1. Introduction
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a globally prevalent chronic joint disease that affects half of those over 60 years old and incurs a significant socioeconomic burden [
1,
2,
3]. OA is a whole joint disease that results in chronic inflammation, cartilage degradation, abnormal subchondral bone remodeling, osteophyte formation, synovitis, and fibrosis of the infrapatellar fat pad [
4,
5,
6,
7,
8]. Articular chondrocytes are the primary cell type present in cartilage and are responsible for secretion and homeostasis of an extracellular matrix (ECM) composed of collagen type-II-α (Col2α) and proteoglycans [
9,
10,
11,
12]. When damaged, chondrocytes are unable to repair the damage and contribute to degradation by undergoing cellular hypertrophy and apoptosis and increasing production of matrix-degrading proteases, such as matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), responsible for breakdown of the collagenous and non-collagenous cartilage matrix components [
13,
14,
15,
16]. Furthermore, the inflammatory conditions within an osteoarthritic joint stimulate chondrocytes to secrete pro-inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-1β (IL-1β) which stimulate the production of mediators such as prostaglandin E2, nitric oxide, cytokines, chemokines, and adhesion molecules that are involved in articular inflammation and enhance cartilage destruction [
17,
18,
19,
20].
Studies have demonstrated that alterations in several key signaling pathways contribute to the onset and progress of OA. One pathway, the nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-κB) has been identified to enhance joint inflammation and contribute to chondrocyte hypertrophy and apoptosis [
21,
22,
23]. Activation of NF-κB also results in increased production of proteolytic enzymes such as matrix-degrading proteinases (MMPs) and aggrecanases a disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain with thrombospondin motifs 4 and 5 (ADAMTS4, ADAMTS5) [
24,
25]. The NF-κB pathway can be directly or indirectly activated by bone morphogenic proteins (BMPs), the Wingless (Wnt) signaling cascade, or through interactions with various non-coding RNAs [
21,
26,
27]. Furthermore, pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-1β has been shown to stimulate NF-κB signaling through binding interactions with interleukin-1 receptor 1 (IL-1RI) [
28,
29].
Another protein recently shown to play a role in NF-κB signaling is trafficking protein particle complex subunit 9 (TRAPPC9), which shows a high degree of evolutionary conservation between species [
30,
31]. TRAPPC9 has been shown to be expressed in multiple tissue types and has been known to function in Golgi vesicle trafficking and been linked to nervous system disorders and various cancers [
31,
32,
33,
34,
35,
36]. Mutations in TRAPPC9 have been associated with autosomal recessive forms of intellectual disability that present clinically with distinctive craniofacial malformations, obesity, polydactyly, and brain abnormalities [
9,
37,
38,
39,
40]. Despite these findings, the physiological role of TRAPPC9 in chondrocytes and cartilage has yet to be explored.
In this study, we examined the role of TRAPPC9 in vitro using primary murine articular chondrocytes and the TC28 human cell chondrocyte cell line, ex vivo using human cartilage explants, and in vivo via the induction of post-traumatic OA through murine destabilization of the medial meniscus (DMM) surgery. Our study provides the first evidence that TRAPPC9 disrupts chondrocyte homeostasis and contributes to increased cartilage degradation and inflammation. Furthermore, we demonstrate that these are a result of NF-κB pathway activation. Together, our data identifies TRAPPC9 as a potential target for inhibitory therapy development in the treatment of OA and other inflammatory diseases.
2. Results
2.1. TRAPPC9 is elevated following pro-inflammatory stimulation with IL-1β
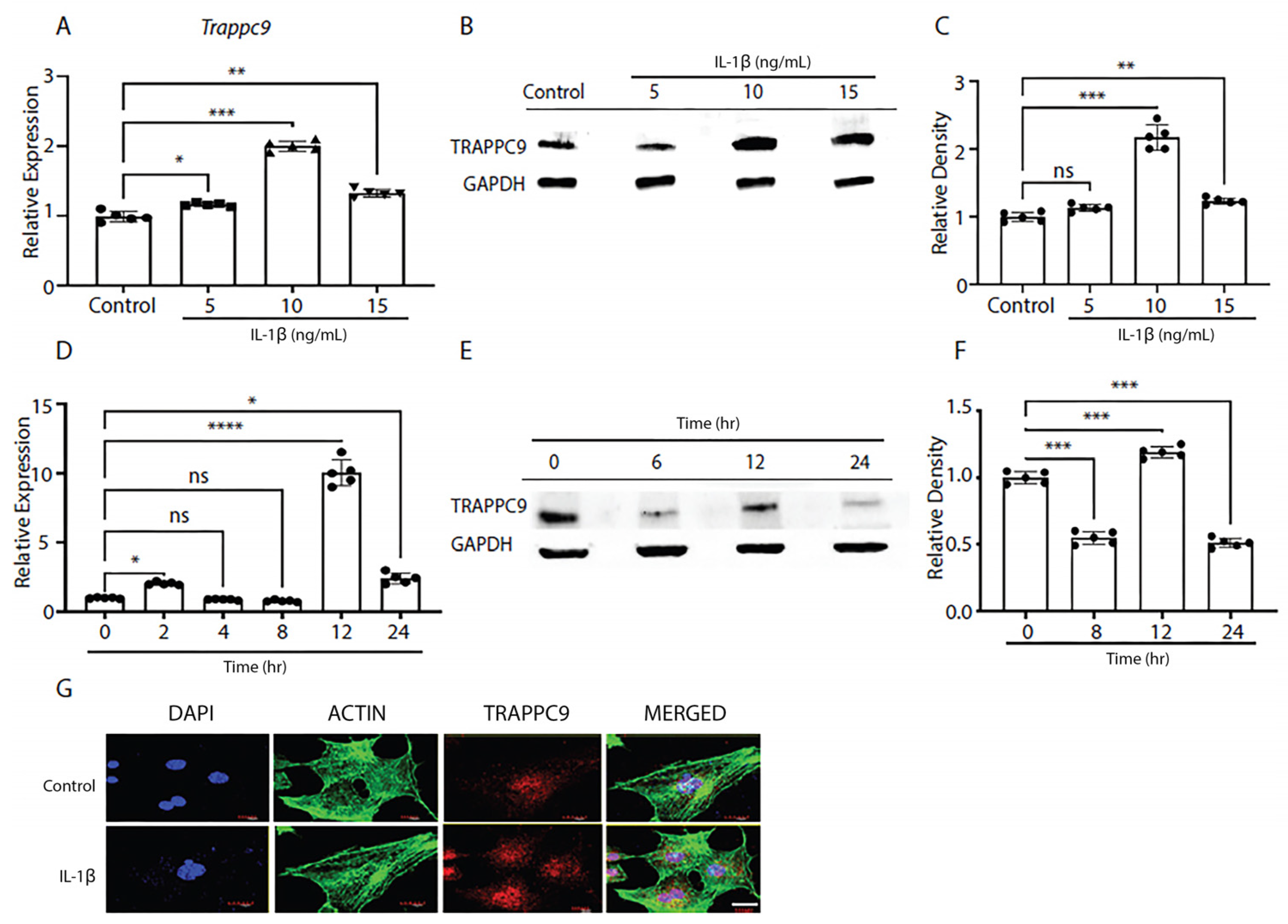
To better understand the biological significance of TRAPPC9 in OA, we first examined the expression of TRAPPC9 in primary murine articular chondrocytes under pro-inflammatory conditions. Cartilage was harvested from 5-day-old C57BL/6 male mice (n=5) and digested to isolate primary chondrocytes following previously published protocols [
41,
42,
60]. Once confluent, cells were serum starved overnight and treated with various doses of IL-1β to determine the effects of pro-inflammatory stimulation on TRAPPC9 mRNA and protein expression. Results indicated a treatment of 10 ng/mL IL-1β was the optimum dose at which TRAPPC9 mRNA and TRAPPC9 protein were significantly enhanced (
Figure 1A-C).
Next, we determined the effects of chronic exposure to pro-inflammatory stimuli on TRAPPC9 levels in murine primary articular chondrocytes to determine the optimum duration for treatment. Primary murine articular chondrocytes were harvested from C57BL/6 male mice cartilage as described above and exposed to IL-1β for up to 24-hours in vitro. During this time, cultures were terminated at several timepoints and TRAPPC9 mRNA and protein expression were assessed. Results showed TRAPPC9 mRNA and TRAPPC9 protein were both significantly enhanced following 12-hours of IL-1β stimulation (
Figure 1D-F). To further confirm these findings, mouse primary articular chondrocytes were subjected to IL-1β stimulation for 12-hours and imaged with fluorescent confocal microscopy. Results showed an enhanced TRAPPC9 level following IL-1β treatment (
Figure 1G). Actin staining did not show any dramatic change following IL-1β treatment. Together, these findings indicate that TRAPPC9 is expressed in primary murine articular chondrocytes and that TRAPPC9 mRNA and protein levels are increased after pro-inflammatory stimulation.
