1. Introduction
Noncommunicable Diseases (NCDs) such as cardiovascular diseases, cancers, chronic respiratory diseases, and diabetes are the world’s largest cause of premature deaths. In 2008, more than 36 million people died annually from NCDs, including 14 million between the ages of 30 and 70. According to World Health Organization (WHO) projections, the total annual number of deaths from NCDs will increase to 55 million by 2030 [
1]. In Brazil, premature mortality rates from NCDs (30 to 69 year-olds) remained stable at 27% in 1990 and 28% in 2017. However, after 2015, the trend reversed, and projections for 2030 indicate increases [
2].
Most of these premature deaths are preventable, if health systems are able to respond more effectively to people’s healthcare needs. To reduce the mortality due to NCDs, the WHO established the Global Action Plan 2013-2020, which involves nine overarching principles [
1]. A tangible way to implement those principles is through the healthcare 4.0 paradigm or smart health (s-health).
Health services are offered in s-health by using context-aware sensing and network infrastructure. S-health can help to redefine and improve the healthcare system with technologies such as cloud computing, data-driven applications, artificial intelligence (AI), and the Internet of Things (IoT) by extending the digital capabilities in three main aspects: customization, user-oriented, and access to several services and knowledge [
3].
Thus, the central goal is to promote health in a distributed, decentralized, connected, and continuous fashion by reusing models and interactions with technologies in a convergent new paradigm of ubiquitous health (u-health). This can make medical care available anywhere through the use of the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) or Wearable IoMT (WIoMT), which are not visible to the user but present in an environment discreetly embedded and always available [
4].
WioMT are devices that interconnect wearable sensors to enable monitoring human factors of including health, wellness, behaviors, and other data useful to improve people’s everyday quality of life. They have been successfully applied, with different purposes, to clinical applications, as presented by [
5,
6,
7], and in the healthcare domain, as discussed by [
8,
9,
10,
11].
Researchers such as [
12,
13] have developed WIoMT for monitoring and prevention of NCDs. Their use in an s-health system is expected to provide long-term support and integrated care management for a specific disease. Consequently, several AI techniques can be used for inspection to retrieve patterns from data.
For that reason, this paper proposes an AI-based Chronic Disease Management (AI-CDM) platform as a widespread solution to deliver smart digital health services everywhere. Our platform interconnects biometric WIoMT devices with cloud services to enable data-driven AI models that detect useful patterns to efficiently address, manage, and support NCD prevention.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows. First, recent related works are briefly reviewed that focus on the identification of s-health systems and their technologies. Next, the proposed AI-based chronic disease management platform is described. Furthermore, implementation of a preliminary diabetes prediction case study of the proposed platform is provided. Then discussions, conclusions, and future directions are presented.
2. Smart Healthcare System: A Brief Review
To identify Smart Healthcare System (SHS) solutions and their related technologies, a literature search was carried out covering the period between 2019 to 2022. IEEEXplore Digital Library, ScienceDirect, ACM Digital Library, Springer Link, and PubMed as well as arXiv and Google Scholar were searched to find published articles. A search phrase combined keywords and Boolean operators as follows: chronic diseases AND smart health AND ubiquitous health AND artificial intelligence AND management. The search retrieved 19 articles that address technologies like IoT, cloud, and fog computing as well as machine learning and deep learning as AI methods.
[
14] provide a framework for orchestrating SHS. The framework has the following elements: temporal displacement of care through ICT infrastructure and integration of AI with IoT to enable analytical operations. [
15] explain that the s-health environment helps practitioners monitor the patient at home providing cloud-based services, implantable wearable medical devices, wireless sensor networks (WSN), IoT, and fog computing. As a result, these technologies create a new broad paradigm called ubiquitous s-health, organized in layers (edge or perception, access gateway, middle-ware, applications, and business) to connect entities.
Defining key technologies to support s-health, [
16] describe health services as an intelligent infrastructure using wearable devices, IoT, mobile internet, cloud computing, big data, 5G, microelectronics, and AI for actively managing and responding to medical ecosystem needs. [
17] establish IoT, cloud computing and big data as the three fundamental pillars for healthcare 4.0. Supplemental technologies such as 5G, radio frequency identification (RFID), WSN, and wireless body area networks (WBAN) support these pillars.
On the other hand, [
18] consider the transition from healthcare 4.0 to healthcare 5.0 (Hc5.0) through AI, IoT, fog computing, cloud computing, blockchain, sensors, 5G, and IoMT. [
19] designed a smart and pervasive health system (SPHS) to monitor patients with chronic illnesses. The main components of SPHS include ambient and wearable sensors, a decision-making module, and patient feedback for effective self-management.
