1. Introduction
Brown-marbled grouper (Epinephelus fuscoguttatus) belongs to Epinephelus of Epinephelidae, which is an important economically edible fish produced by tropical and subtropical sea in Asia (Mukai and Seng Lim, 2016). Because of the excellent meat quality, abundant nutrients and rapid growth, the brown-marbled grouper has high market value and is widely cultured in southern China (Liu, et al., 2019). In addition, due to its long and stable spawning cycle, high spawning quality and quantity, it often was used as female parent in crossbreeding(Amenyogbe, et al., 2020; Sun, et al., 2016; Zhu, et al., 2016). Currently, Hulong grouper is the largest production grouper in China and produced by crossing the brown-marbled grouper with the giant grouper (E. lanceolatus)(Yang, et al., 2020).
The growth trait is one of the important economic characteristics of fish. The fish muscle content comprises 50-70% of their body weight, so the growth is mainly driven by the growth of their muscles(Liu, et al., 2020). Muscle growth in fish differs from that in mammals. On the one hand, the growth of fish mainly increases muscle content through both myocyte proliferation and hypertrophy. On the other hand, the growth of muscle can last throughout the lifespan(Fuentes, et al., 2011; Johnston, et al., 2011). The increase in body length and weight of fish, is not influenced by many factors including environment, nutrition and diseases, but also controlled by genes. The regulatory mechanisms of growth are very intricate (Johnston, 2006).
RNA-Seq is a recently developed approach to drawing transcriptome profiling that uses high-sequencing technologies (Wang, et al., 2009). In last decades, RNA-Seq has been widely used to identify candidate genes associated with economic traits for aquaculture. For example, RNA-seq was used to identify differential expression gene in disease and stress responses in catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) (Liu, et al., 2013; Sun, et al., 2012). RNA-seq is also used to explore the differentially expressed genes related to growth in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss), largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides), schizothoracine fish (Schizothorax prenanti) etc.(Garcia de la Serrana, et al., 2015; Li, et al., 2019; Li, et al., 2017). In the process of fish growth, many genes and signal transduction pathways involved in growth regulation have been found. In a transcriptome study of genes associated with muscle growth in mandarin Fish (Siniperca chuatsi), the results showed that differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were involved in GH-IGF pathways, protein synthesis, ribosome synthesis, and energy metabolism. These genes were expressed at significantly higher levels in larger individuals than in smaller ones (Liu, et al., 2020). There is also have study analyzed the muscle and liver tissues of black carps (Mylopharyngodon piceus) with different growth rates from the same batch using RNA-seq to evaluate their growth traits. The findings revealed that black carps with fast growth rates exhibited significant upregulation of growth-related pathways such as the FoxO signaling pathway, p53 signaling pathway, PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, and insulin signaling pathway (Zhang, et al., 2020). The present study provides the basis for a study of the growth of the black-browed marbled grouper, but differences in species or environmental factors will lead to different results.
In this study, we analyzed the muscle transcriptome of fast- and slow-growing brown-marbled grouper in a half-sibling family by RNA-Seq, exploring the important candidate genes related to the growth of the brown-marbled grouper. Results of this study will promote understanding of the growth regulation mechanisms in brown-marbled grouper.
2. Methods
2.1. Ethics statement
All experiments in the present study have been approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee in School of Life Sciences, Sun Yet-Sen University.
2.2. Experimental fish and sample collection
The brown-marbled groupers were collected from Hainan Chenhai Aquaculture Co., Ltd., a half-sibling family constructed by single-sire and multiple-dams mating. After a year of farming in the same environment, a total of 300 fish randomly selected, measured for body length and weight. Then three fish were selected with the fastest growth rate (average body length:37.7±0.62cm; average body weight:1071.7±5.79g) and the three fish with the slowest growth rate (average body length:29.7±0.94cm; average body weight:393.3±30.35g). The two extreme groups were anesthetized with tricaine eugenol for subsequent sampling, and white muscle was collected immediately. The tissues were frozen in liquid nitrogen quickly, and stored at −80◦C.
2.3. RNA Extraction and Library Construction
Total RNA from each sample of 6 fish was extracted using the Trizol Reagent (Invitrogen, USA). RNA integrity was assessed using 1% agarose gel electrophoresis after removing genomic DNA with DNase I (TaKaRa, Dalian, P R China). RNA quality and quantity were confirmed using the Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer (Agilent Technologies, USA) and ND-2000 platforms (NanoDrop Technologies, USA). mRNA was isolated using oligo (dT) beads and subjected to reverse transcription and fragmentation. Double-stranded cDNA was synthesized using random hexamer primers. Agarose gel electrophoresis was used to select and purify 300-400 bp cDNA fragments, which were then subjected to end repair, "A" base addition, and adapter connection. Library sequencing was performed after amplification by 15 PCR cycles. The cDNA libraries were sequenced on Illumina HiSeq 2000 platform with strategy of paired-end 150 bp (PE 150).
2.4. DEG analysis and GSEA analysis
Fastp v.0.20.1 (Chen, et al., 2018) was utilized to perform quality filtering and removal of residual adaptor sequences on reading pairs. Illumina-specific adaptors were clipped from the reads, and bases with a Phred score <20 at the leading and trailing ends were eliminated. After filtering, only reads with both pairs longer than 36 bp were retained. Illumina specific adaptors were clipped from the reads and leading and trailing bases with a Phred score <20 were removed; only reads where both pairs were longer than 36 bp post-filtering were retained. The high-quality clean reads were mapping the brown-marbled grouper genome (Yang, et al., 2021) with software HISAT2 v2.1.0 (Kim, et al., 2019). The counts were calculated by the number of reads that mapped to the reference sequence.
