Submitted:
17 April 2023
Posted:
19 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Principle
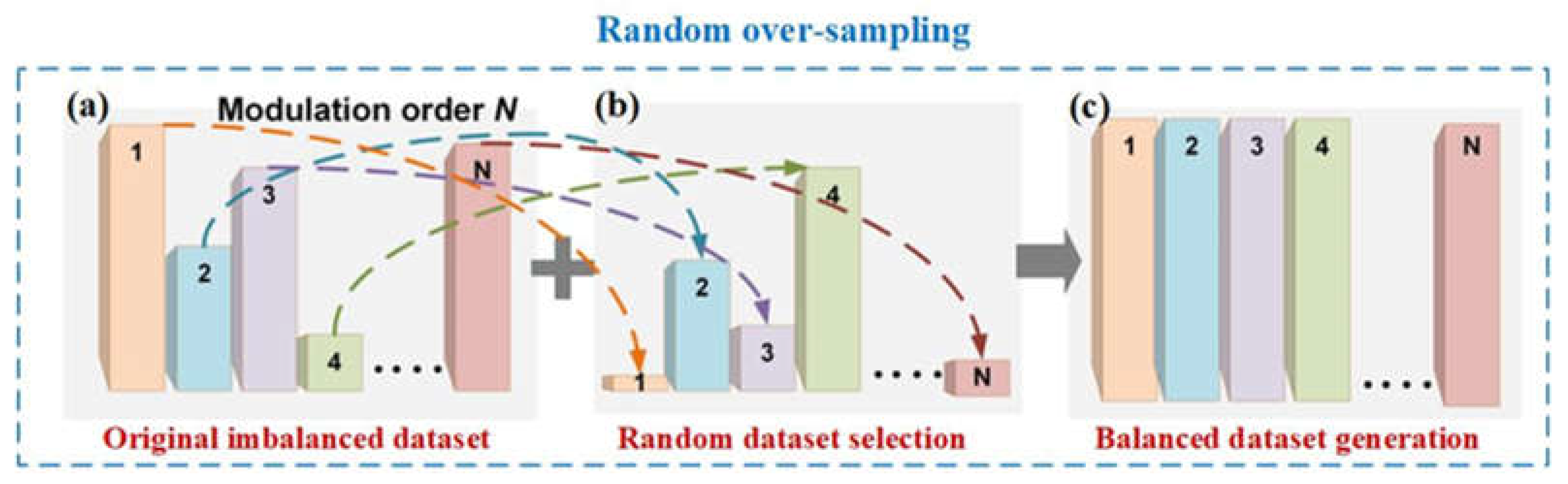
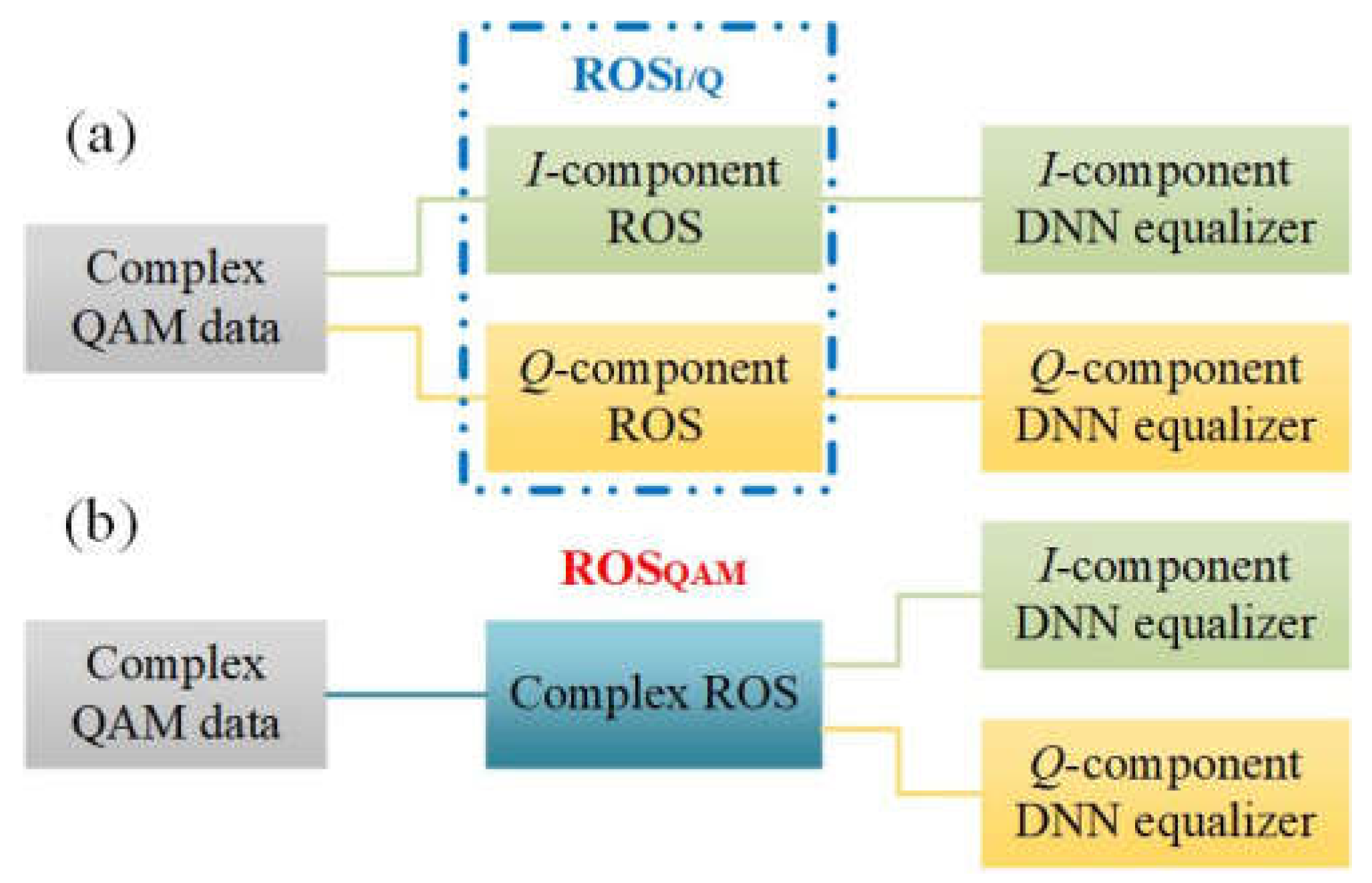
2.1. Random over-sampling (ROS)
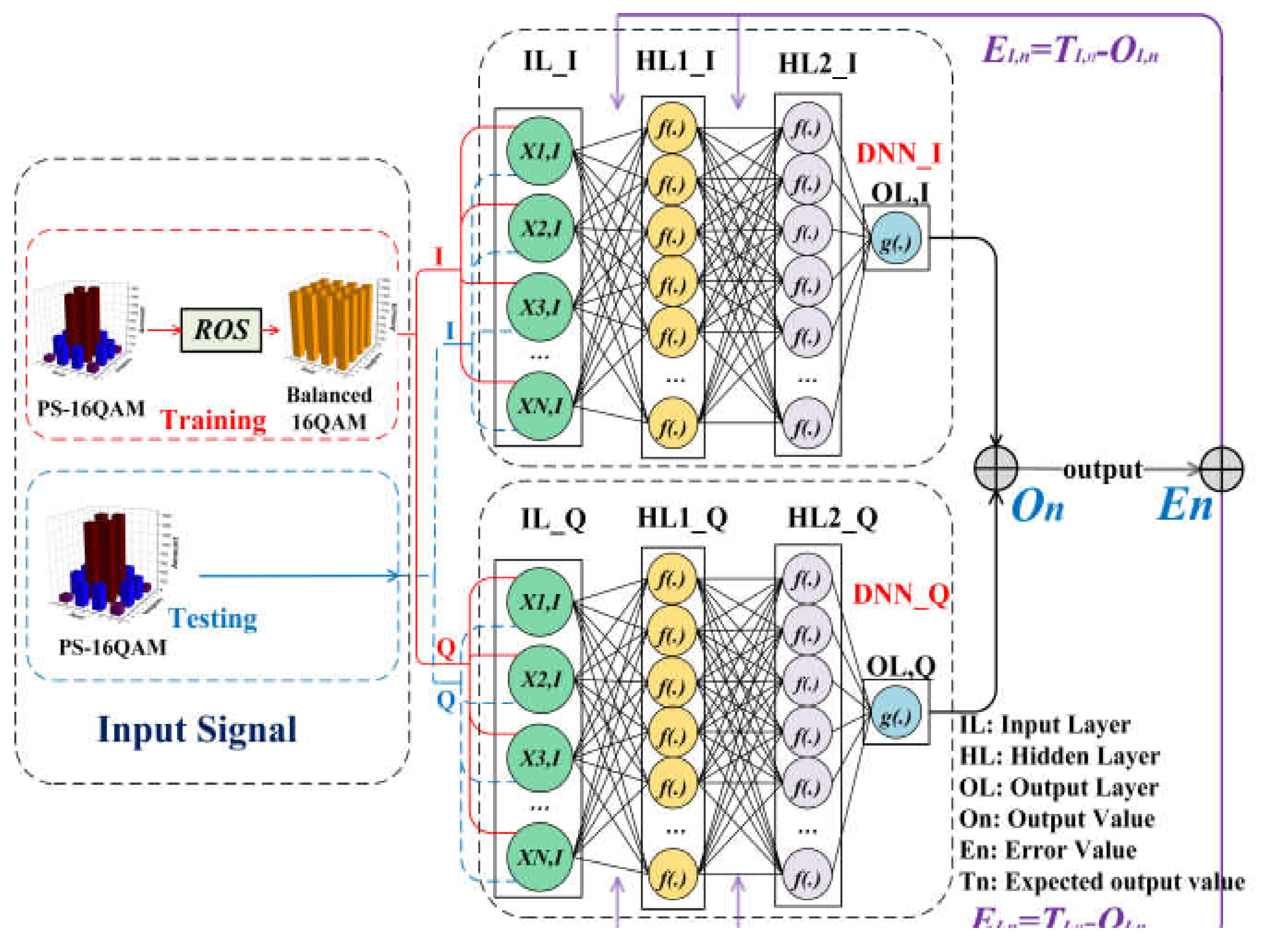
2.2. Two-lane DNN (TLD) Equalizer
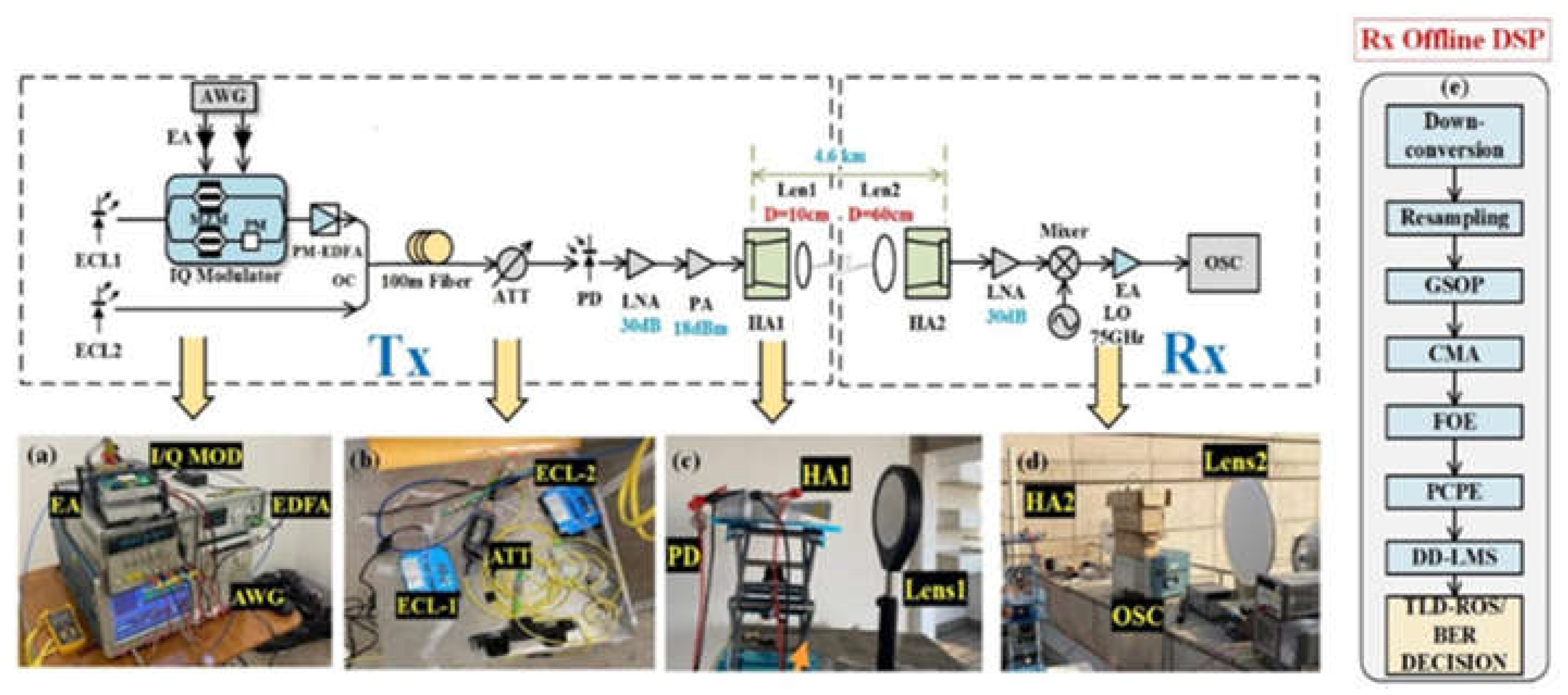
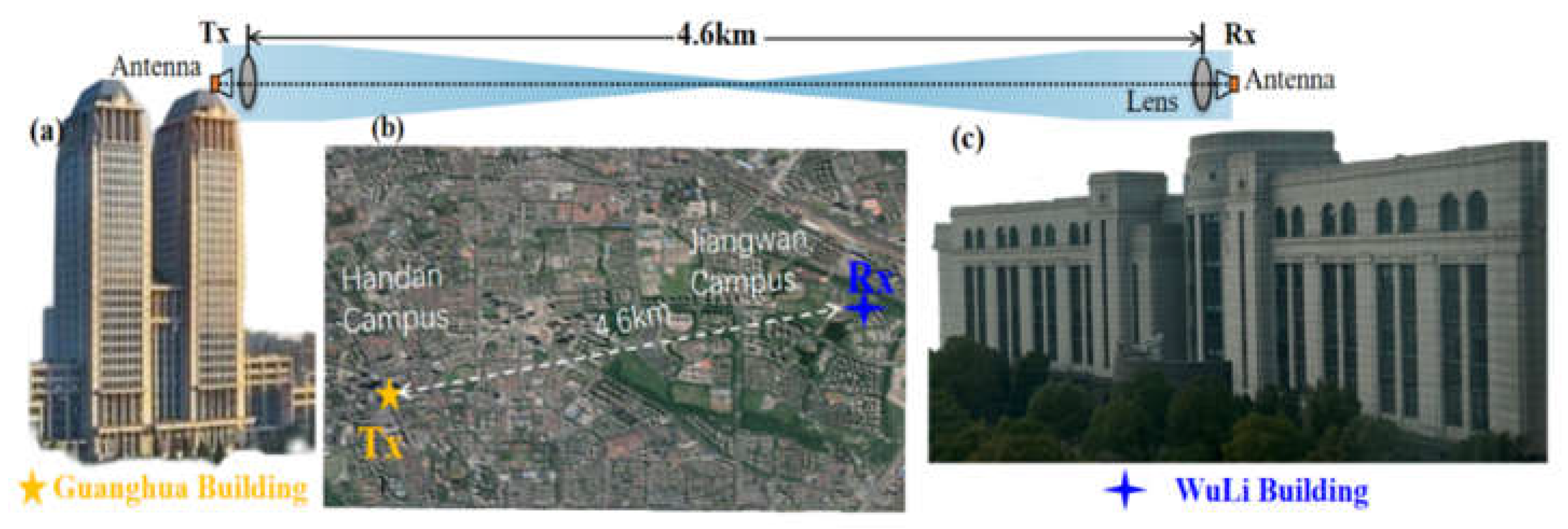
3. Experimental Setup
4. Experimental results and discussions
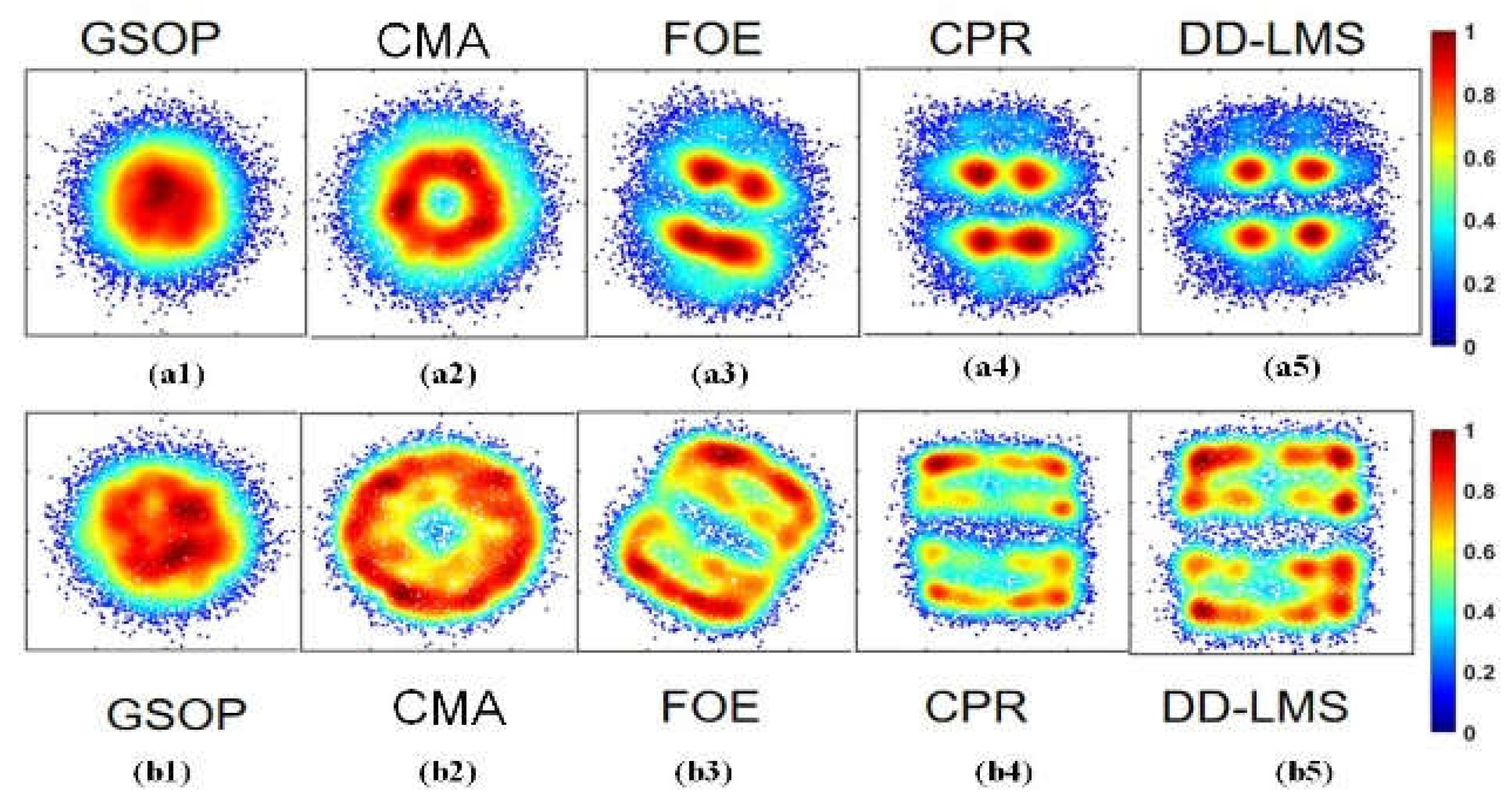
4.1. Traditional DSP Algorithm
4.2. Results of ROS processing
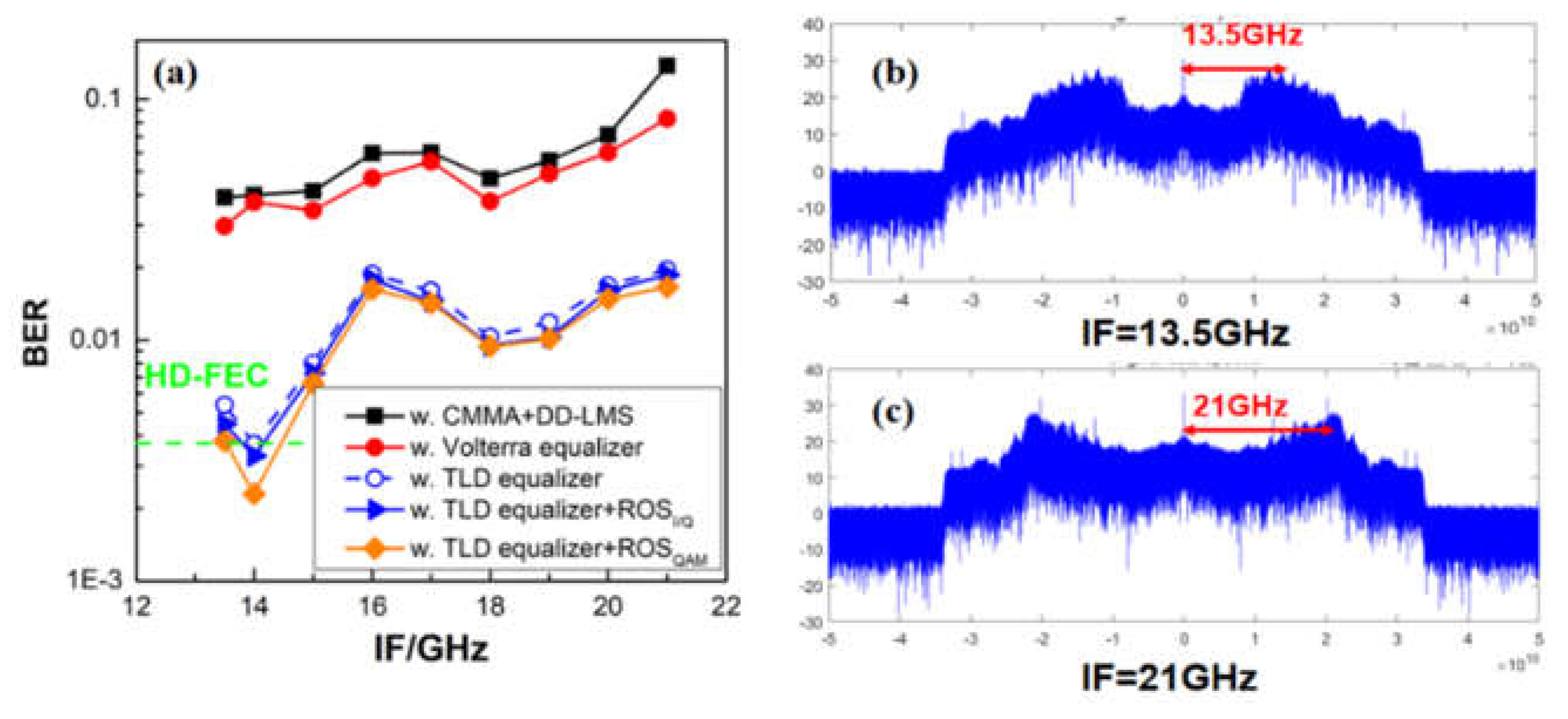
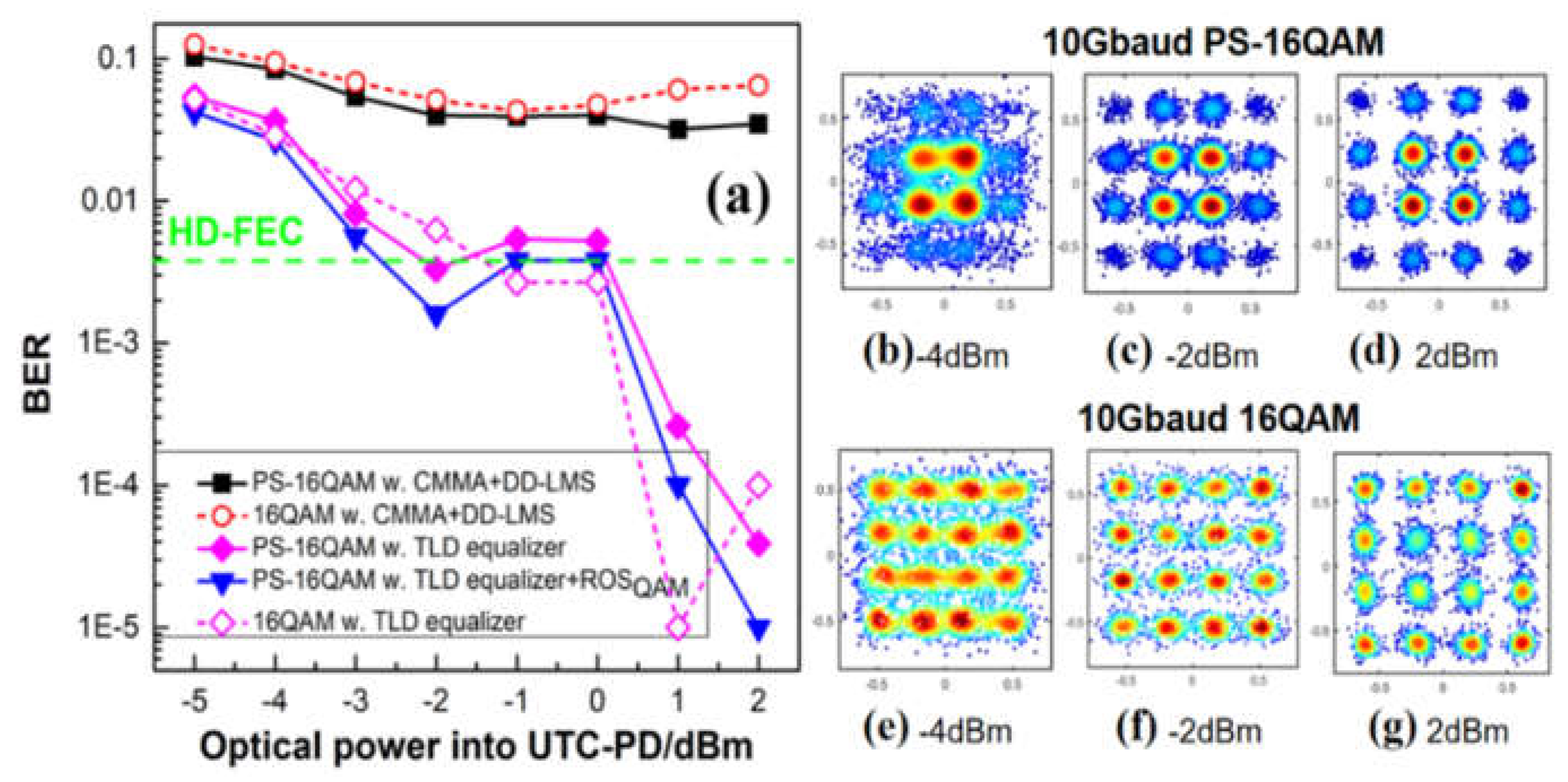
4.3. BER performances using TLD equalizer with/without ROS preprocessing