Identifying the role of IoMT to develop an SHS, [
20] discovered that a SHS operates properly with the following integrated layers. The perception layer consists of sensor systems for data collection. The gateway layer establishes network communication and storage. The management layer processes massive raw data to extract relevant information using analytics, security controls, process modeling, and management. The application layer employs AI methods to monitor trends and changes.
A general architecture for IoMT focused on health monitoring is presented by [
21]. The solution includes three different levels. In the edge level, portable devices perform preprocessing and data acquisition throughout WBAN. In the fog level, servers/gateways gather data from edge devices to perform local processing and storage. In the cloud level, services are called for computing tasks.
The study of [
22] presents a patient-centric framework based on AI, blockchain, and wearable devices for applications in chronic disease management. [
23] discuss the current state-of-the-art of SHS, highlighting wearable and smartphone devices for health monitoring as well as machine learning (ML) for disease diagnosis. They also present an integrated software architecture to create SHS with the benefit of data analytics and AI tools.
A hybrid real-time remote monitoring (HRRM) framework is proposed by [
24]. HRRM consists of four layers. Layer 1 is responsible for gathering medical data with IoT devices. Layer 2 processes and aggregates the sensor data. Layer 3 acts as a personal information cloud repository for every patient monitored. Layer 4 contains components on both local and cloud sides used for knowledge extraction and classification of patient’s health status.
Detailed by [
25], an s-health monitoring system includes deep learning algorithms and data generated by IoMT devices. [
26] propose redefining healthcare with an architecture for patient monitoring that considers IoT and telemedicine for continuous online condition monitoring. [
27] discuss the role of ML as well as IoMT. The general architecture for IoMT systems consists of three levels, including the edge, where preprocessing is performed by devices; the fog, where data is collected from sensor networks and edge devices; and the cloud, which involves services for high-level computing tasks.
A framework for IoT-WBN with ML algorithms is proposed by [
28]. The framework has four layers. Layer 1 involves data acquisition from an IoT device. Layer 2 is the gateway between the data acquisition and layer 3. Layer 3 is a cloud where ML-based disease diagnosis is built. Layer 4 is the diagnosis alert generation. For an SHS wide-scale adoption, [
29] identify technical challenges in IoT device security and privacy, as well as standardization, authentication, information exchange, device communication, and data management. Some proposed AI algorithms for data analysis and mining are neural network, genetic algorithms, ant colony optimization, and simulated annealing.
[
30] discuss the state-of-the-art of deep learning (DL) based pervasive health monitoring focusing on human activity recognition and physiological monitoring. The two classes of DL architectures used are standard models, such as multi-layer perceptron (MLP), convolutional neural network, long short-term memory, deep belief network, and deep auto-encoder, and customized models, where more than one standard model is combined to improve performance.
[
31] present a health monitoring system that consists of four layers: physical measurements (sensing), extracting features (perception), data analysis (reasoning), and triggering alarms (actuation). Moreover, these authors classified real-time data analysis techniques into statistical and ML. Their findings indicate that ML is not a universal solution for all health domains; however, support vector machine is a predominant method. Among the application domains, cardiovascular disease is the most investigated.
Federated Learning (FL) is an AI distributed paradigm that coordinates multiple clients to perform training without sharing raw data. [
32] present a generic FL s-health process that includes the following steps: System initialization and client selection, where the aggregation server selects an analytic task along with model requirements; Distributed training and updates, where the server sends an initial model to the client to trigger the distributed training; and Model aggregation and download, in which, after receiving all updates, the server calculates a new version of the model and broadcasts it to all clients.
