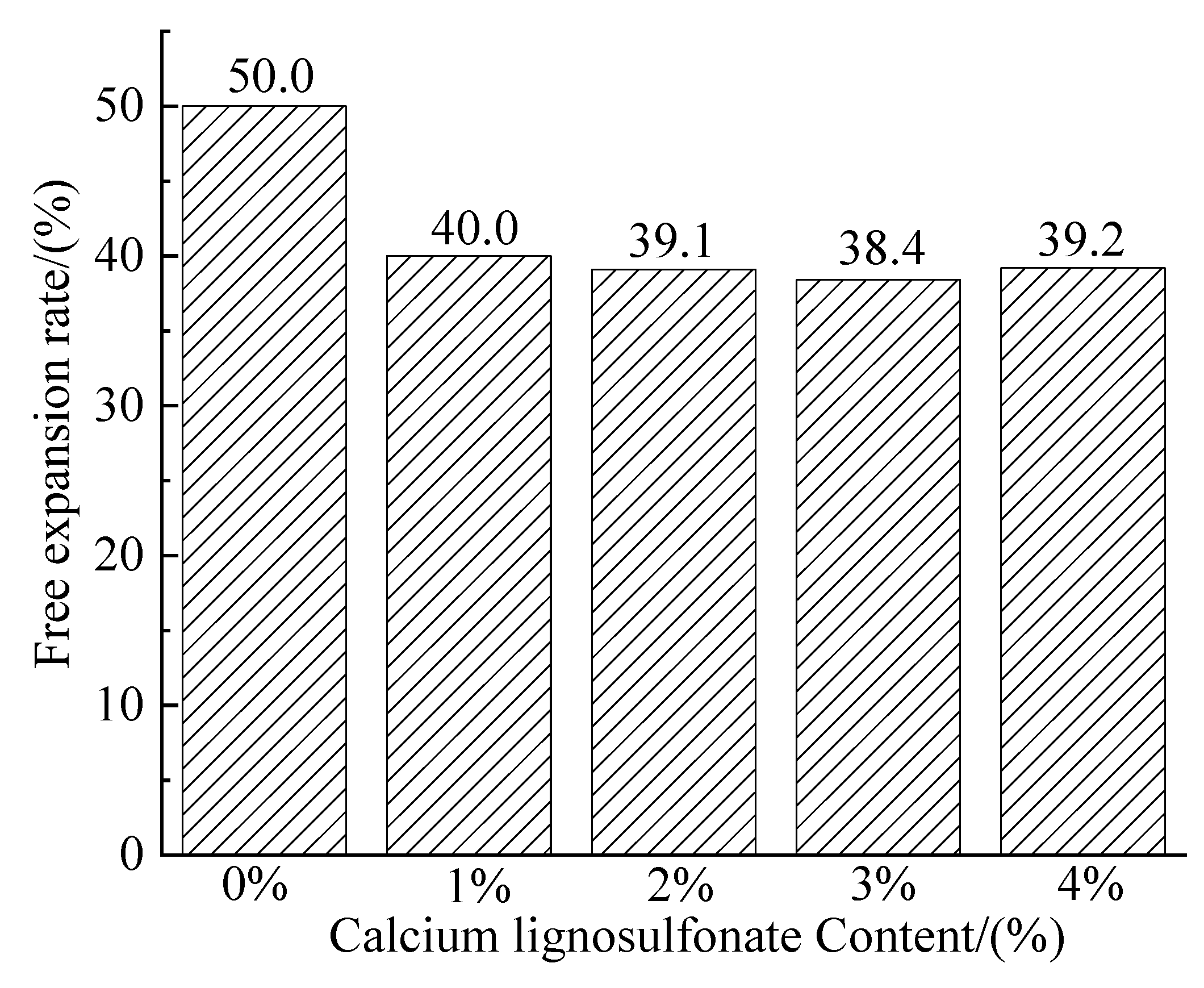
Figure 4 is a histogram of the change in the free expansion rate of the sample at various dosages. After the addition of calcium lignosulfonate, the lowest free expansion rate of the improved soil is the sample with 3% calcium lignosulfonate content, which drops to 38.4%, which is lower than 40%, which can be judged as non-expandable soil; the content exceeds 3% After that, the free expansion rate of the sample rebounded slightly and increased to 39.2%. This is mainly because adding calcium lignosulfonate will form a floc structure to adsorb on the clay surface, coat, and agglomerate, and the ion exchange between the admixture and the expansive soil will increase the interlayer distance of the mineral components. Both significantly inhibit water migration to the interior and reduce the free expansion rate of the improved soil; After too much calcium lignosulfonate is added, the flocs formed in the soil increase, which increases the repulsion effect between the same-sex ions, making the expansion rate tend to increase [
20].
3.2. Changes of Mechanical Properties of Expansive Soil Modified by Single Addition of Calcium Lignosulfonate
3.2.1. Direct shear test
Slope collapse in expansive soil usually occurs in the shallow surface layer, that is, under low everyday stress [
5]. In this regard, it is necessary to conduct shear strength tests of improved soil under low-stress conditions to explore the variation of c,φ, and shear strength with the addition of calcium lignosulfonate, which is very necessary for evaluating the shear effect of calcium lignosulfonate improved expansive soil.
