I. INTRODUCTION
Modern technology relies heavily on Artificial Intelligence (AI), which operates covertly to mimic the human mind and assist us in several ways. We are currently experiencing unprecedented advancements in the field of AI as it keeps growing and advancing. With a plethora of innovations, ChatGPT is one to demonstrate exactly how far AI has progressed [
1].
ChatGPT-3 was developed using an upgraded form of GPT-3, also an improved language-developing AI standard created by OpenAI. The Deep Learning Neural Network (DLNN) utilized in GPT-3 has almost 175 billion Machine Learning (ML) parameters. To place things in context, the biggest acquired language model before GPT-3 was Microsoft'sTuring-Natural Language Generation (T-NLG) framework, which includes 10 billion parameters. By the beginning of 2021, GPT-3 will be the largest Neural Network (NN) ever built. So far as creating content that looks to have been written by a human, GPT-3 is better than all preceding versions [
2].
A chatbot called OpenAI ChatGPT is built using the OpenAI GPT-3 language structure. It is intended to create text replies that sound like human answers to operator data entered in a chat setting. With the help of a vast database of human communications, OpenAI ChatGPT was developed to provide replies to a variety of subjects and cues. The chatbot is able to respond in many languages and be utilized for language translation, client support, and content development activities. The OpenAI API makes OpenAI ChatGPT accessible, allowing programmers to use and incorporate it into their apps and devices [
3].
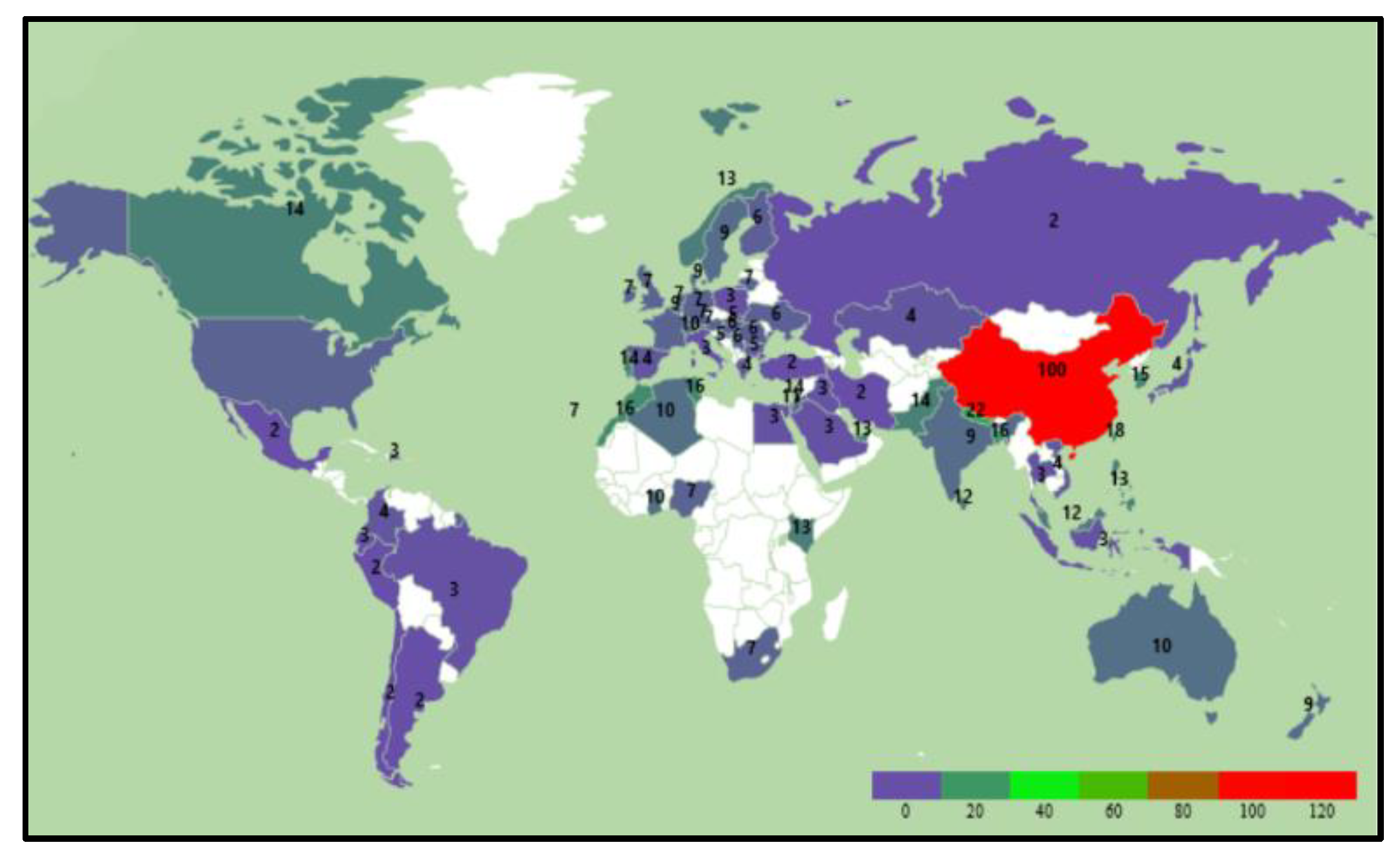
ChatGPT has sparked a lot of interest around the world.
Figure 1 shows worldwide search interest for the term “ChatGPT” from March 3, 2022, to March 3, 2023, as measured by Google Trends. The figure shows that the search interest is currently highest in China, but that the interest in also relatively high in several large countries such as the United States, Canada, India, Australia. At the same time, search interest is quite low in countries such as Mexico, Russia, Turkey, Chile, Peru, Argentina, and Iran. It is also notable that there is very little search activity in many of the African countries.
In this brief narrative review [
4], we will look at key aspects of ChatGPT, including its technical background, mechanisms, merits, advantages, disadvantages, reasons why it is popular, and its future development and trajectory.
