Submitted:
14 March 2023
Posted:
14 March 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
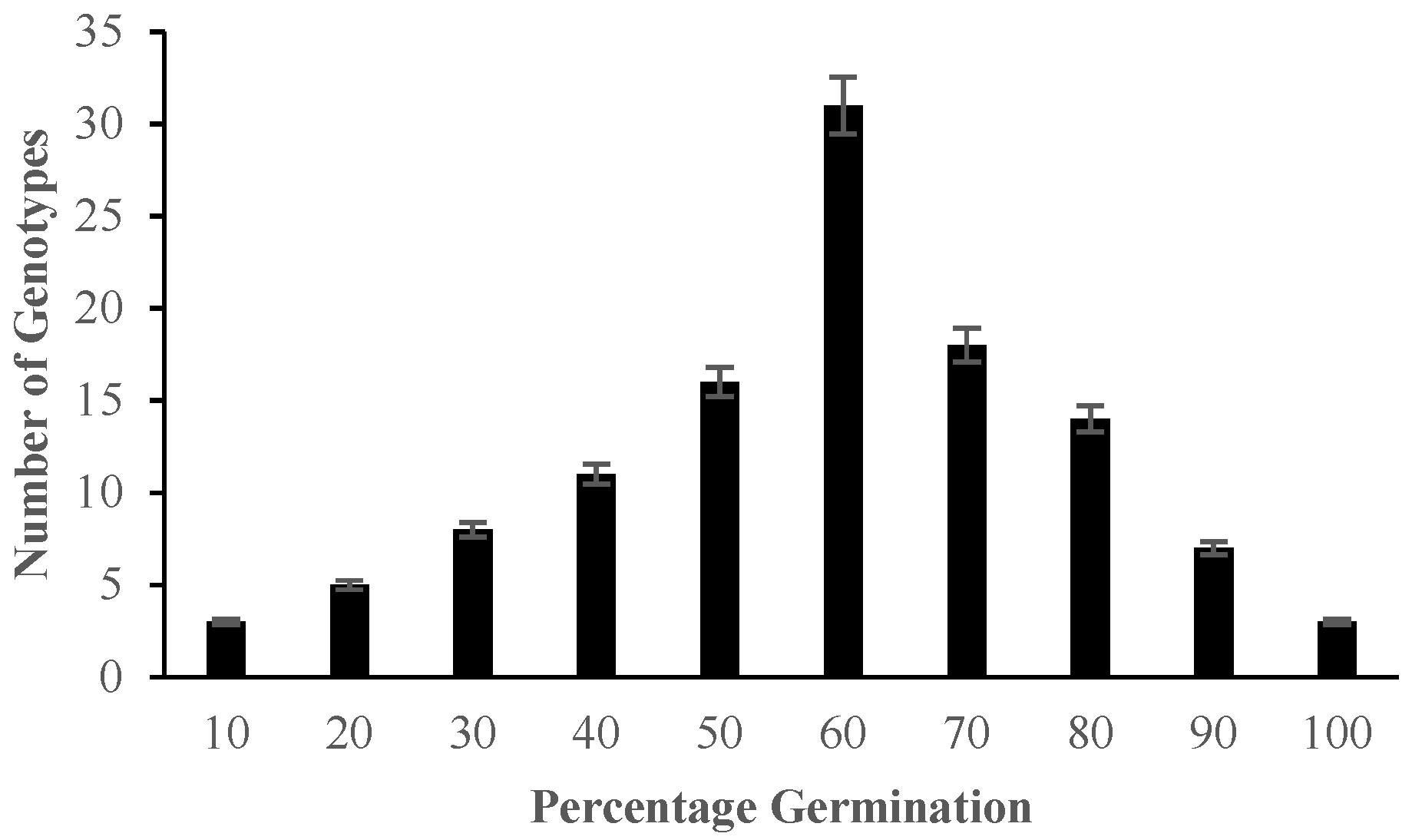
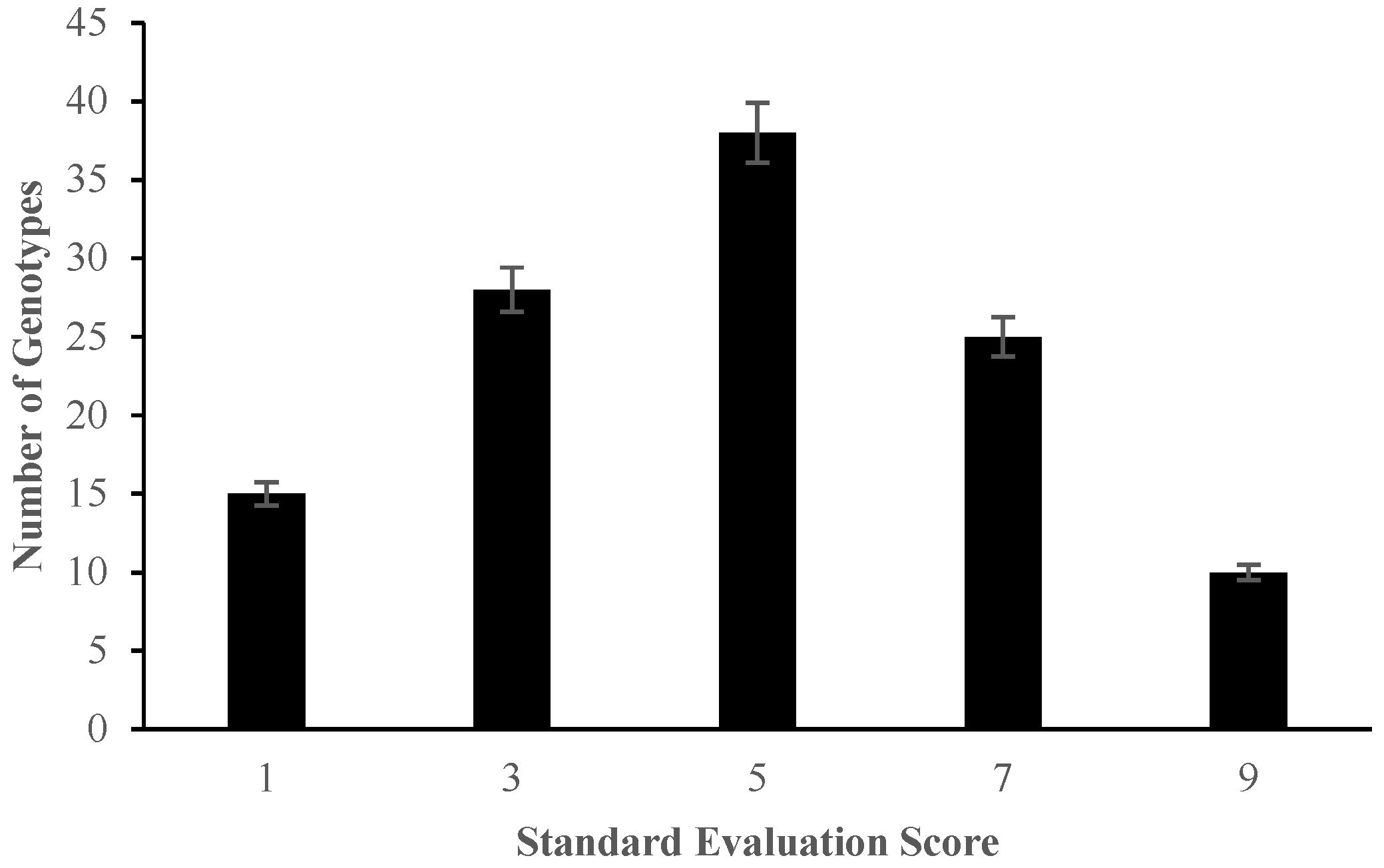
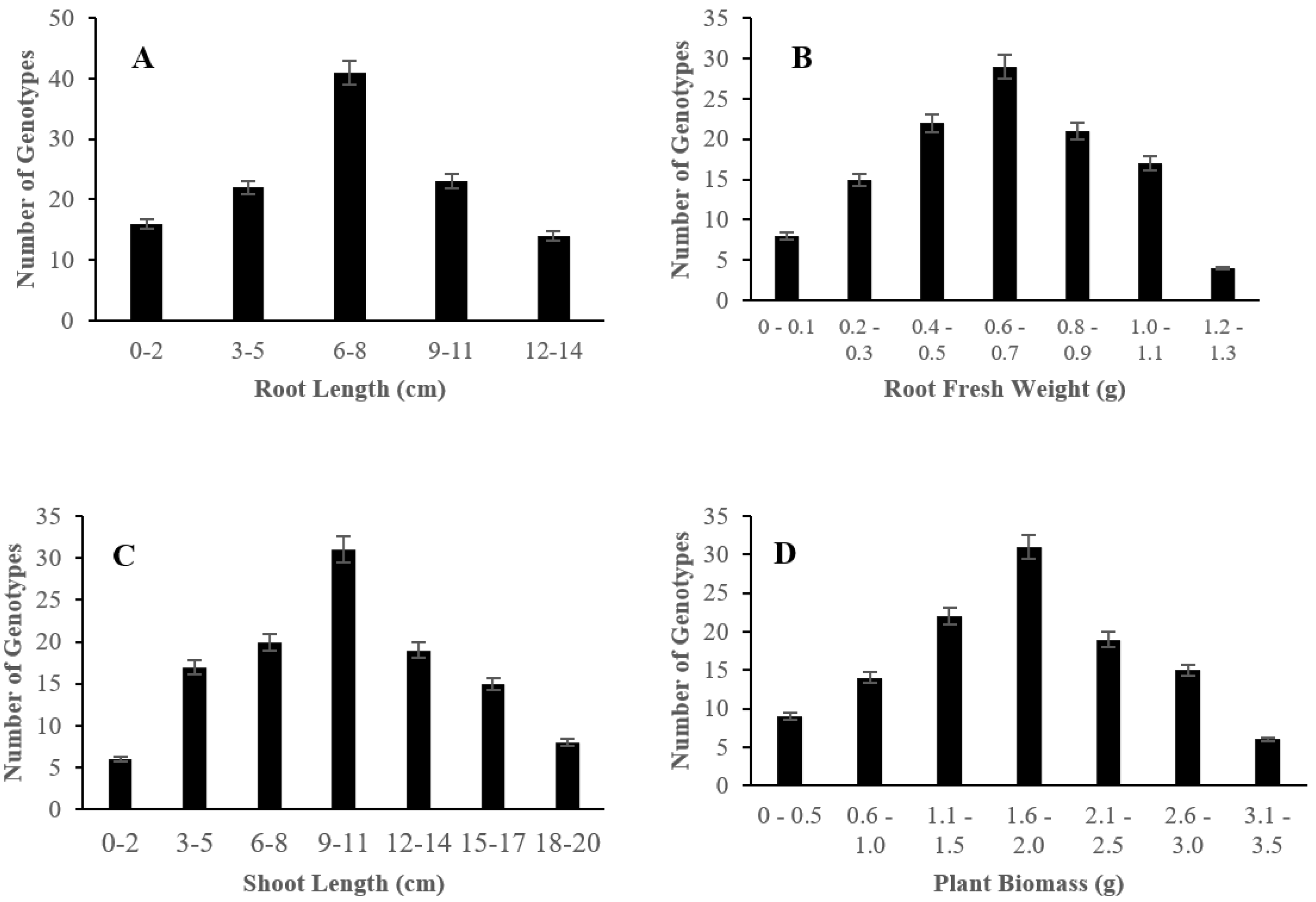
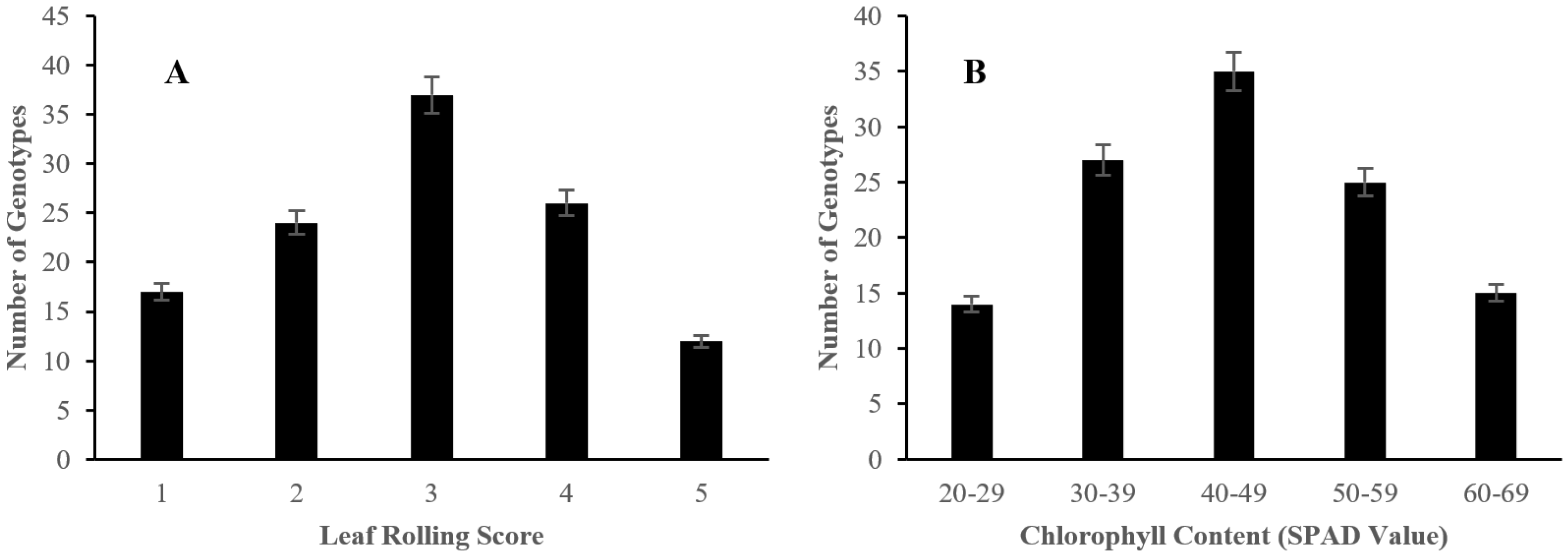
2.1. Morphological Responses of Asian Rice Cultivars to Salt Stress at Seedling and Early Vegetative Stages
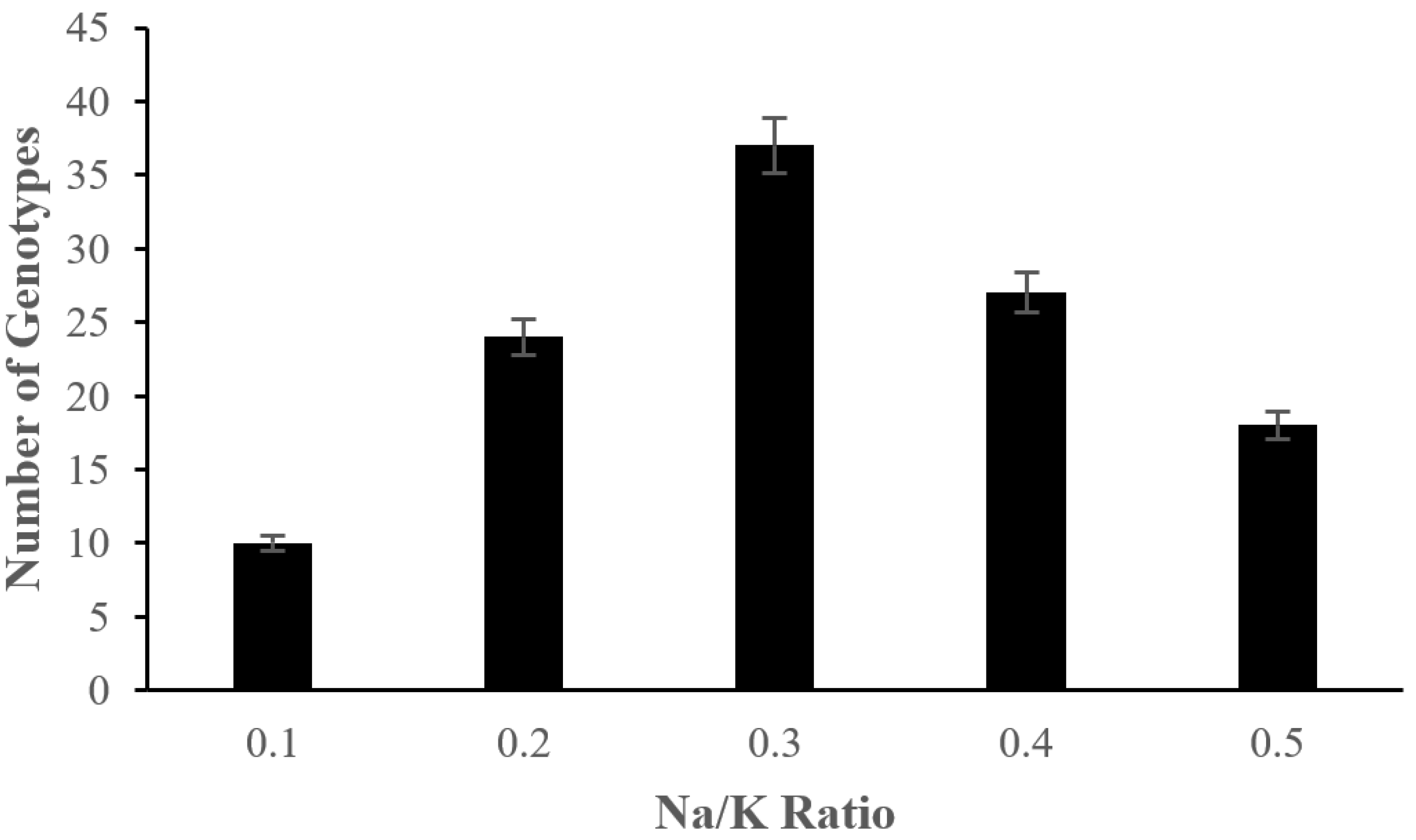
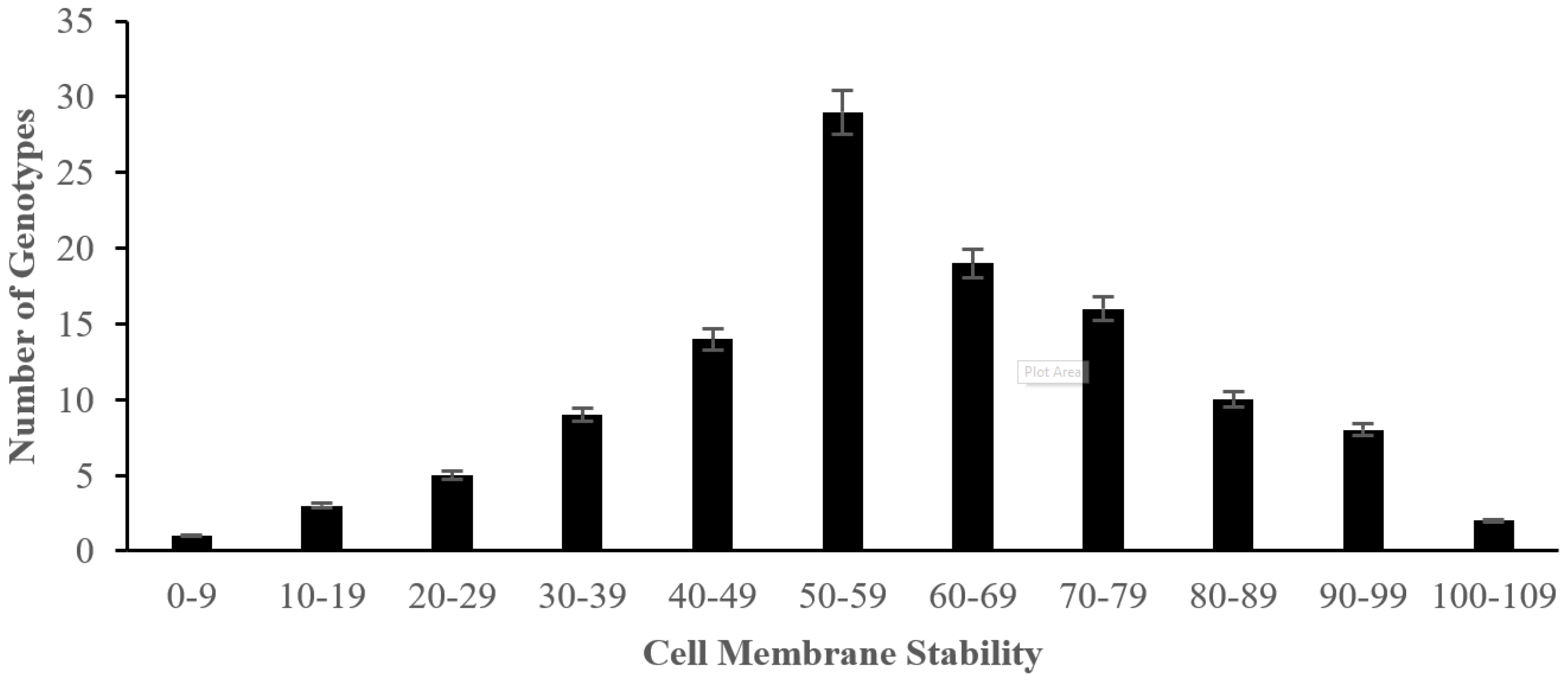
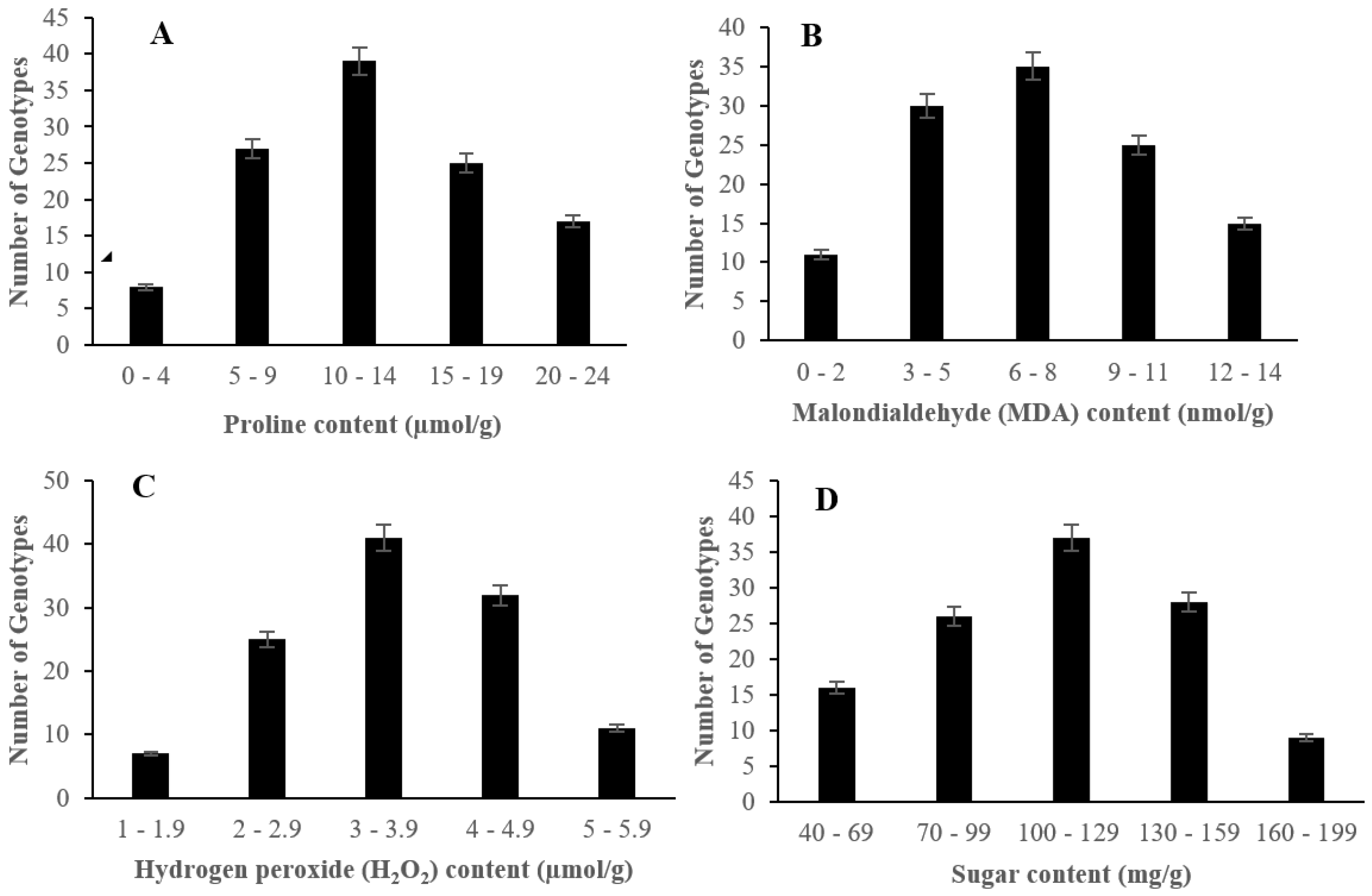