Uniquely mapped PE-reads were counted and assigned to genes using FeatureCounts (Liao, et al., 2014) from the SourceForge Subread package v.1.5.0. Differential expression analysis was conducted between fast- and slow-growing brown-marbled grouper samples using the edgeR package (
http://www.r-project.org/) (Robinson, et al., 2010). Genes with an absolute log2 fold change (|log2FC|) greater than 1 and a false discovery rate (FDR) less than 0.05 were considered significant differential genes.
DEGs were compared with the GO database (
http://www.geneontology.org/) to obtain a list and count of transcripts associated with GO functions. Hypergeometric tests were conducted to identify significantly enriched GO entries compared to the entire set of transcripts. Similarly, DEGs were compared with the KEGG database, and hypergeometric tests were used to identify significantly enriched KEGG pathways (Kanehisa, et al., 2008). Analyzing GO terms and pathways can provide insight into the biological functions of transcripts. All expression data were statistically analyzed and visualized using R (version 4.1.3,
https://www.r-project.org).
Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) was utilized to determine whether a pre-defined set of genes exhibit statistically significant, concordant differences between two biological states. The expressed genes were analyzed using GSEA software version 4.1.0 (Subramanian, et al., 2005) to identify pathways that contribute to differences in growth.
2.5. Discovery of SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism)
SNPs in significant differential genes were identified and counted using BCFtools (version 1.10.2,
https://github.com/samtools/bcftools) with the reference genome. Raw reads from each fish were mapped onto the reference genome assembly, and high-quality SNP markers were obtained by screening SNPs with a read depth greater than 10 and a quality score greater than 40 using VCFtools (version 0.1.16) (Danecek, et al., 2011). Then VCFtools was also used to calculate Fst (fixation index) of SNPs and further filter those SNPs with Fst ≥ 0.8.
2.6. Real-time PCR
To validate the transcriptome data, 25 DEGs were selected as verification genes to confirm the reliability of RNA-seq results. The expression levels of the selected growth-related genes were verified using real-time PCR (RT-PCR) analysis with three replicates for each RNA sample. Specific primers were designed for each gene using Primer Premier 6.0 (
Table S1) (Ye, et al., 2012). The beta-actin gene was used as an internal control. Each reaction system contained 10 μL of first-strand cDNA, 250nM primers, and 5µl Power SYBR Green PCR MasterMix (Vazyme Biotech, Nanjing, China). Quantitative Fluorescence PCR assay was performed using the LightCyclerR
Ⓡ 480 II Real-Time PCR System (Roche) and 384-well plates with Power SYBR Green PCR MasterMix (Vazyme Biotech, Nanjing, China). Each reaction was repeated three times, and the relative expression levels were calculated using the 2
−ΔΔCT method.
2.7. Statistical analyses
Data analysis was performed using R version 4.1.3, and the results were presented as means ± SEM. The body weight of fish in the fast-growing and slow-growing groups was compared using Student's t-test, with a significance level set at P < 0.05.
3. Result
3.1. Next-generation sequencing and mapping to the reference genome
In total, transcriptome sequencing of 6 samples produced a total of 361,058,385 high-quality clean reads (
Table S2). All the clean reads were mapped to the brown-marbled grouper genome by HISAT2, and then compressed and sorted using the samtools software. More than 97% of the data from six samples were mapping to the reference genome.
3.2. Identification of differentially expressed genes
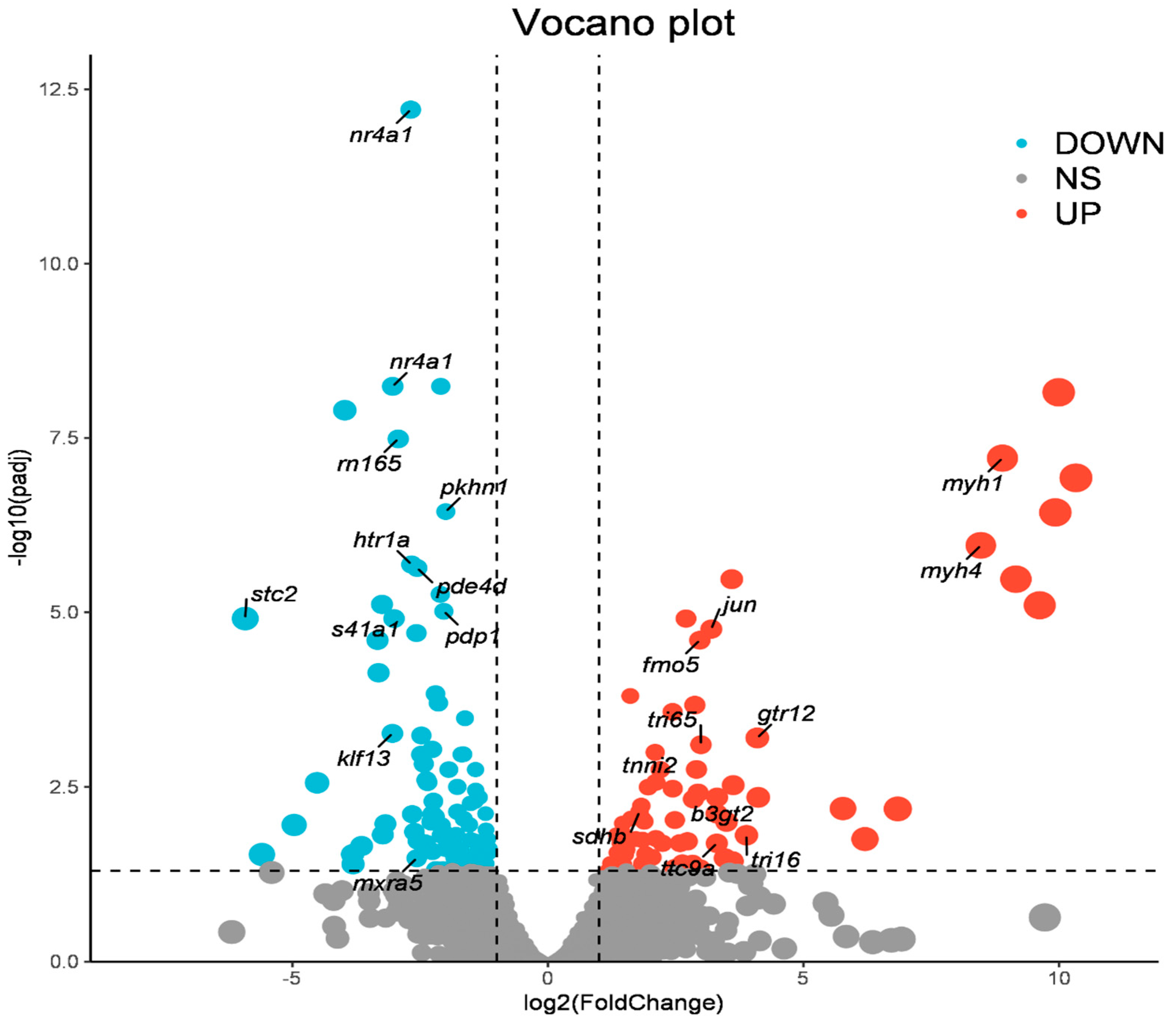
A total of 77 significantly up-regulated genes and 92 significant down-regulated genes were identified between the fast- and slow-growing group. In the process of identification of differential genes, many functional genes related to growth were recognized, such as
myh1,
myh4,
tnni2,
gtr12,
fmo5,
ttc9a,
ghr. Based on the result of the analysis, the volcano plot was drawn using R and important genes associated with growth were marked (
Figure 1).