3. Proposed Approach for AI-CDM
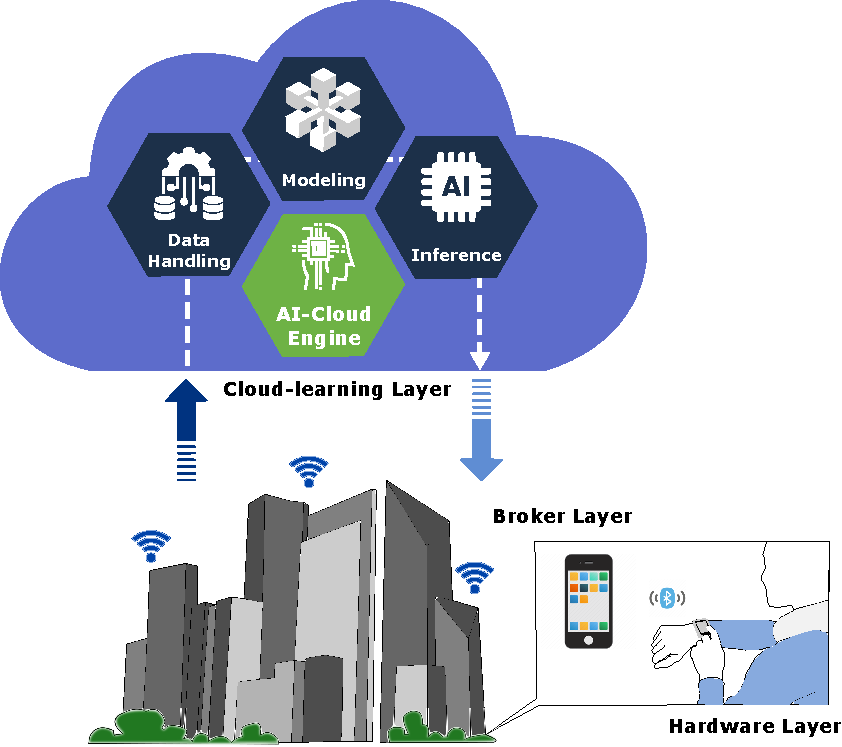
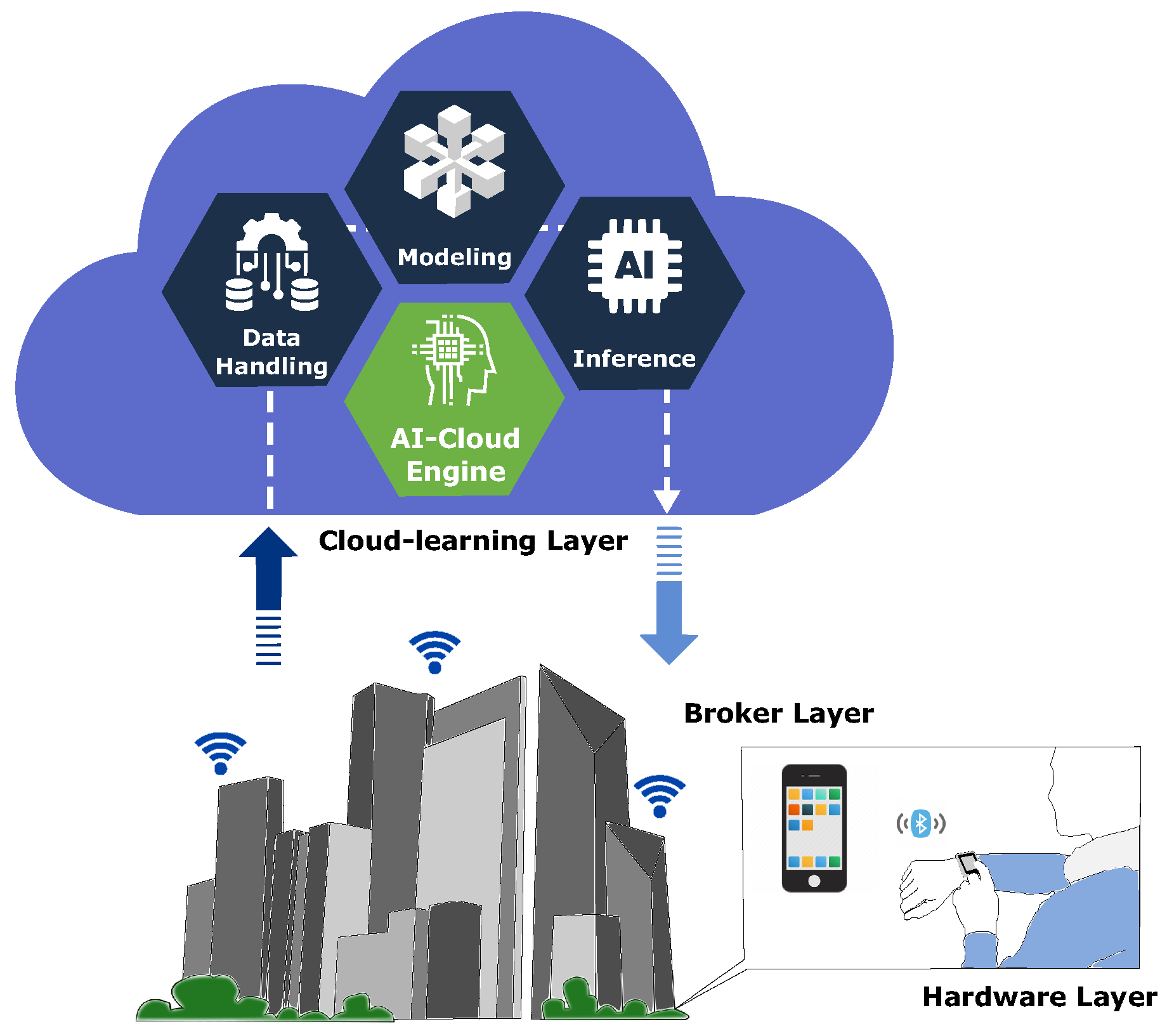
The related works helped identify the fundamental components to build an SHS such as AI, IoT, wearable devices, cloud computing, fog computing, edge computing, big data, mobile cloud, and blockchain. As shown in
Figure 1, the proposed AI-based chronic diseases management platform is organized into three separate layers: hardware, broker, and cloud learning.
