Submitted:
23 May 2023
Posted:
25 May 2023
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Coronavirus Disease 2019
1.2. Ultrasound in COVID-2019 Diagnosis
1.3. AI for Ultrasound-based COVID-2019 Management
1.4. Main Contributions
- We exhaustively survey articles that used publicly available lung ultrasound datasets for COVID-19. To our knowledge, this survey is the first that is organized focusing on dataset accessibility.
- We list and review the publicly available lung ultrasound COVID-19 datasets and organize ultrasound-based AI studies per dataset.
- We analyze and tabulate studies in several dimensions, such as data preprocessing, AI models, cross-validation, and evaluation criteria.
- We summarize all reviewed works in a tabular fashion to facilitate an easier comparison among studies.
- Last by not least, we also include many ultrasound-based COVID-19 AI studies that used private lung ultrasound datasets to elucidate a clear picture of the field.
1.5. Search Strategy
- Its full text is available online or it is published in any of the common and well-known publications, which are usually accessible through an institutional subscription. In our case, we took help from fellow scientists working in top North American universities for accessing papers, if not accessible through our own institutional subscription.
- It used any form of artificial intelligence techniques (i.e., conventional machine learning or deep learning) for COVID-19 detection or analysis from lung ultrasound data.
- It used a publicly available lung ultrasound dataset of COVID-19.
- The hypothesis of the article is supported by its qualitative and quantitative results.
- The article maintained a minimum standard of quality (e.g., abstract or methodology section is not missing, no reference missing error, clear legends/axis titles in the figure, etc.)
1.6. Paper Organization
2. Input Data
2.1. Public Dataset
2.2. Private Dataset
2.3. Data Pre-processing and Augmentation
2.3.1. Curve-to-linear Conversion
2.3.2. Image Resizing
2.3.3. Intensity Normalization
2.3.4. Image Augmentation
2.3.5. Other Image Processing Techniques
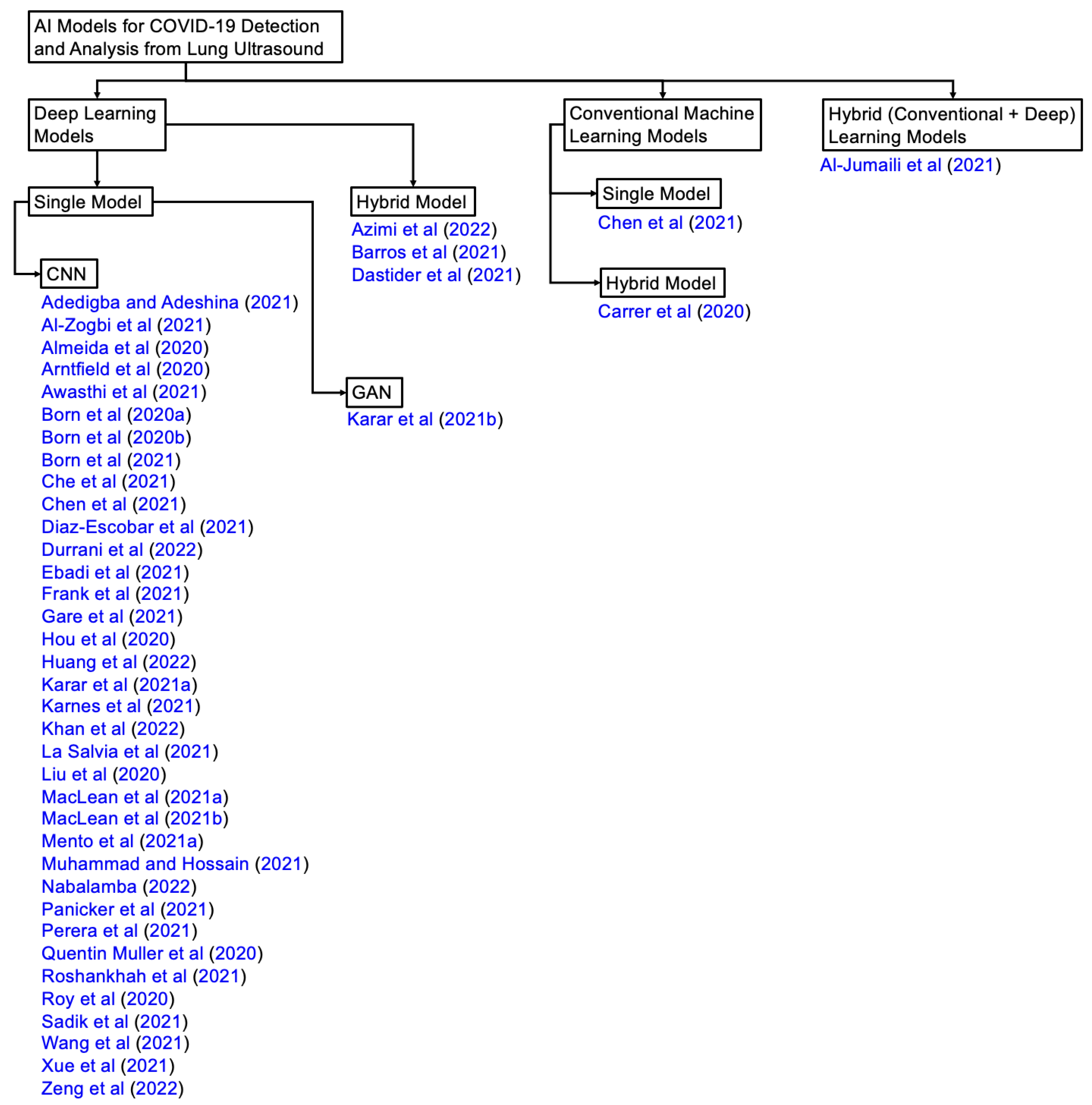
3. AI in Ultrasound COVID-2019 Studies
3.1. AI Models
3.1.1. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN)
3.1.2. Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN)
3.1.3. COVID-Net
3.1.4. Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM)
3.1.5. Hidden Markov Model (HMM)
3.1.6. Support Vector Machine (SVM)
3.1.7. Decision Tree
3.1.8. Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN)
3.1.9. Spatial Transformer Network (STN)
3.1.10. UNet
3.1.11. Few-shot Learning
3.1.12. Transfer Learning
3.1.13. Other Architectures
3.2. Loss Functions
3.2.1. Cross-entropy Loss
3.2.2. Categorical Cross-entropy
3.2.3. L1 Loss
3.2.4. Focal Loss
3.2.5. Soft Ordinal (SORD) Loss
3.3. Evaluation Criteria
- True Positive (TP): A result that is positive as both the actual value and expected value.
- True Negative (TN): A result that is negative as both the actual value and expected value.
- False Positive (FP): A false positive occurs when a projected outcome is indicated as being positive when it is actually negative.
- False Negative (FN): A false negative occurs when a projected outcome is indicated as being negative when it is actually positive.
3.3.1. Precision
3.3.2. Recall
3.3.3. Specificity
3.3.4. Accuracy
3.3.5. F1–score
3.3.6. Intersection over Union (IoU)
3.3.7. Sørensen–Dice coefficient
4. Studies using POCUS Dataset
4.1. Studies
4.2. Evaluation
5. Studies using ICLUS-DB Dataset
5.1. Studies
5.2. Evaluation
6. Studies using COVIDx-US Dataset
6.1. Studies
6.2. Evaluation
7. Studies using Private Dataset
7.1. Studies
7.2. Evaluation
8. Discussion and Future Works
8.1. COVID-19 Severity Assessment
8.2. Data Partition for Benchmarking
8.3. Public Sharing of Code
8.4. Description of Image Pre-processing/augmentation
8.5. Potential Future Work
- Developing a standardized protocol for ultrasound-based severity assessment of COVID-19: The studies in the survey highlight the potential of ultrasound in assessing the severity of COVID-19. However, there is a need to develop a standardized protocol for ultrasound-based severity assessment to ensure consistency across studies and to facilitate comparisons between different AI models. This protocol should include standardized imaging techniques, imaging parameters, and diagnostic criteria.