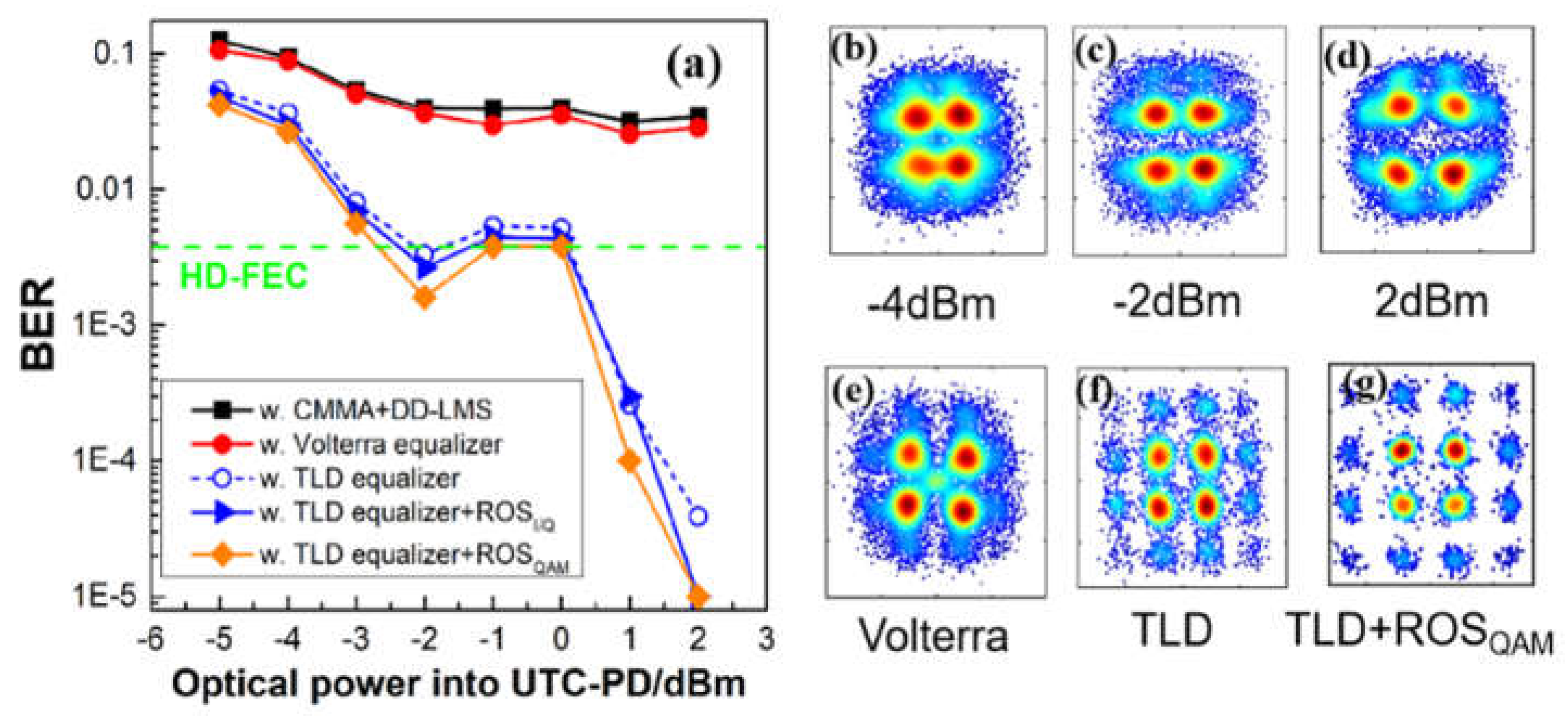
4.4. BER performance comparison using different equalizer schemes
4.4.1. Training Accuracy
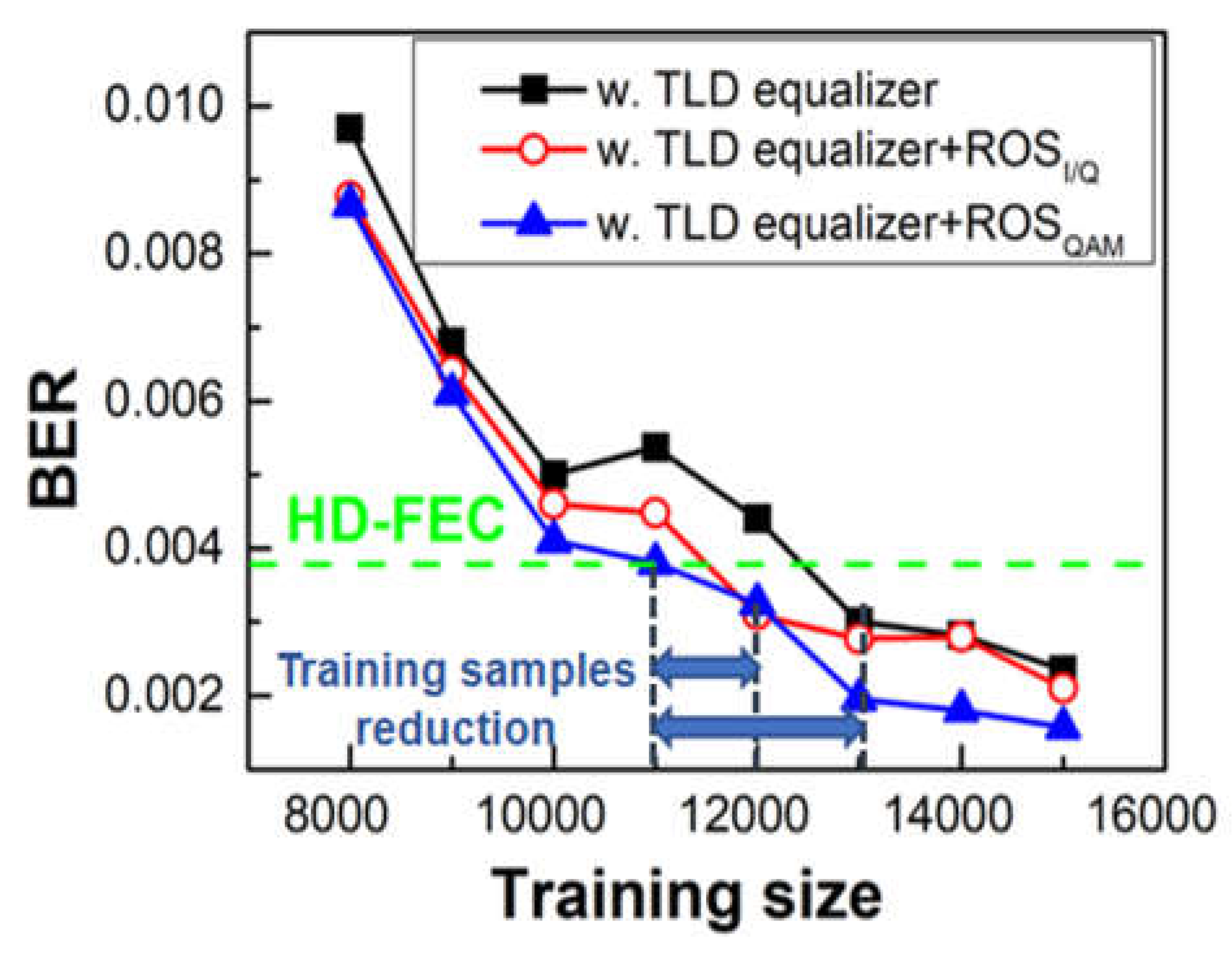
4.4.2. Training Data Size
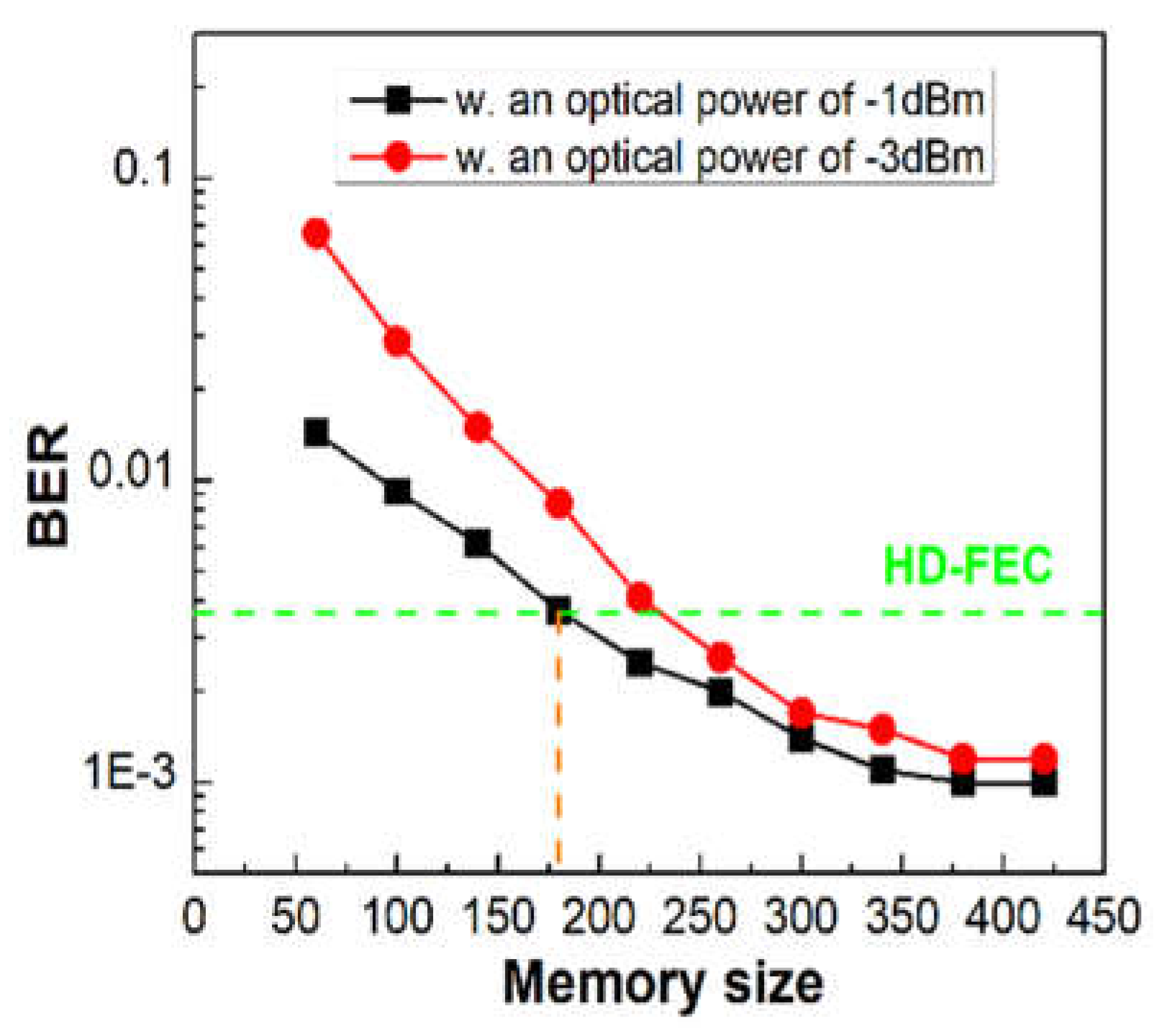
4.4.3. Memory Size in Input Layer
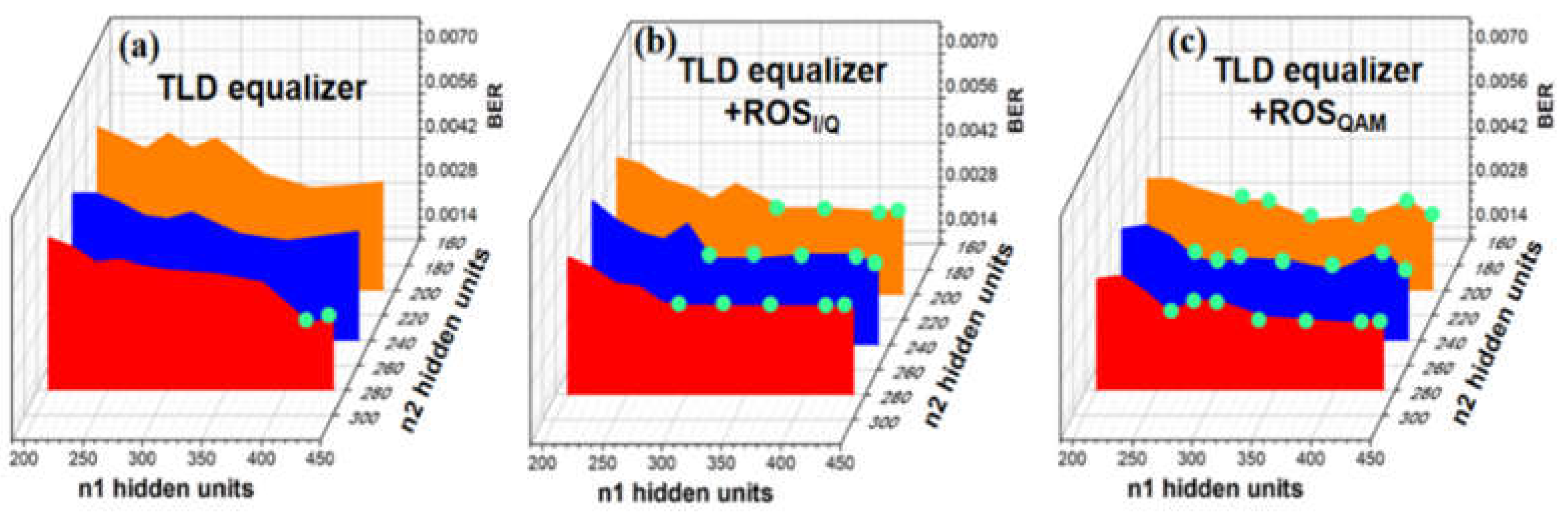
4.4.4. Neuron Number in Hidden Layer
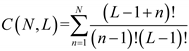 [35], with N representing the Volterra order and L denoting the memory length. According to Table. 1, the complexity of the optimal 2nd Volterra with 321 taps is close to that of TLD-ROS equalizers, whereas its effect on nonlinear compensation is far