The hardware layer collects the patient’s physiological data from the wearable device for further manipulation. The WIoMT devices in this layer contain sensors, a microcontroller, and a Bluetooth communication module. The broker layer receives data from the hardware layer. Thus, the acquired data are managed and temporarily saved before being sent to the next layer. Furthermore, the broker layer renders data from the cloud after AI model inference is performed.
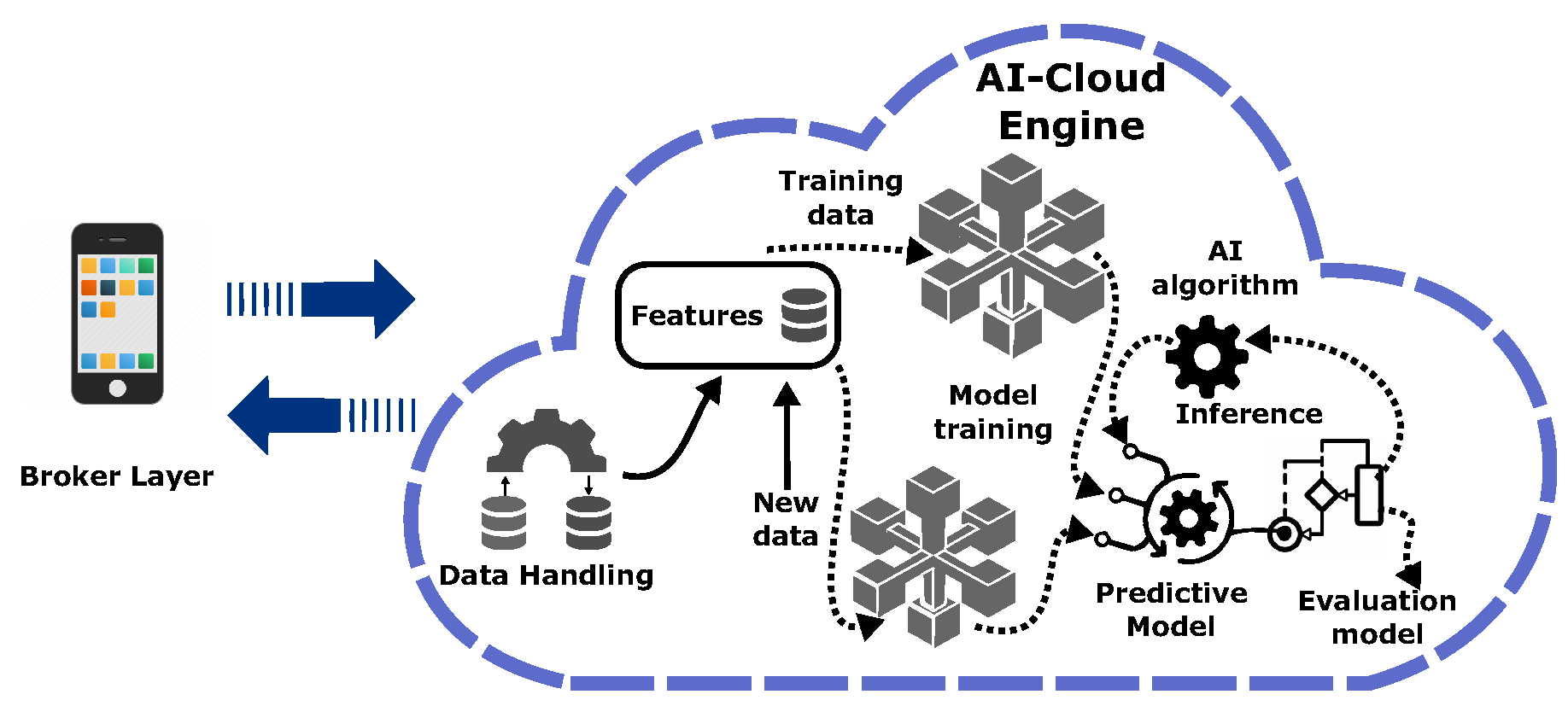
The final layer - cloud learning - links the broker layer with an inner AI-cloud engine, which implements three asynchronous components into a pipeline: data handling, modeling, and inference. Thus, the AI-cloud engine pulls in a large amount of data, processes it, trains models, and presents a result that interacts with the broker layer.