2.2. TRAPPC9 modulation reduces catabolic gene and protein expression following IL-1β treatment in chondrocytes
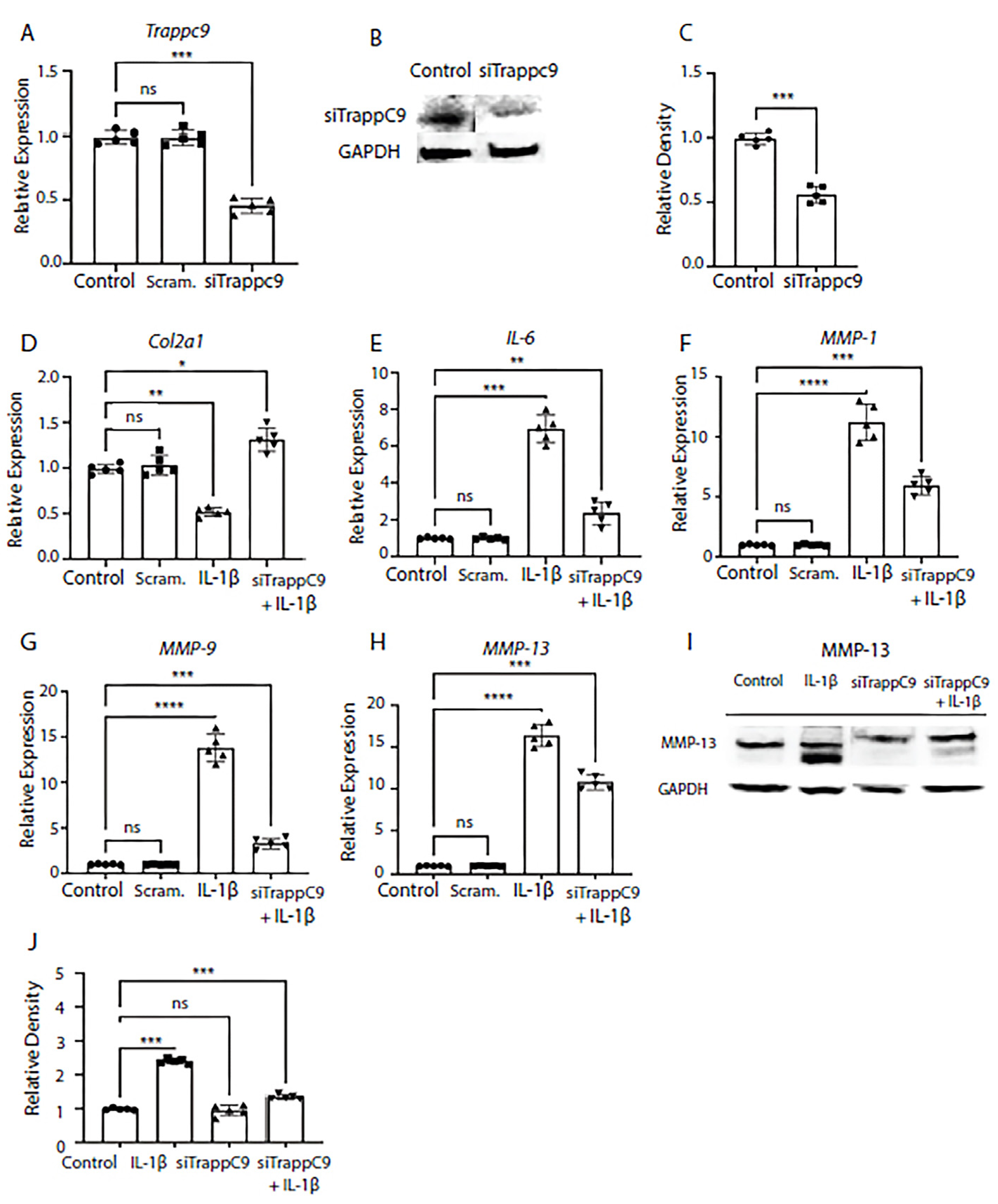
We next tested what effects modulation of TRAPPC9 would have on anabolic and catabolic markers in murine primary chondrocytes. As previously published, expression of anabolic markers was reduced while catabolic markers were enhanced in inflamed OA joints [
17,
61,
62]. To test this, TRAPPC9 was knocked down with siRNA and efficiency was confirmed through qPCR and immunoblot analyses (
Figure 2A-C). We then examined the mRNA expression of anabolic factor Col2α1 and pro-inflammatory makers interleukin-6 (IL-6), and MMP-1, MMP-9, and MMP-13. Primary chondrocytes were either left untreated (control), treated with scrambled siRNA control (Scram.) alone, IL-1β alone, or with a combination of siRNA treatment followed by IL-1β treatment (siTRAPPC9 + IL-1β). Results demonstrated that modulation of TRAPPC9 enhanced Col2α1 expression under pro-inflammatory conditions (
Figure 2D) and that expression of IL-6 and MMPs were significantly reduced with TRAPPC9 knockdown compared to IL-1β treatment alone (
Figure 2E-H). To further confirm these findings, we examined MMP-13 protein levels and results confirmed MMP-13 is reduced following siTRAPPC9 treatment and that MMP-13 levels were significantly reduced with TRAPPC9 knockdown compared to IL-1β treatment alone (
Figure 2I,2J). Together, these findings suggest inhibition of TRAPPC9 attenuates inflammation in primary murine articular chondrocytes.
2.3. TRAPPC9 over expression increases catabolic gene and protein expression in human TC28 chondrocytes
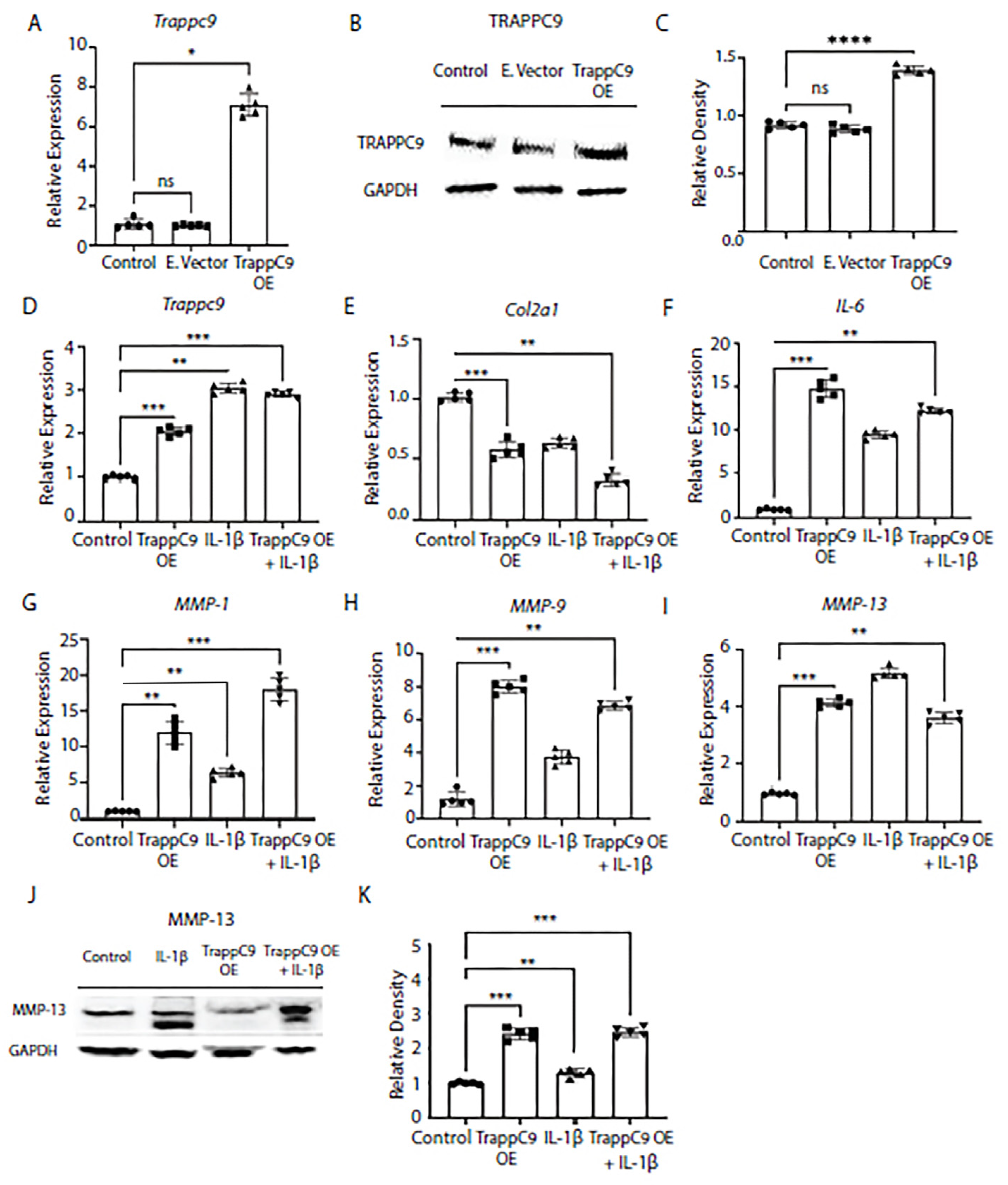
To further confirm our findings that TRAPPC9 plays a role in the chondrocyte inflammatory response, we next over expressed TRAPPC9 in TC28 chondrocyte cell line and confirmed over expression through gene expression and immunoblot (
Figure 3A-D). Then, cells were either left untreated (control), treated with TRAPPC9 over expression plasmid alone (TRAPPC9 OE), IL-1β alone, or with a combination of TRAPPC9 over expression plasmid followed by IL-1β treatment (TRAPPC9 OE + IL-1β). We then measured gene expression of anabolic Col2α1 and catabolic markers IL-6, MMP-1, MMP-9, and MMP-13 under these conditions by qPCR. Results demonstrated TRAPPC9 over expression alone was sufficient to significantly decrease Col2α1 expression and significantly increase catabolic gene expression in TC28 cells (
Figure 3E-I). Furthermore, the combination treatment with IL-1β and TRAPPC9 OE increased expression of IL-6, MMP-1, and MMP-9 above levels obtained with IL-1β treatment alone (
Figure 3F-H). Protein levels of MMP-13 were found to be increased following IL-1β treatment alone and significantly enhanced when IL-1β was combined with TRAPPC9 OE (
Figure 3J,K). These findings demonstrate that increases in TRAPPC9 expression result in upregulation of ECM catabolic markers.
