Submitted:
13 April 2023
Posted:
13 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
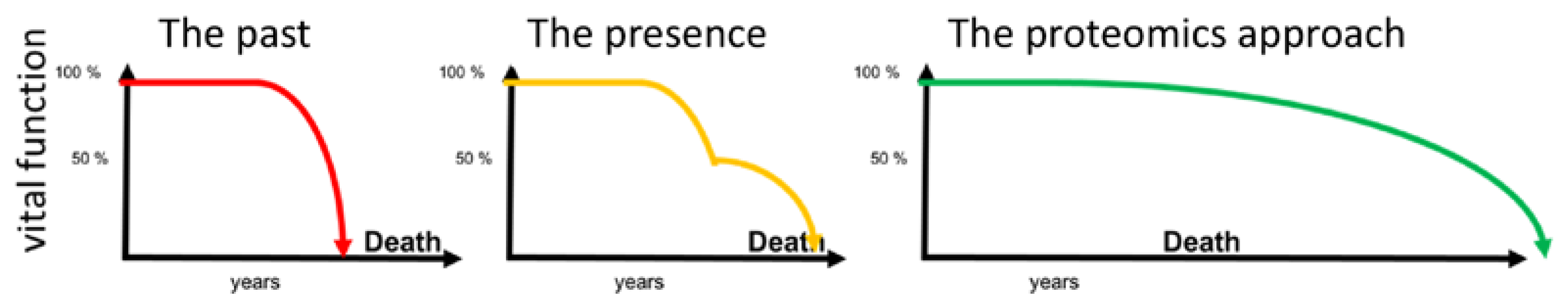
1. Introduction
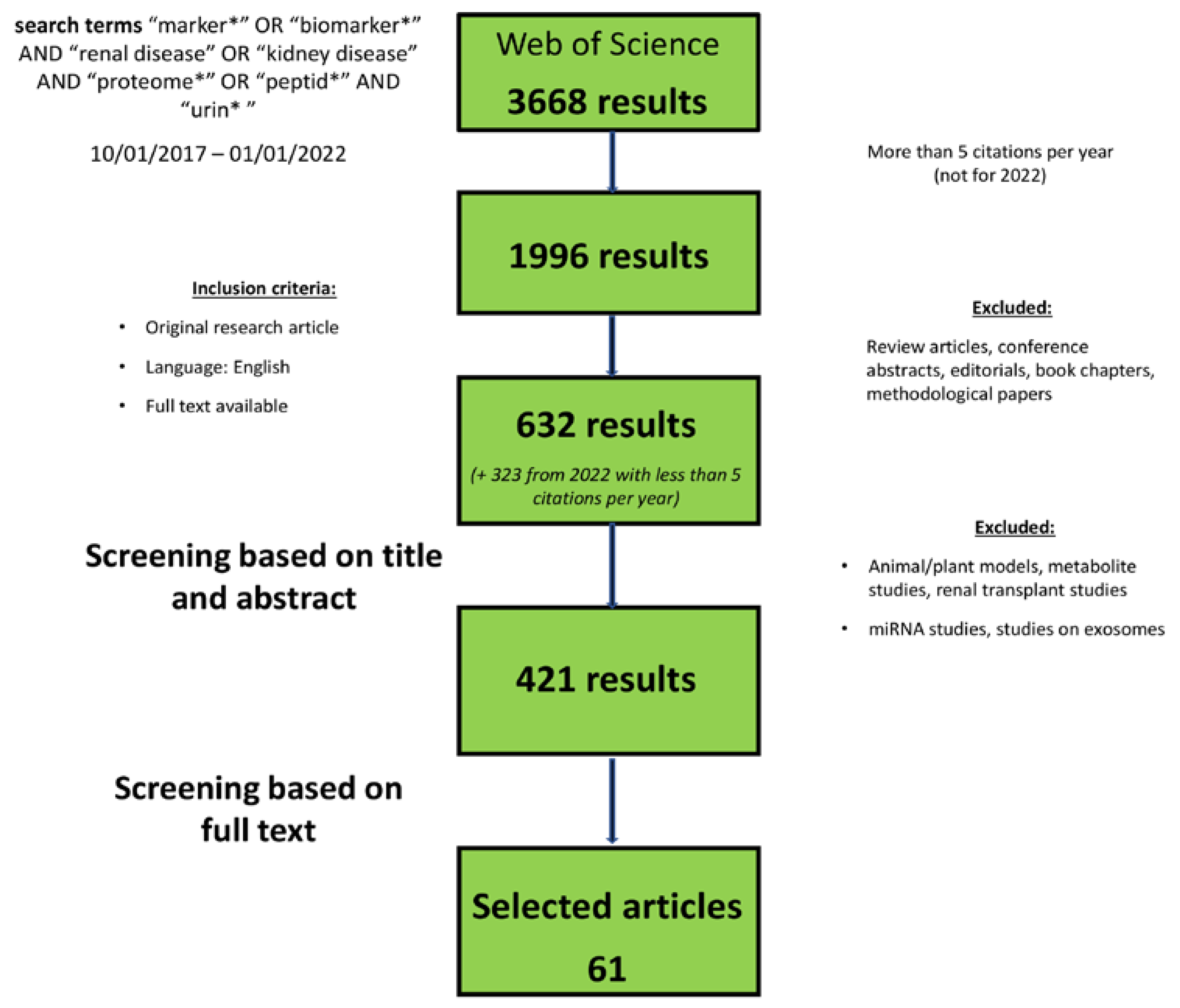
2. Methods/Search Criteria
3. Results
Uprising Single-Protein Urine Biomarkers of Chronic Kidney Disease
CD80
Epidermal growth factor
Kidney injury molecule 1
Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1
Matrix metalloproteinase 7
Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin
Uromodulin
Other single biomarkers
Peptidomic/Proteomic-Based Biomarker Panels
CKD273
Other biomarkers of DKD
Biomarkers of kidney fibrosis
Biomarkers in different CKD entities
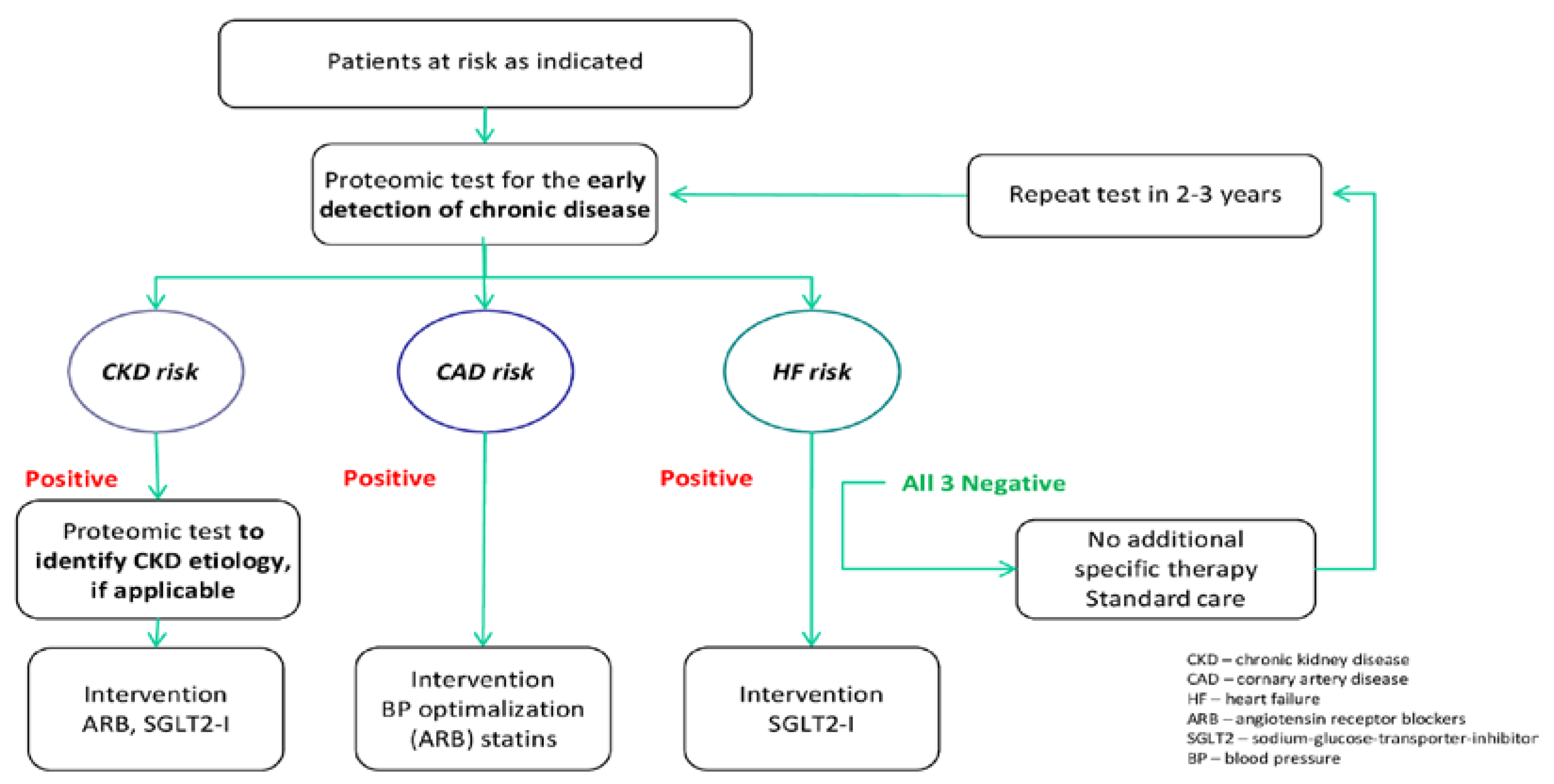
4. Discussion
5. Summary and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD Chronic Kidney Disease Collaboration. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Chronic Kidney Disease, 1990-2017: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2020, 395 (10225), 709–733. [CrossRef]
- KDIGO CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2012 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease. Guideline 2013, 3 (1), 1–150.
