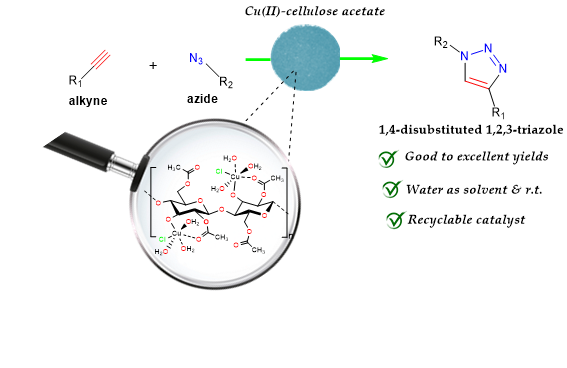
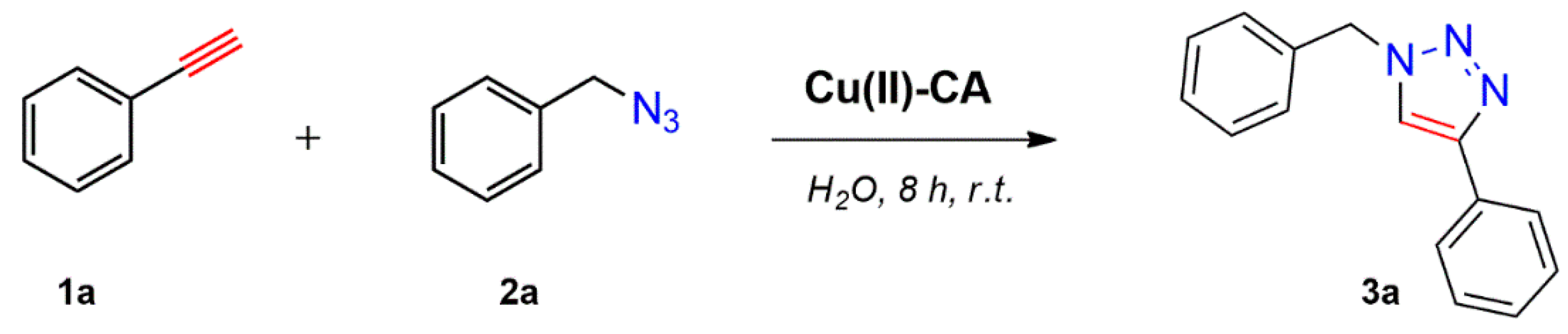1. Introduction
Recently, the preparation, characterization, and catalytic activity of heterogeneous catalyzed reactions have been reviewed focusing on their positive and negative points as well as on using bio-heterogeneous catalytic systems that involve biological macromolecules, such as cellulose, alginate, chitosan etc, as biosupports for metal catalysts [
1,
2]. The great interest in sustainable chemistry has led to the investigation of natural resources such as biopolymers. Among the most abundant naturally-occurring and biodegradable polymers, cellulose known by its large number of interesting structure related properties was utilized in various industrial applications, specifically in water treatment, cosmetics, and the industry of paper [
3,
4,
5]. The introduction of functional groups on the cellulose structure has attracted great attention due to the possibility of modification of the chemical and physical properties of the cellulose surface [
6,
7,
8], and their ability to catch metal ions being one of the best methods to introduce the eco-friendly character of the heterogeneous catalysts [
9,
10,
11,
12]. Since its introduction by Sharpless, the click chemistry concept is reported to feature a high regioselectivity, high yields, and only low reaction times for the synthesis of a great variety of organic molecules with a potential application [
13]. The copper-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition reaction (CuAAC) is the well-known reaction in the click chemistry regime. It is an excellent ligation process for the selective synthesis of 1,4-disubstituted-1,2,3-triazoles [
14,
15]. Triazole derivatives are excellent candidates in medicinal chemistry [
16], biological science [
17], and material chemistry [
18]. In this regard, the development of new catalysts to afford 1,2,3-triazole moiety with high yields under sustainable conditions has increased in recent decades [
19,
20,
21]. We report here the heterogenization of copper(II) ions on cellulose acetate (CA)
via the coordination of copper(II) by carbonyl and other oxygen-containing groups on the CA surface. The obtained catalyst (Cu(II)-CA) is highly active and regioselective in synthesis of the corresponding 1,4-disubstituted-1,2,3-triazoles at room temperature using water as solvent. The heterogeneity and reusability of the prepared sustainable catalyst have also been investigated.
