Submitted:
16 May 2023
Posted:
17 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Mitochondrial Deficiencies and Oxidative Stress as Close Partners in Alzheimer’s Disease
Ca2+ Dysregulation and Downstream Effects in Alzheimer’s Disease
Impaired Mitochondrial Function and Associated Oxidative Damage in Parkinson’s Disease
Altered Ca2+ Homeostasis and Concomitant Neurotoxicity in Parkinson’s Disease
Modulation of Calcium Signaling and Homeostasis by Heterocyclic Compounds in Alzheimer’s Disease and Parkinson’s Disease
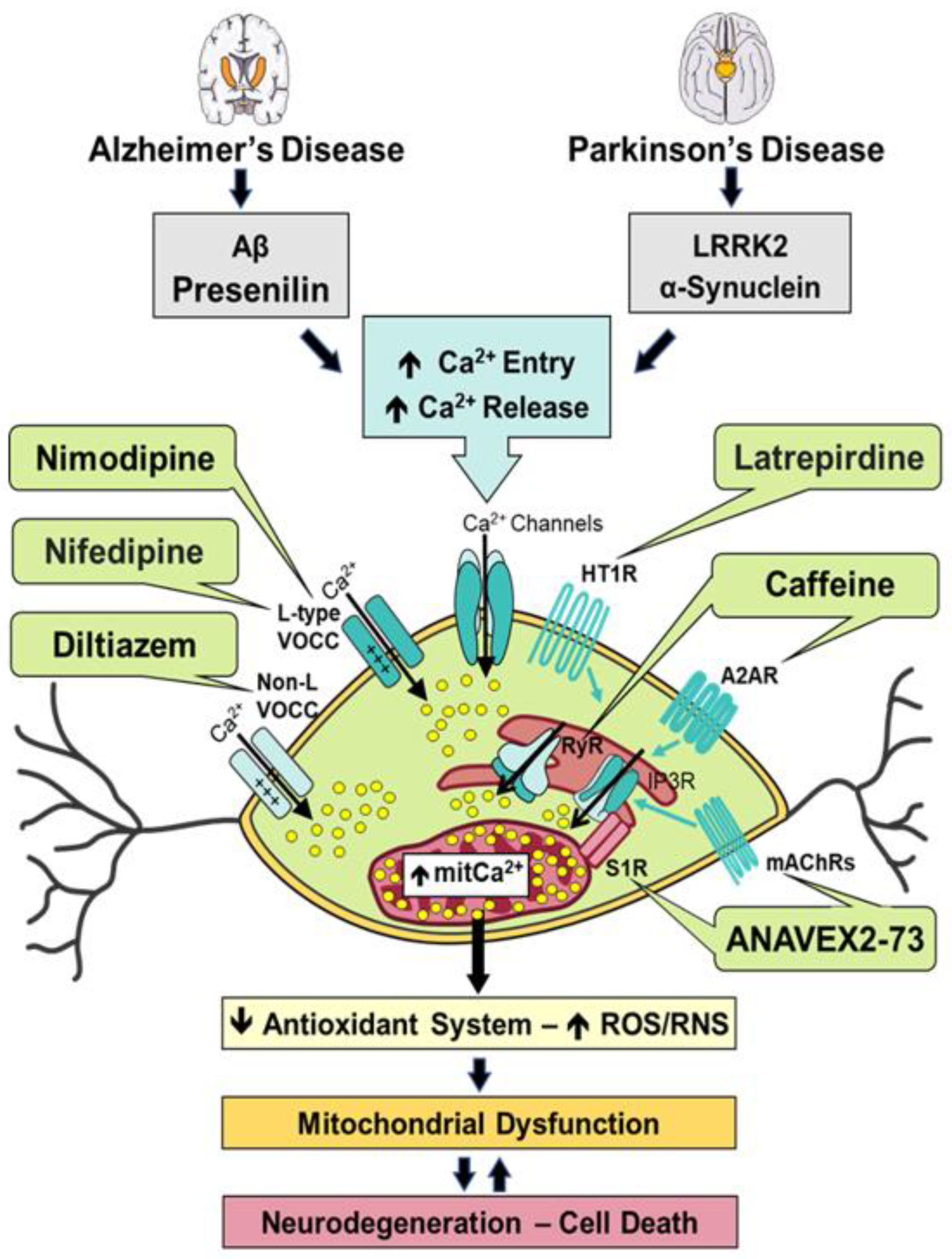
1. ANAVEX2-73
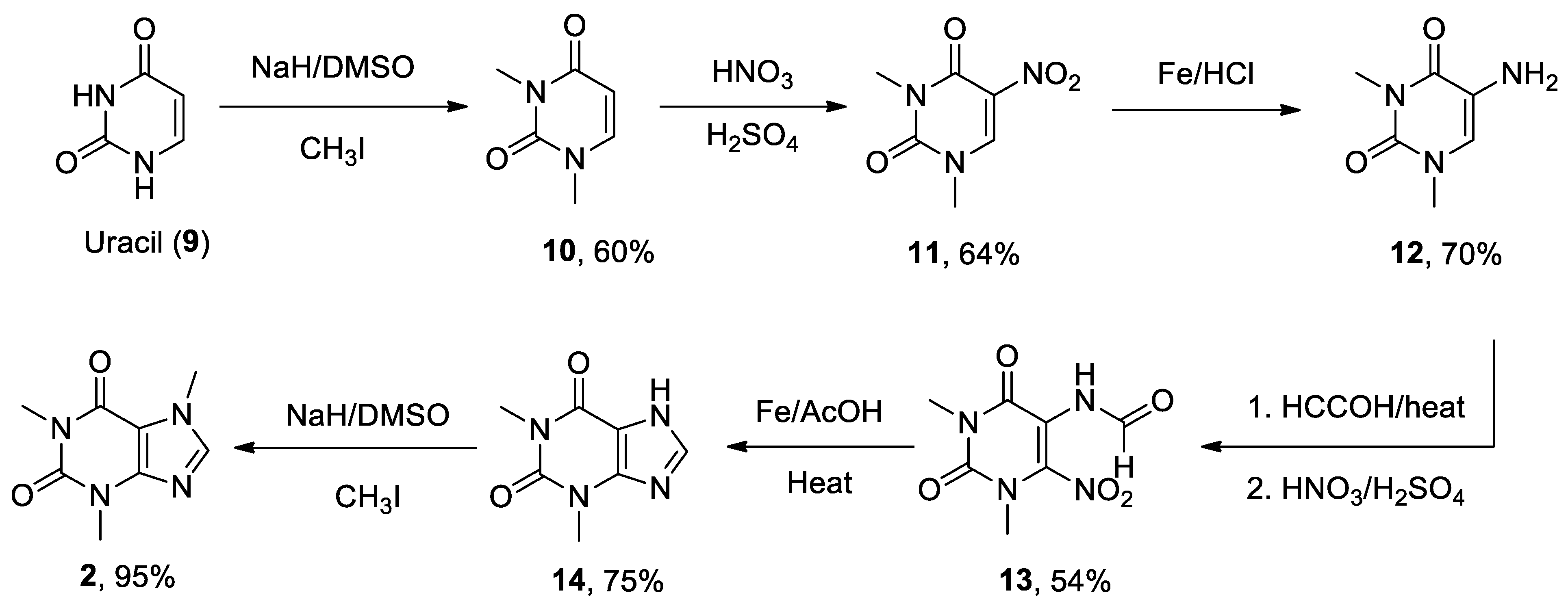
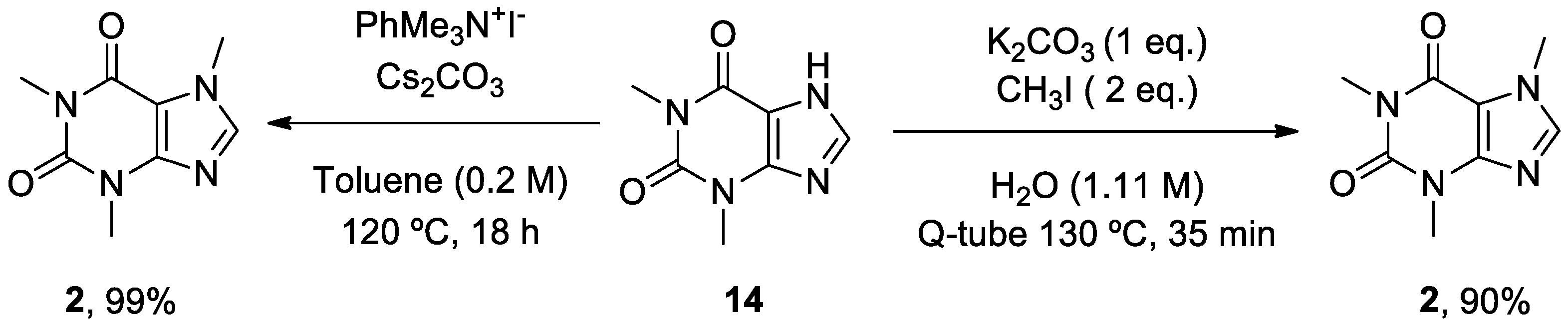
2. Caffeine
3. Diltiazem
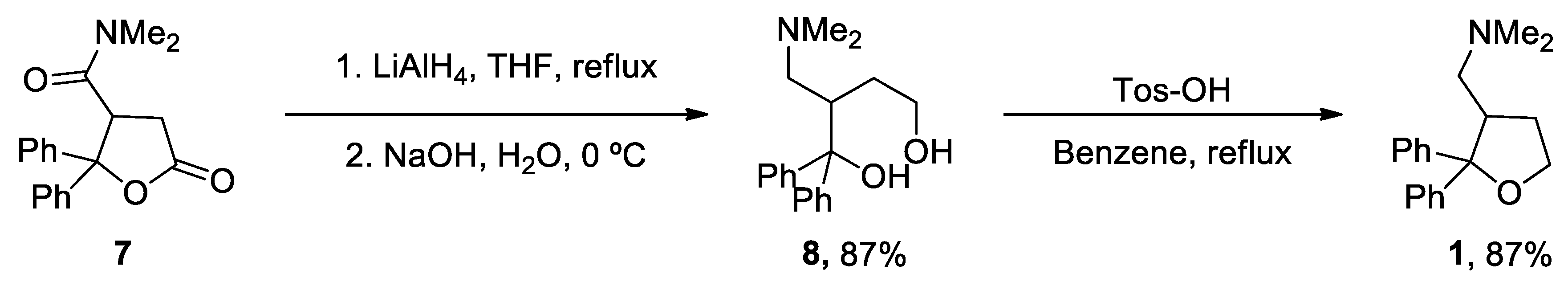
4. Latrepirdine
5. Nifedipine
6. Nimodipine
Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Abbreviations
References
- Yoboue, E.D.; Sitia, R.; Simmen, T. Redox crosstalk at endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane contact sites (MCS) uses toxic waste to deliver messages. Cell Death Dis 2018, 9, 331. [CrossRef]
- Rao, V.K.; Carlson, E.A.; Yan, S.S. Mitochondrial permeability transition pore is a potential drug target for neurodegeneration. Biochim Biophys Acta 2014, 1842, 1267-1272. [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.J.; Cho, S.S.; Jeong, Y.; Park, K.C.; Kang, S.J.; Kang, E.; Kim, S.E.; Lee, K.H.; Na, D.L. Glucose metabolism in early onset versus late onset Alzheimer's disease: an SPM analysis of 120 patients. Brain 2005, 128, 1790-1801. [CrossRef]
- Bosetti, F.; Brizzi, F.; Barogi, S.; Mancuso, M.; Siciliano, G.; Tendi, E.A.; Murri, L.; Rapoport, S.I.; Solaini, G. Cytochrome c oxidase and mitochondrial F1F0-ATPase (ATP synthase) activities in platelets and brain from patients with Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging 2002, 23, 371-376. [CrossRef]
- Parker, W.D., Jr.; Filley, C.M.; Parks, J.K. Cytochrome oxidase deficiency in Alzheimer's disease. Neurology 1990, 40, 1302-1303. [CrossRef]
- Hirai, K.; Aliev, G.; Nunomura, A.; Fujioka, H.; Russell, R.L.; Atwood, C.S.; Johnson, A.B.; Kress, Y.; Vinters, H.V.; Tabaton, M.; et al. Mitochondrial abnormalities in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurosci 2001, 21, 3017-3023. [CrossRef]
- Manczak, M.; Calkins, M.J.; Reddy, P.H. Impaired mitochondrial dynamics and abnormal interaction of amyloid beta with mitochondrial protein Drp1 in neurons from patients with Alzheimer's disease: implications for neuronal damage. Hum Mol Genet 2011, 20, 2495-2509. [CrossRef]
- Calkins, M.J.; Manczak, M.; Mao, P.; Shirendeb, U.; Reddy, P.H. Impaired mitochondrial biogenesis, defective axonal transport of mitochondria, abnormal mitochondrial dynamics and synaptic degeneration in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Hum Mol Genet 2011, 20, 4515-4529. [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Guo, L.; Yan, S.; Sosunov, A.A.; McKhann, G.M.; Yan, S.S. Early deficits in synaptic mitochondria in an Alzheimer's disease mouse model. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2010, 107, 18670-18675. [CrossRef]
- Devi, L.; Prabhu, B.M.; Galati, D.F.; Avadhani, N.G.; Anandatheerthavarada, H.K. Accumulation of amyloid precursor protein in the mitochondrial import channels of human Alzheimer's disease brain is associated with mitochondrial dysfunction. J Neurosci 2006, 26, 9057-9068. [CrossRef]
- Hansson Petersen, C.A.; Alikhani, N.; Behbahani, H.; Wiehager, B.; Pavlov, P.F.; Alafuzoff, I.; Leinonen, V.; Ito, A.; Winblad, B.; Glaser, E.; et al. The amyloid beta-peptide is imported into mitochondria via the TOM import machinery and localized to mitochondrial cristae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2008, 105, 13145-13150. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Su, B.; Siedlak, S.L.; Moreira, P.I.; Fujioka, H.; Wang, Y.; Casadesus, G.; Zhu, X. Amyloid-beta overproduction causes abnormal mitochondrial dynamics via differential modulation of mitochondrial fission/fusion proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2008, 105, 19318-19323. [CrossRef]
- Cho, D.H.; Nakamura, T.; Fang, J.; Cieplak, P.; Godzik, A.; Gu, Z.; Lipton, S.A. S-nitrosylation of Drp1 mediates beta-amyloid-related mitochondrial fission and neuronal injury. Science 2009, 324, 102-105. [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.I.; Lee, K.H.; Gabr, A.A.; Choi, G.E.; Kim, J.S.; Ko, S.H.; Han, H.J. Abeta-Induced Drp1 phosphorylation through Akt activation promotes excessive mitochondrial fission leading to neuronal apoptosis. Biochim Biophys Acta 2016, 1863, 2820-2834. [CrossRef]
