1. Introduction
Electric vehicle (EV) sales have significantly grown in the recent years. In Europe, for example, EV registrations have tripled from 3.5% in 2019 to 11.6% in 2020. This includes a 6.2% increase in fully electric vehicles [
1]. Indeed, EVs are perceived to be a sustainable alternative to traditional combustion engine vehicles, offering advantages in terms of performance and reduced emissions [
2]. However, a number of barriers impede a wider EV uptake. These include high purchase costs, limited autonomy, scarce charging infrastructure and lengthy charging times. To counter some of these barriers, an increasing number of decision support tools facilitating the use of EVs are being deployed. Such tools mainly rely on optimizing operational issues related EVs. In this vein, several contributions from the transportation science community have developed models and solution methods to EV routing problems (see Kucukoglu et al. [
3] and Froger et al. [
4] for examples).
We propose a methodology for planning EV paths considering user preferences, where charging is performed at public Charging Stations (CSs). The need for such a methodology for private EV users was identified through the eCharge4Drivers project, which is funded by the European Union Horizon 2020 programme. The proposed methodology was integrated in a web interface enabling a large audience to use it. The core optimization problem we deal with relates to planning the shortest path (in terms of time) for an EV needing to travel between a given origin and a given destination. This problem is particularly relevant for long-distance trips, where the shortest path between the origin and the destination exceeds the EV’s autonomy. The key decisions to be made in such problems are where to charge and how much to charge. The latter entails an amount of time which depends on the CS technology, the EV characteristics and follows a non-linear function. Moreover, as the charging infrastructure in road networks outside cities is fairly sparse, EVs often need to deviate from their shortest paths to reach CSs. The intertwined relationship between the time spent in detouring and the time spent charging is the main complicating feature of Electric Vehicle Shortest Path Problem (EVSPP).
As EV charging times may take several hours, users (i.e., drivers) may prefer having charging stops at locations that match their interests. We consider that such interests may be captured via Points of Interests (POIs) that include categories such as restaurants, shopping areas, and nature sites. Moreover, we also consider that the user may want to perform some particular activity during specific time windows, like having lunch or spending the night at a hotel. Such user defined time windows are also matched with relevant POIs locations. Thus, our overarching goal is to propose an efficient offline methodology integrating user preferences for POIs and user-specific time window into an EVSSP setting. To do so, we introduce the Electric Vehicle Shortest Path Problem with time windows and user preferences (EVSPPWP).
We model the EVSPPWP and propose an efficient heuristic algorithm to solve it. In particular, the algorithm prioritizes CSs that are close to POIs matching the user preferences. Furthermore, while we provide planned (offline) paths, we propose a number of algorithmic enhancements aimed at producing solutions that are practically executable in real time on large road networks. Specifically, the algorithm provides the user with robust and flexible solutions. To incorporate robustness, we only consider paths that have at least a given number CSs in their vicinity. This ensures that the EV could always reach a CS, in case its predicted energy consumption does not match the actual one. Additionally, it may occur that the EV encounters an occupied CS, which was planned in its path. To counter such situations, our algorithm produces flexible solutions by considering a CS as a cluster of charging points (CPs). Specifically, we produce small sized clusters of CPs that we treat as separate CSs. We plan the path based on those CSs. This entails having a number of CPs in the vicinity of a planned charging stop. Thus, if a CP is busy upon arrival, the user would have multiple alternatives in its vicinity.
Considering the previously discussed enhancements, we develop an algorithm for the EVSPPWP. We first include weights for each CS according to its vicinity to POIs that match the user defined preferences. We then use a modified
algorithm to establish the nodes where the user defined time windows are going to be performed. Considering these nodes along with the user defined origin and destination, we sequentially solve a series of modified EVSPPs (using the algorithm of Kullman et al. [
5]), which we then aggregate into a complete solution. Lastly, the algorithm provides up to three alternative paths in a web interface where the users can visualize the path details. The main contributions of this papers are: (1) we model user defined time windows for activities during the trip such as having lunch, visiting POIs, or spending the night; (2) we account for user preferences by the using weights for different POI categories; (3) we consider CSs based on clusters of CPs with sufficient proximity, thus allowing the user flexibility in the choice of a CP upon arrival; (4) we ensure resilient paths that have a minimum number of CSs within a minimal distance; and (5) we propose an efficient algorithm to solve the resulting EVSPPWP.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. In
Section 2 we present a brief literature review on related work. In
Section 3 we describe the EVSPPWP and present a Mixed Integer Linear Programming (MILP) model for it. In
Section 4 we present our solution methodology. In
Section 5 we illustrate the usage of the algorithm, giving usage examples and comparing different settings in the area of northern Italy and the north of Italy. Finally, we provide conclusions in
Section 6.
2. Related Work
Our core problem falls into the category of EVSPPs, which mainly consists of shortest path problems in which the objective is to minimize the travel time between a given origin and a given destination accounting for the EV’s limited autonomy and charging constraints. The main decisions in the EVSPP relate to where and how much to charge at a given set of available CSs. Our algorithm for solving the EVSPP is embedded in a decision support tool for planning EV paths. There are existing decision tools for planning variants of the EVSPP, examples include: A Better Route Planner [
6], Zap-Map EV [
7], and PlugShare [
8]. These tools allow the user to select an origin and a destination including user defined waypoint stops. As these tools are commercial, we are not able to verify their modeling assumptions, nor certify the quality of their solutions. Therefore, in the following we focus on academic contributions on the EVSPP.
The EVSPP is strongly related to the Electric Vehicle Routing Problem (EVRP). The main decisions in this latter problem relate to routing a set of EVs from a central depot to serve a set of customers. The limited autonomy of the EV is typically handled by allowing it to detour to CSs and recharge. There has been a rapid growth in studies addressing the EVRP in the last years, with several variants being proposed (see Schniffer et al. [
9] and Kucukoglu et al. [
3] for comprehensive reviews). From the early formulations of the problem [
10], variants of the EVRP have evolved to include features such as time windows and cargo capacity constraints [
11]; heterogeneous fleets and charging infrastructure [
12,
13]; energy consumption functions and charging profiles [
14,
15,
16]; energy consumption uncertainty [
17]; and limited charging capacity [
4].
A critical modeling assumption in the EVRP regards the amount of energy to charge at each recharging stop. While some studies assume the EV must completely recharge before leaving a CS [
10,
18,
19], other works consider the charging amount to be a decision of the model [
11,
20,
21]. Several studies have assumed linear charging functions [
12,
22]. In practice, the charging function of an EV is nonlinear with respect to time, and depends on the charging technology of the CS. The nonlinear charging functions are modeled as piece-wise linear concave functions by Montoya et al. [
21] and Froger et al. [
20]. We adopt similar assumptions in this paper. For a repository with such functions for approximately 300 EV models, used in our tests, the reader is referred to OpenEV [
23].
Different variants and methodologies have been proposed to solve the EVSPP. These variants use different assumptions, objective functions, and solution methods. Zündorf [
24] studies the EVSPP considering different types of charging stations having distinct technologies with variable charging quantities. The author proposes heuristics to solve large EVSPP instances based on a multi-objective search and obtains fast and feasible path on continental graphs. Sweda et al. [
25] focus on the EVSPP considering that the availability of CSs is uncertain. They present two heuristic methods for finding adaptive policies considering both adaptive recharging decisions only, and adaptive routing and recharging decisions. Baum et al. [
26] study the EVSPP with varying charging power and battery-swapping stations. The authors propose a combination of algorithmic techniques to achieve good performance using realistic instances. Baum et al. [
27] propose a functional representation of the optimal energy consumption between two locations, which subsequently led to the development of an efficient heuristic algorithm for computing energy-optimal paths.
An important subproblem of the EVRP is the Fixed Route Vehicle Charging Problem (FRVCP), which was first introduced by Montoya et al. [
18]. Given a fixed sequence of customers, the FRVCP determines which CSs to visit and the amount of energy to charge in them. The objective is to minimize the completion time of the path, while respecting the battery capacity constraints. Roberti and Wen [
28] propose a labeling algorithm for the FRVCP considering a linear charging function and partial charging. Montoya et al. [
16] propose a mixed integer linear programming model and a heuristic considering piece-wise linear charging functions and partial charging. Froger et al. [
20] propose an exact labeling algorithm for the same problem considered by Montoya et al. [
16]. The exact labeling algorithm is available in the Python
frvcpy package [
5] and used in the implementation of our algorithm. Specifically, we solve FRVCP instances in the second step of our algorithm (see
Section 4.2.2).