2. Results
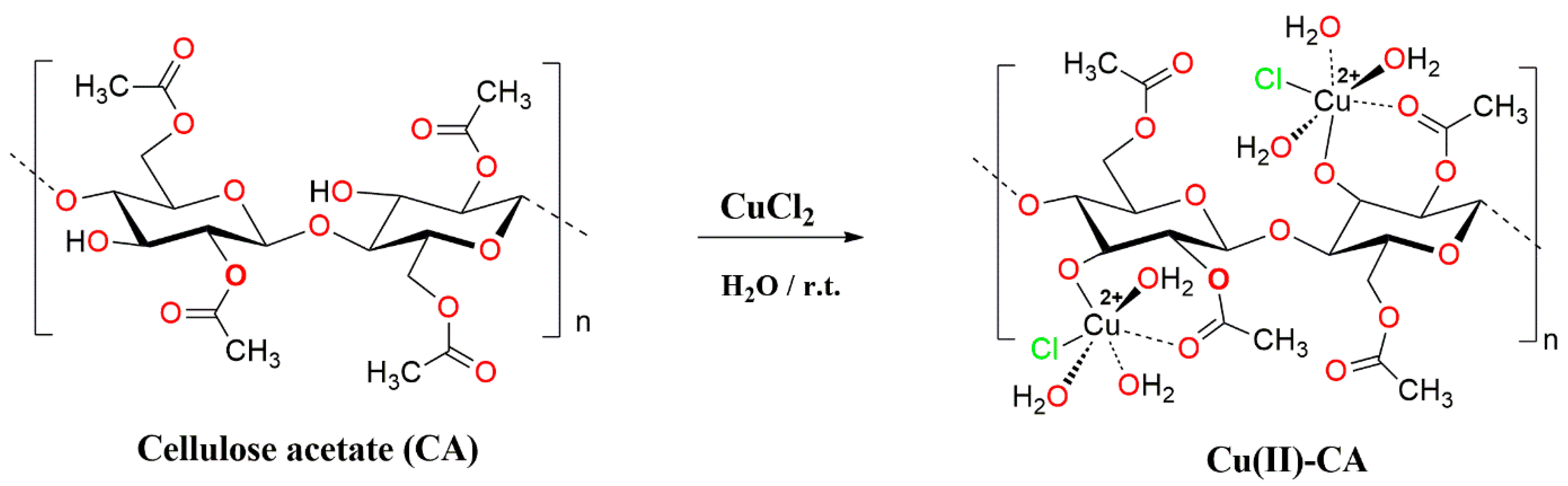
The immobilization of copper(II) ions on the cellulose acetate (CA) surface was conducted
via a simple complexation process by using copper(II) chloride dihydrate as a source of copper(II) and water as solvent at room temperature. In fact, this immobilization reaction occurs through a complexation reaction between Cu(II) ions and both carbonyl oxygen and hydroxyl groups as donors on the CA surface (
Scheme 1). The ICP analysis was performed to determine the contents of copper(II) ions in the Cu(II)-CA catalyst that was found to be 0.72 % w/w. The morphology and structural investigations of the prepared Cu(II)-CA catalyst were carried out by means of FTIR, UV-Vis, Scanning Electronic Microscopy (SEM), and Energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) spectroscopy.
2.1. Characterisation of the Cu(II)-Catalyst
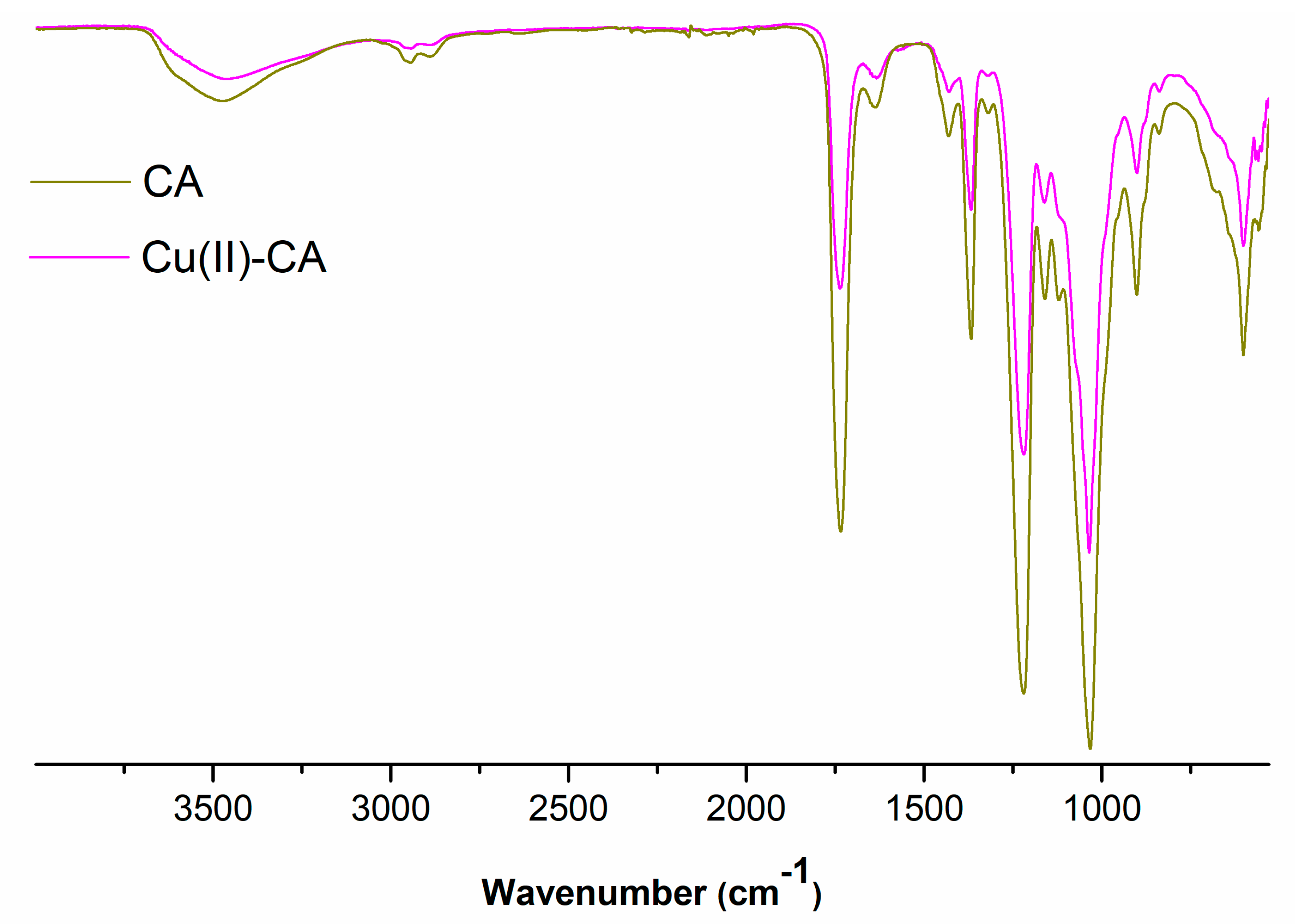
Cellulose acetate (CA) before and after its complexation reaction with copper(II) ions was analysed by FTIR in order to get more insights on the chemical structure of the prepared catalyst. The obtained results are summarized in
Figure 1. The FTIR spectrum of the pure CA in the high frequency region shows a broad band centred at ca. 3500 cm
-1 which is related to OH groups plus other absorption peaks at 2948 and 2880 cm
-1 due to C-H stretching vibrations. The peaks at 1733 and 1431cm
-1 are assigned to the C=O stretching and C-O-H in-plane bending at C6, respectively. Other absorptions around 1366 cm
-1 are attributed to C-O-H bending at C2 or C3. Finally, the absorption peaks at 1215 and 902 cm
-1 are attributed to C-O-C stretching of the β-(1-4) glycosidic linkage, which is the characteristic link in the cellulose structure. As far as the infrared spectrum of Cu(II)-CA is concerned, no new bands appeared, the only change being the intensity of all characteristic bands of CA, confirming the interaction of functional ester and hydroxyl groups from CA with copper(II) ions, see
Figure 1.
