1. Introduction
Within the field of Computer Vision, the process of image preprocessing is crucial for achieving accurate and efficient processing of images for a range of tasks, including object recognition, text extraction, and other applications. Deskewing an image of a document is a fundamental preprocessing step that corrects the image's skew or slant to make it more accessible to analyse.
This paper centres on presenting an effective and straightforward solution for deskewing document images, which can substantially improve the accuracy and efficiency of subsequent Computer Vision tasks. The proposed solution is based on advanced image processing techniques, including the Hough Line Transformation algorithm and deep learning-based image classification.
Previous research has employed the Hough Line Transformation [
1] only to correct document skew, but this technique has some strong limitations. In particular, this approach may sometimes deskew the images into an upside-down orientation. Other methods use Deep Learning models to correct document skew. However, these models are associated with high human labour and computational resources costs, and they still may need to correct orientation while deskewing.
The most commonly utilised approach for text deskewing is Optical Character Recognition (OCR) [
2], which involves the conversion of scanned document images into editable text format through the analysis of visual patterns of text. OCR libraries generally rely on image processing techniques, such as Hough Line Transformation or deep learning-based methods, for text deskewing.
Correcting document skew is an important problem since it is often necessary for other automation-based tasks, such as data extraction using OCR technology and storing the data in a database, which reduces manual labour. This paper proposes a novel, simple, cost-effective deep learning-based method that fixes document skew and orientation. The working principle of this approach involves reducing the search space for the machine learning model to simplify the prediction process. While a model could be trained to predict the angle of the document tilt, this requires predicting a number between 0 and 360, representing the various tilt angles, resulting in a vast search space that necessitates extensive training data and computational resources. Instead, we reduced the search space to two orientations, namely, upside-down and upright, and we used a pre-trained MobileNetV2 [
3] model trained on ImageNet [
4] with just 200 images.
The contributions of this paper include providing a cost-effective solution to document skew correction and reducing the search space for the machine learning model to simplify the prediction process.
Figure 1 illustrates the spectrum of angles at which a document can be positioned and resolved using the proposed approach.
The article is divided as follows. In
Section 2, we briefly review the related literature. Then
Section 3 discusses the details of our proposed method.
Section 4 presents the preliminary results, followed by a discussion in
Section 5 and conclusions in
Section 6.
2. Related Works
In image processing, Tesseract OCR is a widely used open-source Optical Character Recognition engine that has gained popularity due to its high accuracy rate and support for over 120 languages, including right-to-left written languages such as Hebrew and Arabic [
5]. Despite some limitations, such as its lower accuracy compared to more advanced AI-based OCR solutions, Tesseract remains a popular choice for text recognition tasks due to its cost-effectiveness and open-source nature. However, it is important to note that Tesseract may produce errors if the foreground and background of the image are not well separated. Additionally, developing a custom solution using Tesseract OCR may require significant resources and time. Tesseract also has limitations regarding file format support and cannot recognise handwriting. Despite these limitations, Tesseract OCR remains a widely used OCR engine due to its high accuracy rate, support for multiple languages, and open-source nature. Tesseract offers two key functions for this purpose: deskew and orientation prediction. Both functions rely on the Hough Line Transformation algorithm to identify a line within the document. The pseudocode for this algorithm is as follows.
Convert the input image to grayscale.
Create an accumulator array with dimensions based on the image size and the range of angles to consider.
Perform the Hough Line Transform to find the lines in the image.
Accumulate the points for each line in the accumulator array.
Find the angle with the most intersecting points.
Calculate the angle.
Rotate the input image by the calculated angle to obtain the rotated image.
The Hough Line Detection algorithm [
6,
7,
8,
9,
10], utilised in the aforementioned algorithm, involves the following steps:
Initialize the Hough accumulator array with a grid of cells of appropriate size, where each cell corresponds to a particular line in the image space.
For each point (x,y) in the input image that is part of an edge, do the following:
For each angle theta in the range of angles that you are looking for lines (e.g., 0 to 180 degrees), calculate the corresponding distance r between the origin and the line perpendicular to theta that passes through point (x,y).
Increase the accumulator cell at the (r, theta) position by 1.
After all edge points have been processed, the accumulator array contains peaks at cells corresponding to the lines that were detected in the image. These peaks are identified as cells with values above a certain threshold.
From the peaks, extract the (r, theta) values and convert them into the x, and y coordinates of the lines in the image space.