3.3. Enrichment Analysis of GO and KEGG Pathways on the Basis of DEGs
GO annotation was used to categorize the 110 DEGs into biological process, cell composition, and molecular function, which were further classified into 27 functional categories across three ontologies. Cellular component, molecular function, and biological process contained 9 functional categories each (
Figure S1). Notably, significant changes were observed in myosin complex, cytoskeleton, actin cytoskeleton (Cellular Component), and motor activity (Molecular Function) based on the results of GO analysis (
Figure S2).
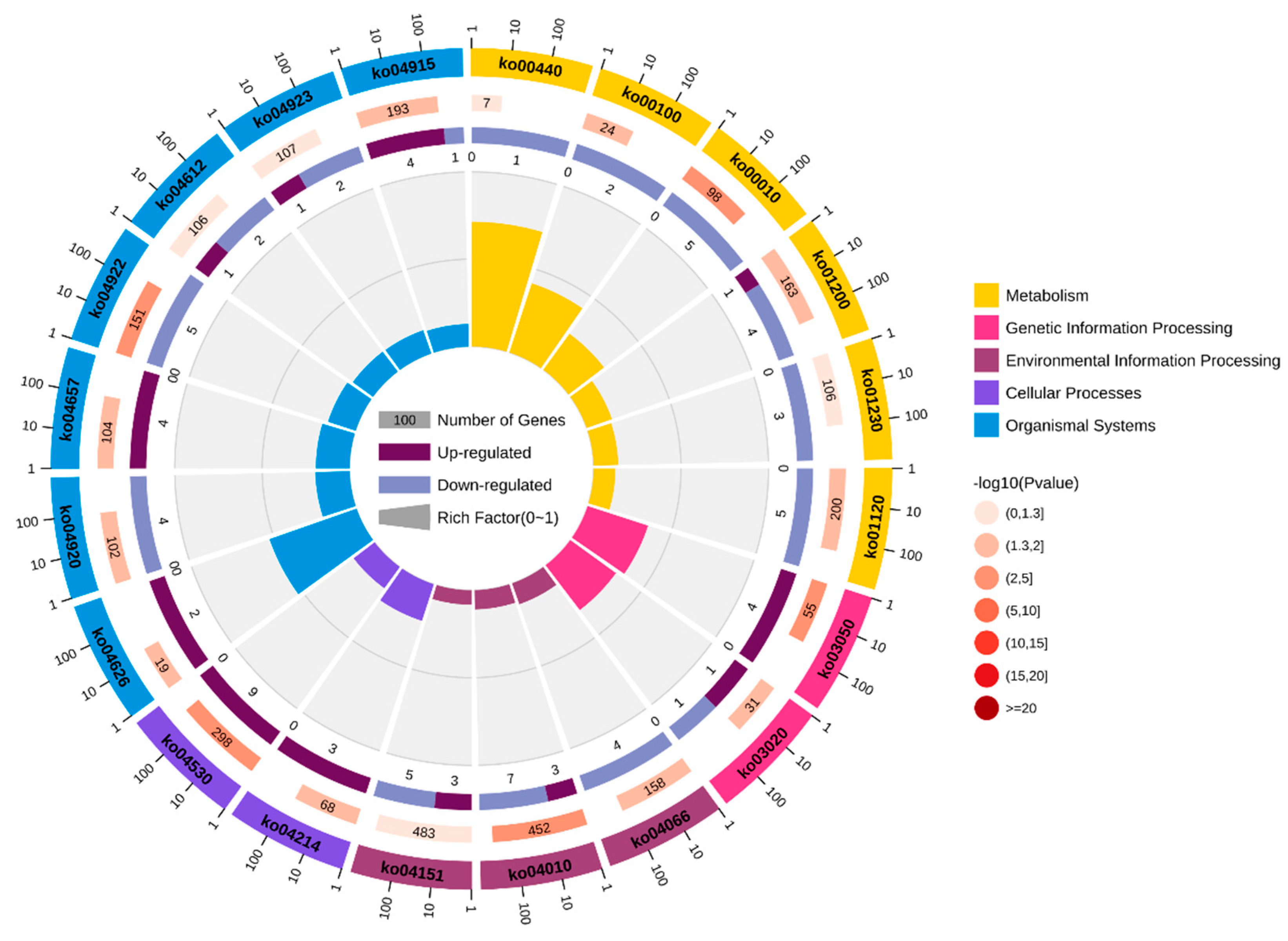
After excluding pathways associated with human disease, KEGG pathway analysis identified 125 DEGs enriched in various metabolic and organismal systems pathways. The major pathways related to growth included steroid biosynthesis (ko00100), glycolysis/gluconeogenesis (ko00010), carbon metabolism(ko01200), biosynthesis of amino acids (ko01230), MAPK signaling pathway (ko04010), PI3K-Akt signaling pathway (ko04151), and glucagon signaling pathway(ko04922) (
Figure 2,
Table 1). These significant pathway enrichments provide insight into the molecular mechanisms underlying growth-related traits in the leopard coral grouper.