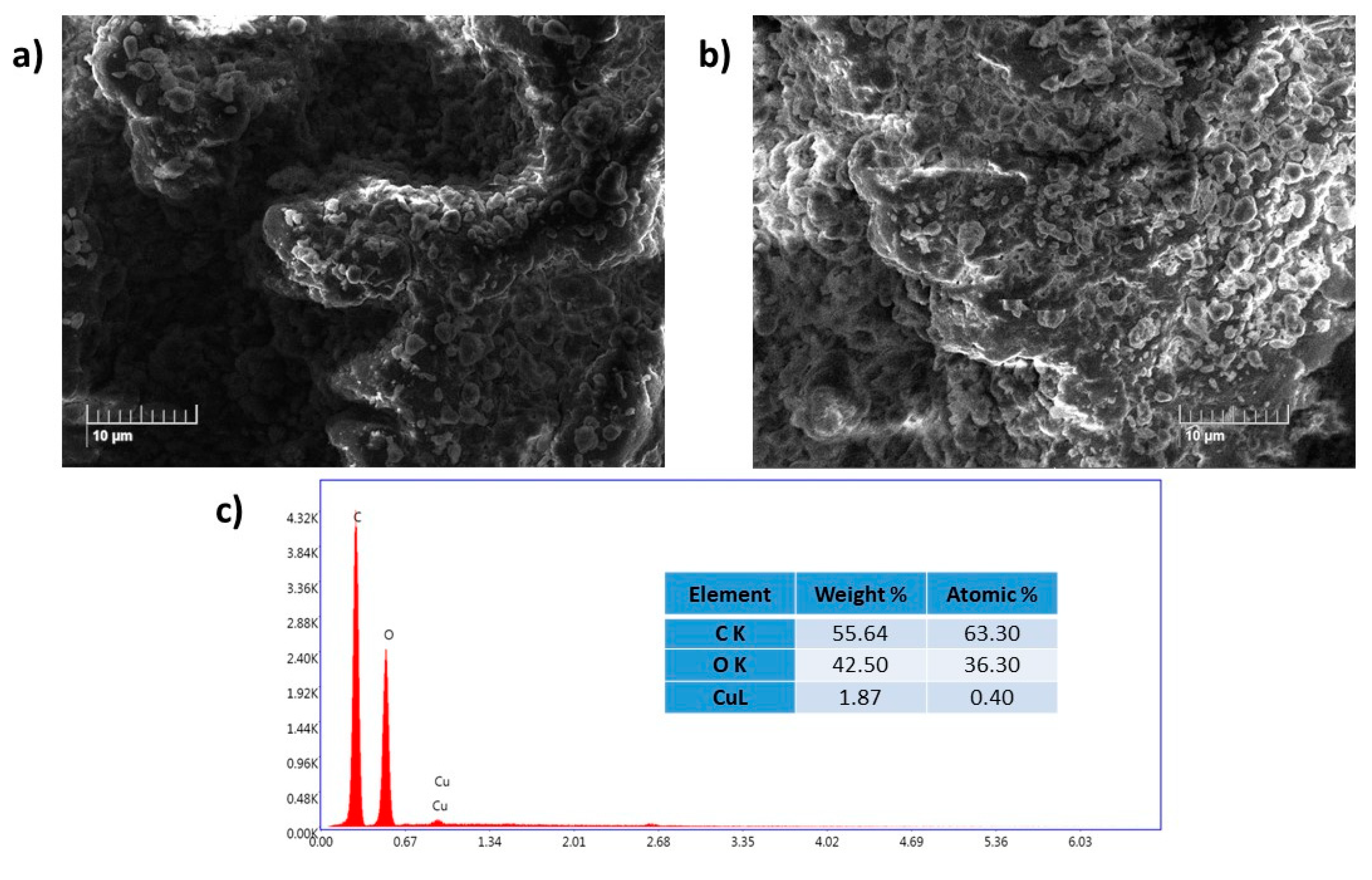
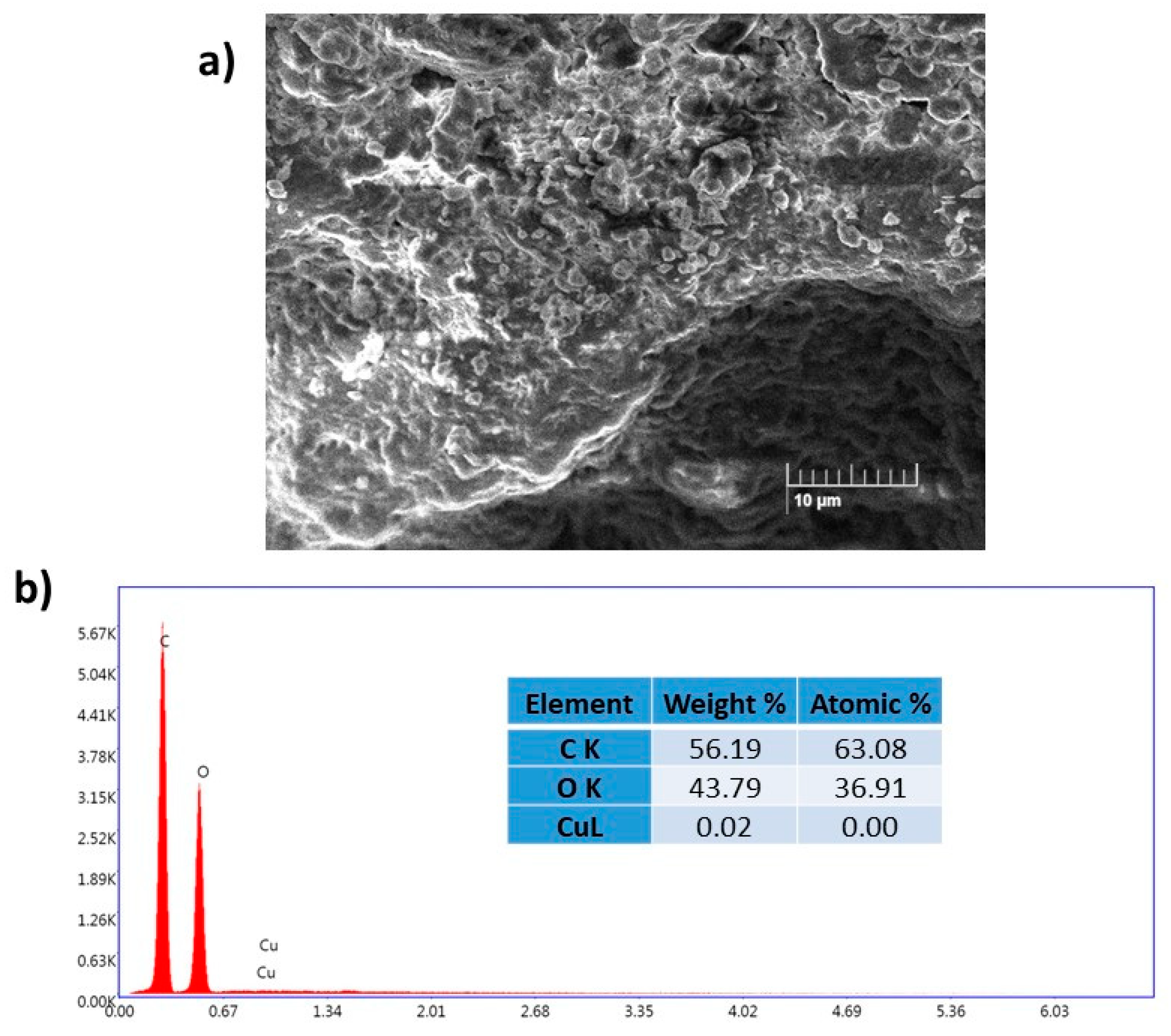
The morphology and surface analysis of the obtained Cu(II)-CA catalyst was performed through SEM and EDX techniques (see
Figure 2). The SEM image for the pure cellulose acetate shows no homogeneous surface with the presence of a microporous pattern, indicating the ability of this material to adsorb metal ions (
Figure 2a) [
22,
23,
24]. In the case of the Cu(II)-CA catalyst, the SEM image shows a low dispersity of copper (
Figure 2b), and the absence of the metal aggregate which is due to the high solubility of copper(II) chloride in water, reducing the interaction of copper(II) ions with the functional groups on the cellulose acetate surface. The amount of copper on the surface of the polysaccharide cellulose acetate was examined by EDX analysis. The obtained result confirms the presence of copper in the Cu-CA catalyst and the copper loading of 1.87 wt% (
Figure 2c). The difference between the obtained copper loading by ICP and EDX analyses is that EDX analysis can measure only the copper which is present on the surface of the cellulose acetate but it is unable to detect the copper loading inside of this polysaccharide polymer.
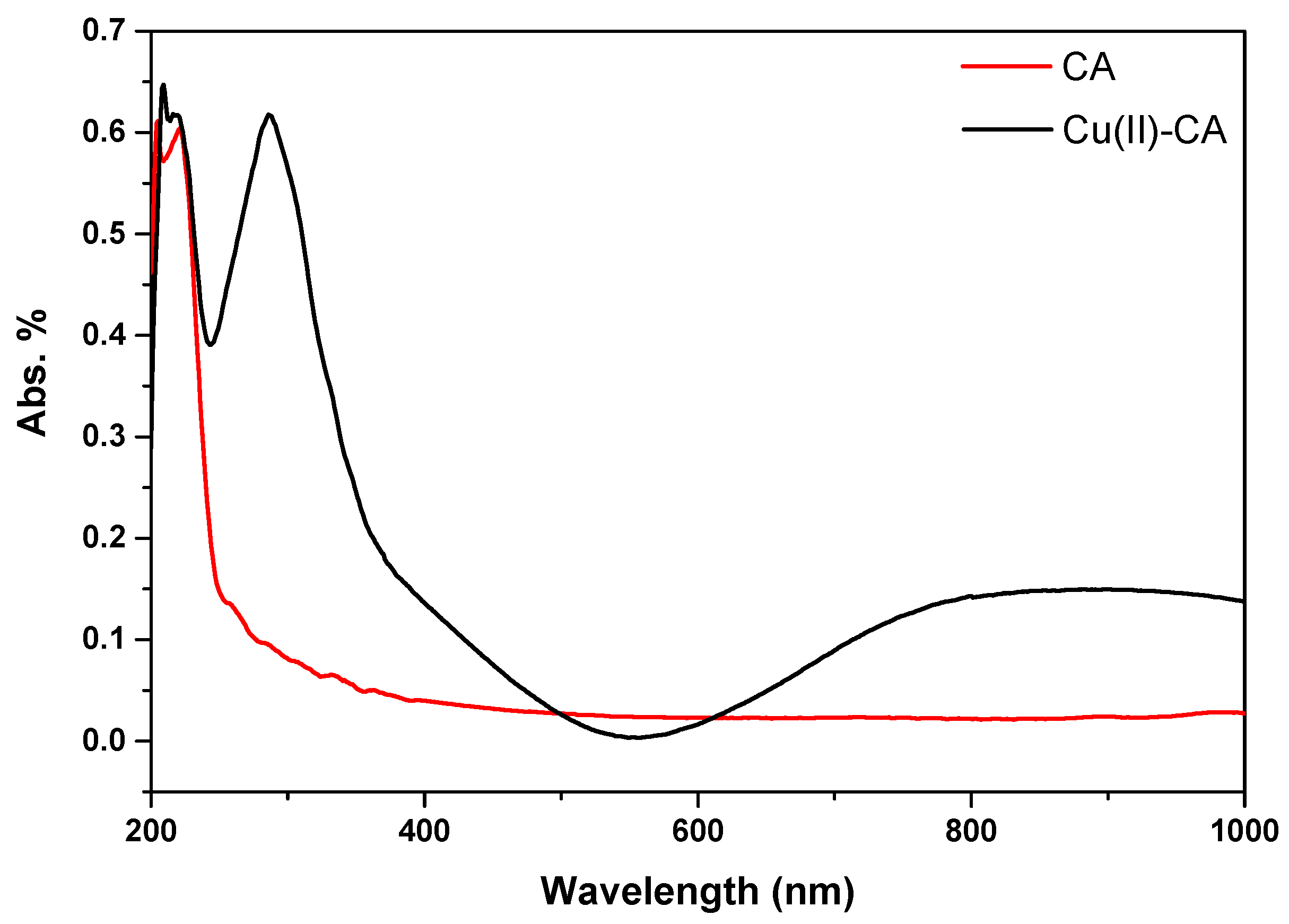
The optical characteristics of the Cu(II)-CA catalyst were also investigated by UV-Vis spectroscopy in the solid state. As shown in
Figure 3, no absorption was located in the case of the pure cellulose acetate between 200 to 1000 nm. Meanwhile, the UV-Vis analysis of the Cu(II)-CA catalyst shows the occurrence of two new bands. The first one which is located in the UV domain at around 290 nm (
Figure 3) is attributed to the presence of the Cu-O bond. [
25,
26,
27]. The other one is a broad band located around 800 nm and it is attributed to d-d transitions of copper(II) ions immobilized on the cellulose acetate polysaccharide.