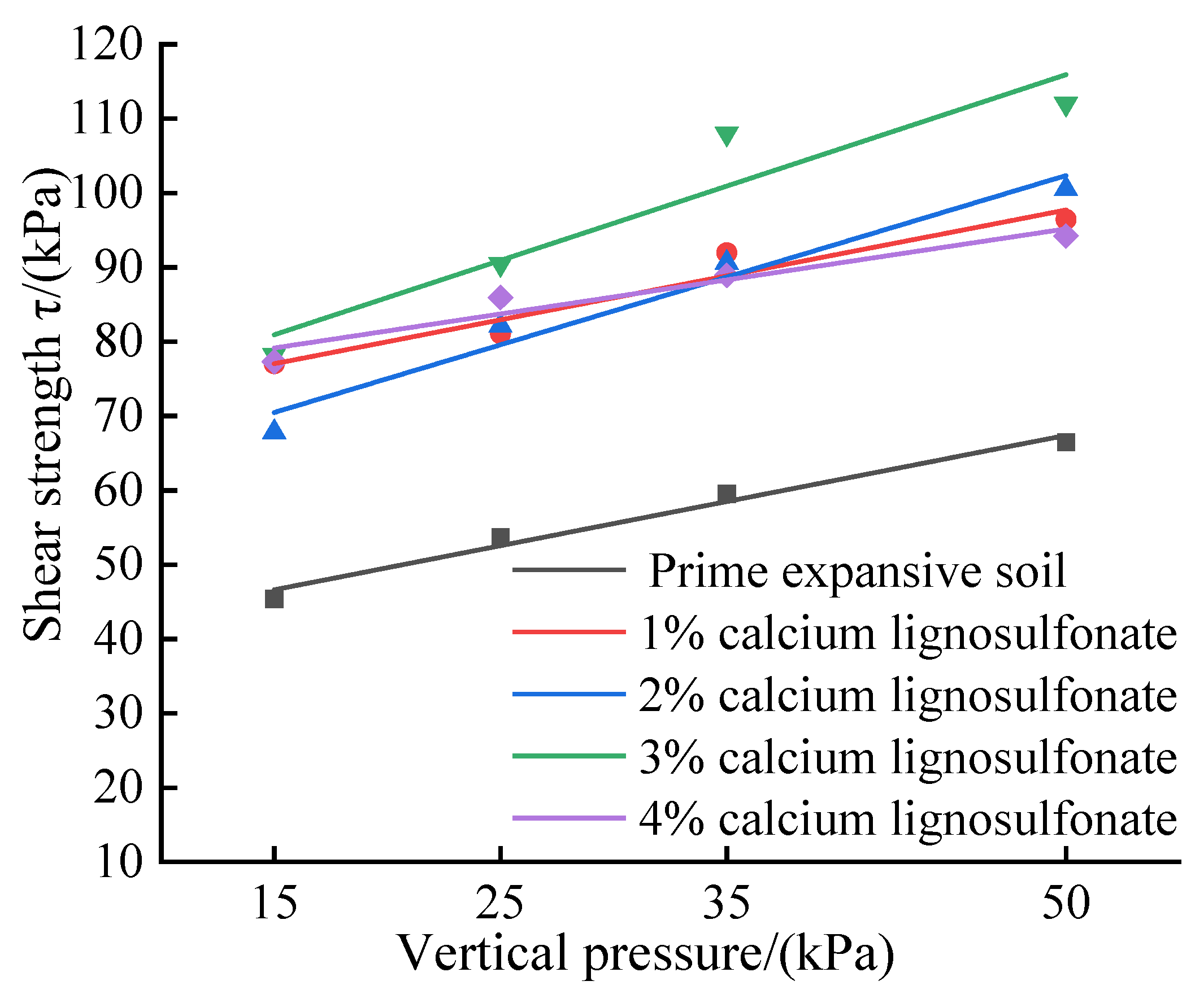
As shown in
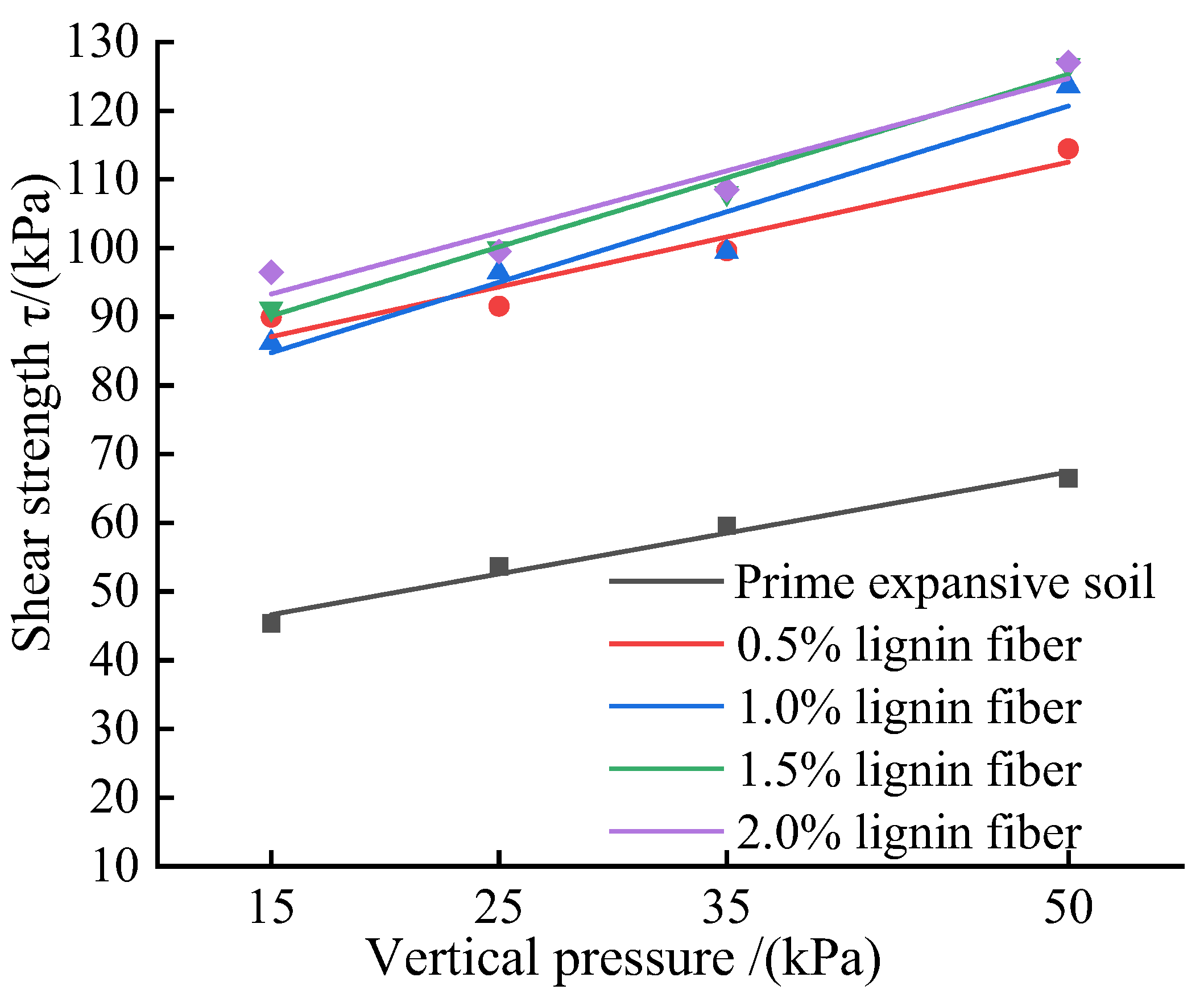
Figure 4, after adding calcium lignosulfonate, the shear strength of the improved soil is significantly improved compared with that of the prime expansive soil, and the change rule is that with the increase of calcium lignosulfonate content, the shear strength first increases then decreases. Among them, the shear strength of the improved soil with 3% calcium lignosulfonate content is the highest. For the changing law of c and φ values of soils with different calcium lignosulfonate content,
Table 3 shows the fitting parameters of cohesion and internal friction angle of soil improved with other calcium lignosulfonate content. With increased calcium lignosulfonate content, the cohesion force maintained an overall upward trend, up to 72.897kPa, especially when calcium lignosulfonate was just added; the increase rate was pronounced, from 37.702 kPa to 68.158kPa, an increase of 80.7%.In comparison, the change of internal friction angle is slightly smaller, fluctuating up and down in the range of 24.2%~46.6% compared with plain soil. This is mainly because, after adding calcium lignosulfonate, cementing substances will be generated in the soil to fill the pores. Compared with the prime expansive soil, the specific surface area of the particles in the improved soil increases and has a more substantial bonding effect, which is reflected in the improved soil macroscopically. The cohesion and internal friction angle increased, and the increase in cohesion was more pronounced. The test results show that under low-stress conditions, the improved soil with calcium lignosulfonate alone has better shear strength and significant improvement effect and can be used appropriately in soil improvement of slope engineering with expansive soil distributed in the shallow surface layer.