Each AI-cloud engine component has distinct roles, which work together to enhance learning of a new capability by reinforcing the wrong ones. Details of the three inner components are shown in
Figure 2 and are as follows. The data handling (DH) component accepts data from the broker layer and stores it in the cloud. DH also involves data conversion, scaling for standardization of attributes (features), and feature engineering to select and extract relevant features for the model to be developed.
The modeling component involves the selection and training of an appropriate algorithm for the problem statement to make predictions based on the available features. Thus, the trained model is used for inference. The inference component is responsible for making predictions on new unknown input data and returns an outcome. During the training, the algorithm generates a model with optimized parameters ready to be deployed for inference tasks. Thus, the model accepts the input data, executes it, and returns the predicted output. Inference does not reevaluate models, apply knowledge from the training, and use it to infer a result. Finally, the model result is transmitted to the broker layer.
4. Diabetes Prediction: A Case of Study
Diabetes management is more than just tracking markers, such as glycated hemoglobin. This section presents a closer look at the proposed AI-CDM platform in a diabetes prediction study case to demostrate how it can be managed. Initially, the hardware layer allows people with diabetes to monitor their blood glucose levels in real-time, sensing heterogeneous physiological parameters (bio-impedance, oxygen concentration, pulse rate, skin impedance, and skin temperature). A smartphone app (broker layer) stores the data temporarily and sends it to the cloud.
In the cloud, the platform performs data analysis, processing, and training then predicts fluctuations in glucose levels by applying an AI model. Thus, the results allow the patient to take corrective measures to maintain blood glucose levels within the preferred range. Moreover, AI algorithms habituate with the users’ physiology data and gradually become more accurate at predicting blood glucose as it amasses data from the user.
This case study presents an initial practical application of diabetes. The dataset used was generated by a homemade bio-impedance WIoMT multi-parametric meter prototype. Measurements were taken every 15 minutes for 2 hours. At the same time, capillary blood glucose was collected with a digital glucometer (®Accu-Check Guide) and samples of venous glucose with a spectrophotometer (®Bioplus BIO-2000).
In the first measurement, the volunteer fasted for 12 hours and then consumed a liquid substance containing 75 g of glucose to assess the glycemic response. There are 18 instances available in the dataset. The independent parameters for this dataset are bio-impedance, oxygen concentration, pulse rate, skin impedance, and skin temperature. The first step is to conduct feature scaling techniques for standardization before implementing AI model estimators. After the dataset is scaled, sequential feature selection is applied to reduce over-fitting and provide suitable performance on each AI model.
Several AI models were explored to predict blood glucose levels. The AI learning algorithms used to structure a baseline were multiple linear regression, support vector regressor, k-nearest neighbors regressor, decision tree regressor (DTR), Bagging DTR (B-DTR), random forest regressor (RFR), AdaBoost regressor (ABR), gradient boosting regressor, xgboost regressor, and MLP.
To train AI models, a random partitioning was created of the dataset split with an 80-20% ratio for training and testing sets, respectively. For the MLP neural network, the hyperparameters were fine-tuned using the grid-search algorithm to obtain the best parameters. Thus, MLP was implemented with two hidden layers (150 and 100 neurons), fully connected with a hyperbolic tangent activation function and quasi-newton optimizer.
For the performance evaluation of the different AI models, well-known regression metrics were implemented, including mean square error (MSE), root mean squared error (RMSE), and coefficient of determination (
).
