Submitted:
01 April 2023
Posted:
03 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Measuring Human Impact on the Environment
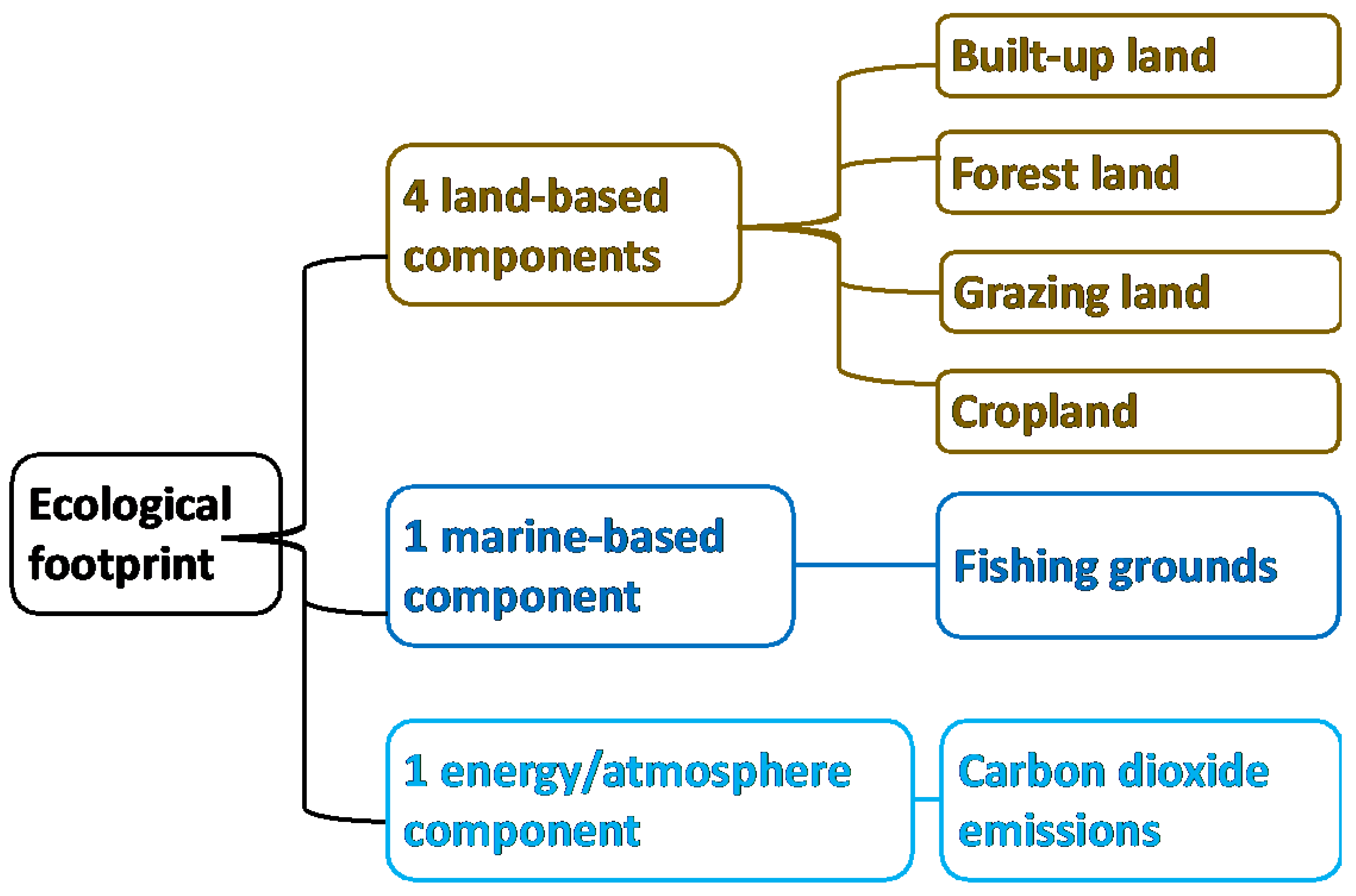
Ecological Footprint
Human Appropriation of Net Primary Production (HANPP)
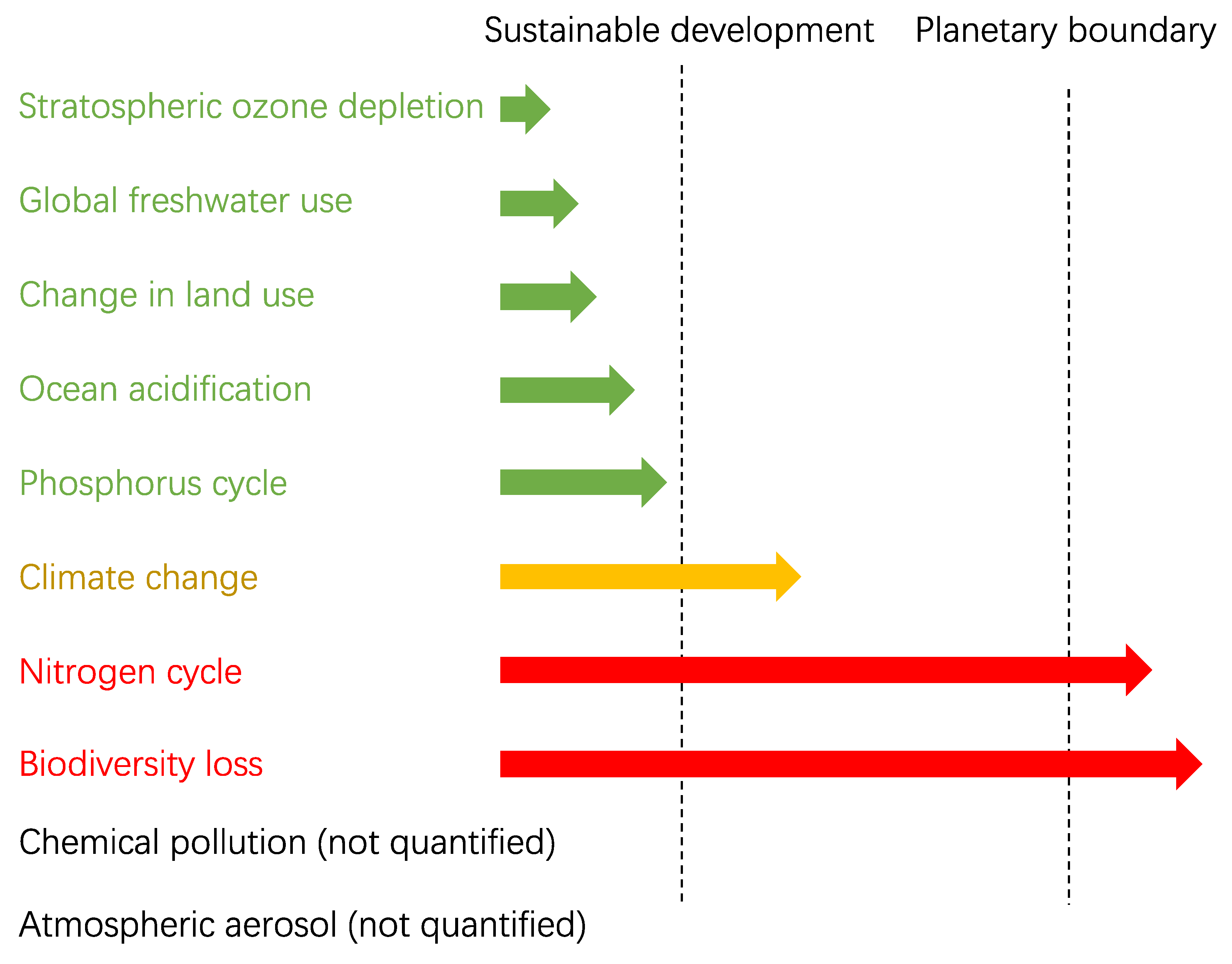
Planetary Boundary
Living Planet Index
| Methods | Basic concept | Main components | Unit | Advantages | Limitations | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ecological footprint | Human activities measured in terms of productive land | Land, marine, and atmosphere | Hectare (ha) | General view of ecology | Difficulty during calculation of mixed land areas | [28,29,30] |
| HANPP | Human contribution fraction based on net primary production | Potential NPP, ecosystem NPP, land use NPP, harvest NPP | annual carbon exchange fluxes (Pg C/yr) | Trackable data; Good understanding of land use | Lack of considering the land differences | [31,32,33] |
| Planetary boundaries | 9 major indicators representing earth system’s limit | Climate change, ozone depletion, biodiversity loss, etc | Different units for different indicators | Easy understanding to public | Controversial view during defining the limits | [20,34,35] |
| Living planet index | The complex index calculating the planet condition | Terrestrial index, marine index, freshwater index | No unit | Clear figure and trend | Questionable calculating methods | [25,36,37] |
3. Big Data and Machine Learning on Human Activity Prediction
4. Conclusion
References
- Wackernagel, M.; Monfreda, C.; Deumling, D. Ecological footprint of nations: November 2002 update. Redefining Progress. Sustainability Issue Brief. November 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kolbert, E. The sixth extinction: An unnatural history; A&C Black: 2014.