3.4. GSEA Analysis
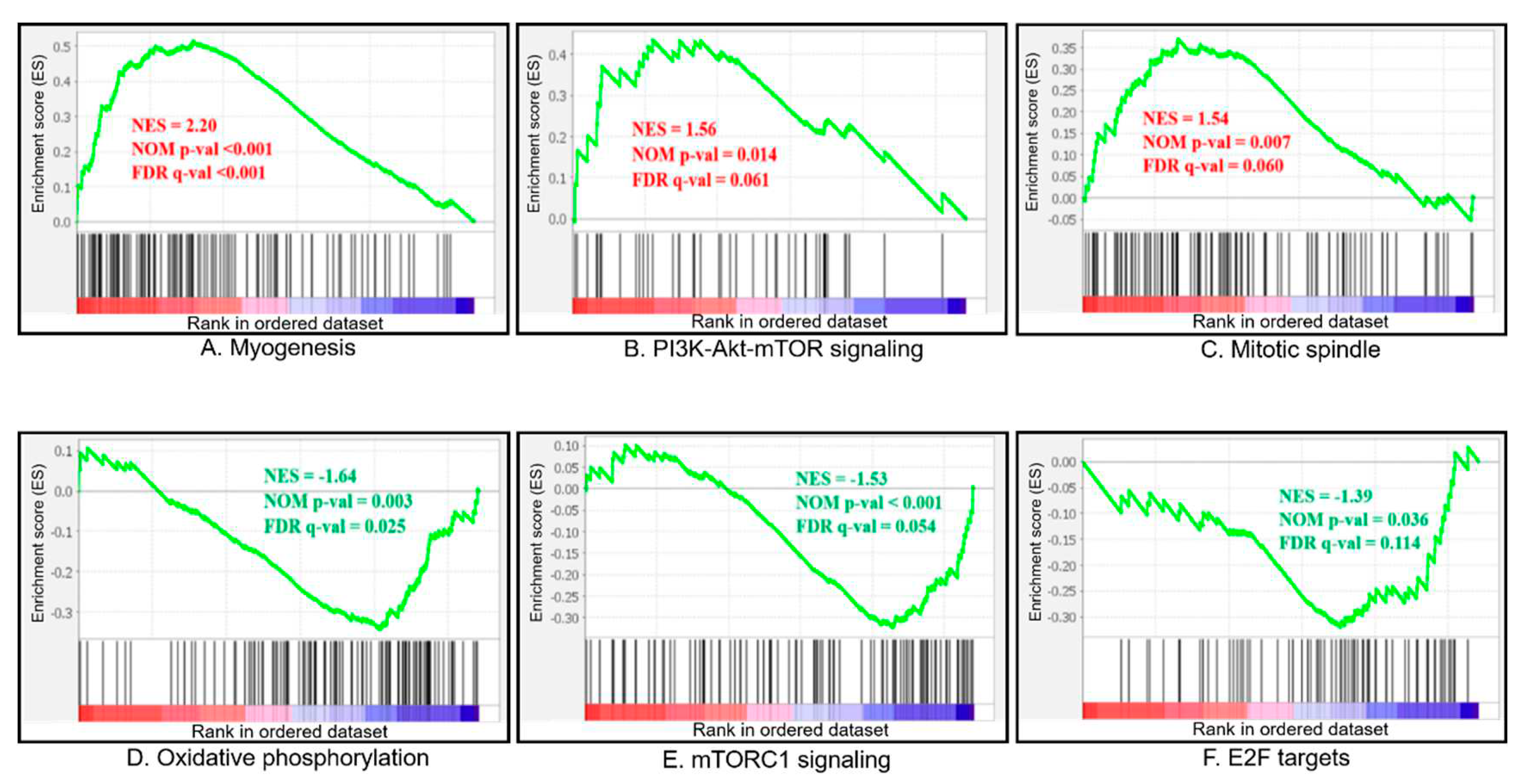
GSEA analysis was conducted according to | NES | > 1, Nom p-val < 0.05 and FDR q-val < 0.25. A total of 14 gene sets were found that significantly enriched for differentially expressed genes in fast-growing group compared with slow-growing group. The full list of significantly enriched gene sets can be found in
Table 2. Of these, 7 gene sets were significantly upregulated and 7 gene sets were downregulated in the fast-growing group. The important pathways which were related to growth enriched in fast- and slow-growing group (
Figure 4).
Compared with the slow-growing group, gene set which involved in development of skeletal muscle (myogenesis), activating of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway (PI3K-Akt-mTOR signaling) and the mitotic spindle assembly (Mitotic spindle) in fast-growing group significantly up-regulated. Compared with the slow-growing group, gene set which encoding proteins involved in oxidative phosphorylation (Oxidative phosphorylation), activating of mTORC1 complex (mTORC1 signaling), encoding cell cycle related targets of E2F transcription factors (E2F targets) in fast-growing group significantly up-regulated. The heat map of the top 50 features for each phenotype in GSEA_data at
Figure S3.