The addition of POIs into vehicle routing decisions has been studied in the literature mainly in tourist routing applications [
29]. One of the main treated problems in this context is the Tourist Trip Design Problem (TTDP) [
30]. The objective of this problem is to define paths that maximize the number of visited attractions or POIs, while minimizing the total travel costs or meet time constraints. An extension of the TTDP including EVs is known as the Electric Vehicle Routing Tour Planning (EVRTP) [
31]. In this problem, the maximization of the tourist satisfaction is considered while meeting path constraints such as total length, visiting times at each POI, or budget constraints. Extensions of the TTDP include the use of uncertain scenarios [
32], hybrid fleets [
2], and multi-period fleets [
33]. To the best of our knowledge, Cassia et al. [
34] is the first study to consider the EVSPP with both user preferences as POIs and time windows. However, the proposed heuristic in that paper considers a limited set of charging levels, and thus greatly simplifies the problem.
3. The Electric Vehicle Shortest Path Problem with Time Windows and User Preferences
We define the EVSPPWP as follows. Let be a directed graph, where is a set of nodes containing the origin , destination , and the set of CSs at which recharging may take place. is the set of arcs connecting each pair of nodes . Each arc is associated with a driving time , a distance , and an energy consumption . These parameters are computed based on the fastest path on the real road network. The EV has an average consumption of (kWh/km). To account for the EV’s limited autonomy, we discard all arcs with a distance larger than . The path between the and nodes is performed by a single EV with a battery capacity of Q that may be partially recharged at CSs. The EV starts at node at with an initial state of charge (SoC) (i.e., percentage of the level of the battery with respect of its capacity), equal to , and it must arrive to the destination node with a final SoC greater or equal than . The EV must arrive at each CS with an amount of energy which is greater or equal to . Both and are user-defined parameters.
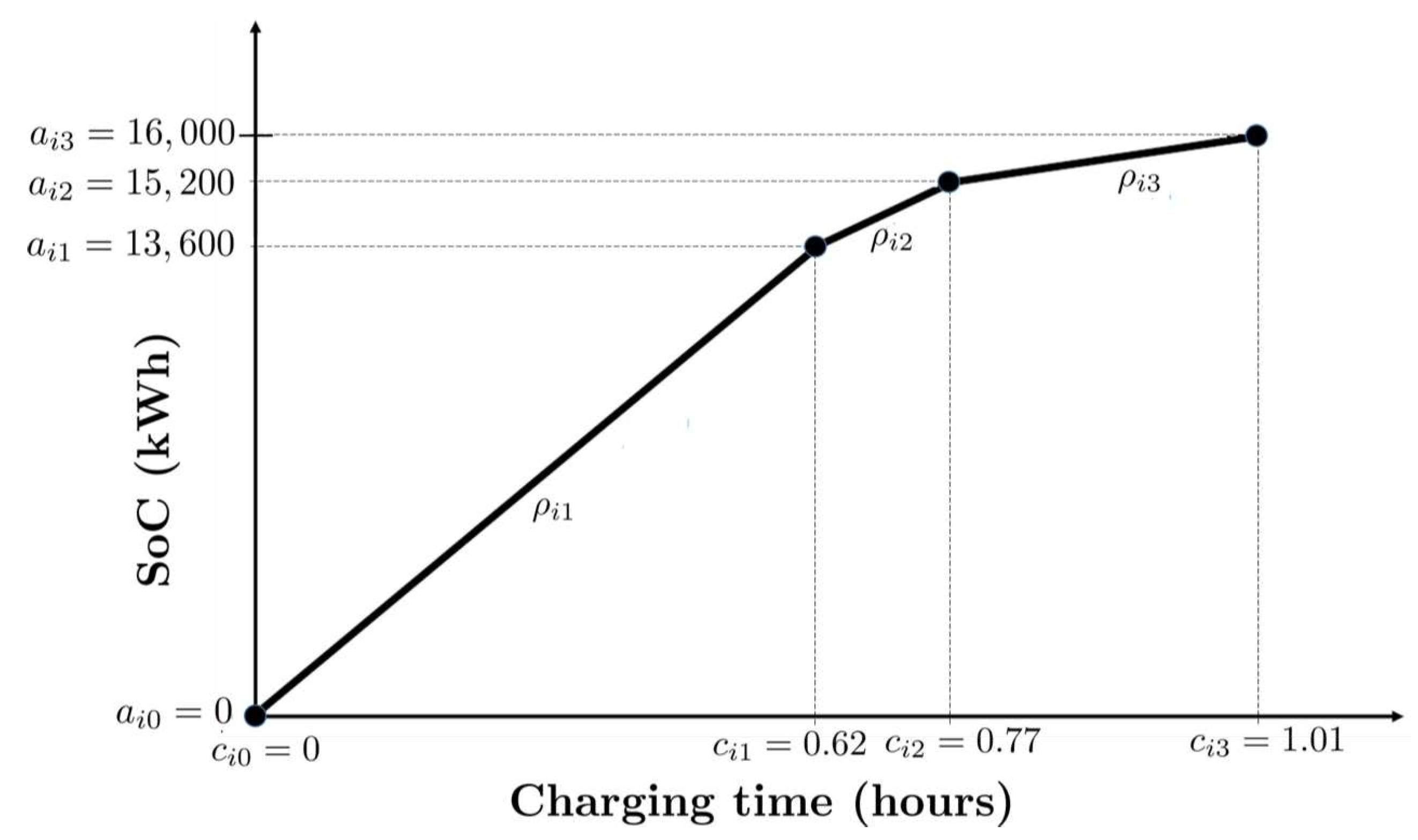
Each CS,
, has a piece-wise linear concave charging function
, where
is the time spent charging. If
q is the SoC of the EV when it arrives at the charging station
i, then the SoC when it leaves is
. Let
be the ordered set of breakpoints of the piece-wise linear approximation of the charging curve of CS
i. Let
and
be the charging time and SoC of breakpoint
. Each breakpoint connects
and
with a linear function with slope equal to
(see
Figure 1).
Let
be the set of categories of POIs. Each CS is associated with an importance value for each category
(see
Section 4.1.2 for their computation procedure), which represents the accessibility of POIs (relevant to
p) from the CS. As minimizing total travel times conflicts with maximizing the total collected importance when visiting nodes, we use a modified arc weight
defined as:
where
represents the importance value of
for POI category
,
is a weight on the total importance value of the POIs with respect to travel time, and
is the time spent charging at CS
j.
We consider that the user can impose certain types of stops during the path, and use the time spent at the stops to charge the EV. We model this feature by a set of ordered time windows
. Each time window requires a specific POI category, and the EV must stop during all the time windows in their given order. A time window
is defined by a minimum start time
, a maximum start time
, and a minimum time that the EV needs to stop
. We define the set
as the set of CSs with POIs in their neighborhood that match the POI specified for
. The objective is to find the path that minimizes the total modified weights (defined in Equation (
1)) of the selected arcs between
and
, while satisfying all the charging and time windows constraints.
3.1. A Mixed-Integer Linear Programming Formulation
We now present a MILP formulation for the EVSPPWP. This formulation is an adaptation of the one presented by Cassia et al. [
34]. Let
,
. Let
and
be the SoC when the EV arrives and depart from CS
i. The variables
and
are respectively the start and end time for charging an EV. The variables
and
represents the coefficients associated with the breakpoint
in the linear approximation, when the EV enters and leaves CS
i. Let
and
be binary variables equal to 1 when the SoC is in the interval
, when respectively the EV enters and leaves the CS
i, and 0 otherwise. Variables
and
track respectively the time when the EV arrives and leaves the CS
.
The binary variable
equals 1 if the EV uses arc
, and 0 otherwise. Binary variable
equals 1 if the EV stops in
j in time window
w, and 0 otherwise. The model is defined as follows:
The objective function (
2) minimizes the total modified weights of the used arcs. Constraints (3) require a CS to be visited at most once. Constraints (4) impose the flow conservation conditions. Constraints (5) track the SoC of the EV for each pair of nodes. Constraint (6) imposes that at the beginning to the trip the EV has a charge equal to
. Similarly, constraint (7) imposes the minimum charge at destination. Constraints (
8) require that the SoC of the EV when leaving a SC is greater than the SoC when it arrives. These constraints also impose that the EV must arrive at the CS with a minimum residual energy, and leave with less than the EV battery capacity.