3.2.2. Unconfined Compressive Strength Test
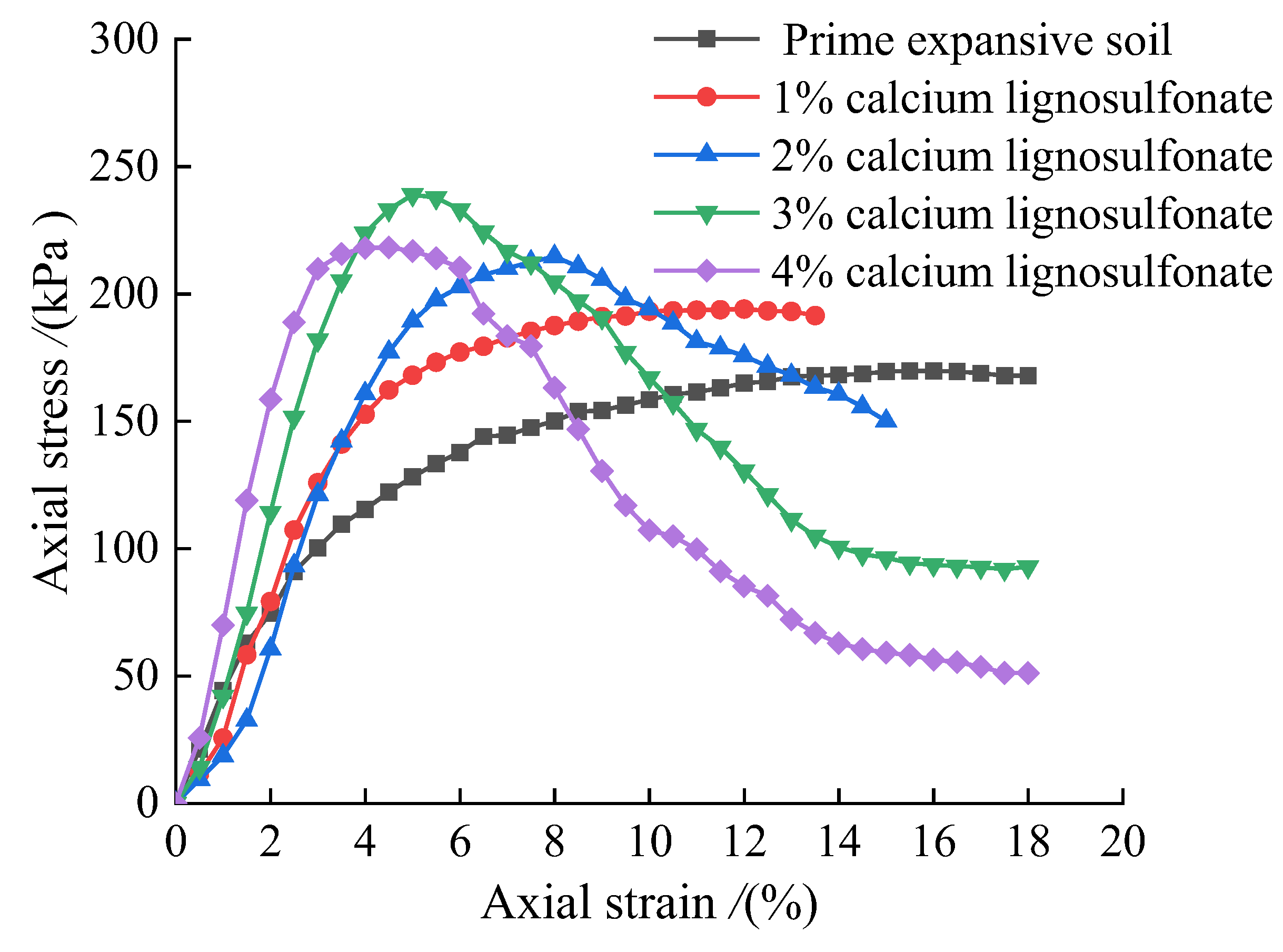
Figure 6 is the stress-strain curve of the modified expansive soil mixed with calcium lignosulfonate alone. It can be seen from the figure that the plain soil exhibits strain hardening, and its stress-strain turn is "short and fat" as a whole, with an obvious yield process; after adding calcium lignosulfonate, the strength of the sample begins to increase, and the stress-strain curve of the improved soil is 1%. Consistent with plain soil performance. With the gradual increase of the content, the sample began to show a strain softening type, and the stress-strain curve showed a "thin and tall" style and then began to decrease after reaching the peak strength, and the residual strength of the sample also reduced with the increase of calcium lignosulfonate content. Small. It can be seen that 3% calcium lignosulfonate content is the optimal content when only calcium lignosulfonate is added.
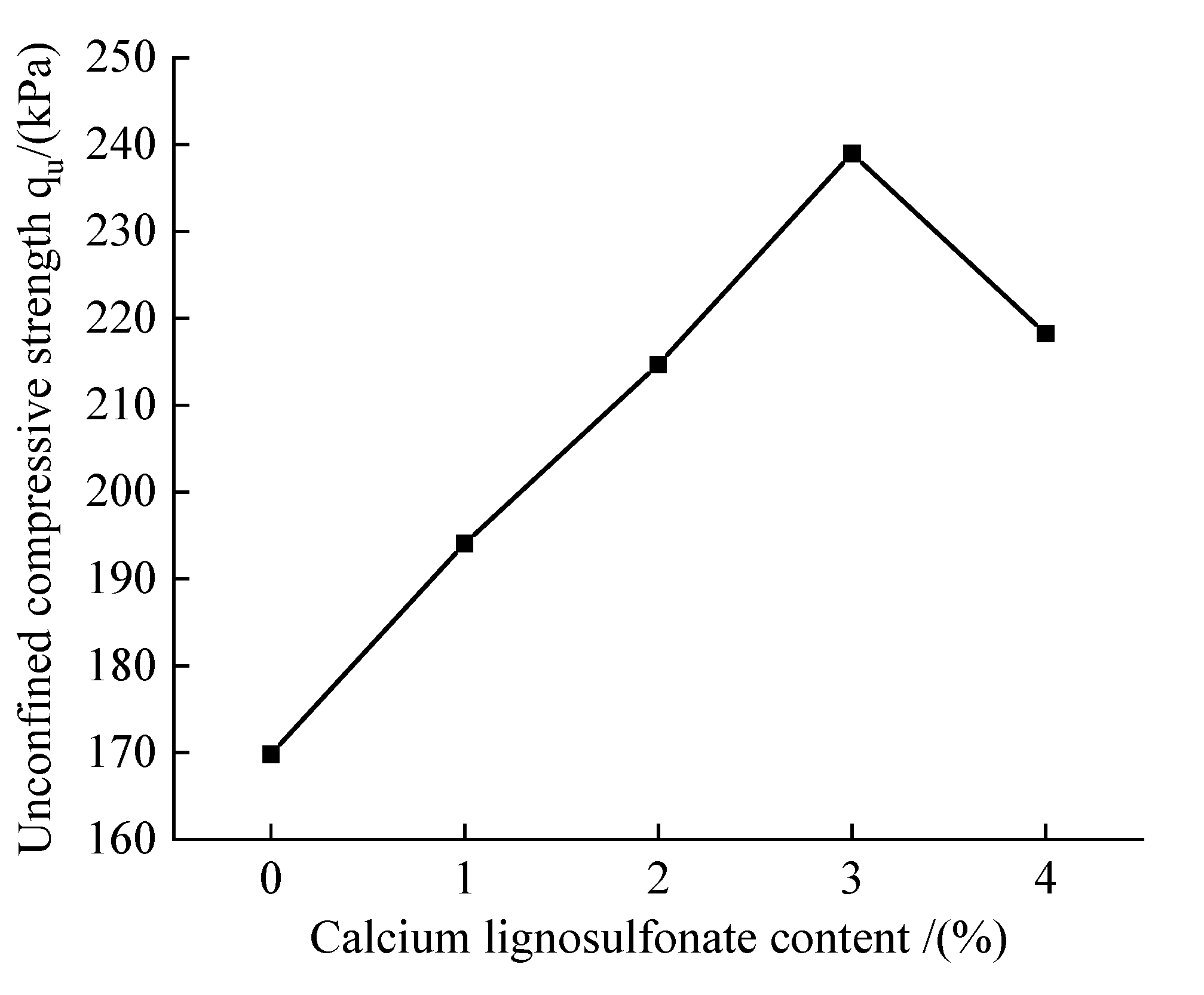
Figure 7 is a diagram of the variation of unconfined compressive strength of soil improved with different calcium lignosulfonate content, and the curing period of the sample is seven days. It can be seen from the figure that with the addition of calcium lignosulfonate, the unconfined compressive strength of the improved soil increases first and then decreases, which is 1.14-1.41 times higher than that of the plain soil sample. When the calcium lignosulfonate content is 3%, the improved soil The unconfined compressive strength reaches the maximum value, which is 238.96 kPa, and the power of the sample begins to decline after exceeding this content.
