Submitted:
21 April 2023
Posted:
23 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
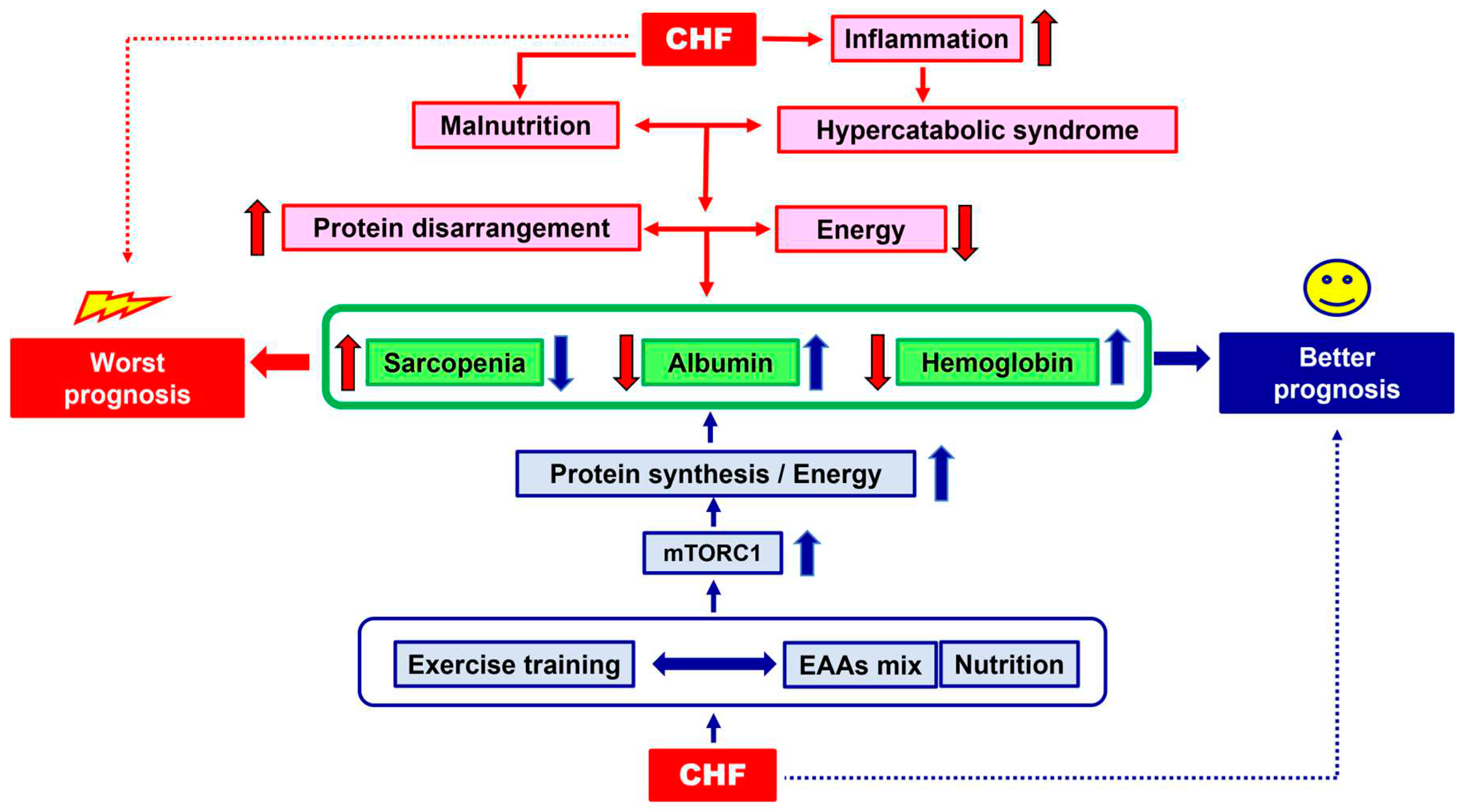
1. The Clinical Problem
2. Why and How to Quantify Malnutrition?
3. The Physio-Pathology of Malnutrition: The Hypercatabolic Syndrome and Protein Disarrangements
4. Therapeutical Strategies: Exercise Training and Nutritional Supplementation
4.1. Exercise Training
4.2. Nutritional Supplementation.
5. Molecular Hypothesis of Exercise Training and Nutritional Supplementation Alliance: The Role of AMPK and mTOR
6. Conclusion and Clinical Suggestions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sandek, A., Doehner, W., Anker, S.D., von Haehling, S. Nutrition in heart failure: an update. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care. 2009,12(4), 384-391.
- Butler, J., Kalogeropoulos, A. Worsening heart failure hospitalization epidemic we do not know how to prevent and we do not know how to treat! J Am Coll Cardiol, 2008, 5,52(6), 435-437.
- von Haehling, S., Ebner, N., Dos Santos, M.R., Springer, J., Anker, S.D. Muscle wasting and cachexia in heart failure: mechanisms and therapies. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2017, 14(6), 323-341.
- Anker, S.D, Coats, A., J. Cardiac cachexia: a syndrome with impaired survival and immune and neuroendocrine activation. Chest. 1999, 115(3), 836-847.
- Pasini, E., Aquilani, R., Corsetti, G., Dioguardi, F.S. Malnutrition and Gut Flora Dysbiosis: Specific Therapies for Emerging Comorbidities in Heart Failure. Biomed Res Int. 2015, 2015, 382585.
- Aquilani, R., Opasich, C., Verri, M., Boschi, F., Febo, O., Pasini, E., Pastoris, O. Is nutritional intake adequate in chronic heart failure patients? J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003, 1,42(7),1218-1223.