2.4. TRAPPC9 binds NIK in primary murine articular chondrocytes
TRAPPC9 has been shown to bind NF-κB inducing kinase (NIK/MAP3K14) in neuronal cells, cancer cells, and osteoclasts, but it is still unknown if this binding occurs in primary chondrocytes [
31,
35,
36,
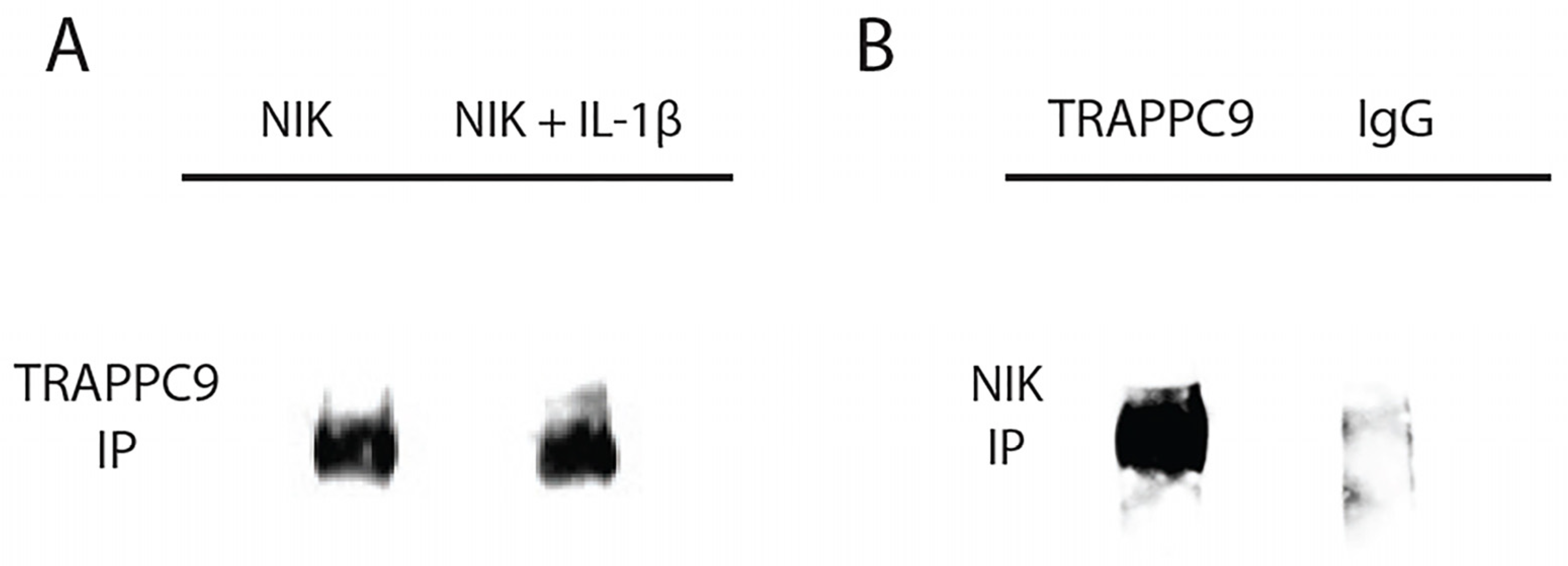
63]. To test this interaction, primary murine articular chondrocytes were isolated from C57BL/6 male mice (n=5) and grown to confluency in culture. Chondrocytes were then either left untreated or serum starved overnight followed by IL-1β treatment as described above. Cell lysates were isolated and immunoprecipitated with an anti-NIK antibody and immunoblotted using anti-TRAPPC9 antibody (
Table 1). Results demonstrated that TRAPPC9 binds to NIK under both control and IL-1β stimulated conditions (
Figure 4A). To confirm these findings, we performed a reverse immunoprecipitation with an anti- TRAPPC9 antibody and immunoblotted using an anti-NIK antibody. The results from this reverse immunoprecipitation validated the binding of TRAPPC9 and NIK and suggest that TRAPPC9 may stimulate inflammation via activation of the NF-kB pathway (
Figure 4B).
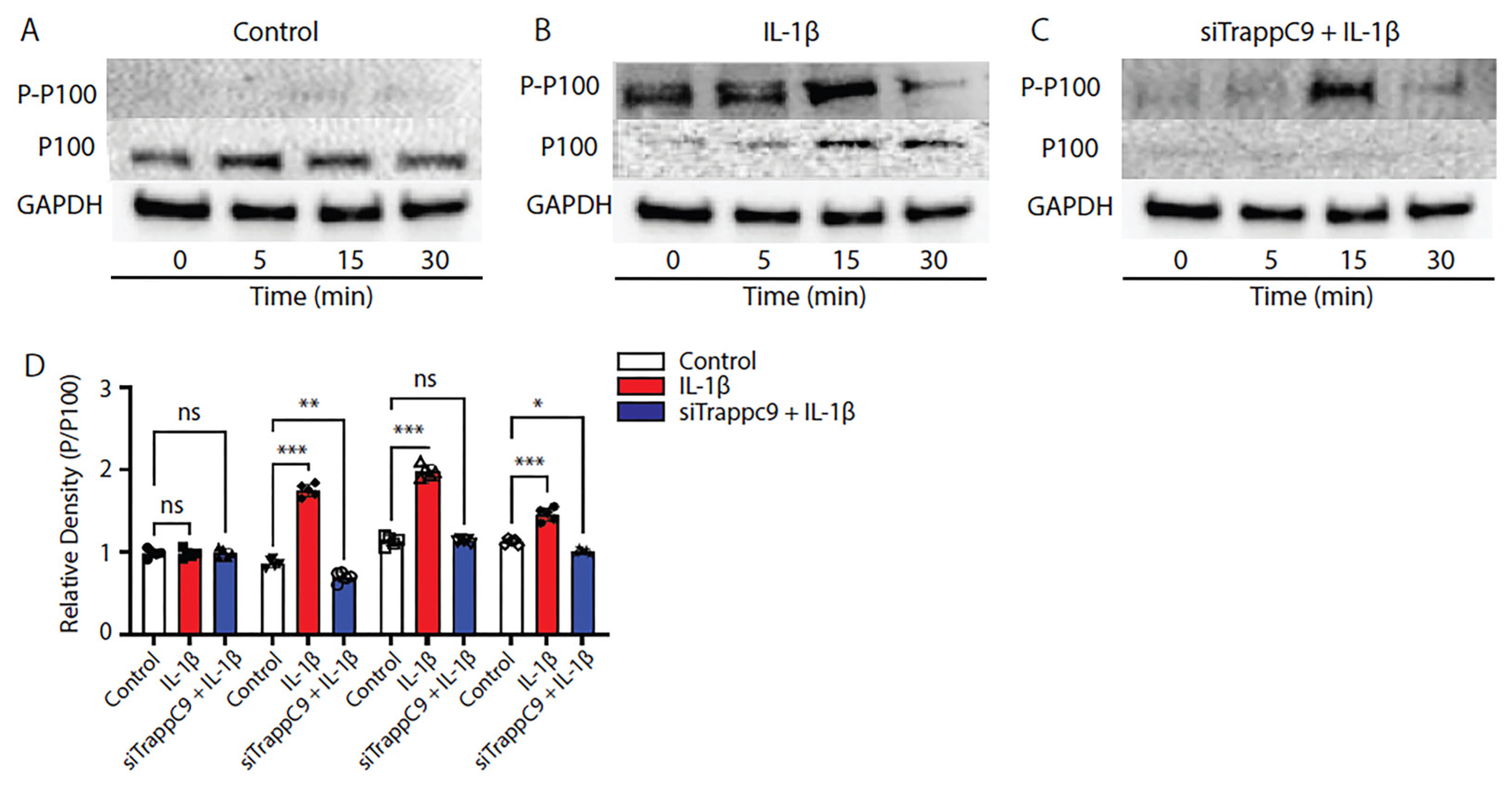
2.5. TRAPPC9 knockdown inhibits non-canonical NF-κB signaling in primary murine articular chondrocytes
Recent studies into tumorigenesis and cancer metastases have shown that TRAPPC9 inhibition is beneficial and that inhibition results in decreased NF-κB signaling [
64,
65]. Having demonstrated that TRAPPC9 binds NIK in primary chondrocytes (
Figure 4), we next examined the specifics of TRAPPC9 NF-κB activation. TC28 cells were grown to confluency in vitro and either left untreated (control), treated with IL-1β alone or treated with a combination of IL-1β and siTRAPPC9. Cell lysates were harvested at four different time points (0-30 minutes) and immunoblotted with anti-P-100, anti-phospho-P-100 antibodies with Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) utilized as the loading control. Results demonstrated a significant increase in NF-κB signaling (evident by enhanced phosphorylation of P-P100) following IL-1β stimulation (
Figure 5B,D) compared to untreated controls (
Figure 5A,D). Inhibition of TRAPPC9 with siRNA significantly reduced P-P100 (
Figure 5C,D).