- Li, X.C.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Z.H.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.P.; Feng, Q.; Wang, Q.; Ye, K.; Liu, G.P.; et al. Human wild-type full-length tau accumulation disrupts mitochondrial dynamics and the functions via increasing mitofusins. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 24756. [CrossRef]
- Tapias, V.; Jainuddin, S.; Ahuja, M.; Stack, C.; Elipenahli, C.; Vignisse, J.; Gerges, M.; Starkova, N.; Xu, H.; Starkov, A.A.; et al. Benfotiamine treatment activates the Nrf2/ARE pathway and is neuroprotective in a transgenic mouse model of tauopathy. Hum Mol Genet 2018, 27, 2874-2892. [CrossRef]
- Vossel, K.A.; Xu, J.C.; Fomenko, V.; Miyamoto, T.; Suberbielle, E.; Knox, J.A.; Ho, K.; Kim, D.H.; Yu, G.Q.; Mucke, L. Tau reduction prevents Abeta-induced axonal transport deficits by blocking activation of GSK3beta. J Cell Biol 2015, 209, 419-433. [CrossRef]
- Bobba, A.; Amadoro, G.; Valenti, D.; Corsetti, V.; Lassandro, R.; Atlante, A. Mitochondrial respiratory chain Complexes I and IV are impaired by beta-amyloid via direct interaction and through Complex I-dependent ROS production, respectively. Mitochondrion 2013, 13, 298-311. [CrossRef]
- Lovell, M.A.; Ehmann, W.D.; Butler, S.M.; Markesbery, W.R. Elevated thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances and antioxidant enzyme activity in the brain in Alzheimer's disease. Neurology 1995, 45, 1594-1601. [CrossRef]
- Markesbery, W.R.; Lovell, M.A. Four-hydroxynonenal, a product of lipid peroxidation, is increased in the brain in Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging 1998, 19, 33-36. [CrossRef]
- Youssef, P.; Chami, B.; Lim, J.; Middleton, T.; Sutherland, G.T.; Witting, P.K. Evidence supporting oxidative stress in a moderately affected area of the brain in Alzheimer's disease. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 11553. [CrossRef]
- Quinn, J.F.; Montine, K.S.; Moore, M.; Morrow, J.D.; Kaye, J.A.; Montine, T.J. Suppression of longitudinal increase in CSF F2-isoprostanes in Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis 2004, 6, 93-97. [CrossRef]
- Sultana, R.; Poon, H.F.; Cai, J.; Pierce, W.M.; Merchant, M.; Klein, J.B.; Markesbery, W.R.; Butterfield, D.A. Identification of nitrated proteins in Alzheimer's disease brain using a redox proteomics approach. Neurobiol Dis 2006, 22, 76-87. [CrossRef]
- Reed, T.; Perluigi, M.; Sultana, R.; Pierce, W.M.; Klein, J.B.; Turner, D.M.; Coccia, R.; Markesbery, W.R.; Butterfield, D.A. Redox proteomic identification of 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal-modified brain proteins in amnestic mild cognitive impairment: insight into the role of lipid peroxidation in the progression and pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Dis 2008, 30, 107-120. [CrossRef]
- Castegna, A.; Thongboonkerd, V.; Klein, J.B.; Lynn, B.; Markesbery, W.R.; Butterfield, D.A. Proteomic identification of nitrated proteins in Alzheimer's disease brain. J Neurochem 2003, 85, 1394-1401. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Weber, D.; Raupbach, J.; Dakal, T.C.; Fliessbach, K.; Ramirez, A.; Grune, T.; Wullner, U. Advanced glycation end products and protein carbonyl levels in plasma reveal sex-specific differences in Parkinson's and Alzheimer's disease. Redox Biol 2020, 34, 101546. [CrossRef]
- Mecocci, P.; MacGarvey, U.; Beal, M.F. Oxidative damage to mitochondrial DNA is increased in Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol 1994, 36, 747-751. [CrossRef]
- Valero, R.A.; Senovilla, L.; Nunez, L.; Villalobos, C. The role of mitochondrial potential in control of calcium signals involved in cell proliferation. Cell Calcium 2008, 44, 259-269. [CrossRef]
- Nunez, L.; Senovilla, L.; Sanz-Blasco, S.; Chamero, P.; Alonso, M.T.; Villalobos, C.; Garcia-Sancho, J. Bioluminescence imaging of mitochondrial Ca2+ dynamics in soma and neurites of individual adult mouse sympathetic neurons. J Physiol 2007, 580, 385-395. [CrossRef]
- Núñez, L.; Villalobos, C.; García-Sancho, J. Coupling or not coupling of mitochondria to Ca2+ sources in neurones. Soma and neurites differ. Physiol News. 2008, 70, 23-24.
