Submitted:
19 April 2023
Posted:
19 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study registration and ethical components
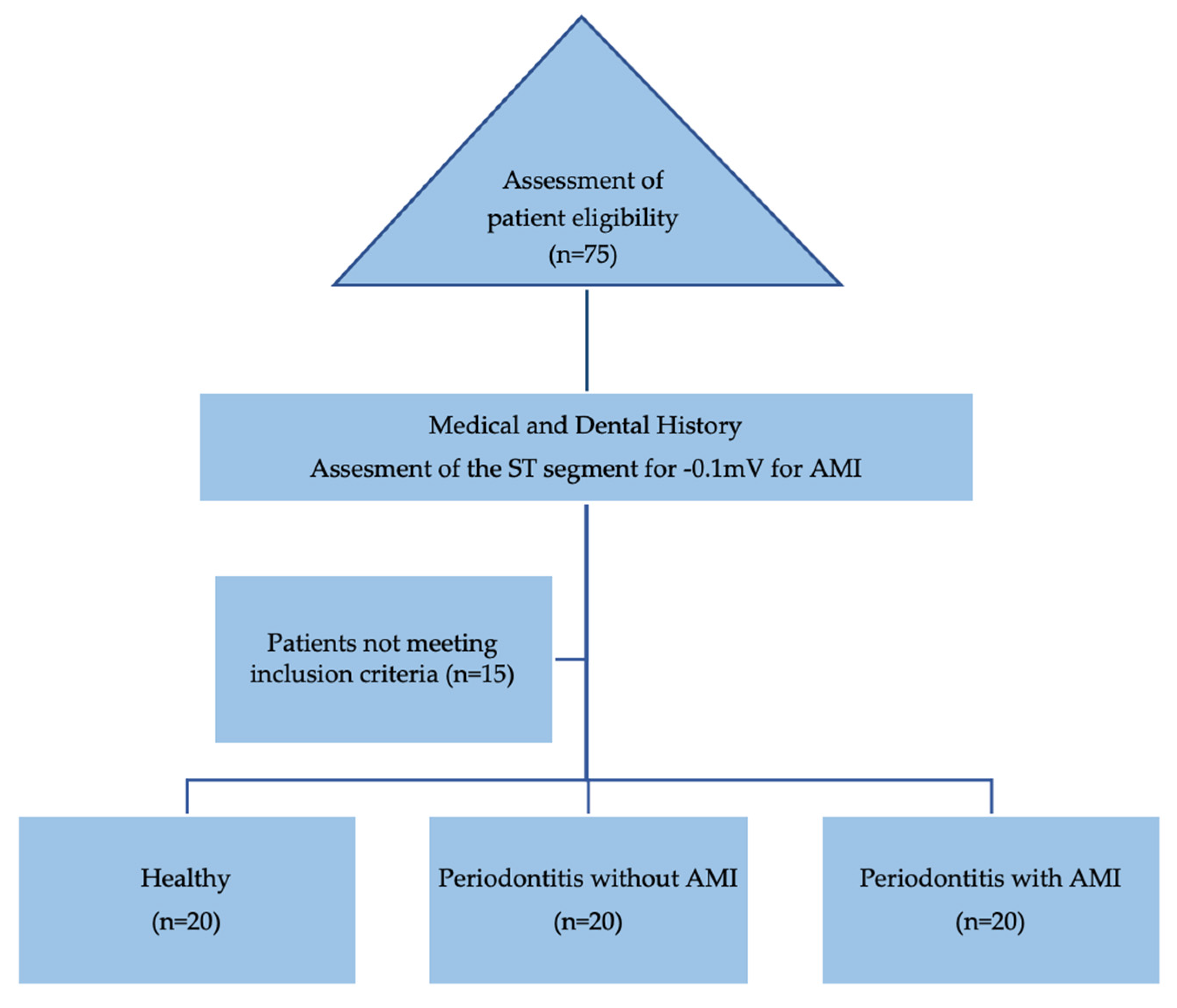
2.2. Selection criteria
2.3. Study groups distribution and characteristics
2.4. Steps and data collection
2.1. Statistical analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tonetti, M.S.; Greenwell, H.; Kornman, K.S. Staging and grading of periodontitis: framework and proposal of a new classification and case definition. Journal of Periodontology 2018, 89 Suppl 1, S159–S172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andriankaja, O.M.; Genco, R.J.; Dorn, J.; Dmochowski, J.; Hovey, K.; Falkner, K.L.; Scannapieco, F. The use of different measurements and definitions of periodontal disease in the study of the association between periodontal disease and risk of myocardial infarction. J Periodontol 2006, 77, 1067–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schenkein, H.A.; Loos, B.G. Inflammatory mechanisms linking periodontal diseases to cardiovascular diseases. J Clin Periodontol. 2013, 14, S51–S69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, F.C.; Genco, C.A. Porphyromonas gingivalis mediated periodontal disease and atherosclerosis: disparate diseases with commonalities in pathogenesis through TLRs. Curr Pharm Des 2007, 13, 3665–3675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonetti, M.S.; D’Aiuto, F.; Nibali, L.; Donald, A.; Storry, C.; Parkar, M.; Suvan, J. Treatment of periodontitis and endothelial function. N Engl J Med. 2007, 356, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graves, D. Cytokines that promote periodontal tissue destruction. J. Periodontol. 2008, 79, 1585–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhavsar, I.; Miller, C.; Al-Sabbagh, M. Macrophage Inflammatory Protein-1 Alpha (MIP-1 alpha)/CCL3: As a biomarker. 2015, 223–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denzel, M.S.; Scimia, M.C.; Zumstein, P.M.; Walsh, K.; Ruiz-Lozano, P.; Ranscht, B. Tcadherin is critical for adiponectin-mediated cardioprotection in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 4342–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obata, Y.; Kita, S.; Koyama, Y.; Fukuda, S.; Takeda, H.; Takahashi, M.; Fujishima, Y. Adiponectin/T-cadherin system enhances exosome biogenesis and decreases cellular ceramides by exosomal release. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e99680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, J.V.; Abraheem, A.; Dotsenko, O.; Creamer, J.; Gunning, M.; Hughes, E.A.; Lip, G.Y. Circulating serum adiponectin levels in patients with coronary artery disease: relationship to atherosclerotic burden and cardiac function. J Intern Med. 2008, 264, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siasos, G.; Tousoulis, D.; Kollia, C.; Oikonomou, E.; Siasou, Z.; Stefanadis, C.; Papavassiliou, A.G. Adiponectin and cardiovascular disease: mechanisms and new therapeutic approaches. Current medicinal chemistry. 