Submitted:
13 April 2023
Posted:
14 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of HRV Parameters
3.2. Analysis of the Cognitive Task Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Agorastos, A.; Nicolaides, N.C.; Bozikas, V.P.; Chrousos, G.P.; Pervanidou, P. Multilevel Interactions of Stress and Circadian System: Implications for Traumatic Stress. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leliavski, A.; Shostak, A.; Husse, J.; Oster, H. Impaired Glucocorticoid Production and Response to Stress in Arntl-Deficient Male Mice. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Destici, E.; Jacobs, E.H.; Tamanini, F.; Loos, M.; van der Horst, G.T.J.; Oklejewicz, M. Altered Phase-Relationship between Peripheral Oscillators and Environmental Time in Cry1 or Cry2 Deficient Mouse Models for Early and Late Chronotypes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallmann, R.; Touma, C.; Palme, R.; Albrecht, U.; Steinlechner, S. Impaired Daily Glucocorticoid Rhythm in Per1 Brd Mice. J Comp Physiol A 2006, 192, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, K.P.; Drake, A.L.; Frey, D.J.; Fleshner, M.; Desouza, C.A.; Gronfier, C.; Czeisler, C.A. Influence of Sleep Deprivation and Circadian Misalignment on Cortisol, Inflammatory Markers, and Cytokine Balance. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity 2015, 47, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karatsoreos, I.N.; Bhagat, S.; Bloss, E.B.; Morrison, J.H.; McEwen, B.S. Disruption of Circadian Clocks Has Ramifications for Metabolism, Brain, and Behavior. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2011, 108, 1657–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanifin, J.P.; Lockley, S.W.; Cecil, K.; West, K.; Jablonski, M.; Warfield, B.; James, M.; Ayers, M.; Byrne, B.; Gerner, E.; et al. Randomized Trial of Polychromatic Blue-Enriched Light for Circadian Phase Shifting, Melatonin Suppression, and Alerting Responses. Physiology & Behavior 2019, 198, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharov, A.V.; Khivintseva, E.V.; Pyatin, V.F.; Sergeeva, M.S.; Antipov, O.I. Melatonin – Known and Novel Areas of Clinical Application. Neurosci Behav Physi 2019, 49, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharov, A.V.; Khivintseva, E.V.; Pytin, V.F.; Sergeeva, M.S.; Antipov, O.I. Melatonin — known problems and perspectives of clinical usage. Z. nevrol. psikhiatr. im. S.S. Korsakova 2017, 117, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharov, A.; Khivintseva, E. Clinical Use of Melatonin in the Treatment of Sleep Disorders. In Melatonin - The Hormone of Darkness and its Therapeutic Potential and Perspectives; Vlachou, M., Ed.; IntechOpen, 2020; ISBN 978-1-83962-908-2. [Google Scholar]
- Pyatin, V.F. Ustrojstvo dlya funkcional'nogo upravleniya cirkadiannymi chasami organizma cheloveka”. RU patent for utility model RU 182615 U1 /15.01.2018. (In Russian).