- Sanz-Blasco, S.; Valero, R.A.; Rodriguez-Crespo, I.; Villalobos, C.; Nunez, L. Mitochondrial Ca2+ overload underlies Abeta oligomers neurotoxicity providing an unexpected mechanism of neuroprotection by NSAIDs. PLoS One 2008, 3, e2718. [CrossRef]
- Calvo, M.; Sanz-Blasco, S.; Caballero, E.; Villalobos, C.; Nunez, L. Susceptibility to excitotoxicity in aged hippocampal cultures and neuroprotection by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: role of mitochondrial calcium. J Neurochem 2015, 132, 403-417. [CrossRef]
- Calvo-Rodriguez, M.; Garcia-Durillo, M.; Villalobos, C.; Nunez, L. Aging Enables Ca2+ Overload and Apoptosis Induced by Amyloid-beta Oligomers in Rat Hippocampal Neurons: Neuroprotection by Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs and R-Flurbiprofen in Aging Neurons. J Alzheimers Dis 2016, 54, 207-221. [CrossRef]
- Calvo-Rodriguez, M.; Garcia-Durillo, M.; Villalobos, C.; Nunez, L. In vitro aging promotes endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-mitochondria Ca(2+) cross talk and loss of store-operated Ca(2+) entry (SOCE) in rat hippocampal neurons. Biochim Biophys Acta 2016, 1863, 2637-2649. [CrossRef]
- Calvo-Rodriguez, M.; Hernando-Perez, E.; Nunez, L.; Villalobos, C. Amyloid beta Oligomers Increase ER-Mitochondria Ca(2+) Cross Talk in Young Hippocampal Neurons and Exacerbate Aging-Induced Intracellular Ca(2+) Remodeling. Front Cell Neurosci 2019, 13, 22. [CrossRef]
- Caballero, E.; Hernando-Perez, E.; Tapias, V.; Calvo-Rodriguez, M.; Villalobos, C.; Nunez, L. Amyloid Beta Oligomers-Induced Ca(2+) Entry Pathways: Role of Neuronal Networks, NMDA Receptors and Amyloid Channel Formation. Biomedicines 2022, 10. [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Andres, P.; Fernandez-Pena, L.; Diez-Poza, C.; Villalobos, C.; Nunez, L.; Barbero, A. Marine Heterocyclic Compounds That Modulate Intracellular Calcium Signals: Chemistry and Synthesis Approaches. Mar Drugs 2021, 19. [CrossRef]
- Edison, P.; Ahmed, I.; Fan, Z.; Hinz, R.; Gelosa, G.; Ray Chaudhuri, K.; Walker, Z.; Turkheimer, F.E.; Brooks, D.J. Microglia, amyloid, and glucose metabolism in Parkinson's disease with and without dementia. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 938-949. [CrossRef]
- Trimmer, P.A.; Swerdlow, R.H.; Parks, J.K.; Keeney, P.; Bennett, J.P., Jr.; Miller, S.W.; Davis, R.E.; Parker, W.D., Jr. Abnormal mitochondrial morphology in sporadic Parkinson's and Alzheimer's disease cybrid cell lines. Exp Neurol 2000, 162, 37-50. [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Jimenez, F.J.; Molina, J.A.; Hernanz, A.; Fernandez-Vivancos, E.; de Bustos, F.; Barcenilla, B.; Gomez-Escalonilla, C.; Zurdo, M.; Berbel, A.; Villanueva, C. Cerebrospinal fluid levels of thiamine in patients with Parkinson's disease. Neurosci Lett 1999, 271, 33-36. [CrossRef]
- Gibson, G.E.; Kingsbury, A.E.; Xu, H.; Lindsay, J.G.; Daniel, S.; Foster, O.J.; Lees, A.J.; Blass, J.P. Deficits in a tricarboxylic acid cycle enzyme in brains from patients with Parkinson's disease. Neurochem Int 2003, 43, 129-135. [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, Y.; Matuda, S.; Yoshino, H.; Mori, H.; Hattori, N.; Ikebe, S. An immunohistochemical study on alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex in Parkinson's disease. Ann Neurol 1994, 35, 204-210. [CrossRef]
- Mallajosyula, J.K.; Chinta, S.J.; Rajagopalan, S.; Nicholls, D.G.; Andersen, J.K. Metabolic control analysis in a cellular model of elevated MAO-B: relevance to Parkinson's disease. Neurotox Res 2009, 16, 186-193. [CrossRef]
- Schapira, A.H.; Cooper, J.M.; Dexter, D.; Clark, J.B.; Jenner, P.; Marsden, C.D. Mitochondrial complex I deficiency in Parkinson's disease. J Neurochem 1990, 54, 823-827. [CrossRef]
- Mann, V.M.; Cooper, J.M.; Daniel, S.E.; Srai, K.; Jenner, P.; Marsden, C.D.; Schapira, A.H. Complex I, iron, and ferritin in Parkinson's disease substantia nigra. Ann Neurol 1994, 36, 876-881. [CrossRef]
- Zilocchi, M.; Finzi, G.; Lualdi, M.; Sessa, F.; Fasano, M.; Alberio, T. Mitochondrial alterations in Parkinson's disease human samples and cellular models. Neurochem Int 2018, 118, 61-72. [CrossRef]
- Lynch, D.S.; Loh, S.H.Y.; Harley, J.; Noyce, A.J.; Martins, L.M.; Wood, N.W.; Houlden, H.; Plun-Favreau, H. Nonsyndromic Parkinson disease in a family with autosomal dominant optic atrophy due to OPA1 mutations. Neurol Genet 2017, 3, e188. [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Morfini, G.A.; Langhamer, L.B.; He, Y.; Brady, S.T.; Kordower, J.H. Alterations in axonal transport motor proteins in sporadic and experimental Parkinson's disease. Brain 2012, 135, 2058-2073. [CrossRef]
- Tapias, V.; McCoy, J.L.; Greenamyre, J.T. Phenothiazine normalizes the NADH/NAD(+) ratio, maintains mitochondrial integrity and protects the nigrostriatal dopamine system in a chronic rotenone model of Parkinson's disease. Redox Biol 2019, 24, 101164. [CrossRef]
- Beal, M.F.; Chiluwal, J.; Calingasan, N.Y.; Milne, G.L.; Shchepinov, M.S.; Tapias, V. Isotope-reinforced polyunsaturated fatty acids improve Parkinson's disease-like phenotype in rats overexpressing alpha-synuclein. Acta Neuropathol Commun 2020, 8, 220. [CrossRef]
- Devi, L.; Raghavendran, V.; Prabhu, B.M.; Avadhani, N.G.; Anandatheerthavarada, H.K. Mitochondrial import and accumulation of alpha-synuclein impair complex I in human dopaminergic neuronal cultures and Parkinson disease brain. J Biol Chem 2008, 283, 9089-9100. [CrossRef]
- Guardia-Laguarta, C.; Area-Gomez, E.; Rub, C.; Liu, Y.; Magrane, J.; Becker, D.; Voos, W.; Schon, E.A.; Przedborski, S. alpha-Synuclein is localized to mitochondria-associated ER membranes. J Neurosci 2014, 34, 249-259. [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Nemani, V.M.; Azarbal, F.; Skibinski, G.; Levy, J.M.; Egami, K.; Munishkina, L.; Zhang, J.; Gardner, B.; Wakabayashi, J.; et al. Direct membrane association drives mitochondrial fission by the Parkinson disease-associated protein alpha-synuclein. J Biol Chem 2011, 286, 20710-20726. [CrossRef]
- Tapias, V.; Hu, X.; Luk, K.C.; Sanders, L.H.; Lee, V.M.; Greenamyre, J.T. Synthetic alpha-synuclein fibrils cause mitochondrial impairment and selective dopamine neurodegeneration in part via iNOS-mediated nitric oxide production. Cell Mol Life Sci 2017, 74, 2851-2874. [CrossRef]
- Pozo Devoto, V.M.; Dimopoulos, N.; Alloatti, M.; Pardi, M.B.; Saez, T.M.; Otero, M.G.; Cromberg, L.E.; Marin-Burgin, A.; Scassa, M.E.; Stokin, G.B.; et al. alphaSynuclein control of mitochondrial homeostasis in human-derived neurons is disrupted by mutations associated with Parkinson's disease. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 5042. [CrossRef]
- Ulusoy, A.; Rusconi, R.; Perez-Revuelta, B.I.; Musgrove, R.E.; Helwig, M.; Winzen-Reichert, B.; Di Monte, D.A. Caudo-rostral brain spreading of alpha-synuclein through vagal connections. EMBO Mol Med 2013, 5, 1119-1127. [CrossRef]
- Di Maio, R.; Barrett, P.J.; Hoffman, E.K.; Barrett, C.W.; Zharikov, A.; Borah, A.; Hu, X.; McCoy, J.; Chu, C.T.; Burton, E.A.; et al. alpha-Synuclein binds to TOM20 and inhibits mitochondrial protein import in Parkinson's disease. Sci Transl Med 2016, 8, 342ra378. [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.S.; Guzman, J.N.; Ilijic, E.; Mercer, J.N.; Rick, C.; Tkatch, T.; Meredith, G.E.; Surmeier, D.J. 'Rejuvenation' protects neurons in mouse models of Parkinson's disease. Nature 2007, 447, 1081-1086. [CrossRef]
- Parkinson Study Group, S.-P.D.I.I.I.I. Isradipine Versus Placebo in Early Parkinson Disease: A Randomized Trial. Ann Intern Med 2020, 172, 591-598. [CrossRef]
- Abe, K.; Kimura, H. Amyloid beta toxicity consists of a Ca(2+)-independent early phase and a Ca(2+)-dependent late phase. J Neurochem 1996, 67, 2074-2078.
- Verma, M.; Callio, J.; Otero, P.A.; Sekler, I.; Wills, Z.P.; Chu, C.T. Mitochondrial Calcium Dysregulation Contributes to Dendrite Degeneration Mediated by PD/LBD-Associated LRRK2 Mutants. J Neurosci 2017, 37, 11151-11165. [CrossRef]
- Hampel, H.; Williams, C.; Etcheto, A.; Goodsaid, F.; Parmentier, F.; Sallantin, J.; Kaufmann, W.E.; Missling, C.U.; Afshar, M. A precision medicine framework using artificial intelligence for the identification and confirmation of genomic biomarkers of response to an Alzheimer's disease therapy: Analysis of the blarcamesine (ANAVEX2-73) Phase 2a clinical study. Alzheimers Dement (N Y) 2020, 6, e12013. [CrossRef]
- Villard, V.; Espallergues, J.; Keller, E.; Vamvakides, A.; Maurice, T. Anti-amnesic and neuroprotective potentials of the mixed muscarinic receptor/sigma 1 (sigma1) ligand ANAVEX2-73, a novel aminotetrahydrofuran derivative. J Psychopharmacol 2011, 25, 1101-1117. [CrossRef]
- Lahmy, V.; Meunier, J.; Malmstrom, S.; Naert, G.; Givalois, L.; Kim, S.H.; Villard, V.; Vamvakides, A.; Maurice, T. Blockade of Tau hyperphosphorylation and Abeta(1)(-)(4)(2) generation by the aminotetrahydrofuran derivative ANAVEX2-73, a mixed muscarinic and sigma(1) receptor agonist, in a nontransgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 1706-1723. [CrossRef]
- Lahmy, V.; Long, R.; Morin, D.; Villard, V.; Maurice, T. Mitochondrial protection by the mixed muscarinic/sigma1 ligand ANAVEX2-73, a tetrahydrofuran derivative, in Abeta25-35 peptide-injected mice, a nontransgenic Alzheimer's disease model. Front Cell Neurosci 2015, 8, 463. [CrossRef]
- Goguadze, N.; Zhuravliova, E.; Morin, D.; Mikeladze, D.; Maurice, T. Sigma-1 Receptor Agonists Induce Oxidative Stress in Mitochondria and Enhance Complex I Activity in Physiological Condition but Protect Against Pathological Oxidative Stress. Neurotox Res 2019, 35, 1-18. [CrossRef]