II. BACKGROUND OF CHATGPT
To evaluate ChatGPT's future potential, it is essential to first briefly examine its background. Several of the most well-known figures from Santa Clara Valley have participated in the development of chatbot technology in the past. The business that created ChatGPT, OpenAI, was launched as a charity in 2015 by Greg Brockman, Elon Musk, Ilya Sutskever, Wojciech Zaremba, Peter Thiel, and other technology developers. Its objective was to prevent the centralized control of AI by providing its work and copyrights open to the general population. As per the material posted on OpenAI's site on 11, December 2015, the business sought to create AI in the method that is most probable to benefit humankind in its entire life [
5].
Elon Musk resigned from the panel in 2018 because of a conflict of interest with Tesla AI. In 2019, OpenAI changed its status from a non-business entity
, to "capped-gain," enabling investors to earn 100X possible profits while still supporting non-profit endeavors with the leftover funds. The two businesses formed a relationship in the same year that Microsoft spent
$1 billion in OpenAI and licensed Microsoft as the exclusive recipient of its innovation. Thanks to the partnership, Microsoft can now compete with Google's AI business, DeepMind [
6].
On 30, November 2022 OpenAI's projected valuation increased to
$29 billion and released a downloadable demo of ChatGPT. A chatbot is a computer application powered by AI that can interact with human communication. The technique answers in a couple of seconds when operators request queries. Within five days after its release, ChatGPT had 1 million members. As we indicated in the introduction, ChatGPT immediately became well-known for its thorough and clear replies across a broad spectrum of subject areas. It is the very first time such a potent chatbot online interface has been released, which is freely accessible to everyone, and is simple to implement. But, it is doubtful that the free service will always be available [
7].
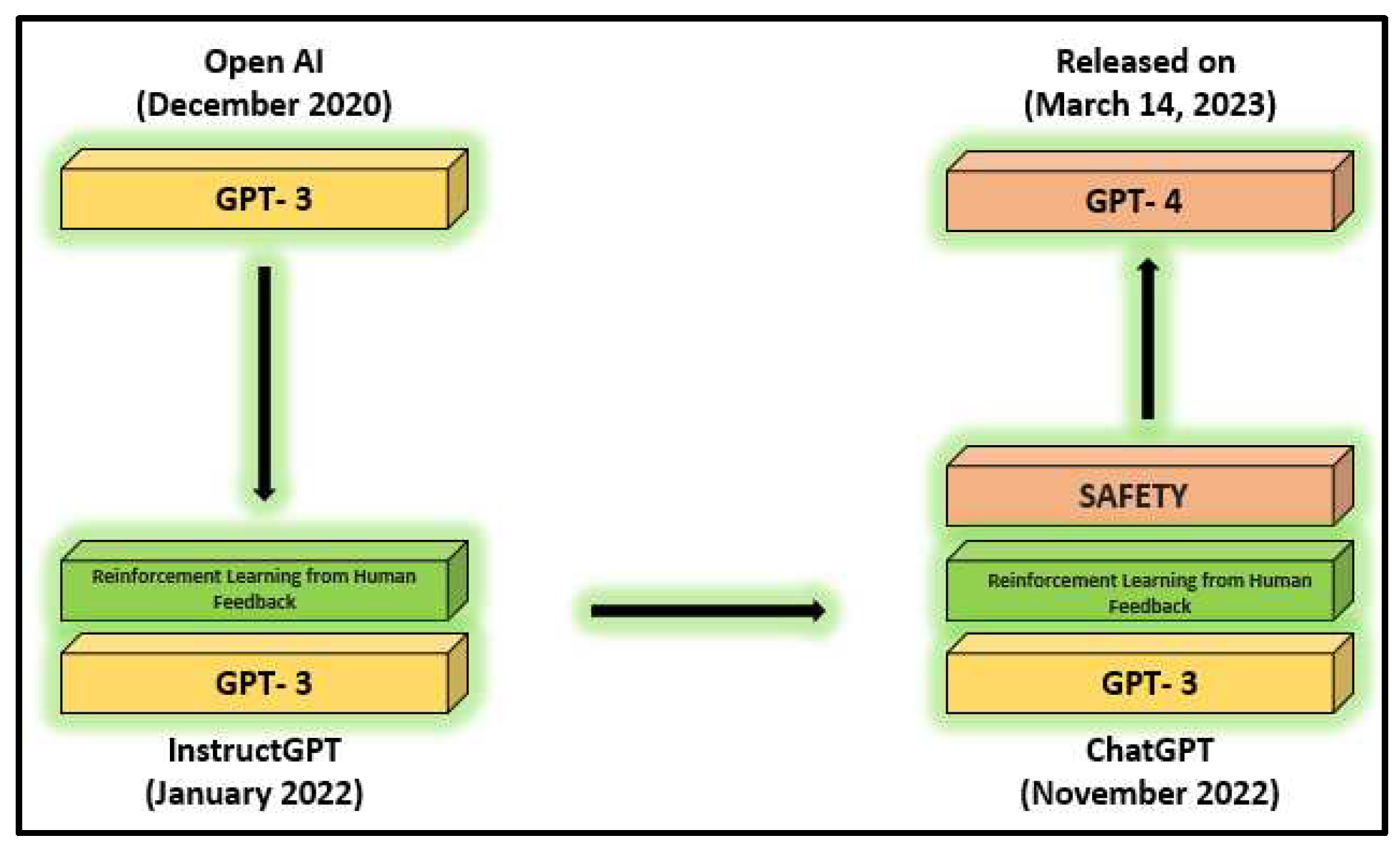
The GPT-4 (Generative Pre-Trained Transformer 4) is the 4th version in the GPT classes; it is a big structure LLM developed by OpenAI. On 14, March 2023, it was made public through API and to ChatGPT+ subscribers. Microsoft acknowledged that earlier iterations of Bing that utilized GPT actually did so before GPT-4 was formally released. GPT-4 was taught to anticipate the coming unit as a transformer implementing both public and private information and was then enhanced with RL (Reinforcement Learning) via user and AI input for quality management and human synchronization [
8]. The following are some potential improvements that GPT-4 offers:
Improved Language Modeling: GPT-4 is anticipated to contain more parameters and to have been trained on a broader range of data sets, which might result in more accurate and reliable language modeling skills.