Figure 4.
Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA)-enrichment plots of representative gene sets from
Table 2: myogenesis (A), PI3K-Akt-mTOR signaling (B), mitotic spindle (C), Oxidative phosphorylation (D), mTORC1 signaling (E), E2F targets (F). NES, normalized enrichment score; NOM p-val, the statistical significance of the enrichment score; FDR q-val, false discovery rate. Positive and negative NES indicate higher and lower expression in fast-growing group, respectively.
Figure 4.
Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA)-enrichment plots of representative gene sets from
Table 2: myogenesis (A), PI3K-Akt-mTOR signaling (B), mitotic spindle (C), Oxidative phosphorylation (D), mTORC1 signaling (E), E2F targets (F). NES, normalized enrichment score; NOM p-val, the statistical significance of the enrichment score; FDR q-val, false discovery rate. Positive and negative NES indicate higher and lower expression in fast-growing group, respectively.
3.5. SNPs detection
A total of 32,679 SNPs were obtained after screening and filtering, there were 507 Fst≥0.8 and 61 Fst=1.0. Among SNPs with Fst≥0.8, 13 SNPs (
Table 3) are in the significantly different genes which include genes involved in glycolysis (
pdp1,
g6pi), skeletal muscle protein synthesis (
tnni2) and fatty acid synthesis(
s27a2).
3.6. qPCR
To verify the accuracy of the RNA-seq data, we screened 25 DEGs involved in muscle contraction related (
myh1,
myh4), growth hormone receptor (
ghr), Troponin I, fast skeletal muscle (
tnni2), facilitated glucose transporter member 12 (
gtr12), skeletal development (
ttc9a), Glycolysis (
pdp1), Citric Acid Cycle (
sdhb), Beta-1,3-galactosyltransferase 2 (
b3gt2), immunity (
mxra5) and others (
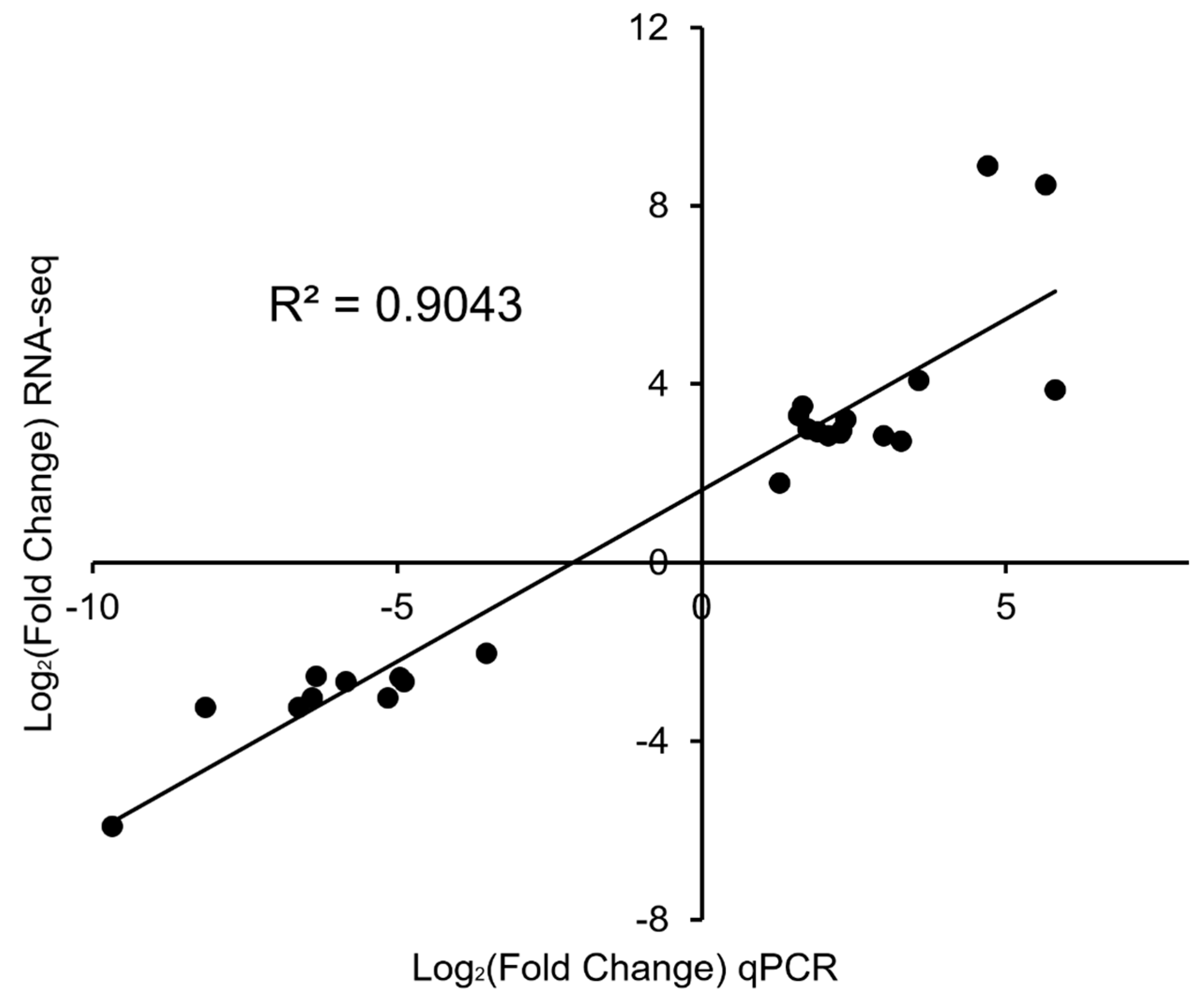
Figure S4). The gene expression changes obtained from qPCR were remarkably consistent with those obtained from the RNA-Seq result, with R
2 values of 0.9043 (
Figure 3). Therefore, the qPCR results confirmed the reliability and accuracy of the RNA-seq data.