- Maurice, T. Protection by sigma-1 receptor agonists is synergic with donepezil, but not with memantine, in a mouse model of amyloid-induced memory impairments. Behav Brain Res 2016, 296, 270-278. [CrossRef]
- Christ, M.G.; Huesmann, H.; Nagel, H.; Kern, A.; Behl, C. Sigma-1 Receptor Activation Induces Autophagy and Increases Proteostasis Capacity In Vitro and In Vivo. Cells 2019, 8. [CrossRef]
- Foscolos, G.B.; Kolocouris, N.; Fytas, G.; Marakos, P.; Pouli, N.; Vamvakides, A. Synthesis and pharmacological study of some new beta-(dialkylaminomethyl)- gamma-butyrolactones and their tetrahydrofuran analogues. Farmaco 1996, 51, 19-26. [CrossRef]
- Han, M.E.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, D.H.; Choi, J.T.; Pan, C.S.; Yoon, S.; Baek, S.Y.; Kim, B.S.; Kim, J.B.; et al. Regulation of cerebrospinal fluid production by caffeine consumption. BMC Neurosci 2009, 10, 110. [CrossRef]
- Zeitlin, R.; Patel, S.; Burgess, S.; Arendash, G.W.; Echeverria, V. Caffeine induces beneficial changes in PKA signaling and JNK and ERK activities in the striatum and cortex of Alzheimer's transgenic mice. Brain Res 2011, 1417, 127-136. [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Jia, N.; Li, J.; Yang, L.; Min, L.Q. Chronic caffeine treatment reverses memory impairment and the expression of brain BNDF and TrkB in the PS1/APP double transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Mol Med Rep 2013, 8, 737-740. [CrossRef]
- Larsson, S.C.; Woolf, B.; Gill, D. Plasma Caffeine Levels and Risk of Alzheimer's Disease and Parkinson's Disease: Mendelian Randomization Study. Nutrients 2022, 14. [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Byun, M.S.; Yi, D.; Lee, J.H.; Jeon, S.Y.; Jung, G.; Lee, H.N.; Sohn, B.K.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, Y.K.; et al. Coffee intake and decreased amyloid pathology in human brain. Transl Psychiatry 2019, 9, 270. [CrossRef]
- Eskelinen, M.H.; Kivipelto, M. Caffeine as a protective factor in dementia and Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis 2010, 20 Suppl 1, S167-174. [CrossRef]
- Arendash, G.W.; Schleif, W.; Rezai-Zadeh, K.; Jackson, E.K.; Zacharia, L.C.; Cracchiolo, J.R.; Shippy, D.; Tan, J. Caffeine protects Alzheimer's mice against cognitive impairment and reduces brain beta-amyloid production. Neuroscience 2006, 142, 941-952. [CrossRef]
- Cheung, K.H.; Shineman, D.; Muller, M.; Cardenas, C.; Mei, L.; Yang, J.; Tomita, T.; Iwatsubo, T.; Lee, V.M.; Foskett, J.K. Mechanism of Ca2+ disruption in Alzheimer's disease by presenilin regulation of InsP3 receptor channel gating. Neuron 2008, 58, 871-883. [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Cirrito, J.R.; Lin, X.; Wang, L.; Verges, D.K.; Dickson, A.; Mamcarz, M.; Zhang, C.; Mori, T.; Arendash, G.W.; et al. Caffeine suppresses amyloid-beta levels in plasma and brain of Alzheimer's disease transgenic mice. J Alzheimers Dis 2009, 17, 681-697. [CrossRef]
- Stazi, M.; Lehmann, S.; Sakib, M.S.; Pena-Centeno, T.; Buschgens, L.; Fischer, A.; Weggen, S.; Wirths, O. Long-term caffeine treatment of Alzheimer mouse models ameliorates behavioural deficits and neuron loss and promotes cellular and molecular markers of neurogenesis. Cell Mol Life Sci 2021, 79, 55. [CrossRef]
- Laurent, C.; Eddarkaoui, S.; Derisbourg, M.; Leboucher, A.; Demeyer, D.; Carrier, S.; Schneider, M.; Hamdane, M.; Muller, C.E.; Buee, L.; et al. Beneficial effects of caffeine in a transgenic model of Alzheimer's disease-like tau pathology. Neurobiol Aging 2014, 35, 2079-2090. [CrossRef]
- Ross, G.W.; Abbott, R.D.; Petrovitch, H.; Morens, D.M.; Grandinetti, A.; Tung, K.H.; Tanner, C.M.; Masaki, K.H.; Blanchette, P.L.; Curb, J.D.; et al. Association of coffee and caffeine intake with the risk of Parkinson disease. JAMA 2000, 283, 2674-2679. [CrossRef]
- Ascherio, A.; Zhang, S.M.; Hernan, M.A.; Kawachi, I.; Colditz, G.A.; Speizer, F.E.; Willett, W.C. Prospective study of caffeine consumption and risk of Parkinson's disease in men and women. Ann Neurol 2001, 50, 56-63. [CrossRef]
- Altman, R.D.; Lang, A.E.; Postuma, R.B. Caffeine in Parkinson's disease: a pilot open-label, dose-escalation study. Mov Disord 2011, 26, 2427-2431. [CrossRef]
- Postuma, R.B.; Lang, A.E.; Munhoz, R.P.; Charland, K.; Pelletier, A.; Moscovich, M.; Filla, L.; Zanatta, D.; Rios Romenets, S.; Altman, R.; et al. Caffeine for treatment of Parkinson disease: a randomized controlled trial. Neurology 2012, 79, 651-658. [CrossRef]
- Saaksjarvi, K.; Knekt, P.; Rissanen, H.; Laaksonen, M.A.; Reunanen, A.; Mannisto, S. Prospective study of coffee consumption and risk of Parkinson's disease. Eur J Clin Nutr 2008, 62, 908-915. [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Li, S. Dose-response meta-analysis on coffee, tea and caffeine consumption with risk of Parkinson's disease. Geriatr Gerontol Int 2014, 14, 430-439. [CrossRef]
- Ascherio, A.; Chen, H.; Schwarzschild, M.A.; Zhang, S.M.; Colditz, G.A.; Speizer, F.E. Caffeine, postmenopausal estrogen, and risk of Parkinson's disease. Neurology 2003, 60, 790-795. [CrossRef]
- Powers, K.M.; Kay, D.M.; Factor, S.A.; Zabetian, C.P.; Higgins, D.S.; Samii, A.; Nutt, J.G.; Griffith, A.; Leis, B.; Roberts, J.W.; et al. Combined effects of smoking, coffee, and NSAIDs on Parkinson's disease risk. Mov Disord 2008, 23, 88-95. [CrossRef]
- Khadrawy, Y.A.; Salem, A.M.; El-Shamy, K.A.; Ahmed, E.K.; Fadl, N.N.; Hosny, E.N. Neuroprotective and Therapeutic Effect of Caffeine on the Rat Model of Parkinson's Disease Induced by Rotenone. J Diet Suppl 2017, 14, 553-572. [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Singh, K.; Patel, S.; Patel, D.K.; Singh, C.; Nath, C.; Singh, M.P. Nicotine and caffeine-mediated modulation in the expression of toxicant responsive genes and vesicular monoamine transporter-2 in 1-methyl 4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced Parkinson's disease phenotype in mouse. Brain Res 2008, 1207, 193-206. [CrossRef]
- Bagga, P.; Chugani, A.N.; Patel, A.B. Neuroprotective effects of caffeine in MPTP model of Parkinson's disease: A (13)C NMR study. Neurochem Int 2016, 92, 25-34. [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, L.M.; Nobre, H.V., Jr.; Macedo, D.S.; Oliveira, A.A.; Freitas, R.M.; Vasconcelos, S.M.; Cunha, G.M.; Sousa, F.C.; Viana, G.S. Neuroprotective effects of caffeine in the model of 6-hydroxydopamine lesion in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2006, 84, 415-419. [CrossRef]
- Luan, Y.; Ren, X.; Zheng, W.; Zeng, Z.; Guo, Y.; Hou, Z.; Guo, W.; Chen, X.; Li, F.; Chen, J.F. Chronic Caffeine Treatment Protects Against alpha-Synucleinopathy by Reestablishing Autophagy Activity in the Mouse Striatum. Front Neurosci 2018, 12, 301. [CrossRef]
- Zajac, M.A.; Zakrzewski, A.G.; Kowal, M.G.; Narayan, S. A Novel Method of Caffeine Synthesis from Uracil. Synth. Commun. 2003, 33, 3291-3297. [CrossRef]
- Scimmi, C.; Cardinali, M.; Abenante, L.; Amatista, M.; Nacca, F.G.; Lenardao, E.J.; Sancineto, L.; Santi, C. Q-Tube®-Assisted Alkylation and Arylation of Xanthines and Other N-H-Containing Heterocycles in Water. Chemistry 2021, 3, 1126-1137. [CrossRef]
- Templ, J.; Gjata, E.; Getzner, F.; Schnürch, M. Monoselective N-Methylation of Amides, Indoles, and Related Structures Using Quaternary Ammonium Salts as Solid Methylating Agents. Org. Lett. 2022, 24, 7315-7319. [CrossRef]
- Sberna, G.; Saez-Valero, J.; Beyreuther, K.; Masters, C.L.; Small, D.H. The amyloid beta-protein of Alzheimer's disease increases acetylcholinesterase expression by increasing intracellular calcium in embryonal carcinoma P19 cells. J Neurochem 1997, 69, 1177-1184. [CrossRef]
- Paris, D.; Bachmeier, C.; Patel, N.; Quadros, A.; Volmar, C.H.; Laporte, V.; Ganey, J.; Beaulieu-Abdelahad, D.; Ait-Ghezala, G.; Crawford, F.; et al. Selective antihypertensive dihydropyridines lower Abeta accumulation by targeting both the production and the clearance of Abeta across the blood-brain barrier. Mol Med 2011, 17, 149-162. [CrossRef]
- Mok, S.S.; Clippingdale, A.B.; Beyreuther, K.; Masters, C.L.; Barrow, C.J.; Small, D.H. A beta peptides and calcium influence secretion of the amyloid protein precursor from chick sympathetic neurons in culture. J Neurosci Res 2000, 61, 449-457. [CrossRef]
- Bouras, C.; Giannakopoulos, P.; Good, P.F.; Hsu, A.; Hof, P.R.; Perl, D.P. A laser microprobe mass analysis of brain aluminum and iron in dementia pugilistica: comparison with Alzheimer's disease. Eur Neurol 1997, 38, 53-58. [CrossRef]
- Rani, A.; Neha; Sodhi, R.K.; Kaur, A. Protective effect of a calcium channel blocker "diltiazem" on aluminum chloride-induced dementia in mice. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 2015, 388, 1151-1161. [CrossRef]
- Ritz, B.; Rhodes, S.L.; Qian, L.; Schernhammer, E.; Olsen, J.H.; Friis, S. L-type calcium channel blockers and Parkinson disease in Denmark. Ann Neurol 2010, 67, 600-606. [CrossRef]
- Guzman, J.N.; Sanchez-Padilla, J.; Chan, C.S.; Surmeier, D.J. Robust pacemaking in substantia nigra dopaminergic neurons. J Neurosci 2009, 29, 11011-11019. [CrossRef]
- Mosharov, E.V.; Larsen, K.E.; Kanter, E.; Phillips, K.A.; Wilson, K.; Schmitz, Y.; Krantz, D.E.; Kobayashi, K.; Edwards, R.H.; Sulzer, D. Interplay between cytosolic dopamine, calcium, and alpha-synuclein causes selective death of substantia nigra neurons. Neuron 2009, 62, 218-229. [CrossRef]
- Anjaneyulu, M.; Chopra, K. Diltiazem attenuates oxidative stress in diabetic rats. Ren Fail 2005, 27, 335-344.