Constraints (9)–(15) define the SoC and the charging time based on linear approximation of the charging function of a CS. In the same fashion, Constraints (16)–(22) define the SoC and the charging time upon departure from a CS. Constraints (23) define the time spent at CS i. Constraint (24) imposes the starting time. Constraints (25) impose that the arrival time has to be lower than the departure, and both must be greater than . Constraints (26) link arrival, departure and waiting times. Constraints (27) assure that every CS must be used for at most one time window , while constraints (28) link and variables. Constraints (29) and (30) impose that, for every , the arrival time is between and . Constraints (31) ensure that every required time window is served. Constraints (32) impose a minimum waiting time. Finally, (33)–(40) define the domains of the variables.
4. Solution Method
In this section, we present our methodology to solve the EVSPPWP. The main innovations of this methodology are: (1) we create CSs composed of clusters of CPs with sufficient proximity, thus providing the user with alternative CPs within a cluster; (2) we account for user preferences by assigning weights for different POI categories and attribute weights to each CS according to its proximity to POIs; (3) we use resilient paths, that is, using only arcs that only have a minimum number of CSs within a distance of
to ensure access to CSs in case of emergencies; and (4) we consider user-define time windows for activities during the trip such as having lunch, visit POIs, or spending a night at a hotel. The proposed methodology has been successfully applied to five geographical regions (see
Section 5 for details).
We divide this section into two parts. First, in
Section 4.1 we present a pre-processing step to generate the graph which is used for planning the path. This pre-processing step is used to create a more compact graph in the backend. In
Section 4.2 we describe the two-step algorithm that is used to produce up to three paths for a given user request, .i.e., an origin and a destination along with other user preference specifications.
4.1. Graph Generation
In this pre-processing step we generate a graph based on CP data and POI locations, which were provided by the project partners. To generate this graph, we create a set of CSs by clustering CPs, compute the modified weight of the arcs , including the importance value of the CSs, and filter arcs by computing the resilience value for each arc in the graph. We describe each of these steps in the subsequent sections.
4.1.1. Clustering
We consider public charging interoperable CSs. Each such CS may group several CPs. At the same time, each CP may have different plug types. The data is typically provided in terms of CPs and not CSs. We generate CSs by clustering the CP data using the following procedure. We consider a maximum number of CPs per cluster, a minimum number of CPs per cluster, and the maximum geodesic distance between CPs in a cluster. These parameters are selected to provide the user with alternative CPs that are close enough to each other. The purpose of this procedure is to cover the case when a selected CP is not available at the moment of arrival, by providing alternatives to the user. Thus, the selection of the parameters depends on the characteristics of the geographical area, such as the total number of CPs and their sparsity.
Let be the set of original CP locations, and be the set of clustered CPs, initially . The clustering algorithm starts by selecting a random CP which initializes the first cluster. The coordinates of the center of the cluster are set to be the coordinates of CP i. Sequentially, we add CPs that are within a distance to the center of the cluster. Each time a CP is added, the coordinates of the center of the cluster are updated to be the average between the previous center and the coordinates of the new CP. A cluster is closed when either is reached or there are no other CPs available within . When a cluster is closed, a new random CP is selected, and the procedure is repeated with the remaining CPs in the dataset. The algorithm terminates when there are no other CPs available. If the final size of a cluster is lower than the cluster is removed from . At the end of the procedure, each cluster is characterized by the coordinates of its center, and the information of each of the CPs in the cluster. In what follows we refer to a cluster of CPs as a CS and all distances are computed based on the center of the clusters.
4.1.2. Modified Arc Weights
In order to compute the modified weights of the arcs
as defined in Equation (
1), we first compute the importance value
associated with CS
j and POI category
p. To do so, we divide the POIs into three categories: (1) food (the user prefers to stop in clusters with restaurants), (2) nature (the user prefers to stop in clusters close to nature sites), and (3) shop (the user prefers to stop in places with several shops like malls, department stores, etc.). For each such category
p, the importance value
is computed as the number of available POIs within a distance
from the CS
in the given category
.
4.1.3. Resilience Value
For each arc
we define a resilience value
to represent the availability of CSs within a critical distance from the actual road path represented by the arc. The resilience value ensures a minimum number of CSs are within a critical distance
from the path in case of charging emergencies. To compute the resilience value, we divide the path between nodes
i and
j into sections of length
. For each section
k, we define the number of CSs that are within a distance of
as
, where
represents the shortest geodesic distance between CS
j and section
k. The resilience value
for the path between nodes
i and
j is defined as:
where
is the median value of the set. In our methodology, we consider a modified set of arcs
, where
is the minimum resilience value allowed for each arc. The later condition (i.e.,
) implies that if two CS are close enough to each other, the arc connecting them is considered to be resilient.
4.1.4. User Input Parameters
A user request is an origin-destination pair of locations. The user must also specify the EV type from a preset list. This choice establishes EV related parameters (i.e., the capacity
Q of the battery, the average consumption of
, and the breaks in the charging curve
). Such parameters are obtained from the OpenEV repository [
23]. In addition, the user may specify the starting SoC (
), desired SoC at destination (
), start time at the origin, and a rating for each POI category. These ratings are established with a slidebar that defines a weight parameter ranging from 0 to 100%. These user-defined weights are included in the model by directly multiplying them with the corresponding importance value
. The user may also specify two type of time windows, one for lunch and one for night stays. Lunch stops are clusters that have at least one restaurant, whereas night stops consider hotels with CSs on their premises. Each optional intermediate stop is defined by a minimum start time
, a maximum start time
, and a minimum time that the EV needs to stop
. Finally, the user may select the plug types (“Type 2” and “Ccs”). CPs in CSs that do not match the selected plug types are discarded. Subsequently, the compatible CP with the maximum charging power in each CS is considered, ties are broken arbitrarily. Thus, the final address and CP specifications in the solution corresponds to the fastest compatible CP in the cluster.