- Integration of ultrasound with other imaging modalities: While ultrasound is a useful tool for COVID-19 assessment, it has some limitations, such as limited penetration depth and difficulty in imaging certain structures. Future work can focus on combining ultrasound with other imaging modalities, such as CT or MRI (if available), to provide a more comprehensive assessment of COVID-19.
- Integrating AI models for early detection and monitoring of COVID-19: Ultrasound can detect early lung involvement and monitor disease progression in COVID-19 patients. Future work can focus not only on developing but also integrate AI models in clinical settings that can accurately detect COVID-19 at an early stage and monitor disease progression over time, enabling timely intervention and better patient outcomes.
- Comparison of AI models using benchmark datasets: As highlighted in the discussion, there is a need for benchmark datasets for quantitative accuracy comparison of different AI models. Future work can focus on developing benchmark datasets and using them to compare the performance of different AI models for COVID-19 detection and analysis.
- Integration of AI models into clinical practice: The potential of AI models for COVID-19 detection and analysis is vast, but their integration into clinical practice is still limited. Future work can focus on developing user-friendly and interpretable AI models that can be easily integrated into clinical workflows, improving the accuracy and speed of COVID-19 diagnosis and treatment.
- Exploration of novel pre-processing and augmentation techniques: The quality of input data is crucial for the accuracy of AI models. Future work can focus on exploring novel pre-processing and augmentation techniques for ultrasound images to improve the quality of input data and the performance of AI models. These techniques can include advanced filtering, contrast enhancement, or more sophisticated augmentation methods.
- Integration of clinical and imaging data: AI models for COVID-19 detection and analysis can benefit from the integration of clinical and imaging data. Future work can focus on developing AI models that can integrate clinical and imaging data to provide a more comprehensive assessment of COVID-19 and its impact on patients.
9. Conclusions
References
- Worldometer. COVID-19 CORONAVIRUS PANDEMIC, 2023. https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/. Accessed: 3-13-2023.
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; others. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. The lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stokes, E.K.; Zambrano, L.D.; Anderson, K.N.; Marder, E.P.; Raz, K.M.; Felix, S.E.B.; Tie, Y.; Fullerton, K.E. Coronavirus disease 2019 case surveillance—United States, january 22–may 30, 2020. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report 2020, 69, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Zhou, B.; Sohn, J.J.; Zhou, J.; Jacob, J.T.; Higgins, K.A.; Bradley, J.D.; Liu, T. Review of Machine Learning in Lung Ultrasound in COVID-19 Pandemic. J. Imaging 2022, 8, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, D.; Tang, Z.; Wang, S.; Hui, H.; Gong, L.; Lu, Y.; Xue, Z.; Liao, H.; Chen, F.; Yang, F.; others. The role of imaging in the detection and management of COVID-19: A review. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 14, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, X.; Wodnicki, R.; Kang, H.; Zhang, J.; Tchelepi, H.; Zhou, Q. Current ultrasound technologies and instrumentation in the assessment and monitoring of COVID-19 positive patients. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2020, 67, 2230–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willemink, M.J.; Koszek, W.A.; Hardell, C.; Wu, J.; Fleischmann, D.; Harvey, H.; Folio, L.R.; Summers, R.M.; Rubin, D.L.; Lungren, M.P. Preparing medical imaging data for machine learning. Radiology 2020, 295, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Jang, H.Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, S.J.; Won, H.J.; Byun, J.H.; Choi, S.H.; Lee, S.S.; An, J.; Lim, Y.S. Non-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging as a surveillance tool for hepatocellular carcinoma: Comparison with ultrasound. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Ye, D.; Chen, S.; Chen, H. Therapeutic ultrasound-enhanced immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy. Front. Phys. 2021, 9, 636985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prentice, R.; Wright, E.K.; Flanagan, E.; Ross, A.L.; Bell, S.J. The Use of Fecal Calprotectin and Intestinal Ultrasound in the Evaluation and Management of Stricturing Crohn’s Disease in Pregnancy. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2022, 28, e13–e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allinovi, M.; Parise, A.; Giacalone, M.; Amerio, A.; Delsante, M.; Odone, A.; Franci, A.; Gigliotti, F.; Amadasi, S.; Delmonte, D.; others. Lung ultrasound may support diagnosis and monitoring of COVID-19 pneumonia. Ultrasound Med. & Biol. 2020, 46, 2908–2917. [Google Scholar]
- Born, J.; Brändle, G.; Cossio, M.; Disdier, M.; Goulet, J.; Roulin, J.; Wiedemann, N. POCOVID-Net: Automatic detection of COVID-19 from a new lung ultrasound imaging dataset (POCUS). Arxiv Prepr. Arxiv:2004.12084 2020. [CrossRef]
- Born, J.; Wiedemann, N.; Cossio, M.; Buhre, C.; Brändle, G.; Leidermann, K.; Goulet, J.; Aujayeb, A.; Moor, M.; Rieck, B.; others. Accelerating detection of lung pathologies with explainable ultrasound image analysis. Applied Sciences 2021, 11, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, R.; Marathe, A. Soft labels for ordinal regression. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2019, pp. 4738–4747. [CrossRef]
- Gare, G.R.; Schoenling, A.; Philip, V.; Tran, H.V.; Bennett, P.d.; Rodriguez, R.L.; Galeotti, J.M. Dense pixel-labeling for reverse-transfer and diagnostic learning on lung ultrasound for COVID-19 and pneumonia detection. 2021 IEEE 18th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI). IEEE, 2021, pp. 1406–1410. [CrossRef]
- Carrer, L.; Donini, E.; Marinelli, D.; Zanetti, M.; Mento, F.; Torri, E.; Smargiassi, A.; Inchingolo, R.; Soldati, G.; Demi, L.; others. Automatic pleural line extraction and COVID-19 scoring from lung ultrasound data. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2020, 67, 2207–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; Radbel, J.; Sunderram, J.; Nosher, J.L.; Patel, V.M.; Hacihaliloglu, I. Multi-feature multi-scale CNN-derived COVID-19 classification from lung ultrasound data. 2021 43rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC). IEEE, 2021, pp. 2618–2621. [CrossRef]
- Dastider, A.G.; Sadik, F.; Fattah, S.A. An integrated autoencoder-based hybrid CNN-LSTM model for COVID-19 severity prediction from lung ultrasound. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 132, 104296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, O.; Schipper, N.; Vaturi, M.; Soldati, G.; Smargiassi, A.; Inchingolo, R.; Torri, E.; Perrone, T.; Mento, F.; Demi, L.; others. Integrating domain knowledge into deep networks for lung ultrasound with applications to COVID-19. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2021, 41, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Menapace, W.; Oei, S.; Luijten, B.; Fini, E.; Saltori, C.; Huijben, I.; Chennakeshava, N.; Mento, F.; Sentelli, A.; others. Deep learning for classification and localization of COVID-19 markers in point-of-care lung ultrasound. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 39, 2676–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, W.; Cao, C.; Liu, J.; Duan, Y.; Cao, H.; Wang, J.; Tao, X.; Chen, Z.; Wu, M.; Zhang, J.; others. Modality alignment contrastive learning for severity assessment of COVID-19 from lung ultrasound and clinical information. Med. Image Anal. 2021, 69, 101975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soldati, G.; Demi, M.; Smargiassi, A.; Inchingolo, R.; Demi, L. The role of ultrasound lung artifacts in the diagnosis of respiratory diseases. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2019, 13, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelao, J.; Graziani, D.; Soriano, J.B.; Izquierdo, J.L. Findings and prognostic value of lung ultrasound in COVID-19 pneumonia. J. Ultrasound Med. 2021, 40, 1315–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldati, G.; Smargiassi, A.; Inchingolo, R.; Buonsenso, D.; Perrone, T.; Briganti, D.F.; Perlini, S.; Torri, E.; Mariani, A.; Mossolani, E.E.; others. Proposal for international standardization of the use of lung ultrasound for patients with COVID-19: A simple, quantitative, reproducible method. J. Ultrasound Med. 2020, 39, 1413–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, M.A.; Ali, M.A.; Deriche, M. On the Early Detection of COVID19 using Advanced Machine Learning Techniques: A Review. 2021 18th International Multi-Conference on Systems, Signals & Devices (SSD). IEEE, 2021, pp. 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Mondal, M.R.H.; Bharati, S.; Podder, P. Diagnosis of COVID-19 using machine learning and deep learning: A review. Curr. Med. Imaging 2021, 17, 1403–1418. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, M.A.; Mirikharaji, Z.; Momeny, M.; Marhamati, M.; Neshat, A.A.; Garbi, R.; Hamarneh, G. Active deep learning from a noisy teacher for semi-supervised 3D image segmentation: Application to COVID-19 pneumonia infection in CT. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2022, 102, 102127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Lediju Bell, M.A. A review of deep learning applications in lung ultrasound imaging of COVID-19 patients. BME Frontiers 2022, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzubaidi, M.; Zubaydi, H.D.; Bin-Salem, A.A.; Abd-Alrazaq, A.A.; Ahmed, A.; Househ, M. Role of deep learning in early detection of COVID-19: Scoping review. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. Update 2021, 1, 100025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J. Review of Deep Learning-based Approaches for COVID-19 Detection. 2021 2nd International Conference on Computing and Data Science (CDS). IEEE, 2021, pp. 366–371. [CrossRef]
- Gudigar, A.; Raghavendra, U.; Nayak, S.; Ooi, C.P.; Chan, W.Y.; Gangavarapu, M.R.; Dharmik, C.; Samanth, J.; Kadri, N.A.; Hasikin, K.; others. Role of artificial intelligence in COVID-19 detection. Sensors 2021, 21, 8045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulhaq, A.; Born, J.; Khan, A.; Gomes, D.P.S.; Chakraborty, S.; Paul, M. COVID-19 control by computer vision approaches: A survey. Ieee Access 2020, 8, 179437–179456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynants, L.; Van Calster, B.; Collins, G.S.; Riley, R.D.; Heinze, G.; Schuit, E.; Bonten, M.M.; Dahly, D.L.; Damen, J.A.; Debray, T.P.; others. Prediction models for diagnosis and prognosis of COVID-19: Systematic review and critical appraisal. bmj 2020, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebadi, A.; Xi, P.; MacLean, A.; Florea, A.; Tremblay, S.; Kohli, S.; Wong, A. COVIDx-US: An Open-Access Benchmark Dataset of Ultrasound Imaging Data for AI-Driven COVID-19 Analytics. Front. Biosci. -Landmark 2022, 27, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durrani, N.; Vukovic, D.; van der Burgt, J.; Antico, M.; van Sloun, R.J.; Canty, D.; Steffens, M.; Wang, A.; Royse, A.; Royse, C.; others. Automatic Deep Learning-Based Consolidation/Collapse Classification in Lung Ultrasound Images for COVID-19 Induced Pneumonia, 2022. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-1531881/v1. [CrossRef]
- Panicker, M.R.; Chen, Y.T.; Narayan, K.V.; Kesavadas, C.; Vinod, A.; others. An Approach Towards Physics Informed Lung Ultrasound Image Scoring Neural Network for Diagnostic Assistance in COVID-19. Arxiv Prepr. Arxiv:2106.06980 2021. [CrossRef]
- Quentin Muller, M.; Aleandro Eccel, M.; Arnaud Robert, M. Extracting high value lung ultrasound images from video for the diagnosis and prognosis of COVID-19. Epfl Proj. Rep. 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Arntfield, R.; VanBerlo, B.; Alaifan, T.; Phelps, N.; White, M.; Chaudhary, R.; Ho, J.; Wu, D. Development of a deep learning classifier to accurately distinguish COVID-19 from look-a-like pathology on lung ultrasound. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Camacho, J.; Muñoz, M.; Genovés, V.; Herraiz, J.L.; Ortega, I.; Belarra, A.; González, R.; Sánchez, D.; Giacchetta, R.C.; Trueba-Vicente, Á.; others. Artificial Intelligence and Democratization of the Use of Lung Ultrasound in COVID-19: On the Feasibility of Automatic Calculation of Lung Ultrasound Score. Int. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 2, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; He, C.; Yin, J.; Li, J.; Duan, X.; Cao, Y.; Sun, L.; Hu, M.; Li, W.; Li, Q. Quantitative analysis and automated lung ultrasound scoring for evaluating COVID-19 pneumonia with neural networks. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2021, 68, 2507–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Lei, Y.; Xing, W.; He, C.; Wei, G.; Miao, Z.; Hao, Y.; Li, G.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; others. Evaluation of pulmonary edema using ultrasound imaging in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia based on a non-local Channel attention ResNet. Ultrasound Med. & Biol. 2022, 48, 945–953. [Google Scholar]
- La Salvia, M.; Secco, G.; Torti, E.; Florimbi, G.; Guido, L.; Lago, P.; Salinaro, F.; Perlini, S.; Leporati, F. Deep learning and lung ultrasound for COVID-19 pneumonia detection and severity classification. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 136, 104742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; He, Q.; Liao, H.; Luo, J. A semi-automatic ultrasound image analysis system for the grading diagnosis of COVID-19 pneumonia. Arxiv Prepr. Arxiv:2111.02676 2021. [CrossRef]
- Mento, F.; Perrone, T.; Fiengo, A.; Smargiassi, A.; Inchingolo, R.; Soldati, G.; Demi, L. Deep learning applied to lung ultrasound videos for scoring COVID-19 patients: A multicenter study. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2021, 149, 3626–3634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roshankhah, R.; Karbalaeisadegh, Y.; Greer, H.; Mento, F.; Soldati, G.; Smargiassi, A.; Inchingolo, R.; Torri, E.; Perrone, T.; Aylward, S.; others. Investigating training-test data splitting strategies for automated segmentation and scoring of COVID-19 lung ultrasound images. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2021, 150, 4118–4127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mento, F.; Perrone, T.; Macioce, V.N.; Tursi, F.; Buonsenso, D.; Torri, E.; Smargiassi, A.; Inchingolo, R.; Soldati, G.; Demi, L. On the impact of different lung ultrasound imaging protocols in the evaluation of patients affected by coronavirus disease 2019: How many acquisitions are needed? J. Ultrasound Med. 2021, 40, 2235–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrone, T.; Soldati, G.; Padovini, L.; Fiengo, A.; Lettieri, G.; Sabatini, U.; Gori, G.; Lepore, F.; Garolfi, M.; Palumbo, I.; others. A new lung ultrasound protocol able to predict worsening in patients affected by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 pneumonia. J. Ultrasound Med. 2021, 40, 1627–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Lei, W.; Wan, X.; Liu, L.; Luo, Y.; Feng, C. Semi-supervised active learning for COVID-19 lung ultrasound multi-symptom classification. 2020 IEEE 32nd International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence (ICTAI). IEEE, 2020, pp. 1268–1273. [CrossRef]
- Nabalamba, I. Machine learning-aided classification of COVID-19 in lung Ultrasound Images. PhD thesis, Makerere University, 2022.