Multimodal Learning: GPT-4 may be created to learn from a variety of modalities, including text, graphics, audio, and video, enabling it to comprehend and provide answers across several media types.
Better Contextual Understanding: The contextual comprehension and reasoning capabilities of GPT-4 may be more sophisticated, enabling it to produce more logical and pertinent replies depending on the conversation's context.
Increased Efficiency: GPT-4 may be quicker and more energy-efficient than its forerunners, opening it up to a wider variety of applications and devices.
Enhanced Creativity: Beyond the facts and information, it has been educated on, GPT-4 may have increased creativity and produced more inventive and varied replies.
Figure 2.
ChatGPT Development Process.
Figure 2.
ChatGPT Development Process.
III. THE MECHANISM SUPPORTING CHATGPT
Generative Pre-Training Transformer 3 or Simply GPT-3 is a state-of-the-art AI system. It enables chatbots to interpret and develop normal language similar to that of humans with impressive precision and fluency. With 175 billion parameters and the potential to quickly action millions of texts, it is the broadest language standard created to date [
9].
A Deep Neural Network (DNN) has been already tested by OpenAI using a sizable sentence database, and its functionality has been enhanced for purposes like creating sentences or responding to queries. This is the core tech behind Chat GPT-3. The grid is built from several converter units that analyze the entered sentence and show results. In addition, the connection has intra-attention features that allow it to evaluate the significance of various words and terms about one another and the discussions as a whole. Generators also enable Chat GPT-3 to produce meaningful sentences even from minimal information [
10].
A noteworthy development in Natural Language Processing (NLP) is Chat GPT-3, which utilizes a transformer-built structure to analyze massive volumes of information concurrently and create a language that is closer to what a human would interpret [
11]. There are several applications for this innovation, including text categorization services, bots, and automatic translation applications. Nevertheless, Chat GPT-3 is unable to connect to the Web and can only function by utilizing the Internet it has learned during development, which restricts its ability to acquire outside knowledge [
12].
Figure 3 displays a word cloud for ChatGPT that is evidence of its vast lexicon and subject-matter expertise. It serves as a display of words from various fields, including technology, science, and current events. Artificial Intelligence-related terms like "Machine Learning, "ChatGPT,” "Neural Networks," and "Deep Learning" are included in the word cloud. It also contains words like "natural language processing," "language generation," and "text completion".
IV. MERITS OF CHATGPT
ChatGPT has extensive knowledge of content from various sources, including books, journals, and web pages, that may contain both biased and neutral information. Its ability to recall and provide reliable information is critical for several sensitive applications and other essential AI technologies. However, it is not perfect, and its accuracy can be compromised, as it relies on a learning algorithm.
Since its introduction, there has been an exponential increase in the number of studies on ChatGPT, some of which have even been co-authored with ChatGPT [e.g., 13]. Many of the studies have looked ChatGPT’s impact and implications in the educational sector. In a study by Rudolph, Tan and Tan [
12], ChatGPT was discussed in the context of current research on artificial intelligence in education. The authors examined how ChatGPT can be implemented for use by teachers, students, and systems, as well as the potential benefits and risks associated with its use. To conclude their study, the authors provided recommendations for learners, educators, and universities [
12]. Tate et al. investigated the impact of ChatGPT and similar message-generation tools on education as a component of a broader methodology [
14]. Huh's brief report concluded that ChatGPT's ability to comprehend and analyze data was not yet at the level of Korean medical graduates who were tested on their knowledge of parasitology [
15].
Cotton
, et al. [
16] took a practical approach to evaluating the pros and cons of using ChatGPT, with a focus on utilizing AI-powered writing assistants. This is in contrast to Yeadon
, et al. [
17] who viewed ChatGPT as a significant threat to the validity of short-form essays. Wang
, et al. [
18] enhanced and developed Boolean Queries (BQ) for systematic reviews using ChatGPT. They compiled a comprehensive set of questions for over 100 systematic review topics and evaluated queries generated by the most advanced automatic query generation systems, including ChatGPT. Their results showed that while ChatGPT's queries had lower recall, they had greater accuracy. Additionally, they demonstrated that ChatGPT can construct BQ more successfully when given a directed response. However, one limitation of their findings was that even when using the same answer, ChatGPT generates multiple inquiries with varying levels of effectiveness [
18].
Sallam [
19] conducted an extensive analysis of the potential benefits and limitations of using ChatGPT as a Large Language Model (LLM) in healthcare, education, research, and performance. The author utilized the term "ChatGPT" to conduct a thorough exploration of English-language articles on Google Scholar and PubMed, adhering to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) standards [
19]. In the first peer-reviewed academic article on ChatGPT and higher education, Pavlik [
20] discussed the benefits and drawbacks of using ChatGPT in this context. Pavlik also explored the implications of sentence generators like ChatGPT for journalism and media education [
20]
When Gilson et al. evaluated ChatGPT's performance on the United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) related queries, they discovered that the AI only completely functioned at the standard of 3rd year graduate students [
21]. Using ChatGPT to create an academic article as part of a pilot project, Zhai [
22] found that it aided in producing a readable, correct, relevant, and methodical document. The author suggested that instructors should put more effort into making learners ability to think critically and innovate by creating AI-integrated learning tasks that include educators in resolving actual issues [
22]. According to Nisar and Aslam [
23], GPT-3 may be utilized by Standard Chinese Medicine learners in Malaysia who are learning pharmacology as their learning tool and rapid reference. Atlas [
24] argued that ChatGPT can be a useful tool in university education for enhancing writing by speeding up and boosting writing performance. For example, it can produce sentences, summarize data, and create ideas. It is also able to spot grammatical and stylistic mistakes and improving the comprehension of written text. Moreover, Kasneci
, et al. [
25] mentioned that ChatGPT might aid learners in the growth of research abilities by supplying them with data and resources on a particular subject, offering unexplored angles, and exposing them to fresh study subjects, allowing them to build deeper comprehension and appraisal of the subject [
25]. Because it generates precise responses on medical licensure examinations, Kung
, et al. [
26] discovered that it can help with healthcare training as well as a clinical assessment.