4.1.5. Graph Reduction
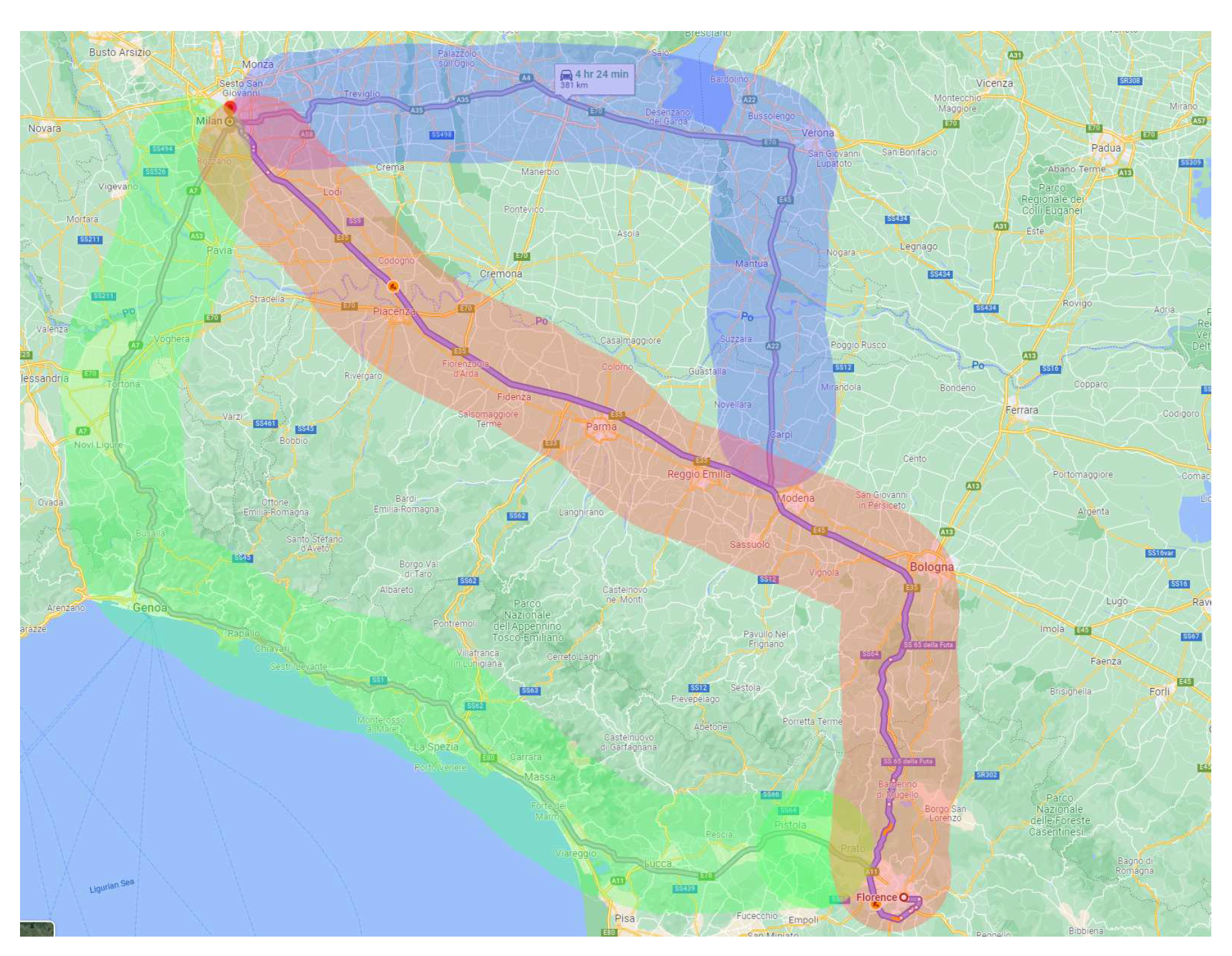
In order to reduce computational run-times, we apply another filtering strategy using non EV-paths. In this step, we compute up to three alternative shortest paths between the origin and destination without considering CSs. These three paths are computed using mapbox [
35]. We filter the graph
by only considering the CSs in
that are within a threshold of
kilometers around the three non EV-paths. This step defines a new reduced graph
, where
is the filtered set of nodes and
is the set of considered arcs between
. In
Figure 2 we illustrate the graph in this reduction step. The three solid lines show the three non EV-paths between the origin and destination. The colored areas show an approximation of the threshold from each path using
km. All arcs and nodes that do not fall into the colored area are discarded.
4.2. Two-Step Algorithm
We solve the EVSPPWP on the modified graph
using a two-step algorithm. In the first step, we use a modified
algorithm to establish the nodes where the user defined time windows are going to be performed. The result of this step is a set of consecutive nodes, each one representing the location at which each time window is performed. Let
be the ordered set of nodes selected by the algorithm to perform time windows in
. The output of the algorithm defines then
legs. In what follows, we refer to legs as the paths to be performed from
to the first node in
, the path between the ordered nodes in
, and the path between the last node in
and
. In the second step, we solve the FRVCP for each leg defined in the first step using the labeling algorithm proposed by Kullman et al. [
5]. The final solution of the algorithm is the merged solution of each FRVCP instance defined by the legs in the first step.
4.2.1. Algorithm
We implement a modified
search algorithm to find the nodes in which the user specified time windows are performed in order to minimize the total travel time. For this search, we assume that recharging stops are only performed when the remaining energy in the battery is less than the needed to reach the next node. At each recharging stop, we assume that the EV is fully charged. The algorithm starts at node
and sequentially generates the tree of all paths to reach the next node using a best-first search until the destination node is reached. The best-first search is done by selecting the next node that minimizes the following objective:
where
i is the current node,
is the duration of the path from
to
i, and
is an estimate of the duration of the shortest path from
i to
. Duration computed in
and
include both travel and charging times. We use the modified travel times
as defined in Eq. (
1). By the use of a labeling search, the modified
algorithm finds the nodes in
where times windows
are performed, which define the legs in the following step.
4.2.2. FRVCP
We solve the FRVCP for each leg (i.e., considering the two extreme nodes of the legs as the fixed nodes) to determine the decisions on where and how much to charge at each recharging stop while minimizing the total travel time. To ensure the final SOC requirement
is fulfilled at the destination, we add a dummy node at the end of each leg with a sufficient distance from the leg destination node, which is removed at the end of this step. We solve the problem for each leg exactly by the labeling algorithm of Kullman et al. [
5] using the Python library
frvcpy. The algorithm returns the optimal energy-feasible path, i.e., the location of the stops, the amount to be charged at each stop, and the total duration. After computing the optimal solution for each leg, we merge together all solutions to obtain a single complete EV-path from
to
.
5. Case Study
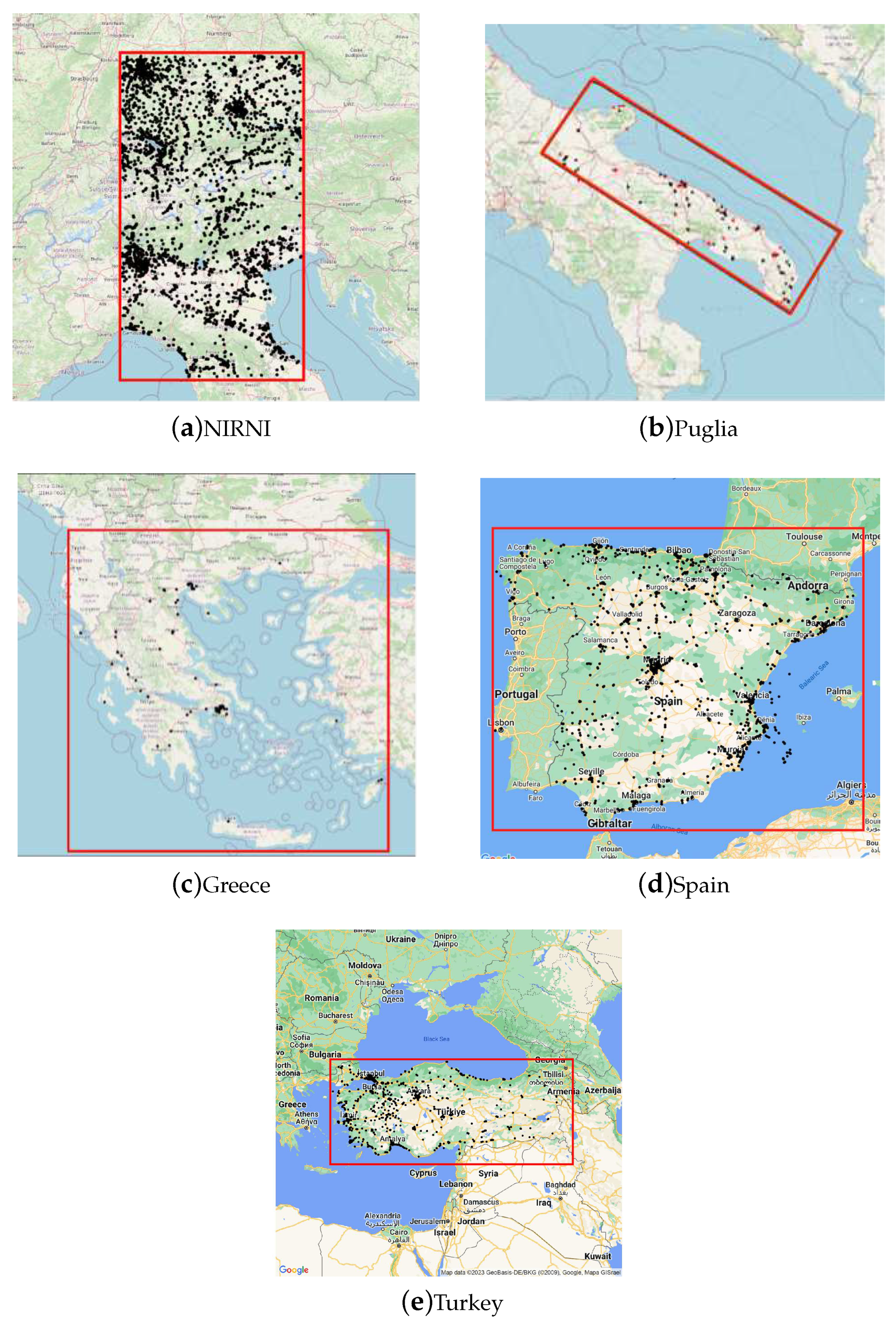
Within the eCharge4Drivers project and with the support of project partner Route 220 S.p.A. (Evway), we implemented our path planning methodology in the webpage available at
https://planner.evway.net/. Specifically, the tool was implemented in five regions: Northern Italy and Regions North of Italy (NIRNI), Puglia, Greece, Turkey, and Spain. In
Figure 3 we show the original CPs used in each of the five regions. For each region, the algorithm was tested using several combinations of origins and destinations. We implemented all parts of the algorithm in Python 3.8. In our tests, all run times for a single path were observed to be under 30 seconds. In the following, we focus on examples in the NIRNI area. In
Section 5.1 we demonstrate how the graph is generated. In
Section 5.2, we provide examples on various user inputs, and in
Section 5.3 we demonstrate the results of our path planner on various origin-destination examples.