- Koller, P.T.; Bergmann, S.R. Reduction of lipid peroxidation in reperfused isolated rabbit hearts by diltiazem. Circ Res 1989, 65, 838-846. [CrossRef]
- Gizur, T.; Harsànyi, K. Some Applications of Isopropenyl Acetate To O-, N-and C-Acetylation. Synthetic Communications 1990, 20, 2365-2371. [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, A.; Madan, P.B.; Mohacsi, E.; O'Brien, J.P.; Todaro, L.J.; Coffen, D.L. Enantioselective synthesis of calcium channel blockers of the diltiazem group. The Journal of Organic Chemistry 1992, 57, 851-856. [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, E.N.; Deng, L.; Furukawa, Y.; Martínez, L.E. Enantioselective catalytic epoxidation of cinnamate esters. Tetrahedron 1994, 50, 4323-4334. [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, M.; Sang, D.; Huang, Z.; Chen, F. Biocatalytic dynamic reductive kinetic resolution of aryl α-chloro β-keto esters: divergent, stereocontrolled synthesis of diltiazem, clentiazem, and siratiazem. Chemical Communications 2022, 58, 9010-9013. [CrossRef]
- Bachurin, S.; Bukatina, E.; Lermontova, N.; Tkachenko, S.; Afanasiev, A.; Grigoriev, V.; Grigorieva, I.; Ivanov, Y.; Sablin, S.; Zefirov, N. Antihistamine agent Dimebon as a novel neuroprotector and a cognition enhancer. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2001, 939, 425-435. [CrossRef]
- Doody, R.S.; Gavrilova, S.I.; Sano, M.; Thomas, R.G.; Aisen, P.S.; Bachurin, S.O.; Seely, L.; Hung, D.; dimebon, i. Effect of dimebon on cognition, activities of daily living, behaviour, and global function in patients with mild-to-moderate Alzheimer's disease: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Lancet 2008, 372, 207-215. [CrossRef]
- Cano-Cuenca, N.; Solis-Garcia del Pozo, J.E.; Jordan, J. Evidence for the efficacy of latrepirdine (Dimebon) treatment for improvement of cognitive function: a meta-analysis. J Alzheimers Dis 2014, 38, 155-164. [CrossRef]
- Lermontova, N.N.; Lukoyanov, N.V.; Serkova, T.P.; Lukoyanova, E.A.; Bachurin, S.O. Dimebon improves learning in animals with experimental Alzheimer's disease. Bull Exp Biol Med 2000, 129, 544-546. [CrossRef]
- Webster, S.J.; Wilson, C.A.; Lee, C.H.; Mohler, E.G.; Terry, A.V., Jr.; Buccafusco, J.J. The acute effects of dimebolin, a potential Alzheimer's disease treatment, on working memory in rhesus monkeys. Br J Pharmacol 2011, 164, 970-978. [CrossRef]
- Peters, O.M.; Shelkovnikova, T.; Tarasova, T.; Springe, S.; Kukharsky, M.S.; Smith, G.A.; Brooks, S.; Kozin, S.A.; Kotelevtsev, Y.; Bachurin, S.O.; et al. Chronic administration of Dimebon does not ameliorate amyloid-beta pathology in 5xFAD transgenic mice. J Alzheimers Dis 2013, 36, 589-596. [CrossRef]
- Bachurin, S.O.; Shelkovnikova, T.A.; Ustyugov, A.A.; Peters, O.; Khritankova, I.; Afanasieva, M.A.; Tarasova, T.V.; Alentov, II; Buchman, V.L.; Ninkina, N.N. Dimebon slows progression of proteinopathy in gamma-synuclein transgenic mice. Neurotox Res 2012, 22, 33-42. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ferruzzi, M.G.; Varghese, M.; Qian, X.; Cheng, A.; Xie, M.; Zhao, W.; Ho, L.; Pasinetti, G.M. Preclinical study of dimebon on beta-amyloid-mediated neuropathology in Alzheimer's disease. Mol Neurodegener 2011, 6, 7. [CrossRef]
- Day, M.; Chandran, P.; Luo, F.; Rustay, N.R.; Markosyan, S.; LeBlond, D.; Fox, G.B. Latrepirdine increases cerebral glucose utilization in aged mice as measured by [18F]-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography. Neuroscience 2011, 189, 299-304. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Hedskog, L.; Petersen, C.A.; Winblad, B.; Ankarcrona, M. Dimebon (latrepirdine) enhances mitochondrial function and protects neuronal cells from death. J Alzheimers Dis 2010, 21, 389-402. [CrossRef]
- Bachurin, S.O.; Shevtsova, E.P.; Kireeva, E.G.; Oxenkrug, G.F.; Sablin, S.O. Mitochondria as a target for neurotoxins and neuroprotective agents. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2003, 993, 334-344; discussion 345-339. [CrossRef]
- Shevtzova, E.F.; Kireeva, E.G.; Bachurin, S.O. Effect of beta-amyloid peptide fragment 25-35 on nonselective permeability of mitochondria. Bull Exp Biol Med 2001, 132, 1173-1176. [CrossRef]
