1. Introduction
Sea cucumber (
Stichopus japonicus) is an important commercially developed variety with production reached globally 22,270 tons in 2021 [
1]. As the main edible part, sea cucumber body wall (SCBW) is keen on consumers because of its special taste and high nutritional value. Fresh SCBW is rich in collagen and has a network structure maintained by collagen fibers and fibrillin microfibrils, which makes it is very tough and hard to chew. Heat treatment can improve the texture and sensory properties of SCBW and give it excellent edible properties. In recent years, the health effects of food have attracted increasing attention from consumer. In addition to the sensory aspects of food, consumers tend to choose food based on nutritional quality. Studies have shown that heat treatment of aquatic products can affect the digestion properties and bioavailability of proteins during gastrointestinal tract, which has a serious impact on the nutritional value [
2].
The digestibility and absorption of proteins in the small intestine are key factors that shape the nutritional quality of meat proteins. In general, most studies indicate that heat treatment affects the
in vitro protein digestibility of meat in two parts. Short time gentle heat treatment result in slightly higher levels of protein digestion, while severer heat treatment conditions (an increase in temperature or an extension of time) result in a decrease of
in vitro protein digestibility [
3]. This is because mild heat treatment induces protein denaturation and unfolding, thereby increasing the site of action for protease and thus improving digestibility [
4]. However, interactions between hydrophobic regions within proteins occur as they unfold. Meanwhile, heat-induced protein oxidation can lead to the modifications of amino acid and the generation of various oxidation products, including carbonyl (from basic amino acids), disulfide bonds (from cysteine (thiol groups)) and dityrosine bonds (from tyrosine) [
5]. The bonds between different proteins further originate the polymerization and aggregation of proteins [
6,
7]. Thus, access to the hydrolysis site becomes more difficult for proteases, and protein hydrolysis is blocked, resulting in decreased digestibility. Yet so far, the current research mainly focuses on the implications of heat treatment on digestibility of meat, fish and seafood proteins [
2], and few relevant studies have been conducted on collagen-dominated SCBW.
Proteins are broken down by proteases in the digestive tract into free amino acids as well as smaller peptides (di-, tri- or tetrapeptides) then pass through the epithelium of the small intestine to enter the bloodstream by active transport or facilitative diffusion [
8,
9]. The digestibility of meat proteins determines the size and sequence of peptide segments and the composition of amino acid after digestion, which may affect the absorption [
4,
10]. Heat treatment can affect the digestibility of food proteins, hence it can also affect the absorption of protein digestion products in the small intestine epithelium barrier. The current studies involve the effects of different heat treatments (high pressure, steam cooking) on the bioavailability of myofibril [
10], myosin model systems [
11] and oyster proteins [
12]. However, their research objects were mainly limited to meat, protein model systems prepared from meat and aquatic muscle foods. Few studies have been reported on collagen-dominated sea cucumbers.
Our previous studies have shown that different boiling time had significant effects on the texture properties of SCBW. Insufficient heat treatment (100 °C-0.5 h) caused large hardness and poor chewiness of SCBW, while excessive heat treatment (100 °C-4 h) led to soft, rotten and inelastic SCBW. Only moderate heat treatment (100 °C-2 h) could give sea cucumber products moderate shear force, hardness and elasticity [
13]. However, the protein digestion and absorption properties of sea cucumber with different degrees of heat treatment are not clear. Hence, this study aimed to study the effect of boiling time on protein digestion and transport properties in boiled sea cucumber body wall (BSCBW) via simulated digestion combine with everted-rat-gut-sac models. Meanwhile, the protein oxidation, crosslinking and aggregation in BSCBW with different treatment time were also investigated to reveal the mechanism behind change of protein digestion and transport properties.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
Choose and purchase freshly harvested sea cucumbers (Stichopus japonicus) from the local aquatic market in Dalian, Liaoning, China with an average weight (100-120 g) and length (8-12 cm). The samples were always placed in ice sea water conditions during transport to the laboratory.
2.2. Heat Treatment Program
Fresh sea cucumbers were divided into four groups after being dissected, gutted, and washed. One group served as the control group without treatment, and the other three groups were heat treated at 100 °C for 0.5 h, 2 h and 4 h, respectively. They were named as fresh SCBW, 0.5 h-boiled SCBW (0.5 h-BSCBW), 2 h-BSCBW and 4 h-BSCBW. The samples were cooled and placed on ice for further analysis.
2.3. The Degree of Protein Oxidation
2.3.1. Free Radical Intensity
The measurement of free radical intensity was implemented according to Liu’s method [
14]. 0.1g freeze-dried sea cucumber powder was placed in a 5mm NMR tube (Wilmad, NJ, USA) and then placed in the sample cavity. Spectra was recorded via an Brucker a 200 electron spin resonance (ESR) spectrometer (Karisruhe, Germany) at room temperature. The free radical intensity was acquired through calculating the average value of the absolute values of the highest and lowest signal intensity on the ESR spectrum.
2.3.2. Thiobarbituric Acid Reactive Substances Content (TBARS)
The measurement of TBARS was implemented according to Xie’s method [
15].
2.3.3. Protein Carbonyl Content
The measurement of protein carbonyl content of SCBW was implemented by using a carbonyl assay kit (Jiancheng Technology Co., Nanjing, Jiangsu, China).
2.3.4. Determination of Free Sulfhydryl Groups (SH) and Disulfide Bonds (S-S)
The measurement of SH (expressed as nmol/mg protein) and S-S (expressed as nmol/mg protein) of SCBW were implemented according to Ellman’s method [
16].
2.3.5. Structural Changes of Water-Soluble Fraction
Boiled sea cucumbers and cooking liquors were homogenized together, and then were centrifuged at 13,500 g for 20 min (40 °C). The supernatant obtained was taken as water soluble fraction. The extraction procedure in fresh samples as same as above, but the extraction temperature was 4 °C.
Water soluble fraction obtained above was diluted to 0.2 mg/mL with distilled water. Then, dityrosine intensity [
17], fluorescence spectroscopy [
18] and advanced glycation end products (AGEs) intensity [
19] were measured by using a Hitachi F-2700 spectrofluorimeter (Hitachi, Japan). The width of both the excitation slit and emission slits was set as 10.0 nm. For dityrosine intensity, the excitation wavelength was 325 nm and the emission wavelength was 420 nm. For fluorescence measurements, the excitation wavelength was 280 nm, and the scanning range of the emission wavelength was 300-500 nm. The scan speed was 1500 nm/min and the experimental temperature was 25 °C. For AGEs intensity, the excitation and emission wavelength were set to 370 nm and 440 nm, respectively.
Water soluble fraction obtained above was diluted to 0.025 mg/mL with distilled water. Circular dichroism (CD) spectra [
18] were measured in the extreme ultraviolet region of 190-250 nm at 25 °C using Jasco J-1500 CD spectropolarimeter (Jasco Corp., Japan). The measurements were repeated three times to obtain CD images. The fractions of α-helix, β-sheet, β-turn, and random coil were obtained using the Secondary Structure Estimation software.
2.3.6. Protein Surface Hydrophobicity
The measurement of sea cucumber protein hydrophobicity was implemented according to Chelh’s method [
20]. Briefly, water soluble fraction obtained above was diluted to 1 mg/mL with distilled water. Firstly, the protein diluent and bromophenol blue solution were mixed. The absorption value of supernatant at 595 nm was determined after incubation (10 min), centrifugation (7500 rpm, 15 min, 4 °C), and dilution (10 times). The control group was given distilled water instead of protein solution.