- Walker, B.; Meyers, J.A. Thresholds in ecological and social–ecological systems: a developing database. Ecology and society 2004, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, S.L.; Maslin, M.A. Defining the anthropocene. Nature 2015, 519, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osenberg, C.W.; Schmitt, R.J. Detecting ecological impacts caused by human activities. In Detecting ecological impacts; Elsevier: 1996; pp. 3–16.
- Treweek, J. Ecological impact assessment. Impact Assessment 1995, 13, 289–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smil, V. Harvesting the biosphere: The human impact. Population and development review 2011, 37, 613–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, A.K. Sustainable development and environmental ethics. International Journal on Environmental Sciences 2019, 10, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Galli, A.; Wiedmann, T.; Ercin, E.; Knoblauch, D.; Ewing, B.; Giljum, S. Integrating ecological, carbon and water footprint into a “footprint family” of indicators: definition and role in tracking human pressure on the planet. Ecological indicators 2012, 16, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, A.; Wackernagel, M.; Iha, K.; Lazarus, E. Ecological footprint: Implications for biodiversity. Biological Conservation 2014, 173, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haberl, H.; Krausmann, F.; Erb, K.-H.; Schulz, N.B. Human appropriation of net primary production. Science 2002, 296, 1968–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitousek, P.M.; Ehrlich, P.R.; Ehrlich, A.H.; Matson, P.A. Human appropriation of the products of photosynthesis. BioScience 1986, 36, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haberl, H.; Erb, K.-H.; Krausmann, F. Human appropriation of net primary production (HANPP). International Society for Ecological Economics. Internet Encyclopedia of Ecological Economics 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Haberl, H.; Erb, K.H.; Krausmann, F.; Gaube, V.; Bondeau, A.; Plutzar, C.; Gingrich, S.; Lucht, W.; Fischer-Kowalski, M. Quantifying and mapping the human appropriation of net primary production in earth's terrestrial ecosystems. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2007, 104, 12942–12947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeSouza, P.; Malhi, Y. Land Use Change in India (1700–2000) as Examined through the Lens of Human Appropriation of Net Primary Productivity. Journal of Industrial Ecology 2018, 22, 1202–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musel, A. Human appropriation of net primary production in the United Kingdom, 1800–2000: changes in society's impact on ecological energy flows during the agrarian–industrial transition. Ecological Economics 2009, 69, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, V.K.; Badarinth, K.V.S. Land use changes and trends in human appropriation of above ground net primary production (HANPP) in India (1961–98). Geographical Journal 2004, 170, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krausmann, F.; Erb, K.-H.; Gingrich, S.; Haberl, H.; Bondeau, A.; Gaube, V.; Lauk, C.; Plutzar, C.; Searchinger, T.D. Global human appropriation of net primary production doubled in the 20th century. Proceedings of the national academy of sciences 2013, 110, 10324–10329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffen, W.; Richardson, K.; Rockström, J.; Cornell, S.E.; Fetzer, I.; Bennett, E.M.; Biggs, R.; Carpenter, S.R.; De Vries, W.; De Wit, C.A. Planetary boundaries: Guiding human development on a changing planet. Science 2015, 347, 1259855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockström, J.; Steffen, W.; Noone, K.; Persson, Å.; Chapin Iii, F.S.; Lambin, E.; Lenton, T.M.; Scheffer, M.; Folke, C.; Schellnhuber, H.J. Planetary boundaries: exploring the safe operating space for humanity. Ecology