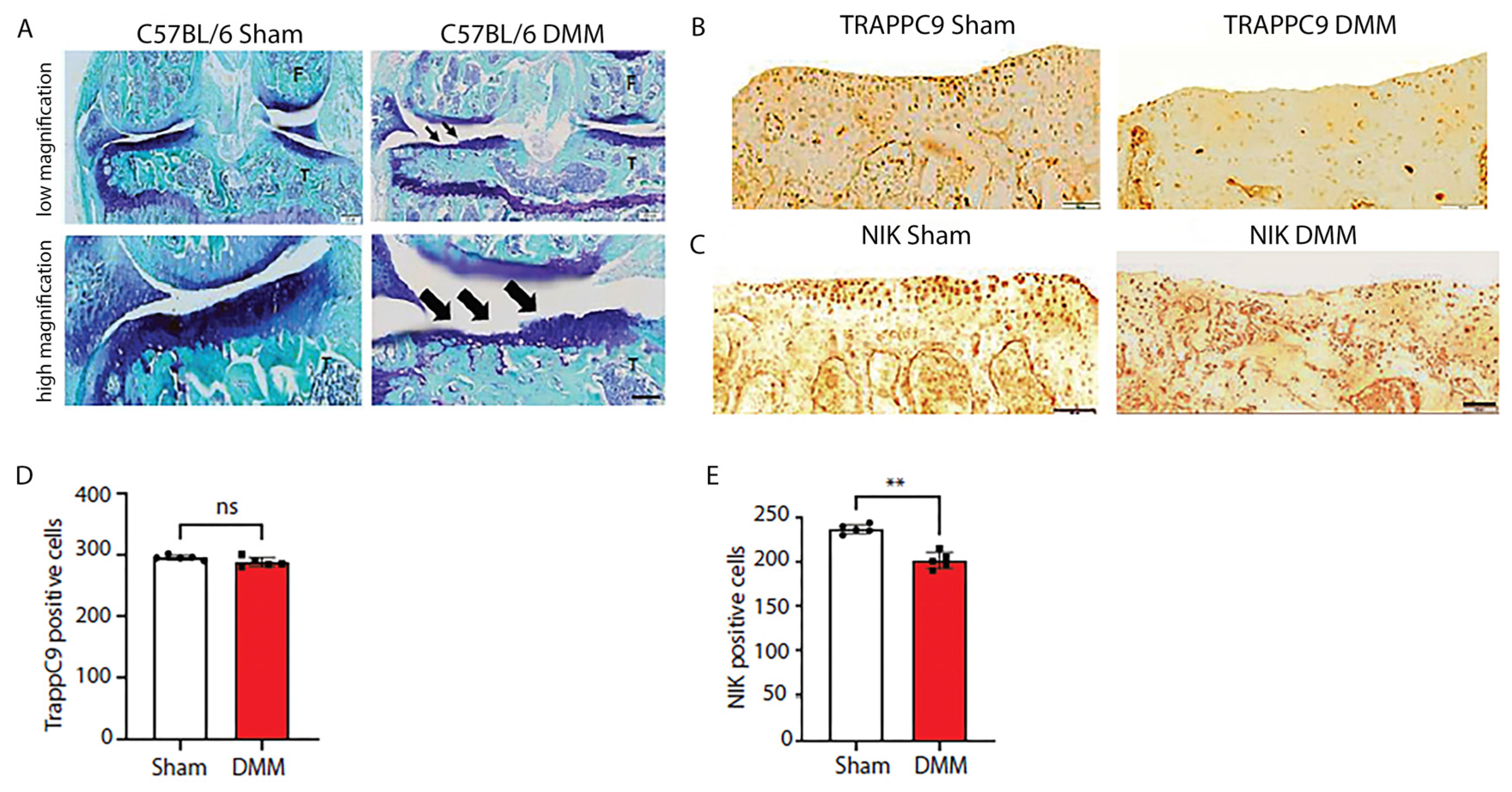
2.6. C57BL/6 mice develop severe cartilage damage following DMM surgery while demonstrating lower NIK positive cells
Having determined that TRAPPC9 increases pro-inflammatory expression in vitro, we next examined these findings in vivo. We utilized DMM, which is a well-established model for the induction of post-traumatic OA in a murine system [
56,
57]. C57BL/6 male mice (n=5) were subjected to DMM surgery on the right knee with the left knee serving as the internal control. An additional five C57BL/6 male mice underwent sham surgery, where the joint was opened but there was no surgical separation of the meniscus. Ten weeks post-surgery, the animals were euthanized, and the joints processed for histological and immunohistochemical (IHC) analyses. Results demonstrated that DMM animals developed severe cartilage damage compared to sham operated controls (
Figure 6A). While no significant changes in TRAPPC9 were detected with IHC (
Figure 6B, D), there was a significant reduction in NIK positive cells following DMM surgery (
Figure 6C, E). These findings suggest that TRAPPC9 expression is not significantly upregulated 10-weeks post-surgery resulting in decreased NIK expression within the joint.
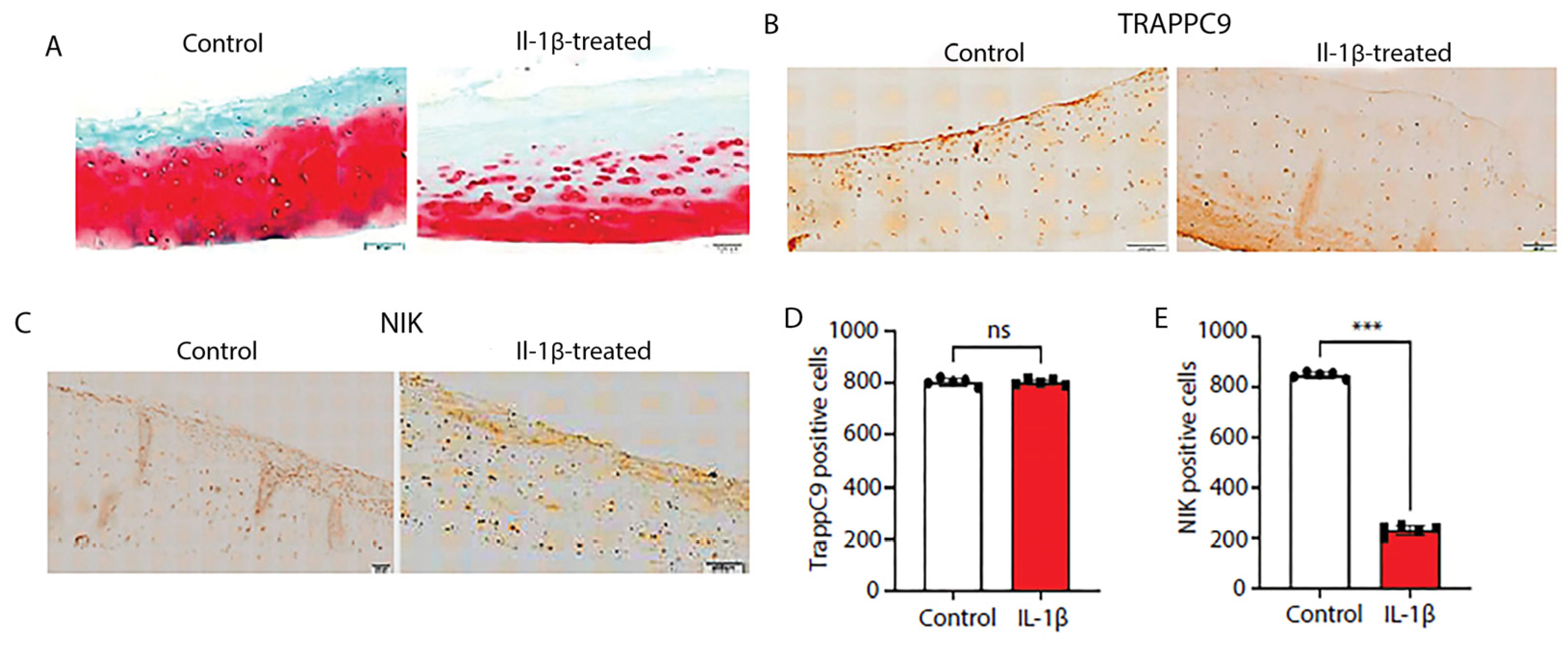
2.7. Human cartilage explants show severe ECM degradation following inflammatory stimulation and reduced numbers of NIK positive cells
Next, we assessed the effects of IL-1β stimulation on TRAPPC9 and NIK protein expression in human cartilage explants. Undamaged cartilage was identified with Indian ink staining, rinsed in sterile PBS, and maintained in culture for 24 hours prior to IL-1β treatment. Results demonstrate that IL-1β treatment showed significant ECM degradation (
Figure 7A). We then assess protein levels of TRAPPC9 and NIK via IHC. The results from the human explant cultures were similar to those seen in the murine DMM samples (
Figure 6C,E). TRAPPC9 expression was not significantly altered between untreated control and IL-1β-stimulated samples and NIK expression was reduced following IL-1β stimulation (
Figure 7B-E). These findings suggest that TRAPPC9 expression was not significantly altered following pro-inflammatory stimulation.
3. Discussion
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a degenerative joint disease that results in cartilage damage and chronic pain and disability in those affected [
66,
67]. Known risk factors include age, obesity, traumatic or developmental joint instability, chronic inflammatory conditions, and modulation of epigenetic regulation [
10,
68,
69,
70]. Studies have shown that inflammation plays a key role in the onset and progression of OA through increased expression of matrix proteases and stimulation of chondrocyte hypertrophy and apoptosis [
15,
71]. Furthermore, inflammation contributes to disease symptoms inducing pain, joint swelling, and impaired mobility [
1,
66,
72]. Alterations in several key signaling pathways have been linked with OA that contribute to chondrocyte hypertrophy and inflammation, such as Wingless (Wnt), bone morphogenic protein (BMP), interleukin-1-beta (IL-1β), pI3K/AKT/mTOR, and NF-κB [
73,
74,
75].