- Steele, J.W.; Gandy, S. Latrepirdine (Dimebon(R)), a potential Alzheimer therapeutic, regulates autophagy and neuropathology in an Alzheimer mouse model. Autophagy 2013, 9, 617-618. [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Wang, M.; Hutchins, G.D.; Zheng, Q.-H. [11C]Dimebon, radiosynthesis and lipophilicity of a new potential PET agent for imaging of Alzheimer’s disease and Huntington’s disease. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 2529-2532. [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Latka, R.T.; Driver, T.G. Ruthenium-Catalyzed γ-Carbolinium Ion Formation from Aryl Azides; Synthesis of Dimebolin. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 2726-2729. [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.J.; Gasperini, R.; Foa, L.; Small, D.H. Amyloid-beta decreases cell-surface AMPA receptors by increasing intracellular calcium and phosphorylation of GluR2. J Alzheimers Dis 2010, 21, 655-666. [CrossRef]
- Lovell, M.A.; Abner, E.; Kryscio, R.; Xu, L.; Fister, S.X.; Lynn, B.C. Calcium Channel Blockers, Progression to Dementia, and Effects on Amyloid Beta Peptide Production. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2015, 2015, 787805. [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, M.; Miura, M.; Aosaki, T.; Shirasawa, T. Deficiency of presenilin-1 increases calcium-dependent vulnerability of neurons to oxidative stress in vitro. J Neurochem 2001, 78, 807-814. [CrossRef]
- Hefter, D.; Kaiser, M.; Weyer, S.W.; Papageorgiou, I.E.; Both, M.; Kann, O.; Muller, U.C.; Draguhn, A. Amyloid Precursor Protein Protects Neuronal Network Function after Hypoxia via Control of Voltage-Gated Calcium Channels. J Neurosci 2016, 36, 8356-8371. [CrossRef]
- Lopez, J.R.; Lyckman, A.; Oddo, S.; Laferla, F.M.; Querfurth, H.W.; Shtifman, A. Increased intraneuronal resting [Ca2+] in adult Alzheimer's disease mice. J Neurochem 2008, 105, 262-271. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Mattson, M.P. L-type Ca2+ currents at CA1 synapses, but not CA3 or dentate granule neuron synapses, are increased in 3xTgAD mice in an age-dependent manner. Neurobiol Aging 2014, 35, 88-95. [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, K.; Wang, Y.; Yao, P.J.; Fu, W.; Mattson, M.P.; Itoyama, Y.; Onodera, H.; D'Souza, I.; Poorkaj, P.H.; Bird, T.D.; et al. Alteration in calcium channel properties is responsible for the neurotoxic action of a familial frontotemporal dementia tau mutation. J Neurochem 2003, 87, 427-436. [CrossRef]
- Pasternak, B.; Svanstrom, H.; Nielsen, N.M.; Fugger, L.; Melbye, M.; Hviid, A. Use of calcium channel blockers and Parkinson's disease. Am J Epidemiol 2012, 175, 627-635. [CrossRef]
- Beurrier, C.; Congar, P.; Bioulac, B.; Hammond, C. Subthalamic nucleus neurons switch from single-spike activity to burst-firing mode. J Neurosci 1999, 19, 599-609. [CrossRef]
- Garcia, L.; Audin, J.; D'Alessandro, G.; Bioulac, B.; Hammond, C. Dual effect of high-frequency stimulation on subthalamic neuron activity. J Neurosci 2003, 23, 8743-8751. [CrossRef]
- Eaton, M.E.; Macias, W.; Youngs, R.M.; Rajadhyaksha, A.; Dudman, J.T.; Konradi, C. L-type Ca2+ channel blockers promote Ca2+ accumulation when dopamine receptors are activated in striatal neurons. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 2004, 131, 65-72. [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Ma, Z.; Wang, J.; Xie, J. L-type Cav1.2 calcium channel is involved in 6-hydroxydopamine-induced neurotoxicity in rats. Neurotox Res 2012, 21, 266-270. [CrossRef]
- Yabuki, Y.; Ohizumi, Y.; Yokosuka, A.; Mimaki, Y.; Fukunaga, K. Nobiletin treatment improves motor and cognitive deficits seen in MPTP-induced Parkinson model mice. Neuroscience 2014, 259, 126-141. [CrossRef]
- Nedergaard, S.; Flatman, J.A.; Engberg, I. Nifedipine- and omega-conotoxin-sensitive Ca2+ conductances in guinea-pig substantia nigra pars compacta neurones. J Physiol 1993, 466, 727-747.
- Sai, Y.; Chen, J.; Ye, F.; Zhao, Y.; Zou, Z.; Cao, J.; Dong, Z. Dopamine Release Suppression Dependent on an Increase of Intracellular Ca(2+) Contributed to Rotenone-induced Neurotoxicity in PC12 Cells. J Toxicol Pathol 2013, 26, 149-157. [CrossRef]
- Paraskar, A.; Sudalai, A. Cu(OTf)2 Catalyzed High Yield Synthesis of Hantzsch 1,4-Dihydropyridines. Cheminform 2007, 38. [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Bian, Q.; Ding, T.; Tang, M.; Zhang, W.; Xu, Y.; Liu, B.; Xu, H.; Li, H.-B.; Fu, H. Photoinduced Iron-Catalyzed ipso-Nitration of Aryl Halides via Single-Electron Transfer. ACS Catalysis 2021, 11, 9561-9568. [CrossRef]