2.2. The Effect of Salinity Stress on Physiological and Biochemical Characteristics of Asian Rice Cultivars at Seedling and Early Vegetative Stages
2.3. Correlation among Morphological, Physiological, and Biochemical Traits under Salt Stress
| SS | PG | RL | RFW | SL | PB | PH | LR | CC | CMS | Na/K | Proline | MDA | H2O2 | Sugar | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
SS PG RL RFW SL PB PH LR CC CMS Na/K Proline MDA H2O2 Sugar |
1 -0.87* -0.91* -0.93* -0.92* -0.85* -0.89* 0.95* -0.87* -0.14 0.92* -0.90* 0.57 0.91* -0.91* |
1 0.61 0.57 0.68 0.73 0.67 0.53 0.56 0.51 -0.47 -0.67 -0.61 -0.73 -0.64 |
1 0.89* 0.83 0.87* 0.88* 0.51 -0.73 0.81 -0.61 -0.58 -0.51 -0.62 -0.64 |
1 0.75 0.91* 0.68 0.42 0.83 0.69 -0.47 -0.53 -0.42 -0.39 -0.54 |
1 0.92* 0.79 0.39 0.74 0.51 -0.68 -0.53 -0.41 -0.36 -0.31 |
1 0.92* 0.41 0.86 0.62 -0.57 -0.41 -0.47 -0.58 -0.64 |
1 0.37 0.79 0.84 -0.62 -0.68 -0.79 -0.61 -0.57 |
1 -0.59 0.68 0.55 0.61 0.69 0.54 0.62 |
1 0.36 -0.27 -0.22 -0.22 -0.27 -3.48 |
1 -0.35 -0.29 -0.41 -0.32 -0.37 |