Trafficking Protein Particle Complex 9 (TRAPPC9) is a major subunit of the TRAPPII Complex that has been shown to stimulate the NF-κB signaling cascade either through the canonical (through the IKKα/IKKβ/IKK-NEMO complex) or non-canonical (through NIK) pathway [
25,
76,
77]. Furthermore, patients with TRAPPC9 frame-shift mutations present with both neuronal and skeletal abnormalities due to deleterious TRAPPC9-NF-κB signaling [
9,
34,
63,
78]. Despite these findings, no studies have examined the biological role of TRAPPC9 in chondrocytes or cartilage [
33,
36]. Here, we provide the first evidence of the pro-inflammatory role of TRAPPC9 in chondrocytes and demonstrate its stimulation of the non-canonical NF-κB pathway via binding interactions with NIK.
We began by first demonstrating that TRAPPC9 mRNA and protein were significantly increased following IL-1β pro-inflammatory stimulation in primary murine articular chondrocytes. We then modulated TRAPPC9 using both loss-of-function and gain-of-function approaches and demonstrated that TRAPPC9 inhibition enhanced anabolic Col2α1 mRNA expression and inhibited expression of pro-inflammatory IL-6 and matrix metalloproteinases MMP-1, MMP-9, and MMP-13 (
Figure 2D-J). We confirmed these findings by performing TRAPPC9 over expression assays, which resulted in decreased anabolic expression and enhanced catabolic mRNA and protein levels (
Figure 3A-K).
Next, we examined the mechanism by which TRAPPC9 enhances catabolic gene expression. Studies of TRAPPC9 signaling have demonstrated that TRAPPC9 (also known as NIK- and IKK2-binding protein (NIBP)) directly binds NIK and stimulates NF-κB signaling in neuronal, bone and cancer cells, where NF-κB activation maintains cancer cell malignancy and tumorigenesis [
31,
33,
36,
63,
79]. Here, we provide the first evidence that TRAPPC9 binds NIK in primary murine chondrocytes, and that binding stimulates non-canonical NF-κB signaling through modulation of phospho-P-100, which has been shown to increase matrix catabolism and inflammation in OA [
21,
22,
23] (
Figure 4A, 5A-D). These findings provide additional support for the hypothesis that TRAPPC9-NF-κB signaling plays a role in joint and skeletal maintenance.
Finally, we examined the localization of TRAPPC9 and NIK in vivo in a murine model of post-traumatic OA. Destabilization of the medial meniscus (DMM) is a well-established murine model for the induction of post-traumatic OA where the medial meniscus ligament is transected during surgery resulting in joint instability [
56,
57]. Results from our studies in C57BL/6 mice demonstrated severe cartilage damage in DMM mice, compared to sham controls, but no significant difference in TRAPPC9 positive cells (
Figure 6A, B, D). Additionally, we detected significantly fewer NIK positive cells following DMM (
Figure 6C, E). Similar results were seen in evaluations of TRAPPC9 and NIK levels in human explants following IL-1β stimulation (
Figure 7). NF-κB signaling is complex and involves both canonical and non-canonical pathways. The dominant pathway is canonical, which involves the phosphorylation of IκB and the formation of IKKα/IKKβ complexes [
80,
81]. The alternative non-canonical pathway involves NIK and P-100 phosphorylation [
25,
82]. It is likely that we failed to detect elevated TRAPPC9 levels 10-weeks post-surgery or following 24-hour incubation with IL-1β because the increase in TRAPPC9 levels is transitory. Furthermore, the decreased levels of NIK seen in both our murine and human explant experiments may be a result of enhance canonical NF-κB signaling, not non-canonical. This suggests that, while TRAPPC9 has been shown to stimulate canonical and non-canonical signaling, there may be a preference for the pathway of activation in primary chondrocytes under pro-inflammatory conditions [
33,
36]. However, additional studies are needed to confirm these findings.
In this study, we sought to uncover the biological significance of TRAPPC9 in primary chondrocytes. Here, we demonstrate that TRAPPC9 expression is enhanced in primary chondrocytes under pro-inflammatory conditions and activation enhances expression of pro-inflammatory makers while reducing anabolic gene expression. Furthermore, we demonstrate that TRAPPC9 binds NIK and activates the non-canonical NF-κB signaling pathway in murine primary chondrocytes. Together, these findings suggest that TRAPPC9 may be a potential therapeutic target to decrease inflammation and matrix degradation during OA pathology.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Isolation and culture of primary murine chondrocytes
Primary murine articular chondrocytes were isolated from 5-day old C57BL/6 male pups. The femoral head, condyle and tibia plateau were collected and digested overnight in 2 mg/ml collagenase D (Sigma) then washed and seeded in a 6 well plate at a density of 2 x105 cells/well for 7 days [
41,
42]. Cells were maintained in DMEM/F12 media (Cellgro) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and penicillin/streptomycin (penicillin 50 U/mL, streptomycin 50 µg/mL). After cells reached confluence, they were serum starved overnight before treatment with IL-1β (10 ng/ml) (R&D Systems).
4.2. Human explant culture
Cartilage was isolated from de-identified knee joints of patients undergoing total knee replacement surgery (arthroplasty) with minor modifications [
43,
44]. Cartilage from undamaged regions of the knee were identified using Indian ink and were rinsed three times with sterile phosphate buffered saline (PBS) [
45]. The cartilage was then cut into 2 x 2 mm pieces and cultured for 24 hours in DMEM/F12 media supplemented with 10% FBS and penicillin/streptomycin as described above. Cartilage explants were serum-starved overnight prior to treatment with Il-1β (10 ng/mL) for 24 hours. Following treatment, the explants was fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde (Corning) for 24 hours and paraffin embedded. Histology sections were cut at a 5µm thickness and stained with Safranin-O (Fisher Scientific) [
46,
47].
4.3. Immunofluorescent staining
Primary murine articular chondrocytes were grown in a 4-well chamber slides (Corning) and maintained in DMEM/F12 supplemented media as previously described. For the IL-1β treatment group, cells were serum starved overnight and then treated with IL-1β (10 ng/ml) for 24 hours. Slides were rinsed in sterile PBS and fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 20 minutes. The cells were then washed twice for 2 minutes each in PBS and blocked in 5% BSA in Tris Buffered Saline with Tween® 20 (TBST). Chondrocytes were permeabilized in a solution of 10% BSA and 0.1 Triton-X100 in PBS for 15 minutes at room temperature. Slides were washed 3 times in PBS and incubated overnight in primary antibodies at 4°C. The next day, cells were incubated with fluorescently labeled secondary antibodies for 1 hour and mounted in a DAPI-containing medium. Images were acquired using Olympus FV1000 confocal microscope.
4.4. Immunohistochemistry
For immunohistochemistry (IHC) analyses, paraffin was removed from joint sections and the tissues was rehydrated as previously described [
48,
49]. Antigen retrieval was performed by incubating the slides in trypsin (25mg/ml) at 60°C water bath overnight. Slides were cooled with distilled water and incubated in serum for blocking for 30 minutes followed by primary antibody overnight at 4°C. Slides were then rinsed three times (5 minutes each) with 10X TBST and incubated for 30 minutes with Avidin-Biotin complex (ABC). Slides were then rinsed three times in washing buffer and rinsed again and incubated with Diaminobenzidine (DAB), rinsed in water and counterstained with hematoxylin. Following staining, slides were dehydrated and covered slipped. Slides were then imaged on an Olympus BX61VS slide scanning microscope and positively stained cells were counted.
4.5. Immunoblotting
The total protein was extracted from murine primary chondrocytes using 1X radioimmunoprecipitation assay (RIPA) buffer (EMD Millipore) supplemented with a proteinase inhibitor cocktail (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Protein lysates were kept on ice for 30 minutes and then centrifuged at 12000g for 30 minutes. Total protein concentrations were determined via BCA assay following the manufacture’s recommendation (Biorad). A total of 20μg of protein lysate was used for each sample and loaded on a 12% SDS-polyacrylamide gel. Proteins were transferred to a PVDF membrane (Biorad) as previously described [
50,
51]. Membranes were blocked for 1 hour in 5% BSA in TBST at room temperature and probed with primary antibody overnight at 4C°. Primary antibody was removed and the blot was washed with TBST then probed with primary antibodies (
Table 1) overnight at 4°C. Blots were rinsed three times in TBST (5 minutes per wash) and incubated with an HRP-conjugated secondary antibody for 1 hour at room temperature. Blots were then imaged using a luminata forte Western Blot HRP substrate and imaged on the Syngen Pxi imaging system. Relative protein expression was then evaluated using ImageJ ver. 1.50i.
4.6. Immunoprecipitation
Primary murine articular chondrocytes were isolated from 5-day old C57BL/6 male pups. The femoral head, condyle, and tibia plateau were collected, digested (Collagenase D), plated into 6-well culture dishes, and maintained in culture to confluence as described above. Once confluent, cells were serum starved overnight then treated with IL-1β (10 ng/ml) for 24 hours. Protein was isolated, and 100µg of protein was combined with 10µg of anti-TRAPPC9 or anti-NIK antibodies and incubated overnight at 4°C. The proteins were added to a 1.5mL microcentrifuge tubes containing 25 µL of Pierce Protein A/G pre-washed magnetic beads (Thermo Scientific Fisher) and incubated at room temperature for 2 hours with gentle shaking. Beads were collected with a magnetic stand and co-immunoprecipitation was confirmed by immunoblot as described above. To confirm the binding, a reverse immunoprecipitation was performed with NIK and was co-precipitated with TRAPPC9.
4.7. Real time qPCR analysis
Total RNA was extracted from primary murine articular chondrocytes using the RNeasy kit (Qiagen) and cDNA generated using 1 μg total RNA with the High-Capacity Reverse Transcription Kit following manufacturer recommended protocols (Applied Biosystems). In-house primers were designed for gene expression analyses via RT-qPCR (
Table 2). qRT-PCR was performed using a StepOne Plus machine (Applied Biosystems) with SYBRGreen PCR Master Mix (Applied Biosystems). Reactions were performed in triplicate and normalized against GAPDH mRNA expression following the delta-delta CT (ΔΔCT) method [
52,
53].