Figure 3.
Comparison of gene expression changes measured by RNA-seq and qPCR. The log2 (fold-change) values from qPCR results are plotted on the x-axis, while those from the RNA-seq results are plotted on the y-axis. The correlation between the two methods is shown.
Figure 3.
Comparison of gene expression changes measured by RNA-seq and qPCR. The log2 (fold-change) values from qPCR results are plotted on the x-axis, while those from the RNA-seq results are plotted on the y-axis. The correlation between the two methods is shown.
4. Discussion
Animal muscle growth is influenced by a variety of factors, including metabolic, behavioral, and reproductive activities (Saxton and Sabatini, 2017). Similarly, fish muscle growth is a complex process, which is controlled by genes, environment, diet and other factors (Dutta, 1994). We conducted this study after finding that the fast- and slow-growing brown marbled grouper developed differently during cultivation. This study first reported the difference of brown-marbled grouper muscle transcriptome between fast- and slow-growing groups. Using the resulting muscle transcriptome sequences, we obtained the DEGs between the fast- and slow-growing brown-marbled grouper which potentially influencing the muscle growth. GO, KEGG and GSEA analysis were used to explore closely related signaling pathways that may contribute to growth differences.
In our experiments, compared with slow-growing group, the genes of ghr and tnni2 in fast-growing group were significantly up-regulated. In addition, during the discovery of SNPs, a SNP been found in the exon of tnni2, which further indicates that tnni2 gene is an important gene regulating growth. ghr (The growth hormone receptor) is a cell membrane receptor that specifically binds to growth hormone (GH). Upon binding, ghr initiates a phosphorylation cascade that regulates signaling and gene expression, ultimately regulating various physiological functions such as growth, metabolism, appetite, reproduction, and social behavior.(Behncken and Waters, 1999; Zhu, et al., 2001). Based on the study of Rohu (Labeo rohita), it was found that several molecules have agonistic effects on growth hormone receptor protein, and these molecules can be utilized to enhance fish growth (Dhandare, et al., 2020). tnni2 is a member of the troponin I gene family that encodes a fast-twitch skeletal muscle protein. It is a constituent of the troponin complex, which comprises troponin T, troponin C, and troponin I subunits (Mullen and Barton, 2000). This complex, along with tropomyosin, plays a crucial role in regulating striated muscle contraction in a calcium-dependent manner. The studies in mice show that tnni2 knock-out affects bone development in mice, leading them growth retardation than wild-type mice (Zhu, et al., 2014). stc2 (Mammalian stanniocalcin-2) is a secreted polypeptide which prevents PAPP-A cleavage of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein (IGFBP)-4 and hence release within tissues of bioactive IGF, required for normal growth (Jepsen, et al., 2015). stc2 was down-regulated expression at the fast-growing group which indicate low levels of expression were more beneficial to grouper growth.
Both GO and KEGG enrichment analysis revealed that DEGs were enriched in muscle growth synthesis, protein and carbohydrate metabolism pathways. In general, muscle growth is associated with increased protein anabolism and glycogen anabolism (Valente, et al., 2013). Although the GH/IGF axis-related pathway was not seen in the differential gene enrichment results, its downstream-related phosphonate and phosphinate metabolism, glucose metabolism, carbon metabolism and biosynthesis of amino acids were observed in the KEGG pathway enrichment analysis. In the Hulong grouper (E. fuscogutatus♀×E. lanceolatus♂), the growth advantage appears to be associated with the upregulation of DEGs related to the GH/IGF axis and its downstream signaling pathways, which enhance protein and glycogen synthesis (Sun, et al., 2016).
In this study, the KEGG pathway enrichment analysis revealed that certain DEGs were enriched in the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. Furthermore, the GSEA analysis indicated a significant upregulation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in the fast-growing group compared to the slow-growing group.Prior studies have established that the core components of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway include the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3Ks) and its downstream targets, Protein Kinase B (AKT) and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) (Saxton and Sabatini, 2017). mTOR is a downstream effector protein of the PI3K protein kinase family signal pathway. In mammals, it is present in two separate complexes, mTORC1 and mTORC2, which are differentiated by their respective accessory proteins raptor and rictor (Laplante and Sabatini, 2012).
mTORC1 is a key regulator of nutrient storage that promotes the synthesis of enzymes involved in glucose biosynthesis, as well as the production of proteins, lipids, nucleotides, and ATP, thereby facilitating muscle growth (Liu and Sabatini, 2020; Schiaffino, et al., 2013). Additionally, the PI3K/AKT/mTOR cascade serves as a crucial effector of insulin signaling and plays a major role in inducing glycolysis and lipogenesis while simultaneously repressing glycogenolysis (Ribback, et al., 2015).
Activation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway through feeding can stimulate mRNA translation and protein synthesis, while also regulating a variety of processes such as nutrient absorption, cell growth, proliferation, and anabolism (Hietakangas and Cohen, 2009; Liu and Sabatini, 2020).
Insulin binds to cell surface receptors to activate the PI3K-AKT pathway via IRS1. AKT promotes glucose absorption and activates mTORC1 activity through the AKT-TSC1/2-RheB-mTORC1 pathway (Menon, et al., 2014). In a recent study involving crucian carp, heterozygous deletion of pik3r1 was utilized to enhance PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway activity, leading to improvements in somatic cell growth and food utilization efficiency (Huang, et al., 2021). Some studies have also shown that zebrafish (Danio rerio) swimming training can increase the activation and expression of mTOR pathway in skeletal muscle, and then increase the growth of zebrafish skeletal muscle(Rovira, et al., 2017). Other studies have shown that amino acid supplementation in mice can stimulate the mTOR pathway to optimize muscle synthesis after feeding, but does not increase the speed of protein synthesis (Norton, et al., 2009). Juvenile rainbow trout can regulate the activation of mTOR pathway through feeding, and then enhancing protein synthesis (Lansard, et al., 2009; Seiliez, et al., 2008). Therefore, compared with slow-growing group, the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway of fast-growing group was significantly up-regulated, may indicating that the expression of this signal pathway leads to a higher nutrient absorption efficiency in fast-growing group. In the growth process of grouper, nutrition digestion and absorption play an important role. Higher nutrition utilization is beneficial to the growth of muscle and the increase of body length and weight of fish.