Numerous research papers, including [
11,
12,
13,
14], have previously proposed and discussed the method. However, this widely accepted and commonly practised approach has a significant limitation. Specifically, the images must be skewed within a particular angle range; otherwise, the output image will be deskewed in the opposite direction, resulting in an upside-down output image. This issue has also been identified by Riaz et al in their recent publication, “Efficient skew detection and correction in scanned document images through clustering of probabilistic hough transforms” [
10,
13].
A recent study by Yang et al [
15] has proposed a novel deep learning-based approach to solve the deskewing problem. The proposed method involves converting the task into a classification problem by creating two classes: Horizontal and Vertical. Specifically, the Horizontal class corresponds to images that fall within the following angles: -180° and -135°, -45° and 45°, and 135° and 180°, while the remaining images are classified as Vertical. The model predicts whether the input image is horizontal or vertical. However, this solution is both computationally expensive and challenging to implement. Furthermore, it does not address the issue of images being deskewed into an upside-down orientation. The proposed method requires many images for training and involves masking the area of interest in all images before training the machine learning model. The authors of this study used 80,000 images to train their model. However, the machine learning model fails if the input image is upside-down, even if it outputs a horizontal orientation.
Another common practice among engineers is to use Optical Character Recognition (OCR) to identify the text in a document and rotate the image based on the detected text. However, this method is not effective for several reasons. Firstly, there is a limited amount of computerised text in many documents, which makes text detection a challenging task for traditional solutions. Additionally, real-life documents are often scanned or are copies of documents that are difficult for classic OCR techniques to process accurately. Our work involved processing photocopies of cheques and ID cards that occupied a random portion of an A4-sized paper. In this scenario, applying OCR-based techniques would require either manually extracting the regions of interest or training a model specifically for that task, which is both expensive and cumbersome.
The image below serves as an example of a document for which most existing methods would fail to correct the skew (
Figure 2).
3. Methods
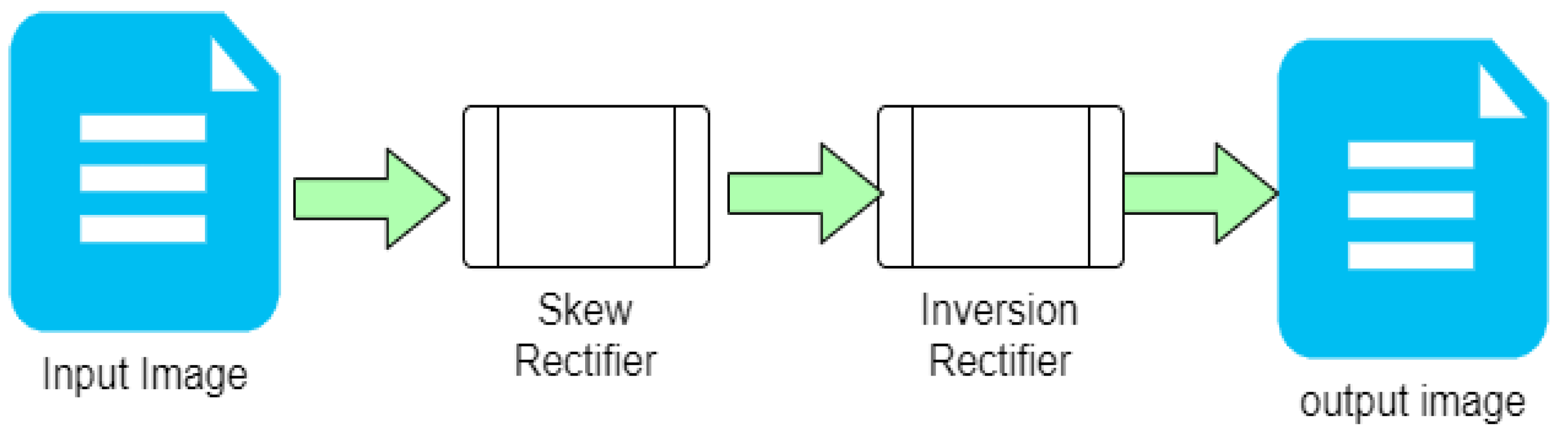
The proposed solution presents a straightforward approach that can be implemented in two sequential steps, as depicted in
Figure 3. The initial stage involves a Skew Rectifier, eliminating any undesirable tilt or skews and orients the document at a 180-degree angle. However, it is worth noting that the resulting output may still be inverted due to various factors. To address this, the image is subsequently forwarded to the Inversion Rectifier, which is a Neural-Net-based Machine Learning model designed to classify whether the input image is upside down or not. In the subsequent sections, we will delve into the working principles of both building blocks that constitute the proposed method.