4.8. TRAPPC9 modulation using gain-of-function and loss-of-function approaches
TRAPPC9 was overexpressed in both murine primary articular chondrocytes and the TC28 human chondrocyte cell line using retroviral particles expressing pMX-IRES-GFP (control retrovirus vector encoding green fluorescent protein (GFP]) and pMX-IRES-TRAPPC9 (treatment encoding constitutively activeTRAPPC9 protein) (Genecopoeia) and packaging plasmids (Origene). Plasmids (100pg-100ng) were transformed into competent E. coli (NEB) following recommended protocols, plated, and incubated overnight at 37°C. Colonies expressing control and treatment plasmids were identified and cultured in Luria-Bertani (LB) broth (Corning Inc). Plasmids were isolated and purified with the MINIprep kit (Quiagen) following previously published protocols [
54,
55]. Cells were transfected using 1 µg/mL of the purified plasmids and XtremeGENE™ HP DNA transfection reagent (Roche) in a serum free medium. Six hours later, the medium was supplied with 10% FBS and was left for 24 hours prior to RNA isolation and 36 hours for protein isolation. For loss-of-function assays, murine primary articular chondrocytes were incubated with purchased siRNAs targeting TRAPPC9 and XtremeGENE™ siRNA transfection reagent (Roche) overnight in serum free media. The next day, the transfection media was aspirated and replaced with supplemented DMEM/F12 for 24 hours prior to isolation for RNA or protein analyses.
4.9. Induction of post-traumatic osteoarthritis in a murine model
To induce post-traumatic osteoarthritis (PT-OA) in a murine model, we used the destabilization of the medial meniscus surgical approach, a well-characterized model [
56,
57]. Twelve-week-old male C57Bl/6 mice were purchased from Jackson labs (Cat # 000664). Male mice were housed and surgery conducted following the guidelines of the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of Northeast Ohio Medical University (NEOMED). Animals were anesthetized and the right knee was subjected to microsurgery and the medial meniscus was severed to induce joint instability [
56,
57]. The left knee served as internal control. Separate sham animals underwent surgery to open the joint, but the medial meniscus was left intact. Animals were euthanized 10 weeks post-surgery and the joints harvested for histological and histomorphometric analyses.
4.10. Statistical analysis
The Prism 6 software version 6.01 was used to analyze the statistical differences between individual groups. All individual experiments were independently repeated for a minimum of three times. Comparison of multiple groups was analyzed using a one-way analysis of variance (1-way ANOVA) followed by a Turkey’s for multiple comparison post hoc test. An unpaired t-test was performed to compare two groups. Differences were statistically calculated with a p-value less than 0.05. Group means or means ± standard error of the mean (±SEM) were graphed.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, NJH,FFS; methodology, NJH,FFS ; software, NJH,FFS; validation, NJH,FFS; formal analysis, NJH,FFS; investigation, NJH,FFS,ALA; resources, NJH,FFS,ALA; data curation, NJH,FFS, ALA, RP; writing—original draft preparation, NJH,ALA,HCB; writing—review and editing, NJH, ALA, HCB, FFS; visualization, NJH, ALA, HCB; supervision, FFS; project administration, NJH,FFS; funding acquisition, NJH,FFS. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript
Funding
This study was partially funded by Kent State University School of Biomedical Sciences and Rebecca D. Considine Akron Children’s Hospital.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study protocol was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Northeast Ohio Medical University.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable
Data Availability Statement
not applicable
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest
References
- Loeser, R.F., J.A. Collins, and B.O. Diekman, Ageing and the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Nature Reviews Rheumatology, 2016. 12(7): p. 412-420. [CrossRef]
- Musumeci, G.; et al., Osteoarthritis in the XXIst Century: Risk Factors and Behaviours that Influence Disease Onset and Progression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2015. 16(3): p. 6093-6112. [CrossRef]
- Quicke, J.; et al., Osteoarthritis year in review 2021: Epidemiology & therapy. Osteoarthritis and cartilage, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; et al., Systemic and local adipose tissue in knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis and cartilage, 2018. 26(7): p. 864-871. [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; et al., Subchondral bone microenvironment in osteoarthritis and pain. Bone research, 2021. 9(1): p. 1-13. [CrossRef]
- Roelofs, A.J.; et al., Identification of the skeletal progenitor cells forming osteophytes in osteoarthritis. Annals of the rheumatic diseases, 2020. 79(12): p. 1625-1634. [CrossRef]
- Zeng, N.; et al., Infrapatellar fat pad and knee osteoarthritis. Aging and disease, 2020. 11(5): p. 1317. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; et al., The crosstalk between epigenetic mechanisms and alternative RNA processing regulation. Frontiers in Genetics, 2020. 11: p. 998. [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, A.A.; et al., Identification of a novel homozygous TRAPPC9 gene mutation causing non-syndromic intellectual disability, speech disorder, and secondary microcephaly. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet, 2017. 174(8): p. 839-845. [CrossRef]
- Ball, H.C.; et al., Epigenetic Regulation of Chondrocytes and Subchondral Bone in Osteoarthritis. Life, 2022. 12(4): p. 582. [CrossRef]
- Goldring, S.R. and M.B. Goldring, Changes in the osteochondral unit during osteoarthritis: Structure, function and cartilage–bone crosstalk. Nature Reviews Rheumatology, 2016. 12(11): p. 632-644. [CrossRef]
- McKee, T.J.; et al., Extracellular matrix composition of connective tissues: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Scientific reports, 2019. 9(1): p. 1-15. [CrossRef]
- Barreto, G., M. Manninen, and K. K. Eklund, Osteoarthritis and toll-like receptors: When innate immunity meets chondrocyte apoptosis. Biology, 2020. 9(4): p. 65. [CrossRef]
- Mehana, E.-S.E., A.F. Khafaga, and S.S. El-Blehi, The role of matrix metalloproteinases in osteoarthritis pathogenesis: An updated review. Life sciences, 2019. 234: p. 116786. [CrossRef]
- Rim, Y.A., Y. Nam, and J.H. Ju, The role of chondrocyte hypertrophy and senescence in osteoarthritis initiation and progression. International journal of molecular sciences, 2020. 21(7): p. 2358. [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.M.G. and F. Beier, Chondrocyte hypertrophy in skeletal development, growth, and disease. Birth Defects Research Part C: Embryo Today: Reviews, 2014. 102(1): p. 74-82. [CrossRef]
- Goldring, M.; et al., Defining the roles of inflammatory and anabolic cytokines in cartilage metabolism. Annals of the rheumatic diseases, 2008. 67(Suppl 3): p. iii75-iii82. [CrossRef]
- Goldring, M.B., Chondrogenesis, chondrocyte differentiation, and articular cartilage metabolism in health and osteoarthritis. Therapeutic advances in musculoskeletal disease, 2012. 4(4): p. 269-285. [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, C.A.; et al., Dysregulated inflammatory response related to cartilage degradation after ACL injury. Medicine and science in sports and exercise, 2020. 52(3): p. 535. [CrossRef]
- Jacques, C.; et al., The role of IL-1 and IL-1Ra in joint inflammation and cartilage degradation. Vitamins & Hormones, 2006. 74: p. 371-403. [CrossRef]
- Feng, T. and Q.-f. Wu, A review of non-coding RNA related to NF-κB signaling pathway in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. International Immunopharmacology, 2022. 106: p. 108607. [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.A.; et al., IGF-1 facilitates cartilage reconstruction by regulating PI3K/AKT, MAPK, and NF-kB signaling in rabbit osteoarthritis. Journal of Inflammation Research, 2021. 14: p. 3555. [CrossRef]
- Mueller, M.B. and R.S. Tuan, Anabolic/catabolic balance in pathogenesis of osteoarthritis: Identifying molecular targets. PM&R, 2011. 3: p. S3-S11. [CrossRef]
- B Marcu, K.; et al., NF-κB signaling: Multiple angles to target OA. Current drug targets, 2010. 11(5): p. 599-613. [CrossRef]
- Rigoglou, S. and A.G. Papavassiliou, The NF-κB signalling pathway in osteoarthritis. The international journal of biochemistry & cell biology, 2013. 45(11): p. 2580-2584. [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.-P.; et al., Requirement of the NF-κB pathway for induction of Wnt-5A by interleukin-1β in condylar chondrocytes of the temporomandibular joint: Functional crosstalk between the Wnt-5A and NF-κB signaling pathways. Osteoarthritis and cartilage, 2011. 19(1): p. 111-117. [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.; et al., Protective effects of Erdosteine on interleukin-1β-stimulated inflammation via inhibiting the activation of MAPK, NF-κB, and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways in rat osteoarthritis. European Journal of Pharmacology, 2020. 873: p. 172925. [CrossRef]
- Herrero-Beaumont, G.; et al., Targeting chronic innate inflammatory pathways, the main road to prevention of osteoarthritis progression. Biochemical Pharmacology, 2019. 165: p. 24-32. [CrossRef]
- Koh, R.H.; et al., Inflammation-modulating hydrogels for osteoarthritis cartilage tissue engineering. Cells, 2020. 9(2): p. 419. [CrossRef]
- Aslam Khattak, N. and A. Mir, Computational analysis of TRAPPC9: Candidate gene for autosomal recessive non-syndromic mental retardation. CNS & Neurological Disorders-Drug Targets (Formerly Current Drug Targets-CNS & Neurological Disorders), 2014. 13(4): p. 699-711. [CrossRef]
- Bodnar, B.; et al., Emerging role of NIK/IKK2-binding protein (NIBP)/trafficking protein particle complex 9 (TRAPPC9) in nervous system diseases. Transl Res, 2020. 224: p. 55-70. [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.-H.; et al., NIBP, a novel NIK and IKKβ-binding protein that enhances NF-κB activation. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2005. 280(32): p. 29233-29241. [CrossRef]
- Mbimba, T.; et al., TRAPPC9: Novel insights into its trafficking and signaling pathways in health and disease (Review). Int J Mol Med, 2018. 42(6): p. 2991-2997. [CrossRef]
- Mochida, G.H.; et al., A truncating mutation of TRAPPC9 is associated with autosomal-recessive intellectual disability and postnatal microcephaly. Am J Hum Genet, 2009. 85(6): p. 897-902. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; et al., Expression and function of NIK-and IKK 2-binding protein (NIBP) in mouse enteric nervous system. Neurogastroenterology & Motility, 2014. 26(1): p. 77-97. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; et al., Elevated NIBP/TRAPPC9 mediates tumorigenesis of cancer cells through NFkappaB signaling. Oncotarget, 2015. 6(8): p. 6160-78. [CrossRef]
- Hnoonual, A.; et al., Novel Compound Heterozygous Mutations in the TRAPPC9 Gene in Two Siblings With Autism and Intellectual Disability. Front Genet, 2019. 10: p. 61. [CrossRef]
- Kakar, N.; et al., A homozygous splice site mutation in TRAPPC9 causes intellectual disability and microcephaly. Eur J Med Genet, 2012. 55(12): p. 727-31. [CrossRef]
- Kramer, J.; et al., Two Novel Compound Heterozygous Mutations in the TRAPPC9 Gene Reveal a Connection of Non-syndromic Intellectual Disability and Autism Spectrum Disorder. Front Genet, 2020. 11: p. 972. [CrossRef]
- Marangi, G.; et al., TRAPPC9-related autosomal recessive intellectual disability: Report of a new mutation and clinical phenotype. Eur J Hum Genet, 2013. 21(2): p. 229-32. [CrossRef]
- Gosset, M.; et al., Primary culture and phenotyping of murine chondrocytes. Nature protocols, 2008. 3(8): p. 1253-1260. [CrossRef]
- Mirando, A.J.; et al., Isolation and culture of murine primary chondrocytes, in Skeletal Development and Repair. 2014, Springer. p. 267-277. [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; et al., Inhibition of cellular communication network factor 1 (CCN1)-driven senescence slows down cartilage inflammaging and osteoarthritis. Bone, 2020. 139: p. 115522. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; et al., Effects of insulin-like growth factor-1 and dexamethasone on cytokine-challenged cartilage: Relevance to post-traumatic osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis and cartilage, 2015. 23(2): p. 266-274. [CrossRef]
- Aspden, R., India ink and cartilage. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage, 2011. 19(3): p. 332.