In this part of the study for the identification of SNPs, several genes involved in muscle growth were identified in the brown-marbled grouper. In addition to tnni2, a number of genes were also overlaps with significantly different genes, such as pdp1, g6pi, and s27a2. pdp1, a transcription factor found in the muscle activator region, has been shown to play a role in regulating the expression of the Tropomyosin I gene in somatic wall and pharyngeal muscles. This is achieved through binding to specific DNA sequences within the muscle activator that are essential for activation function (Lin, et al., 1997). g6pi is involved in glycolysis(Yang, et al., 2015), and s27a2 is involved in fatty acid synthesis(Ignatz, et al., 2022). The SNPs were located in other genes that were also involved in regulation of growth. Additional research is necessary to validate the association between SNP alleles in these genes and muscle growth, and to assess their potential utility as growth biomarkers for selective breeding programs.
5. Conclusion
In the present experiments, RNA samples from brown-marbled grouper muscle were subjected to RNA-seq analysis, and many DEGs were obtained. myh1, myh4, ghr, gtr12, tnni2 and other genes was up-regulated in fast-growing fish while sct2, pdp1, mxra5 and others was down-regulated might promote the muscle growth. GO and KEGG enrichment analyses revealed significant differential gene involved in steroid biosynthesis, carbohydrate metabolism, glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, skeletal system development, motor activity, cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process. The GSEA analysis result show that the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway significantly up-regulated in fast-growing grouper, which indicates the fast-growing groupers have higher nutrition utilization. In addition, of the SNPS with Fst≥0.8 obtained from transcriptome data, 13 SNPs are in significantly different genes and these SNPs may affect growth. The transcriptome sequences generated in this study have great potential in facilitating gene function analysis and molecular marker development based on gene sequence data, which can accelerate the research progress for researchers. Furthermore, the availability of sample data can enable a more in-depth investigation into the growth and other traits of brown-marbled grouper.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.
Author Contributions
Tong Wang and Yang Yang conceived and designed the study. Leilei Zeng and Yuhao Tao was responsible for fish rearing and sampling. Chaoyue Zhong and Leling Song performed RNA-Seq and qPCR analyses, respectively, inferring the biological significance of DE genes. Xi Wu and Tong Wang carried out the SNP shot experiments and analyses. Tong Wang and Shirui Gong analysed the data and wrote the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by National Key Research and Development Program (2018YFD0900203), National Natural Science Foundation of China (32273132, U22A20531), China Agriculture Research System of MOF and MARA (CARS-47), Project of Hainan Academician Team Innovation Center (YSPTZX202122), Huizhou Swan Project (20170214023102296).
Data Availability Statement
Raw sequence reads have been deposited in NCBI’s Short Read Archive (SRR19851482-SRR19851487) under BioProject accession PRJNA850911.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
- Amenyogbe, E. , Chen, G. and Wang, Z. Identification, characterization, and expressions profile analysis of growth hormone receptors (GHR1 and GHR2) in Hybrid grouper (Epinephelus fuscoguttatus ♀ × Epinephelus polyphekadion ♂). Genomics 2020, 112, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behncken, S.N. and Waters, M.J. Molecular recognition events involved in the activation of the growth hormone receptor by growth hormone. Journal of Molecular Recognition 1999, 12, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; et al. fastp: an ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danecek, P.; et al. The variant call format and VCFtools. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2156–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhandare, B.C.; et al. Molecular modeling, docking and dynamic simulations of growth hormone receptor (GHR) of Labeo rohita. J Biomol Struct Dyn 2020:1-14.
- Dutta, H. Growth in fishes. Gerontology 1994, 40, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuentes, E.N.; et al. IGF-I/PI3K/Akt and IGF-I/MAPK/ERK pathways in vivo in skeletal muscle are regulated by nutrition and contribute to somatic growth in the fine flounder. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2011, 300, R1532–R1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia de la Serrana, D. , Devlin, R.H. and Johnston, I.A. RNAseq analysis of fast skeletal muscle in restriction-fed transgenic coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch): an experimental model uncoupling the growth hormone and nutritional signals regulating growth. BMC Genomics 2015, 16, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hietakangas, V. and Cohen, S.M. Regulation of tissue growth through nutrient sensing. Annu Rev Genet 2009, 43, 389–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; et al. Heterozygous depletion of pik3r1 improves growth and feed conversion efficiency in Gibel carp (Carassius gibelio). Aquaculture 2021;545.
- Ignatz, E.H.; et al. RNA-Seq Analysis of the Growth Hormone Transgenic Female Triploid Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) Hepatic Transcriptome Reveals Broad Temperature-Mediated Effects on Metabolism and Other Biological Processes. Front Genet 2022, 13, 852165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jepsen, M.R.; et al. Stanniocalcin-2 inhibits mammalian growth by proteolytic inhibition of the insulin-like growth factor axis. J Biol Chem 2015, 290, 3430–3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, I.A. Environment and plasticity of myogenesis in teleost fish. J Exp Biol 2006;209(Pt 12):2249-2264.
- Johnston, I.A., Bower, N.I. and Macqueen, D.J. Growth and the regulation of myotomal muscle mass in teleost fish. J Exp Biol 2011, 214 (Pt 10), 1617-1628.