- Pasini, E., Aquilani, R., Dioguardi F.S. "The enemy within". How to identify chronic diseases induced-protein metabolism impairment and its possible pharmacological treatment. Pharmacol Res. 2013, 76, 28-33.
- Soukoulis, V., Dihu J.B., Sole, M., Anker S.D, Cleland, J., Fonarow G.,C, Metra, M., Pasini, E., Strzelczyk, T., Taegtmeyer, H., Gheorghiade, M. Micronutrient deficiencies an unmet need in heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009, 27,54(18), 1660-1673.
- Lehninger, A.L.; Nelson, D.L., Cox, M.M. Principles of Biochemistry, 2nd Ed.; Worth Publishers Inc., N.Y., 2000.
- O'Keeffe , M., Kelly, M., O'Herlihy, E., O'Toole, P., W., Kearney, P., M., Timmons, S., O'Shea, E., Stanton, C., Hickson, M., Rolland, Y., Sulmont, Rossé, C., Issanchou, S., Maitre, I., Stelmach-Mardas, M., Nagel, G., Flechtner-Mors, M., Wolters, M., Hebestreit, A., De Groot, L.C.P.G.M., van de Rest, O., The, R., Peyron, M., A., Dardevet, D., Papet, I., Schindler, K., Streicher, M., Torbahn, G., Kiesswetter, E., Visser, M., Volkert, D., O'Connor, E., M.; MaNuEL, consortium. Potentially modifiable determinants of malnutrition in older adults: A systematic review. Clin Nutr. 2019, 38(6), 2477-2498.
- Pasini, E., Aquilani, R., Testa, C., Baiardi, P., Angioletti, S., Boschi, F., Verri, M., Dioguardi F.S. Pathogenic Gut Flora in Patients With Chronic Heart Failure. J Am Coll Cardiol Heart Fail. 2014, (3), 220-227.
- Pasini, E., Flati, V., Paiardi. S., Rizzoni, D., Porteri, E., Aquilani, R., Assanelli, D., Corsetti, G., Speca, S., Rezzani, R., De Ciuceis, C., Agabiti-Rosei, E. Intracellular molecular effects of insulin resistance in patients with metabolic syndrome. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2010, 1,9, 46-50.