- Alibegović, A., R. Blagus, and I.Z. Martinez, Safranin O without fast green is the best staining method for testing the degradation of macromolecules in a cartilage extracellular matrix for the determination of the postmortem interval. Forensic Science, Medicine and Pathology, 2020. 16(2): p. 252-258. [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.-J.; et al., Age-related changes in the cartilage of the temporomandibular joint. GeroScience, 2020. 42(3): p. 995-1004. [CrossRef]
- Crosby, K.; et al., Immunohistochemistry protocol for parraffin-embedded tissue sections-ADVERTISEMENT. JoVE, Cambridge, MA, 2014.
- Hofman, F.M. and C.R. Taylor, Immunohistochemistry. Current Protocols in Immunology, 2013. 103(1): p. 21.4. 1-21.4. 26.
- Chapman, K.; et al., A meta-analysis of European and Asian cohorts reveals a global role of a functional SNP in the 5′ UTR of GDF5 with osteoarthritis susceptibility. Human molecular genetics, 2008. 17(10): p. 1497-1504. [CrossRef]
- Janes, K.A., An analysis of critical factors for quantitative immunoblotting. Science signaling, 2015. 8(371): p. rs2-rs2. [CrossRef]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; et al., Real-time PCR quantification of precursor and mature microRNA. Methods, 2008. 44(1): p. 31-8. [CrossRef]
- Schmittgen, T.D. and K.J. Livak, Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nature protocols, 2008. 3(6): p. 1101-1108. [CrossRef]
- Figueroa-Bossi, N., R. Balbontín, and L. Bossi, Preparing Plasmid DNA from Bacteria. Cold Spring Harbor Protocols, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S. and M.D. Cahalan, Purifying plasmid DNA from bacterial colonies using the QIAGEN Miniprep Kit. JoVE (Journal of Visualized Experiments), 2007(6): p. e247. [CrossRef]
- Glasson, S., T. Blanchet, and E. Morris, The surgical destabilization of the medial meniscus (DMM) model of osteoarthritis in the 129/SvEv mouse. Osteoarthritis and cartilage, 2007. 15(9): p. 1061-1069. [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.-L.; et al., Osteoarthritis severity is sex dependent in a surgical mouse model. Osteoarthritis and cartilage, 2007. 15(6): p. 695-700. [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.J.; et al., Rigosertib ameliorates the effects of oncogenic KRAS signaling in a murine model of myeloproliferative neoplasia. Oncotarget, 2019. 10(20): p. 1932. [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.; et al., Comparison of joint degeneration and pain in male and female mice in DMM model of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis and cartilage, 2021. 29(5): p. 728-738. [CrossRef]
- Ball, H.C.; et al., A retrotransposon gag-like-3 gene RTL3 and SOX-9 co-regulate the expression of COL2A1 in chondrocytes. Connective Tissue Research, 2021. 62(6): p. 615-628. [CrossRef]
- Goldring, M.B.; et al., Roles of Inflammatory and Anabolic Cytokines in Cartilage Metabolism: Signals and Multiple Effectors Converge Upon Mmp-13 Regulation in Osteoarthritis. European Cells & Materials, 2011. 21: p. 202-220. [CrossRef]
- Greene, M.A. and R.F. Loeser, Aging-related inflammation in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis and cartilage, 2015. 23(11): p. 1966-1971. [CrossRef]
- Hussein, N.J.; et al., A novel regulatory role of TRAPPC9 in L-plastin-mediated osteoclast actin ring formation. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 2020. 121(1): p. 284-298. [CrossRef]
- D’Amato, V.; et al., Mechanisms of lapatinib resistance in HER2-driven breast cancer. Cancer treatment reviews, 2015. 41(10): p. 877-883. [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; et al., NF-κB pathways in the development and progression of colorectal cancer. Translational Research, 2018. 197: p. 43-56. [CrossRef]
- Cui, A.; et al., Global, regional prevalence, incidence and risk factors of knee osteoarthritis in population-based studies. EClinicalMedicine, 2020. 29: p. 100587. [CrossRef]
- Sellam, J. and F. Berenbaum, The role of synovitis in pathophysiology and clinical symptoms of osteoarthritis. Nature Reviews Rheumatology, 2010. 6(11): p. 625-635. [CrossRef]
- Georgiev, T. and A.K. Angelov, Modifiable risk factors in knee osteoarthritis: Treatment implications. Rheumatology International, 2019. 39(7): p. 1145-1157. [CrossRef]
- Georgiev, T.; et al., Cartilage oligomeric protein, matrix metalloproteinase-3, and Coll2-1 as serum biomarkers in knee osteoarthritis: A cross-sectional study. Rheumatology international, 2018. 38(5): p. 821-830. [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; et al., Pathogenesis of osteoarthritis: Risk factors, regulatory pathways in chondrocytes, and experimental models. Biology, 2020. 9(8): p. 194. [CrossRef]
- Chu, L.; et al., Articular cartilage degradation and aberrant subchondral bone remodeling in patients with osteoarthritis and osteoporosis. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research, 2020. 35(3): p. 505-515. [CrossRef]
- Loeser, R.F.; et al., Osteoarthritis: A disease of the joint as an organ. Arthritis and Rheumatism, 2012. 64(6): p. 1697-1707. [CrossRef]
- Jenei-Lanzl, Z., A. Meurer, and F. Zaucke, Interleukin-1β signaling in osteoarthritis–chondrocytes in focus. Cellular Signalling, 2019. 53: p. 212-223. [CrossRef]
- Lories, R.J. and S. Monteagudo, is Wnt signaling an attractive target for the treatment of osteoarthritis? Rheumatology and Therapy, 2020. 7(2): p. 259-270. [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; et al., The PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in osteoarthritis: A narrative review. Osteoarthritis and cartilage, 2020. 28(4): p. 400-409. [CrossRef]
- Peat, G. and M. Thomas, Osteoarthritis year in review 2020: Epidemiology & therapy. Osteoarthritis and cartilage, 2021. 29(2): p. 180-189. [CrossRef]
- Saito, T. and S. Tanaka, Molecular mechanisms underlying osteoarthritis development: Notch and NF-κB. Arthritis research & therapy, 2017. 19(1): p. 1-7. [CrossRef]
- Radenkovic, S.; et al., TRAPPC9-CDG: A novel congenital disorder of glycosylation with dysmorphic features and intellectual disability. Genetics in Medicine, 2022. 24(4): p. 894-904. [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.H.; et al., NIK-and IKKβ-binding protein contributes to gastric cancer chemoresistance by promoting epithelial-mesenchymal transition through the NF-κB signaling pathway. Oncology reports, 2018. 39(6): p. 2721-2730. [CrossRef]
- Gasparini, C. and M. Feldmann, NF-κB as a target for modulating inflammatory responses. Current pharmaceutical design, 2012. 18(35): p. 5735-5745. [CrossRef]
- Roman-Blas, J. and S. Jimenez, NF-κB as a potential therapeutic target in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoarthritis and cartilage, 2006. 14(9): p. 839-848. [CrossRef]
- Appleton, C.T., Osteoarthritis year in review 2017: Biology. Osteoarthritis Cartilage, 2018. 26(3): p. 296-303. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
TRAPPC9 expression is enhanced following IL-1β treatment. TRAPPC9 mRNA expression (A) and protein (B) levels were measured and semi-quantified (C) in primary murine articular chondrocytes under various doses of IL-1β treatment. A time point study was conducted with primary murine articular chondrocytes and mRNA expression (D) and (E) protein levels were measured and (F) semi-quantified. (G) Primary murine articular chondrocytes were either left untreated (control) or treated with IL-1β (10ng/mL) and stained for DAPI (blue), actin (green), and TRAPPC9 (red). Scale bar- 20µm. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001, ns-non-significant. N=5 with experiments run in triplicate.