2.2. Catalytic tests
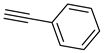
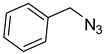
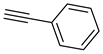
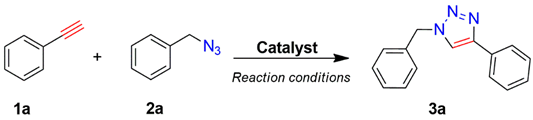
The prepared material, Cu(II)-CA, was then tested in CuAAC reactions under strict click reaction conditions. As a model reaction, the one between phenylacetylene (
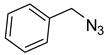
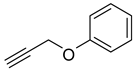
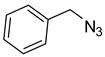
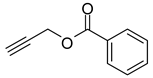
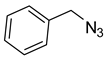
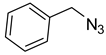
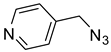
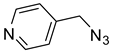
1a) and benzyl azide (
2a) was selected for a systematic evaluation under various conditions (
Scheme 2).
The experimental results show that the use of CuCl
2 only affords a moderate yield of the desired product (
3a) after 24 h at room temperature (
Table 1). Importantly, the Cu(II)-CA catalyst leads to a selective synthesis of one regioisomer triazole derivative, 1,4-disubstituted 1,2,3-triazole, in an excellent yield (99%) at room temperature using water as solvent. Subsequently, the effect of the amount of the catalyst on the efficiency of the catalyzed CuAAC reaction was also investigated (
Table 1). The use of 3 mol% of Cu(II)-CA leads to an excellent yield after only 8 h, and the decreasing of catalyst loading is not good for CuAAC reactions. However, no significant promotion in the yield was observed increasing the amount of catalyst to 10 mol%. Also, when the reaction temperature was increased to 60 °C, the results show that this Cu(II)-CA catalyst led to an excellent yield (> 90%) within 4 h (