- Pasini, E., Aquilani, R., Dioguardi, F.S. Amino acids: chemistry and metabolism in normal and hypercatabolic states. Am J Cardiol. 2004, 22,93(8A), 3A-5A.
- Pasini, E, Aquilani, R., Dioguardi, F.S., D'Antona, G., Gheorghiade, M., Taegtmeyer, H. Hypercatabolic syndrome: molecular basis and effects of nutritional supplements with amino acids. Am J Cardiol. 2008, 2,101(11A), 11E-15E.
- Pasini, E., Corsetti, G., Aquilani, R., Romano, C., Picca, A., Calvani, R., Dioguardi, F.S. Protein-Amino Acid Metabolism Disarrangements: The Hidden Enemy of Chronic Age-Related Conditions. Nutrients. 2018, 22,10(4), 391.
- Hasten, D.L., Pak-Loduca, J., Obert, K.A., Yarasheski, K.E. Resistance exercise acutely increases MHC and mixed muscle protein synthesis rates in 78-84 and 23-32 yr olds. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2000, 278(4), E620-E626.
- Taylor, R.S., Dalal, H.M., McDonagh, S.T.J. The role of cardiac rehabilitation in improving cardiovascular outcomes. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2022, 19(3), 180-194.
- Aquilani, R., Opasich, C., Dossena, M., Iadarola, P., Gualco, A., Arcidiaco, P., Viglio, S., Boschi, F., Verri, M., Pasini, E. Increased skeletal muscle amino acid release with light exercise in deconditioned patients with heart failure.. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005, 4;45(1), 158-160.
- Aquilani, R., Opasich, C., Gualco, A., Verri, M., Testa, A., Pasini, E., Viglio, S., Iadarola, P., Pastoris, O., Dossena, M., Boschi, F. Adequate energy-protein intake is not enough to improve nutritional and metabolic status in muscle-depleted patients with chronic heart failure.. Eur J Heart Fail. 2008, 10(11), 1127-1135.
- Gwin, J.A, Church, D.D, Hatch-McChesney, A., Allen, J.T., Wilson, M.A., Varanoske, A.N., Carrigan C.T., Murphy N.E., Margolis L.M., Carbone J.W., Wolfe R.R., Ferrando A.A., Pasiakos S.M. Essential amino acid-enriched whey enhances post-exercise whole-body protein balance during energy deficit more than iso-nitrogenous whey or a mixed-macronutrient meal: a randomized, crossover study. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2021, 7;18(1), 4.
- Azhar, G., Verma, A., Zhang, X., Pangle, A., Patyal, P., Zhang, W., Che, Y., Coker, K., Wolfe, R.R., Wei, J.Y. Differential plasma protein expression after ingestion of essential amino acid-based dietary supplement verses whey protein in low physical functioning older adults. Geroscience. 2023, 1.
- Church, D.D., Hirsch, K.R., Park, S., Kim, I.Y., Gwin, J.A., Pasiakos, S.M., Wolfe, R.R., Ferrando, A.A. Essential Amino Acids and Protein Synthesis: Insights into Maximizing the Muscle and Whole-Body Response to Feeding.. Nutrients. 2020, 2,12(12), 3717.
- Romano, C., Corsetti, G., Flati, V., Pasini, E., Picca, A., Calvani, R., Marzetti, E., Dioguardi F.S. Influence of Diets with Varying Essential/Nonessential Amino Acid Ratios on Mouse Lifespan. Nutrients. 2019, 1811(6), 1367.
- Aquilani, R., Zuccarelli, G.C., Condino, A.M., Catani, M., Rutili, C., Del Vecchio C., Pisano, P., Verri, M., Iadarola, P., Viglio, S., Boschi, F. Despite Inflammation, Supplemented Essential Amino Acids May Improve Circulating Levels of Albumin and Haemoglobin in Patients after Hip Fractures.. Nutrients. 2017, 21;9(6), 637.