- Sergeeva, M.S.; Pyatin, V.F.; Korovina, E.S. Kontrol' upravlenija funkcional'nym sostojaniem organizma cheloveka cirkadiannoj sistemoj v rannie utrennie chasy. Biomedicinskaja radiojelektronika 2015, 4, 72–74. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Alsaggaf, M.A.; Wali, S.O.; Merdad, R.A.; Merdad, L.A. Sleep Quantity, Quality, and Insomnia Symptoms of Medical Students during Clinical Years: Relationship with Stress and Academic Performance. SMJ 2016, 37, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kötter, T.; Wagner, J.; Brüheim, L.; Voltmer, E. Perceived Medical School Stress of Undergraduate Medical Students Predicts Academic Performance: An Observational Study. BMC Med Educ 2017, 17, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruffaerts, R.; Mortier, P.; Kiekens, G.; Auerbach, R.P.; Cuijpers, P.; Demyttenaere, K.; Green, J.G.; Nock, M.K.; Kessler, R.C. Mental Health Problems in College Freshmen: Prevalence and Academic Functioning. Journal of Affective Disorders 2018, 225, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, B.; Shah, M.A.A.; Kumari, R.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, J.; Tahir, A. Depression, Anxiety, and Stress Among Final-Year Medical Students. Cureus 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernando, D.; Roca, S.; Sancho, J.; Alesanco, Á.; Bailón, R. Validation of the Apple Watch for Heart Rate Variability Measurements during Relax and Mental Stress in Healthy Subjects. Sensors 2018, 18, 2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baevskij, R.M. Problema ocenki i prognozirovaniya funkcional'nogo sostoyaniya organizma i ee razvitie v kosmicheskoj medicine. Uspekhi fiziologicheskih nauk 2006, 37, 42–57. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.-G.; Cheon, E.-J.; Bai, D.-S.; Lee, Y.H.; Koo, B.-H. Stress and Heart Rate Variability: A Meta-Analysis and Review of the Literature. Psychiatry Investig 2018, 15, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriev, D.A.; Saperova, E.V.; Dimitriev, A.D. State Anxiety and Nonlinear Dynamics of Heart Rate Variability in Students. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shook, N.; Pena, P.; Fazio, R.H.; Sollers, J.J.; Thayer, J.F. Friend or foe: heart rate varability and the negativity bias in learning about novel objects, Proceedings of the 47th Annual Meeting of the Society-for-Psychophysiological-Research. Psychophysiology 2007, 44, S39. [Google Scholar]
- Thayer, J.F.; Åhs, F.; Fredrikson, M.; Sollers, J.J.; Wager, T.D. A Meta-Analysis of Heart Rate Variability and Neuroimaging Studies: Implications for Heart Rate Variability as a Marker of Stress and Health. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews 2012, 36, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, S.J. Neurocognitive Mechanisms of Anxiety: An Integrative Account. Trends in Cognitive Sciences 2007, 11, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blons, E.; Arsac, L.M.; Gilfriche, P.; McLeod, H.; Lespinet-Najib, V.; Grivel, E.; Deschodt-Arsac, V. Alterations in Heart-Brain Interactions under Mild Stress during a Cognitive Task Are Reflected in Entropy of Heart Rate Dynamics. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 18190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shook, N.J.; Fazio, R.H.; Vasey, M.W. Negativity Bias in Attitude Learning: A Possible Indicator of Vulnerability to Emotional Disorders? Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry 2007, 38, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litscher, D.; Wang, L.; Gaischek, I.; Litscher, G. The Influence of New Colored Light Stimulation Methods on Heart Rate Variability, Temperature, and Well-Being: Results of a Pilot Study in Humans. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2013, 2013, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- KUANG, X.D.; YU, X.B.; CAO, Y.; LI, D.S.; ZHU, H.Y. Interaction between the Circadian Clock and Chronic Stress. Biomedical and Environmental Sciences 2018, 31, 686–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helfrich-Förster, C. Interactions between Psychosocial Stress and the Circadian Endogenous Clock. PsyCh Journal 2017, 6, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oster, H. The Interplay between Stress, Circadian Clocks, and Energy Metabolism. Journal of Endocrinology 2020, 247, R13–R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, C.E.; Leinweber, B.; Drengberg, B.C.; Blaum, C.; Oster, H. Interaction between Circadian Rhythms and Stress. Neurobiology of Stress 2017, 6, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landgraf, D.; Long, J.E.; Proulx, C.D.; Barandas, R.; Malinow, R.; Welsh, D.K. Genetic Disruption of Circadian Rhythms in the Suprachiasmatic Nucleus Causes Helplessness, Behavioral Despair, and Anxiety-like Behavior in Mice. Biological Psychiatry 2016, 80, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portaluppi, F.; Tiseo, R.; Smolensky, M.H.; Hermida, R.C.; Ayala, D.E.; Fabbian, F. Circadian Rhythms and Cardiovascular Health. Sleep Medicine Reviews 2012, 16, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandewalle, G.; Gais, S.; Schabus, M.; Balteau, E.; Carrier, J.; Darsaud, A.; Sterpenich, V.; Albouy, G.; Dijk, D.J.; Maquet, P. Wavelength-Dependent Modulation of Brain Responses to a Working Memory Task by Daytime Light Exposure. Cerebral Cortex 2007, 17, 2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuts, A.; Poluektov, M.; Zakharov, A.; Govzman, A.; Ponomareva, I.; Yakupov, E.; Tikhomirova, O.; Sviryaev, Y.; Yakovlev, A.; Polyakov, A.; Melnikov, A.; Basetti, C.L.A. Clinical and neurophysiological characteristics of 89 patients with narcolepsy and cataplexy from the Russian Narcolepsy Network. Journal of clinical sleep medicine 2023, 19, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Parameter | Definition |
|---|---|
| SDNN, ms | Standard deviation of the NN-interval duration for the sample |
| RMSSD, ms | The square root of the sum of the squared differences in the durations of consecutive NN-intervals pairs |
