Submitted:
04 April 2023
Posted:
04 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Material and methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Recent and significant papers
4.2. Bibliometric analysis on the machine learning in biofilm research
4.3. Future recommendation of using ML in bacterial and biofilm studies
References
- Flemming, H.-C.; Wingender, J. The biofilm matrix. Nature reviews microbiology 2010, 8, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufour, D.; Leung, V.; Lévesque, C.M. Bacterial biofilm: structure, function, and antimicrobial resistance. Endod. Top. 2010, 22, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galié, S.; García-Gutiérrez, C.; Miguélez, E.M.; Villar, C.J.; Lombó, F. Biofilms in the Food Industry: Health Aspects and Control Methods. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Christiansen, D.E.; Mehraeen, S.; Cheng, G. Winning the fight against biofilms: the first six-month study showing no biofilm formation on zwitterionic polyurethanes. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 4709–4721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artini, M.; Papa, R.; Sapienza, F.; Božović, M.; Vrenna, G.; Tuccio Guarna Assanti, V.; Sabatino, M.; Garzoli, S.; Fiscarelli, E.V.; Ragno, R. Essential Oils Biofilm Modulation Activity and Machine Learning Analysis on Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolates from Cystic Fibrosis Patients. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artini, M.; Patsilinakos, A.; Papa, R.; Božović, M.; Sabatino, M.; Garzoli, S.; Vrenna, G.; Tilotta, M.; Pepi, F.; Ragno, R. Antimicrobial and antibiofilm activity and machine learning classification analysis of essential oils from different Mediterranean plants against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Molecules 2018, 23, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patsilinakos, A.; Artini, M.; Papa, R.; Sabatino, M.; Božović, M.; Garzoli, S.; Vrenna, G.; Buzzi, R.; Manfredini, S.; Selan, L. Machine learning analyses on data including essential oil chemical composition and in vitro experimental antibiofilm activities against Staphylococcus species. Molecules 2019, 24, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, R.; Garzoli, S.; Vrenna, G.; Sabatino, M.; Sapienza, F.; Relucenti, M.; Donfrancesco, O.; Fiscarelli, E.V.; Artini, M.; Selan, L. Essential oils biofilm modulation activity, chemical and machine learning analysis—Application on Staphylococcus aureus isolates from cystic fibrosis patients. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2020, 21, 9258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavallin, A.; Downs, J.A. Machine learning in geography–Past, present, and future. Geography Compass 2021, 15, e12563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.H.; Ivanisevic, J.; Siuzdak, G. Metabolomics: beyond biomarkers and towards mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Tong, X.; Wang, T.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Qian, L.; Liao, J.; Diao, W.; Zhou, J.; Wu, W. Biofilms in wound healing: A bibliometric and visualised study. Int. Wound J. 2022, 20, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talafidaryani, M.; Jalali, S.M.J.; Moro, S. Tracing the evolution of digitalisation research in business and management fields: Bibliometric analysis, topic modelling and deep learning trend forecasting. J. Inf. Sci. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, M.A.; Zhang, Q.; Asmi, F.; Hussain, N.; Plantinga, A.; Zafar, M.W.; Sinha, A. Global perspectives on environmental kuznets curve: A bibliometric review. Gondwana Res. 2021, 103, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Mao, G.; Crittenden, J.; Liu, X.; Du, H. Groundwater remediation from the past to the future: A bibliometric analysis. Water Res. 2017, 119, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlRyalat, S.A.S.; Malkawi, L.W.; Momani, S.M. Comparing bibliometric analysis using PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science databases. JoVE (Journal of Visualized Experiments) 2019, e58494.