- Rojas-Azabache, C.; Vilca-Janampa, K.; Guerrero-Huayta, R.; Núñez-Fernández, D. Detection of COVID-19 Disease using Deep Neural Networks with Ultrasound Imaging. Arxiv Prepr. Arxiv:2104.01509 2021. [CrossRef]
- Bottenus, N.; Üstüner, K.F. Acoustic reciprocity of spatial coherence in ultrasound imaging. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2015, 62, 852–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebadi, S.E.; Krishnaswamy, D.; Bolouri, S.E.S.; Zonoobi, D.; Greiner, R.; Meuser-Herr, N.; Jaremko, J.L.; Kapur, J.; Noga, M.; Punithakumar, K. Automated detection of pneumonia in lung ultrasound using deep video classification for COVID-19. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2021, 25, 100687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karar, M.E.; Reyad, O.; Abd-Elnaby, M.; Abdel-Aty, A.H.; Shouman, M.A. Lightweight transfer learning models for ultrasound-guided classification of COVID-19 patients. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2021, pp. 2295–2312. [CrossRef]
- Karnes, M.; Perera, S.; Adhikari, S.; Yilmaz, A. Adaptive Few-Shot Learning PoC Ultrasound COVID-19 Diagnostic System. 2021 IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference (BioCAS). IEEE, 2021, pp. 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Perera, S.; Adhikari, S.; Yilmaz, A. Pocformer: A lightweight transformer architecture for detection of COVID-19 using point of care ultrasound. 2021 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP). IEEE, 2021, pp. 195–199. [CrossRef]
- Karar, M.E.; Shouman, M.A.; Chalopin, C. Adversarial neural network classifiers for COVID-19 diagnosis in ultrasound images. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2021, pp. 1683–1697. [CrossRef]
- Mateu, M.; Montiel, J.O.; Escalante-Ramírez, B. COVID-19 detection from lung ultrasound images. Optics, Photonics and Digital Technologies for Imaging Applications VII. SPIE, 2022, Vol. 12138, pp. 75–83. [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, G.; Hossain, M.S. COVID-19 and non-COVID-19 classification using multi-layers fusion from lung ultrasound images. Information Fusion 2021, 72, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adedigba, A.P.; Adeshina, S.A. Deep Learning-based Classification of COVID-19 Lung Ultrasound for Tele-operative Robot-assisted diagnosis. 2021 1st International Conference on Multidisciplinary Engineering and Applied Science (ICMEAS). IEEE, 2021, pp. 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.A.; Amir-Khalili, A.; Hamarneh, G.; Abugharbieh, R. Segmentation-free kidney localization and volume estimation using aggregated orthogonal decision CNNs. International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Springer, 2017, pp. 612–620. [CrossRef]
- Momeny, M.; Neshat, A.A.; Hussain, M.A.; Kia, S.; Marhamati, M.; Jahanbakhshi, A.; Hamarneh, G. Learning-to-augment strategy using noisy and denoised data: Improving generalizability of deep CNN for the detection of COVID-19 in X-ray images. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 136, 104704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.K.; Bhardwaj, A.; Shukla, A. A Review on Despeckling Filters in Ultrasound Images for Speckle Noise Reduction. 2021 International Conference on Advance Computing and Innovative Technologies in Engineering (ICACITE). IEEE, 2021, pp. 973–978. [CrossRef]
- de Araujo, A.F.; Constantinou, C.E.; Tavares, J.M.R. Smoothing of ultrasound images using a new selective average filter. Expert Syst. Appl. 2016, 60, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.A.; Anas, E.M.A.; Alam, S.K.; Lee, S.Y.; Hasan, M.K. Direct and gradient-based average strain estimation by using weighted nearest neighbor cross-correlation peaks. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2012, 59, 1713–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, M.A.; Shourov, R.M.; Khan, S.N. Towards real-time 3D geometric nonlinear diffusion filter and its application to CT and MR imaging. 2015 18th International Conference on Computer and Information Technology (ICCIT). IEEE, 2015, pp. 462–467. [CrossRef]
- Sadik, F.; Dastider, A.G.; Fattah, S.A. SpecMEn-DL: Spectral mask enhancement with deep learning models to predict COVID-19 from lung ultrasound videos. Health Inf. Sci. Syst. 2021, 9, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Escobar, J.; Ordóñez-Guillén, N.E.; Villarreal-Reyes, S.; Galaviz-Mosqueda, A.; Kober, V.; Rivera-Rodriguez, R.; Lozano Rizk, J.E. Deep-learning based detection of COVID-19 using lung ultrasound imagery. PLOS ONE 2021, 16, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jumaili, S.; Duru, A.D.; Uçan, O.N. COVID-19 Ultrasound image classification using SVM based on kernels deduced from Convolutional neural network. 2021 5th International Symposium on Multidisciplinary Studies and Innovative Technologies (ISMSIT). IEEE, 2021, pp. 429–433. [CrossRef]
- Barros, B.; Lacerda, P.; Albuquerque, C.; Conci, A. Pulmonary COVID-19: Learning Spatiotemporal Features Combining CNN and LSTM Networks for Lung Ultrasound Video Classification. Sensors 2021, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Zogbi, L.; Singh, V.; Teixeira, B.; Ahuja, A.; Bagherzadeh, P.S.; Kapoor, A.; Saeidi, H.; Fleiter, T.; Krieger, A. Autonomous Robotic Point-of-Care Ultrasound Imaging for Monitoring of COVID-19-Induced Pulmonary Diseases. Front. Robot. AI 2021, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, A.; Bilbao, A.; Ruby, L.; Rominger, M.B.; López-De-Ipiña, D.; Dahl, J.; ElKaffas, A.; Sanabria, S.J. Lung ultrasound for point-of-care COVID-19 pneumonia stratification: Computer-aided diagnostics in a smartphone. First experiences classifying semiology from public datasets. 2020 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS), 2020, pp. 1–4. [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, N.; Dayal, A.; Cenkeramaddi, L.R.; Yalavarthy, P.K. Mini-COVIDNet: Efficient Lightweight Deep Neural Network for Ultrasound Based Point-of-Care Detection of COVID-19. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2021, 68, 2023–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, H.; Ebadi, A.; Song, J.; Xi, P.; Wong, A. COVID-Net UV: An End-to-End Spatio-Temporal Deep Neural Network Architecture for Automated Diagnosis of COVID-19 Infection from Ultrasound Videos. Arxiv Prepr. Arxiv:2205.08932 2022. [CrossRef]
- Born, J.; Wiedemann, N.; Brändle, G.; Buhre, C.; Rieck, B.; Borgwardt, K.M. Accelerating COVID-19 Differential Diagnosis with Explainable Ultrasound Image Analysis. CoRR 2020, abs/2009.06116.