2012, 19, 1193–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagrand, W.K.; Visser, C.A.; Hermens, W.T.; Niessen, H.W.; Verheugt, F.W.; Wolbink, G.J.; Hack, C.E. C-reactive protein as a cardiovascular risk factor: more than an epiphenomenon? Circulation 1999, 100, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannobile, W.V.; Wong, D.T. Salivary diagnostics: oral health and beyond. J Dent Res 2011, 90, 1153–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebersole, J.L.; Nagarajan, R.; Akers, D.; Miller, C.S. Targeted salivary biomarkers for discrimination of periodontal health and disease (s). Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2015, 5, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Kang, N.; Xue, F.; Qiao, J.; Duan, J.; Chen, F.; Cai, Y. Evaluation of salivary biomarkers for the diagnosis of periodontitis. BMC Oral Health. 2021, 21, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, C.A.; Schafer, J.J.; Yakob, M.; Lima, P.; Camargo, P.; Wong, D.T. Saliva diagnostics: utilizing oral fluids to determine health status. Monographs in oral science 2014, 24, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, C.S.; Foley, J.D.; Bailey, A.L.; Campell, C.L.; Humphries, R.L.; Christodoulides, N.; Floriano, P.N. Current developments in salivary diagnostics. Biomark Med. 2010, 4, 171–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Chaturvedi, R.; Jain, A. Role of cardiovascular disease markers in periodontal infection: understanding the risk. Indian J Dent Res 2015, 26, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebersole, J.L.; Kryscio, R.J.; Campbell, C.; Kinane, D.F.; McDevitt, J.; Christodoulides, N.; Floriano, P.N. Salivary and serum adiponectin and C-reactive protein levels in acute myocardial infarction related to body mass index and oral health. J Periodontal Res 2017, 52, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henson, B.S.; Wong, D.T. Collection, storage, and processing of saliva samples for downstream molecular applications. Methods Mol Biol. 2010, 666, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisha, K.J.; Aparna, S.; Anilkumar, A.; Shyam, P. MIP-1alpha and MCP-1 as salivary biomarkers in periodontal disease. Saudi dental journal 2018, 30, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Sabbagh, M.; Alladah, A.; Lin, Y.; Kryscio, R.J.; Thomas, M.V.; Ebersole, J.L.; Miller, C.S. Bone remodelling associated salivary biomarker MIP-1a distinguishes periodontal disease from health. J. Periodontal Res 2012, 47, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syndergaard, B.; Al-Sabbagh, M.; Kryscio, R.J.; Xi, J.; Ding, X.; Ebersole, J.L.; Miller, C.S. Salivary biomarkers associated with gingivitis and response to therapy. J Periodontol 2014, 85, e295–e303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez, M.; Krall, E.A.; Garcia, R.I.; Vokonas, P.S.; Dietrich, T. Periodontitis and incidence of cerebrovascular disease in men. Ann Neurol 2009, 66, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonetti, M.S.; Van Dyke, T.E. Working Group 1 of the Joint EFP/AAP Workshop. Periodontitis and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: consensus report of the Joint EFP/AAP Workshop on Periodontitis and Systemic Diseases. J Periodontol 2013, 84, S24–S29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seymour, G.J.; Ford, P.J.; Cullinan, M.P.; Leishman, S.; Yamazaki, K. Relationship between periodontal infections and systemic disease. Clinical microbiology and infection 2007, 13 (Suppl 4), 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jotwani, R.; Eswaran, S.V.; Moonga, S.; Cutler, C.W. MMP-9/TIMP-1 imbalance induced in human dendritic cells by Porphyromonas gingivalis. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 2010, 58, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Ngo, L.Q.; Promsudthi, A.; Surarit, R. Salivary Lipid Peroxidation in Patients with Generalized Chronic Periodontitis and Acute Coronary Syndrome. J Periodontol 2016, 87, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaee, M.; Fereydooni, G.M.; Maliji, G.; Bijani, A.; Aghajanpour, M.S.M.; Mousavi, K.S.N. C - reactive protein levels in patients with periodontal disease and normal subjects. International journal of molecular and cellular medicine 2013, 2, 151–155. [Google Scholar]
- Toda, M.; Tsukinoki, R.; Morimoto, K. Measurement of salivary adiponectin levels. Acta Diabetol 2007, 44, 20–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toda, M.; Morimoto, K. Comparison of saliva sampling methods for measurement of salivary adiponectin levels. Scandinavian journal of clinical and laboratory investigation 2008, 68, 823–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, R.W.; Kantarci, A.; LaMonte, M.J.; Andrews, C.A.; Hovey, K.M.; Falkner, K.L.; Cekici, A. Performance of multiplex cytokine assays in serum and saliva among community-dwelling postmenopausal women. PLoS One 2013, 8, e59498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehzad, A.; Iqbal, W.; Shehzad, O.; Lee, Y.S. Adiponectin: Regulation of its production and its role in human diseases. Hormones (Athens). 2012, 11, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishida, K.; Funahashi, T.; Shimomura, I. Molecular mechanisms of diabetes and atherosclerosis: Role of adiponectin. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2012, 12, 118–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.I.; Vora, N.; Langworthy, R.; Stock, S.; Momin, A.; Sherwood, R.; Le Roux, C.W. Leptin/adiponectin ratio in patients with coronary heart disease: comparing subjects with and without metabolic syndrome. Annals of clinical biochemistry. 2011, 48, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magge, S.N.; Stettler, N.; Koren, D.; LevittKatz, L.E.; Gallagher, P.R.; Mohler, E.R. Adiponectin is associated with favorable lipoprotein profile, independent of BMI and insulin resistance, in adolescents. The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism. 2011, 96, 1549–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tascilar, M.E.; Cekmez, F.; Meral, C.; Pirgon, O.; Tanju, I.A.; Canpolat, F.E.; Abaci, A. Evaluation of adipocytokines in obese children with insulin resistance. Turk J Pediatr. 2011, 53, 269–273. [Google Scholar]