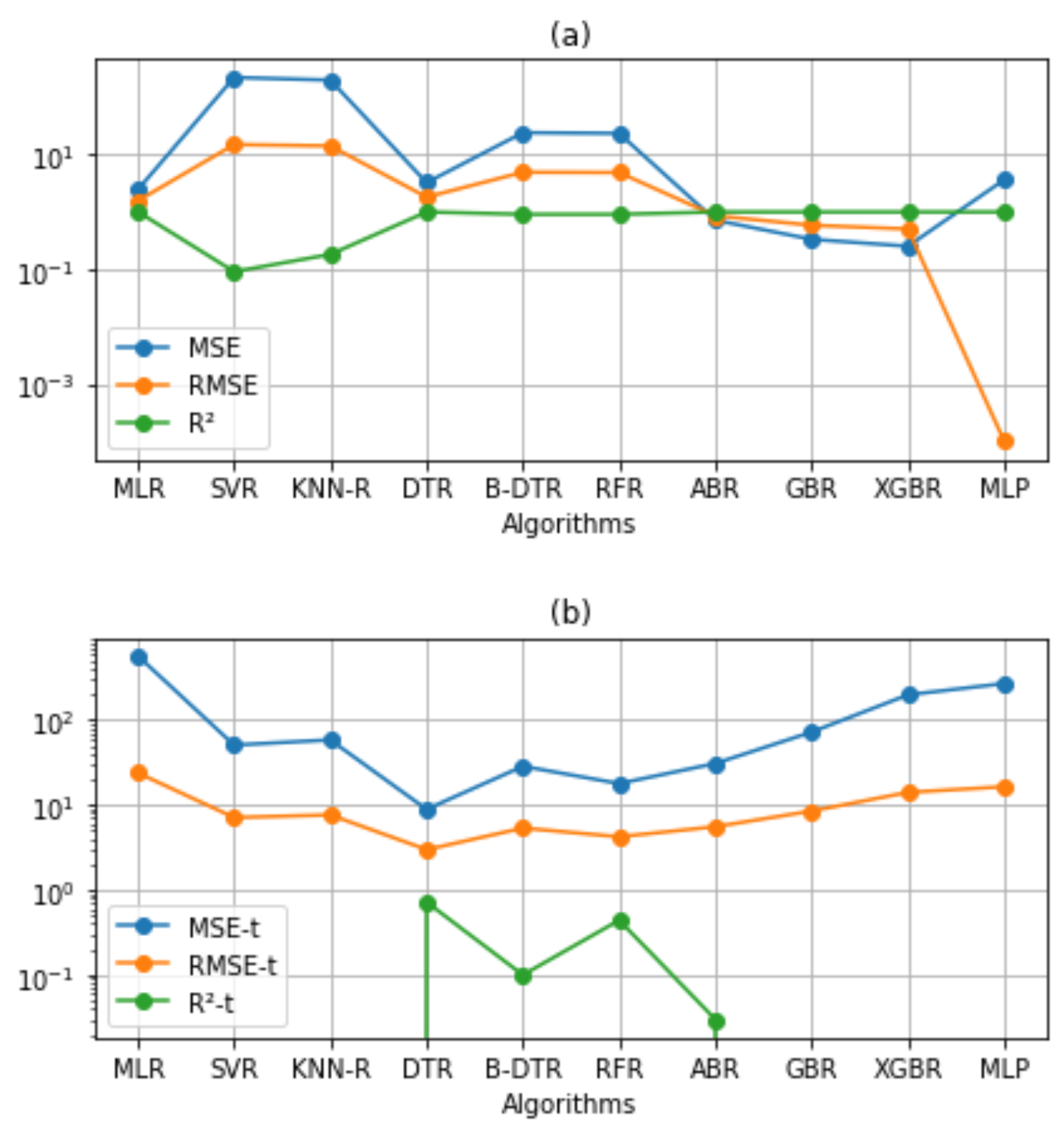
Figure 3 shows the performance of the AI model on the training and test sets. Comparision of the AI models elucidated that DTR and three ensemble methods (B-DTR, RFR, ABR) yielded slight improvement over the other models. Moreover, a comparison among these models revealed that DTR outperformed by a wide margin; 3.22, 1.80 in MSE; 0.99, 8.88 in RMSE; 2.98, 0.72 in (
), respectively, on training and test sets. RFR is the second best with 23.22, 4.82 in MSE, 0.90, 17.83 in RMSE, and 4.22, 0.44 in (
), respectively, on training and test sets.
On the one hand, the goal of decision trees is to create a model that predicts the value of a target variable by learning simple decision rules inferred from the data features. On the other hand, random forest is a meta-estimator that fits several classifying decision trees on various sub-samples of the dataset and uses averaging to improve the predictive accuracy and control over-fitting. In addition, ensemble methods combine the predictions of several base estimators built with a given learning algorithm to improve generalization, and robustness over a single estimator. In
Figure 4, the DTR outcome is compared with capillary blood glucose (FPG) acquired by the digital glucometer.
5. Discussions and Conclusions
The development and implementation of AI, IoT, and cloud-enabled technologies for a smart healthcare system feasibly allow monitoring of the blood glucose level in real-time to control diabetes and prevent serious consequences. This work proposed an AI-based chronic disease management platform. The proposed scenario connects WIoMT to the cloud server continuously through a smartphone app for real-time monitoring of physiological signals.