- Archambault. ; Campbell, D.; Gingras, Y.; Larivière, V. Comparing bibliometric statistics obtained from the Web of Science and Scopus. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2009, 60, 1320–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorraiz, J.; Schloegl, C. A bibliometric analysis of pharmacology and pharmacy journals: Scopus versus Web of Science. J. Inf. Sci. 2008, 34, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.H.H.; Lei, S.; Ali, M.; Doronin, D.; Hussain, S.T. Prosumption: bibliometric analysis using HistCite and VOSviewer. Kybernetes, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, B.; Zhao, Y.; Vymazal, J.; Mander. ; Lust, R.; Tang, C. Mapping the field of constructed wetland-microbial fuel cell: A review and bibliometric analysis. Chemosphere 2020, 262, 128366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Malule, H.; Quiñones-Murillo, D.H.; Manotas-Duque, D. Emerging contaminants as global environmental hazards. A bibliometric analysis. Emerg. Contam. 2020, 6, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, J.J.; Reng, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, R.; Wang, B. Global trends of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm research in the past two decades: A bibliometric study. Microbiologyopen 2020, 9, 1102–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Xia, H. Structure and evolution of co-authorship network in an interdisciplinary research field. Scientometrics 2015, 103, 101–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Reniers, G.; Li, J.; Yang, M.; Wu, C.; van Gelder, P. A Bibliometric and Visualized Overview for the Evolution of Process Safety and Environmental Protection. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Heal. 2021, 18, 5985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, Y.; Zhang, F.; Yu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, P.; Xu, P.; Sun, L.; Bao, Y.; Long, H. A Bibliometric Analysis of Research on Bacterial Persisters. BioMed Res. Int. 2023, 2023, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, S.J.; Bak, N.; Khan, F.; Hawboldt, K.; Lefsrud, L.; Wolodko, J. Bibliometric Analysis of Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion (MIC) of Oil and Gas Engineering Systems. Corrosion 2017, 74, 468–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rickert, C.A.; Hayta, E.N.; Selle, D.M.; Kouroudis, I.; Harth, M.; Gagliardi, A.; Lieleg, O. Machine Learning Approach to Analyze the Surface Properties of Biological Materials. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 4614–4625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Chen, X.; Hu, Z.; Song, C.; Cui, Y. Bibliometric Analysis of Algal-Bacterial Symbiosis in Wastewater Treatment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Heal. 2019, 16, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Yin, X.; Yang, X.; Man, J.; He, Q.; Wu, Q.; Lu, M. Research trends on the relationship between Microbiota and Gastric Cancer: A Bibliometric Analysis from 2000 to 2019. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 4823–4831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, L.K.B.; Tapety, F.I.; Mobim, M.; Lago, E.C.; de LobÃ, E.S.; Leal, C.M.d.C.L.; Santos, T.C.; Monte, T.L. Bacterial association and oral biofilm formation: A bibliometric analysis. African Journal of Microbiology Research 2016, 10, 1654–1661. [Google Scholar]
- Colares, G.S.; Dell'Osbel, N.; Wiesel, P.G.; Oliveira, G.A.; Lemos, P.H.Z.; da Silva, F.P.; Lutterbeck, C.A.; Kist, L.T.; Machado. L. Floating treatment wetlands: A review and bibliometric analysis. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 714, 136776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesnik, K.L.; Liu, H. Predicting Microbial Fuel Cell Biofilm Communities and Bioreactor Performance using Artificial Neural Networks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 10881–10892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahiri, D.; Nag, M.; Sarkar, T.; Dutta, B.; Ray, R.R. Antibiofilm Activity of α-Amylase from Bacillus subtilis and Prediction of the Optimized Conditions for Biofilm Removal by Response Surface Methodology (RSM) and Artificial Neural Network (ANN). Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2021, 193, 1853–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Ramón-Fernández, A.; Salar-García, M.; Fernández, D.R.; Greenman, J.; Ieropoulos, I. Evaluation of artificial neural network algorithms for predicting the effect of the urine flow rate on the power performance of microbial fuel cells. Energy 2020, 213, 118806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shengxian, C.; Yanhui, Z.; Jing, Z.; Dayu, Y. Experimental Study on Dynamic Simulation for Biofouling Resistance Prediction by Least Squares Support Vector Machine. Energy Procedia 2012, 17, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modak, S.; Lahorkar, A.; Valadi, J. Recent Advances in Applications of Support Vector Machines in Fungal Biology. Laboratory Protocols in Fungal Biology: Current Methods in Fungal Biology 2022, 117-136.