less than TLD-ROS equalizers. Therefore, it can further prove the superiority of a TLD-ROSQAM equalizer because it reaches the HD-FEC threshold with the simplest structure.
[35], with N representing the Volterra order and L denoting the memory length. According to Table. 1, the complexity of the optimal 2nd Volterra with 321 taps is close to that of TLD-ROS equalizers, whereas its effect on nonlinear compensation is far less than TLD-ROS equalizers. Therefore, it can further prove the superiority of a TLD-ROSQAM equalizer because it reaches the HD-FEC threshold with the simplest structure. 5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Y. Takahashi, K. Muraoka, J. Mashino, S. Suyama and Y. Okumura, “5G downlink throughput performance of 28 GHz band experimental trial at 300 km/h”, 2018 IEEE 29th Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC, 2018), pp. 1140-1141.
- N. Nonaka, K. Muraoka, T. Okuyama, S. Suyama, Y. Okumura, T. Asai, and Y. Matsumura, “28 GHz-Band experimental trial at 283 km/h using the Shinkansen for 5G evolution”, 2020 IEEE 91st Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC, 2020), pp. 1-5.
- T. Okuyama, S. Suyama, N. Nonaka, Y. Okumura and T. Asai, “Two millimeter-wave base station cooperation technologies in high-mobility environments for 5G evolution,” 2020 IEEE 91st Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC, 2020), pp. 1-5.