Table 1, entries 16-21). The long reaction time (~ 8 h) in the CuAAC reaction using Cu(II)-CA catalyst is due to the reaction rate for the formation of copper(I), the catalytic species for CuAAC reaction, which is pgenerated by the reduction of Cu(II) by terminal alkyne
via the oxidative alkyne homocoupling reaction [
28]. Alkyne and azide derivatives were then investigated in the CuAAC reaction by using the Cu(II)-CA catalyst in water at room temperature (
Table 2). In all cases, the different azides and terminal alkynes bearing either electron-donating, electron-withdrawing, or heterocycle substituents have not any significant effect using this catalyst, and the desired products are well achieved in excellent yields. Moreover, the obtained 1,2,3-triazoles did not require any further purification by conventional methods as confirmed by their analysis by 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopy (see Supporting Information).
2.3. Reusability of Cu(II)-CA catalyst
To examine the recyclability and stability of the prepared catalyst in the CuAAC reaction, a model reaction was chosen between phenylacetylene (
1a) and benzyl azide (
2a) under the optimized reaction conditions (
Scheme 3). The results show that a moderate yield was obtained after three cycles (62%) and also a lack of non-change selectivity (
Table 3). The morphology of the reused catalyst was examined by SEM and EDX analyses after four cycles (
Figure 4). The results show that the morphology of the fresh and reused Cu(II)-CA catalyst are almost similar. Moreover, the copper percentage in the reused catalyst was also investigated by EDX analysis and the results show a low amount of copper on the surface of the recovered Cu(II)-CA catalyst which can explain the low yield achieved after 4 cycles. The reusability, catalytic activity, and biocompatibility of this Cu(II)-CA catalyst make it a potential candidate not only for CuAAC reactions but also for other copper-catalyzed organic reactions.