| pNN50, % | Percentage of the adjacent NN-intervals pairs that differ in duration by more than 50 ms |
| HRVind, c.u. | Triangular index of heart rate variability |
| Heart rate, beats/min | Heart rate |
| Mode, ms | NN-interval duration mode |
| AMo, % | Amplitude of the NN-interval duration mode |
| DX, ms | Variation range of NN-interval duration |
| VLF, thousand ms 2 | The power of very low-frequency (0.003-0.04 Hz) fluctuations in the duration of NN-interval |
| LF, thousand ms 2 | The power of low-frequency (0.04-0.15 Hz) fluctuations in the duration of NN-interval |
| HF, ms 2 | The power of high-frequency (0.15-0.40 Hz) fluctuations in the duration NN-interval |
| Total, thousand ms 2 | The power of fluctuations in the duration of NN-interval in all ranges (0.003 - 0.40 Hz) |
| LF norm, % | The normalized value of the power of low-frequency (0.04-0.15 Hz) fluctuations in the NN-interval duration |
| HF norm, % | The normalized value of the power of high-frequency (0.15-0.40 Hz) fluctuations in the NN-interval duration |
| LF/HF | The ratio of low-frequency (0.04-0.15 Hz) and high-frequency (0.15-0.40 Hz) fluctuations in the NN-interval duration |
| SIM, c.u. | Intensity index of influences of the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system |
| PAR, c.u. | Intensity index of influences of the parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system |
| IB, c.u. | Stress index of regulatory systems according to R.M. Baevsky |
| Parameter | Definition | Formula |
|---|---|---|
| A , symbols /sec | Attention speed | Number of letters viewed / operating time |
| T1 , c.u. | Work accuracy (option 1) | Total crossed out / should have been crossed out |
| T2 , c.u. | Work accuracy (option 2) | Correctly crossed out / should have been crossed out |
| T3 , c.u. | Work accuracy (option 3) | Correctly crossed out / (crossed out + skipped) |
| E , signs | Coefficient of mental productivity | Number of letters viewed * 2nd option for work accuracy |