- Kanehisa, M.; et al. KEGG for linking genomes to life and the environment. Nucleic Acids Res 2008, 36, D480–D484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; et al. Graph-based genome alignment and genotyping with HISAT2 and HISAT-genotype. Nat Biotechnol 2019, 37, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lansard, M.; et al. Hepatic protein kinase B (Akt)-target of rapamycin (TOR)-signalling pathways and intermediary metabolism in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) are not significantly affected by feeding plant-based diets. Br J Nutr 2009, 102, 1564–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laplante, M. and Sabatini, D.M. mTOR signaling in growth control and disease. Cell 2012, 149, 274–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; et al. Characterization and expression profiles of muscle transcriptome in Schizothoracine fish, Schizothorax prenanti. Gene 2019, 685, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; et al. Transcriptome assembly and identification of genes and SNPs associated with growth traits in largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Genetica 2017, 145, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y. , Smyth, G.K. and Shi, W. featureCounts: an efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.C.; et al. PDP1, a novel Drosophila PAR domain bZIP transcription factor expressed in developing mesoderm, endoderm and ectoderm, is a transcriptional regulator of somatic muscle genes. Development 1997, 124, 4685–4696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G., Gong, Z. and Li, Q. The complete mitochondrial genome of the breed Ningbo brown-marbled grouper (Epinephelus fuscoguttatus). Mitochondrial DNA B Resour 2019, 4, 2109–2110. [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.Y. and Sabatini, D.M. mTOR at the nexus of nutrition, growth, ageing and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2020, 21, 183–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; et al. RNA-Seq reveals expression signatures of genes involved in oxygen transport, protein synthesis, folding, and degradation in response to heat stress in catfish. Physiol Genomics 2013, 45, 462–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; et al. Identifying the Related Genes of Muscle Growth and Exploring the Functions by Compensatory Growth in Mandarin Fish (Siniperca chuatsi). Front Physiol 2020, 11, 553563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, S.; et al. Spatial control of the TSC complex integrates insulin and nutrient regulation of mTORC1 at the lysosome. Cell 2014, 156, 771–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukai, Y. and Seng Lim, L. Morphogenesis of free neuromasts in the larvae of brown-marbled grouper Epinephelus fuscoguttatus. Marine and Freshwater Behaviour and Physiology 2016, 49, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullen, A.J. and Barton, P.J.R. Structural characterization of the human fast skeletal muscle troponin I gene (TNNI2). Gene 2000, 242, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norton, L.E.; et al. The leucine content of a complete meal directs peak activation but not duration of skeletal muscle protein synthesis and mammalian target of rapamycin signaling in rats. J Nutr 2009, 139, 1103–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribback, S.; et al. PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway plays a major pathogenetic role in glycogen accumulation and tumor development in renal distal tubules of rats and men. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 13036–13048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, M.D., McCarthy, D.J. and Smyth, G.K. edgeR: a Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [CrossRef]
- Rovira, M., Arrey, G. and Planas, J.V. Exercise-Induced Hypertrophic and Oxidative Signaling Pathways and Myokine Expression in Fast Muscle of Adult Zebrafish. Front Physiol 2017, 8, 1063. [CrossRef]
- Saxton, R.A. and Sabatini, D.M. mTOR Signaling in Growth, Metabolism, and Disease. Cell 2017, 168, 960–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiaffino, S.; et al. Mechanisms regulating skeletal muscle growth and atrophy. FEBS J 2013, 280, 4294–4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seiliez, I.; et al. An in vivo and in vitro assessment of TOR signaling cascade in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2008, 295, R329–R335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, A.; et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, F.; et al. Transcriptomic signatures of attachment, NF-kappaB suppression and IFN stimulation in the catfish gill following columnaris bacterial infection. Dev Comp Immunol 2012, 38, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; et al. Transcriptome analysis reveals the molecular mechanisms underlying growth superiority in a novel grouper hybrid (Epinephelus fuscogutatus ♀ × E. lanceolatus ♂). BMC Genet 2016, 17, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valente, L.M.P.; et al. What determines growth potential and juvenile quality of farmed fish species? Reviews in Aquaculture 2013, 5, S168–S193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z., Gerstein, M. and Snyder, M. RNA-Seq: a revolutionary tool for transcriptomics. Nat Rev Genet 2009, 10, 57–63. [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.J.; et al. Two Chitin Biosynthesis Pathway Genes in Bactrocera dorsalis (Diptera: Tephritidae): Molecular Characteristics, Expression Patterns, and Roles in Larval-Pupal Transition. J Econ Entomol 2015, 108, 2433–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; et al. Whole-genome sequencing of brown-marbled grouper (Epinephelus fuscoguttatus) provides insights into adaptive evolution and growth differences. Mol Ecol Resour 2021. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; et al. Identification of Candidate Growth-Related SNPs and Genes Using GWAS in Brown-Marbled Grouper (Epinephelus fuscoguttatus). Mar Biotechnol (NY) 2020, 22, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; et al. Primer-BLAST: a tool to design target-specific primers for polymerase chain reaction. BMC Bioinformatics 2012, 13, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; et al. Transcriptome Analysis of the Liver and Muscle Tissues of Black Carp (Mylopharyngodon piceus) of Different Growth Rates. Mar Biotechnol (NY) 2020, 22, 706–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, K.; et al. The complete mitochondrial genome of the hybrid grouper Epinephelus fuscoguttatus (♀) × Epinephelus lanceolatus (♂). Mitochondrial DNA A DNA Mapp Seq Anal 2016, 27, 1968–1969. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhu, T.; et al. Signal transduction via the growth hormone receptor. Cellular Signalling 2001, 13, 599–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; et al. A gain-of-function mutation in Tnni2 impeded bone development through increasing Hif3a expression in DA2B mice. PLoS Genet 2014, 10, e1004589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).