2.4. Heterogeneity test
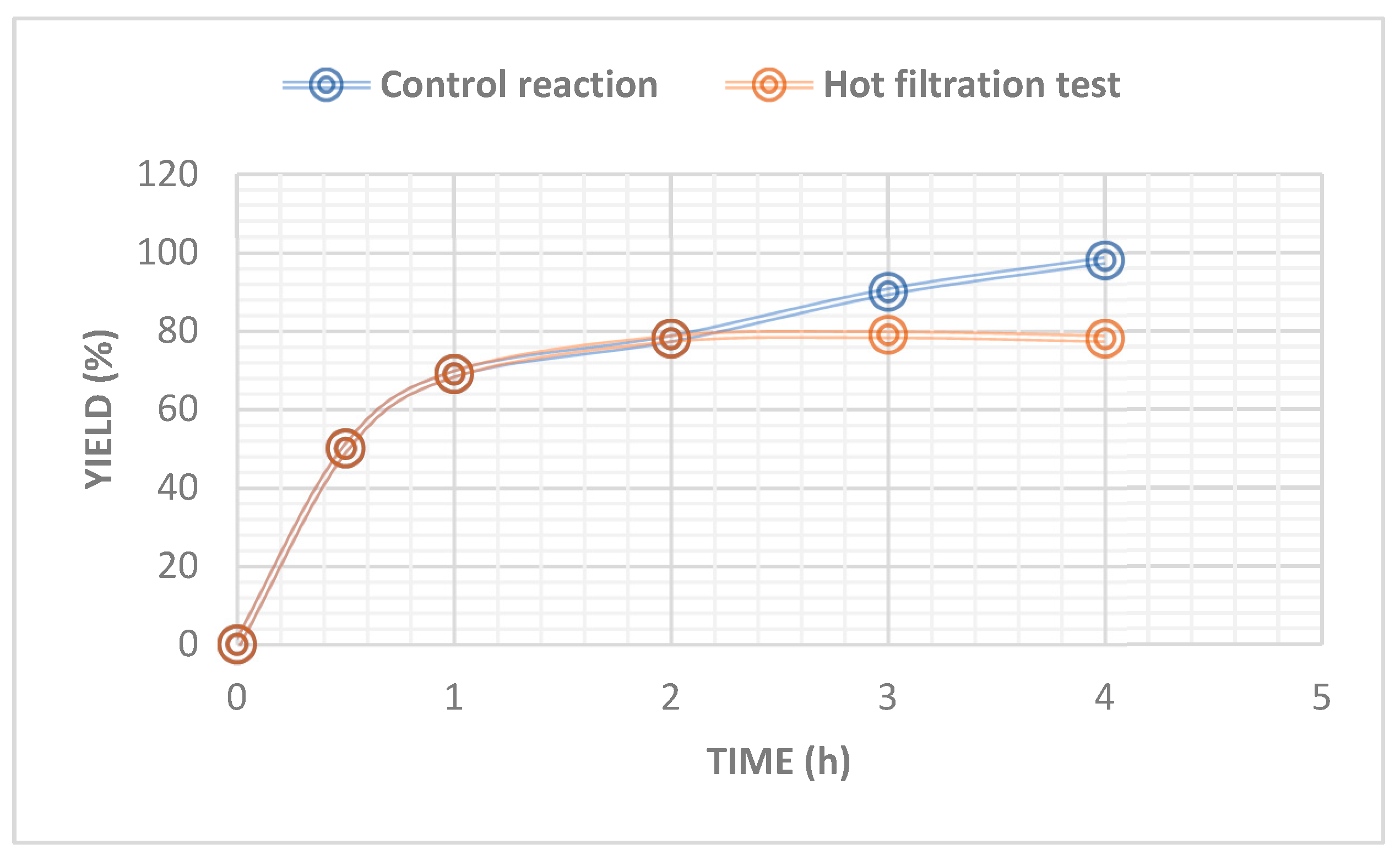
The heterogeneity test of the prepared catalyst for the CuAAC reaction was also investigated through a hot filtration test (
Figure 5). The cycloaddition reaction between benzyl azide and phenylacetylene in the presence of the prepared catalyst was performed in a reaction tube at 60 °C using water as solvent. At reaction halftime; the CuAAC reaction was stopped and then the catalyst was removed by hot filtration. The reaction filtrate was then stirred at the same reaction temperature for a further reaction time of 2 h. The results confirm that no corresponding 1,2,3-triazole was obtained after the hot filtration of the catalyst, unveiling the heterogeneous nature of the Cu(II)-CA catalyst.
2.5. Comparison with other catalytic methods
To illustrate the merits of the Cu(II)-CA catalyst in the CuAAC reaction, its catalytic activity was compared with other reported catalytic systems. The CuAAC reaction between phenylacetylene (
1a) and benzyl azide (
2a) was chosen as the model reaction to get more light on the efficiency of our catalytic system. As shown in
Table 4, the Cu(II)-CA catalyst is similar to the Cu(II) ions complexed with the naturally occurring biopolymers as well as with the modified biopolymer. Excellent results were observed compared to the Cu(II)-polyethyleneimine both in the reactivity and reaction time. Moreover, the formation of copper(I), which is the catalytic species for the CuAAC reaction, does not require an external reducing reagent in our case. All these qualities confirm that this catalyst is a good eco-friendly candidate for other organic synthesis reactions catalyzed by Cu(II)/Cu(I) ions.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General experimental information
All used reagents in this investigation were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. The thin layer chromatography (TLC) plate (Merck Kieselgel 60 F254) was used to monitor the catalytic reactions. All obtained products were characterized through 1H and 13C NMR analysis by using the BRUKER DRX-300 AVANCE spectrometer and CDCl3 as solvent. FT-IR spectra were taken on a Nicolet spectrophotometer 5700. The scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images were obtained by means of an electron microscopy Philips XL-30 ESEM coupled to Tescan Vega-3 w/ EDX.