| Au , symbols /sec | Coefficient of mental performance | Attention speed * ((correctly crossed out - skipped) / should have been crossed out) |
| K , % | Concentration of attention | Correctly crossed out / should have been crossed out |
| Ku , c.u. | Stability of concentration | Lines viewed * (lines viewed / (letters omitted and erroneously crossed out + 1)) |
| V , symbols | The volume of visual information | 0.5936 * number of letters viewed |
| Q , symbols /sec | The speed of processing visual information | (Volume of visual information - 2.807 * (skipped + erroneously crossed out)) / operating time |
| Baseline condition | The letter cancellation test | Blue Sky Pro session | The letter cancellation test | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 min | 5 min | 20 min | 5 min | |||
| 5 min | 5 min | |||||
| HRV | HRV | HRV | HRV | HRV | ||
| Fon | Cor | Blue1 | Blue2 | BlueCor | ||
| Parameter | Condition1 | Сomparison2 (p0) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fon | Cor | Blue1 | Blue2 | BlueCor | Fon vs Cor | Fon vs BluCor | Cor vs BluCor | |
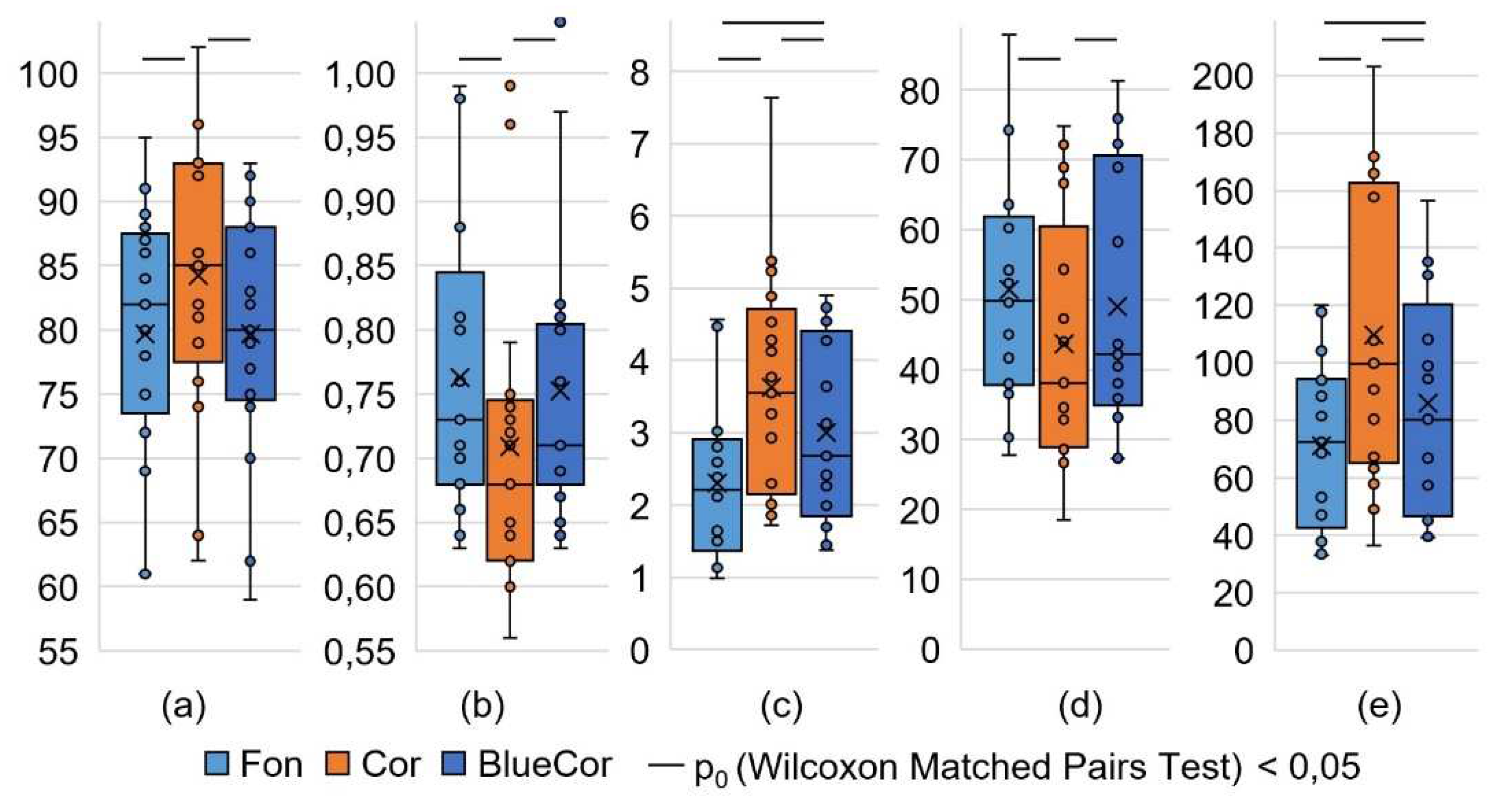
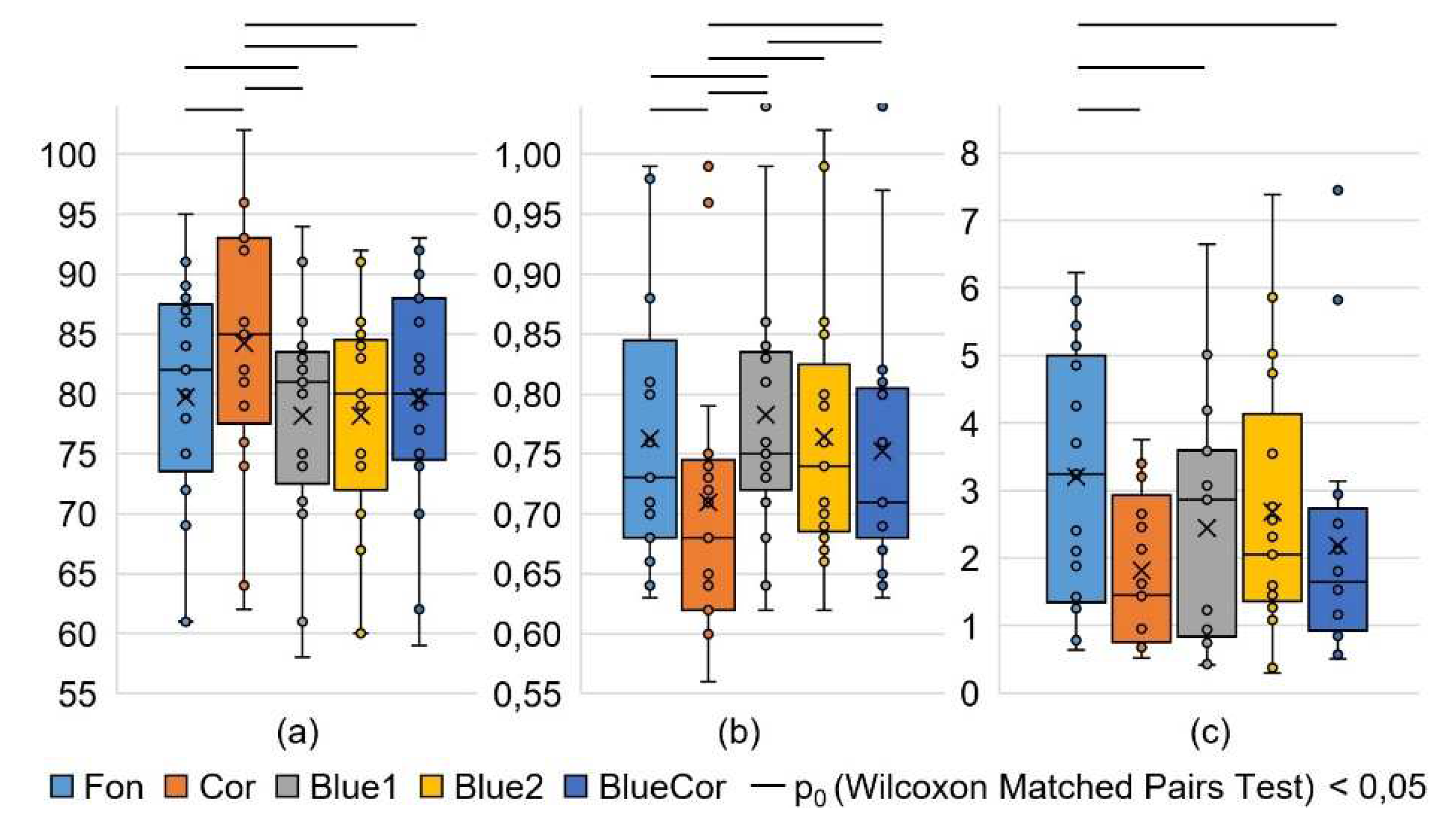
| SDNN, ms | 61,6 ±2,9 | 55,1 ±3,7 | 61,7 ±4,6 | 62,4 ±3,4 | 56,9 ±3,3 | 0,049 | 0,136 | 0,379 |
| RMSSD, ms | 50 (38; 60) |
38 (29; 54) |
48 (36; 63) |
45 (38; 67) |
42 (36; 69) |
0,044 | 0,177 | 0,044 |
| NN50, ms | 86 (58; 127) |
49 (29; 117) |
92 (44; 124) |
81 (46; 145) |
57 (45; 155) |
0,080 | 0,276 | 0,055 |
| HRVind, c.u. | 11,9 ±0,6 | 10,2 ±0,7 | 11,1 ±0,7 | 12,1 ±0,7 | 10,5 ±0,6 | 0,023 | 0,079 | 0,351 |
| Moda, ms | 730 (680; 810) |
680 (620; 740) |
750 (730; 830) |
740 (690; 800) |
710 (690; 800) |
0,002 | 0,394 | 0,002 |
| AMo, % | 7,8 ±0,4 | 9,5 ±0,6 | 8,8 ±0,7 | 7,7 ±0,5 | 9,0 ±0,4 | 0,016 | 0,081 | 0,209 |
| DX, ms | 350 (330; 390) |
330 (260; 390) |
360 (310; 390) |
310 (300; 370) |
330 (310; 380) |
0,047 | 0,281 | 0,551 |
| Heart rate, bpm | 79,7 ±2,4 | 84,2 ±2,7 | 78,2 ±2,3 | 78,2 ±2,3 | 79,7 ±2,4 | 0,002 | 0,778 | 0,001 |