- Li, X.; Chen, S.; Zhang, J.; Yu, L.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Y. Optimization of Ultrasonic-Assisted Extraction of Active Components and Antioxidant Activity from Polygala tenuifolia: A Comparative Study of the Response Surface Methodology and Least Squares Support Vector Machine. Molecules 2022, 27, 3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, G.N.; Malwe, A.S.; Sharma, A.K.; Shastri, V.; Hibare, K.; Sharma, V.K. Molib: A machine learning based classification tool for the prediction of biofilm inhibitory molecules. Genomics 2020, 112, 2823–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, D.; Natarajan, J. Integrated meta-analysis and machine learning approach identifies acyl-CoA thioesterase with other novel genes responsible for biofilm development in Staphylococcus aureus. Infection, Genetics and Evolution 2021, 88, 104702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Jiang, Z.; Wei, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, F.; Yang, Y.; Song, H.; Yuan, Q. Multiplexed Identification of Bacterial Biofilm Infections Based on Machine-Learning-Aided Lanthanide Encoding. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 3300–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mdarhri, H.A.; Benmessaoud, R.; Yacoubi, H.; Seffar, L.; Assimi, H.G.; Hamam, M.; Boussettine, R.; Filali-Ansari, N.; Lahlou, F.A.; Diawara, I.; et al. Alternatives Therapeutic Approaches to Conventional Antibiotics: Advantages, Limitations and Potential Application in Medicine. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Ding, Y. Machine Learning and Its Applications in Studying the Geographical Distribution of Ants. Diversity 2022, 14, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobeyn, S.; Mouton, A.M.; Cord, A.F.; Kaim, A.; Volk, M.; Goethals, P.L. Evolutionary algorithms for species distribution modelling: A review in the context of machine learning. Ecol. Model. 