5.1. Graph Generation
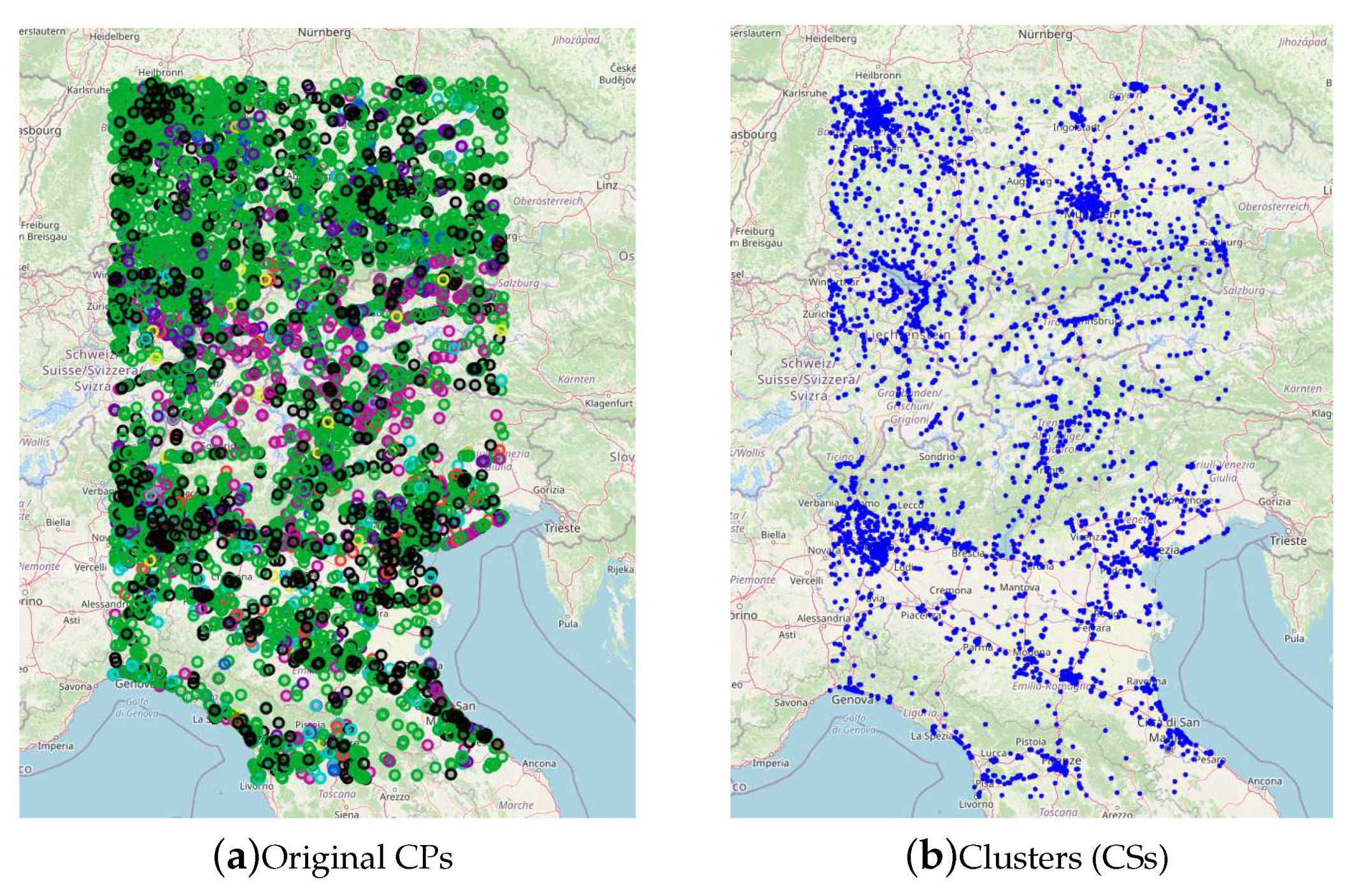
The original dataset provided by the project partners contains 14,767 CPs, providing the location, address, and plug types. A second dataset contains the information on the POIs. This dataset was obtained by both the partner company and OpenStreetMap. Given the high density of CPs in the NIRNI area, we calibrated the three parameters of our clustering algorithm to have a balance between the number of clusters and the availability of CPs outside urban areas. We selected the following parameters in the graph generation step:
,
,
km,
km,
km,
km,
,
, and
. In
Figure 4 we show the original CP locations and the final CPs clustered in CSs using the procedure described in
Section 4.1.1. The resulting graph contains a total number of 3,223 CSs.
5.2. User Input
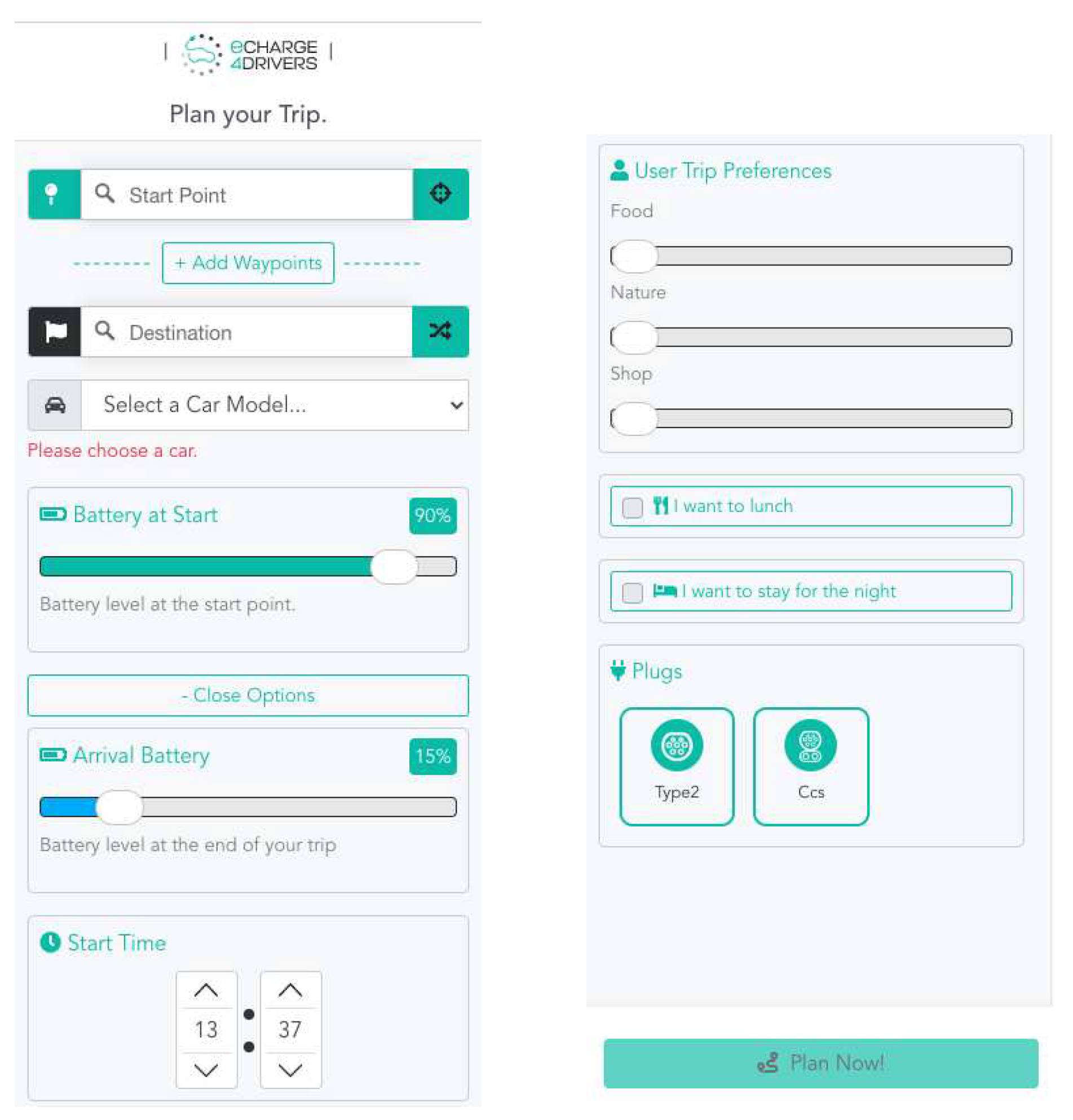
On the web interface, the user preferences can be selected directly from the preferences tab as illustrated in
Figure 5. The user can directly provide input for:
Start Point: Location of the origin .