2.3.7. Protein Aggregation
The measurement of sea cucumber protein aggregation was implemented according to Santé-Lhoutellier’s method [
5]. Briefly, Water soluble fraction obtained above was diluted to 1 mg/mL with distilled water. The fluorescence intensity of the mixture sample of protein diluent and Nile Red solution was measured by using a Hitachi F-2700 spectrofluorimeter (Hitachi, Japan). The excitation wavelength: 560 nm; the emission wavelength: 620 nm; the excitation slit width: 10.0 nm; the emission slit width: 10.0 nm.
2.4. In vitro Simulated Gastrointestinal Tract Digestion
The static digestion of sea cucumber protein was simulated by gastrointestinal digestion
in vitro according to Minekus’s method [
21]. Sea cucumber freeze-dried powder (0.05 g) were vorticised with 6 mL simulated salivary fluid (SSF), and then the mixture was incubated by shaking at 100 rpm in a 37 °C water bath for 10 min. Then 6 mL simulated gastric fluid (SGF) was added, and the digestive system was adjusted to pH 3.0. The mixture was further incubated for 120 min. After the simulated gastric digestion, 12 mL of simulated intestinal fluid (SIF) was added to chyme, and the mixture was adjusted to pH 7.0 and further incubated for 120 min. Boiling for 10 min to stop the reaction after digestion was completed. This made the digestion samples suitable for subsequent experiments.
2.4.1. Release of Primary Free Amino Group
The primary free amino group of digest sample was quantified using the OPA method [
22]. The supernatant was obtained after the digest sample was centrifuged at 12000 g for 10 min, which was the sample solution. After taking 200 μL sample solution, adding 1.5 mL OPA reagent, incubating for 2 min, and immediately determining the absorbance value at 340 nm. The time of recording the absorption value must be synchronized because the absorption value changes with time. At the same time, the concentration curve of serine standard solution (0.1 mg/mL) was drawn, and the content of free amino group was calculated according to the standard curve.
2.4.2. Determination of Trichloroacetic Acid-Soluble Peptide Yield (TCA-Ysp)
The TCA-Ysp was measured according to the method reported by Chen [
23] with some modifications. The digest sample (500 μL) were mixed with 20% (w/w) TCA (500 μL). Then the mixture was centrifugated at 12000 rpm for 10 min (4 °C). The peptide content in the supernatant was determined by Folin-phenol method. After mixing the supernatant (100 μL) and folin-phenol A solution (500 μL), incubating at room temperature for 10 min. Folin-phenol B solution (50 μL) was added, mixed and incubated in 30 °C water bath for 30 min, and cooled naturally. The absorbance (500 nm) was measured. Meanwhile, the standard curve of BSA as the standard protein was drawn. TCA-Ysp (%) was obtained by calculating the ratio of peptide content in the supernatant to total protein before digestion.
2.5. Everted Gut Sac Model
2.5.1. Construction of Everted-Rat-Gut Sacs
Choose and purchase male Sprague Dawley rats (100-150 g) from Liaoning Changsheng Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Benxi, Liaoning, China). All animal procedures were subject to the approval of the Committee on the Ethics of Animal Experiments of Dalian Polytechnic University (approval number: DLPU2022037). All procedures for animal experiments followed the guidelines of the National Institutes of Health. The constructed everted-rat-gut sacs was obtained according to Yin’s method [
24].
2.5.2. Digestion Product Transport across Everted-Rat-Gut Sacs
The supernatant was obtained after the digest sample was centrifuged at 12000 g for 10 min, which was the sample solution. Sample solution was added to the mucosal side, i.e., 7 mL sample solution was lyophilized and redissolved in 7 mL Krebs-Ringer buffer solution.
After incubation at 37 °C for 0, 20, 40, 60, 80, 100, 120 min, 50 μL of serosal fluid was taken out and mixed with 50 μL of methanol to terminate the reaction. At the same time, serosal fluid filled with 50 μL Krebs-Ringer buffer. The serosal fluid sample supernatant was collected after centrifugation (19000 g, 4 °C, 25 min) to determine the peptide content.
2.5.3. Determination of Total Amino Acid Transport Rate
The measurement of amino acid content was carried out via an automatic amino acid analyzer (LA8080, HITACHI, Japan) [
25]. The total amino acid transport rate was obtained by calculating the ratio of the content of total amino acid transported to the serosal side (inside the sac) to that of the simulated gastrointestinal digestion product.