and society 2009, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mace, G.M.; Reyers, B.; Alkemade, R.; Biggs, R.; Chapin Iii, F.S.; Cornell, S.E.; Díaz, S.; Jennings, S.; Leadley, P.; Mumby, P.J. Approaches to defining a planetary boundary for biodiversity. Global Environmental Change 2014, 28, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newbold, T.; Hudson, L.N.; Arnell, A.P.; Contu, S.; De Palma, A.; Ferrier, S.; Hill, S.L.L.; Hoskins, A.J.; Lysenko, I.; Phillips, H.R.P. Has land use pushed terrestrial biodiversity beyond the planetary boundary? A global assessment. Science 2016, 353, 288–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockström, J.; Steffen, W.; Noone, K.; Persson, Å.; Chapin, F.S.; Lambin, E.F.; Lenton, T.M.; Scheffer, M.; Folke, C.; Schellnhuber, H.J. A safe operating space for humanity. nature 2009, 461, 472–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collen, B.E.N.; Loh, J.; Whitmee, S.; McRae, L.; Amin, R.; Baillie, J.E.M. Monitoring change in vertebrate abundance: the Living Planet Index. Conservation Biology 2009, 23, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loh, J.; Green, R.E.; Ricketts, T.; Lamoreux, J.; Jenkins, M.; Kapos, V.; Randers, J. The Living Planet Index: using species population time series to track trends in biodiversity. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 2005, 360, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buschke, F.T.; Hagan, J.G.; Santini, L.; Coetzee, B.W.T. Random population fluctuations bias the Living Planet Index. Nature Ecology & Evolution 2021, 5, 1145–1152. [Google Scholar]
- Vačkář, D.; ten Brink, B.; Loh, J.; Baillie, J.E.M.; Reyers, B. Review of multispecies indices for monitoring human impacts on biodiversity. Ecological Indicators 2012, 17, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedmann, T.; Barrett, J. A review of the ecological footprint indicator—perceptions and methods. Sustainability 2010, 2, 1645–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, W. Ecological footprint. In Companion to environmental studies; Routledge: 2018; pp. 43–48.
- Wackernagel, M.; Monfreda, C.; Schulz, N.B.; Erb, K.-H.; Haberl, H.; Krausmann, F. Calculating national and global ecological footprint time series: resolving conceptual challenges. Land use policy 2004, 21, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erb, K.-H.; Krausmann, F.; Lucht, W.; Haberl, H. Embodied HANPP: Mapping the spatial disconnect between global biomass production and consumption. Ecological Economics 2009, 69, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlheb, N.; Krausmann, F. Land use change, biomass production and HANPP: The case of Hungary 1961–2005. Ecological Economics 2009, 69, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plutzar, C.; Kroisleitner, C.; Haberl, H.; Fetzel, T.; Bulgheroni, C.; Beringer, T.; Hostert, P.; Kastner, T.; Kuemmerle, T.; Lauk, C. Changes in the spatial patterns of human appropriation of net primary production (HANPP) in Europe 1990–2006. Regional Environmental Change 2016, 16, 1225–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteman, G.; Walker, B.; Perego, P. Planetary boundaries: Ecological foundations for corporate sustainability. Journal of management studies 2013, 50, 307–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galaz, V.; Biermann, F.; Crona, B.; Loorbach, D.; Folke, C.; Olsson, P.; Nilsson, M.; Allouche, J.; Persson, Å.; Reischl, G. ‘Planetary boundaries’—exploring the challenges for global environmental governance. Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability 2012, 4, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collen, B.; McRae, L.; Loh, J.; Deinet, S.; De Palma, A.; Manley, R.; Baillie, J.E.M. Tracking change in abundance: the living planet index. Biodiversity Monitoring and Conservation: Bridging the Gap between Global Commitment and Local Action.