- Abd, T.T.; Eapen, D.J.; Bajpai, A.; Goyal, A.; Dollar, A.; Sperling, L. The role of C-reactive protein as a risk predictor of coronary atherosclerosis: implications from the JUPITER trial. Curr Atheroscler Rep 2011, 13, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.P.; Tang, X.Y.; Ling, W.H.; Chen, W.Q.; Chen, Y.M. Early C-reactive protein in the prediction of long-term outcomes after acute coronary syndromes: a meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. Heart 2010, 96, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.S.; Ning, H.; Wilkins, J.T.; Allen, N.; Carnethon, M.; Berry, J.D.; Sweis, R.N.N. Association of Body Mass Index with Lifetime Risk of Cardiovascular Disease and Compression of Morbidity. JAMA Cardiol 2018, 3, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Beshbishy, H.A.; Maria, R.A.; Bardi, F.A. Biochemical and C-reactive protein alterations in myocardial infarction periodontitis patients. Am J Med Sci 2014, 348, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathnayake, N.; Gustafsson, A.; Norhammar, A.; Kjellstrom, B.; Klinge, B.; Ryden, L.; Tervahartiala, T. Salivary Matrix Metalloproteinase-8 and-9 and Myeloperoxidase in Relation to Coronary Heart and Periodontal Diseases: A Subgroup Report from the PAROKRANK Study (Periodontitis and Its Relation to Coronary Artery Disease). PLoS One 2015, 10, e0126370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emingil, G.; Atilla, G.; Baskesen, A.; Berdeli, A. Gingival crevicular fluid EMAP-II, MIP-1a and MIP-1b levels of patients with periodontal disease. J Clin Periodontol 2005, 32, 880–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradeep, A.R.; Daisy, H.; Hadge, P. Serum levels of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in periodontal health and disease. Cytokine 2009, 47, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemmell, E.; Carter, C.L.; Seymour, G.J. Chemokines in human periodontal disease tissues. Clin. Exp. Immunol 2001, 125, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lima, C.L.; Acevedo, A.C.; Grisi, D.C.; Taba Jr, M.; Guerra, E.; De Luca Canto, G. Host-derived salivary biomarkers in diagnosing periodontal disease: systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Periodontol 2016 43, 492–502. [CrossRef]
- Fine, D.H.; Markowitz, K.; Fairlie, K.; Tischio-Bereski, D.; Ferrandiz, J.; Godboley, D.; Furgang, D. Macrophage inflammatory protein-1a shows predictive value as a risk marker for subjects and sites vulnerable to bone loss in a longitudinal model of aggressive periodontitis. PLoS One 2014, 9, e98541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrashtehfar, K.I. Patient and miniscrew implant factors influence the success of orthodontic miniscrew implants. Evid Based Dent. 2016, 17, 109–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touyz, L.Z.G.; Afrashtehfar, K.I. Implications of bisphosphonate calcium ion depletion interfering with desmosome epithelial seal in osseointegrated implants and pressure ulcers. Med Hypotheses. 2017, 107, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrashtehfar, K.I.; Afrashtehfar, C.D. Lack of association between overload and peri-implant tissue loss in healthy conditions. Evid Based Dent. 2016, 17, 92–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touyz, L.Z.; Afrashtehfar, K.I. Cryogenically salvaged teeth as a potential source for grafting dentoalveolar, periodontal or maxillofacial defects. Med Hypotheses. 