2.5.4. Determination of peptide transport rate
The peptide transport of digestion products from 0 min to 120 min was measured by Folin-phenol method. The peptide transport rate was evaluated by calculating the ratio of peptide content of transported to the serosal side (inside the sac) to that of the simulated gastrointestinal digestion product.
Where Ci is the peptide content of serosal side of sample (mg/mL), Vi is the volume of solution of serosal side of sample (mL), Cb is the peptide content of serosal side of blank (mg/mL), Vb is the volume of solution of serosal side of blank (mL), C is the initial peptide content of the mucosal side (outside the sac) (mg/mL), V is the initial volume of solution of mucosal side (mL), A is surface area of small intestinal (cm
2).
2.5.5. Determination of Peptide Content by HPLC-UV Analysis
HPLC (Shimadzu LC-20AD, Japan) was used to analyze the peptide content coupled with Elite C18 analytical column (4.6 × 250 mm, 5 μm). Mobile phase: A was 10% methanol; B was methanol. Gradient elution steps: 0-15 min, 25% B; 15-25 min, 25%-90% B; 25-26 min, 95%-25% B; 26-35 min, 25% B. Injection volume: 10 μL; flow rate: 0.5 mL/min; column temperature: 25 °C; the monitored wavelength of chromatogram: 214 nm.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
The everted gut sac experiment was carried out five times in parallel, the other experiments were carried out three times in parallel, and the values were shown as means ± standard deviation. Significant differences were measured via One-way ANOVA and Tukey’s test by using SPSS 22.0 software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). P < 0.05 means significant.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Changes in Oxidative Indicators
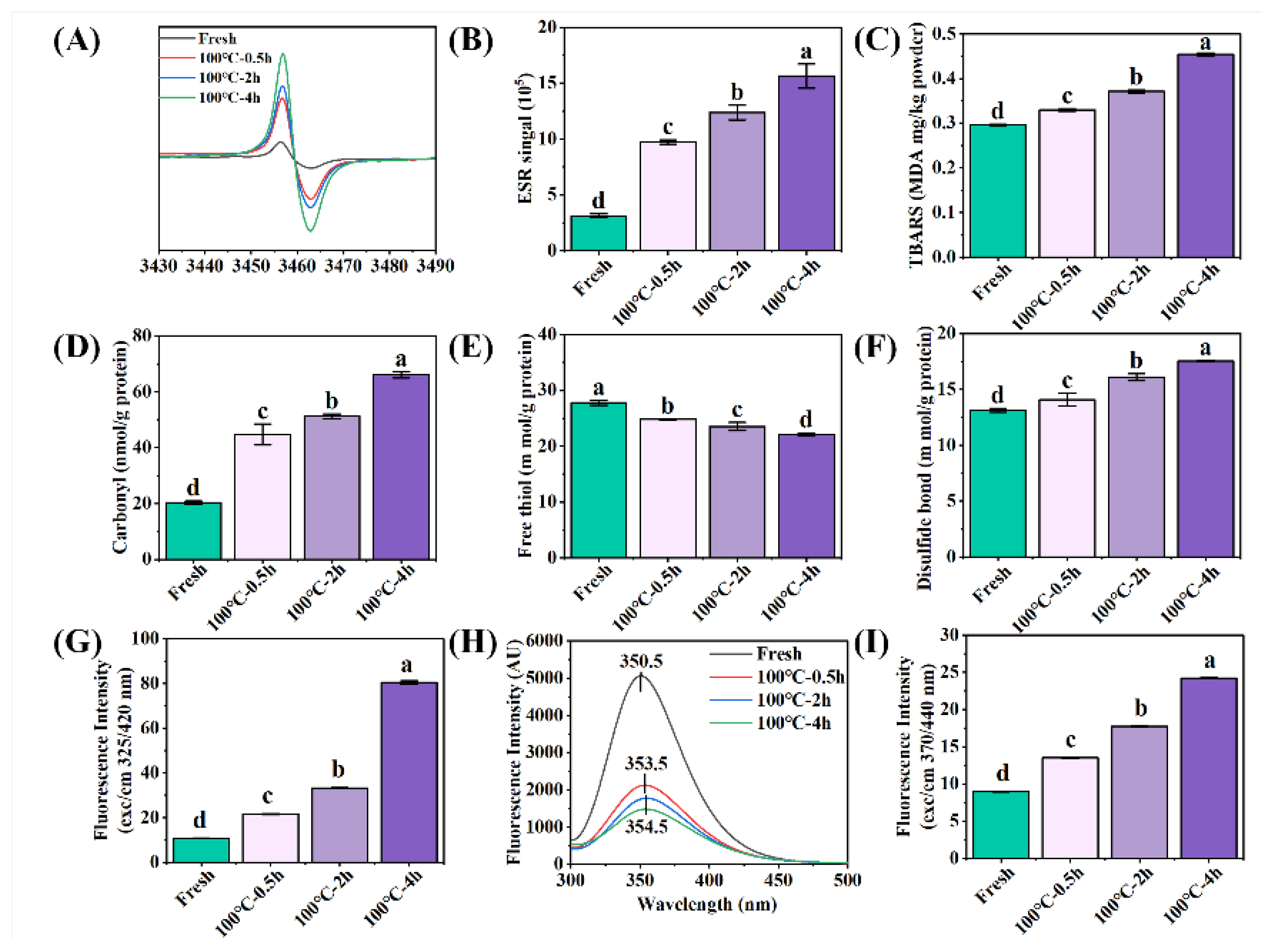
With the extension of boiling time, the free radical intensity (
Figure 1AB), TBARS (
Figure 1C), carbonyl content (
Figure 1D), disulfide bond content (
Figure 1F), dityrosine bond content (
Figure 1G), fluorescence intensity (
Figure 1H) and AGEs content (
Figure 1I) of SCBW increased, while the free sulfhydryl group content (
Figure 1E) decreased. The results showed that protein and lipid oxidation occurred. Moreover, the oxidation degree was enhanced with the extension of heat treatment time. Proteins are generally oxidized and generated free radicals and TBARS during the heat treatment. The increase of free radical production can significantly lead to the modification of amino acid side chain and protein backbone, manifested in the formation of carbonyls (from basic amino acids), disulfide bonds (from cysteine (thiol groups)) and dityrosine bonds (from tyrosine), as well as the reduction of thiol groups and tryptophan [
5].
3.2. Structural Modifications of Proteins
Circular dichroism spectra has been widely used in elucidating structural changes of proteins/peptides at the secondary folding level under heating treatment [
26]. The changes of secondary structure in fresh and boiled SCBW with different boiling times were summarized in
Table 1. The level of α-helix, β-sheet, β-turn and random coil of fresh SCBW were 37.50±3.25, 18.87±6.30, 15.53±0.76 and 28.13±2.44%, respectively. During boiling, α-helix and β-turn fractions decreased significantly accompanied by raising of β-sheet and random coil fractions, indicating a structural shift from an ordered to a disordered state of the protein. This possibly due to the exposure of hydrophobic regions and the breakdown of hydrogen bonds. On the one hand, heat treatment accelerates possibly the denaturation and folding process of protein by loosening the protein structure. On the other hand, long-term high-temperature treatment may lead to the enhancement of kinetic energy of protein molecules and vibration of polar groups, thus changing the secondary structures [
27].
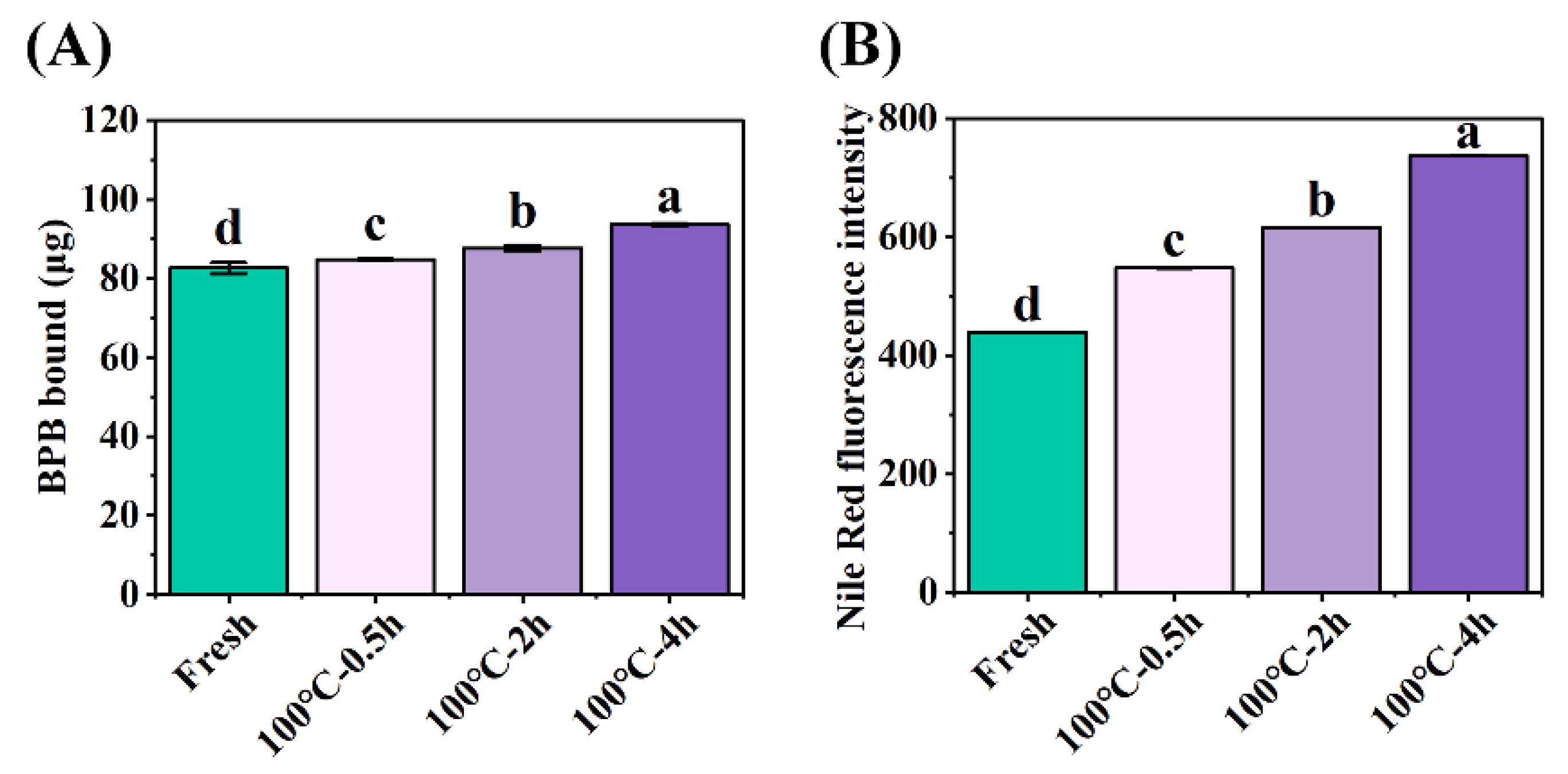
Surface hydrophobicity of protein can be used to evaluate the conformational change of proteins [
5]. The protein surface hydrophobicity increased observably from 82.62±1.38 μg Bound BPB (fresh SCBW) to 93.68±0.33 μg Bound BPB (boiled for 4 h) with the extension of boiling time (
Figure 2A). Hydrophobic amino acids in their natural state are buried in the protein folding core. Heat treatment facilitates the unfolding of protein structure and exposes them to the protein surface [
8].