- Hou, D.; Hou, R.; Hou, J. Interpretable Saab Subspace Network for COVID-19 Lung Ultrasound Screening. 2020 11th IEEE Annual Ubiquitous Computing, Electronics & Mobile Communication Conference (UEMCON), 2020, pp. 0393–0398. [CrossRef]
- Khan, U.; Mento, F.; Giacomaz, L.N.; Trevisan, R.; Smargiassi, A.; Inchingolo, R.; Perrone, T.; Demi, L. Deep Learning-Based Classification of Reduced Lung Ultrasound Data From COVID-19 Patients. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2022, 69, 1661–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLean, A.; Abbasi, S.; Ebadi, A.; Zhao, A.; Pavlova, M.; Gunraj, H.; Xi, P.; Kohli, S.; Wong, A. Covid-net us: A tailored, highly efficient, self-attention deep convolutional neural network design for detection of COVID-19 patient cases from point-of-care ultrasound imaging. In Domain Adaptation and Representation Transfer, and Affordable Healthcare and AI for Resource Diverse Global Health; Springer, 2021; pp. 191–202. [CrossRef]
- MacLean, A.; Ebadi, A.; Florea, A.; XI, P.; Wong, A. An Initial Study into the Feasibility of Deep Learning-Based COVID-19 Severity Classification using Point-of-Care Ultrasound Imaging. J. Comput. Vis. Imaging Syst. 2021, 7, 31–33. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, E.Z.; Florea, A.; Wong, A. COVID-Net US-X: Enhanced Deep Neural Network for Detection of COVID-19 Patient Cases from Convex Ultrasound Imaging Through Extended Linear-Convex Ultrasound Augmentation Learning, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Martinez Redondo, J.; Comas Rodriguez, C.; Pujol Salud, J.; Crespo Pons, M.; Garcia Serrano, C.; Ortega Bravo, M.; Palacin Peruga, J.M. Higher accuracy of lung ultrasound over chest X-ray for early diagnosis of COVID-19 pneumonia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| 1 | |
| 2 | |
| 3 | |
| 4 |
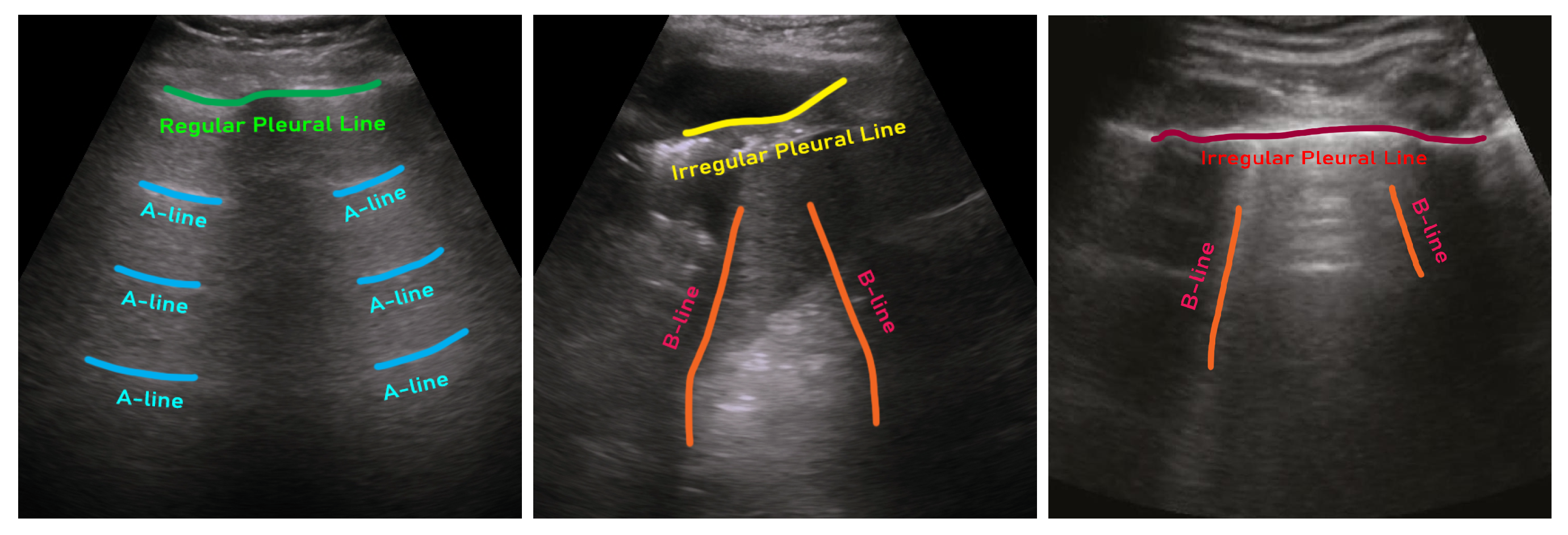
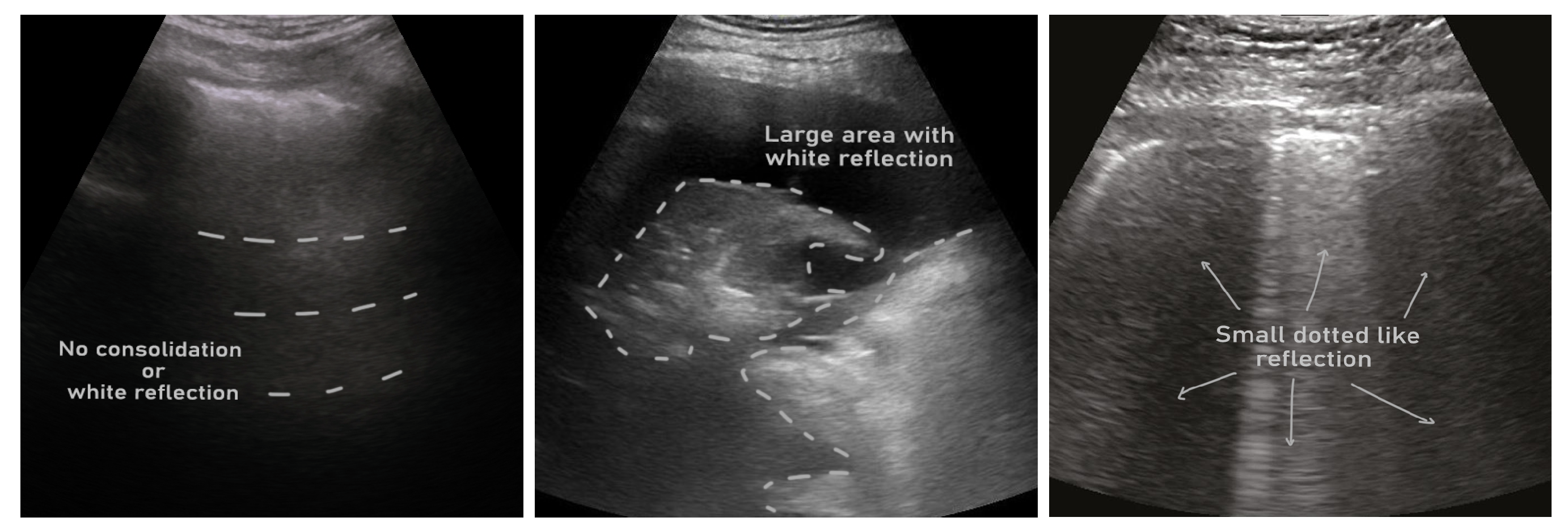
| Sl. | Dataset | Year | Number of Samples | Class Distribution | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
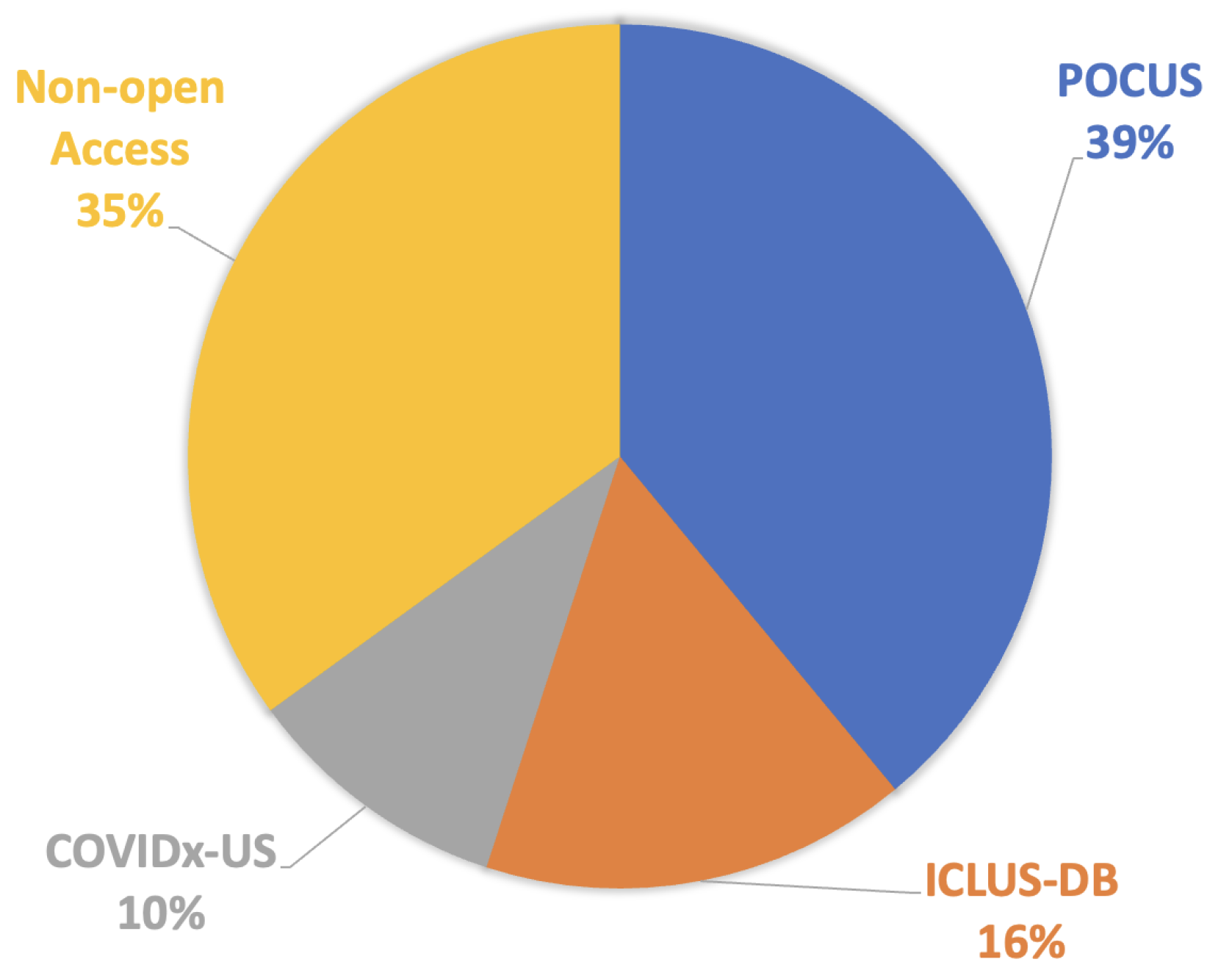
| 1 | POCUS | 2020 | (216 patients) 202 videos 59 images |
COVID-19 (35%) Bacterial Pneumonia (28%) Viral Pneumonia (2%) Healthy (35%) |
Link1 |
| 2 | ICLUS-DB | 2020 | (35 patients) 277 videos 58,924 frames |
Score 0: Continuous A-line (34%) Score 1: Alteration in A-line (24%) Score 2: Small consolidation (32%) Score 3: Large consolidation (10%) |
Link2 |
| 3 | COVIDx-US | 2021 | 242 videos 29,651 images |
COVID-19 (29%) CAP (20%) non-pneumonia diseases (39%) Healthy (12%) |
Link3 |
| Sl. | Dataset | Year | N | Tr/Va/Te | Classes | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | London Health Sciences Centre’s 2 tertiary hospitals (Canada) [38] |
2020 | (243 patients) 600 videos; 121,381 frames |
∼80/20 | COVID, Non-COVID, Hydrostatic Pulmonary Edema |
- |
| 2 | ULTRACOV (Ultrasound in Coronavirus disease) [39] |
2022 | (28 COVID-19 patients) 3 sec video each |
- | A-Lines, B-Lines, consolidations, and pleural effusions |
Available upon request |
| 3 | Huoshenshan Hospital (Wuhan, China) [40] |
2021 | (31 patients) 1,527 images |
- | Normal, septal syndrome, interstitial-alveolar syndrome, white lung |
Source Link2 |
| 4 | Royal Melbourne Hospital (Australia) [35] |
2022 | (9 patients) 27 videos; 3,827 frames |
- | Normal, consolidation/collapse | Available upon request |
| 5 | Ultrasound lung data [34] |
2021 | (300 patients) 1530 videos; 287,549 frames |
80/20 | A-line artifacts, B-line artifacts, presence of consolidation/pleural effusion |
- |
| 6 | Huoshenshan Hospital (Wuhan, China) [41] |
2022 | (31 patients); 2,062 images | - | Normal, septal syndrome, interstitial-alveolar syndrome, white lung |
Source Link3 |
| 7 | Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo’s Emergency Department (Pavia, Italy) [42] |
2021 | (450 patients) 2,908 frames |
75/15/10 | A-lines with two B-lines, slightly irregular pleural line, artefacts in 50% of the pleura, damaged pleural line, visible consolidated areas, damaged pleura/irregular tissue |
- |
| 8 | Third People’s Hospital of Shenzhen (China) [48] |
2020 | (71 COVID-19 patients) 678 videos; 6,836 images |
- | A-line, B-line, pleural lesion, pleural effusion |
- |
| 9 | Fondazione Policlinico Universitario Agostino Gemelli (Rome, Italy), Fondazione Policlinico San Matteo (Pavia, Italy) [44] |
2021 | (82 patients) 1,488 videos; 314,879 frames |
- | 4 severity levels [24] |
- |
| 10 | CHUV (Lausanne, Switzerland) [37] |
2020 | (193 patients) 1,265 videos; 3,455 images |
80/20 | True (experts’ approval), False (experts’ disapproval) |
- |
| 11 | Various online sources [49] |