Destination: Location of the destination .
Add waypoints: The user can select one or more waypoints, which are intermediate stops during the trip.
Car model: EV type. This selection retrieves (based on the OpenEV repository [
23]) the capacity of the battery
Q , the average consumption of
, and the breaks in the charging curve
.
Battery at start: SoC of the EV at , which sets parameter . The value is selected using a slide bar.
Arrival battery: Desired SoC of the EV at , which sets parameter . The value is selected using a slide bar.
Start time: A specific time of departure (hh:mm). This time is used as reference for the optional time windows.
User trip preferences. Three categories of such preferences are considered: Food, Nature, and Shop. The user can select with a slider the level of importance to attribute to each category. The weights are directly multiplied by the importance value for each category .
Lunch option: This option defines a time window for a lunch stop. The user can select the earliest arrival (hh:mm), the latest arrival (hh:mm), and the duration (in hours). These values define parameters , , and , respectively, where w is a lunch time window.
Spend the night option: This option defines a time window for a spending the night at a hotel. The user can select the earliest check-in (hh:mm), the latest check-in (hh:mm), and the check-out time (hh:mm). These values define parameters , , and , respectively, where w is a night stop window.
Plug type: The user can select “Type 2” and/or “Ccs” plug types.
After setting the user preferences on the web interface, the algorithm computes up to three path options between the origin and the destination. These three paths are based on the non EV paths as described in
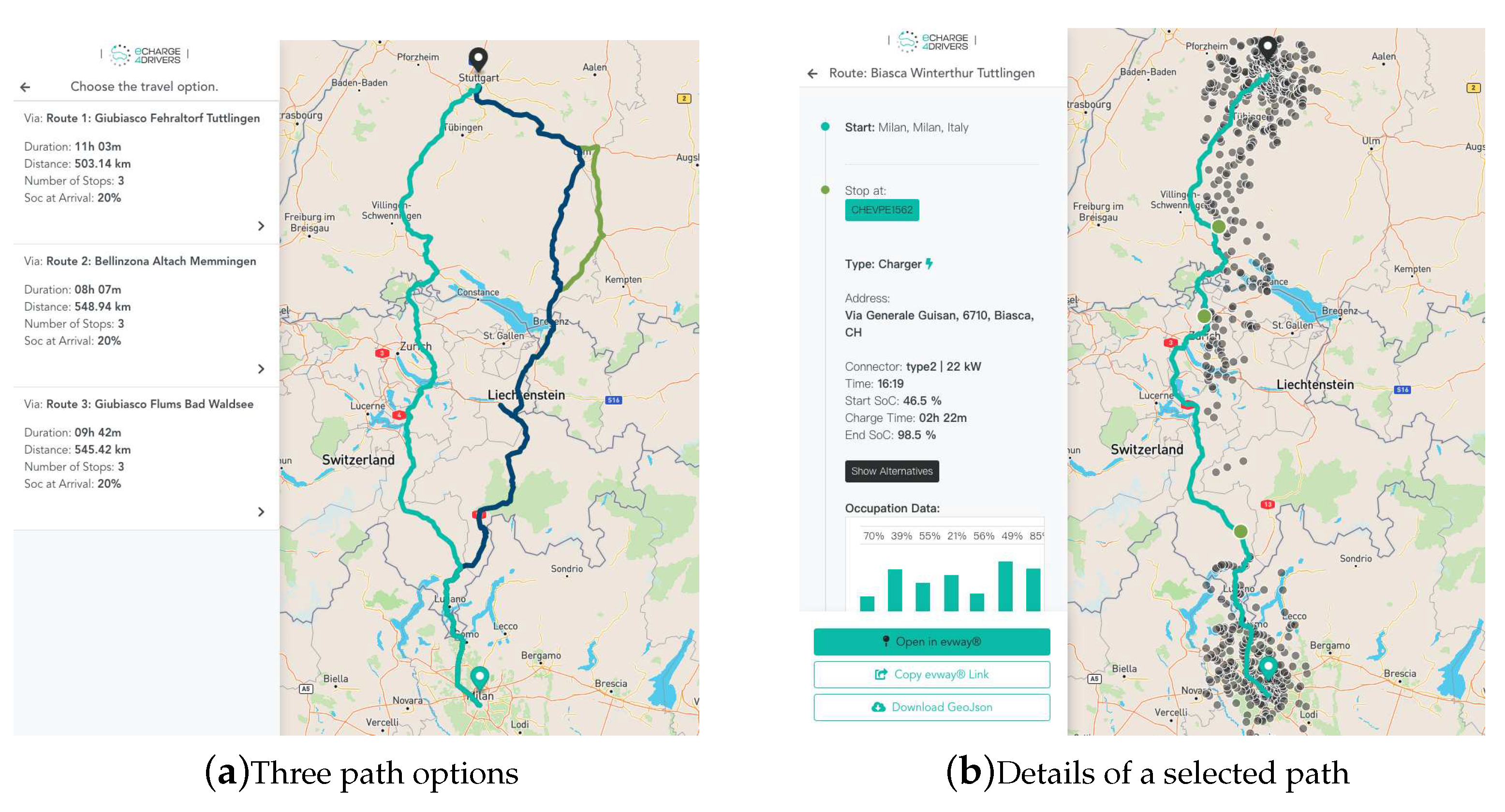
Section 4.1.5. Then the algorithm described in
Section 4.2 is executed on each of the three paths establishing where to stop and how much to charge. In Figure 6a we show the three path options given by the algorithm for a trip between Milan, Italy, and Stuttgart, Germany. The figure consists of a left panel displaying the main results for each path, and a right panel displaying a map with the paths in different colors. Using the left panel, the user can select one of the paths for further details. After selecting the first path, as shown in Figure 6b, details on the place and duration of the recharging stops are shown in the left panel, while in the right panel the selected path is displayed along with grey points representing alternative CPs. In
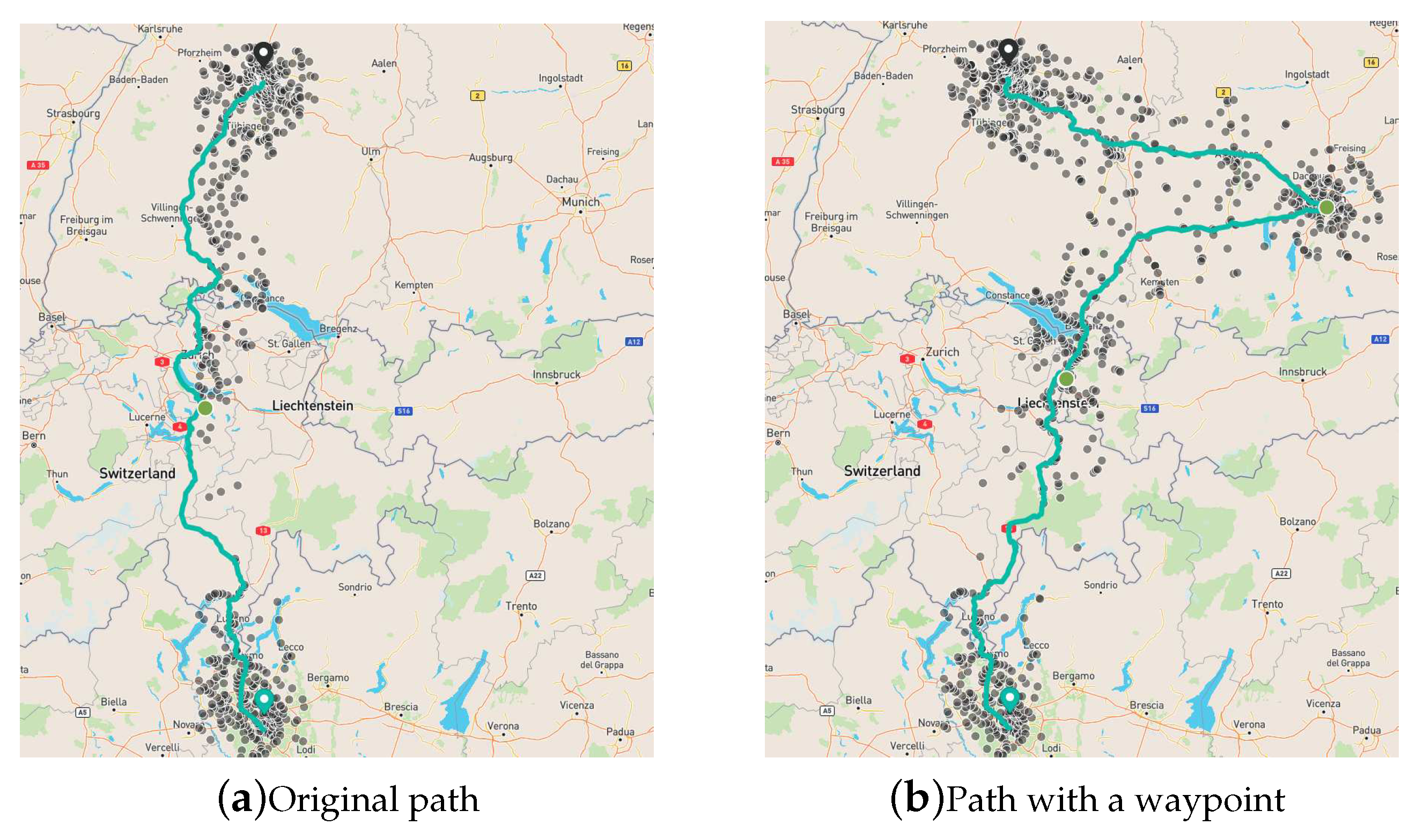