The specificity of fluorescence emitted by the combination of Nile red with aggregates was used to evaluate the degree of protein aggregation [
5]. Compared to fresh SCBW (438.90±0.30), the fluorescence intensity significantly increased to 737.30±0.26 (boiled for 4 h) with the extension of boiling time (
Figure 2B). It is mainly attributed to the formation of high molecular weight aggregates derived from the disruption of protein conformation and the release of hydrophobic groups during heat treatment [
28]. That is, protein oxidation caused the formation of crosslinks between cysteine (disulfide bonds) or tyrosine (dityrosine bonds) [
8] and the alteration of secondary and tertiary structures. This further leads to an increase of the unfolding state of protein structure and protein-protein interaction, resulting in protein aggregation at last.
3.3. Protein Digestion Properties of Boiled SCBW
During gastrointestinal tract (GIT) digestion, protein hydrolysis degree can be evaluated by measuring the release of primary free amino group and the formation of peptides [
29]. So OPA method was used to quantify the free amino group in gastric and intestinal digestion products to assess protein digestion level, as shown in
Figure 3A. Further, the TCA precipitation method combined with Folin-phenol method were used to quantify peptides (< 10 amino acids) and free amino acids generated during digestion to confirm the progress of hydrolysis [
30], the result demonstrated in
Figure 3B. The release of free amino group in small intestinal digestion was significantly increased in comparison with gastric digestion, indicating that protein was mainly digested in intestine (
Figure 3A). During gastric and gastrointestinal digestion, the content of free amino groups released by protein hydrolysis (
Figure 3A) and TCA-soluble peptide yield (Ysp) (
Figure 3B) intensified firstly and then dropped with the prolongation of boiling time. The release of free amino groups and Ysp of 2 h-BSCBW were the highest, and those of 4 h-BSCBW decreased.
During digestion, the peptide bonds of proteins are hydrolyzed by proteases and free amino groups are released [
31]. Type I collagen in fresh SCBW has strong resistance to pepsin due to its tight spatial structure [
32], thus a lower degree of hydrolysis was shown. Moderate heating (from 0.5 h to 2 h) induced the partial expansion or oxidation of type I collagen, exposing more active sites for pepsin action (hydrophobic residues including Phe, Tyr, Trp and Leu) and improving the hydrolysis degree [
33]. While excessive heating (4 h) led to increased oxidation degree of proteins, more prone to cross-linking and aggregation, which enhanced resistance to enzymolytic proteins and reduces hydrolysis degree [
5]. However, during gastrointestinal digestion stage, protein hydrolysis massively under trypsin action led to structural collapse, which could rule out the reason that oxidation-induced molecular aggregation that prevents the protease from approaching the cleavage site. Thus, the decrease in hydrolysis degree was attributed to modification of multiple amino acid residues or enzyme cleavage sites, resulting in digestive enzymes fail to recognize the sites correctly. Kaur et al. [
33] found that long cooking of beef produced limit peptides, which were not further decomposed into free amino acids by digestive enzymes. It could be attributed to the modification of various amino acid residues, for instance, the oxidative modification of aromatic amino acid residues (pepsin hydrolysis site). In this study, the change of Ysp was consistent with that of the release of free amino groups, indicating that boiling for 2 h can raise the digestion level of protein, while boiling for 4 h can reduce the digestion level.
3.4. Transport Properties by Everted-Rat-Gut-sac Model
The degree to which food compounds are absorbed by intestinal epithelial cells and enter the systemic circulation after digestion in the gastrointestinal tract is considered as bioavailability, which is related to the stability of the compounds after digestion in the gastrointestinal tract and the absorption efficiency through intestinal epithelial cells [
34]. In a process that simulated GIT digestion, food proteins are further denatured and hydrolyzed by pepsin to form a mixture of polypeptides and free amino acids. Amino acids are not absorbed in this process. Next, the digested mixture is further hydrolyzed by trypsin into free amino acids, dipeptides, and tripeptides, which are further absorbed through smallintestinal lumen via several transport modes [
35]. Peptidases in the small intestine barrier also further hydrolyze peptides and affect their biological activity. Therefore, an
in vitro tissue-based model of everted sac gut was used to determine peptides absorption in this study. And total amino acid transport rate (
Figure 4A) and transport properties of peptides (
Figure 4B) were measured to evaluate intestinal absorption.