3.3. Changes in mechanical properties of expansive soil modified by calcium lignosulfonate-lignin fiber composite
3.3.1. Direct shear test
Based on the unconfined compressive strength test and direct shear test results when mixed with calcium lignosulfonate alone, 3% calcium lignosulfonate was mixed with 0.5%, 1%, 1.5%, and 2% lignin fiber to carry out the unconfined compressive strength test of composite improved soil. Compressive strength test and direct shear test.
Figure 8 is the direct shear fitting curve of 3% calcium lignosulfonate samples with different lignin fiber content. It can be seen from the figure that when 3% calcium lignosulfonate amended soil is mixed with lignin fiber, the shear strength is improved, and it increases with the increase of lignin fiber content. Combined with the data in
Table 4, the cohesion of the improved soil mixed with lignin fiber is higher than that of the enhanced soil mixed with 3% calcium lignosulfonate alone, and the increase ranges from 5.2% to 21.1%. The internal friction angle varies with the addition of lignin fiber. Fluctuation trend, the fluctuation range is 1.43%~20%. This is because the addition of lignin fibers makes the calcium lignosulfonate particles more connected to each other. After the sample is sheared, the fibers in the soil share part of the tensile stress. The more fibers are added, the more the shearing effect is inhibited. According to Xiao Jie[
5], Hu Xuhui[
6] et al.’s research on the change law of the shear strength index of expansive soil under low-stress conditions, it is found that the cohesion of the soil decays significantly when the shallow layer collapses, and the internal friction angle changes little. The sharp drop of cohesion at the sliding surface is an essential factor inducing the external collapse of expansive soil slope. The improvement method proposed in this paper can correspond to improving soil cohesion. The increase in cohesion is more significant, and the effect is remarkable. It can provide a theoretical basis for shallow slope control.
3.3.2. Unconfined Compressive Strength Test
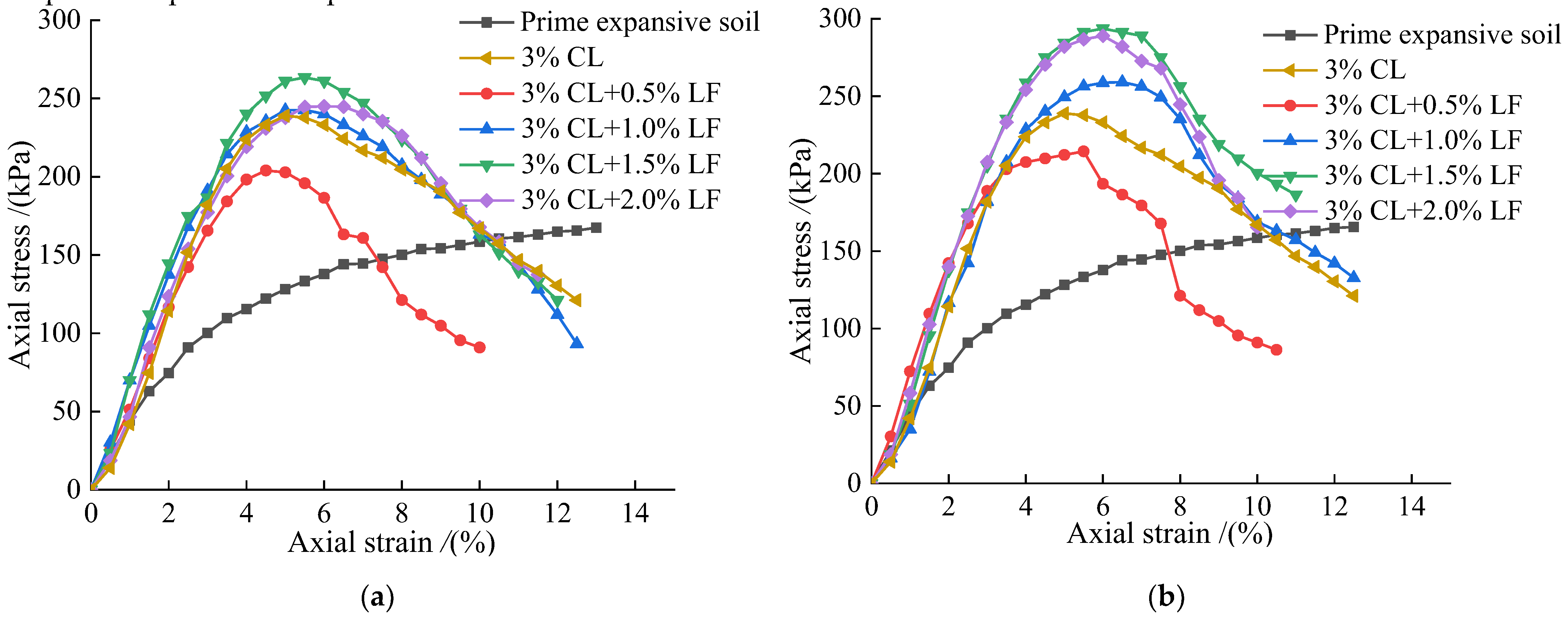
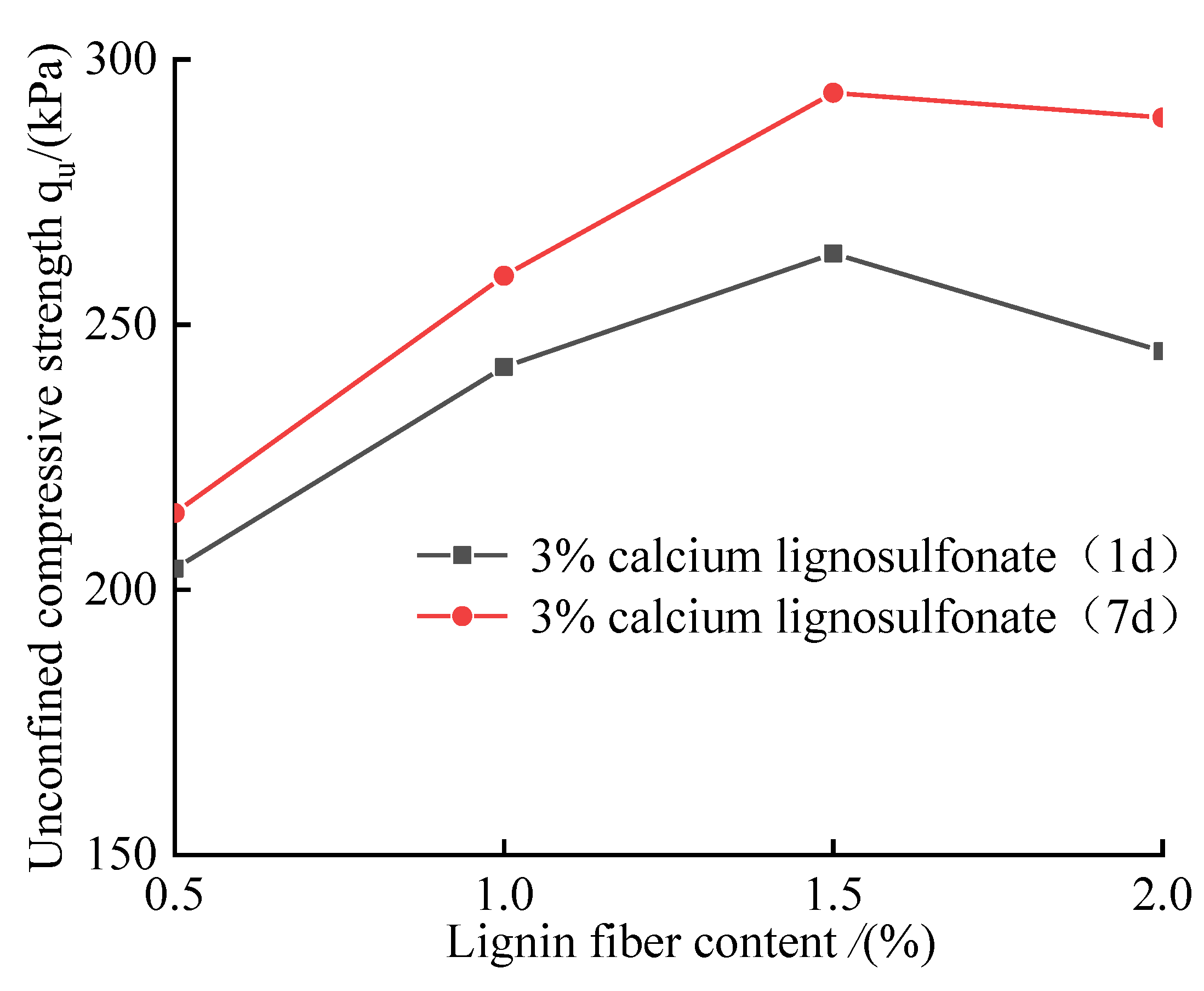
It can be seen from
Figure 9 that the strength of the composite-improved soil mixed with lignin fiber increased first and then decreased with the increase of lignin content at 1d and 7d of maintenance, and the composite-improved soil with 3% calcium lignosulfonate(CL)+1.5% lignin fiber(LF) at seven days of care. The highest intensity is 293.72kPa. Compared with 3% calcium lignosulfonate content and curing for seven days, except for 3% calcium lignosulfonate+0.5% lignin fiber, the others have