- T. Okuyama, S. Suyama, N. Nonaka and T. Asai, “Outdoor experimental trials of 28 GHz band base station cooperation in high-mobility environment of multiple mobile stations, ” 2021 IEEE 94th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC, 2021), pp. 1-5.
- A. Hirata, T. Kosug, H. Takahashi, R. Yamaguchi, F. Nakajima, T. Furuta, H. Ito, H. Sugahara, and Y. Sat, “120-GHz-band millimeter-wave photonic wireless link for 10-Gb/s data transmission,” IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 54(5), 1937-1944 (2006). [CrossRef]
- ClarkS.Durrant-WhyteH., “Autonomous land vehicle navigation using millimeter wave radar,” in IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (IEEE, 1998), pp. 3697-3702.
- W. Zhou, and C. Qin, “Simultaneous generation of 40, 80 and 120 GHz optical millimeter-wave from one Mach-Zehnder modulator and demonstration of millimeter-wave transmission and down-conversion,” Opt. Commun.398, 101-106 (2017). [CrossRef]
- H. Zheng, S. Liu, X. Li, W. Wang, and Z. Tian, “Generation and transmission simulation of 60 G millimeter-wave by using semiconductor optical amplifiers for radio-over-fiber systems,” Opt. Commun.282(22), 4440-4444 (2009). [CrossRef]
- P. T. Shih, J. Chen, C. T. Lin, W. J. Jiang, H. Huang, P. Peng, and S. Chi, “Optical millimeter-wave signal generation via frequency 12-tupling,” J. Lightwave Technol. 28(1), 71-78(2010). [CrossRef]
- X. Li, J. Xiao, Y. Xu, L. Chen, J. Yu. “Frequency-doubling photonic vector millimeter-wave signal generation from one DML,” IEEE Photon. J. 7(6), 1-7 (2015). [CrossRef]
- X. Li, J. Xiao, J. Yu. “W-band vector millimeter-wave signal generation based on phase modulator with photonic frequency quadrupling and precoding, “ J. Lightwave Technol. 35 (13), 2548-2558 (2017). [CrossRef]
- Press release from NTT DOCOMO on, Jan. 2020, [online] Available: https://www.nttdocomo.co.jp/english/info/media_center/pr/2020/0124_00.html.