In the constructed verted sac model, amino acids undergo a transport process from the mucosal side (outside the sac) to the serosal side (inside the sac). The transport rate of total amino acids on the serosal side was calculated from the ratio of amino acids inside the sac to the amino acids outside the sac demonstrated in
Figure 4A. The peptide transport of digestion products from 0 min to 120 min was measured by Folin-phenol method, which was evaluated by calculating the ratio of peptide content of transported to the serosal side (inside the sac) to that of the simulated gastrointestinal digestion product, as shown in
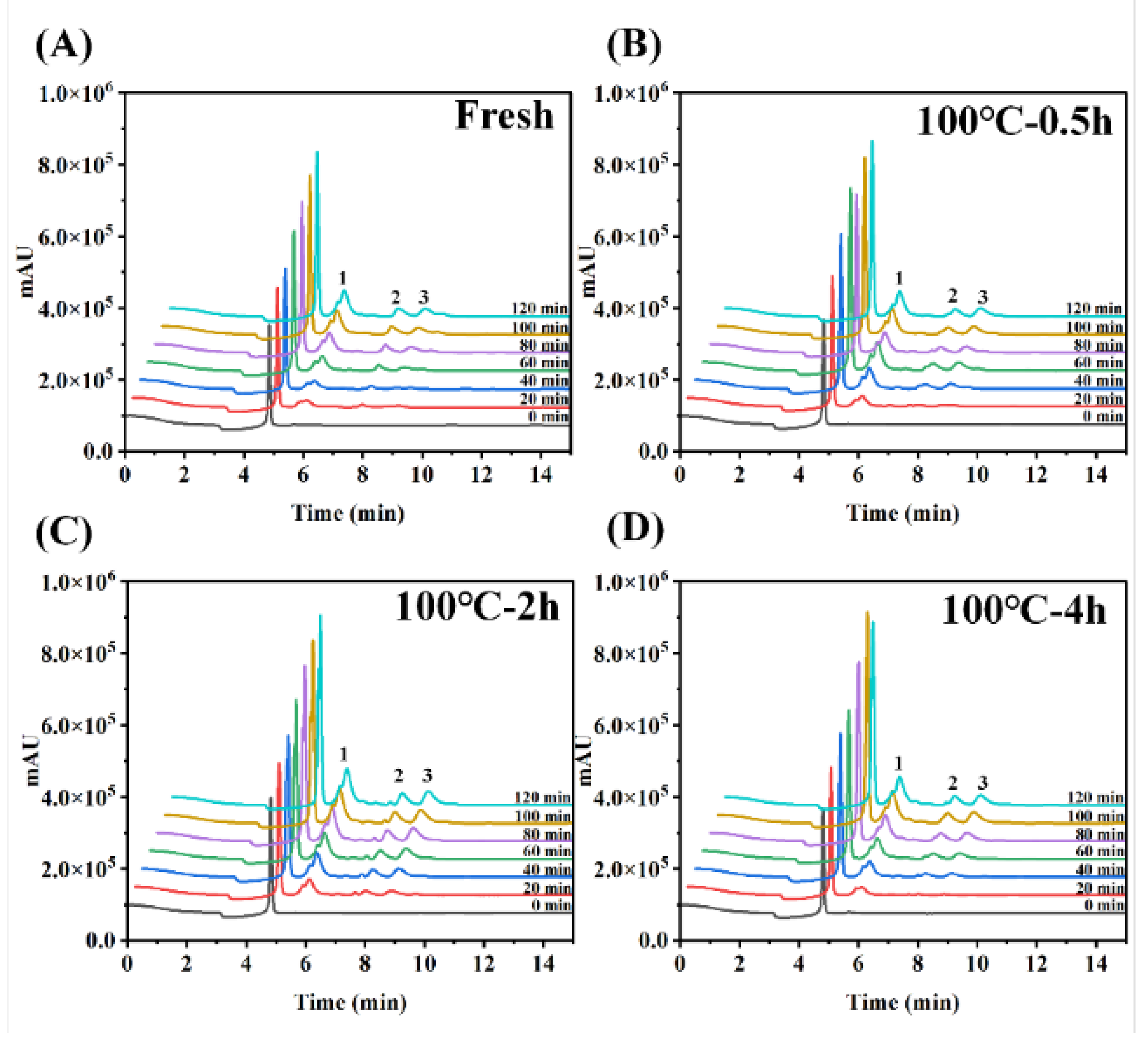
Figure 4B. Further, HPLC was used to determining peptide transport of SCBW with different boiling time in the everted sac model (
Figure 5 and
Figure 6).
With the prolongation of boiling time, total amino acids transport rate of protein digestion products of sea cucumber firstly intensified and then dropped. Moreover, the digestion products of 2 h-BSCBW showed the highest total amino acid transport rate (
Figure 4A). With the progress of incubation time, the peptides transport rate (
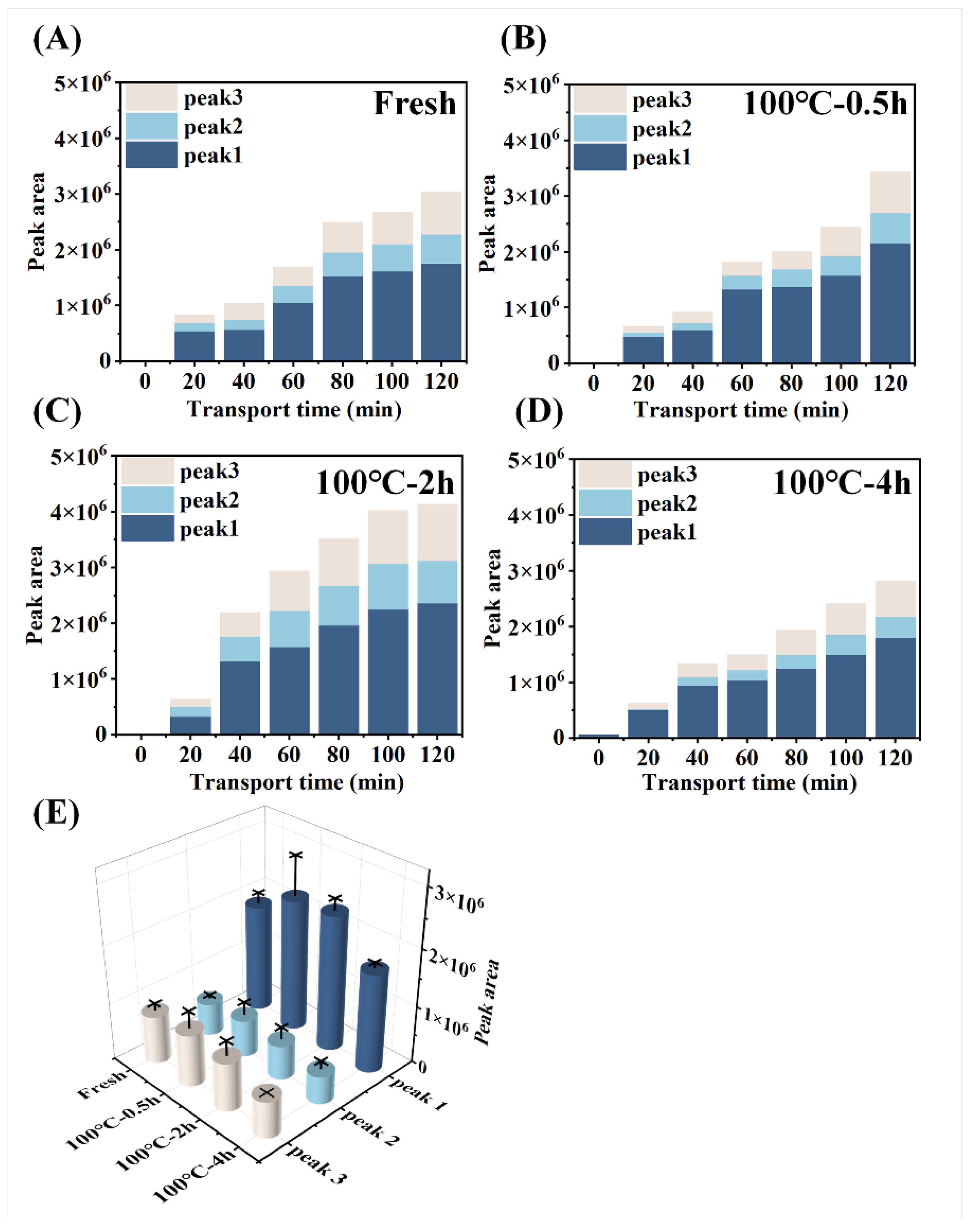
Figure 4B) and the peak area (
Figure 6A-D) of the three major peptide peaks of the chromatogram of serosal side samples (
Figure 5A-D) gradually increased. This suggested that peptide transport from mucosal side to the serosal side raised with pass of time. The heat treatments on SCBW improved the peptides transport. However, 4 h-heat treatments obviously dropped the peptides transport level (
Figure 6E).