increased compared with the single addition of 3% calcium lignosulfonate, which is 1.08~1.23 times of the single mixed. When the lignin fiber content is 0.5%, the strength of the composite improved soil is lower than that of the single-mixed 3% calcium lignosulfonate-improved soil, The main reason is that the incorporation of a small amount of lignin fiber is difficult to improve the strength, but it destroys the cemented structure of the sample mixed with calcium lignosulfonate alone, and the power of the sample is lost. The improved composite soil mixed with lignin has better toughness in the small strain range, and the strain corresponding to the peak strength of the sample is more significant, and the strength of the sample begins to decrease when it reaches the peak value. With the addition of lignin, the stress-strain curve of the sample gradually changed to a "thin and tall" type, but there was a higher residual strength after the sample was destroyed. Among them, 3% calcium lignosulfonate+1.5% lignin fiber composite improved soil performed best.
Figure 10 shows the effect of lignin fiber content and curing age on the unconfined compressive strength of the improved soil. The unconfined compressive strength of composite improved samples increases with the increase of curing age, and when the curing age increases from 1d to 7d, the strength of the sample increases by 1.05~1.18 times.The test shows that when more fibers are added, the curing time can be appropriately increased so that the composite improved soil has higher strength. Combined with the research results of Wang Huan's use of lignin to improve expansive soil, calcium lignosulfonate improved expansive soil mainly forms cementing substances and cohesive particles to fill pores, strengthen the compactness of the soil, and then improve the mechanical strength of the improved soil. In addition, after the soil is compacted, water can be restricted from entering the soil, the expansibility of the improved soil is weakened, and the stability of water immersion is enhanced. Since no new mineral components are formed before and after improvement, the increase in the strength of the sample strength and curing age does not significantly increase the strength of the soil[
16]. In this study, based on single-doped calcium lignosulfonate, lignin fiber was added for composite improvement, which can interconnect the particle structure formed in the improved soil and enhance the failure toughness of the soil. Since no new mineral components are included before and after improvement, the increase in the strength of the sample and the curing age will not increase the strength of the soil much.