3.1. Skew Rectifier
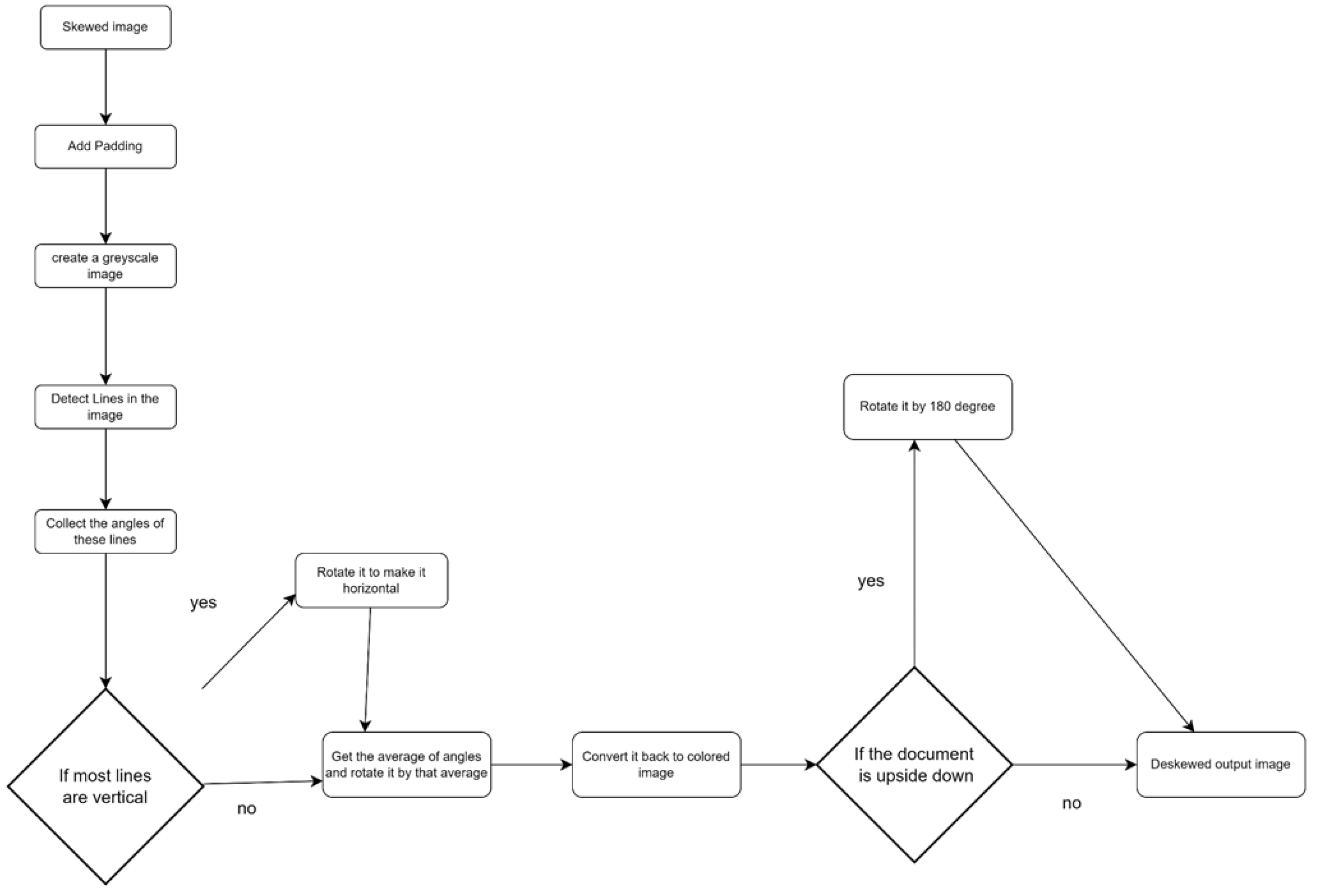
The Skew Rectifier is a critical component of the proposed method that leverages the Hough Line Transformer algorithm. The primary motivation for selecting this algorithm over other machine learning and OCR-based alternatives is its robustness in handling documents with varying levels of text density, such as textbook pages, and documents with minimal text, such as blank application forms or cheques. The following pseudocode outlines the key steps involved in the Skew Rectifier, including preprocessing.
Obtain the height, width, and colour channels of the input image.
Convert the input image to grayscale.