V. PROS OF CHATGPT
Since its launch, ChatGPT has grown in popularity among many demographic groups. However, the response has been relatively mixed. While many are praising ChatGPT for its benefits and future potential, others remain more skeptical and are criticizing it for its shortcomings, constraints and possible disadvantages. In the following, we will examine some of the main advantages of ChatGPT [
27].
A. Aims to Mimic Human Dialogue
The primary role of ChatGPT is to mimic human dialogue based on operator-provided submissions or commands. It is commonly similar to AI assistant innovations and system apps such as Alexa and Siri. It is created on more developed Reinforcement Learning (RL) and Supervised Learning (SL) methods implementing Large Learning models (LLL) algorithm and assessing its functionality, and it imitates real-world discussion.
B. Created Based on GPT-3 Model
Generative Pre-Trained Transformer-3 (GPT-3) is a decoder and language prophecy structure designed by OpenAI. It is considered among the most powerful AI methods ever constructed and is highly not a set of the string language model [
28]. It is tough to decide whether a message is created by an individual due to the standard of the messages it creates. Being trained on a sizable collection of text, GPT-3 is a very intelligent and adaptable language model. As a result, ChatGPT may be used for a variety of tasks since it has a broad range of data [
29].
C. Broad-Variety Implementations
ChatGPT can perform multiple functions. It can generate text that compares to that of skilled Artificial Intelligence (AI) writers. Analyses have disclosed that it is even skilled in noting songs and forming imaginary works for example novels. It can support technical developers or content supporters in creating a summary [
30]. By the chatbot, the enormous volume of content can be examined and demonstrated. Therefore, writing and problem-solving technical developers is an engaging further implementation of ChatGPT [
31].
D. Open to Additional Improvement
The foundation of ChatGPT is a machine learning model, which can be continually improved by being trained on fresh data. Through ChatGPT, the knowledge to make improvements in its responses and available implementation are other benefits. While depending on the presented LLMs, there is always a chance for development via an effective program utilizing SL and RL. An operator can offer additional information in contrast to like and unlike a specific answer [
32].
E. Natural Language Understanding
ChatGPT is based on the GPT (Generative Pre-Trained Transformer) architecture, enabling it to comprehend real language's syntactic and grammatical structures. It has developed the ability to detect typical grammatical constructions and idioms after being trained on a vast corpus of text data, which includes books, papers, and websites [
33]. This implies that even when the data it gets is not properly constructed or includes faults, it may nevertheless provide replies that are grammatically accurate and semantically relevant [
34].
F. Wide Range of Applications
Customer support, personal assistance, and content creation are just a few of the uses for ChatGPT. ChatGPT can assist organizations in automating their customer care assistance procedures, lowering the demand for human agents and enhancing response times. ChatGPT can aid users with personal assistance chores like making appointments or looking for information online [
35]. Finally, ChatGPT can be used to create content, such as text for social media postings or marketing initiatives.
Moreover, ChatGPT is a vital tool for several applications due to its features. For example, it can be a useful tool for interacting with users and enhancing their experience because of its grasp of natural language, contextual awareness, and learning capability [
36]. Moreover, it can be a useful tool for companies and organizations who wish to offer top-notch support or customer care due to its scalability and around-the-clock availability.
VI. CONS OF CHATGPT
Although ChatGPT's ability to maintain a conversation is noteworthy, it is not without its shortcomings, like many other chatbots in the past. The following are some of the primary drawbacks identified in previous studies [
25].
A. Lack of Clarity and Factual Errors
The point that ChatGPT periodically can develop sentences that appear precise or effective but are incorrect or illogical is among the main faults and shortcomings [
37]. Sometimes, ChatGPT cannot completely comprehend a question due to a lack of context, which might result in confused or inaccurate answers. For instance, if a user poses a question that depends on details from an earlier exchange, ChatGPT might not be aware of that context and might give an answer that is inaccurate or ambiguous. It is systematic in statistical language standards and is known as "commotion." Moreover, it delivers no sources or footnotes regarding where to discover the content. Therefore, it is not perfect to implement this bot by itself for digital tracking and study [
38].
B. Poor Understanding of Recent Developments
The edition that was launched in November 2022 can simply offer details on things that developed in 2021 and before. As it persists to provide information bases on words created by individuals, it will finally display more recent occurrences [
39]. Notwithstanding this weakness, operators should understand that it just has a weak understanding of truths because it depends on old databases. Moreover, its inadequate comprehension of current events is one possible ChatGPT drawback. This is so because ChatGPT's knowledge might not reflect the most recent facts or advances as it was trained on a fixed dataset of text [
40].
C. Problems and Questions of Ethics
The point that ChatGPT has come under review is another flaw. Numerous universities have denied its facilities. Because its results rely on human-created sentences, academics and creators have worried about copyright violations. Unintentionally spreading false information or fake news with ChatGPT might have negative repercussions. This may occur if ChatGPT is not educated on trustworthy information sources or accuracy is not prioritized above interaction. It also reaches into query the appropriateness of replacing it with operations that require human association, including 24/7 help or psychic counselling [
41].
D. Other Possible Lawful Effects
ChatGPT was developed using data from The Common Crawl database, which includes copyrighted content from publishers, as well as works by individual authors and scholars [
42]. There is a chance that the advice offered if ChatGPT is utilized to provide legal or financial advice could not be correct or current. The individual or business that relied on the advice may be held accountable for this. Professionals have also warned about the potential of employing AI-built services for computer crime. ChatGPT and other forms are subject to likely lawful grants and administrative necessities [
43].
E. Limited Domain Expertise
Being a general-purpose language model, ChatGPT needs more expertise in particular domains [
44]. While it can produce grammatically and semantically sound replies, it could lack the specialized knowledge needed to respond to some queries or offer appropriate information in some domains. For instance, ChatGPT could not know how to respond appropriately to a user asking for a medical inquiry [
45].
F. Biased Responses
Large volumes of text data, some of which may be skewed or problematic, are used to train ChatGPT. This means it may create replies containing prejudice or preconceptions, particularly if the training data have such biases [
46]. If ChatGPT was trained using biased data, it will pick up on such biases and may repeat them in its answers. For instance, ChatGPT may yield results that reflect prejudices or discrimination if the training data contains such biases. This is a well-known problem with many AI models, and work is being done to fix it by using more representative and varied training data [
47].