3.4. Failure characteristics of improved soil samples
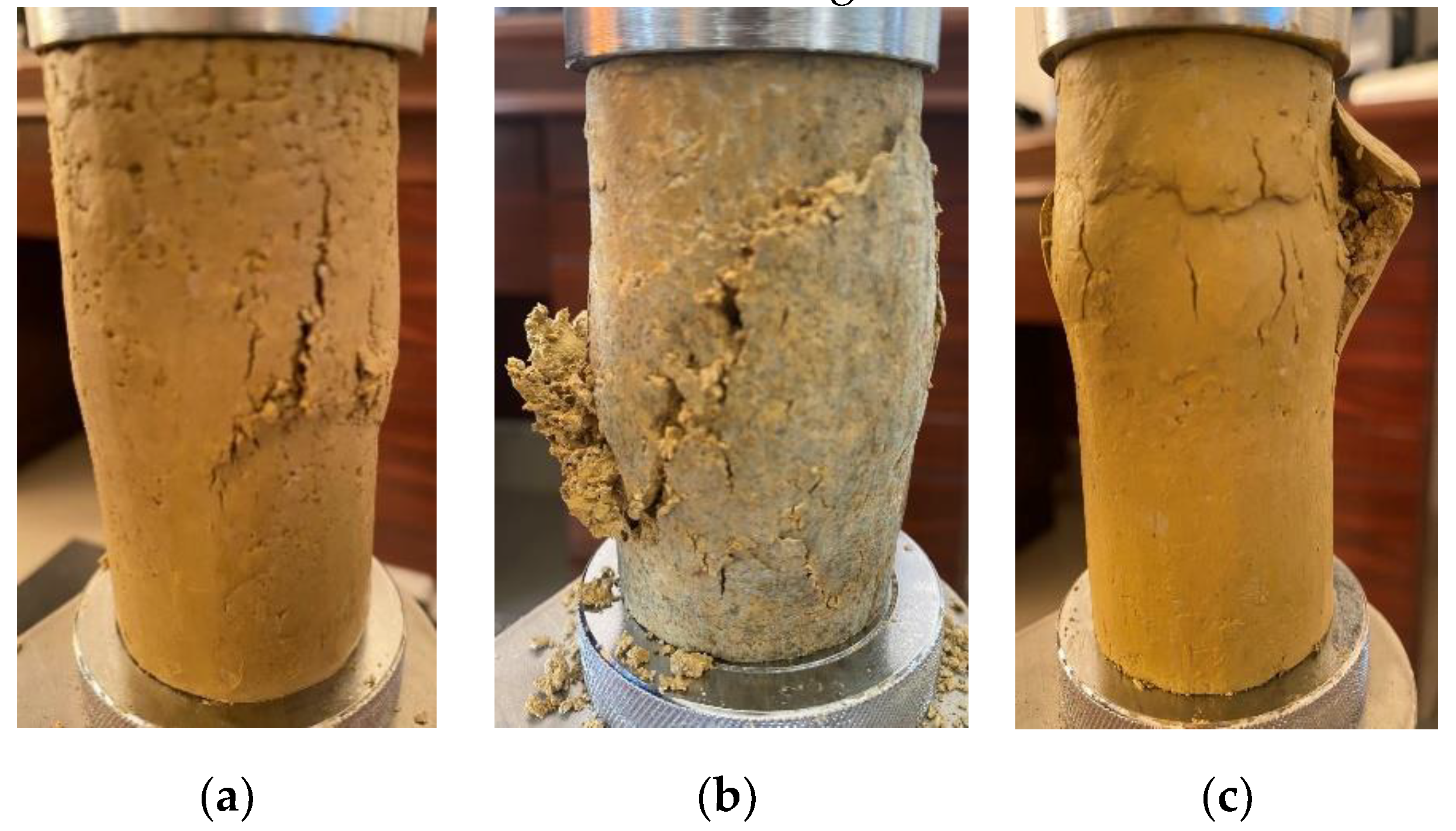
Figure 11 shows the failure patterns of various improved soil samples in the unconfined compressive strength test. (a) to (c) in the figure are prime soil, 3% calcium lignosulfonate improved soil, 3% calcium lignosulfonate +1.5% lignin fiber composite improved soil (7d). It can be seen from the figure that when the loading process of bare soil reaches failure, cracks first appear in the middle and extend from the center to the surrounding until the strength is lost. The overall shape of the sample can be maintained during the test, the strain-hardening characteristics are apparent, and the plasticity is better. For the 3% calcium lignosulfonate modified soil, oblique cracks appeared during the loading process, and the gaps were wide and gradually extended to both ends, transversely penetrating through the outer surface of the sample. The failure surface was more prominent, forming an angle of 45° with the horizontal plane and the loading process. There are peeling fragments in the middle skin, and the strength of the sample rapidly decays after reaching the peak value, and the characteristics of strain softening are apparent, which is manifested as "brittle failure". The crack development of 3% calcium lignosulfonate+1.5% lignin fiber composite improved soil is slightly weaker than that of the former two samples, and the "plastic swelling" type of damage is more prominent. There are many cracks in the bulging section. It can maintain the overall shape, and the development of trials is not apparent. During the test, it is mainly compressed in the axial direction, with no outward cracking.
3.5. Water Stability Test
Select prime expansive soil, 3% calcium lignosulfonate+1.5% lignin fiber composite samples for the water stability test, observe the changes in water stability of samples before and after improvement, and analyze the difference in water stability before and after modification, as shown in
Table 5. After adding the improved substance, the water stability of the sample is enhanced, there are still no cracks in the state of long-term immersion, and the degree of disintegration is significantly reduced. This is because the incorporation of calcium lignosulfonate strengthens the bonding performance of the soil, fully exerts its function as a water-reducing agent, and forms a tighter overall structure combined with lignin fibers, which significantly inhibits the soil samples from being absorbed in water. Disintegration improves the water stability of the soil and can be used for slope engineering construction in expansive soil areas under rainy conditions.
4. Composite improved micro-mechanism analysis
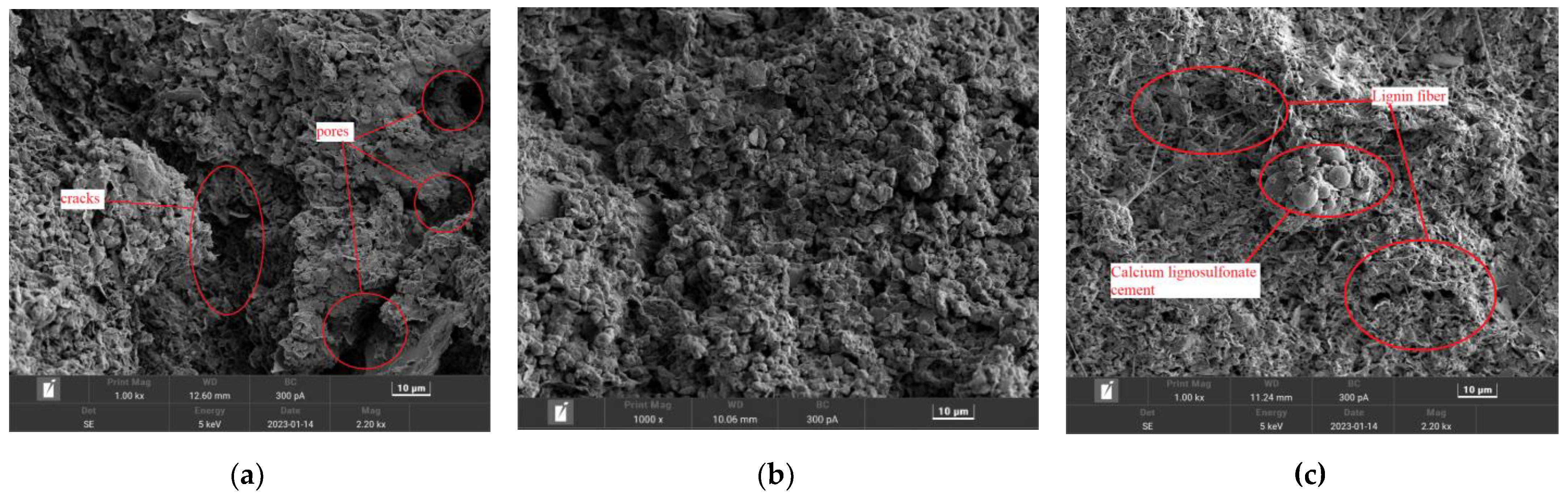
Figure 12 (a~c) shows the microstructure of the sample of plain soil, 3% calcium lignosulfonate, 3% calcium lignosulfonate+1.5% lignin fiber content (curing age 7d) magnified 1000 times. Observing the change law of microstructure inside the soil before and after improvement and under the dosage of various improvement substances, and thus deriving the improvement mechanism.