2019, 392, 179–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Ding, Y. A Machine Learning Approach to Predicting Academic Performance in Pennsylvania’s Schools. Soc. Sci. 2023, 12, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Ding, Y.; Liu, X. Development of the growth mindset scale: evidence of structural validity, measurement model, direct and indirect effects in Chinese samples. Curr. Psychol. 2021, 42, 1712–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammarota, G.; Ianiro, G.; Ahern, A.; Carbone, C.; Temko, A.; Claesson, M.J.; Gasbarrini, A.; Tortora, G. Gut microbiome, big data and machine learning to promote precision medicine for cancer. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 635–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Ding, Y. A Feasibility Study of Machine Learning Models for Cancer Rate Prediction. Preprints.org 2023, 2023030491. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y. Heavy metal pollution and transboundary issues in ASEAN countries. Water Policy 2019, 21, 1096–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Peng, N.; Du, Y.; Ji, L.; Cao, B. Disruption of Putrescine Biosynthesis in Shewanella oneidensis Enhances Biofilm Cohesiveness and Performance in Cr(VI) Immobilization. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 1498–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, J.; Szymanski, C.; Fredrickson, J.; Shi, L.; Cao, B.; Zhu, Z.; Yu, X.-Y. In Situ Molecular Imaging of the Biofilm and Its Matrix. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 11244–11252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, J.; Xiong, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Yu, X.-Y. Molecular evidence of a toxic effect on a biofilm and its matrix. Anal. 2019, 144, 2498–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.-E.; Wu, J.; Ding, Y.; Wang, V.B.; Zhang, Y.; Kjelleberg, S.; Loo, J.S.C.; Cao, B.; Zhang, Q. Hybrid Conducting Biofilm with Built-in Bacteria for High-Performance Microbial Fuel Cells. ChemElectroChem 2015, 2, 619–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Hu, Y.; Cao, B.; Rice, S.A.; Kjelleberg, S.; Song, H. Enhancing Bidirectional Electron Transfer of Shewanella oneidensis by a Synthetic Flavin Pathway. ACS Synth. Biol. 2015, 4, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.-E.; Chen, J.; Ding, Y.; Wang, V.B.; Bao, B.; Kjelleberg, S.; Cao, B.; Loo, S.C.J.; Wang, L.; Huang, W.; et al. Chemically Functionalized Conjugated Oligoelectrolyte Nanoparticles for Enhancement of Current Generation in Microbial Fuel Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 14501–14505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, D.; Ding, Y.; Wang, S. Mechanical performance of strain-hardening cementitious composites (SHCC) with bacterial addition. J. Infrastruct. Preserv. Resil. 2022, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ding, Y.; Qian, S. Influence of bacterial incorporation on mechanical properties of engineered cementitious composites (ECC). Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 196, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Weng, Y.; Ding, Y.; Qian, S. Use of Genetically Modified Bacteria to Repair Cracks in Concrete. Materials 2019, 12, 3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdany, A.H.; Ding, Y.; Qian, S. Visible light antibacterial potential of graphene-TiO2 cementitious composites for self-sterilization surface. Journal of Sustainable Cement-Based Materials 2022, 1-11.