1 -0.47 0.97* 0.96* -0.51 |
1 -0.39 0.42 0.38 |
1 0.85 0.41 |
1 0.25 |
1 |
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. Salinity Screening at Seedling and Early Vegetative Stage
4.3. Measurement of Morphological, Physiological, and Biochemical Traits
4.3.1. Determination of Percentage Germination and Standard Evaluation Score for Salt Injury
4.3.2. Measurement of Root Length, Root Fresh Weight, Shoot Length, and Plant Biomass
4.3.3. Determination of Leaf Rolling
4.3.4. Analysis of Chlorophyll Content
4.3.5. Measurement of Na/K Ratio
4.3.6. Measurement of Cell Membrane Stability
4.3.7. Measurement of Proline Content
4.3.8. Measurement of Malondialdehyde (MDA) Content
4.3.9. Measurement of Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2) Content
4.3.10. Measurement of Sugar Content
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gopalan, C.; Rama Sastri, B.V.; Balasubramanian, S. Nutritive Value of Indian Foods. National Institute of Nutrition (NIN), ICMR, India 2007.
- Khush, G.S.; Virk, P.S. Rice Breeding: Achievements and Future Strategies. Crop Improv. 2000, 27, 115-144.
- GRiSP. Rice Almanac. Fourth ed. International Rice Research Institute, Los Banos, Philippines 2013.
- Dwiningsih, Y.; Kumar, A.; Thomas, J.; Ruiz, C.; Alkahtani, J.; Al-hashimi, A.; Pereira, A. Identification of Genomic Regions Controlling Chalkiness and Grain Characteristics in a Recombinant Inbred Line Rice Population Based on High-Throughput SNP Markers. Genes 2021, 12, 11, 1690. [CrossRef]
- ANU. Technological Transformation of Productivity, Profitability and Sustainability: Rice. In The First Ten K R Narayanan Orations: Essays by Eminent Persons on the Rapidly Transforming Indian Economy. Australia South Asia Research Centre The Australian National University 2006. http://epress.anu.edu.au/narayanan/mobile_ devices/pr01.html.
- Gregorio, G.B. Tagging Salinity Tolerant Genes in Rice Using Amplified Fragment Length Polymorphism (AFLP). Ph.D. dissertation. University of the Philippines Los Baños College, Laguna, Philippines 1997, 118.