It can be seen from Figure(a)that there are many pores distributed in the prime expansive soil, and accompanied by the development of cracks, the cracks are wide and connected, providing favorable conditions for the migration of water and the hydrophilic mineral component montmorillonite forms micro-soil body particles, flat and curved structure, loosely arranged, prone to expansion and contraction deformation when exposed to water. It can be seen from Figure(b)that after adding 3% calcium lignosulfonate, the pores and cracks in the sample are greatly reduced, and the sheet structure is transformed into a micro-particle structure. The condensed micro-particles are scattered and filled, and the compactness of the soil is improved, which effectively improves the soil strength. From Figure(c), it can be seen that after adding 1.5% lignin fiber based on adding 3% calcium lignosulfonate, the micro-cracks in the soil are further reduced, and the micro-particles are close to each other to form a larger particle structure, and they are distributed in the micro-cracks. Lignin fibers are also found in some places, and the bonding effect of the fibers improves the strength of the soil. The addition of fibers inhibits the further development of pores and cracks, forming an intricate network structure that increases the toughness of the sample when it fails.
Plain expansive soil contains many hydrophilic minerals, and water molecules enter the mineral crystal layer, increasing the interlayer spacing of crystals and causing the surface of the clay to thicken the water layer, and the soil expands. The mineral components present in the plain expansive soil form a flat and curved structure, and a large number of surface-surface structures make the sample show lower strength when it is destroyed. In calcium lignosulfonate modified soil, calcium lignosulfonate is randomly embedded between expansive soil particles, flocculation occurs in the diffuse double layer of expansive mineral components, agglomerates to form aggregates, and externally wraps adsorbed non-expandable mineral components jointly change the soil structure of plain expansive soil and promote the transformation of flat, curved shape into particle aggregate structure[
21]. Calcium lignosulfonate dissolves in water to form positively charged aggregates, and after combining with negatively charged expansion substances, neutralization occurs, reducing the surface potential of minerals and reducing the distance between soil particles. And Calcium lignosulfonate agglomerates have cementing properties, and after cementing with soil particles, they jointly fill the pore structure[
22]. Calcium lignosulfonate improved the soil before and after no new substances were formed, and the improvement effect was more stable, which belonged to physical improvement[
16]. After adding lignin fibers, the material structure in the improved soil is more complex, and the fibers further connect the cement and soil particles, and the fiber connection structure contributes part of the strength of the sample to resist external forces. The fibers are randomly distributed in the soil. When the shear surface of the soil is sheared and damaged, the fibers pass through the shear surface at different angles, which inhibits the shear movement between the soil particles and makes the sample show plastic swelling when it fails to destroy. To achieve compound improvement effect[
23].
5. Conclusions
According to the test results, the physical properties, macro-mechanical indicators and micro-structural characteristics of the improved soil with various dosages can be obtained, which verifies the feasibility and effect of compounding lignin and its derivatives to improve expansive soil.
After adding wood calcium, the liquid limit and plasticity index of the improved soil is reduced, and the combination of hydrophilic minerals and water in the soil is reduced to minimize the expansion effect, and the expansion rate of the improved soil is reduced, which can be judged as non-expansive soil. When carrying out the free expansion rate test, the expansion rate will increase slightly if calcium lignosulfonate is continued to be added.
The strength of the soil body increased significantly when wood calcium was added alone, the shear strength increased significantly under low-stress conditions, and the cohesion increased particularly considerably, which can be used as a theoretical basis for shallow slump prevention and control. The effect of 3% is the best when adding calcium lignosulfonate alone, but the strength will be reduced if too much is added. The internal cementation effect of the soil improved with calcium lignosulfonate alone is significant, and the soil structure changes significantly. The flat, curved structure transforms into an agglomerated structure between particles, and the pores and cracks are better filled.
When compounded with lignin fiber for improvement, the internal connection effect of the improved soil is better, and the mechanical properties are further increased based on single-mixed calcium lignosulfonate improvement, manifested as a plastic bulging failure. The incorporation of fiber inhibits the development and extension of tiny pores and fissures, reduces water ingress, and enhances the water stability of the sample. The best ratio for compound improvement is 3% calcium lignosulfonate + 1.5% lignin fiber.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.C. and M.O.; methodology, Y.C.; formal analysis, Y.C.; investigation, M.O.; resources, M.O.; data curation, M.O.; writing—original draft preparation, M.O.; writing—review and visualization, Y.C.; supervision, Y.C.; project administration, M.O.; funding acquisition, M.O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Study on Calculation Model of Earth Pressure in Deep Foundation Pit Supported by Inner-Supported Ground Wall in Peat Soil Stratum, grant number 51968036.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data used to support the findings of this study are included in the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Leng, T; Tang, C. S; Xu, D. Research progress on engineering geological characteristics of expansive soil. J. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2018, 26, 112–128. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, C. G; Stability problems and countermeasures of expansive soil canal slope in Middle Route Project of South-to-North Water Diversion.J.People 's Yangtze River, 2003, 4-6 + 53.2003.05.003.
- Tonini, A.M; Tonatto, F.S; Jordi, B. G. J; Consoli, N.C. Mechanical and Environmental Performance of Eggshell Lime for Expansive Soils Improvement. J. Transportation Geotechnics 2021, 31. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H. P; Wang, J; Zhan, W.T; Study on Treatment Technology and Design Scheme of Expansive Soil Subgrade in Nanning Outer Ring. J.Geotechnical Mechanics 2011, 32, 359–365. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, J, Yang, H. P; Li, H.F; Tang, X.Y. Shear strength test of Nanning expansive soil with different densities under low stress conditions. J. China Journal of Highway 2013, 26, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.H; Zhang, K.Y; Nie, M.J. J. Effect of wetting-drying cycles on strength index of expansive soil. J.Journal of Central South University ( Natural Science Edition) 2022, 53, 269–279. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, A.J; Yang, H.P. Experimental Study on Lime Improved Medium Expansive Soil Embankment of Nanyou Highway. J.Subgrade Engineering 2009, 52–54. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H; Chu, C. F; Guo, K.L; Ye, H. Experimental study on basic engineering properties of expansive soil improved by iron tailings.J.Civil construction and environmental engineering 2017, 39, 98–104.
- Fu, X. S; W, Q; Yang, Z.B; Li, X; Wang, C. Experimental study on compressive and shear strength of weak expansive soil improved by machine-made sand and water glass. J.Journal of Civil and Environmental Engineering 2022, 44, 60–67. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.L. Experiment on mechanical properties of expansive soil improved by fly ash. J.Comprehensive utilization of fly ash 2018, 44–46. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, T.D. Lignin. edition: Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China 2008, 1-3.
- Liu, S. Y; Zhang, T; Cai, G.J; Li, J.H; Jie, D.H. Research progress on soil reinforcement by bioenergy byproduct lignin. J. Chinese Journal of Highways 2014, 27, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Alazigha, D.P. Potential use of lignosulfonate for expansive soil stabilisation. J. Environmental Geotechnics 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu,D.J; She,W; Wei,L.S; Zuo,W.Q; Hu,X.Y; Hong,J.X; Miao,M.C. Stabilization Mechanism of Calcium Lignosulphonate Used in Expansion Sensitive Soil. J. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology-Mater. Sci. Ed.: Materials Science Edition 2020, 35.
- Chavali, R.V. P,Reshmarani B. Characterization of expansive soils treated with lignosulfonate.J. International Journal of Geo-Engineering 2020, 11.
- Wang, H; Cao, S.J; Cao, Y.K; Qiu, A.B. Engineering properties and micro-mechanism of lignin-modified expansive soil.J/OL. ACTA ENGINEERING & ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING ( Chinese and English ) : 1-8 [ 2022-12-30 ].