- Stevens, L. A.; Levey, A. S. Measured GFR as a Confirmatory Test for Estimated GFR. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2009, 20 (11), 2305–2313. [CrossRef]
- Porrini, E.; Ruggenenti, P.; Luis-Lima, S.; Carrara, F.; Jiménez, A.; de Vries, A. P. J.; Torres, A.; Gaspari, F.; Remuzzi, G. Estimated GFR: Time for a Critical Appraisal. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2019, 15 (3), 177–190. [CrossRef]
- Alicic, R. Z.; Rooney, M. T.; Tuttle, K. R. Diabetic Kidney Disease: Challenges, Progress, and Possibilities. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. CJASN 2017, 12 (12), 2032–2045. [CrossRef]
- Perkins, B. A.; Ficociello, L. H.; Roshan, B.; Warram, J. H.; Krolewski, A. S. In Patients with Type 1 Diabetes and New-Onset Microalbuminuria the Development of Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease May Not Require Progression to Proteinuria. Kidney Int. 2010, 77 (1), 57–64. [CrossRef]
- Leong, A.; Ekinci, E. I.; Nguyen, C.; Milne, M.; Hachem, M.; Dobson, M.; MacIsaac, R. J.; Jerums, G. Long-Term Intra-Individual Variability of Albuminuria in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Implications for Categorization of Albumin Excretion Rate. BMC Nephrol. 2017, 18 (1), 355. 355. [CrossRef]
- Bolignano, D.; Zoccali, C. Non-Proteinuric Rather than Proteinuric Renal Diseases Are the Leading Cause of End-Stage Kidney Disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2017, 32 (suppl_2), ii194–ii199. [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, A.; Benediktsson, H.; Muruve, D. A.; Hildebrand, A. M.; Ravani, P. Trends in Biopsy-Based Diagnosis of Kidney Disease: A Population Study. Can. J. Kidney Health Dis. 2018, 5, 2054358118799690. [CrossRef]
- Fassett, R. G.; Venuthurupalli, S. K.; Gobe, G. C.; Coombes, J. S.; Cooper, M. A.; Hoy, W. E. Biomarkers in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Review. Kidney Int. 2011, 80 (8), 806–821. [CrossRef]
- Mischak, H.; Delles, C.; Vlahou, A.; Vanholder, R. Proteomic Biomarkers in Kidney Disease: Issues in Development and Implementation. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2015, 11(4), 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maas, R. J.; Deegens, J. K.; Smeets, B.; Moeller, M. J.; Wetzels, J. F. Minimal Change Disease and Idiopathic FSGS: Manifestations of the Same Disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2016, 12(12), 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez Guerrico, A. M.; Lieske, J.; Klee, G.; Kumar, S.; Lopez-Baez, V.; Wright, A. M.; Bobart, S.; Shevell, D.; Maldonado, M.; Troost, J. P.; Hogan, M. C.; Nephrotic Syndrome Study Network Consortium (NEPTUNE). Urinary CD80 Discriminates Among Glomerular Disease Types and Reflects Disease Activity. Kidney Int. Rep. 2020, 5(11), 2021–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, C.; Liu, X.; Shen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Fan, J.; Jiang, Y.; Meng, Q. Urinary CD80 Excretion Is a Predictor of Good Outcome in Children with Primary Nephrotic Syndrome. Pediatr. Nephrol. Berl. Ger. 2018, 33(7), 1183–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garin, E. H.; Mu, W.; Arthur, J. M.; Rivard, C. J.; Araya, C. E.; Shimada, M.; Johnson, R. J. Urinary CD80 Is Elevated in Minimal Change Disease but Not in Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis. Kidney Int. 2010, 78(3), 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, C.; Liu, X.; Shen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Fan, J.; Jiang, Y.; Meng, Q. Urinary CD80 Levels as a Diagnostic Biomarker of Minimal Change Disease. Pediatr. Nephrol. Berl. Ger. 2015, 30(2), 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Federico, G.; Meister, M.; Mathow, D.; Heine, G. H.; Moldenhauer, G.; Popovic, Z. V.; Nordström, V.; Kopp-Schneider, A.; Hielscher, T.; Nelson, P. J.; Schaefer, F.; Porubsky, S.; Fliser, D.; Arnold, B.; Gröne, H.-J. Tubular Dickkopf-3 Promotes the Development of Renal Atrophy and Fibrosis. JCI Insight 2016, 1(1), e84916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schunk, S. J.; Floege, J.; Fliser, D.; Speer, T. WNT-β-Catenin Signalling - a Versatile Player in Kidney Injury and Repair. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2021, 17(3), 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Álamo, B.; García-Iñigo, F. J.; Shabaka, A.; Acedo, J. M.; Cases-Corona, C.; Domínguez-Torres, P.; Diaz-Enamorado, Y.; Landaluce, E.; Navarro-González, J. F.; Gorriz, J. L.; Martínez-Castelao, A.; Fernández-Juárez, G. Urinary Dickkopf-3: A New Biomarker for CKD Progression and Mortality. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc. - Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2021, 36 (12), 2199–2207. [CrossRef]
- Zewinger, S.; Rauen, T.; Rudnicki, M.; Federico, G.; Wagner, M.; Triem, S.; Schunk, S. J.; Petrakis, I.; Schmit, D.; Wagenpfeil, S.; Heine, G. H.; Mayer, G.; Floege, J.; Fliser, D.; Gröne, H.-J.; Speer, T. Dickkopf-3 (DKK3) in Urine Identifies Patients with Short-Term Risk of EGFR Loss. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2018, 29(11), 2722–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schunk, S. J.; Zarbock, A.; Meersch, M.; Küllmar, M.; Kellum, J. A.; Schmit, D.; Wagner, M.; Triem, S.; Wagenpfeil, S.; Gröne, H.-J.; Schäfers, H.-J.; Fliser, D.; Speer, T.; Zewinger, S. Association between Urinary Dickkopf-3, Acute Kidney Injury, and Subsequent Loss of Kidney Function in Patients Undergoing Cardiac Surgery: An Observational Cohort Study. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2019, 394(10197), 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnick, M. R.; Leonberg-Yoo, A. K.; Litt, H. I.; Cohen, R. M.; Hilton, S.; Reese, P. P. The Controversy of Contrast-Induced Nephropathy With Intravenous Contrast: What Is the Risk? Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 75(1), 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seibert, F. S.; Heringhaus, A.; Pagonas, N.; Rohn, B.; Bauer, F.; Trappe, H.-J.; Landmesser, U.; Babel, N.; Westhoff, T. H. Dickkopf-3 in the Prediction of Contrast Media Induced Acute Kidney Injury. J. Nephrol. 2021, 34(3), 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roscigno, G.; Quintavalle, C.; Biondi-Zoccai, G.; De Micco, F.; Frati, G.; Affinito, A.; Nuzzo, S.; Condorelli, G.; Briguori, C. Urinary Dickkopf-3 and Contrast-Associated Kidney Damage. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 77(21), 2667–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortvrindt, C.; Speeckaert, R.; Delanghe, J. R.; Speeckaert, M. M. Urinary Epidermal Growth Factor: A Promising “Next Generation” Biomarker in Kidney Disease. Am. J. Nephrol. 2022, 53(5), 372–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, N.; Skupien, J.; Smiles, A. M.; Yamanouchi, M.; Niewczas, M. A.; Galecki, A. T.; Duffin, K. L.; Breyer, M. D.; Pullen, N.; Bonventre, J. V.; Krolewski, A. S. Markers of Early Progressive Renal Decline in Type 2 Diabetes Suggest Different Implications for Etiological Studies and Prognostic Tests Development. Kidney Int. 2018, 93(5), 1198–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Li, X.-Q.; Chang, D.-Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.-J.; Wu, S.-L.; Zhang, L.-X.; Chen, M.; Zhao, M.-H. Associations of Urinary Epidermal Growth Factor and Monocyte Chemotactic Protein-1 with Kidney Involvement in Patients with Diabetic Kidney Disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc. - Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2020, 35 (2), 291–297. [CrossRef]