2022 | 792 images | - | COVID-19, healthy | - |
| 12 | Spain, India [36] |
2021 | (10 subjects) 400 videos, 5,000 images |
- | A-lines, lack of A-lines, appearance of B-lines, confluent appearance of B-lines, appearance of C-lines |
Available upon request |
| 13 | Private clinics (Lima, Peru) [50] |
2021 | 1,500 images | - | Healthy, COVID-19 | Available upon request |
| 14 | BresciaMed (Brescia, Italy), Valle del Serchio General Hospital (Lucca, Italy), Fondazione Policlinico Universitario A. Gemelli IRCCS (Rome, Italy), Fondazione Policlinico Universitario San Matteo IRCCS (Pavia, Italy), and Tione General Hospital (Tione, Italy) [45] |
2021 | (32 patients) 203 videos; 1,863 frames |
90/10 | Healthy, indentation of pleural line, discontinuity of the pleural line, white lung |
- |
| 15 | Beijing Ditan Hospital (Beijing, China) [43] |
2021 | (27 COVID-19 patients) 13 moderate, 7 severe, 7 critical |
- | Severe, non-severe | - |
| 16 | Cancer Center of Union Hospital, West of Union Hospital, Jianghan Cabin Hospital, Jingkai Cabin Hospital, Leishenshan Hospital [21] |
2021 | (313 COVID-19 patients) 10 second video from each |
- | Normal, presence of 3-5 B-lines, ≥6 B-lines or irregular pleura line, fused B-lines or thickening pleura line, consolidation |
- |
| Sl. | Studies | AI Methods | CM | DL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Adedigba and Adeshina [59] | SqueezeNet, MobileNetV2 | ✗ | ✓ |
| 2 | Al-Jumaili et al. [68] | ResNet-18, RestNet-50, NASNetMobile, GoogleNet, SVM | ✓ | ✓ |
| 3 | Al-Zogbi et al. [70] | DenseNet | ✗ | ✓ |
| 4 | Almeida et al. [71] | MobileNet | ✗ | ✓ |
| 5 | Arntfield et al. [38] | Xception | ✗ | ✓ |
| 6 | Awasthi et al. [72] | MiniCOVIDNet | ✗ | ✓ |
| 7 | Azimi et al. [73] | InceptionV3, RNN | ✗ | ✓ |
| 8 | Barros et al. [69] | Xception-LSTM | ✗ | ✓ |
| 9 | Born et al. [12] | VGG-16 | ✗ | ✓ |
| 10 | Born et al. [74] | VGG-16 | ✗ | ✓ |
| 11 | Born et al. [13] | VGG-16 | ✗ | ✓ |
| 12 | Carrer et al. [16] | Hidden Markov Model, Viterbi Algorithm, SVM | ✓ | ✗ |
| 13 | Che et al. [17] | Multi-scale Residual CNN | ✗ | ✓ |
| 14 | Chen et al. [40] | 2-layer NN, SVM, Decision tree | ✓ | ✓ |
| 15 | Diaz-Escobar et al. [67] | InceptionV3, VGG-19, ResNet-50, Xception | ✗ | ✓ |
| 16 | Dastider et al. [18] | Autoencoder-based Hybrid CNN-LSTM | ✗ | ✓ |
| 17 | Durrani et al. [35] | Reg-STN | ✗ | ✓ |
| 18 | Ebadi et al. [52] | Kinetics-I3D | ✗ | ✓ |
| 19 | Frank et al. [19] | ResNet-18, MobileNetV2, DeepLabV3++ | ✗ | ✓ |
| 20 | Gare et al. [15] | Reverse Transfer Learning on UNet | ✗ | ✓ |
| 21 | Hou et al. [75] | Saab transform-based SSL, CNN | ✗ | ✓ |
| 22 | Huang et al. [41] | Non-local channel attention ResNet | ✗ | ✓ |
| 23 | Karar et al. [53] | MobileNet, ShuffleNet, MENet, MnasNet | ✗ | ✓ |
| 24 | Karar et al. [56] | A semi-supervised GAN, a modified AC-GAN | ✗ | ✓ |
| 25 | Karnes et al. [54] | Few-shot learning using MobileNet | ✗ | ✓ |
| 26 | Khan et al. [76] | CNN | ✗ | ✓ |
| 27 | La Salvia et al. [42] | ResNet-18, ResNet-50 | ✗ | ✓ |
| 28 | Liu et al. [48] | Multi-symptom multi-label (MSML) network | ✗ | ✓ |
| 29 | MacLean et al. [77] | COVID-Net US | ✗ | ✓ |
| 30 | MacLean et al. [78] | ResNet | ✗ | ✓ |
| 31 | Mento et al. [44] | STN, U-Net, DeepLabV3+ | ✗ | ✓ |
| 32 | Muhammad and Hossain [58] | CNN | ✗ | ✓ |
| 33 | Nabalamba [49] | VGG-16, VGG-19, ResNet | ✗ | ✓ |
| 34 | Panicker et al. [36] | LUSNet (a U-Net like network for ultrasound images) | ✗ | ✓ |
| 35 | Perera et al. [55] | Transformer | ✗ | ✓ |
| 36 | Quentin Muller et al. [37] | ResNet-18 | ✗ | ✓ |
| 37 | Roshankhah et al. [45] | U-Net | ✗ | ✓ |
| 38 | Roy et al. [20] | STN, U-Net, U-Net++, DeepLabv3, Model Genesis | ✗ | ✓ |
| 39 | Sadik et al. [66] | DenseNet-201, ResNet-152V2, Xception, VGG-19, NasNetMobile | ✗ | ✓ |
| 40 | Wang et al. [43] | SVM | ✓ | ✗ |
| 41 | Xue et al. [21] | U-Net | ✗ | ✓ |
| 42 | Zeng et al. [79] | COVID-Net US-X | ✗ | ✓ |
| Studies | AI | Loss | Results | Cross-validation | Augmentation/ | Prediction | Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| models | Pre-processing | Classes | |||||
| Al-Jumaili et al. [68] | ResNet-18, RestNet-50, NASNetMobile, GoogleNet, SVM |
Categorical cross-entropy | Accuracy: 99% | k=5 | ✗ | COVID-19, CAP, Healthy | ✗ |
| Al-Zogbi et al. [70] | DenseNet | L1 | Mean Euclidean error 14.8±7.0 mm | ✗ | ✗ | - | ✗ |
| Almeida et al. [71] | MobileNet | Categorical cross-entropy | Accuracy: 95-100% | ✗ | ✗ | Abnornal, B-lines, Mild B-lines, Severe B-lines, Consolidations, Pleural thickening |
✗ |
| Awasthi et al. [72] | Modified MobileNet, CNN, and other lightweight models |
Focal loss | Accuracy 83.2% | k=5 | ✗ | COVID-19, CAP, Healthy | ✗ |