ChatGPT's drawbacks are attributed to its difficulties in comprehending specialized topics, propensity for producing biased replies, lack of emotional intelligence, and restricted comprehension of context. However, even though these drawbacks may be considerable, continuous work in the field of natural language processing is being done to find solutions [
48].
VII. THE FUTURE OF CHATGPT
Currently, ChatGPT technology has gained traction in many areas of business and society [
49,
50,
51]. In the future, functions might be simplified, and they could radically alter how humans generate value. However, concerns have been raised regarding how it will affect human jobs at the same time. In the following, we will take a look at a few of ChatGPT's applications and speculate about ChatGPT's future development and trajectory.
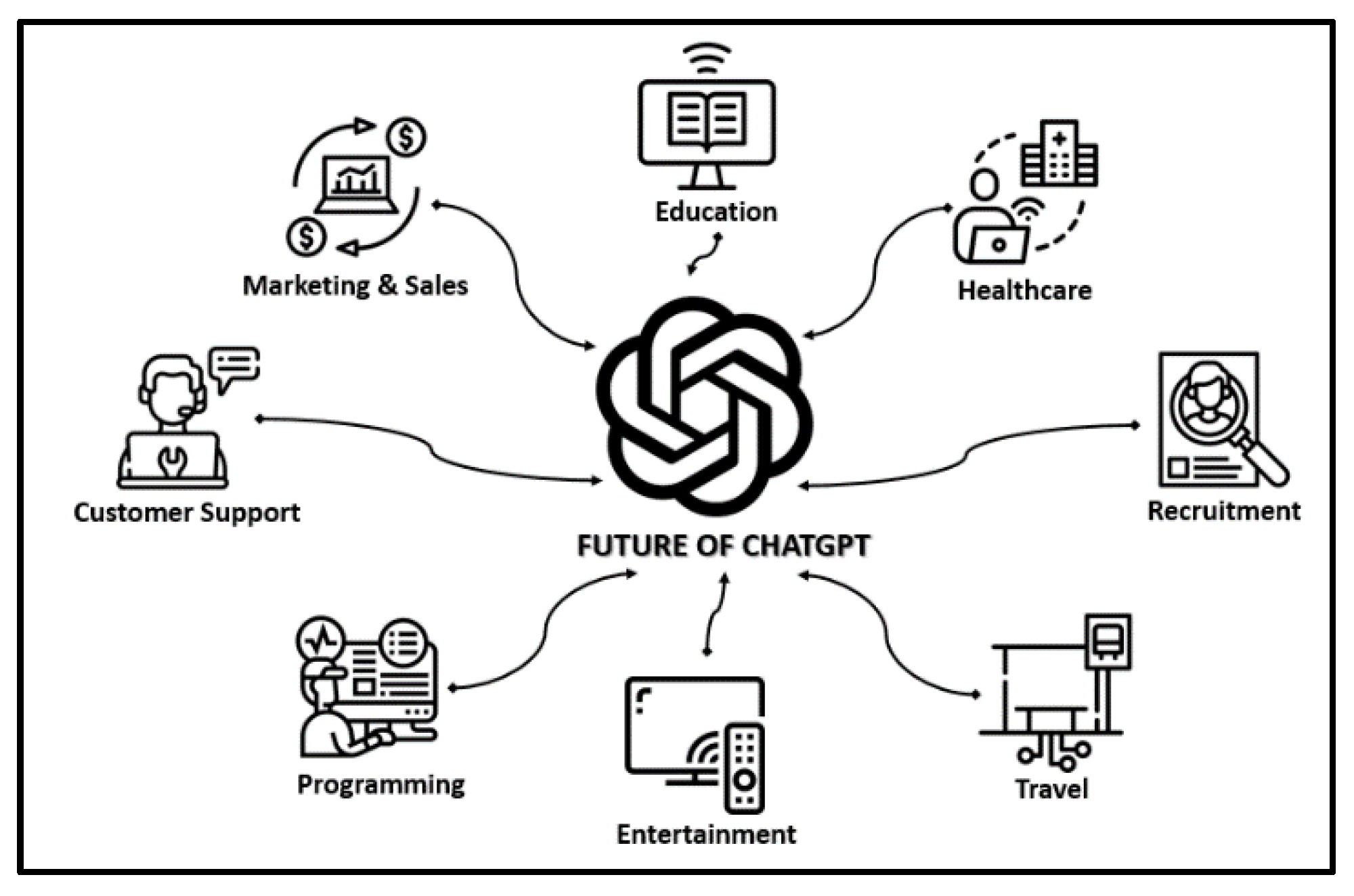
Figure 4.
ChatGPT Future Sectors.
Figure 4.
ChatGPT Future Sectors.
A. Customer Support
AI-based chatbots may respond to consumer inquiries quickly and provide round-the-clock client service. The enthusiasm that ChatGPT has generated is evidence of its ingenuity and growing significance in the AI industry. There is significant scope for ChatGPT to be connected with current interactive AI to enhance user support discussions as the technology develops and many firms use AI innovation to enhance the customer experience. In the coming future, by responding to customers' wants and questions quickly and personally, they can dramatically enhance customer service [
52].
B. Marketing and Sales
By helping clients in the purchasing process, chatbots can aid in information processing, outlook assessment, and proposed settlement. A solid title is necessary for written material to do effectively on search engines, making this a crucial advantage of creative AI technologies like ChatGPT. Marketing professionals may also use this AI tool’s power and ability to create intriguing headlines for articles, seminars, and conferences. Employers can use chatbots to simplify several steps in the hiring process, boosting productivity and reducing costs and time [
53]. Chatbots powered by AI can also assist employers simplifying the hiring process by pre-screened applicants. Also, in the future, they can compile key information about possible clients and offer parameterized testing recommendations to the marketing and sales teams, allowing them to customize their strategy [
54].