- Hamdany, A.H.; Ding, Y.; Qian, S. Cementitious Composite Materials for Self-Sterilization Surfaces. ACI Mater. J. 2022, 119, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdany, A.H.; Ding, Y.; Qian, S. Mechanical and Antibacterial Behavior of Photocatalytic Lightweight Engineered Cementitious Composites. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2021, 33, 04021262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tribedi, P.; Das Gupta, A.; Sil, A.K. Adaptation of Pseudomonas sp. AKS2 in biofilm on low-density polyethylene surface: an effective strategy for efficient survival and polymer degradation. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2015, 2, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, M.; Panahi, B.; Mazlumi, A.; Hejazi, M.A.; Komi, D.E.A.; Nami, Y. Screening of potential probiotic lactic acid bacteria with antimicrobial properties and selection of superior bacteria for application as biocontrol using machine learning models. LWT 2022, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, F.; Fan, J.; Xu, W.; Liu, H. Predicting the performance of medium-chain carboxylic acid (MCCA) production using machine learning algorithms and microbial community data. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordier, T.; Lanzén, A.; Apothéloz-Perret-Gentil, L.; Stoeck, T.; Pawlowski, J. Embracing Environmental Genomics and Machine Learning for Routine Biomonitoring. Trends Microbiol. 2019, 27, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, F.; Wang, L.; Cai, W.; Lesnik, K.; Liu, H. Predicting the performance of anaerobic digestion using machine learning algorithms and genomic data. Water Res. 2021, 199, 117182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