| Barros et al. [69] | POCOVID-Net, DenseNet, ResNet, NASNet, Xception-LSTM |
Categorical cross-entropy |
Accuracy: 93%, Sensitivity: 97% |
k=5 | ✗ | COVID-19, Bacterial Pneumonia, Healthy |
Availablea |
| Born et al. [12] | POCOVID-Net | Categorical cross-entropy |
AUC: 0.94, Accuracy: 0.89, Sensitivity: 0.96, Specificity: 0.79, F1-score: 0.92 |
k=5 | Rotations of up to 10°; Horizontal and vertical flipping; Shifting up to 10% of the image height or width |
COVID-19, CAP, Healthy | ✗ |
| Born et al. [74] | VGG-16 | Categorical cross-entropy |
Sensitivity: 0.98±0.04, specificity: 0.91±0.08 |
k=5 | Horizontal and vertical flips, rotations up to 10° and translations of up to 10% |
COVID-19, CAP, Healthy | ✗ |
| Born et al. [13] | Frame based: VGG-16 Video-based: Models Genesis |
Categorical cross-entropy |
Sensitivity: 0.90±0.08, specificity: 0.96±0.04 |
k=5 | Resizing to 224×224 pixels; Horizontal and vertical flips; Rotation up to 10°; Translations of up to 10% |
COVID-19, CAP, Healthy | Availableb |
| Diaz-Escobar et al. [67] | InceptionV3, ResNet-50, VGG-19, Xception |
Cross-entropy | Accuracy: 89.1%, ROC-AUC: 97.1% |
k=5 | Rotations (10°), horizontal and vertical flips, shifts (10%), and zoom (zoom range of 20%) |
COVID-19, non-COVID | ✗ |
| Gare et al. [15] | U-Net (reverse-transfer learning; segmentation to classification) |
Cross-entropy | mIoU: 0.957±0.002, Accuracy: 0.849, Precision: 0.885, Recall: 0.925, F1-score: 0.897 |
k=3 | Left-to-right flipping; Scaling grey image pixels; |
COVID-19, CAP, Healthy | ✗ |
| Hou et al. [75] | Saab transform based successive subspace CNN model |
Categorical cross-entropy |
Accuracy: 0.96 | ✗ | Saab transformation | A-line, B-line, Consolidation |
✗ |
| Karar et al. [53] | MobileNets, ShuffleNets, MENet, MnasNet |
Categorical cross-entropy |
Accuracy: 99% | ✓ | Grayscale conversion | COVID-19, Bacterial Pneumonia, Healthy |
✗ |
| Karar et al. [56] | A semi-supervised GAN, and a modified AC-GAN with auxiliary classifier |
Min-Max loss: special form of cross-entropy |
Accuracy: 91.22% | ✓ | Grayscale conversion | COVID-19, CAP, Healthy | ✗ |
| Karnes et al. [54] | Few-shot learning (FSL) visual classification algorithm |
Mahalanobis distances | ROC-AUC > 85% | k=10 | ✗ | COVID-19, CAP, Healthy | Available upon request |
| Muhammad and Hossain [58] | CNN | Categorical cross-entropy |
Accuracy 91.8%, Precision 92.5%, Recall 93.2% |
k=5 | Reflection around x- and y-axes; Rotation by [-20°, +20°]; Scaling by a factor [0.8, 1.2] |
COVID-19, CAP, Healthy | ✗ |
| Sadik et al. [66] | DenseNet-201, ResNet-152V2, Xception, VGG-19, NasNetMobile |
Categorical cross-entropy |
Accuracy: 0.906 (with SpecMEn), F1-score: 0.90 |
✓ | Contrast-Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization |
COVID-19, CAP, Healthy | ✗ |
| Perera et al. [55] | Transformer | Categorical cross-entropy |
Accuracy: 93.9% | ✓ | ✗ | COVID-19, CAP, Healthy | ✗ |
| a https://github.com/bmandelbrot/pulmonary-covid19 | |||||||
| b https://github.com/BorgwardtLab/covid19_ultrasound | |||||||
| Studies | AI | Loss | Results | Cross-validation | Augmentation/ | Prediction | Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| models | pre-processing | Classes | |||||
| Carrer et al. [16] | HMM, VA, SVM | ✗ | Accuracy: 88% (convex probe) 94% (linear probe) |
k=10 | ✗ | Severity Score (0, 1, 2, 3) |
✗ |
| Che et al. [17] | Multi-scale residual CNN | Cross-entropy | Accuracy: 95.11%, F1-score: 96.70% |
k=5 | Generation of local phase filtered and radial symmetry transformed images |
COVID-19, non-COVID |
✗ |
| Dastider et al. [18] | Autoencoder-based Hybrid CNN-LSTM |
Categorical cross-entropy |
Accuracy: 67.7% (convex probe) 79.1% (linear probe) |
k=5 | Rotation, horizontal and vertical shift, scaling, horizontal and vertical flips |
Severity Score (0, 1, 2, 3) |
Availablea |
| Frank et al. [19] | ResNet-18, ResNet-101, VGG-16, MobileNetV2, MobileNetV3, DeepLabV3++ |
SORD, cross-entropy |
Accuracy: 93%, F1-Score: 68.8% |
✗ | Affine transformations, rotation, scaling, horizontal flipping, random jittering |
Severity Score (0, 1, 2, 3) |
✗ |
| Roy et al. [20] | Spatial Transformer Network (STN), U-Net, U-Net++, DeepLabV3, Model Genesis |
SORD, cross entropy | Accuracy: 96%, F1-score: 61±12%, Precision: 70±19%, Recall: 60±7% |
k=5 | ✓ | Severity Score (0, 1, 2, 3) |
Availableb |
| Khan et al. [76] | Pre-trained CNN from [20] |
SORD, cross-entropy | Agreement-based scoring (82.3%) |
✗ | ✗ | Severity Score (0, 1, 2, 3) |
✗ |
| a https://github.com/ankangd/HybridCovidLUS | |||||||
| b https://github.com/mhugTrento/DL4covidUltrasound | |||||||