- Guidi, M.; Moon, S.; Anghileri, L.; Cambié, D.; Seeberger, P.H.; Gilmore, K. Combining radial and continuous flow synthesis to optimize and scale-up the production of medicines. Reaction Chemistry & Engineering 2021, 6, 220-224. [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Fan, W.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Guo, S.; Huang, D. Aqueous CO2 fixation: construction of pyridine skeletons in cooperation with ammonium cations. Green Chemistry 2021, 23, 7950-7955. [CrossRef]
- Ban, T.A.; Morey, L.; Aguglia, E.; Azzarelli, O.; Balsano, F.; Marigliano, V.; Caglieris, N.; Sterlicchio, M.; Capurso, A.; Tomasi, N.A.; et al. Nimodipine in the treatment of old age dementias. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 1990, 14, 525-551. [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Arrieta, J.M.; Birks, J. Nimodipine for primary degenerative, mixed and vascular dementia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2002, CD000147. [CrossRef]
- Batuecas, A.; Pereira, R.; Centeno, C.; Pulido, J.A.; Hernandez, M.; Bollati, A.; Bogonez, E.; Satrustegui, J. Effects of chronic nimodipine on working memory of old rats in relation to defects in synaptosomal calcium homeostasis. Eur J Pharmacol 1998, 350, 141-150. [CrossRef]
- Gholami Pourbadie, H.; Naderi, N.; Janahmadi, M.; Mehranfard, N.; Motamedi, F. Calcium channel blockade attenuates abnormal synaptic transmission in the dentate gyrus elicited by entorhinal amyloidopathy. Synapse 2016, 70, 408-417. [CrossRef]
- Veng, L.M.; Mesches, M.H.; Browning, M.D. Age-related working memory impairment is correlated with increases in the L-type calcium channel protein alpha1D (Cav1.3) in area CA1 of the hippocampus and both are ameliorated by chronic nimodipine treatment. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 2003, 110, 193-202. [CrossRef]
- Topcu, A.; Saral, S.; Ozturk, A.; Saral, O.; Kaya, A.K. The effect of the calcium channel blocker nimodipine on hippocampal BDNF/Ach levels in rats with experimental cognitive impairment. Neurol Res 2023, 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Sandin, M.; Jasmin, S.; Levere, T.E. Aging and cognition: facilitation of recent memory in aged nonhuman primates by nimodipine. Neurobiol Aging 1990, 11, 573-575. [CrossRef]
- Pierrot, N.; Ghisdal, P.; Caumont, A.S.; Octave, J.N. Intraneuronal amyloid-beta1-42 production triggered by sustained increase of cytosolic calcium concentration induces neuronal death. J Neurochem 2004, 88, 1140-1150. [CrossRef]
- Ekinci, F.J.; Ortiz, D.; Shea, T.B. Okadaic acid mediates tau phosphorylation via sustained activation of the L-voltage-sensitive calcium channel. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 2003, 117, 145-151. [CrossRef]
- Higham, J.P.; Hidalgo, S.; Buhl, E.; Hodge, J.J.L. Restoration of Olfactory Memory in Drosophila Overexpressing Human Alzheimer's Disease Associated Tau by Manipulation of L-Type Ca(2+) Channels. Front Cell Neurosci 2019, 13, 409. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Wu, K.; Ruan, Q.; Li, D.; Liu, W.; Wang, M.; Li, Y.; Xia, J.; Yang, D.; Guo, J. Suppression of Selective Voltage-Gated Calcium Channels Alleviates Neuronal Degeneration and Dysfunction through Glutathione S-Transferase-Mediated Oxidative Stress Resistance in a Caenorhabditis elegans Model of Alzheimer's Disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2022, 2022, 8287633. [CrossRef]
- Hopp, S.C.; Royer, S.E.; D'Angelo, H.M.; Kaercher, R.M.; Fisher, D.A.; Wenk, G.L. Differential neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects of L-type voltage dependent calcium channel and ryanodine receptor antagonists in the substantia nigra and locus coeruleus. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 2015, 10, 35-44. [CrossRef]
- Putzier, I.; Kullmann, P.H.; Horn, J.P.; Levitan, E.S. Cav1.3 channel voltage dependence, not Ca2+ selectivity, drives pacemaker activity and amplifies bursts in nigral dopamine neurons. J Neurosci 2009, 29, 15414-15419. [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Verma, P.; Balaji, G.; Samantaray, S.; Mohanakumar, K.P. Nimodipine, an L-type calcium channel blocker attenuates mitochondrial dysfunctions to protect against 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced Parkinsonism in mice. Neurochem Int 2016, 99, 221-232. [CrossRef]