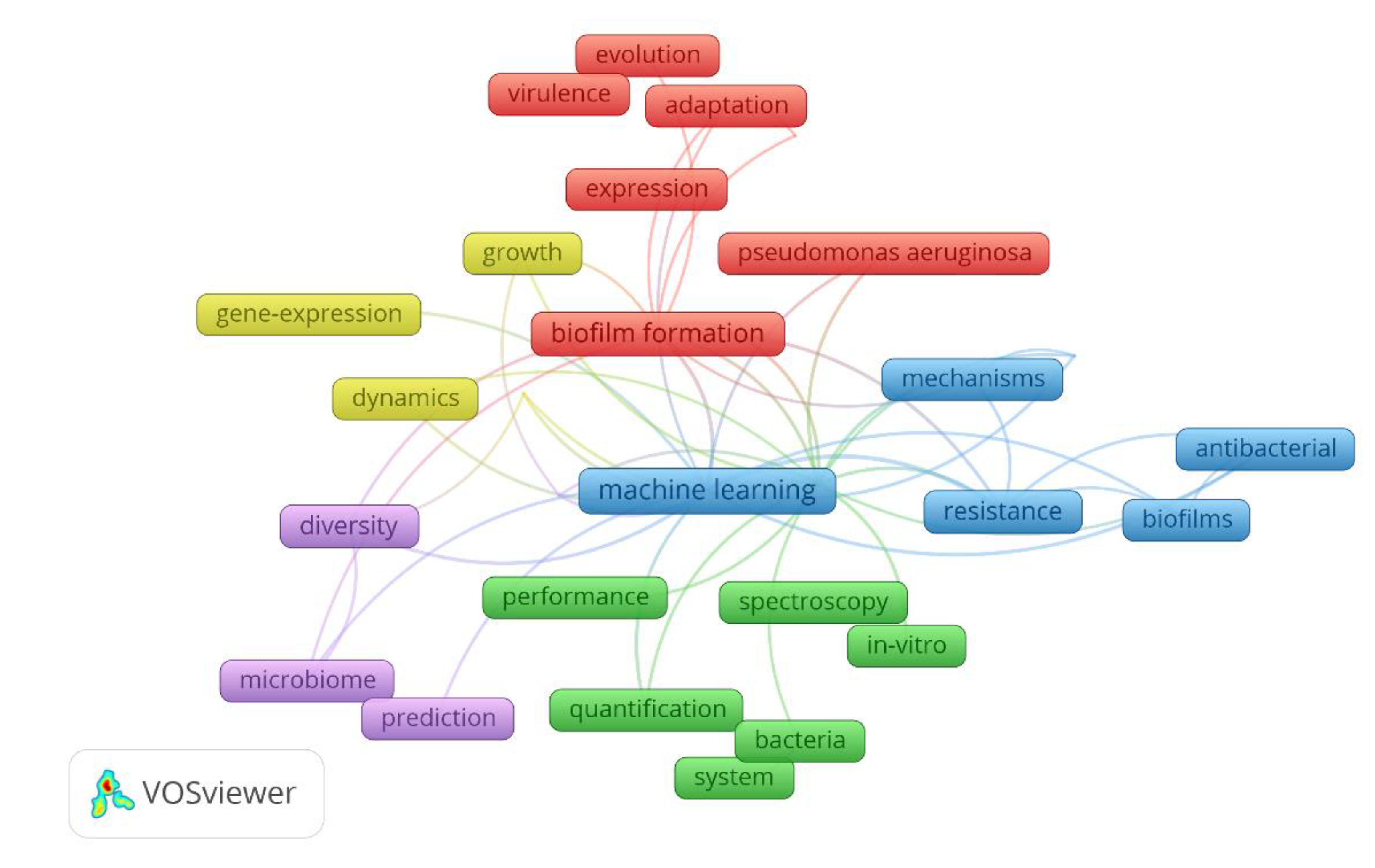
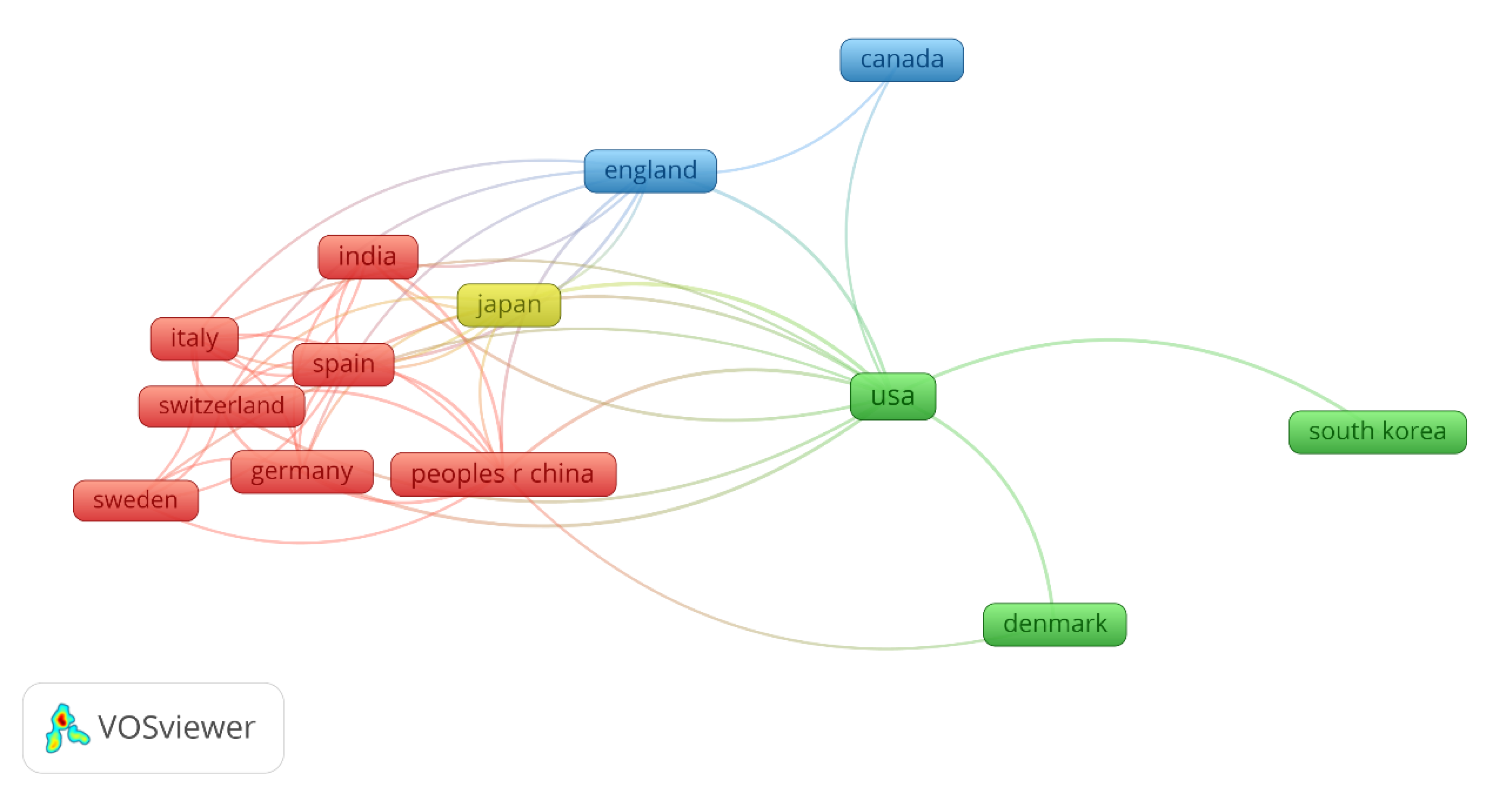
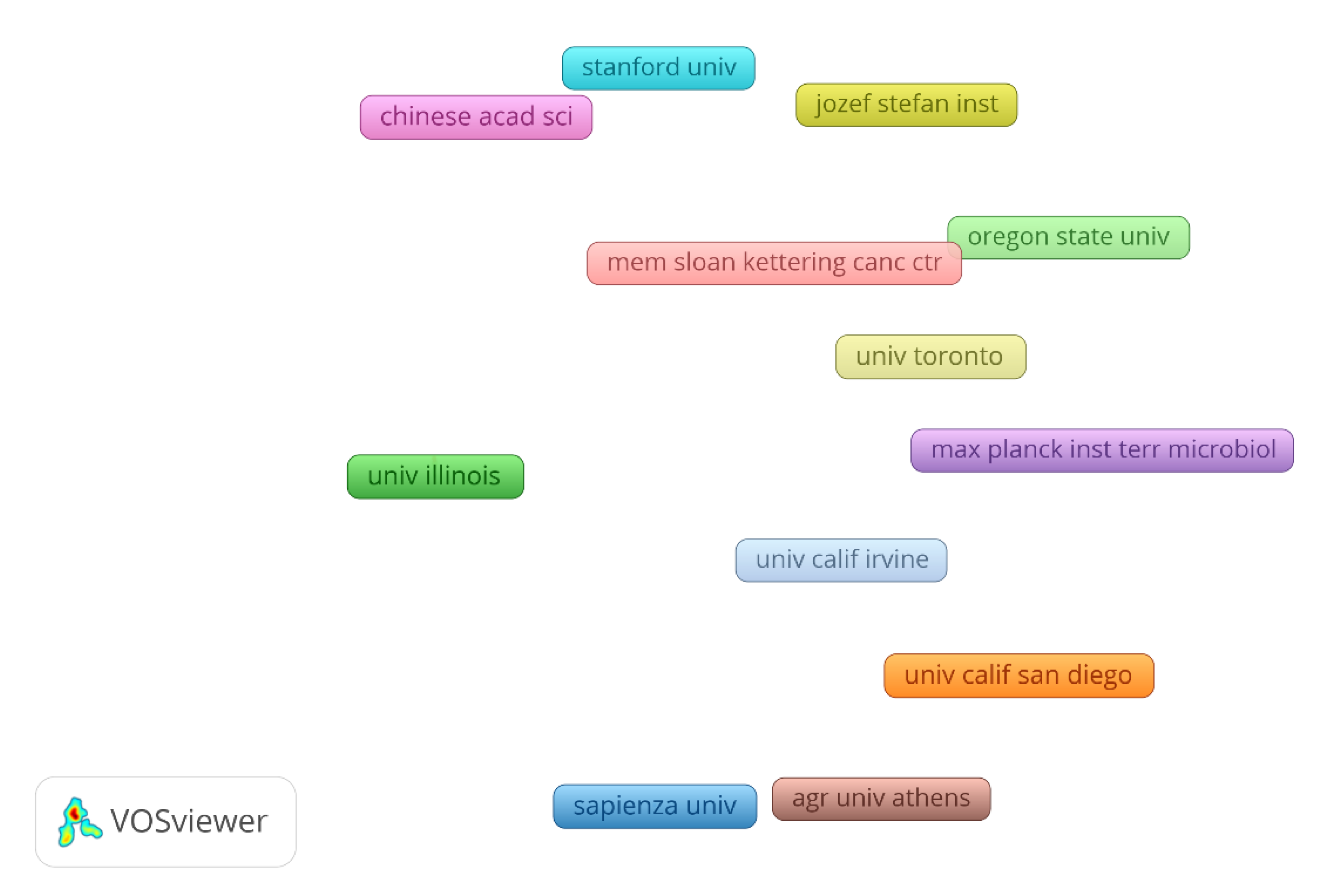
| Model organism | Target/Biofilm process | ML models | ML accuracy | Main contributions | Year | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NA | Biofilm inhibitory molecules | Classification | 88% - 93% | ML to predict biofilm inhibitory molecules | 2020 | [37] |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Essential oil chemical components | Binary Classification | 69% - 98% | ML to identify chemical components responsible for bacterial biofilm formation | 2018-2022 | [5,6] |
| Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis | Essential oil chemical components | Binary Classification | 68.7% - 90.6% | ML to identify chemical component that modulate biofilm production | [7] | |
| S. aureus | Essential oil chemical components | Binary Classification | NA | ML to predict essential oils modulate biofilm production and inhibit biofilm | 2019 | [8] |
| S. aureus | acyl-CoA thioesterase | Classification | 59.46 - 94.59% | Identification of 36 candidate genes including an acyl-CoA thioesterase enzyme and ten hypothetical proteins |
2021 | [38] |
| S. aureus, P. aeruginosa, Acinetobacter baumannii, Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, Escherichia coli | Biofilm infection | Random forest | 95.0% - 100% | Using lanthanide nanoparticles detects pathogenic biofilms based on random forest | 2022 | [39] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