AI, as a computational method for automated learning from experience, enhances performance to deliver better predictions. This provides a conceived AI-based platform available for the prognosis of diabetes. The proposed AI platform analyses multiple physiological signal data to make an inference that could assist patients and physicians to make appropriate decisions for a clinical condition. The purpose of this study was to make AI-based diabetes prognosis available everywhere and for everyone without the requiring blood tests or visiting a hospital.
The vision is to provide accessible healthcare services promoting the tangible concepts of s-health. However, this is only a preliminary prognosis. The metrics performance of all AI models presented in the study case needs to be improved with extensive experiments, the size of dataset samples increased, and the diversification of volunteers extended. Moreover, strategies need to be done including tuning hyperparameters to influence how the parameters of the model will be updated and learned during training.
Ensemble methods could be promising, as observed in the preliminary results. Experiments with an expanded dataset combining knowledge of several models will provide a more accurate final result than the knowledge of any single one of them. In addition, a careful selection and manipulation of the data feature to make accurate predictions can boost the performance of the model by looking for a suitable feature that can be obtained as new knowledge. Thus, the performance of AI models could be improved, and the results could be more convenient.
Funding
Funding for this research was provided by FAPESC under the number 2021TR2264 (Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa e Inovação do Estado de Santa Catarina) and developed at UDESC (Universidade do Estado de Santa Catarina).
References
- WHO. Global action plan for the prevention and control of noncommunicable diseases 2013–2020; WHO Press: Geneva, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Malta, D.C.; Duncan, B.B.; Schmidt, M.I.; Teixeira, R.; Ribeiro, A.L.; Felisbino-Mendes, M.S.; Machado, I.E.; Velasquez-Melendez, G.; Brant, L.C.; Passos, V.M.; Nascimento, B.r.; Cousin, E.; Glenn, S.; Naghavi, M. Trends in mortality due to non-communicable diseases in the Brazilian adult population: National and subnational estimates and projections for 2030. Population Health Metrics 2020, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solanas, A.; Patsakis, C.; Conti, M.; Vlachos, I.S.; Ramos, V.; Falcone, F.; Postolache, O.; Perez-martinez, P.A.; Pietro, R.D.; Perrea, D.N.; Martinez-Balleste, A. Smart health: A context-aware health paradigm within smart cities. IEEE Communications Magazine 2014, 52, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnu, S.; Ramson, S.J.; Jegan, R. Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) - An overview. 2020 5th International Conference on Devices, Circuits and Systems (ICDCS), 2020, pp. 101–104. [CrossRef]
- Dunn, J.; Runge, R.; Snyder, M. Wearables and the medical revolution. Personalized Medicine 2018, 15, 429–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smuck, M.; Odonkor, C.A.; Wilt, J.K.; Schmidt, N.; Swiernik, M.A. The emerging clinical role of wearables: Factors for successful implementation in healthcare. npj digital medicine 2021, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Gayar, O.F.; Ambati, L.S.; Nawar, N. Wearables, Artificial intelligence, and the Future of Healthcare. In AI and Big Data’s Potential for Disruptive Innovation; Strydom, M., Buckley, S., Eds.; IGI Global: Pennsilvania, 2020; pp. 104–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yetisen, A.K.; Martinez-Hurtado, J.L.; Ünal, B.; Khademhosseini, A.; Butt, H. Wearables in Medicine. Advanced Materials 2018, 30, 1706910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casselman, J.; Onopa, N.; Khansa, L. Wearable healthcare: Lessons from the past and a peek into the future. Telematics and Informatics 2017, 34, 1011–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghi Mostafa, Thurow Kerstin, S. R. Wearable Devices in Medical Internet of Things: Scientific Research and Commercially Available Devices. Healthc Inform Res 2017, 23, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.M.A.; Mahgoub, I.; Du, E.; Leavitt, M.A.; Asghar, W. Wearable Devices in Medical Internet of Things: Scientific Research and Commercially Available Devices. npj Flexible Electronics 2021, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristoffersson, A.; Lindén, M. Wearable Sensors for Monitoring and Preventing Noncommunicable Diseases: A Systematic Review. Information 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabong Lyngdoh, L.E. Applications of Internet of things in Non-Communicable Disease Prevention and Management: A Review. Indian Journal of Public Health Research and Development 2018, 9, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, V.; Chakraborty, S. Real-time healthcare monitoring using smart systems: A step towards healthcare service orchestration Smart systems for futuristic healthcare. 2021 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Smart Systems (ICAIS), 2021, pp. 772–777. [CrossRef]
- Kulshrestha, V.; Verma, S. Chapter 10 - Role of trust in the ubiquitous healthcare system: Challenges and opportunities. In Sensors for Health Monitoring; Dey, N.; Chaki, J.; Kumar, R., Eds.; Academic Press, 2019; Vol. 5, Advances in ubiquitous sensing applications for healthcare, pp. 191–212. [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Yang, W.; Grange, J.M.L.; Wang, P.; Huang, W.; Ye, Z. Smart healthcare: Making medical care more intelligent. Global Health Journal 2019, 3, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aceto, G.; Persico, V.; Pescapé, A. Industry 4.0 and Health: Internet of Things, Big Data, and Cloud Computing for Healthcare 4.0. Journal of Industrial Information Integration 2020, 18, 100129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbunge, E.; Muchemwa, B.; Jiyane, S.; Batani, J. Sensors and healthcare 5.0: Transformative shift in virtual care through emerging digital health technologies. Global Health Journal 2021, 5, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopalan, R. Smart and Pervasive Health Systems—Challenges, Trends, and Future Directions. Advances in Information and Communication, 2020, pp. 408–419.