C. Education
AI-based chatbots have many applications in education [
55,
56] and have emerged as a useful tool for instructors to educate learners and provide them with engaging and informative responses to their questions. Among the educational applications of ChatGPT, one possibility is the creation of quizzes and tests that can help evaluate the learners' knowledge and progress. ChatGPT is known for its advanced capabilities and extensive data resources, which make it a powerful educational tool. However, it is important to note that the dataset used to train ChatGPT is compiled from various online sources, some of which may contain errors or inaccuracies. This indicates that learners should utilize ChatGPT as a reference comparable to Wikipedia, which also has been criticized for inaccuracies [
57].
Therefore, it is crucial for instructors to carefully review and validate the responses provided by ChatGPT before incorporating them into their instructional materials. However, with the right precautions and monitoring, ChatGPT can be an effective tool for enhancing the learning experience of students. In particular, ChatGPT can be an useful approach to get a broad understanding and a preliminary step in the learning process [
16].
D. Healthcare
AI-based chatbots can provide individualized health advice and assistance in identifying medical issues. Patients may find it difficult to remember to take their prescriptions on schedule and to adhere to their physician's dose recommendations, especially if they are consuming many medicines. Patients can utilize ChatGPT to handle their medication regimens, containing alerts, dose guidelines, and possible bad impacts. Medicine use, restrictions, and other vital factors impacting pharmacological intervention can also be discussed with patients via ChatGPT. Furthermore, AI-built ChatGPT can help patients have a better healthcare experience by automating organizational activities like consultation registration and treatment plan updates [
11].
E. Language Translation
ChatGPT can be utilized for language translation problems since it has a comprehensive language model [
39]. It can be trained on huge datasets of parallel text and text in two languages that mean the same thing. It can then be implemented to translate text from one language to another because of its capacity to produce a coherent text. By learning the connections between vocabulary and grammatical conventions in both languages, ChatGPT, for instance, may produce a similar phrase in another language given a sentence in one language. It can generate appropriate translations by considering the sentence's context and meaning [
58].
F. Travel
ChatGPT also has a multitude of applications in travel, tourism and hospitality [
59,
60,
61]. Chatbots have become increasingly popular in the tourism industry, providing visitors with a seamless and convenient way to book tickets, hotel rooms, and other accommodations. Additionally, AI-powered chatbots have the potential to revolutionize the tourism industry by offering real-time information on climate conditions, local events, and flight details, making it easier for travelers to plan their journeys and stay up to date on any changes or delays. Altogether, ChatGPT can revolutionize the tourism and hospitality sector by better arranging trips, enhancing the guest experience, offering language translation services, enhancing promotion, and allowing advanced analytics [
60].
G. Entertainment
ChatGPT also has several potential applications in entertainment. For example, chatbots powered by AI may provide individualized suggestions for shows, albums, and other entertainment types. Moreover, they can even create full scripts for films or television programs and compose lyrics to music. Although some are skeptical [
62], it is likely ChatGPT will become a helpful technique for the film industry, providing a variety of benefits, such as audience commentary and actionable insights to directing, writing and personality creation. In this manner, directors may use AI to generate more interesting and popular movies while preserving the craftsmanship and innovation that has long been at the core of the movie industry [
63].
H. Programming
The emergence of AI programmers like ChatGPT will also result in a growth in the need for computer programmers knowledgeable in methods of data science. For instance, developers proficient in Go, Python, and other advanced analytics tools and languages can develop, implement, and deploy applications. Moreover, programmers can write programs faster easily and quickly by using ChatGPT, which can produce program clips depending on particular computer programming and patterns. Finally, it can aid in the review process and with troubleshooting [
64].
I. Personal Assistants
With its capacity to interpret natural language and produce coherent text, ChatGPT has demonstrated considerable promise as a personal assistant. In order to give consumers even more in-depth support, it could integrate with other software programs in the future, such as email and calendar apps. In order to increase its precision and effectiveness over time, ChatGPT may employ machine learning techniques. It will learn from user input and interactions to comprehend specific preferences and requirements better. ChatGPT may become a more potent tool for productivity and personal organizing as technology develops and natural language processing gets better [
65].
VIII. CONCLUSION
According to this brief narrative review of ChatGPT, it is undeniable that AI technology has advanced significantly, and AI language tools like ChatGPT have a multitude of real-world applications. Moreover, it is clear that ChatGPT is a strong NLP system that can produce communications that sound and look human-like. Overall, the development of AI-technologies such as ChatGPT provides many advantages to businesses and society, including higher efficiency, more accuracy, and cost savings. That said, it is important to keep in mind the limitations, which include security issues and restricted capabilities. Notwithstanding these difficulties, ChatGPT is a rapidly evolving AI tool that can automate discussions and provide more precise replies. It is crucial to remember that these technologies still need some human involvement to guarantee that the output meets specified criteria, and therefore as of today cannot replace real authors.
References
- Susnjak, T. ChatGPT: The End of Online Exam Integrity? arXiv 2022, arXiv:2212.09292. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, M.; Er, E. Will ChatGPT get you caught? Rethinking of plagiarism detection. arXiv arXiv:2302.04335, 2023.
- Gozalo-Brizuela, R.; Garrido-Merchan, E.C. ChatGPT is not all you need. A State of the Art Review of large Generative AI models. arXiv arXiv:2301.04655, 2023.
- Ferrari, R. Writing narrative style literature reviews. Medical Writing 2015, 24, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.A.; Jawaid, M.; Khan, A.R.; Sajjad, M. ChatGPT-Reshaping medical education and clinical management. Pak J Med Sci 2023, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehnert, K. AI Insights into Theoretical Physics and the Swampland Program: A Journey Through the Cosmos with ChatGPT. arXiv arXiv:2301.08155, 2023.