Apply fast non-local means denoising to the grayscale image.
Create an inverted binary image using Otsu thresholding.
Utilize the probabilistic Hough transform to detect lines in the binary image.
Compute the angles of the detected lines in radians.
Based on the line angles, determine whether the input image is in landscape or portrait orientation.
Filter outline angle outliers based on a maximum skew angle.
If the number of remaining line angles is less than 5, return the original image.
Compute the median of the remaining line angles in degrees.
If the input image is in landscape orientation, rotate the image by 90 degrees clockwise or counterclockwise as necessary.
Compute a rotation matrix based on the median angle and apply it to the input image.
These steps serve to correct any undesirable tilt accurately and efficiently or skew in the input document, enabling subsequent processing stages to proceed more effectively.
3.2. Inversion Rectifier:
The Inversion Rectifier block is designed to rectify any image inversion issues encountered in the output of the Skew Rectifier. For this purpose, we leveraged the MobilenetV2 machine learning model, which is pre-trained with the weights of the imagenet. In order to minimise computational resources, we selected only 100 layers from the model. We added several new trainable layers, including a GlobalAveragePooling2D layer, a Dense layer with 1024 neurons utilising a ReLU (Rectified Linear Unit) activation function, a Dropout layer with a rate of 0.2, and a Dense layer with a single neuron activated by a sigmoid function. We trained the model on approximately 200 images of cheques, of which 100 were upright and 100 were upside down. Epochs were chosen as per performance with a decaying learning rate every 5 epochs. To optimise the model’s performance, we selected the model with the least validation error during training. Furthermore, we employed the binary cross entropy loss function and the Adam optimiser during training. The reason for such configuration is based on mere common practice, any configuration can be used depending on the problem at hand.
3.3. Dataset Preparation for Inversion Rectifier:
The cost and labour involved in data collection and preparation can be a major challenge in building AI-based solutions. This paper proposes a simple and effective method to make the dataset preparation process more practical and efficient. In real-world scenarios, the dataset used for training the model will likely have images with various types of distortion, such as skew, tilt, and rotation. We use the Skew Rectifier discussed in
Section 3.1 to prepare the dataset to remove skew from all the images. The resulting set of images may still be inverted, and manual labour is required to rotate the inverted images. After manual rotation, we are left with a set of upright, deskewed images. A script can then be used to invert all the images, creating two sets of images - one set of upright images and one set of inverted images. These sets can be used to train the Inversion Rectifier model described in
Section 3.2. To increase the number of images to train on, we extensively used data augmentation techniques [
16], except for rotation and image flipping, which would defeat the purpose of training the model. This method significantly reduces the cost and labour involved in data preparation and makes the proposed solution more practical and efficient.
4. Results
In the present study, we assessed the effectiveness of our proposed image classification algorithm, which consists of two main components: a skew rectifier and an inversion rectifier. The skew rectifier leverages the Hough Line Transformation method to reorient a skewed document into a horizontal position. Initially, we padded the image by converting it into a square shape to ensure that no information is lost in case of image rotation, which might cause the area of interest to shift beyond the original rectangular shape. Subsequently, the image was converted to grayscale to enhance the visibility of the lines and facilitate their detection by the algorithm. The skew angles of the detected lines were then computed, and their average was used to determine the optimal rotation angle. Following this, the image was rotated by the determined angle.
The output of the skew rectifier can be either an upright or upside-down image, depending on the angle at which the input image was tilted. This output is then passed to the inversion rectifier, which is a deep learning-based machine learning model that classifies the image as upright or inverted. If the image is inverted, the inversion rectifier rotates the image by 180 degrees to give an upright image as depicted in
Figure 4.
The present research employs a dataset derived from a real-world scenario involving document data extraction. Specifically, the dataset posed a significant challenge due to numerous tilts and rotations in historical data and the real-time capture of document images via mobile devices. To gather data both historical and production data were collected. To address the issue of tilts and rotations, a skew rectifier was utilised to convert all images to a horizontal orientation, followed by manual adjustment to ensure vertical alignment. Additionally, a second set of images was created by duplicating and rotating the original set by 180 degrees, representing the upside-down class.