3.2. Preparation of the Cu(II)-Catalyst
The complexation process between cellulose acetate and copper(II) ions was achieved by the addition of cellulose acetate (1 g) to an aqueous solution of copper(II) chloride dihydrate ([CuCl2] = 0.093 mol/L in 10 mL of water). The resulting mixture was stirred overnight at room temperature and the obtained biomaterial was filtered off, washed with water, and then dried overnight. The copper(II)-containing cellulose acetate was characterized by FT-IR, SEM-EDX, UV-Vis, and ICP spectroscopy.
3.3. Catalytic synthesis of 1,2,3-triazole derivatives
The corresponding azides(0.6 mmol) and alkyne (0.5 mmol) derivatives plus 3 mol% of Cu(II)-CA catalyst were added to 3 mL of water under continuous magnetic stirring at room temperature and the reaction was monitored by TLC. After the reaction completion, the resulting mixture was then diluted by adding ethyl acetate. The catalyst was recovered by simple filtration and then washed, dried, and stored for the next cycle. The solvent of the organic phase was then removed under vacuum to afford the pure corresponding 1,2,3-triazole derivatives (3a-i).
4. Conclusion
In conclusion, the preparation and the characterization via the immobilization of copper(II) ions on the cellulose acetate (CA) (Cu(II)-CA) were investigated. The Cu(II)-CA catalyst was characterized by FT-IR, UV-Vis, SEM, EDX, and ICP analyses. Such a catalyst exhibits high catalytic activity and selectivity for the synthesis of 1,4-disubstituted-1,2,3-triazoles via CuAAC reaction using water as solvent at room temperature. The stability and heterogeneity of this catalyst were explained by the coordination of carbonyl and hydroxyl groups of the cellulose acetate with copper(II) ions. The simple separation of 1,2,3-triaoles, the t reusability and heterogeneity of this catalyst, the various substrate scope, and the use of water as reaction medium make this catalyst more competitive for sustainable CuAAC reactions. In the light of these features, one can anticipate that this Cu(II)-CA material will be a very useful catalytic material in others copper-mediated organic reactions under mild eco-friendly reaction conditions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.L., S.-E. S; methodology, B. L., S.-E.S.; investigation, and analysis, B.L., K.O., E.B., M.T.; supervision B.L. and M. T. writing original draft B.L. M. J. and S.-E.S.; writing-review and editing B. L., M. J., S.-E.S. All authors have and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dong, K.; Sun, Q.; Tang, Y.; Shan, C.; Aguila, B.; Wang, S.; Meng, X.; Ma, S.; Xiao, F.-S. Bio-Inspired Creation of Heterogeneous Reaction Vessels via Polymerization of Supramolecular Ion Pair. Nat Commun 2019, 10, 3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Yip, A.C.K. Heterogeneous Catalysis: Enabling a Sustainable Future. Frontiers in Catalysis 2021, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaouf, S.; El Barkany, S.; Amhamdi, H.; Jilal, I.; El Ouardi, Y.; Abou-salama, M.; Loutou, M.; El-Houssaine, A.; El Ouarghi, H.; El Idrissi, A. Low Degree of Substitution of Cellulose Acrylate Based Green Polyelectrolyte: Synthesis, Characterization and Application to the Removal of Cu (II) Ions and Colloidal Fe(OH)3 Turbidity. Materials Today: Proceedings 2020, 31, S175–S182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essaghraoui, A.; Khatib, K.; Hamdaoui, B.; Brouillette, F.; Ablouh, E.-H.; Belfkira, A. Handsheet Coated by Polyvinyl Acetate as a Drug Release System. Journal of Pharmaceutical Innovation 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athukoralalage, S.S.; Balu, R.; Dutta, N.K.; Choudhury, N.R. 3D Bioprinted Nanocellulose-Based Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering Applications: A Brief Review. Polymers 2019, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Li, H.; Li, B.; Liu, M.; Zhan, H. Characteristics and Properties of Cellulose Nanofibers Prepared by TEMPO Oxidation of Corn Husk. BioResources 2016, 11, 5276–5284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Kuboyama, K.; Fukuzumi, H.; Ougizawa, T. PMMA/TEMPO-Oxidized Cellulose Nanofiber Nanocomposite with Improved Mechanical Properties, High Transparency and Tunable Birefringence. Cellulose 2018, 25, 2393–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, H.; Saito, T.; Kitaoka, T.; Nogi, M.; Suganuma, K.; Isogai, A. Transparent, Conductive, and Printable Composites Consisting of TEMPO-Oxidized Nanocellulose and Carbon Nanotube. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 1160–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, H. Celluloses as Green Support of Palladium Nanoparticles for Application in Heterogeneous Catalysis: A Brief Review. J Clust Sci 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, S.; Khattab, T.A. Recent Advances in Cellulose Supported Metal Nanoparticles as Green and Sustainable Catalysis for Organic Synthesis. Cellulose 2021, 28, 4545–4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riva, L.; Lotito, A.D.; Punta, C.; Sacchetti, A. Zinc- and Copper-Loaded Nanosponges from Cellulose Nanofibers Hydrogels: New Heterogeneous Catalysts for the Synthesis of Aromatic Acetals. Gels 2022, 8, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.-E.; Lim, S.; Pang, Y.-L.; Ong, H.-C.; Lee, K.-T. Synthesis of Biomass as Heterogeneous Catalyst for Application in Biodiesel Production: State of the Art and Fundamental Review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2018, 92, 235–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, H.C.; Finn, M.G.; Sharpless, K.B. Click Chemistry: Diverse Chemical Function from a Few Good Reactions. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2001, 40, 2004–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutz, J.