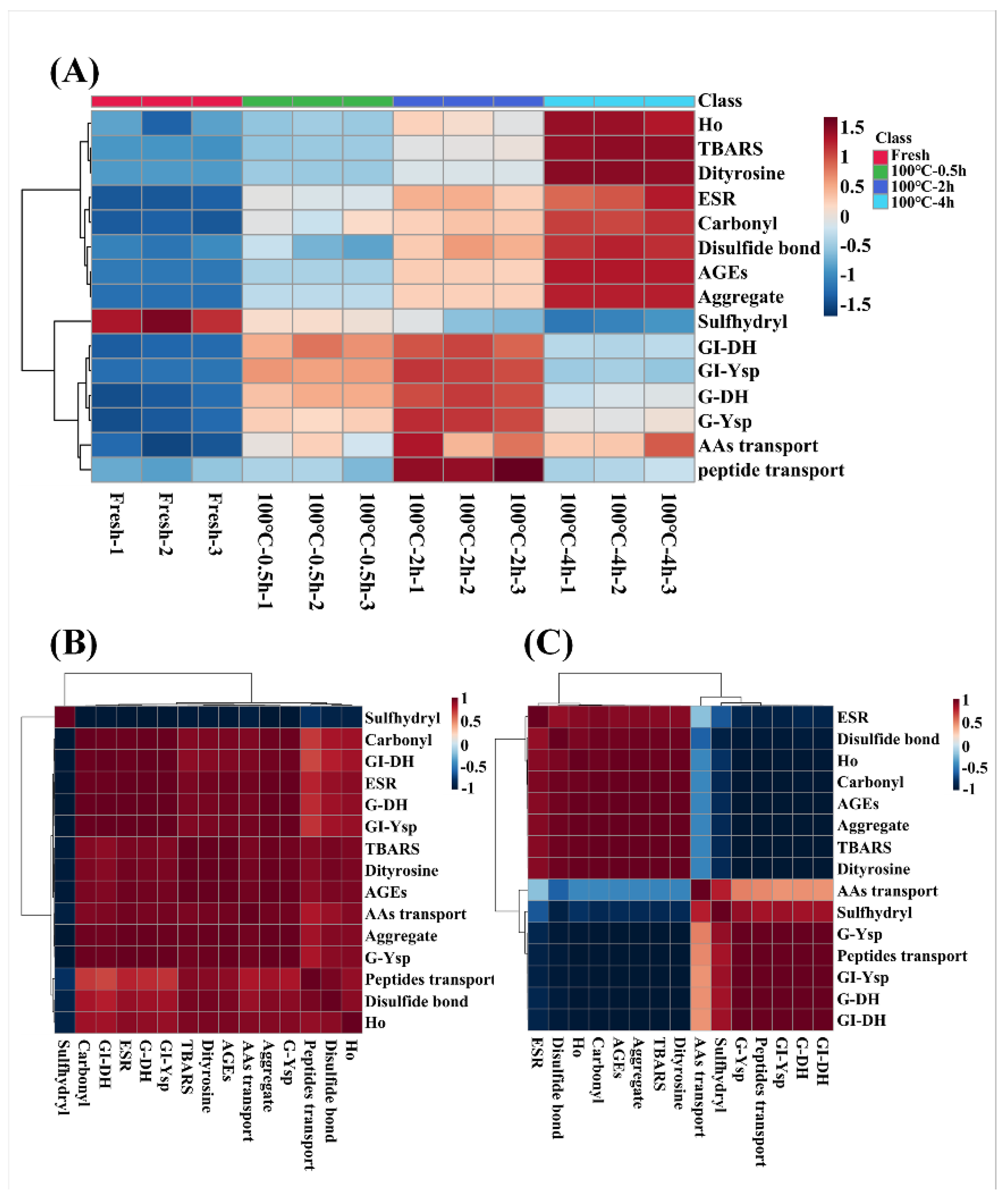
3.5. Heatmap and Correlation Analysis
Association between evaluation indexes of protein oxidation (free radical intensity, TBARS, carbonyl groups, S-H, S-S, dityrosine bonds, AGEs, Ho, and protein aggregation), gastrointestinal tract digestion levels (DH and Ysp) and transport levels (amino acid and peptide transport) of SCBW with different boiling time were analyzed intuitively in heat map, as shown in
Figure 7A. During boiling, the oxidation degree of sea cucumber protein showed a time-dependent increase. The levels of gastrointestinal tract digestion and transport of sea cucumber protein intensified first and then dropped, and the best digestion and transport properties were observed in 2 h-BSCBW.
Obviously, there was an inflection point in the change of digestion and transport properties at boiled-2 h. Therefore, sea cucumber samples before and after boiling for 2 h were selected respectively to conduct correlation analysis between their oxidative indicators, protein digestion and transport indicators, the result demonstrated in
Figure 7BC. The gastrointestinal tract digestion levels and transport levels of protein of fresh SCBW, 0.5 h-BSCBW and 2 h-BSCBW were positively correlated with oxidation degree (
Figure 7B). However, protein digestion and transport levels of 2 h-BSCBW and 4 h-BSCBW were negatively correlated with protein oxidation levels (
Figure 7C). In addition, protein digestion and transport showed an obvious positive correlation. Therefore, it could be considered that the oxidation degree of 2 h-BSCBW was appropriate, and promoted protein hydrolysis, improved the transport level of peptides and amino acids. On the contrary, excessive oxidative modification of 4 h-BSCBW resulted in inability of digestive enzymes to recognize sites, affecting protein hydrolysis and reducing transport levels.
In general, the heat procedures of aquatic muscle foods (such as shrimp, oysters, scallop, abalone etc.) include steaming, boiling, roasting, frying and baking. The above aquatic muscle foods mainly contain myofibrillar proteins, and their digestibility tend to decline after heat treatment. Microwave treatment (75-125 °C, 5-15 min) showed a negative effect on the peptides production and the protein digestibility of shrimp when compared with untreated samples [
27]. Steamed (100 °C, 10-15 min), baked (250 °C, 15-25 min) and fired (160 °C, 1.5-3 min) treatment harmed significantly the
in vitro digestibility and mineral bioaccessibility of raw oysters [
36]. Sea cucumber is rich in collagen, and its heat treatment and digestion properties are completely different from those of the aquatic muscle food mentioned above. Since type I collagen is an anti-digestion protein [
32], the
in vitro digestibility of fresh sea cucumber protein is much lower than that of aquatic muscle food. In addition, our previous study [
13] found that the hierarchy of collagen becomes loose after boiling for 0.5 h, which was manifested as collagen fibers depolymerization and collagen fibrils unfolding. After boiling for 2 h, collagen fibrils broke down into collagen microfibrils. And under the joint action of collagen gelatinization, a spongy network structure was formed. Therefore, it can be speculated that 2 h-heat treatment increased the action site of protease and was conducive to improve the degree of protein hydrolysis. However, excessive boiling (4 h) led to collapse of the gelatin network. This may belong to another sense of aggregation phenomenon, resulting in a large amount of protease action site covering, reducing the degree of hydrolysis. On the other hand, lower digestibility of proteins means less absorbed nutrient. Therefore, in this study, protein digestion and transport properties of sea cucumber protein first increased and then dropped with the extension of heat treatment time. And the best digestion and transport properties were observed in 2 h-BSCBW.