To evaluate the performance of our algorithm, we used a balanced dataset to train the model and tested it on an additional set of 1000 images, comprising 500 upright and 500 upside-down images. Since our test images were also balanced, with an almost equal number of data points in each class, we used accuracy to evaluate the model's performance. Accuracy was calculated using the formula:
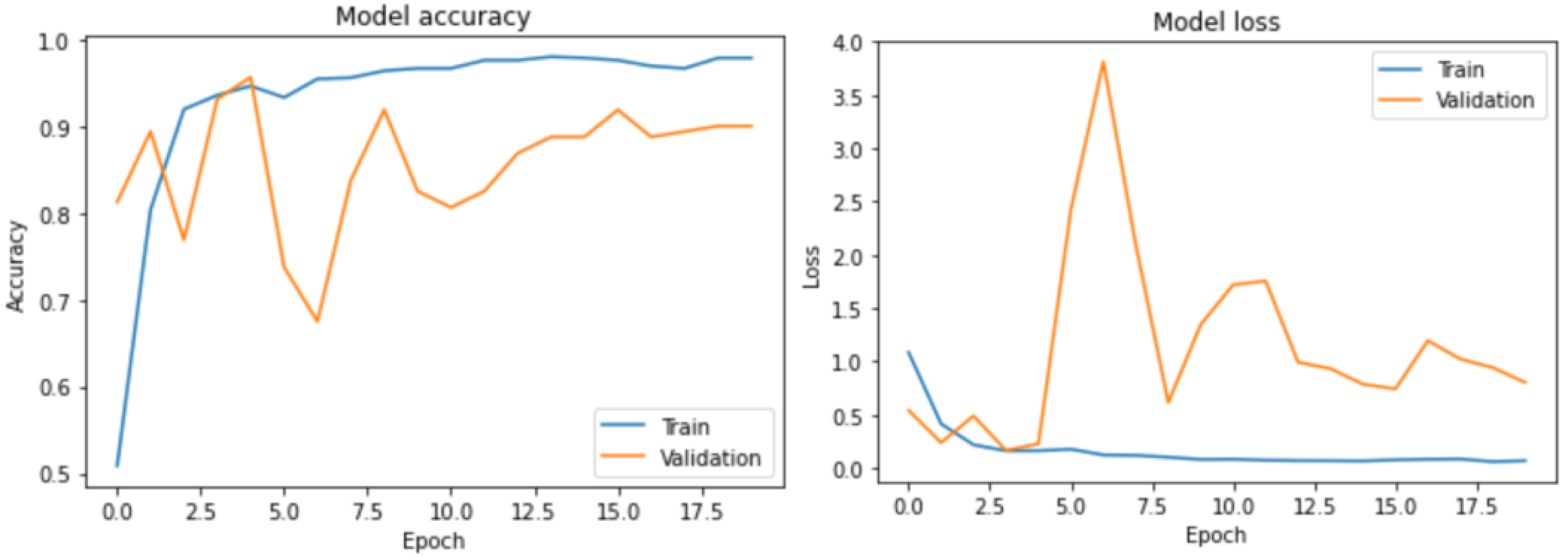
The results obtained from the evaluation demonstrated our model’s high accuracy and robustness, as it achieved an impressive accuracy rate of 97%. These findings have significant implications for developing effective image classification models in real-world applications. Fine-tuning the model was a straightforward and expeditious process given the relatively simple nature of the task at hand, which entailed performing binary image classification.
Figure 5 depicts the training and validation accuracy and loss metrics.
In the context of the present study, the Tesseract software was the only available production-ready option against which the proposed method could be compared. A total of 250 images featuring varying degrees of tilt were obtained for comparative testing purposes, as illustrated in
Table 1. The testing results indicate that the proposed method significantly outperforms the Tesseract Engine when the skew angle exceeds 90 degrees.
In conclusion, our study provides strong evidence that our proposed algorithm can accurately classify images and be effectively deployed in production. The high accuracy rate achieved on the additional set of images demonstrates the robustness and effectiveness of our model in handling complex image classification tasks. Furthermore, successfully deploying our trained model in production without any reported issues indicates its stability and reliability. Overall, the results of this study suggest that our algorithm has a high potential for use in a wide range of image classification tasks.
5. Discussion
The proposed strategy is generally effective for similar problems. We also tested our model on documents it needed to be specifically trained on, such as i-cards and forms, and found that it worked well. However, depending on the problem, different pre-trained models may be more appropriate. For example, we tested our strategy on ResNet-20 [
17] but found that it only performed well once we significantly increased the number of layers. Our approach of using only 100 layers from MobileNetv2 with weights of ImageNet proved efficient for production deployment while still achieving good performance. Additional optimisations, such as data augmentation or generative methods, can be used to address small or imbalanced datasets. In the case of skew rectifiers, depending on the problem at hand, the use of Probabilistic Hough Transformation or Fast Hough Line Transformation may be helpful, as discussed in [9,14, 18]. Overall, as a simple classification model with only two labels, the inversion rectifier is one of the easiest machine-learning problems involving neural networks.