2016, 92, 28–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afrashtehfar, K.I.; Moshaverinia, A. Five Things to Know About Regenerative Periodontal Therapies in Dental Medicine. J N J Dent Assoc. 2015, 86, 12–13. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Contreras, R.; Chavez-Granados, P.A.; Jurado, C.A.; Aranda-Herrera, B.; Afrashtehfar, K.I.; Nurrohman, H. Natural Bioactive Epigallocatechin-Gallate Promote Bond Strength and Differentiation of Odontoblast-like Cells. Biomimetics (Basel). 2023, 8, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Control (Group 1) | Test groups | Total | ||
| Stage III Periodontitis (Group 2) | Stage III Periodontitis with AMI (Group 3) | |||
| Number of participants | 20 | 20 | 20 | 60 |
| Age (years) | 42.5±3.5 | 51.4±4.3 | 54±5.6 | 52.7±4.9 |
| Male | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| Race (ethnicity) | Asian | Asian | Asian | |
| Alcohol use (%) | 6 | 6 | 7 | 6.5 |
| Tobacco use (%) | 2 | 5 | 12 | 8.5* |
| Smokeless tobacco use (%) | 5 | 9 | 10 | 9.5* |
| Group | n | Mean | SD | Minimum | Maximum | ANOVA | ||
| F | p-value | |||||||
| Adiponectin | 1 | 20 | 941.86 | 76.50 | 882.36 | 1210.50 | 76.29 | <0.001 |
| 2 | 20 | 840.27 | 22.54 | 801.79 | 871.20 | |||
| 3 | 20 | 750.80 | 28.76 | 707.75 | 805.86 | |||
| MIP 1 - alpha | 1 | 20 | 310.62 | 32.32 | 270.20 | 376.85 | 73.11 | <0.001 |
| 2 | 20 | 366.60 | 34.77 | 309.90 | 425.60 | |||
| 3 | 20 | 443.94 | 37.74 | 356.95 | 486.85 | |||
| Groups | Sub-groups | Mean Difference | SE | p-value | 95% Confidence Interval | ||
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | ||||||
| Adiponectin | 1 | 2 | 101.59 | 15.48 | <0.001* | 64.35 | 138.84 |
| 3 | 191.06 | 15.48 | <0.001* | 153.81 | 228.30 | ||
| 2 | 3 | 89.46 | 15.48 | <0.001* | 52.22 | 126.71 | |
| MIP 1 - alpha | 1 | 2 | -55.99 | 11.07 | <0.001* | -82.63 | -29.34 |
| 3 | -133.32 | 11.07 | <0.001* | -159.97 | -106.68 | ||
| 2 | 3 | -77.34 | 11.07 | <0.001* | -103.98 | -50.69 | |
| Group | N | Mean (SD) | Range | Median (Q1-Q3) | Kruskal Wallis Test | Mann Whitney U Test | |||
| Chi Square value | p-value | 1 vs 2 | 1 vs 3 | 2 vs 3 | |||||
| 1 | 20 | 0.09 (0.02) | 0.06 - 0.13 | 0.08 (0.08 - 0.11) | 22.79 | <0.001* | 0.02* | <0.001* | 0.001* |
| 2 | 20 | 0.14 (0.15) | 0.08 - 0.73 | 0.10 (0.09 - 0.13) | |||||
| 3 | 20 | 0.50 (0.50) | 0.08 - 1.50 | 0.30 (0.12 - 0.90) | |||||
| Group | Adiponectin MIP 1 - alpha | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | r | 0.06 |
| p-value | 0.80 | |
| 2 | r | 0.04 |
| p-value | 0.86 | |
| 3 | r | 0.24 |
| p-value | 0.31 |
| Group | Adiponectin CRP | MIP 1 – alpha CRP | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Spearman’s Rho | -0.21 | 0.11 |
| p-value | 0.39 | 0.65 | |
| 2 | Spearman’s Rho | -0.06 | -0.04 |
| p-value | 0.80 | 0.88 | |
| 3 | Spearman’s Rho | -0.03 | -0.28 |
| p-value | 0.90 | 0.24 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