| VLF, thousand ms2 | 2,0 (1,2; 3,1) |
1,5 (1,0; 2,8) |
2,9 (1,5; 3,4) |
2,7 (1,6; 5,2) |
1,6 (1,1; 2,3) |
0,523 | 0,266 | 0,868 |
|
LF, thousand ms2 |
3,9 (2,4; 4,3) |
2,1 (1,7; 3,4) |
2,6 (1,6; 3,9) |
4,6 (2,1; 6,1) |
2,3 (2,2; 2,9) |
0,025 | 0,035 | 0,554 |
|
HF, thousand ms2 |
3,2 (1,4; 4,8) |
1,4 (0,8; 2,7) |
2,9(0,9; 3,6) | 2,1(1,5; 3,5) | 1,6 (0,9; 2,5) |
0,006 | 0,044 | 0,332 |
|
Total, thousand ms2 |
9,5 ±1,1 | 6,5 ±0,7 | 9,5 ±1,5 | 10,0 ±1,2 | 6,9 ±0,8 | 0,007 | 0,019 | 0,554 |
| LF norm, % | 55,1 ±3,8 | 57,7 ±3,5 | 58,1 ±3,7 | 60,8 ±3,5 | 57,9 ±4,5 | 0,523 | 0,831 | 0,868 |
| HF norm, % | 44,9 ±3,8 | 42,3 ±3,5 | 41,9 ±3,7 | 39,2 ±3,5 | 42,1 ±4,5 | 0,523 | 0,831 | 0,868 |
| LF/HF | 1,02 (0,81; 2,04) |
1,30 (0,93; 1,99) |
1,18 (0,86; 2,11) |
1,53 (1,08; 2,57) |
1,53 (0,68; 3,03) |
0,796 | 0,758 | 0,943 |
| SIM, c.u. | 2,3 ±0,3 | 3,6 ±0,4 | 2,9 ±0,5 | 2,4 ±0,3 | 3,0 ±0,3 | 0,006 | 0,006 | 0,049 |
| PAR, c.u. | 14,6 ±0,8 | 12,0 ±0,9 | 13,7 ±0,9 | 14,5 ±0,9 | 13,1 ±0,8 | 0,031 | 0,093 | 0,332 |
| IB, c.u. | 71 ±7 | 110 ±13 | 81 ±10 | 73 ±8 | 86 ±9 | 0,006 | 0,049 | 0,028 |
| Parameter | Condition 1 | Сomparison (Wilcoxon Matched Pairs Test) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cor | BlueCor | W | Z | p0 | |
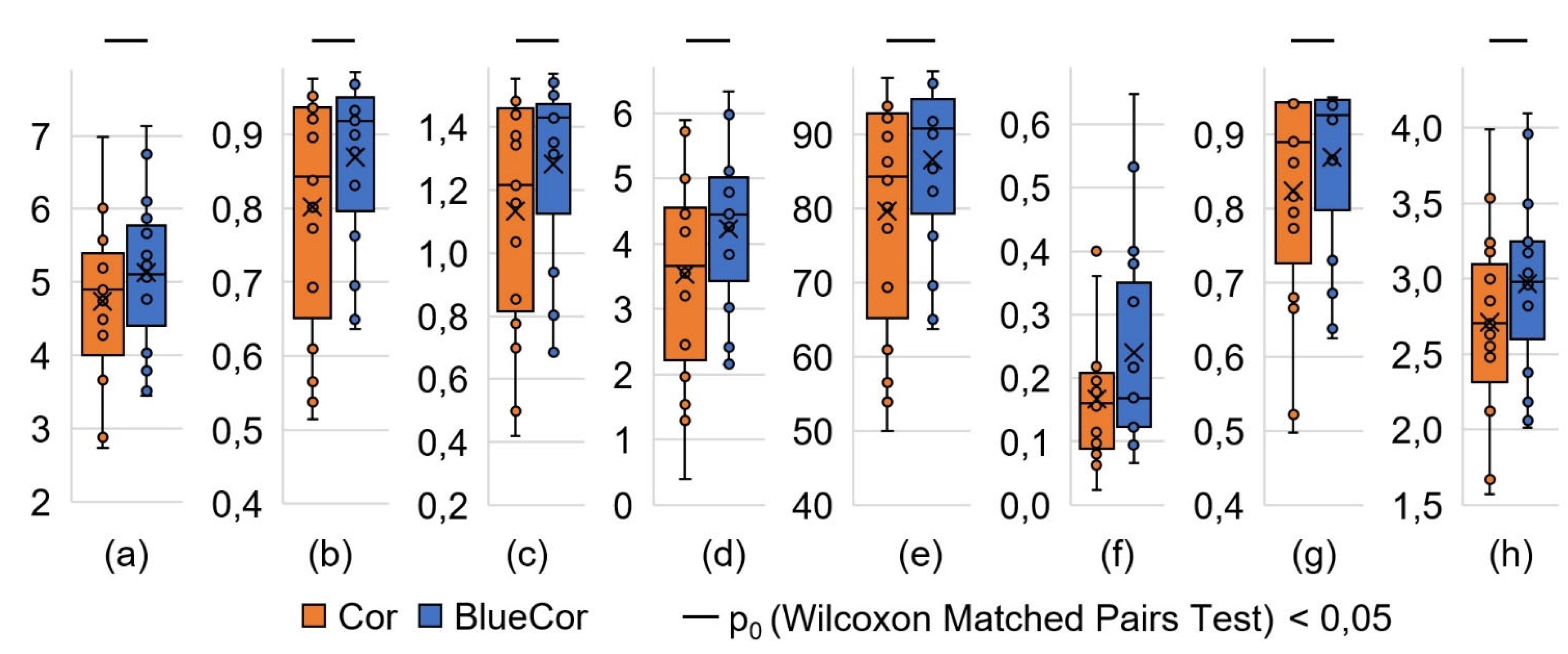
| A, symbols/sec | 4,7 ±0,3 | 5,1 ±0,3 | 18 | 2,769 | 0,006 |
| T1, c.u. | 0,84 (0,69; 0,94) | 0,92 (0,83; 0,93) | 24 | 2,485 | 0,013 |
| T2, c.u. | 0,84 (0,69; 0,92) | 0,91 (0,82; 0,93) | 23 | 2,533 | 0,011 |
| T3, c.u. | 0,94 (0,91; 0,96) | 0,95 (0,91; 0,97) | 58 | 0,876 | 0,381 |
| E, symbols | 1216 (853; 1439) | 1430 (1314; 1446) | 21 | 2,627 | 0,009 |
| Au, symbols/sec | 3,5 ±0,4 | 4,2 ±0,3 | 5 | 3,385 | 0,001 |
| K, % | 84 (69; 92) | 91 (82; 93) | 20 | 2,675 | 0,007 |
| Ku, c.u. | 160 (97; 200) | 169 (123; 320) | 42 | 1,633 | 0,102 |
| V, symbols | 890 (773; 943) | 925 (865; 946) | 22 | 2,379 | 0,017 |
| Q, symbols/sec | 2,7 ±0,2 | 3,0 ±0,1 | 9 | 3,195 | 0,001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