- Kupsch, A.; Gerlach, M.; Pupeter, S.C.; Sautter, J.; Dirr, A.; Arnold, G.; Opitz, W.; Przuntek, H.; Riederer, P.; Oertel, W.H. Pretreatment with nimodipine prevents MPTP-induced neurotoxicity at the nigral, but not at the striatal level in mice. Neuroreport 1995, 6, 621-625. [CrossRef]
- Kupsch, A.; Sautter, J.; Schwarz, J.; Riederer, P.; Gerlach, M.; Oertel, W.H. 1-Methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced neurotoxicity in non-human primates is antagonized by pretreatment with nimodipine at the nigral, but not at the striatal level. Brain Res 1996, 741, 185-196. [CrossRef]
- Soderstrom, K.E.; O'Malley, J.A.; Levine, N.D.; Sortwell, C.E.; Collier, T.J.; Steece-Collier, K. Impact of dendritic spine preservation in medium spiny neurons on dopamine graft efficacy and the expression of dyskinesias in parkinsonian rats. Eur J Neurosci 2010, 31, 478-490. [CrossRef]
- Schuster, S.; Doudnikoff, E.; Rylander, D.; Berthet, A.; Aubert, I.; Ittrich, C.; Bloch, B.; Cenci, M.A.; Surmeier, D.J.; Hengerer, B.; et al. Antagonizing L-type Ca2+ channel reduces development of abnormal involuntary movement in the rat model of L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine-induced dyskinesia. Biol Psychiatry 2009, 65, 518-526. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hu, X.; Liu, Y.; Bao, Y.; An, L. Nimodipine protects dopaminergic neurons against inflammation-mediated degeneration through inhibition of microglial activation. Neuropharmacology 2009, 56, 580-589. [CrossRef]
- Gordeev, M.F.; Patel, D.V.; Gordon, E.M. Approaches to Combinatorial Synthesis of Heterocycles: A Solid-Phase Synthesis of 1,4-Dihydropyridines. J. Org. Chem. 1996, 61, 924-928. [CrossRef]
- Balaev, A.N.; Osipov, V.N.; Fedorov, V.E. Development of nimodipine production technology. Pharm. Chem. J. 2012, 46, 285-287. [CrossRef]
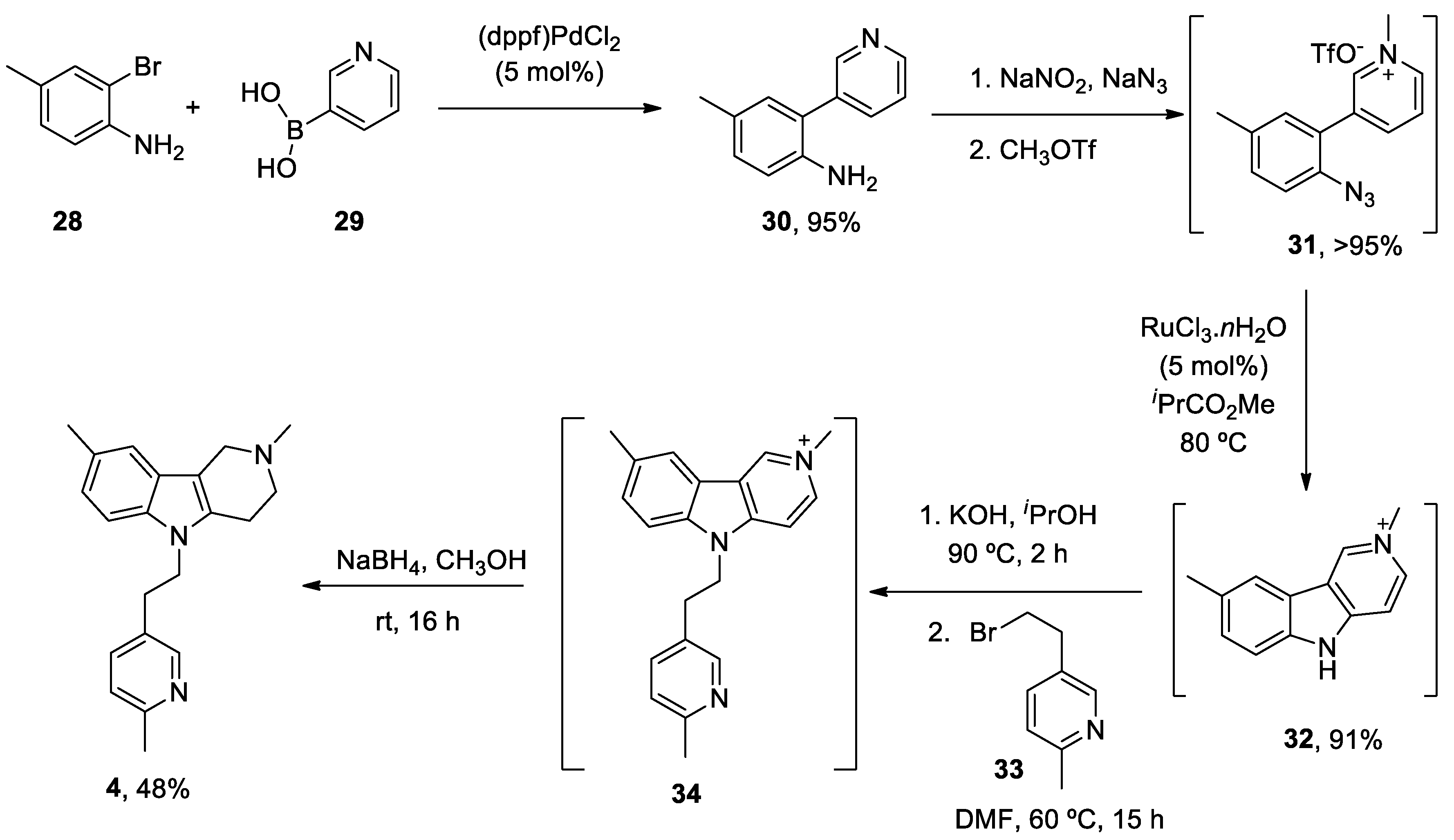
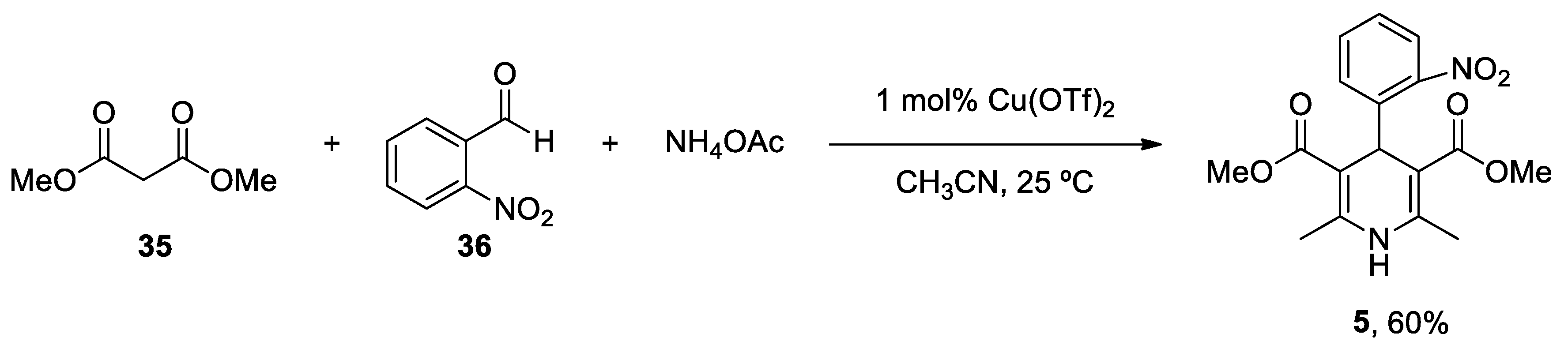
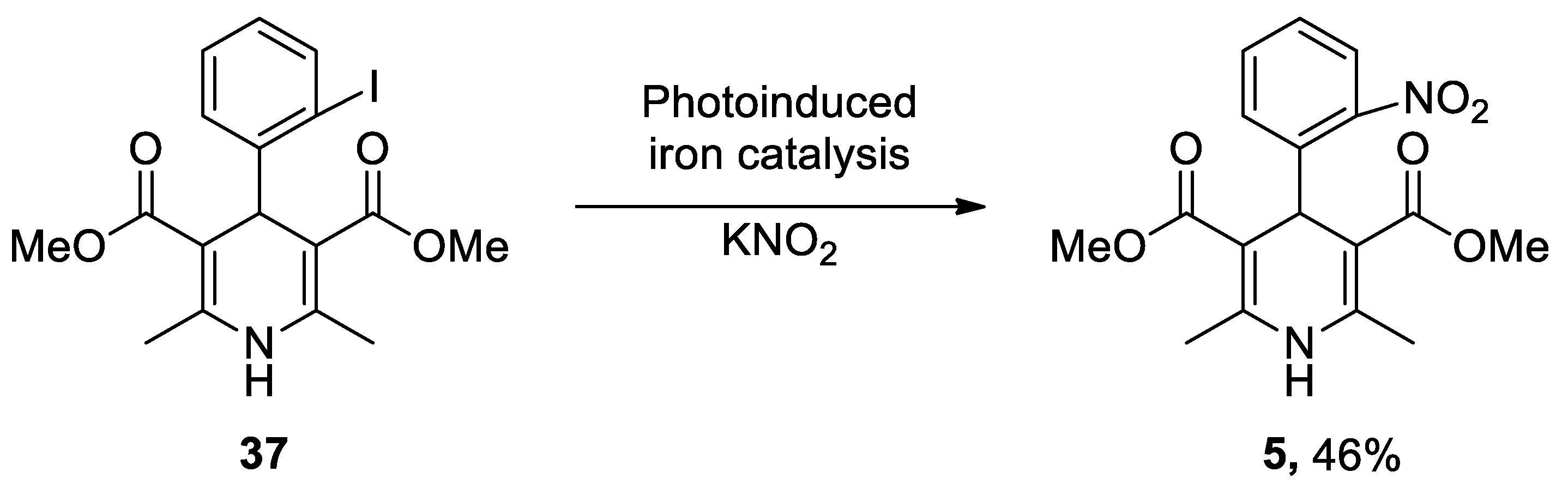
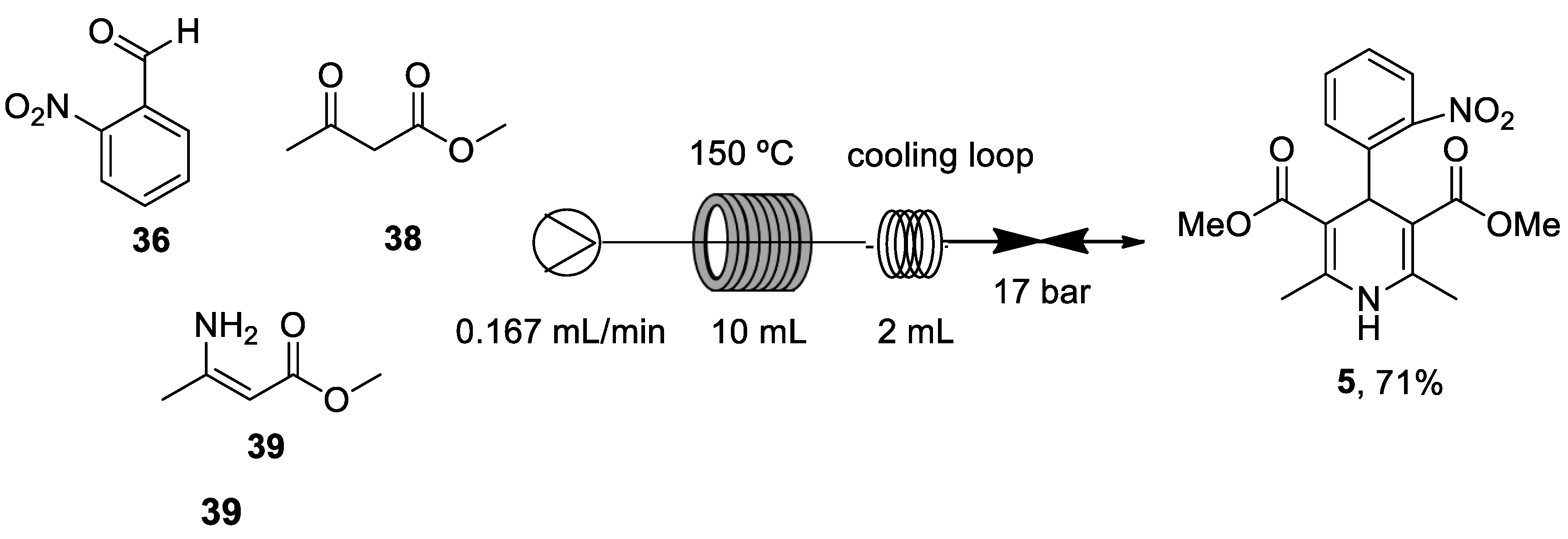
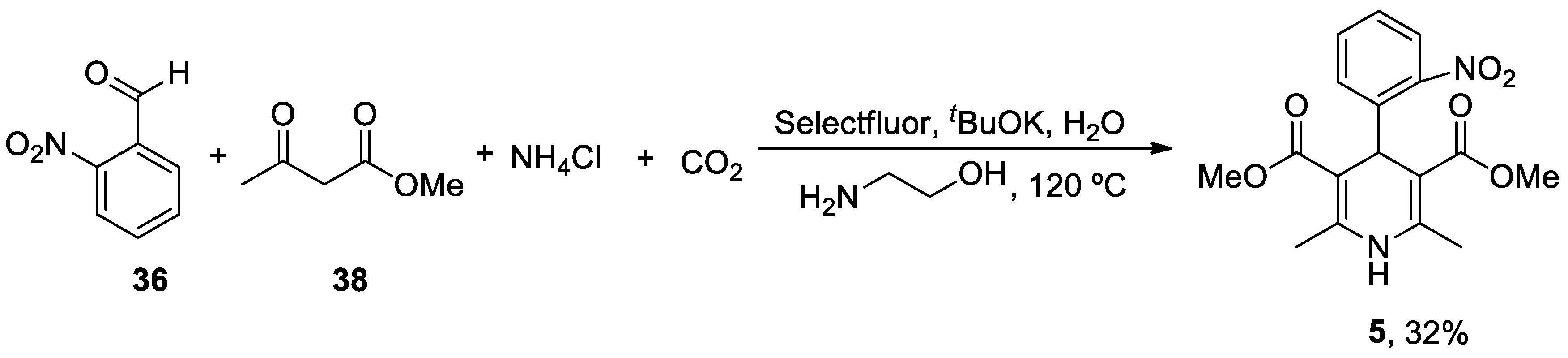
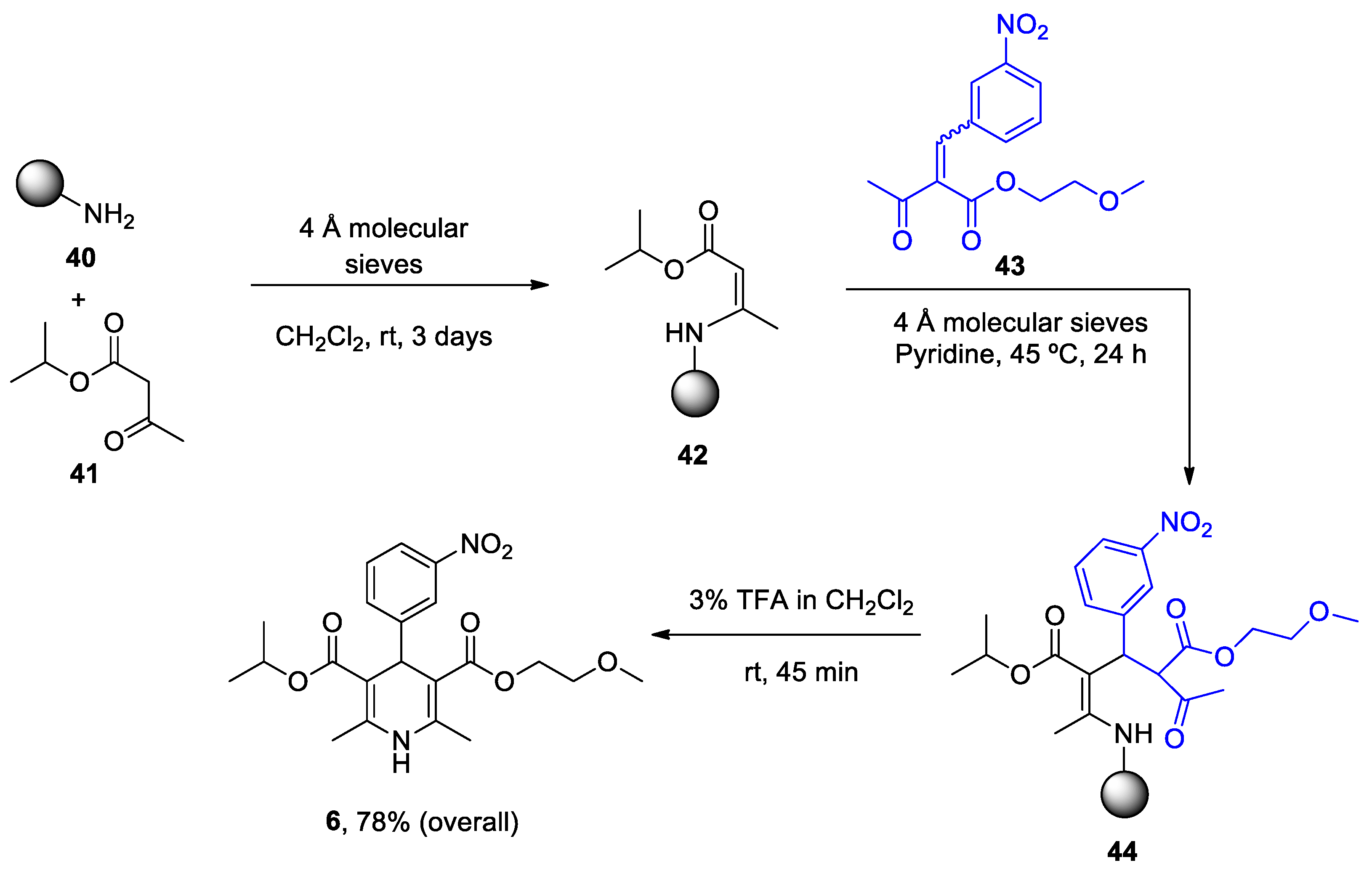
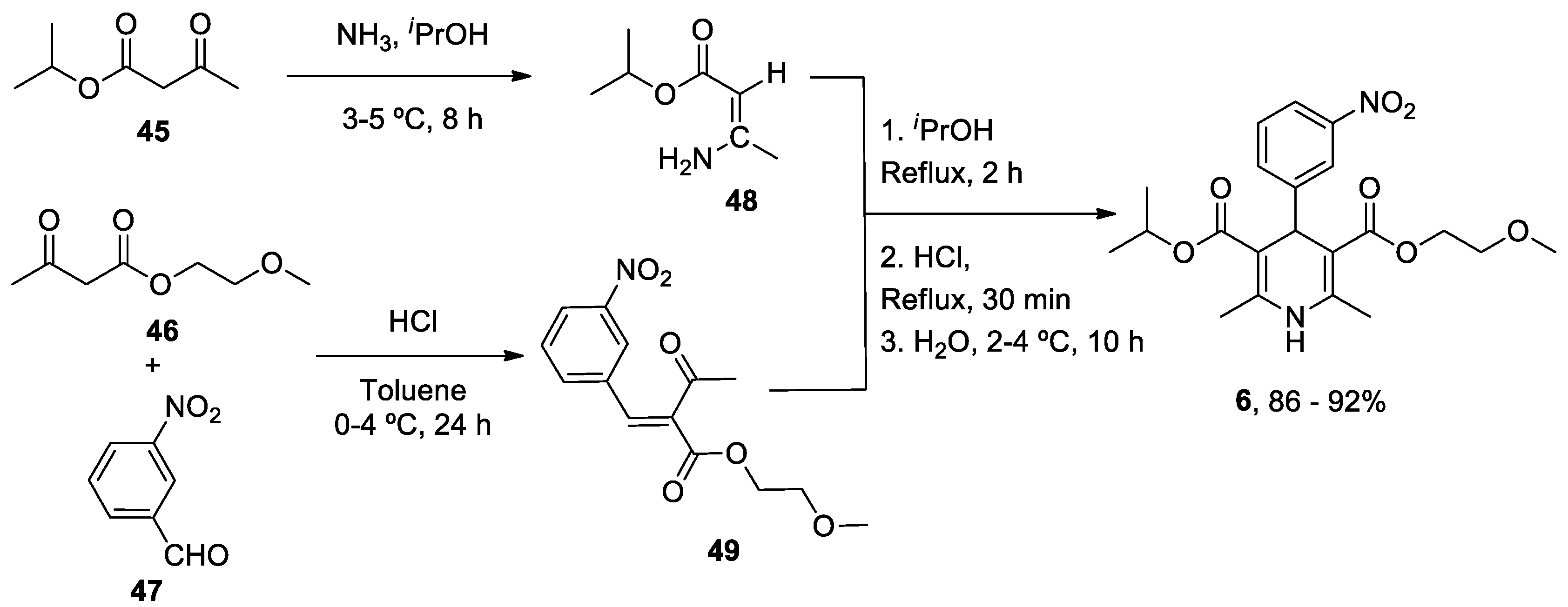
| Heterocyclic Compound | Chemical Name | Target | Proposed Mechanism | Effect on Neurodeg. Dis. Clinical Trial Status | References (Clinical Trials) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANAVEX2-73 (Blarcamesine) | Tetrahydro-N,N-dimethyl-2,2-diphenyl-3-furanmethanamine hydrochloride |
mAChRs S1R |
↓ Ca2+ release ↓ Mitochondrial stress Activated antioxidant response pathways Limited apoptosis |
↓ Risk of developing AD and PD AD (Phase IIb/3) AD (Phase III) PDD (Phase II) PDD (Phase III) |
[62] ANAVEX2-73-AD-004 NCT03790709 NCT04575259 NCT03774459 |
|
Caffeine (Mateine) |
1,3,7-Trimethyl-3,7-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6-dione |
A2AR RyR (+) |
↓ Oxidative damage ↓ Aβ levels ↓ α-Syn aggregates Restored AChE and Na+/K+ ATPase activity |
↓ Risk of developing AD and PD Epidemiological studies: motor benefits in PD |
[73,74,75] [81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88] |
|
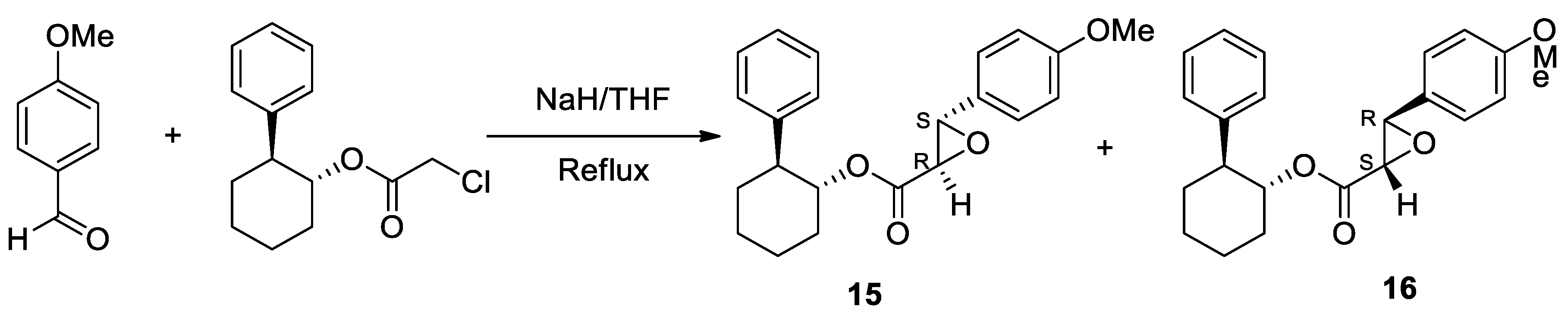
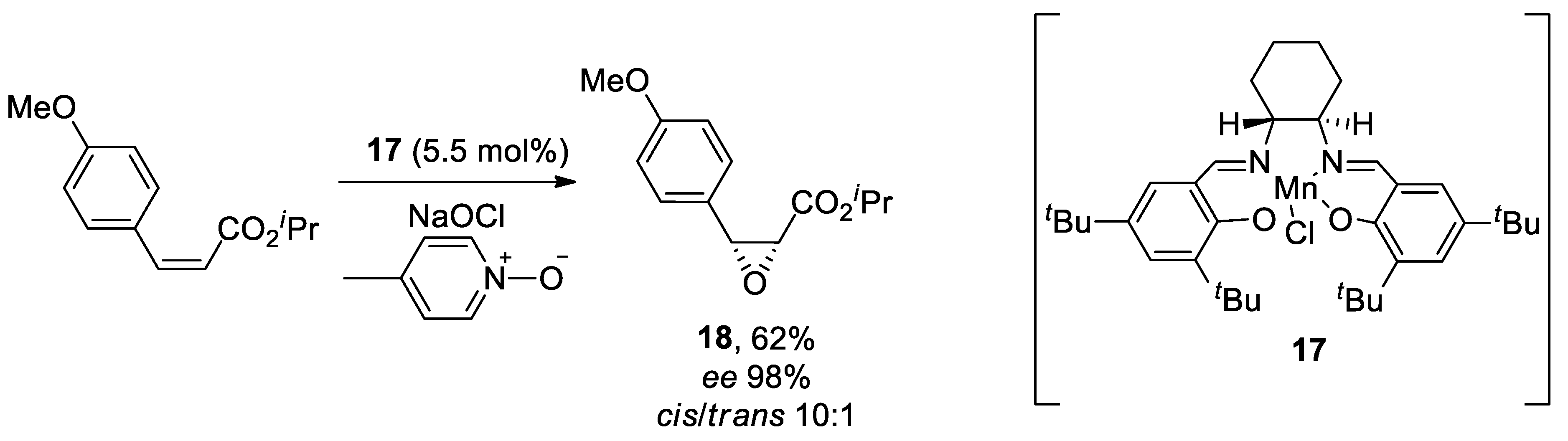
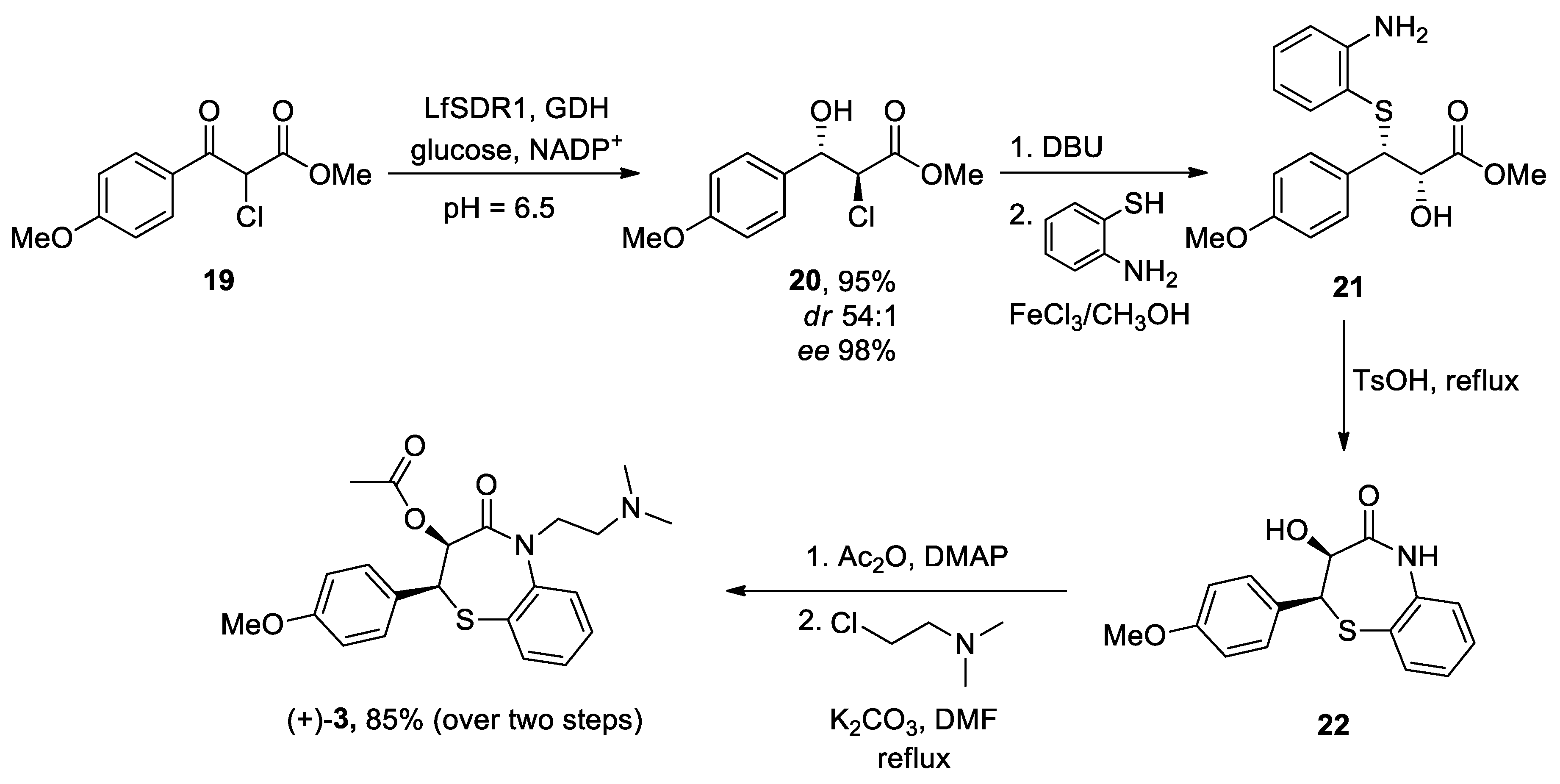
Diltiazen (Cardizem) |
(2S,3S)-5-(2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl)-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxo-2,3,4,5-tetrahydrobenzo[b][1,4]thiazepin-3-yl acetate | Non-dihydro-pyridine VOCC | ↓ Ca2+ entry ↓ Oxidative damage ↓ Inflammation |
↓ Risk of developing PD Epidemiological & Randomization Studies |
[102] |
|
Latrepirdine (Dimebon) |
3,6-Dimethyl-9-(2-methyl-pyridyl-5)-ethyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-γ-carboline dihydrochloride |
H1R Other Ca2+ Channels |
↓ Ca2+ release and entry ↓ Aβ levels ↓ Oxidative damage to lipids Inhibitor AChE ↓ α-Syn |
Cognitive and psychiatric benefits in AD Phase III AD: discontinued |
[111,112,113] NCT00838110 |
|
Nifedipine (Procardia) |
3,5-Dimethyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate | L-Type VOCC | ↓ Ca2+ entry ↓ Aβ production ↓ Oxidative damage |
Do not ↓ risk of developing PD Epidemiological & Randomization Studies |
[133] |
|
Nimodipine (Nimotop) |
3-isopropyl 5-(2-methoxyethyl) 2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate | L-Type VOCC | ↓ Ca2+ entry Neuroprotection ↓ Aβ toxicity ↓ Oxidative damage Abolished pacemaking activity in DA neurons |
↓ Risk of developing AD Epidemiological & Randomization Studies |
[145,146] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