4. Conclusions
Boiling at 100 °C led to protein oxidation of SCBW, which was shown as increased free radical intensity, TBARS, carbonyl groups, disulfide bonds, dityrosine bonds, AGEs, protein hydrophobicity and aggregation, as well as decreases in free sulfhydryl group. Different from aquatic muscle food, collagen-rich sea cucumber still maintained an excellent spongy porous structure after boiling for 2 h at 100 °C. This may be due to the protein structure unfolding caused by moderate oxidation, providing action sites for protease and improving protein digestion and transport properties. In contrast, excessive oxidative modification of 4 h-BSCBW resulted in inability of digestion enzymes to recognize sites, affecting protein hydrolysis and reducing transport levels. Therefore, no matter from the perspective of texture or digestion and transport properties, boiling for 2 h at 100 °C can obtain sea cucumber products with better edible and digestible properties, which is considered to be a better processing condition.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M. Z.; Methodology, Y. L. and Z. W.; Validation, D. L. and D. Z.; Formal Analysis, M. Z.; Investigation, M. J. and P. J.; Resources, Y. L. and Z. W.; Data Curation, M. Z.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, M. Z.; Writing—Review & Editing, M. Z. and D. Z.; Visualization, Y. L.; Supervision, D. Z.; Project Administration, D. Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by “The National Natural Science Foundation of China (U1808203, 31901615)”, “Marine Economic Development Project of Liaoning Province (2022-47)”, “Dalian Science and Technology Innovation Fund Project (2019J11CY005)”, “Central Funds Guiding the Local Science and Technology Development (2020JH6/10500002)” and “High Level Talent Innovation and Entrepreneurship Program of Dalian (2021RQ087)”.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
We like to express our thanks to all the participants in the present research. All the authors confirmed there is no conflicts of interest.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. FIGIS list of species for fishery global production statistics. Available online: http://www.fao.org/fishery/statistics/en (accessed on 14 January 2022).
- Bhat, Z.F.; Morton, J.D.; Bekhit, A.E.A.; Kumar, S.; Bhat, H.F. Thermal processing implications on the digestibility of meat, fish and seafood proteins. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety 2021, 20, 4511–4548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlien, V.; Aalaei, K.; Poojary, M. M.; Nielsen, D. S.; Ahrne, L.; Carrascal, J. R. Effect of processing on in vitro digestibility (IVPD) of food proteins. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition 2021, 1–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bax, M. L.; Aubry, L.; Ferreira, C.; Daudin, J. D.; Santé-Lhoutellier, V. Cooking temperature is a key determinant of in vitro meat protein digestion rate: investigation of underlying mechanisms. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry 2012, 60, 2569–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santé-Lhoutellier, V.; Astrijc, T.; Marinova, P.; Greve, E.; Gatellier, P. Effect of meat cooking on physicochemical state and in vitro digestibility of myofibrillar proteins. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 2008, 56, 1488–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, B.; Rinnan, A.; Ruiz-Carrascal, J. Tracking hydrophobicity state, aggregation behaviour and structural modifications of pork proteins under the influence of assorted heat treatments. Food Research International, 2017, 101, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Promeyrat, A.; Gatellier, P.; Lebret, B.; Kajak-Siemaszko, K.; Aubry, L.; Sante-Lhoutellier, V. Evaluation of protein aggregation in cooked meat. Food Chemistry, 2010, 121, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santé-Lhoutellier, V.; Aubry, L.; Gatellier, P. Effect of oxidation on in vitro digestibility of skeletal muscle myofibrillar proteins. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2007, 55, 5343–5348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, Z. F.; Morton, J. D.; Bekhit, A. E. A.; Kumar, S.; Bhat, H. F. Emerging processing technologies for improved digestibility of muscle proteins. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 2021, 110, 226–239. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, S. Y.; Zhou, G. H; Li, L.; Xu, X. L.; Yu, X. B.; Bai, Y.; Li, C. B. Effect of cooking on in vitro digestion of pork proteins: a peptidomic perspective. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2015, 63, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S. W.; Wang, C.; Kim, Y. H. B.; Bian, G. L.; Han, M. Y.; Xu, X. L.; Zhou, G. H. Application of high-pressure treatment improves the in vitro protein digestibility of gel-based meat product. Food Chemistry, 2020, 306, 125602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C. S.; Tian, L.; Jiao, Y. D.; Tan, Y. Q.; Liu, C. N.; Luo, Y. K.; Hong, H. The effect of steam cooking on the proteolysis of pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas) proteins: digestibility, allergenicity, and bioactivity. Food Chemistry, 2022, 379, 132160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, Y. X.; Zhao, G. H.; Song, L.; Wu, Z. X.; Jiang, P. F.; Zhou, D. Y.; Zhu, B. W. Studying on effects of boiling on texture, microstructure and physiochemical properties of sea cucumber body wall and its mechanism using second harmonic generation (SHG) microscopy. Food Chemistry, 2023, 400, 134055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z. Q.; Li, D. Y.; Song, L.; Liu, Y. X.; Yu, M. M.; Zhang, M.; Rakariyatham, K.; Zhou, D. Y.; Shahidi, F. Effects of proteolysis and oxidation on mechanical properties of sea cucumber (Stichopus japonicus) during thermal processing and storage and their control. Food Chemistry, 2020, 330, 127248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, H. K.; Zhou, D. Y.; Hu, X. P.; Liu, Z. Y.; Song, L.; Zhu, B. W. Changes in lipid profiles of dried clams (Mactra chinensis Philippi and Ruditapes philippinarum) during accelerated storage and prediction of shelf life. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2018, 66, 7764–7774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y. G.; True, A. D.; Chen, J.; Xiong, Y. L. Dual role (anti- and pro-oxidant) of gallic acid in mediating myofibrillar protein gelation and gel in vitro digestion. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2016, 64, 3054–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, P.J.; Williams, S.C. Protein modification by thermal processing. Allergy 1998, 1998 S46, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J. N.; Shang, W. H.; Zhao, J.; Han, J. R.; Jin, W. G.; Wang, H. T.; Du, Y. N.; Wu, H. T.; Janaswamy, S.; Xiong, Y. L. Gelation and microstructural properties of protein hydrolysates from trypsin-treated male gonad of scallop (Patinopecten yessoensis) modified by κ-Carrageenan/K+. Food Hydrocolloids, 2019, 91, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matiacevich, S. B.; Buera, M. P. A critical evaluation of fluorescence as a potential marker for the Maillard reaction. Food Chemistry, 2006, 95, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelh, I.; Gatellier, P.; Santé-Lhoutellier, V. Technical note: a simplified procedure for myofibril hydrophobicity determination. Meat Science, 2006, 74, 681–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minekus, M.; Alminger, M.; Alvito, P.; Ballance, S.; Bohn, T.; Bourlieu, C.; Carriere, F.; Boutrou, R.; Corredig, M.; Dupont, D.; et al. A standardised static in vitro digestion method suitable for food-an international consensus. Food Function, 2014, 5, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, P. M.; Petersen, D.; Dambmann, C. Improved method for determining food protein degree of hydrolysis. Journal of Food Science 2001, 66, 642–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N. N.; Zhao, M. M.; Sun, W. Z. Effect of protein oxidation on the in vitro digestibility of soy protein isolate. Food Chemistry 2013, 141, 3224–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, F. W.; Hu, X. P.; Zhou, D. Y.; Ma, X. C.; Tian, X. G.; Huo, X. K.; Rakariyatham, K.; Shahidi, F.; Zhu, B. W. Hydrolysis and transport characteristics of tyrosol acyl esters in rat intestine. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2018, 66, 12521–12526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
-
Chinese Standard GB/T5009.124; Determination of amino acids in foods. 2003.