- Deng, J.; Lin, Y. The Benefits and Challenges of ChatGPT: An Overview. Frontiers in Computing and Intelligent Systems 2022, 2, 81–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyphert, A.B. A human being wrote this law review article: GPT-3 and the practice of law. UC Davis L. Rev. 2021, 55, 401. [Google Scholar]
- Ufuk, F. The Role and Limitations of Large Language Models Such as ChatGPT in Clinical Settings and Medical Journalism. Radiology 2023, 230276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.A.; Howard, F.M.; Markov, N.S.; Dyer, E.C.; Ramesh, S.; Luo, Y.; Pearson, A.T. Comparing scientific abstracts generated by ChatGPT to original abstracts using an artificial intelligence output detector, plagiarism detector, and blinded human reviewers. bioRxiv 2022, 2022.2012. 2023.521610. [CrossRef]
- Jeblick, K.; Schachtner, B.; Dexl, J.; Mittermeier, A.; Stüber, A.T.; Topalis, J.; Weber, T.; Wesp, P.; Sabel, B.; Ricke, J. ChatGPT Makes Medicine Easy to Swallow: An Exploratory Case Study on Simplified Radiology Reports. arXiv arXiv:2212.14882, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, J.; Tan, S.; Tan, S. ChatGPT: Bullshit spewer or the end of traditional assessments in higher education? Journal of Applied Learning and Teaching 2023, 6. [Google Scholar]
- King, M.R. ChatGPT. A conversation on artificial intelligence, chatbots, and plagiarism in higher education. Cellular and Molecular Bioengineering 2023, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tate, T.; Doroudi, S.; Ritchie, D.; Xu, Y. Educational Research and AI-Generated Writing: Confronting the Coming Tsunami. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Huh, S. Are ChatGPT's knowledge and interpretation ability comparable to those of medical students in Korea for taking a parasitology examination?: a descriptive study. Journal of Educational Evaluation for Health Professions 2023, 20, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotton, D.R.; Cotton, P.A.; Shipway, J.R. Chatting and Cheating: Ensuring academic integrity in the era of ChatGPT. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Yeadon, W.; Inyang, O.-O.; Mizouri, A.; Peach, A.; Testrow, C. The Death of the Short-Form Physics Essay in the Coming AI Revolution. arXiv arXiv:2212.11661, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Scells, H.; Koopman, B.; Zuccon, G. Can chatgpt write a good boolean query for systematic review literature search? arXiv arXiv:2302.03495, 2023.
- Sallam, M. The utility of ChatGPT as an example of large language models in healthcare education, research and practice: Systematic review on the future perspectives and potential limitations. medRxiv 2023, 2023.2002. 2019.23286155. [CrossRef]
- Pavlik, J.V. Collaborating With ChatGPT: Considering the Implications of Generative Artificial Intelligence for Journalism and Media Education. Journalism and Mass Communication Educator 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilson, A.; Safranek, C.; Huang, T.; Socrates, V.; Chi, L.; Taylor, R.A.; Chartash, D. How Well Does ChatGPT Do When Taking the Medical Licensing Exams? The Implications of Large Language Models for Medical Education and Knowledge Assessment. medRxiv 2022, 2022.2012. 2023.22283901. [CrossRef]
- Zh, *!!! REPLACE !!!*. Zhai, X. ChatGPT user experience: Implications for education. Available at SSRN 4312418 2022.
- Nisar, S.; Aslam, M.S. Is ChatGPT a Good Tool for T&CM Students in Studying Pharmacology? Available at SSRN 4324310 2023.
- Atlas, S. ChatGPT for Higher Education and Professional Development: A Guide to Conversational AI. 2023.
- Kasneci, E.; Seßler, K.; Küchemann, S.; Bannert, M.; Dementieva, D.; Fischer, F.; Gasser, U.; Groh, G.; Günnemann, S.; Hüllermeier, E. ChatGPT for good? On opportunities and challenges of large language models for education. Learning and Individual Differences 2023, 103, 102274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, T.H.; Cheatham, M.; Medenilla, A.; Sillos, C.; De Leon, L.; Elepaño, C.; Madriaga, M.; Aggabao, R.; Diaz-Candido, G.; Maningo, J.; et al. Performance of ChatGPT on USMLE: Potential for AI-assisted medical education using large language models. PLOS Digital Health 2023, 2, e0000198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, M. A Day in the Life of ChatGPT as a researcher: Sustainable and Efficient Machine Learning-A Review of Sparsity Techniques and Future Research Directions. 2023.
- Donato, H.; Escada, P.; Villanueva, T. A Transparência da Ciência com o ChatGPT e as Ferramentas Emergentes de Inteligência Artificial: Como se Devem Posicionar as Revistas Científicas Médicas? The Transparency of Science with ChatGPT and the Emerging Artificial Intelligence Language Models: Where Should Medical Journals Stand? 2023.
- Haque, M.U.; Dharmadasa, I.; Sworna, Z.T.; Rajapakse, R.N.; Ahmad, H. " I think this is the most disruptive technology": Exploring Sentiments of ChatGPT Early Adopters using Twitter Data. arXiv arXiv:2212.05856, 2022.
- Zhang, B.; Ding, D.; Jing, L. How would Stance Detection Techniques Evolve after the Launch of ChatGPT? arXiv arXiv:2212.14548, 2022.
- Pardos, Z.A.; Bhandari, S. Learning gain differences between ChatGPT and human tutor generated algebra hints. arXiv arXiv:2302.06871, 2023.
- Hosseini, M.; Horbach, S.P. Fighting reviewer fatigue or amplifying bias? Considerations and recommendations for use of ChatGPT and other Large Language Models in scholarly peer review. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Kocoń, J.; Cichecki, I.; Kaszyca, O.; Kochanek, M.; Szydło, D.; Baran, J.; Bielaniewicz, J.; Gruza, M.; Janz, A.; Kanclerz, K. ChatGPT: Jack of all trades, master of none. arXiv arXiv:2302.10724, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hu, X.; Hou, W.; Chen, H.; Zheng, R.; Wang, Y.; Yang, L.; Huang, H.; Ye, W.; Geng, X. On the Robustness of ChatGPT: An Adversarial and Out-of-distribution Perspective. arXiv arXiv:2302.12095, 2023.
- Dai, H.; Liu, Z.; Liao, W.; Huang, X.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, L.; Liu, W.; Liu, N.; Li, S.; Zhu, D. ChatAug: Leveraging ChatGPT for Text Data Augmentation. arXiv arXiv:2302.13007, 2023.
- Shahriar, S.; Hayawi, K. Let's have a chat! A Conversation with ChatGPT: Technology, Applications, and Limitations. arXiv arXiv:2302.13817, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liang, Y.; Meng, F.; Li, Z.; Qu, J.; Zhou, J. Cross-Lingual Summarization via ChatGPT. arXiv arXiv:2302.14229, 2023.