- McRae, L.; Deinet, S.; Freeman, R. The diversity-weighted living planet index: controlling for taxonomic bias in a global biodiversity indicator. PloS one 2017, 12, e0169156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Ding, Y.; Liu, X. Development of the growth mindset scale: Evidence of structural validity, measurement model, direct and indirect effects in Chinese samples. Current Psychology 2021, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Ding, Y. Machine Learning and Its Applications in Studying the Geographical Distribution of Ants. Diversity 2022, 14, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Ding, Y. A Machine Learning Approach to Predicting Academic Performance in Pennsylvania’s Schools. Social Sciences 2023, 12, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janković, R.; Mihajlović, I.; Štrbac, N.; Amelio, A. Machine learning models for ecological footprint prediction based on energy parameters. Neural Computing and Applications 2021, 33, 7073–7087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roumiani, A.; Mofidi, A. Predicting ecological footprint based on global macro indicators in G-20 countries using machine learning approaches. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2022, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, F.; Liu, T. Modeling of the ecological economic activity based on machine learning. Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems 2021, 40, 2755–2766. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Wang, L.; Siddik, A.B.; Abdul-Samad, Z.; Bhardwaj, A.; Singh, B. Forecasting GHG emissions for environmental protection with energy consumption reduction from renewable sources: A sustainable environmental system. Ecological Modelling 2023, 475, 110181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matlin, S.A.; Cornell, S.E.; Krief, A.; Hopf, H.; Mehta, G. Chemistry must respond to the crisis of transgression of planetary boundaries. Chemical Science 2022, 13, 11710–11720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadić, J.M.; Ilić, V.; Biraud, S. Examination of geostatistical and machine-learning techniques as interpolators in anisotropic atmospheric environments. Atmospheric Environment 2015, 111, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, B.; Lerch, S. Machine learning methods for postprocessing ensemble forecasts of wind gusts: A systematic comparison. Monthly Weather Review 2022, 150, 235–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagan, V.; Peterson, K.T.; Maimaitijiang, M.; Sidike, P.; Sloan, J.; Greeling, B.A.; Maalouf, S.; Adams, C. Monitoring inland water quality using remote sensing: Potential and limitations of spectral indices, bio-optical simulations, machine learning, and cloud computing. Earth-Science Reviews 2020, 205, 103187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jean, N.; Burke, M.; Xie, M.; Davis, W.M.; Lobell, D.B.; Ermon, S. Combining satellite imagery and machine learning to predict poverty. Science 2016, 353, 790–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.-Z.; Shen, X.; Zeng, H.; Li, X.-Q. Triad, a new approach for contaminated site management. Huan Jing ke Xue= Huanjing Kexue 2011, 32, 803–808. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y. Heavy metal pollution and transboundary issues in ASEAN countries. Water Policy 2019, 21, 1096–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, N.; Ding, Y.; Li, X. Preparation of zeolite and zero valent iron composite for cleanup of hexavalent contamination in water. China Environmental Science 2013, 33, 443–447. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Peng, N.; Du, Y.; Ji, L.; Cao, B. Disruption of putrescine biosynthesis in Shewanella oneidensis enhances biofilm cohesiveness and performance in Cr (VI) immobilization. Applied and environmental microbiology 2014, 80, 1498–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Cohen, Y.; Cao, B. Elevated level of the second messenger c-di-GMP in Comamonas testosteroni enhances biofilm formation and biofilm-based biodegradation of 3-chloroaniline. Applied microbiology and biotechnology 2015, 99, 1967–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, J.; Xiong, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Yu, X.-Y. Molecular evidence of a toxic effect on a biofilm and its matrix. Analyst 2019, 144, 2498–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Li, K.; Ding, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Wu, X.; Li, X. Removal of silver nanoparticles in simulated wastewater treatment processes and its impact on COD and NH4 reduction. Chemosphere 2012, 87, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, J.; Szymanski, C.; Fredrickson, J.; Shi, L.; Cao, B.; Zhu, Z.; Yu, X.-Y. In situ molecular imaging of the biofilm and its matrix. Analytical chemistry 2016, 88, 11244–11252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Liu, B.; Shen, X.; Zhong, L.; Li, X. Foam-assisted delivery of nanoscale zero valent iron in porous media. Journal of Environmental Engineering 2013, 139, 1206–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Zhao, L.; Ding, Y.; Liu, B.; Zeng, H.; Zhong, L.; Li, X. Foam, a promising vehicle to deliver nanoparticles for vadose zone remediation. Journal of hazardous materials 2011, 186, 1773–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.; Kamble, S.S.; Gunasekaran, A.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, A. A systematic literature review on machine learning applications for sustainable agriculture supply chain performance. Computers & Operations Research 2020, 119, 104926. [Google Scholar]
- Habila, M.A.; Ouladsmane, M.; Alothman, Z.A. Role of artificial intelligence in environmental sustainability. In Visualization Techniques for Climate Change with Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence; Elsevier: 2023; pp. 449–469.
- Froemelt, A.; Buffat, R.; Hellweg, S. Machine learning based modeling of households: A regionalized bottom-up approach to investigate consumption-induced environmental impacts. Journal of Industrial Ecology 2020, 24, 639–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, P.; Miller, D.C. Machine learning to analyze the social-ecological impacts of natural resource policy: insights from community forest management in the Indian Himalaya. Environmental Research Letters 2019, 14, 024008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, U. Putting machine learning to use in natural resource management—improving model performance. Ecology and Society 2020, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D'Amico, B.; Myers, R.J.; Sykes, J.; Voss, E.; Cousins-Jenvey, B.; Fawcett, W.; Richardson, S.; Kermani, A.; Pomponi, F. Machine learning for sustainable structures: a call for data. 2019; pp. 1–4.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).