- Kelly, S. M.; Jess, T. J.; Price, N. C. How to study proteins by circular dichroism. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Proteins and Proteomics, 2005, 1751, 119–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Wang, J.; Raghavan, V. Impact of microwave processing on the secondary structure, in-vitro protein digestibility and allergenicity of shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) proteins. Food Chemistry, 2021, 337, 127811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F. F.; Du, X.; Wang, B.; Pan, N.; Xia, X. F.; Bao, Y. H. Inhibiting effect of ice structuring protein on the decreased gelling properties of protein from quick-frozen pork patty subjected to frozen storage. Food Chemistry, 2021, 353, 129104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zenker, H. E.; van Lieshout, G. A. A.; van Gool, M. P.; Bragt, M. C. E.; Hettinga, K. A. Lysine blockage of milk proteins in infant formula impairs overall protein digestibility and peptide release. Food Function 2020, 11, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketnawa, S.; Ogawa, Y. In vitro protein digestibility and biochemical characteristics of soaked, boiled and fermented soybeans. Scientific Reports 2021, 11, 14257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassompierre, M.; Borresen, T.; Sandfeld, P.; Ronsholdt, B.; Zimmermann, W.; McLean, E. An evaluation of open and closed systems for in vitro protein digestion of fish meal. Aquaculture Nutrition, 2015, 3, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhao, D.; Zhu, S. R.; Nian, Y. Q.; Xu, X. L.; Zhou, G. H.; Li, C. B. Overheating induced structural changes of type I collagen and impaired the protein digestibility. Food Research International, 2020, 134, 109225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, L.; Maudens, E.; Haisman, D. R.; Boland, M. J.; Singh, H. Microstructure and protein digestibility of beef: the effect of cooking conditions as used in stews and curries. LWT - Food Science and Technology, 2014, 55, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Olguin, M. A.; Beltran-Barrientos, L. M.; Hernandez-Mendoza, A.; Gonzalez-Cordova, A. F.; Vallejo-Cordoba, B. Current trends and perspectives on bioaccessibility and bioavailability of food bioactive peptides: in vitro and ex vivo studies. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2022, 102, 6824–6834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moughan, P. J. Protein: digestion, absorption and metabolism. “Encyclopedia of Food and Health.”; Massey University: Palmerston North, New Zealand, 2016; pp. 524–529. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S. S.; Feng, X.; Zhang, F.; Wang, R. F.; Zeng, M. Y. Effects of cooking methods on the Maillard reaction products, digestibility, and mineral bioaccessibility of Pacific oysters (Crassostrea gigas). LWT - Food Science and Technology, 2021, 141, 110943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Changes in oxidative indicators of sea cucumber body wall (SCBW) with different treatments. (A) electron spin resonance (ESR) spectrum; (B) free radical intensity; (C) thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS); (D) carbonyl content; (E) free sulfhydryl group content; (F) disulfide bonds; (G) dityrosine bonds; (H) fluorescence intensity and (I) AGEs. Values of different groups with different lowercase letters differ significantly (P < 0.05).
Figure 1.
Changes in oxidative indicators of sea cucumber body wall (SCBW) with different treatments. (A) electron spin resonance (ESR) spectrum; (B) free radical intensity; (C) thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS); (D) carbonyl content; (E) free sulfhydryl group content; (F) disulfide bonds; (G) dityrosine bonds; (H) fluorescence intensity and (I) AGEs. Values of different groups with different lowercase letters differ significantly (P < 0.05).
Figure 2.
Changes in (A) protein surface hydrophobicity and (B) protein aggregation of SCBW with different treatments. Values of different groups with different lowercase letters differ significantly (P < 0.05).
Figure 2.
Changes in (A) protein surface hydrophobicity and (B) protein aggregation of SCBW with different treatments. Values of different groups with different lowercase letters differ significantly (P < 0.05).
Figure 3.
Changes in gastric and gastrointestinal digestion of SCBW with different treatments. (A) proteolysis degree (BD, before digestion; GD, after gastric digestion; GID, after gastrointestinal digestion); (B) TCA-soluble peptide yield. Values of different groups with different letters differ significantly (P < 0.05).
Figure 3.
Changes in gastric and gastrointestinal digestion of SCBW with different treatments. (A) proteolysis degree (BD, before digestion; GD, after gastric digestion; GID, after gastrointestinal digestion); (B) TCA-soluble peptide yield. Values of different groups with different letters differ significantly (P < 0.05).
Figure 4.
Changes in (A) total amino acid transport rate and (B) peptide transport rate across everted-rat-gut sacs of SCBW with different treatments. Values of different groups with different letters differ significantly (P < 0.05).
Figure 4.
Changes in (A) total amino acid transport rate and (B) peptide transport rate across everted-rat-gut sacs of SCBW with different treatments. Values of different groups with different letters differ significantly (P < 0.05).
Figure 5.
The chromatographic profiles of fluid on the inside of everted-rat-gut-sac. The chromatogram of serosal fluid samples incubated with digestion product after 0, 20, 40, 60, 80, 100, 120-min incubation.
Figure 5.
The chromatographic profiles of fluid on the inside of everted-rat-gut-sac. The chromatogram of serosal fluid samples incubated with digestion product after 0, 20, 40, 60, 80, 100, 120-min incubation.
Figure 6.
Changes in the polypeptide content transported across the everted-rat-gut sacs. The peak area of serosal fluids incubated with (A) fresh SCBW, (B) 0.5 h-BSCBW, (C) 2 h-BSCBW and (D) 4 h-BSCBW digestion products. (E) The peak area of serosal fluids after 120 min incubation with different sea cucumber digestion products.
Figure 6.
Changes in the polypeptide content transported across the everted-rat-gut sacs. The peak area of serosal fluids incubated with (A) fresh SCBW, (B) 0.5 h-BSCBW, (C) 2 h-BSCBW and (D) 4 h-BSCBW digestion products. (E) The peak area of serosal fluids after 120 min incubation with different sea cucumber digestion products.
Figure 7.
The heatmap analysis and correlation analysis of protein oxidative indicators (free radicals, TBARS, carbonyl groups, sulfhydryl groups, disulfide bonds, dityrosine, AGEs, protein hydrophobicity (Ho), and aggregation), protein digestion properties (gastric degree of hydrolysis (G-DH) and gastrointestinal DH (GI-DH), and TCA-soluble peptide yield of gastric (G-Ysp) and gastrointestinal (GI-Ysp)) and transport properties (amino acid and peptide transport) of SCBW with different heat treatment. (A) the heatmap analysis of SCBWs with different treatments; (B) the correlation analysis between fresh SCBW, 0.5 h-BSCBW and 2 h-BSCBW; (C) the correlation analysis between 2 h-BSCBW and 4 h-BSCBW.
Figure 7.
The heatmap analysis and correlation analysis of protein oxidative indicators (free radicals, TBARS, carbonyl groups, sulfhydryl groups, disulfide bonds, dityrosine, AGEs, protein hydrophobicity (Ho), and aggregation), protein digestion properties (gastric degree of hydrolysis (G-DH) and gastrointestinal DH (GI-DH), and TCA-soluble peptide yield of gastric (G-Ysp) and gastrointestinal (GI-Ysp)) and transport properties (amino acid and peptide transport) of SCBW with different heat treatment. (A) the heatmap analysis of SCBWs with different treatments; (B) the correlation analysis between fresh SCBW, 0.5 h-BSCBW and 2 h-BSCBW; (C) the correlation analysis between 2 h-BSCBW and 4 h-BSCBW.
Table 1.
Changes in secondary structure of protein of SCBWs with different treatments.
Table 1.
Changes in secondary structure of protein of SCBWs with different treatments.
| % |
fresh |
100 °C -0.5 h |
100 °C -2 h |
100 °C - 4 h |
| α-helix |
37.50±3.25a |
28.10±5.52b |
7.33±1.11c |
0.27±0.25d |
| β-sheet |
18.87±6.30c |
39.40±8.79b |
52.83±1.11c |
55.17±0.80a |
| β-turn |
15.53±0.76a |
4.23±2.37b |
3.07±2.45b |
3.13±0.72c |
| random coil |
28.13±2.44a |
28.27±2.80a |
36.80±2.17b |
41.7±1.37b |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).