- Menez, S.; Ju, W.; Menon, R.; Moledina, D. G.; Thiessen Philbrook, H.; McArthur, E.; Jia, Y.; Obeid, W.; Mansour, S. G.; Koyner, J. L.; Shlipak, M. G.; Coca, S. G.; Garg, A. X.; Bomback, A. S.; Kellum, J. A.; Kretzler, M.; Parikh, C. R.; Translational Research Investigating Biomarker Endpoints in AKI (TRIBE-AKI) Consortium and the Kidney Precision Medicine Project. Urinary EGF and MCP-1 and Risk of CKD after Cardiac Surgery. JCI Insight 2021, 6 (11), e147464, 147464. [CrossRef]
- Norvik, J. V.; Harskamp, L. R.; Nair, V.; Shedden, K.; Solbu, M. D.; Eriksen, B. O.; Kretzler, M.; Gansevoort, R. T.; Ju, W.; Melsom, T. Urinary Excretion of Epidermal Growth Factor and Rapid Loss of Kidney Function. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc. - Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2021, 36 (10), 1882–1892. [CrossRef]
- Satirapoj, B.; Dispan, R.; Radinahamed, P.; Kitiyakara, C. Urinary Epidermal Growth Factor, Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 or Their Ratio as Predictors for Rapid Loss of Renal Function in Type 2 Diabetic Patients with Diabetic Kidney Disease. BMC Nephrol. 2018, 19(1), 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, F.; Nair, V.; Ding, F.; Xiao, H.; Yao, Y.; Kretzler, M.; Ju, W.; Ding, J. Urinary Epidermal Growth Factor as a Prognostic Marker for the Progression of Alport Syndrome in Children. Pediatr. Nephrol. Berl. Ger. 2018, 33(10), 1731–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Yu, J.; Prayogo, G. W.; Cao, W.; Wu, Y.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, A. Understanding Kidney Injury Molecule 1: A Novel Immune Factor in Kidney Pathophysiology. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11(3), 1219–1229. [Google Scholar]
- Gohda, T.; Kamei, N.; Koshida, T.; Kubota, M.; Tanaka, K.; Yamashita, Y.; Adachi, E.; Ichikawa, S.; Murakoshi, M.; Ueda, S.; Suzuki, Y. Circulating Kidney Injury Molecule-1 as a Biomarker of Renal Parameters in Diabetic Kidney Disease. J. Diabetes Investig. 2020, 11(2), 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żyłka, A.; Dumnicka, P.; Kuśnierz-Cabala, B.; Gala-Błądzińska, A.; Ceranowicz, P.; Kucharz, J.; Ząbek-Adamska, A.; Maziarz, B.; Drożdż, R.; Kuźniewski, M. Markers of Glomerular and Tubular Damage in the Early Stage of Kidney Disease in Type 2 Diabetic Patients. Mediators Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 7659243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunner, H. I.; Gulati, G.; Klein-Gitelman, M. S.; Rouster-Stevens, K. A.; Tucker, L.; Ardoin, S. P.; Onel, K. B.; Mainville, R.; Turnier, J.; Aydin, P. O. A.; Witte, D.; Huang, B.; Bennett, M. R.; Devarajan, P. Urine Biomarkers of Chronic Kidney Damage and Renal Functional Decline in Childhood-Onset Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Pediatr. Nephrol. Berl. Ger. 2019, 34(1), 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satirapoj, B.; Pooluea, P.; Nata, N.; Supasyndh, O. Urinary Biomarkers of Tubular Injury to Predict Renal Progression and End Stage Renal Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus with Advanced Nephropathy: A Prospective Cohort Study. J. Diabetes Complications 2019, 33(9), 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, F. W. K.; Ong, A. C. M. Renal Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1: An Emerging Universal Biomarker and Therapeutic Target for Kidney Diseases? Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2019, gfz082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puthumana, J.; Thiessen-Philbrook, H.; Xu, L.; Coca, S. G.; Garg, A. X.; Himmelfarb, J.; Bhatraju, P. K.; Ikizler, T. A.; Siew, E. D.; Ware, L. B.; Liu, K. D.; Go, A. S.; Kaufman, J. S.; Kimmel, P. L.; Chinchilli, V. M.; Cantley, L. G.; Parikh, C. R. Biomarkers of Inflammation and Repair in Kidney Disease Progression. J. Clin. Invest. 2021, 131(3), e139927, 139927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, J. C.; Carlsson, E.; Midgley, A.; Smith, E. M. D.; Bruce, I. N.; Beresford, M. W.; Hedrich, C. M.; BILAG-BR and MRC MASTERPLANS Consortia. A Panel of Urinary Proteins Predicts Active Lupus Nephritis and Response to Rituximab Treatment. Rheumatol. Oxf. Engl. 2021, 60(8), 3747–3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.; Tian, Y.; Sun, L.; Zhou, L.; Xiao, L.; Tan, R. J.; Tian, J.; Fu, H.; Hou, F. F.; Liu, Y. Matrix Metalloproteinase-7 Is a Urinary Biomarker and Pathogenic Mediator of Kidney Fibrosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2017, 28(2), 598–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Chen, C.; Teng, S.; Fu, X.; Zha, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, L.; Tian, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Nie, J.; Hou, F. F. Urinary Matrix Metalloproteinase-7 Predicts Severe AKI and Poor Outcomes after Cardiac Surgery. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2017, 28(11), 3373–3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolignano, D.; Donato, V.; Coppolino, G.; Campo, S.; Buemi, A.; Lacquaniti, A.; Buemi, M. Neutrophil Gelatinase–Associated Lipocalin (NGAL) as a Marker of Kidney Damage. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2008, 52(3), 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Yi, B.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Dai, Q.; Huang, Y.; Li, Y. C.; Zhang, H. Urinary NGAL and RBP Are Biomarkers of Normoalbuminuric Renal Insufficiency in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 2019, 5063089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Chen, J.; Wu, L.; Nie, G.; Sun, L.; Zhang, C.; Huang, Z.; Xing, C.; Zhang, B.; Yuan, Y. Assessment of Urinary NGAL for Differential Diagnosis and Progression of Diabetic Kidney Disease. J. Diabetes Complications 2020, 34(10), 107665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steubl, D.; Block, M.; Herbst, V.; Schlumberger, W.; Nockher, A.; Angermann, S.; Schmaderer, C.; Heemann, U.; Renders, L.; Scherberich, J. Serum Uromodulin Predicts Graft Failure in Renal Transplant Recipients. Biomarkers 2017, 22(2), 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steubl, D.; Block, M.; Herbst, V.; Nockher, W. A.; Schlumberger, W.; Satanovskij, R.; Angermann, S.; Hasenau, A.-L.; Stecher, L.; Heemann, U.; Renders, L.; Scherberich, J. Plasma Uromodulin Correlates With Kidney Function and Identifies Early Stages in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 2016, 95(10), e3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steubl, D.; Schneider, M. P.; Meiselbach, H.; Nadal, J.; Schmid, M. C.; Saritas, T.; Krane, V.; Sommerer, C.; Baid-Agrawal, S.; Voelkl, J.; Kotsis, F.; Köttgen, A.; Eckardt, K.-U.; Scherberich, J. E.; GCKD Study Investigators. Association of Serum Uromodulin with Death, Cardiovascular Events, and Kidney Failure in CKD. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 15 (5), 616–624. [CrossRef]