- Kuzman, T.; Ljubešić, N.; Mozetič, I. ChatGPT: Beginning of an End of Manual Annotation? Use Case of Automatic Genre Identification. arXiv arXiv:2303.03953, 2023.
- Jiao, W.; Wang, W.; Huang, J.-t.; Wang, X.; Tu, Z. Is ChatGPT a good translator? A preliminary study. arXiv arXiv:2301.08745, 2023.
- Cao, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Yan, Z.; Dai, Y.; Yu, P.S.; Sun, L. A Comprehensive Survey of AI-Generated Content (AIGC): A History of Generative AI from GAN to ChatGPT. arXiv arXiv:2303.04226, 2023.
- Antaki, F.; Touma, S.; Milad, D.; El-Khoury, J.; Duval, R. Evaluating the performance of chatgpt in ophthalmology: An analysis of its successes and shortcomings. medRxiv 2023, 2023.2001. 2022.23284882. [CrossRef]
- Sinha, R.K.; Roy, A.D.; Kumar, N.; Mondal, H.; Sinha, R. Applicability of ChatGPT in assisting to solve higher order problems in pathology. Cureus 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manohar, N.; Prasad, S.S. Use of ChatGPT in Academic Publishing: A Rare Case of Seronegative Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in a Patient With HIV Infection. Cureus Journal of Medical Science 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGee, R.W. Who Were the 10 Best and 10 Worst US Presidents? The Opinion of Chat GPT (Artificial Intelligence). The Opinion of Chat GPT (Artificial Intelligence)(February 23, 2023) 2023. 23 February.
- Halaweh, M. ChatGPT in education: Strategies for responsible implementation. Contemporary Educational Technology 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, V.W.; Lei, P.; Cho, W.C. The potential impact of ChatGPT in clinical and translational medicine. Clinical and Translational Medicine 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlAfnan, M.A.; Dishari, S.; Jovic, M.; Lomidze, K. ChatGPT as an Educational Tool: Opportunities, Challenges, and Recommendations for Communication, Business Writing, and Composition Courses. Journal of Artificial Intelligence and Technology 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Han, D.; Chen, S.; Zeng, F.; Wang, C. How Can ChatGPT Benefit Pharmacy: A Case Report on Review Writing. 2023. [CrossRef]
- George, A.S.; George, A.H. A Review of ChatGPT AI's Impact on Several Business Sectors. Partners Universal International Innovation Journal 2023, 1, 9–23. [Google Scholar]
- Hassani, H.; Silva, E.S. The Role of ChatGPT in Data Science: How AI-Assisted Conversational Interfaces Are Revolutionizing the Field. Big Data and Cognitive Computing 2023, 7, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haleem, A.; Javaid, M.; Singh, R.P. An era of ChatGPT as a significant futuristic support tool: A study on features, abilities, and challenges. BenchCouncil Transactions on Benchmarks, Standards and Evaluations 2023, 100089.
- Sanmarchi, F.; Golinelli, D.; Bucci, A. A step-by-step Researcher's Guide to the use of an AI-based transformer in epidemiology: an exploratory analysis of ChatGPT using the STROBE checklist for observational studies. medRxiv 2023, 2023.2002. 2006.23285514. [CrossRef]
- Korzynski, P.; Mazurek, G.; Altmann, A.; Ejdys, J.; Kazlauskaite, R.; Paliszkiewicz, J.; Wach, K.; Ziemba, E. Generative artificial intelligence as a new context for management theories: analysis of ChatGPT. Central European Management Journal 2023, ahead-of-print. [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.; Kim, J.; Kamineni, M.; Pang, M.; Lie, W.; Succi, M.D. Evaluating ChatGPT as an adjunct for radiologic decision-making. medRxiv 2023, 2023.2002. 2002.23285399. [CrossRef]
- Baidoo-Anu, D.; Owusu Ansah, L. Education in the era of generative artificial intelligence (AI): Understanding the potential benefits of ChatGPT in promoting teaching and learning. Available at SSRN 4337484 2023.
- Tlili, A.; Shehata, B.; Adarkwah, M.A.; Bozkurt, A.; Hickey, D.T.; Huang, R.; Agyemang, B. What if the devil is my guardian angel: ChatGPT as a case study of using chatbots in education. Smart Learning Environments 2023, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman Rector, L. Comparison of and other encyclopedias for accuracy, breadth, and depth in historical articles. Reference Services Review 2008, 36, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarifhonarvar, A. Economics of ChatGPT: A Labor Market View on the Occupational Impact of Artificial Intelligence. Available at SSRN 4350925 2023.
- Dwivedi, Y.K.; Kshetri, N.; Hughes, L.; Slade, E.L.; Jeyaraj, A.; Kar, A.K.; Baabdullah, A.M.; Koohang, A.; Raghavan, V.; Ahuja, M. “So what if ChatGPT wrote it?” Multidisciplinary perspectives on opportunities, challenges and implications of generative conversational AI for research, practice and policy. International Journal of Information Management 2023, 71, 102642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F. Let the devil speak for itself: Should ChatGPT be allowed or banned in hospitality and tourism schools? Journal of Global Hospitality and Tourism 2023, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iskender, A. Holy or Unholy? Interview with Open AI’s ChatGPT. European Journal of Tourism Research 2023, 34, 3414–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, K.S. How ChatGPT Could Harm The Film Industry. Entrepreneur India 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Haensch, A.-C.; Ball, S.; Herklotz, M.; Kreuter, F. Seeing ChatGPT Through Students' Eyes: An Analysis of TikTok Data. arXiv arXiv:2303.05349, 2023.
- Sobania, D.; Briesch, M.; Hanna, C.; Petke, J. An analysis of the automatic bug fixing performance of chatgpt. arXiv arXiv:2301.08653, 2023.
- Murk, W.; Goralnick, E.; Brownstein, J.S.; Landman, A.B. An Opportunity to Standardize and Enhance Intelligent Virtual Assistant-Delivered Layperson Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Instructions. medRxiv 2023, 2023.2003. 2009.23287050. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).