- Dwivedi, R.; Mehrotra, D.; Chandra, S. Potential of Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) applications in building a smart healthcare system: A systematic review. Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research 2022, 12, 302–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, L.; Percannella, G.; Ritrovato, P.; Tortorella, F.; Vento, M. Trends in IoT based solutions for health care: Moving AI to the edge. Pattern Recognition Letters 2020, 135, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Lu, L.; Gao, F.; jiang He, S.; juan Zhao, H.; Fang, Y.; ming Yang, J.; An, Y.; wei Ye, Z.; Dong, Z. Integration of Artificial Intelligence, Blockchain, and Wearable Technology for Chronic Disease Management: A New Paradigm in Smart Healthcare. Current Medical Science 2021, 41, 1123–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr, M.; Islam, M.M.; Shehata, S.; Karray, F.; Quintana, Y. Smart Healthcare in the Age of AI: Recent Advances, Challenges, and Future Prospects. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 145248–145270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.K.; El Desouky, A.I.; Elghamrawy, S.M.; Sarhan, A.M. A Hybrid Real-time remote monitoring framework with NB-WOA algorithm for patients with chronic diseases. Future Generation Computer Systems 2019, 93, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujith, A.; Sajja, G.S.; Mahalakshmi, V.; Nuhmani, S.; Prasanalakshmi, B. Systematic review of smart health monitoring using deep learning and Artificial intelligence. Neuroscience Informatics 2022, 2, 100028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi, G.J.; Ghonge, M.; Obaid, A.J. Cloud based IoT Smart Healthcare System for Remote Patient Monitoring. EAI Endorsed Transactions on Pervasive Health and Technology 2021, 7, e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, A.; Mishra, S.; González-Briones, A. Integration of Machine Learning and IoT in Healthcare Domain. In Hybrid Artificial Intelligence and IoT in Healthcare; Kumar Bhoi, A.; Mallick, P.K.; Narayana Mohanty, M.; Albuquerque, V.H.C.d., Eds.; Springer Singapore, 2021; pp. 223–244. [CrossRef]
- Awotunde, J.B.; Folorunso, S.O.; Bhoi, A.K.; Adebayo, P.O.; Ijaz, M.F. Disease Diagnosis System for IoT-Based Wearable Body Sensors with Machine Learning Algorithm. In Hybrid Artificial Intelligence and IoT in Healthcare; Kumar Bhoi, A.; Mallick, P.K.; Narayana Mohanty, M.; Albuquerque, V.H.C.d., Eds.; Springer Singapore, 2021; pp. 201–222. [CrossRef]
- Zeadally, S.; Siddiqui, F.; Baig, Z.; Ibrahim, A. Smart healthcare: Challenges and potential solutions using internet of things (IoT) and big data analytics. PSU Research Review 2020, 4, 149–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulemtafes, A.; Khemissa, H.; Derki, M.S.; Amira, A.; Djedjig, N. Deep learning in pervasive health monitoring, design goals, applications, and architectures: An overview and a brief synthesis. Smart Health 2021, 22, 100221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paganelli, A.I.; Mondéjar, A.G.; da Silva, A.C.; Silva-Calpa, G.; Teixeira, M.F.; Carvalho, F.; Raposo, A.; Endler, M. Real-time data analysis in health monitoring systems: A comprehensive systematic literature review. Journal of Biomedical Informatics 2022, 127, 104009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.C.; Pham, Q.V.; Pathirana, P.N.; Ding, M.; Seneviratne, A.; Lin, Z.; Dobre, O.; Hwang, W.J. Federated Learning for Smart Healthcare: A Survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2022, 55, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).