Figure 7 we compare the original path with a path using the option of adding a waypoint. Figure 7a shows the recommended path, whereas Figure 7b shows the path after the user selects a waypoint in Munich, Germany. The actual path and the charging stops are shown in green, and alternative CPs are shown in grey. The user may change a proposed CP by selecting an alternative CP. If an alternative CP is selected, the algorithm is re-run while fixing the selected CP.
5.3. Origin-Destination Examples
We illustrate the use of our path planner methodology using three origin-destination pairs accounting for short, medium, and long-distance trips in the NIRNI area. For each trip, we compute the path using four configurations of user preferences: a base case without preferences, one assigning POI weights, one having a lunch stop, and one having a night stop. From the three possible path recommendations we selected the fastest path. In all cases, we set the EV type to be BWM i3S 120Ah, a start SoC of 80%, and a desired end SoC of 20%. For the lunch break, the earliest arrival is set to 12:30, latest arrival is set to 13:30, and a duration of 2 hours is selected. For the night rest, the earliest desired check-in is 20:00, the latest check-in is 22:00, and the check-out is at 8:30.
Table 1 reports the results for the three origin and destinations: Venice–Milan, Trento–Stuttgart, and Florence–Munich. All paths are set to start at 10:00, except from Venice–Milan and Trento–Stuttgart with night stops, which are set to start at 20:00 for its duration to match a night stop. For each path we report the start time, end time, duration, distance, and number of recharging stops. We observe that the duration and distance of the trips vary depending on the preference selection. These differences are due to different selected stops and/or different charging times at the stops given the preferences. For example, trips with the night stop option have a notable increase in the total duration since this preference has a fixed check out at 8:30.
In
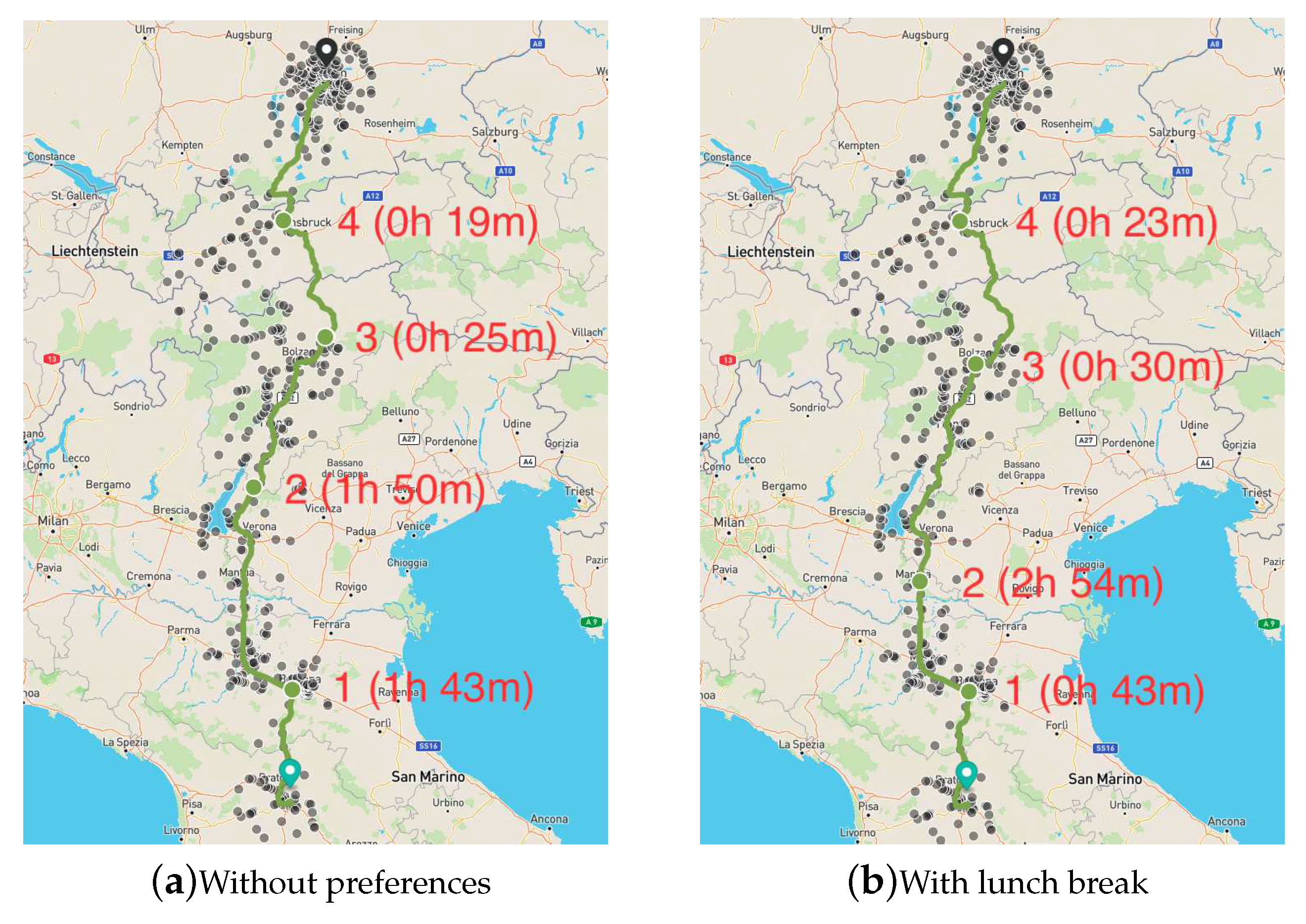
Table 2 we show the address, start time, duration, SoC at start, and SoC at end for all four recharging stops in the path between Florence and Munich, for the four user preferences combinations. Except from the first stop, the addresses for the charging stops differ depending on the preference. A similar behavior can be observed in terms of the start time and duration of the charging stops. In
Figure 8 we show a comparison of the paths without preferences and with lunch break. We can observe in the map that the first and last charging stops (1 and 4) are the same, however, they have different charging times. The intermediate charging stops (2 and 3) both show different locations and charging times.