- Delgado, G. E.; Kleber, M. E.; Scharnagl, H.; Krämer, B. K.; März, W.; Scherberich, J. E. Serum Uromodulin and Mortality Risk in Patients Undergoing Coronary Angiography. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28(7), 2201–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alesutan, I.; Luong, T. T. D.; Schelski, N.; Masyout, J.; Hille, S.; Schneider, M. P.; Graham, D.; Zickler, D.; Verheyen, N.; Estepa, M.; Pasch, A.; Maerz, W.; Tomaschitz, A.; Pilz, S.; Frey, N.; Lang, F.; Delles, C.; Müller, O. J.; Pieske, B.; Eckardt, K.-U.; Scherberich, J.; Voelkl, J. Circulating Uromodulin Inhibits Vascular Calcification by Interfering with Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Signalling. Cardiovasc. Res. 2021, 117(3), 930–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Then, C.; Herder, C.; Then, H.; Thorand, B.; Huth, C.; Heier, M.; Meisinger, C.; Peters, A.; Koenig, W.; Rathmann, W.; Roden, M.; Stumvoll, M.; Maalmi, H.; Meitinger, T.; Lechner, A.; Scherberich, J.; Seissler, J. Serum Uromodulin Is Inversely Associated with Biomarkers of Subclinical Inflammation in the Population-Based KORA F4 Study. Clin. Kidney J. 2021, 14(6), 1618–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rampoldi, L.; Scolari, F.; Amoroso, A.; Ghiggeri, G.; Devuyst, O. The Rediscovery of Uromodulin (Tamm–Horsfall Protein): From Tubulointerstitial Nephropathy to Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2011, 80(4), 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchinger, H.; Calderon-Gutierrez, F.; Obeid, W.; Xu, L.; Shaw, M. M.; Luciano, R. L.; Kuperman, M.; Moeckel, G. W.; Kashgarian, M.; Wilson, F. P.; Parikh, C. R.; Moledina, D. G. Urine Uromodulin as a Biomarker of Kidney Tubulointerstitial Fibrosis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. CJASN 2022, 17(9), 1284–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, M. R.; Pyles, O.; Ma, Q.; Devarajan, P. Preoperative Levels of Urinary Uromodulin Predict Acute Kidney Injury after Pediatric Cardiopulmonary Bypass Surgery. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2018, 33(3), 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Gomez, M. V.; Pizarro-Sanchez, S.; Gracia-Iguacel, C.; Cano, S.; Cannata-Ortiz, P.; Sanchez-Rodriguez, J.; Sanz, A. B.; Sanchez-Niño, M. D.; Ortiz, A. Urinary Growth Differentiation Factor-15 (GDF15) Levels as a Biomarker of Adverse Outcomes and Biopsy Findings in Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Nephrol. 2021, 34(6), 1819–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takei, Y.; Takahashi, S.; Nakasatomi, M.; Sakairi, T.; Ikeuchi, H.; Kaneko, Y.; Hiromura, K.; Nojima, Y.; Maeshima, A. Urinary Activin A Is a Novel Biomarker Reflecting Renal Inflammation and Tubular Damage in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14(10), e0223703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y. H.; Kim, K. P.; Park, S.-H.; Kim, D.-J.; Kim, Y.-G.; Moon, J.-Y.; Jung, S.-W.; Kim, J. S.; Jeong, K.-H.; Lee, S.-Y.; Yang, D.-H.; Lim, S.-J.; Woo, J.-T.; Rhee, S. Y.; Chon, S.; Choi, H.-Y.; Park, H.-C.; Jo, Y.-I.; Yi, J.-H.; Han, S.-W.; Lee, S.-H. Urinary Chemokine C-X-C Motif Ligand 16 and Endostatin as Predictors of Tubulointerstitial Fibrosis in Patients with Advanced Diabetic Kidney Disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc. - Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2021, 36 (2), 295–305. [CrossRef]
- Ou, S.-M.; Tsai, M.-T.; Chen, H.-Y.; Li, F.-A.; Lee, K.-H.; Tseng, W.-C.; Chang, F.-P.; Lin, Y.-P.; Yang, R.-B.; Tarng, D.-C. Urinary Galectin-3 as a Novel Biomarker for the Prediction of Renal Fibrosis and Kidney Disease Progression. Biomedicines 2022, 10(3), 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, D. G. K.; Fenton, A.; Jesky, M.; Ferro, C.; Boor, P.; Tepel, M.; Karsdal, M. A.; Genovese, F.; Cockwell, P. Urinary Endotrophin Predicts Disease Progression in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7(1), 17328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilemann-Lyberg, S.; Rasmussen, D. G. K.; Hansen, T. W.; Tofte, N.; Winther, S. A.; Holm Nielsen, S.; Theilade, S.; Karsdal, M. A.; Genovese, F.; Rossing, P. Markers of Collagen Formation and Degradation Reflect Renal Function and Predict Adverse Outcomes in Patients With Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2019, 42(9), 1760–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, D.; Yang, J. Y. C.; Sarwal, R. D.; Sigdel, T. K.; Liberto, J. M.; Damm, I.; Louie, V.; Sigdel, S.; Livingstone, D.; Soh, K.; Chakraborty, A.; Liang, M.; Lin, P.-C.; Sarwal, M. M. A Novel Multi-Biomarker Assay for Non-Invasive Quantitative Monitoring of Kidney Injury. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8(4), 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J. Y. C.; Sarwal, R. D.; Fervenza, F. C.; Sarwal, M. M.; Lafayette, R. A. Noninvasive Urinary Monitoring of Progression in IgA Nephropathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20(18), 4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dakna, M.; Harris, K.; Kalousis, A.; Carpentier, S.; Kolch, W.; Schanstra, J. P.; Haubitz, M.; Vlahou, A.; Mischak, H.; Girolami, M. Addressing the Challenge of Defining Valid Proteomic Biomarkers and Classifiers. BMC Bioinformatics 2010, 11, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavrogeorgis, E.; Mischak, H.; Latosinska, A.; Siwy, J.; Jankowski, V.; Jankowski, J. Reproducibility Evaluation of Urinary Peptide Detection Using CE-MS. Mol. Basel Switz. 2021, 26(23), 7260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, D. M.; Zürbig, P.; Argilés, À.; Bauer, H. W.; Behrens, G.; Coon, J. J.; Dakna, M.; Decramer, S.; Delles, C.; Dominiczak, A. F.; Ehrich, J. H. H.; Eitner, F.; Fliser, D.; Frommberger, M.; Ganser, A.; Girolami, M. A.; Golovko, I.; Gwinner, W.; Haubitz, M.; Herget-Rosenthal, S.; Jankowski, J.; Jahn, H.; Jerums, G.; Julian, B. A.; Kellmann, M.; Kliem, V.; Kolch, W.; Krolewski, A. S.; Luppi, M.; Massy, Z.; Melter, M.; Neusüss, C.; Novak, J.; Peter, K.; Rossing, K.; Rupprecht, H.; Schanstra, J. P.; Schiffer, E.; Stolzenburg, J.-U.; Tarnow, L.; Theodorescu, D.; Thongboonkerd, V.; Vanholder, R.; Weissinger, E. M.; Mischak, H.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P. Naturally Occurring Human Urinary Peptides for Use in Diagnosis of Chronic Kidney Disease. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2010, 9(11), 2424–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argilés, À.; Siwy, J.; Duranton, F.; Gayrard, N.; Dakna, M.; Lundin, U.; Osaba, L.; Delles, C.; Mourad, G.; Weinberger, K. M.; Mischak, H. CKD273, a New Proteomics Classifier Assessing CKD and Its Prognosis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8(5), e62837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, S.; Mischak, H.; Zürbig, P.; Parving, H.-H.; Rossing, P. Urinary Proteome Analysis Enables Assessment of Renoprotective Treatment in Type 2 Diabetic Patients with Microalbuminuria. BMC Nephrol. 2010, 11(1), 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zürbig, P.; Jerums, G.; Hovind, P.; MacIsaac, R. J.; Mischak, H.; Nielsen, S. E.; Panagiotopoulos, S.; Persson, F.; Rossing, P. Urinary Proteomics for Early Diagnosis in Diabetic Nephropathy. Diabetes 2012, 61(12), 3304–3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roscioni, S. S.; de Zeeuw, D.; Hellemons, M. E.; Mischak, H.; Zürbig, P.; Bakker, S. J. L.; Gansevoort, R. T.; Reinhard, H.; Persson, F.; Lajer, M.; Rossing, P.; Heerspink, H. J. L. A Urinary Peptide Biomarker Set Predicts Worsening of Albuminuria in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetologia 2013, 56(2), 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siwy, J.; Schanstra, J. P.; Argiles, A.; Bakker, S. J. L.; Beige, J.; Boucek, P.; Brand, K.; Delles, C.; Duranton, F.; Fernandez-Fernandez, B.; Jankowski, M.