| Studies | AI | Loss | Results | Cross-validation | Augmentation/ | Prediction | Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| models | pre-processing | Classes | |||||
| Adedigba and Adeshina [59] | SqueezeNet, MobileNetV2 |
Categorical cross-entropy |
Accuracy: 99.74%, Precision: 99.58%, Recall: 99.39% |
✗ | Rotation, Gaussian blurring, random zoom, random lighting, random warp |
COVID-19, CAP, Normal, Other |
✗ |
| Azimi et al. [73] | InceptionV3, RNN | Cross-entropy | Accuracy: 94.44% | ✗ | Padding | Positive (COVID-19), Negative (non-COVID-19) |
Availablea |
| MacLean et al. [77] | COVID-Net US | Cross-entropy | ROC-AUC: 0.98 | ✗ | ✗ | Positive (COVID-19) Negative (non-COVID-19) |
Availableb |
| MacLean et al. [78] | ResNet | Categorical cross-entropy |
Accuracy: 0.692 | ✗ | ✗ | Lung ultrasound severity score (0, 1, 2, 3) |
✗ |
| Zeng et al. [79] | COVID-Net US-X | Cross-entropy | Accuracy: 88.4%, AUC: 93.6% |
✗ | Random projective augmentation |
Positive (COVID-19) Negative (non-COVID-19) |
✗ |
| a https://github.com/lindawangg/COVID-Net | |||||||
| b https://github.com/maclean-alexander/COVID-Net-US/ | |||||||
| Studies | AI | Loss | Results | Cross-validation | Augmentation/ | Prediction | Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| models | pre-processing | Classes | |||||
| Arntfield et al. [38] | Xception | Binary Cross Entropy | ROC-AUC: 0.978 | ✗ | Random zooming in/out by ≤10%, horizontal flipping, horizontal stretching/contracting by ≤20%, vertical stretching/contracting (≤5%), and bi-directional rotation by |
Hydrostatic pulmonary edema (HPE), onn-COVID acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), COVID-19 ARDS |
Availablea |
| Chen et al. [40] | 2-layer NN, SVM, Decision Tree |
✗ | Accuracy: 87% | k=5 | Curve-to-linear conversion |
Score 0: Normal, Score 1: Septal syndrome, Score 2: Interstitial-alveolar syndrome, Score 3: White lung syndrome |
✗ |
| Durrani et al. [35] | CNN, Reguralized STN (Reg-STN) |
SORD | Accuracy: 89%, PR-AUC: 73% |
k=10 | Replacing overlays, resizing to 806×550 pixels |
Consolidation present, consolidation absent |
✗ |
| Ebadi et al. [52] | Kinetics-I3D | Focal loss | Accuracy: 90% Precision: 95% |
k=5 | ✗ | A-line (normal), B-line, Consolidation and/or pleural effusion |
✗ |
| Huang et al. [41] | Non-local Channel Attention ResNet |
Cross-entropy | Accuracy: 92.34%, F1-score: 92.05%, Precision: 91.96% Recall: 90.43%, |
✗ | Resizing to 300×300 pixels |
Score 0: normal, Score 1: septal syndrome, Score 2: interstitial-alveolar syndrome, Score 3: white lung syndrome |
Availableb |
| La Salvia et al. [42] | ResNet-18, ResNet-50 | Cross-entropy | F1-score: 98% | ✗ | Geometric, filtering, random centre cropping, and colour transformations |
Severity Score: 0, 0*, 1, 1*, 2, 2*, 3 |
✗ |
| Liu et al. [48] | Multi-symptom multi-label (MSML) network |
Cross-entropy | Accuracy: 100% (with 14.7% data) |
✗ | Random rotation (up to 10 degrees) and horizontal flips |
A-line, B-line, Pleural lesion, Pleural effusion |
✗ |
| Mento et al. [44] | STN, U-Net, DeepLabV3+ | ✗ | Agreement between AI scoring and expert scoring 85.96% |
✗ | ✗ | Expert scores: 0, 1, 2, 3 |
✗ |
| Quentin Muller et al. [37] | ResNet-18 | Cross-entropy | Accuracy (Val): 100% | ✗ | Resizing to 349×256 | Ultrasound frames with (positive) and without (negative) clinical predictive value |
✗ |
| Nabalamba [49] | VGG-16, VGG-19, ResNet | Binary cross-entropy | Accuracy: 98%, Recall: 1, Precision: 96%, F1-score: 97.82%, ROC-AUC: 99.9% |
✗ | Width and height shifting, random zoom within 20%, brightness variations within [0.4, 1.3], rotation up to 10 degrees |
COVID-19, Healthy | ✗ |
| Panicker et al. [36] | LUSNet (U-Net based CNN) | Categorical cross-entropy | Accuracy: 97%, Sensitivity: 93%, Specificity: 98% |
k=5 | Generation of local phase and shadow back scatter product images |
Classes: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 | Availablec |
| Roshankhah et al. [45] | U-Net | Categorical cross-entropy | Accuracy: 95% | ✗ | Randomly cropping and rotating the frames |
Severity Score: 0, 1, 2, 3 |
✗ |
| Wang et al. [43] | SVM | ✗ | ROC-AUC: 0.93, Sensitivity: 0.93, Specificity: 0.85 |
✗ | ✗ | Non-severe, severe | ✗ |
| Xue et al. [21] | UNet (with modality alignment contrastive learning of representation (MA-CLR)) |
Dice, cross-entropy |
Accuracy: 75% (4-level) 87.5% (binary) |
✗ | Affine transformations (translation, rotation, scaling, shearing), reflection, contrast change, Gaussian noise, and Gaussian filtering |
Severity score: 0, 1, 2, 3 |
✗ |
| a https://github.com/bvanberl/covid-us-ml | |||||||
| b https://biohsi.ecnu.edu.cn | |||||||
| c https://github.com/maheshpanickeriitpkd/ALUS | |||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