- Fan, K. W; Yan, J; Liu, L. J; Pei, Q.Y; Zou, W.L. Study on strength characteristics and microstructure of lignin fiber modified expansive soil in seasonal frozen area.J.Journal of Central South University ( Natural Science Edition) 2022, 53, 326–334. [Google Scholar]
-
GB 50112-2013;Technical code for buildings in expansive soil regions. Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2013.
-
GB/T 50123-2019; Geotechnical test method standard Press: Beijing, China Plan Publishing House, 2019.
- Sarkanen, K. V ;Ludwig CH (1971) Lignins: Occurrence,Formation, Structure and Reactions. Wiley, New York,NY, USA.
- Alazigha,D.P. The swelling behaviour of lignosulfonate-treated expansive soil.J. Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers - Ground Improvement 2016, 169.
- Zhang, T; Cai, G.J;Liu, S.Y; Li, J.H; Ji, D.H. Microcosmic Mechanism of Industrial By-product Lignin Improving Roadbed Silt.J. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2016,37(06):1665-1672. [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.B; Zhang, H; Li, G.C; Liu, Z.Y; Huang, J.X; Jiang, Z.W. Strength and crack development characteristics of expansive soil improved by fly ash-sisal fiber composite.J. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering 2022, 19, 2620–2628. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Particle grading curve of Mengzi expansive soil.
Figure 1.
Particle grading curve of Mengzi expansive soil.
Figure 2.
Lignin fiber and calcium lignosulfonate powder: (a) Lignin fiber; (b) Calcium lignosulfonate powder.
Figure 2.
Lignin fiber and calcium lignosulfonate powder: (a) Lignin fiber; (b) Calcium lignosulfonate powder.
Figure 3.
Influence Curve of Different Calcium lignosulfonate Content on atterberg limits.
Figure 3.
Influence Curve of Different Calcium lignosulfonate Content on atterberg limits.
Figure 4.
Sample free expansion rate change histogram.
Figure 4.
Sample free expansion rate change histogram.
Figure 5.
The fitting curve of direct shear test of improved soil with different calcium lignosulfonate content.
Figure 5.
The fitting curve of direct shear test of improved soil with different calcium lignosulfonate content.
Figure 6.
Stress-strain curves of modified expansive soil mixed with calcium lignosulfonate alone (7d).
Figure 6.
Stress-strain curves of modified expansive soil mixed with calcium lignosulfonate alone (7d).
Figure 7.
Variation of unconfined compressive strength of improved soil with different calcium lignosulfonate content (7d).
Figure 7.
Variation of unconfined compressive strength of improved soil with different calcium lignosulfonate content (7d).
Figure 8.
Direct shear fitting curves of 3% calcium lignosulfonate samples with different lignin fiber content.
Figure 8.
Direct shear fitting curves of 3% calcium lignosulfonate samples with different lignin fiber content.
Figure 9.
Stress-strain curves of composite improved expansive soil at different curing ages: (a) Stress-strain curve of the compound improved expansive soil (1d); (b) Stress-strain curve of the compound improved expansive soil (7d).
Figure 9.
Stress-strain curves of composite improved expansive soil at different curing ages: (a) Stress-strain curve of the compound improved expansive soil (1d); (b) Stress-strain curve of the compound improved expansive soil (7d).
Figure 10.
Effects of lignin fiber content and curing age on unconfined compressive strength of improved soil.
Figure 10.
Effects of lignin fiber content and curing age on unconfined compressive strength of improved soil.
Figure 11.
Failure mode of samples: (a) prime expansive soil; (b) 3% calcium lignosulfonate improved soil; (c) 3% calcium lignosulfonate+1.5% lignin fiber composite improved soil.
Figure 11.
Failure mode of samples: (a) prime expansive soil; (b) 3% calcium lignosulfonate improved soil; (c) 3% calcium lignosulfonate+1.5% lignin fiber composite improved soil.
Figure 12.
Microstructure of samples: (a) prime expansive soil; (b) 3% calcium lignosulfonate improved soil; (c) 3% calcium lignosulfonate+1.5% lignin fiber composite improved soil.
Figure 12.
Microstructure of samples: (a) prime expansive soil; (b) 3% calcium lignosulfonate improved soil; (c) 3% calcium lignosulfonate+1.5% lignin fiber composite improved soil.
Table 1.
Physical parameters of Mengzi expansive soil.
Table 1.
Physical parameters of Mengzi expansive soil.
| Liquid limit (%) |
Plastic limit (%) |
Plasticity index |
Maximum dry density (g/cm3) |
Optimum moisturecontent (%) |
Free swelling ratio (%) |
| 54.01 |
22.58 |
31.43 |
1.65 |
19.03 |
50.0 |
Table 2.
Sample modifier incorporation design ratio.
Table 2.
Sample modifier incorporation design ratio.
| Sample name |
Calcium lignosulfonate content/% |
Lignin fiber/% |
| Prime expansive soil |
/ |
/ |
| Calcium lignosulfonate improved soil |
1.0/2.0/3.0/4.0 |
/ |
| Composite improved soil |
Optimal Calcium lignosulfonate content |
0.5 |
| 1.0 |
| 1.5 |
| 2.0 |
Table 3.
Fitting parameters of cohesion and internal friction angle of soil improved with different calcium lignosulfonate content.
Table 3.
Fitting parameters of cohesion and internal friction angle of soil improved with different calcium lignosulfonate content.
| Calcium lignosulfonate content/% |
C/kPa |
φ/(°) |
R2
|
| 0 |
37.702 |
30.689 |
0.9803 |
| 1 |
68.158 |
30.575 |
0.9407 |
| 2 |
56.799 |
42.323 |
0.9644 |
| 3 |
65.924 |
44.991 |
0.9016 |
| 4 |
72.897 |
23.258 |
0.9138 |
Table 4.
Fitting parameters of cohesion and internal friction angle of 3% calcium lignosulfonate improved soil with different fiber content.
Table 4.
Fitting parameters of cohesion and internal friction angle of 3% calcium lignosulfonate improved soil with different fiber content.
| lignin fiber content/% |
C/kPa |
φ/(°) |
R2
|
| Prime expansive soil |
37.702 |
30.689 |
0.9803 |
| 0 |
65.924 |
44.991 |
0.9016 |
| 0.5 |
76.181 |
35.990 |
0.9367 |
| 1.0 |
69.351 |
45.210 |
0.9379 |
| 1.5 |
75.041 |
45.635 |
0.9887 |
| 2.0 |
79.837 |
41.324 |
0.9460 |
Table 5.
Changes in water stability of samples before and after improvement.
Table 5.
Changes in water stability of samples before and after improvement.
| Sample name |
Start to soak in water (within 30min) |
Soaking process (48h) |
Final result (96h) |
| Prime expansive soil |
There are many tiny gaps on the sample's surface, accompanied by bubbles |
The cracks on the sample begin to develop, gradually extending to both ends of the sample, and there are small cracks at the end |
The cracks in the sample gradually increase, running through the entire sample, the end cracks are fully developed, and the crack width increases |
| 3% calcium lignosulfonate+1.5% lignin fiber composite samples |
There is no noticeable change in the overall sample, a small amount of air bubbles are generated on the surface, and no cracks are formed |
Some "foaming" particles appeared in the sample, and the overall sample increased slightly |
Cracks appear on the edge of the sample and start to peel off, but no shots are formed in the middle, and the integrity can still be maintained |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).