6. Conclusions
In conclusion, the proposed strategy for document image preprocessing presents a two-step approach that involves a Skew Rectifier and an Inversion Rectifier. The Skew Rectifier, which employs the Hough Line Transformer algorithm, corrects any undesirable tilt or skew in the input document. At the same time, the Inversion Rectifier, which leverages a MobilenetV2 machine learning model, rectifies any image inversion issues encountered in the output of the Skew Rectifier. The proposed solution has demonstrated impressive performance, achieving an accuracy of 97% on a dataset of 500 images consisting of 250 upright and 250 upside-down images. Additionally, to make the dataset preparation process more practical and efficient, the paper proposes a simple and effective method that significantly reduces the cost and labour involved in data preparation. The proposed strategy is a promising approach for preprocessing document images and can be utilised in various applications such as OCR, document classification, and information retrieval.
References
- Zhao, K.; Han, Q.; Zhang, C.B.; Xu, J.; Cheng, M.M. Deep hough transform for semantic line detection. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 2021, 44, 4793–4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaló, Á.Z.; Sipos, M.L. Key-Value Pair Searhing System via Tesseract OCR and Post Processing. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 19th World Symposium on Applied Machine Intelligence and Informatics (SAMI), Herl'any, Slovakia, 21–23 January 2021; pp. 000461–000464. [Google Scholar]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.C. Mobilenetv2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar]
- Recht, B.; Roelofs, R.; Schmidt, L.; Shankar, V. Do imagenet. In International conference on machine learning; PMLR: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 5389–5400. [Google Scholar]
- Hegghammer, T. OCR with Tesseract, Amazon Textract, and Google Document AI: a benchmarking experiment. Journal of Computational Social Science 2022, 5, 861–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Fang, J.; Wu, Y.; Kang, K. Research on improved image edge detection based on Hough transform. International Conference on Image Processing and Intelligent Control (IPIC 2021) 2021, 11928, 146–150. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, R.; Naz, S.; Razzak, I. Efficient skew detection and correction in scanned document images through clustering of probabilistic hough transforms. Pattern Recognition Letters 2021, 152, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudraa, O.; Hidouci, W.K.; Michelucci, D. Using skeleton and Hough transform variant to correct skew in historical documents. Mathematics and computers in simulation 2020, 167, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chettat, M.; Gaceb, D.; Belhadi, S. A fast high precision skew angle estimation of digitized documents. Int. Arab J. Inf. Technol. 2020, 17, 825–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Liu, J. Practical limitations of lane detection algorithm based on Hough transform in challenging scenarios. International Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems 2021, 18, 17298814211008752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scazzoli, D.; Bartezzaghi, G.; Uysal, D.; Magarini, M.; Melacini, M.; Marcon, M. Usage of Hough transform for expiry date extraction via optical character recognition. In Proceedings of the 2019 Advances in Science and Engineering Technology International Conferences (ASET), Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 26 March 2019–10 April 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Prabhu, S.; Ponduru, P.S.; Palanisamy, R. An Approach for Improved Data matrix distortion correction using Median filtered Hough Transform. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 6th Conference on Information and Communication Technology (CICT), Gwalior, India, 18-20 November 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, R.; Naz, S.; Razzak, I. Efficient skew detection and correction in scanned document images through clustering of probabilistic hough transforms. Pattern Recognition Letters 2021, 152, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezmaternykh, P.V.; Nikolaev, D.P. A document skew detection method using fast Hough transform. In Twelfth International Conference on Machine Vision (ICMV 2019), SPIE, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, ; Volume 11433, pp. 132–137. In Proceedings of the Twelfth International Conference on Machine Vision (ICMV 2019), SPIE, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 16–18 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Lin, Y.; Ho, C. A Masked Bounding-Box Selection Based ResNet Predictor for Text Rotation Prediction. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2209.09198. [Google Scholar]
- Shorten, C.; Khoshgoftaar, T.M. A survey on image data augmentation for deep learning. Journal of big data 2019, 6, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J. Image classification based on RESNET. Journal of Physics: Conference Series 2020, 1634, 012110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzougui, M.; Alasiry, A.; Kortli, Y.; Baili, J. A lane tracking method based on progressive probabilistic Hough transform. IEEE access 2020, 8, 84893–84905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).