- S. Suyama, T. Okuyama, Y. Kishiyama, S. Nagata and T. Asai, “A study on extreme wideband 6G radio access technologies for achieving 100 Gbps data rate in higher frequency bands”, IEICE Trans. Commun.E104-B (9), 992-999 (2021). [CrossRef]
- J. Xiao, J. Yu, X. Li, Y. Xu and Z. Zhang, “20-Gb/s PDM-QPSK signal delivery over 1.7-km wireless distance at W-band”, 2015 Optical Fiber Communications Conference and Exhibition (OFC, 2015), pp. 1-3.
- X. Li, J. Yu, J. Xiao, Z. Zhang, Y. Xu and L. Chen, “Field trial of 80-Gb/s PDM-QPSK signal delivery over 300-m wireless distance with MIMO and antenna polarization multiplexing at W-band”, 2015 Optical Fiber Communications Conference and Exhibition (OFC, 2015), pp. 1-3.
- J. A. Nanzer, P. T. Callahan, M. L. Dennis, T. R. Clark, D. Novak and R. B. Waterhouse, “Millimeter-wave wireless communication using dual-wavelength photonic signal generation and photonic upconversion”, IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 50(12), 3522-3530(2011). [CrossRef]
- J. Xiao, X. Li, J. Yu, Y. Xu, Z. Zhang and L. Chen, “40-Gb/s PDM-QPSK signal transmission over 160-m wireless distance at W-band”, Opt. Lett 40(6), 998-1001 (2015). [CrossRef]
- X. Li, J. Xiao and J. Yu, “Long-Distance Wireless mm-Wave Signal Delivery at W-Band,” J. Lightwave Technol. 34(2), pp. 661-668 (2016). [CrossRef]
- X. Li, J. Yu, J. Zhang, F. Li, Y. Xu, Z. Zhang, and J. Xiao, “Fiber-wireless-fiber link for 100-Gb/s PDM-QPSK signal transmission at W-band.” IEEE Photonics Technology Letters 26(18), 1825-1828 (2014). [CrossRef]
- Yu, Jianjun, Xinying Li, and Nan Chi. “Faster than fiber: over 100-Gb/s signal delivery in fiber wireless integration system.” Opt. express 21(19), 22885-22904 (2013). [CrossRef]
- J. Yu, Z. Jia, L. Yi, Y. Su, G. K. Chang and T. Wang, “Optical millimeter-wave generation or up-conversion using external modulators,” in IEEE Photonics Technology Letters 18(1), 265-267 (2006). [CrossRef]
- W. Idler, F. Buchali, L. Schmalen, E. Lach, R. Braun, G. Boecherer, P. Schulte and F. Steiner, “Field Demonstration of 1 Tbit/s Super-Channel Network Using Probabilistically Shaped Constellations,” 2016 42nd European Conference on Optical Communication (ECOC, 2016), pp. 1-3.
- Q. Xu, L. Wang, D. Wang, X. Chen and S. Sun, “Probabilistic Shaping QC-LDPC Coded Modulation Scheme for Optical Fiber Systems,” 2018 Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics Pacific Rim (CLEO-PR, 2018), pp. 1-2.
- K. M. Gharaibeh, Nonlinear Distortion in Wireless Systems: Modeling and Simulation with Matlab (Wiley-IEEE Press, 2012).
- K. B. Petrov, C. Mathieu, T. Felix, T. A. Eriksson, B. Henning, L. Domanic, B. Polina and S. Laurent, “End-to-End Deep Learning of Optical Fiber Communications,” J. Lightwave Technol. 36(20), 4843 – 4855 (2018). [CrossRef]
- S. Guob, G Peng, A Yangd and Y Qiaoe, “Deep Neural Network Based Chromatic Dispersion Estimation With Ultra-Low Sampling Rate for Optical Fiber Communication Systems,” IEEE Access 7, 84155-84162 (2019). [CrossRef]
- W. Wang and B. Chang, “Graph-based Dependency Parsing with Bidirectional LSTM,” in Proceedings of the 54th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Academic, 2016), pp. 2306-2315.
- C. Liu, C. Wang, W. Zhou, F. Wang, M. Kong, and J. Yu, “81-GHz W-band 60-Gbps 64-QAM wireless transmission based on a dual-GRU equalizer,” Opt. Express 30, 2364-2377 (2022). [CrossRef]
- R. Liu, Y. Guo and S. Zhu, “Modulation Recognition Method of Complex Modulation Signal Based on Convolution Neural Network,” in Proc. 2020 IEEE 9th Joint International Information Technology and Artificial Intelligence Conference (ITAIC, 2020), pp. 1179-1184.
- Al-Nuaimi, Dhamyaa H., Muhammad F. Akbar, Laith B. Salman, Intan S. Zainal Abidin, and Nor Ashidi Mat Isa, “AMC2N: Automatic Modulation Classification Using Feature Clustering-Based Two-Lane Capsule Networks,” Electronics 10(1), 76 (2021). [CrossRef]
- A. Ghazikhani, H. S. Yazdi and R. Monsefi, “Class imbalance handling using wrapper-based random oversampling,” 20th Iranian Conference on Electrical Engineering (ICEE, 2012), pp. 611-616.
- S. Wang and X. Yao, “Multiclass Imbalance Problems: Analysis and Potential Solutions,” IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B (Cybernetics) 42(4), 1119-1130 (2012). [CrossRef]
- S. Choirunnisa and J. Lianto, “Hybrid Method of Undersampling and Oversampling for Handling Imbalanced Data,” in Proc. 2018 International Seminar on Research of Information Technology and Intelligent Systems (ISRITI, 2018), pp. 276-280.
- P. J. Freire, Y. Osadchuk, B. Spinnler, A. Napoli, W. Schairer, N. Costa, J. E. Prilepsky, and S. K. Turitsyn, “Performance Versus Complexity Study of Neural Network Equalizers in Coherent Optical Systems,” J. Lightwave Technol. 39(19), 6085-6096 (2021). [CrossRef]
- J. Tsimbinos and K. V. Lever, “The computational complexity of nonlinear compensators based on the Volterra inverse,” Proceedings of 8th Workshop on Statistical Signal and Array Processing (Academic, 1996), pp. 387-390.

| type | Training size | n1/tap | n2/tap | Minimum multiplication | Complexity reduction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TLD | 13000 | 410 | 280 | 377760 | 0% |
| TLD-ROSI/Q | 12000 | 320 | 200 | 243600 | 35.5% |
| TLD-ROSQAM | 11000 | 270 | 200 | 205600 | 45.6% |
| 2nd Volterra | 13000 | 321 | 321 | 207366 | 45.1% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