-L.; Al Khatib, M.; Kunt, T.; Lajer, M.; Lichtinghagen, R.; Lindhardt, M.; Maahs, D. M.; Mischak, H.; Mullen, W.; Navis, G.; Noutsou, M.; Ortiz, A.; Persson, F.; Petrie, J. R.; Roob, J. M.; Rossing, P.; Ruggenenti, P.; Rychlik, I.; Serra, A. L.; Snell-Bergeon, J.; Spasovski, G.; Stojceva-Taneva, O.; Trillini, M.; von der Leyen, H.; Winklhofer-Roob, B. M.; Zürbig, P.; Jankowski, J. Multicentre Prospective Validation of a Urinary Peptidome-Based Classifier for the Diagnosis of Type 2 Diabetic Nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2014, 29(8), 1563–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.-M.; Thijs, L.; Liu, Y.-P.; Zhang, Z.; Jacobs, L.; Koeck, T.; Zürbig, P.; Lichtinghagen, R.; Brand, K.; Kuznetsova, T.; Olivi, L.; Verhamme, P.; Delles, C.; Mischak, H.; Staessen, J. A. The Urinary Proteome as Correlate and Predictor of Renal Function in a Population Study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2014, 29(12), 2260–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schanstra, J. P.; Zürbig, P.; Alkhalaf, A.; Argiles, A.; Bakker, S. J. L.; Beige, J.; Bilo, H. J. G.; Chatzikyrkou, C.; Dakna, M.; Dawson, J.; Delles, C.; Haller, H.; Haubitz, M.; Husi, H.; Jankowski, J.; Jerums, G.; Kleefstra, N.; Kuznetsova, T.; Maahs, D. M.; Menne, J.; Mullen, W.; Ortiz, A.; Persson, F.; Rossing, P.; Ruggenenti, P.; Rychlik, I.; Serra, A. L.; Siwy, J.; Snell-Bergeon, J.; Spasovski, G.; Staessen, J. A.; Vlahou, A.; Mischak, H.; Vanholder, R. Diagnosis and Prediction of CKD Progression by Assessment of Urinary Peptides. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26(8), 1999–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontillo, C.; Jacobs, L.; Staessen, J. A.; Schanstra, J. P.; Rossing, P.; Heerspink, H. J. L.; Siwy, J.; Mullen, W.; Vlahou, A.; Mischak, H.; Vanholder, R.; Zürbig, P.; Jankowski, J. A Urinary Proteome-Based Classifier for the Early Detection of Decline in Glomerular Filtration. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2016, gfw239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontillo, C.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Schanstra, J. P.; Jacobs, L.; Zürbig, P.; Thijs, L.; Ramírez-Torres, A.; Heerspink, H. J. L.; Lindhardt, M.; Klein, R.; Orchard, T.; Porta, M.; Bilous, R. W.; Charturvedi, N.; Rossing, P.; Vlahou, A.; Schepers, E.; Glorieux, G.; Mullen, W.; Delles, C.; Verhamme, P.; Vanholder, R.; Staessen, J. A.; Mischak, H.; Jankowski, J. Prediction of Chronic Kidney Disease Stage 3 by CKD273, a Urinary Proteomic Biomarker. Kidney Int. Rep. 2017, 2(6), 1066–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zürbig, P.; Mischak, H.; Menne, J.; Haller, H. CKD273 Enables Efficient Prediction of Diabetic Nephropathy in Nonalbuminuric Patients. Diabetes Care 2019, 42(1), e4–e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangri, N.; Stevens, L. A.; Griffith, J.; Tighiouart, H.; Djurdjev, O.; Naimark, D.; Levin, A.; Levey, A. S. A Predictive Model for Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease to Kidney Failure. JAMA 2011, 305(15), 1553–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Ortiz, M. E.; Pontillo, C.; Rodríguez, M.; Zürbig, P.; Mischak, H.; Ortiz, A. Novel Urinary Biomarkers For Improved Prediction Of Progressive Egfr Loss In Early Chronic Kidney Disease Stages And In High Risk Individuals Without Chronic Kidney Disease. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8(1), 15940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currie, G. E.; von Scholten, B. J.; Mary, S.; Flores Guerrero, J.-L.; Lindhardt, M.; Reinhard, H.; Jacobsen, P. K.; Mullen, W.; Parving, H.-H.; Mischak, H.; Rossing, P.; Delles, C. Urinary Proteomics for Prediction of Mortality in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Microalbuminuria. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2018, 17(1), 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Critselis, E.; Vlahou, A.; Stel, V. S.; Morton, R. L. Cost-Effectiveness of Screening Type 2 Diabetes Patients for Chronic Kidney Disease Progression with the CKD273 Urinary Peptide Classifier as Compared to Urinary Albumin Excretion. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc. - Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2018, 33 (3), 441–449. [CrossRef]
- Verbeke, F.; Siwy, J.; Van Biesen, W.; Mischak, H.; Pletinck, A.; Schepers, E.; Neirynck, N.; Magalhães, P.; Pejchinovski, M.; Pontillo, C.; Lichtinghagen, R.; Brand, K.; Vlahou, A.; De Bacquer, D.; Glorieux, G. The Urinary Proteomics Classifier Chronic Kidney Disease 273 Predicts Cardiovascular Outcome in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc. - Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2021, 36 (5), 811–818. [CrossRef]
- Tofte, N.; Lindhardt, M.; Adamova, K.; Bakker, S. J. L.; Beige, J.; Beulens, J. W. J.; Birkenfeld, A. L.; Currie, G.; Delles, C.; Dimos, I.; Francová, L.; Frimodt-Møller, M.; Girman, P.; Göke, R.; Havrdova, T.; Heerspink, H. J. L.; Kooy, A.; Laverman, G. D.; Mischak, H.; Navis, G.; Nijpels, G.; Noutsou, M.; Ortiz, A.; Parvanova, A.; Persson, F.; Petrie, J. R.; Ruggenenti, P. L.; Rutters, F.; Rychlík, I.; Siwy, J.; Spasovski, G.; Speeckaert, M.; Trillini, M.; Zürbig, P.; von der Leyen, H.; Rossing, P.; PRIORITY investigators. Early Detection of Diabetic Kidney Disease by Urinary Proteomics and Subsequent Intervention with Spironolactone to Delay Progression (PRIORITY): A Prospective Observational Study and Embedded Randomised Placebo-Controlled Trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8 (4), 301–312. [CrossRef]
- Lindhardt, M.; Persson, F.; Zürbig, P.; Stalmach, A.; Mischak, H.; de Zeeuw, D.; Lambers Heerspink, H.; Klein, R.; Orchard, T.; Porta, M.; Fuller, J.; Bilous, R.; Chaturvedi, N.; Parving, H.-H.; Rossing, P. Urinary Proteomics Predict Onset of Microalbuminuria in Normoalbuminuric Type 2 Diabetic Patients, a Sub-Study of the DIRECT-Protect 2 Study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc. - Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2017, 32 (11), 1866–1873. [CrossRef]
- Lindhardt, M.; Persson, F.; Oxlund, C.; Jacobsen, I. A.; Zürbig, P.; Mischak, H.; Rossing, P.; Heerspink, H. J. L. Predicting Albuminuria Response to Spironolactone Treatment with Urinary Proteomics in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Hypertension. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc. - Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2018, 33 (2), 296–303. [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.-L.; Chang, C.-T.; Chen, C.-C.; Lee, W.-J.; Lin, S.-Y.; Liao, H.-Y.; Wu, C.-M.; Chang, Y.-W.; Chen, C.-J.; Tsai, F.-J. Urinary Proteomics for the Early Diagnosis of Diabetic Nephropathy in Taiwanese Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7(12), 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brondani, L. de A.; Soares, A. A.; Recamonde-Mendoza, M.; Dall’Agnol, A.; Camargo, J. L.; Monteiro, K. M.; Silveiro, S. P. Urinary Peptidomics and Bioinformatics for the Detection of Diabetic Kidney Disease. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10 (1), 1242. [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.-S.; Kim, J. H.; Jeong, H.; Yu, J.; Yeom, J.; Song, S. H.; Kim, S. S.; Kim, I. J.; Kim, K. Differential Urinary Proteome Analysis for Predicting Prognosis in Type 2 Diabetes Patients with and without Renal Dysfunction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21(12), 4236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panizo, S.; Martínez-Arias, L.; Alonso-Montes, C.; Cannata, P.; Martín-Carro, B.; Fernández-Martín, J. L.; Naves-Díaz, M.; Carrillo-López, N.; Cannata-Andía, J. B. Fibrosis in Chronic Kidney Disease: Pathogenesis and Consequences. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22(1), 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, P.; Pejchinovski, M.; Markoska, K.; Banasik, M.; Klinger, M.; Švec-Billá, D.; Rychlík, I.; Rroji, M.; Restivo, A.; Capasso, G.; Bob, F.; Schiller, A.; Ortiz, A.; Perez-Gomez, M. V.; Cannata, P.; Sanchez-Niño, M. D.; Naumovic, R.; Brkovic, V.; Polenakovic, M.; Mullen, W.; Vlahou, A.; Zürbig, P.; Pape, L.; Ferrario, F.; Denis, C.; Spasovski, G.; Mischak, H.; Schanstra, J. P. Association of Kidney Fibrosis with Urinary Peptides: A Path towards Non-Invasive Liquid Biopsies? Sci. Rep. 2017, 7(1), 16915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catanese, L.; Siwy, J.; Mavrogeorgis, E.; Amann, K.; Mischak, H.; Beige, J.; Rupprecht, H. A Novel Urinary Proteomics Classifier for Non-Invasive Evaluation of Interstitial Fibrosis and Tubular Atrophy in Chronic Kidney Disease. Proteomes 2021, 9 (3). [CrossRef]
- Mavrogeorgis, E.; Mischak, H.; Latosinska, A.; Vlahou, A.; Schanstra, J. P.; Siwy, J.; Jankowski, V.; Beige, J.; Jankowski, J. Collagen-Derived Peptides in CKD: A Link to Fibrosis. Toxins 2021, 14(1), 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, K. N.; Tang, S. C. W.; Schena, F. P.; Novak, J.; Tomino, Y.; Fogo, A. B.; Glassock, R. J. IgA Nephropathy. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primer 2016, 2(1), 16001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnicki, M.; Siwy, J.; Wendt, R.; Lipphardt, M.; Koziolek, M. J.; Maixnerova, D.; Peters, B.; Kerschbaum, J.; Leierer, J.; Neprasova, M.; Banasik, M.; Sanz, A. B.; Perez-Gomez, M. V.; Ortiz, A.; Stegmayr, B.; Tesar, V.; Mischak, H.; Beige, J.; Reich, H. N.; PERSTIGAN working group. Urine Proteomics for Prediction of Disease Progression in Patients with IgA Nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc. - Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2021, 37 (1), 42–52. [CrossRef]
- Pejchinovski, M.; Siwy, J.; Mullen, W.; Mischak, H.; Petri, M. A.; Burkly, L. C.; Wei, R. Urine Peptidomic Biomarkers for Diagnosis of Patients with Systematic Lupus Erythematosus. Lupus 2018, 27(1), 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pejchinovski, M.; Siwy, J.; Metzger, J.; Dakna, M.; Mischak, H.; Klein, J.; Jankowski, V.; Bae, K. T.; Chapman, A. B.; Kistler, A. D. Urine Peptidome Analysis Predicts Risk of End-Stage Renal Disease and Reveals Proteolytic Pathways Involved in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Progression. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc. - Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2017, 32 (3), 487–497. [CrossRef]
- Doykov, I. D.; Heywood, W. E.; Nikolaenko, V.; Śpiewak, J.; Hällqvist, J.; Clayton, P. T.; Mills, P.; Warnock, D. G.; Nowak, A.; Mills, K. Rapid, Proteomic Urine Assay for Monitoring Progressive Organ Disease in Fabry Disease. J. Med. Genet. 2020, 57(1), 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caterino, M.; Zacchia, M.; Costanzo, M.; Bruno, G.; Arcaniolo, D.; Trepiccione, F.; Siciliano, R. A.; Mazzeo, M. F.; Ruoppolo, M.; Capasso, G. Urine Proteomics Revealed a Significant Correlation Between Urine-Fibronectin Abundance and Estimated-GFR Decline in Patients with Bardet-Biedl Syndrome. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2018, 43(2), 389–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, V.; López, D.; Boixadera, E.; Ibernón, M.; Espinal, A.; Bonet, J.; Romero, R. Comparative Differential Proteomic Analysis of Minimal Change Disease and Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis. BMC Nephrol. 2017, 18(1), 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mejia-Vilet, J. M.; Shapiro, J. P.; Zhang, X. L.; Cruz, C.; Zimmerman, G.; Méndez-Pérez, R. A.; Cano-Verduzco, M. L.; Parikh, S. V.; Nagaraja, H. N.; Morales-Buenrostro, L. E.; Rovin, B. H. Association Between Urinary Epidermal Growth Factor and Renal Prognosis in Lupus Nephritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. Hoboken NJ 2021, 73(2), 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siwy, J.; Zürbig, P.; Argiles, A.; Beige, J.; Haubitz, M.; Jankowski, J.; Julian, B. A.; Linde, P. G.; Marx, D.; Mischak, H.; Mullen, W.; Novak, J.; Ortiz, A.; Persson, F.; Pontillo, C.; Rossing, P.; Rupprecht, H.; Schanstra, J. P.; Vlahou, A.; Vanholder, R. Noninvasive Diagnosis of Chronic Kidney Diseases Using Urinary Proteome Analysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc. - Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2017, 32 (12), 2079–2089. [CrossRef]
- Wendt, R.; Siwy, J.; He, T.; Latosinska, A.; Wiech, T.; Zipfel, P. F.; Tserga, A.; Vlahou, A.; Rupprecht, H.; Catanese, L.; Mischak, H.; Beige, J. Molecular Mapping of Urinary Complement Peptides in Kidney Diseases. Proteomes 2021, 9(4), 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wörn, M.; Bohnert, B. N.; Alenazi, F.; Boldt, K.; Klose, F.; Junger, K.; Ueffing, M.; Birkenfeld, A. L.; Kalbacher, H.; Artunc, F. Proteasuria in Nephrotic Syndrome-Quantification and Proteomic Profiling. J. Proteomics 2021, 230, 103981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petra, E.; Siwy, J.; Vlahou, A.; Jankowski, J. Urine Peptidome in Combination with Transcriptomics Analysis Highlights MMP7, MMP14 and PCSK5 for Further Investigation in Chronic Kidney Disease. PLoS ONE 2022, 17(1), e0262667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magalhães, P.; Pontillo, C.; Pejchinovski, M.; Siwy, J.; Krochmal, M.; Makridakis, M.; Carrick, E.; Klein, J.; Mullen, W.; Jankowski, J.; Vlahou, A.; Mischak, H.; Schanstra, J. P.; Zürbig, P.; Pape, L. Comparison of Urine and Plasma Peptidome Indicates Selectivity in Renal Peptide Handling. Proteomics Clin. Appl. 2018, 12(5), e1700163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minamikawa, S.; Nozu, K.; Maeta, S.; Yamamura, T.; Nakanishi, K.; Fujimura, J.; Horinouchi, T.; Nagano, C.; Sakakibara, N.; Nagase, H.; Shima, H.; Noda, K.; Ninchoji, T.; Kaito, H.; Iijima, K. The Utility of Urinary CD80 as a Diagnostic Marker in Patients with Renal Diseases. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8(1), 17322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, O. P. Urinary CD 80 in Nephrotic Syndrome: A Biomarker to Distinguish Minimal Change Disease From Other Glomerular Diseases. Kidney Int. Rep. 2020, 5(11), 1851–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garin, E. H.; Diaz, L. N.; Mu, W.; Wasserfall, C.; Araya, C.; Segal, M.; Johnson, R. J. Urinary CD80 Excretion Increases in Idiopathic Minimal-Change Disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20(2), 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cara-Fuentes, G.; Wei, C.; Segarra, A.; Ishimoto, T.; Rivard, C.; Johnson, R. J.; Reiser, J.; Garin, E. H. CD80 and SuPAR in Patients with Minimal Change Disease and Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis: Diagnostic and Pathogenic Significance. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2014, 29(8), 1363–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciascia, S.; Barinotti, A.; Radin, M.; Cecchi, I.; Menegatti, E.; Terzolo, E.; Rossi, D.; Baldovino, S.; Fenoglio, R.; Roccatello, D. Dickkopf Homolog 3 (DKK3) as a Prognostic Marker in Lupus Nephritis: A Prospective Monocentric Experience. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11(11), 2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piek, A.; Smit, L.; Suthahar, N.; Bakker, S. J. L.; de Boer, R. A.; Silljé, H. H. W. The Emerging Plasma Biomarker Dickkopf-3 (DKK3) and Its Association with Renal and Cardiovascular Disease in the General Population. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11(1), 8642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Hu, J.; Chen, Y.; Shen, W.; Ke, B. Dickkopf-3: Current Knowledge in Kidney Diseases. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 533344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, J.; Bascands, J.-L.; Buffin-Meyer, B.; Schanstra, J. P. Epidermal Growth Factor and Kidney Disease: A Long-Lasting Story. Kidney Int. 2016, 89(5), 985–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betz, B. B.; Jenks, S. J.; Cronshaw, A. D.; Lamont, D. J.; Cairns, C.; Manning, J. R.; Goddard, J.; Webb, D. J.; Mullins, J. J.; Hughes, J.; McLachlan, S.; Strachan, M. W. J.; Price, J. F.; Conway, B. R. Urinary Peptidomics in a Rodent Model of Diabetic Nephropathy Highlights Epidermal Growth Factor as a Biomarker for Renal Deterioration in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Kidney Int. 2016, 89(5), 1125–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worawichawong, S.; Worawichawong, S.; Radinahamed, P.; Muntham, D.; Sathirapongsasuti, N.; Nongnuch, A.; Assanatham, M.; Kitiyakara, C. Urine Epidermal Growth Factor, Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 or Their Ratio as Biomarkers for Interstitial Fibrosis and Tubular Atrophy in Primary Glomerulonephritis. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2016, 41(6), 997–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, D. D.; Rossini, M.; Manno, C.; Mattace-Raso, F.; D’Altri, C.; Ranieri, E.; Pontrelli, P.; Grandaliano, G.; Gesualdo, L.; Schena, F. P. The Ratio of Epidermal Growth Factor to Monocyte Chemotactic Peptide-1 in the Urine Predicts Renal Prognosis in IgA Nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2008, 73(3), 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Liu, N.; Zhuang, S. Role of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in Acute and Chronic Kidney Injury. Kidney Int. 2013, 83(5), 804–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaka, Y. Epidermal Growth Factor as a Prognostic Biomarker in Chronic Kidney Diseases. Ann. Transl. Med. 2016, 4 (Suppl 1), S62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W. K.; Bailly, V.; Abichandani, R.; Thadhani, R.; Bonventre, J. V. Kidney Injury Molecule-1 (KIM-1): A Novel Biomarker for Human Renal Proximal Tubule Injury. Kidney Int. 2002, 62(1), 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonventre, J. V. Kidney Injury Molecule-1 (KIM-1): A Specific and Sensitive Biomarker of Kidney Injury. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest. 2008, 68 (sup241), 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonventre, J. V. Kidney Injury Molecule-1 (KIM-1): A Urinary Biomarker and Much More. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2009, 24(11), 3265–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prozialeck, W. C.; Vaidya, V. S.; Liu, J.; Waalkes, M. P.; Edwards, J. R.; Lamar, P. C.; Bernard, A. M.; Dumont, X.; Bonventre, J. V. Kidney Injury Molecule-1 Is an Early Biomarker of Cadmium Nephrotoxicity. Kidney Int. 2007, 72(8), 985–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P. L.; Rothblum, L. I.; Han, W. K.; Blasick, T. M.; Potdar, S.; Bonventre, J. V. Kidney Injury Molecule-1 Expression in Transplant Biopsies Is a Sensitive Measure of Cell Injury. Kidney Int. 2008, 73(5), 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, W. K.; Alinani, A.; Wu, C.-L.; Michaelson, D.; Loda, M.; McGovern, F. J.; Thadhani, R.; Bonventre, J. V. Human Kidney Injury Molecule-1 Is a Tissue and Urinary Tumor Marker of Renal Cell Carcinoma. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2005, 16(4), 1126–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haller, H.; Bertram, A.; Nadrowitz, F.; Menne, J. Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 and the Kidney: Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2016, 25(1), 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M. J.; Tam, F. W. K. Urinary Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 in Renal Disease. Clin. Chim. Acta 2011, 412 (23–24), 2022–2030. [CrossRef]
- Tesch, G. H. MCP-1/CCL2: A New Diagnostic Marker and Therapeutic Target for Progressive Renal Injury in Diabetic Nephropathy. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2008, 294 (4), F697–F701. [CrossRef]
- Gregg, L. P.; Tio, M. C.; Li, X.; Adams-Huet, B.; de Lemos, J. A.; Hedayati, S. S. Association of Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 with Death and Atherosclerotic Events in Chronic Kidney Disease. Am. J. Nephrol. 2018, 47(6), 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, F. W. K. Urinary Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1) Is a Marker of Active Renal Vasculitis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2004, 19(11), 2761–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Tan, R. J.; Liu, Y. The Many Faces of Matrix Metalloproteinase-7 in Kidney Diseases. Biomolecules 2020, 10(6), 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surendran, K.; Simon, T. C.; Liapis, H.; McGuire, J. K. Matrilysin (MMP-7) Expression in Renal Tubular Damage: Association with Wnt4. Kidney Int. 2004, 65(6), 2212–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, B.; Fan, C.; Yang, L.; Fang, X. Matrix Metalloproteinases-7 and Kidney Fibrosis. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarangi, R.; Tripathy, K. P.; Bahinipati, J.; Gupta, P.; Pathak, M.; Mahapatra, S.; Mohapatra, S. R. Urinary MMP-7: A Predictive, Noninvasive Early Marker for Chronic Kidney Disease Development in Patients with Hypertension. Lab. Med. 2022, 53(4), 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enoksen, I. T.; Svistounov, D.; Norvik, J. V.; Stefansson, V. T. N.; Solbu, M. D.; Eriksen, B. O.; Melsom, T. Serum Matrix Metalloproteinase 7 and Accelerated Glomerular Filtration Rate Decline in a General Non-Diabetic Population. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2022, 37(9), 1657–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, J.; Ma, Q.; Prada, A.; Mitsnefes, M.; Zahedi, K.; Yang, J.; Barasch, J.; Devarajan, P. Identification of Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin as a Novel Early Urinary Biomarker for Ischemic Renal Injury. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2003, 14(10), 2534–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, J.; Mori, K.; Ma, Q.; Kelly, C.; Barasch, J.; Devarajan, P. Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin: A Novel Early Urinary Biomarker for Cisplatin Nephrotoxicity. Am. J. Nephrol. 2004, 24(3), 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, J.; Dent, C.; Tarabishi, R.; Mitsnefes, M. M.; Ma, Q.; Kelly, C.; Ruff, S. M.; Zahedi, K.; Shao, M.; Bean, J.; Mori, K.; Barasch, J.; Devarajan, P. Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin (NGAL) as a Biomarker for Acute Renal Injury after Cardiac Surgery. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2005, 365(9466), 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, J.; Ma, Q.; Kelly, C.; Mitsnefes, M.; Mori, K.; Barasch, J.; Devarajan, P. Kidney NGAL Is a Novel Early Marker of Acute Injury Following Transplantation. Pediatr. Nephrol. Berl. Ger. 2006, 21(6), 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachorzewska-Gajewska, H.; Malyszko, J.; Sitniewska, E.; Malyszko, J. S.; Dobrzycki, S. Neutrophil-Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin and Renal Function after Percutaneous Coronary Interventions. Am. J. Nephrol. 2006, 26(3), 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, R.; Dent, C.; Pfriem, H.; Allen, J.; Beekman, R. H.; Ma, Q.; Dastrala, S.; Bennett, M.; Mitsnefes, M.; Devarajan, P. NGAL Is an Early Predictive Biomarker of Contrast-Induced Nephropathy in Children. Pediatr. Nephrol. Berl. Ger. 2007, 22(12), 2089–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagener, G.; Jan, M.; Kim, M.; Mori, K.; Barasch, J. M.; Sladen, R. N.; Lee, H. T. Association between Increases in Urinary Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin and Acute Renal Dysfunction after Adult Cardiac Surgery. Anesthesiology 2006, 105(3), 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devarajan, P. Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin (NGAL): A New Marker of Kidney Disease. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. Suppl. 2008, 241, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leiherer, A.; Muendlein, A.; Saely, C. H.; Brandtner, E. M.; Geiger, K.; Fraunberger, P.; Drexel, H. The Value of Uromodulin as a New Serum Marker to Predict Decline in Renal Function. J. Hypertens. 2018, 36(1), 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bostom, A.; Steubl, D.; Garimella, P. S.; Franceschini, N.; Roberts, M. B.; Pasch, A.; Ix, J. H.; Tuttle, K. R.; Ivanova, A.; Shireman, T.; Kim, S. J.; Gohh, R.; Weiner, D. E.; Levey, A. S.; Hsu, C.; Kusek, J. W.; Eaton, C. B. Serum Uromodulin: A Biomarker of Long-Term Kidney Allograft Failure. Am. J. Nephrol. 2018, 47(4), 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Seaghdha, C. M.; Hwang, S.-J.; Larson, M. G.; Meigs, J. B.; Vasan, R. S.; Fox, C. S. Analysis of a Urinary Biomarker Panel for Incident Kidney Disease and Clinical Outcomes. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2013, 24(11), 1880–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garimella, P. S.; Biggs, M. L.; Katz, R.; Ix, J. H.; Bennett, M. R.; Devarajan, P.; Kestenbaum, B. R.; Siscovick, D. S.; Jensen, M. K.; Shlipak, M. G.; Chaves, P. H. M.; Sarnak, M. J. Urinary Uromodulin, Kidney Function, and Cardiovascular Disease in Elderly Adults. Kidney Int. 2015, 88(5), 1126–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mischak, H.; Vlahou, A.; Ioannidis, J. P. A. Technical Aspects and Inter-Laboratory Variability in Native Peptide Profiling: The CE-MS Experience. Clin. Biochem. 2013, 46(6), 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latosinska, A.; Siwy, J.; Faguer, S.; Beige, J.; Mischak, H.; Schanstra, J. P. Value of Urine Peptides in Assessing Kidney and Cardiovascular Disease. Proteomics Clin. Appl. 2021, 15(1), e2000027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Biomarker | Potential Context of Use | Studies/References | Evidence as biomarker for CKD |
|---|---|---|---|
| CD80 | Differentiation of MCD and FSGS; Response to immunosuppressive treatment in nephrotic syndrom; CKD progression in nephrotic syndrome | Gonzalez Guerrico et al. 13; Ling et al. 14; Garin et al. 15; Ling et al. 16 | Intermediate |
| DKK3 | Association with CKD diagnosis, CKD progression, proteinuria; association with IFTA; Determinant of AKI in cardiac surgery; potential biomarker in contrast-media associated kidney injury | Sánchez-Álamo et al. 19; Zewinger et al. 20; Schunk et al. 21; Rudnick et al. 22; Seibert et al. 23; Roscigno et al. 24 | High |
| EGF | Association with occurrence of DKD, eGFR and eGFR slope in DKD; potential biomarker of disease progression in Alport syndrome | Wu et al. 26; Menez et al. 27; Norvik et al. 28; Satirapoj et al 29; Li et al 30 | High |
| KIM-1 | Biomarker in DKD, associated with UACR, eGFR and eGFR loss; biomarker for progression of albuminuria in early stage DKD; possible biomarker for histological damage in LN | Gohda et al. 32; Żyłka et al. 33; Brunner et al. 34; Satirapoj et al. 35 | Intermediate/partly conflictive |
| MCP-1 | Association with CKD incidence, progression, ESRD and death; potential biomarker in DKD; Possible biomarker after cardiac surgery and development of CKD; Promising biomarker in LN for kidney involvment, histological damage and response to treatment | Wu et al. 26; Menez et al. 27; Satirapoj et al. 29; Puthumana et al. 37; Davies et al. 38 | Conflicitve |
| MMP-7 | Biomarker of CKD, association with renal fibrsis; Biomarker for AKI after cardiac surgery | Zhou et al. 39; Yang et al. 40 | Low |
| NGAL | Multiple evidence as biomarker for DKD; biomarker for AKI after cardiopulmonary bypass | Żyłka et al. 33; Brunner et al. 34; Satirapoj et al. 35; Li et al. 42; Duan et al. 43; | Conflictive |
| Uromodulin | Inversely correlated with serum creatinine and renal fibrosis and glomerulosclerosis in CKD; Potential protective effect and correlation with better outcome | Menez et al. 27; Żyłka et al 33; Melchinger et al. 51; Bennet et al. 52 | Intermediate |
| GDF15 | Association with DKD; Predictive of kidney replacement and survival | Perez-Gomez et al. 53 | Low |
| Activin A | Association with renal involvement in AAV; correlation with histological damage; decrease as potential marker of treatment response | Takei et al. 54 | Low |
| CXCL16 | Predictive of fibrosis, rapid eGFR loss and poor renal prognosis in cohort of advance CKD | Lee et al. 55 | Low |
| Galectin-3 | Association with kidney fibrosis and CKD progression | Ou et al. 56 | Low |
| Marker of collagen formation and degradation | Collagen VI deposition marker associated with CKD progression and ESKD; Collagen formation marker inversely correlated with eGFR decline | Rasmussen et al. 57; Pileman-Lyberg et al. 58 | Intermediate |
| CKD273 | Peptide based biomarker panel superior to UACR in predicting early-stage disease progression in DKD; subclassifier for better risk stratification in early stages of DKD or healthy individuals; predictor for death and cardiovascular events in certain subgroups; predicitve value cinformed in RCTs PRIORITY and DIRECT-Protect-2 | Pontillo et al. 72; Zürbig et al. 73; Rodríguez-Ortiz et al. 75; Currie et al. 76; Verbeke et al. 78; Tofte et al. 79; Lindhardt et al. 80 | High |
| FFP_BH29 | Peptide based biomarker panel for estimatinon of degree of renal fibrosis | Catanese et al. 87 | Intermediate |
| IgAN237 | Peptide based biomarker panel with significant added value regarding prediction of progress in IgA nephropathy | Rudnicki et al. 90 | Intermediate |
| 65SLE | Peptide based biomarker panel for early diagnosis of SLE patients | Pejchinovski et al. 91 | Intermediate |
| ADPKD biomarker model | Peptide based biomarker panel predicting relevant clinical outcomes in ADPKD patients a | Pejchinovski et al. 92 | Intermediate |
| MCD vs FSGS urinary proteins biomarkers | Biomarkers differential diagnosis of MCD and FSGS | Pérez et al. 95 | Intermediate |
| CKD differential diagnosis peptide panels | Biomarkers differential diagnosis of DN/Nephrosclerosis, IgAN, MN, LN, Vasculitis, MCD and FSGS | Siwy et al. 95 | Intermediate |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