- D'Antona, G., Ragni, M., Cardile, A., Tedesco, L., Dossena, M., Bruttini, F., Caliaro, F., Corsetti, G., Bottinelli, R., Carruba, M.O., Valerio, A., Nisoli E.Branched-chain amino acid supplementation promotes survival and supports cardiac and skeletal muscle mitochondrial biogenesis in middle-aged mice. Cell Metab. 2010, 6;12(4), 362-372.
- Romano,, C., Corsetti, G., Pasini, E., Flati, V., Dioguardi F.S. Dietary Modifications of Nitrogen Intake Decreases Inflammation and Promotes Rejuvenation of Spleen in Aged Mice. Journal of Food and Nutrition Research. 2018, 6(7), 419-432.
- Liu, H., Liu, R., Xiong, Y., Li, X., Wang, X., Ma, Y., Guo, H., Hao, L., Yao, P., Liu, L., Wang, D., Yang, X. Leucine facilitates the insulin-stimulated glucose uptake and insulin signaling in skeletal muscle cells: involving mTORC1 and mTORC2. Amino Acids. 2014, 46(8), 1971-9.
- Molfino, A., Gioia, G., Rossi Fanelli, F., Muscaritoli, M., Beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate supplementation in health and disease: a systematic review of randomized trials. Amino Acids. 2013, 45(6), 1273-1292.
- Valerio, A., D'Antona, G., Nisoli. E. Branched-chain amino acids, mitochondrial biogenesis, and healthspan: an evolutionary perspective. Aging (Albany NY). 2011, 3(5), 464-478.
- Voulgaridou, G., Papadopoulou, S.D., Spanoudaki, M., Kondyli, F.S., Alexandropoulou, I., Michailidou, S., Zarogoulidis, P., Matthaios, D., Giannakidis, D., Romanidou, M., Papadopoulou, S.K. Increasing Muscle Mass in Elders through Diet and Exercise: A Literature Review of Recent RCTs. Foods. 2023, 13,12(6), 1218.
- DeBerardinis, R.J., Thompson, C.B., Cellular metabolism and disease: what do metabolic outliers teach us?. Cell. 2012, 16,148(6), 1132-1144.
- Pasini, E., Corsetti, G., Romano, C., Aquilani, R., Scarabelli, T., Chen-Scarabelli, C., Dioguardi, F.S. Management of Anaemia of Chronic Disease: Beyond Iron-Only Supplementation. Nutrients. 2021, 15,13(1), 237.
- An, P., Wan, S., Luo, Y., Luo, J., Zhang, X., Zhou, S., Xu, T., He, J., Mechanick, J.I., Wu, W.C., Ren, F., Liu, S. Micronutrient Supplementation to Reduce Cardiovascular Risk. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2022, 13,80(24), 2269-2285.
- Yoon, K.,J., Zhang, D., Kim, S.J., Lee, M.C., Moon, H.Y. Exercise-induced AMPK activation is involved in delay of skeletal muscle senescence. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019, 7,512(3), 604-610.
- Shimobayashi, M., Hal,l M.N., Making new contacts: the mTOR network in metabolism and signalling crosstalk. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014, 15(3), 155-162.
- Wälchli, M., Berneiser, K., Mangia, F., Imseng, S., Craigie, L.M., Stuttfeld, E., Hall, M.N., Maier, T. Regulation of human mTOR complexes by DEPTOR. Elife. 2021, 14,10, e70871.
- Shimkus, K.L., Jefferson, L.S., Gordon, B.S., Kimball, S.R. Repressors of mTORC1 act to blunt the anabolic response to feeding in the soleus muscle of a cast-immobilized mouse hindlimb. Physiol Rep. 2018, 6(20), e13891.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