Figure 1.
TRAPPC9 expression is enhanced following IL-1β treatment. TRAPPC9 mRNA expression (A) and protein (B) levels were measured and semi-quantified (C) in primary murine articular chondrocytes under various doses of IL-1β treatment. A time point study was conducted with primary murine articular chondrocytes and mRNA expression (D) and (E) protein levels were measured and (F) semi-quantified. (G) Primary murine articular chondrocytes were either left untreated (control) or treated with IL-1β (10ng/mL) and stained for DAPI (blue), actin (green), and TRAPPC9 (red). Scale bar- 20µm. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001, ns-non-significant. N=5 with experiments run in triplicate.
Figure 2.
Modulation of TRAPPC9 significantly reduces chondrocyte markers gene expression in murine primary articular chondrocytes. TRAPPC9 mRNA expression (A) and protein levels (B, C) were reduced in primary murine articular chondrocytes. Modulation of TRAPPC9 in the presence of IL-1β significantly enhanced Col2α1 expression (D) while significantly reducing mRNA expression of IL-6 (E), MMP-1 (F), MMP-9 (G), MMP-13 (H) and MMP-13 protein levels (I, J). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001, ns-non-significant. N=5 with experiments run in triplicate.
Figure 2.
Modulation of TRAPPC9 significantly reduces chondrocyte markers gene expression in murine primary articular chondrocytes. TRAPPC9 mRNA expression (A) and protein levels (B, C) were reduced in primary murine articular chondrocytes. Modulation of TRAPPC9 in the presence of IL-1β significantly enhanced Col2α1 expression (D) while significantly reducing mRNA expression of IL-6 (E), MMP-1 (F), MMP-9 (G), MMP-13 (H) and MMP-13 protein levels (I, J). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001, ns-non-significant. N=5 with experiments run in triplicate.
Figure 3.
Overexpression of TRAPPC9 enhances catabolic markers and reduces collagen markers in human TC28 chondrocyte cell line. Cells were infected with retrovirus particles expressing GFP (E.vector) to serve as an infection control or particles overexpressing TRAPPC9 (TRAPPC9 OE). RNA was isolated for qPCR (A) and Western blot (B, C) using anti-TRAPPC9 and GAPDH (loading control) antibodies. After infection, TRAPPC9 was successfully overexpressed in TC28 cells (D). Expression of Col2α1 (E), and pro-inflammatory markers IL-6 (F), MMP-1 (G), MMP-9 (H), MMP-13 (I) were assessed by qPCR and MMP-13 protein levels by immunoblot (J, K). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001, ns-non-significant. N=5 with experiments run in triplicate.
Figure 3.
Overexpression of TRAPPC9 enhances catabolic markers and reduces collagen markers in human TC28 chondrocyte cell line. Cells were infected with retrovirus particles expressing GFP (E.vector) to serve as an infection control or particles overexpressing TRAPPC9 (TRAPPC9 OE). RNA was isolated for qPCR (A) and Western blot (B, C) using anti-TRAPPC9 and GAPDH (loading control) antibodies. After infection, TRAPPC9 was successfully overexpressed in TC28 cells (D). Expression of Col2α1 (E), and pro-inflammatory markers IL-6 (F), MMP-1 (G), MMP-9 (H), MMP-13 (I) were assessed by qPCR and MMP-13 protein levels by immunoblot (J, K). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001, ns-non-significant. N=5 with experiments run in triplicate.
Figure 4.
TRAPPC9 co-immunoprecipitated with NIK in primary murine articular chondrocytes. Cell lysate was immunoprecipitated with anti-NIK antibody and were blotted for TRAPPC9 (A). Reverse IP for NIK using anti-TRAPPC9 antibody and IgG (negative control) were blotted for NIK (B). Experiment was run three times with similar results.
Figure 4.
TRAPPC9 co-immunoprecipitated with NIK in primary murine articular chondrocytes. Cell lysate was immunoprecipitated with anti-NIK antibody and were blotted for TRAPPC9 (A). Reverse IP for NIK using anti-TRAPPC9 antibody and IgG (negative control) were blotted for NIK (B). Experiment was run three times with similar results.
Figure 5.
TRAPPC9 modulation inhibits P-P100 in TC28 cells following IL-1β treatment. Immunoblot of TC28 cells without IL-1β (control) does not significantly alter P-P100 protein levels (A, D). Following IL-1β treatment, P-P100 protein levels were significantly increased (B, D). Modulation of TRAPPC9 inhibited P-P100 protein (C, D). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ns-non-significant. Experiment was run three times with similar results.
Figure 5.
TRAPPC9 modulation inhibits P-P100 in TC28 cells following IL-1β treatment. Immunoblot of TC28 cells without IL-1β (control) does not significantly alter P-P100 protein levels (A, D). Following IL-1β treatment, P-P100 protein levels were significantly increased (B, D). Modulation of TRAPPC9 inhibited P-P100 protein (C, D). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ns-non-significant. Experiment was run three times with similar results.
Figure 6.
C57BL/6 mice display severe articular cartilage damage and reduced NIK positive cells following DMM. C57BL/6 male mice were subjected to DMM surgery on the right knee with the left knee serving as an internal sham control (A). TRAPPC9 positive cells (B, D) were not significantly altered following DMM, while NIK positive cells (C, E) were shown to be significantly reduced compared to sham operated joints. **p<0.01, ns-non-significant. Scale bar = 200µm for low magnification and 100µm for high magnification. Experiment was run five times with similar results.
Figure 6.
C57BL/6 mice display severe articular cartilage damage and reduced NIK positive cells following DMM. C57BL/6 male mice were subjected to DMM surgery on the right knee with the left knee serving as an internal sham control (A). TRAPPC9 positive cells (B, D) were not significantly altered following DMM, while NIK positive cells (C, E) were shown to be significantly reduced compared to sham operated joints. **p<0.01, ns-non-significant. Scale bar = 200µm for low magnification and 100µm for high magnification. Experiment was run five times with similar results.
Figure 7.
Human cartilage explants treated with IL-1β demonstrate significant ECM degradation and decreased numbers of NIK-positive cells. Human cartilage explants were isolated from de-identified arthroplasty samples and undamaged cartilage isolated using India ink (A). Explants were paraffin embedded, sectioned, and stained with Saffrin-O. Following treatment with IL-1β, explants showed severe ECM degradation. Explants were stained with an anti-TRAPPC9 antibody. There were no significant differences in TRAPPC9 positive cells following IL-1β treatment (B, D) compared to control, while NIK positive cells were reduced following IL-1β treatment (C, E). Scale bar = 200µm for low magnification and 100µm for high magnification. ***p<0.001, ns-non-significant. N=5 with experiments run in triplicate.
Figure 7.
Human cartilage explants treated with IL-1β demonstrate significant ECM degradation and decreased numbers of NIK-positive cells. Human cartilage explants were isolated from de-identified arthroplasty samples and undamaged cartilage isolated using India ink (A). Explants were paraffin embedded, sectioned, and stained with Saffrin-O. Following treatment with IL-1β, explants showed severe ECM degradation. Explants were stained with an anti-TRAPPC9 antibody. There were no significant differences in TRAPPC9 positive cells following IL-1β treatment (B, D) compared to control, while NIK positive cells were reduced following IL-1β treatment (C, E). Scale bar = 200µm for low magnification and 100µm for high magnification. ***p<0.001, ns-non-significant. N=5 with experiments run in triplicate.
Table 1.
Antibodies.
| Target |
Source |
| TRAPPC9 |
Proteintech |
| NIK |
Cell signaling |
| P-100 |
Cell signaling |
| P-P-100 |
Cell signaling |
| GAPDH |
Cell signaling |
| MMP-13 |
Proteintech |
| β-actin |
Cell signaling |
| HRP-conjugated secondary |
Cell signaling |
Table 2.
RT-qPCR Primers.
Table 2.
RT-qPCR Primers.
| Gene |
Forward |
Reverse |
| TRAPPC9 |
GCT GTC ACC TTG GAG AAC AT |
GCT CAA GAA GTC GCC ATA CA |
| IL-6 |
CCA ATT TCC AAT GCT CTC CT |
ACC ACA GTG AGG AAT GTC CA |
| Collagen-2α1 |
TTC TGC TGC TAA TGT TCT TGA |
GGG ATG AAG TAT TGT GTC TTG GG |
| GAPDH |
CGA CTT CAA CAG CAA ATA CCA CTC TTC |
TGG GTG GTC CAG TTC TTA CTC CTT |
| MMP-1 |
TTG CTG CTC ATG AAC TTG GC |
AGA GAT GGA AAC GGG ACA AGT |
| MMP-9 |
GCA TAC TTG TAC CGC TAT GGT |
TGT GAT GTT ATG ATG GTC CC |
| MMP-13 |
TGA TGG ACC TTC TGG TCT TCT GGC |
CAT CCA CAT GGT TGG GAA GTT CTG |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).