-F.; Zarafshani, Z. Efficient Construction of Therapeutics, Bioconjugates, Biomaterials and Bioactive Surfaces Using Azide-Alkyne “Click” Chemistry. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2008, 60, 958–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seath, C.P.; Burley, G.A.; Watson, A.J.B. Determining the Origin of Rate-Independent Chemoselectivity in CuAAC Reactions: An Alkyne-Specific Shift in Rate-Determining Step. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2017, 56, 3314–3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirumurugan, P.; Matosiuk, D.; Jozwiak, K. Click Chemistry for Drug Development and Diverse Chemical–Biology Applications. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 4905–4979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katerina, I.S.; Lozan, T.T.; Nataliya, P.B.; Mauricio, A.P.; Irena, P.K. Developments in the Application of 1,2,3-Triazoles in Cancer Treatment. Recent Patents on Anti-Cancer Drug Discovery 2020, 15, 92–112. [Google Scholar]
- Nandikolla, A.; Srinivasarao, S.; Khetmalis, Y.M.; Kumar, B.K.; Murugesan, S.; Shetye, G.; Ma, R.; Franzblau, S.G.; Sekhar, K.V.G.C. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel 1,2,3-Triazole Analogues of Imidazo-[1,2-a]-Pyridine-3-Carboxamide against Mycobacterium Tuberculosis. Toxicology in Vitro 2021, 74, 105137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Yip, A.C.K. Heterogeneous Catalysis: Enabling a Sustainable Future. Frontiers in Catalysis 2021, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bystrzanowska, M.; Petkov, P.; Tobiszewski, M. Ranking of Heterogeneous Catalysts Metals by Their Greenness. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 18434–18443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ablouh, E.-H.; Bahsis, L.; Sehaqui, H.; Anane, H.; Julve, M.; Stiriba, S.-E.; El Achaby, M. TEMPO-Oxidized-Cellulose Nanofibers-Immobilized Copper(II) Foam as an Efficient Heterogeneous Catalyst for the Azide-Alkyne Reaction in Water. Sustainable Chemistry and Pharmacy 2022, 30, 100837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, D.T.; Ribeiro, I.H.S.; Pereira, D.H. DFT Study of the Application of Polymers Cellulose and Cellulose Acetate for Adsorption of Metal Ions (Cd2+, Cu2+ and Cr3+) Potentially Toxic. Polym. Bull. 2020, 77, 3443–3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Wu, M.; Liu, R.; Li, Y.; Wang, D.; Tan, J.; Wu, R.; Huang, Y. Electrospun Membrane of Cellulose Acetate for Heavy Metal Ion Adsorption in Water Treatment. Carbohydrate Polymers 2011, 83, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atmani, H.; Zazouli, S.; Ezzahra Bakkardouch, F.; Laallam, L.; Jouaiti, A. Insights into Interactions of Cellulose Acetate and Metal Ions (Zn2+, Cu2+, and Ag+) in Aqueous Media Using DFT Study. Computational and Theoretical Chemistry 2021, 1202, 113322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, J.; Siddiq, M.; Akram, B.; Ashraf, M.A. In-Situ Synthesis of CuO Nanoparticles in P(NIPAM-Co-AAA) Microgel, Structural Characterization, Catalytic and Biological Applications. Arabian Journal of Chemistry 2018, 11, 897–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culica, M.E.; Chibac-Scutaru, A.L.; Melinte, V.; Coseri, S. Cellulose Acetate Incorporating Organically Functionalized CeO2 NPs: Efficient Materials for UV Filtering Applications. Materials 2020, 13, 2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, O.; Bhagat, M.; Gopalakrishnan, C.; Arunachalam, K.D. Ultrafine Dispersed CuO Nanoparticles and Their Antibacterial Activity. Journal of Experimental Nanoscience 2008, 3, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindhu, K.S.; Anilkumar, G. Recent Advances and Applications of Glaser Coupling Employing Greener Protocols. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 27867–27887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahsis, L.; Ablouh, E.-H.; Anane, H.; Taourirte, M.; Julve, M.; Stiriba, S.-E. Cu(II)-Alginate-Based Superporous Hydrogel Catalyst for Click Chemistry Azide–Alkyne Cycloaddition Type Reactions in Water. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 32821–32832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajender Reddy, K.; Rajgopal, K.; Lakshmi Kantam, M. Copper-Alginates: A Biopolymer Supported Cu(II) Catalyst for 1,3-Dipolar Cycloaddition of Alkynes with Azides and Oxidative Coupling of 2-Naphthols and Phenols in Water. Catal Lett 2007, 114, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahsis, L.; El Ayouchia, H.B.; Anane, H.; Benhamou, K.; Kaddami, H.; Julve, M.; Stiriba, S.-E. Cellulose-copper as Bio-Supported Recyclable Catalyst for the Clickable Azide-Alkyne [3 + 2] Cycloaddition Reaction in Water. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2018, 119, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, B.H.; Rahman, Md.L.; Yusoff, M.M.; Chong, K.F.; Sarkar, S.M. Bio-Waste Corn-Cob Cellulose Supported Poly(Hydroxamic Acid) Copper Complex for Huisgen Reaction: Waste to Wealth Approach. Carbohydrate Polymers 2017, 156, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baig, R.B.N.; Varma, R.S. Copper on Chitosan: A Recyclable Heterogeneous Catalyst for Azide–Alkyne Cycloaddition Reactions in Water. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 1839–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben El Ayouchia, H.; ElMouli, H.; Bahsis, L.; Anane, H.; Laamari, R.; Gómez-García, C.J.; Julve, M.; Stiriba, S.-E. Hyperbranched Polyethylenimine-Supported Copper(II) Ions as a Macroliganted Homogenous Catalyst for Strict Click Reactions of Azides and Alkynes in Water. Journal of Organometallic Chemistry 2019, 898, 120881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).