In
Table 3 we compare the duration, distance (km), and number of stops in a trip from Florence and Munich for four EV models. We show results using different starting SoC, ranging from 60% to 100%, and the same desired SoC at arrival of 10%. We observe clear differences in the duration and number of stops in the trip depending on the selected EV type. Considering a starting SoC of 100%, the Tesla Roadster 2022 shows the fastest path with a duration of 7 hours and 5 minutes with no recharging stops, while the slowest trip with Kia EV6 2WD 2021 lasts 12 hours and 21 minutes with two recharging stops. The same pattern can be seen when comparing EV models with lower starting SoC. As expected, we observe for all EV models a decrease in the number of stops as the starting SoC. In all cases, decreasing this value from 100% to 60% of SoC results in one additional recharging stop.
6. Conclusions
Given an origin and a destination, we proposed a path planning methodology for EVs considering user preferences. The main innovations in our methodology are the use of weights for three categories of POIs to reflect user preferences in the selection of CSs, the use of clustered CSs to ensure alternatives in the vicinity of CSs, the use of resilient paths, and allowing the user to define time windows for activities such as lunch and hotel stays. We divided our methodology into two parts. We first performed a pre-processing step in which we generate a graph with clustered CSs and resilient paths from raw CP and POI data. Then, we proposed a two-step algorithm to solve the shortest path problem. Finally, we provided a description of the usage of our methodology via its web interface, and presented examples using different origins and destinations, different configurations of user preferences, and different EV types.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.C., M.D., O.J., F.M. and E.T.; methodology, M.C. M.D., O.J., F.M. and E.T.; software, M.C. and E.T.; validation, M.C., M.D., O.J., F.M. and E.T.; formal analysis, M.C., M.D., O.J., F.M. and E.T.; writing—original draft preparation, M.C. and O.J.; writing—review and editing, M.C. and O.J.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is a part of the eCharge4Drivers project. This project has received funding from the European Union Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 875131. This content reflects only the authors view and the European Commission is not responsible for any use that may be made of the information this publication contains.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- EEA. Average carbon dioxide emissions from new cars registered in Europe decreased by 12% in 2020, final data shows, 2022. Accessed 2023-13-04. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/highlights/average-carbon-dioxide-emissions-from.
- Martins, L.d.C.; Tordecilla, R.D.; Castaneda, J.; Juan, A.A.; Faulin, J. Electric vehicle routing, arc routing, and team orienteering problems in sustainable transportation. Energies 2021, 14, 5131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucukoglu, I.; Dewil, R.; Cattrysse, D. The electric vehicle routing problem and its variations: A literature review. Computers & Industrial Engineering 2021, 161, 107650. [Google Scholar]
- Froger, A.; Jabali, O.; Mendoza, J.E.; Laporte, G. The electric vehicle routing problem with capacitated charging stations. Transportation Science 2022, 56, 460–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kullman, N.D.; Froger, A.; Mendoza, J.E.; Goodson, J.C. frvcpy: An open-source solver for the fixed route vehicle charging problem. INFORMS Journal on Computing 2021, 33, 1277–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ABetterRoutePlanner. A Better Route Planner, 2023. Accessed: 2023-15-03. Available online: https://abetterrouteplanner.com.
- ZapMapEV. Zap-Map EV, 2023. Accessed: 2023-15-03. Available online: https://www.zap-map.com.
- PlugShare. PlugShare, 2023. Accessed: 2023-15-03. Available online: https://www.plugshare.com.
- Schiffer, M.; Schneider, M.; Walther, G.; Laporte, G. Vehicle routing and location routing with intermediate stops: A review. Transportation Science 2019, 53, 319–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdoğan, S.; Miller-Hooks, E. A green vehicle routing problem. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review 2012, 48, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.; Stenger, A.; Goeke, D. The electric vehicle-routing problem with time windows and recharging stations. Transportation Science 2014, 48, 500–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felipe, Á.; Ortuño, M.T.; Righini, G.; Tirado, G. A heuristic approach for the green vehicle routing problem with multiple technologies and partial recharges. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review 2014, 71, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiermann, G.; Hartl, R.F.; Puchinger, J.; Vidal, T. Routing a mix of conventional, plug-in hybrid, and electric vehicles. European Journal of Operational Research 2019, 272, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goeke, D.; Schneider, M. Routing a mixed fleet of electric and conventional vehicles. European Journal of Operational Research 2015, 245, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskin, M.; Çatay, B. Partial recharge strategies for the electric vehicle routing problem with time windows. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies 2016, 65, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, A.; Guéret, C.; Mendoza, J.E.; Villegas, J.G. The electric vehicle routing problem with nonlinear charging function. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological 2017, 103, 87–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, S.; Jabali, O.; Laporte, G. The electric vehicle routing problem with energy consumption uncertainty. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological 2019, 126, 225–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, A.; Guéret, C.; Mendoza, J.E.; Villegas, J.G. A multi-space sampling heuristic for the green vehicle routing problem. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies 2016, 70, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andelmin, J.; Bartolini, E. An exact algorithm for the green vehicle routing problem. Transportation Science 2017, 51, 1288–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froger, A.; Mendoza, J.E.; Jabali, O.; Laporte, G. Improved formulations and algorithmic components for the electric vehicle routing problem with nonlinear charging functions. Computers & Operations Research 2019, 104, 256–294. [Google Scholar]
- Montoya, A.; Guéret, C.; Mendoza, J.E.; Villegas, J.G. The electric vehicle routing problem with nonlinear charging function. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological 2017, 103, 87–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desaulniers, G.; Errico, F.; Irnich, S.; Schneider, M. Exact algorithms for electric vehicle-routing problems with time windows. Operations Research 2016, 64, 1388–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OpenEV. GitHub - chargeprice/open-ev-data, 2022. Accessed: 2023-15-03. Available online: https://github.com/chargeprice/open-ev-data.
- Zündorf, T. Electric vehicle routing with realistic recharging models. Unpublished Master’s thesis, Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, Karlsruhe, Germany 2014.
- Sweda, T.M.; Dolinskaya, I.S.; Klabjan, D. Adaptive routing and recharging policies for electric vehicles. Transportation Science 2017, 51, 1326–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, M.; Dibbelt, J.; Gemsa, A.; Wagner, D.; Zündorf, T. Shortest feasible paths with charging stops for battery electric vehicles. Transportation Science 2019, 53, 1627–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, M.; Dibbelt, J.; Pajor, T.; Sauer, J.; Wagner, D.; Zündorf, T. Energy-optimal routes for battery electric vehicles. Algorithmica 2020, 82, 1490–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberti, R.; Wen, M. The electric traveling salesman problem with time windows. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review 2016, 89, 32–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Meza, J.; Montoya-Torres, J.R. A systematic literature review for the tourist trip design problem: extensions, solution techniques and future research lines. Operations Research Perspectives 2022, p. 100228.
- Gavalas, D.; Konstantopoulos, C.; Mastakas, K.; Pantziou, G. A survey on algorithmic approaches for solving tourist trip design problems. Journal of Heuristics 2014, 20, 291–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.W.; Lin, C.C.; Lee, T.J. Electric vehicle tour planning. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment 2018, 63, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbowska-Chilinska, J.; Chociej, K. Genetic algorithm for generation multistage tourist route of electrical vehicle. International Conference on Computer Information Systems and Industrial Management. Springer, 2020, pp. 366–376.
- Cortés-Murcia, D.L.; Afsar, H.M.; Prodhon, C. Multi-period profitable tour problem with electric vehicles and mandatory stops. International Journal of Sustainable Transportation 2022, pp. 1–17.
- Cassia, A.; Jabali, O.; Malucelli, F.; Pascoal, M. The electric vehicle shortest path problem with time windows and prize collection. 2022 17th Conference on Computer Science and Intelligence Systems (FedCSIS). IEEE, 2022, pp. 313–322.
- Mapbox. Mapbox optimization tool, 2023. Available online: https://www.mapbox.comAccessed: 2023-15-03.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).