- Abdullah, Z.; Khan, M.A.; Flowers, T.J. Causes of Sterility in Seed Set of Rice under Salinity Stress. J. Agron. Crop. Sci. 2001, 187, 25–32. [CrossRef]
- Dwiningsih, Y. Molecular genetic analysis of drought resistance and productivity traits of rice genotypes. University of Arkansas, Fayetteville, USA. 2020.
- Aref, F.; Rad, H.E. 2012. Physiological Characterization of Rice under Salinity Stress during Vegetative and Reproductive Stages. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 2012, 5, 2578-2586.
- Bhowmik, S.K.; Titov, S.; Islam, M.M.; Siddika, A.; Sultana, S.; Haque, M. Phenotypic and genotypic screening of rice genotypes at seedling stage for salt tolerance. African Journal of Biotechnology 2009, 8, 23, 6490-6494.
- Dwiningsih, Y.; Kumar, A.; Thomas, J.; Yingling, S.; Pereira, A. Molecular genetic analysis of drought resistance and productivity in US rice cultivars. Plant and Animal Genome XXVII Conference (January 12-16, 2019). 2019.
- Bado, S.; Forster, B.P.; Ghanim, A.; Jankowicz-Cieslak, J.; Berthold, G.; Luxiang, L. Protocols for pre-field screening of mutants for salt tolerance in rice, wheat and barley. Springer 2016. [CrossRef]
- Ueda, A.; Yahagi, H.; Fujikawa, Y.; Nagaoka, T.; Esaka, M.; Calcaño, M.; González, M.; Martich, J.; Saneoka, H. Comparative physiological analysis of salinity tolerance in rice. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition 2013, 59, 6, 896-903. [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Khan, Z.I.; Chen, F.; Akhtar, M.; Ahmad, K.; Ejaz, A.; Ashraf, M.A.; Nadeem, M.; Akhtar, S.; Alkahtani, J.; Dwiningsih, Y.; Elshikh, M.S. A study on the contamination assessment, health risk and mobility of two heavy metals in the soil-plants-ruminants system of a typical agricultural region in the semi-arid environment. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2022, 29,14584–14594. [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.S.; Choi, W.Y.; Ko, J.C.; Kim, T.S.; Gregorio, G.B. Salinity tolerance of japonica and indica rice (Oryza sativa L.) at the seedling stage. Planta 2003, 216, 1043–1046. [CrossRef]
- Kordrostami, M.; Rabiei, B.; Kumleh, H. Biochemical, physiological and molecular evaluation of rice cultivars differing in salt tolerance at the seedling stage. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 2017, 23, 3, 529–544. [CrossRef]
- Maqsood, A.; Khan, Z.I.; Ahmad, K.; Akhtar, S.; Ashfaq, A.; Malik, I.S.; Sultana, R.; Nadeem, M.; Alkahtani, J.; Dwiningsih, Y.; Elshikh, M. Quantitative evaluation of zinc metal in meadows and ruminants for health assessment: implications for humans. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2022, 29, 15, 21634–21641. [CrossRef]
- Munns, R.; Tester, M. Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 651–681. [CrossRef]
- Hoang, T.M.L.; Williams, B.; Khanna, H.; Dale, J.; Mundree, S.G. Physiological basis of salt stress tolerance in rice expressing the antiapoptotic gene SfIAP. Funct. Plant Biol. 2014, 41, 1168–1177. [CrossRef]
- Marschner, H. Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants. Academic Press, London. 1995.
- Dwiningsih, Y.; Thomas, J.; Kumar, A.; Gupta, C.; Ruiz, C.; Yingling, S.; Crowley, E.; Pereira, A. Molecular genetic analysis of drought resistance and productivity mechanisms in rice. Plant and Animal Genome XXVIII Conference, January 11-15, 2020.
- Hasegawa, P.M.; Bressan, R.A.; Zhu, J.K.; Bohnert, H.J. Plant cellular and molecular responses to high salinity. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 2000, 51, 463–499.
- Dwiningsih, Y.; Kumar, A.; Thomas, J.; Ruiz, C.; Alkahtani, J.; Baisakh, N.; Pereira, A. Quantitative trait loci and candidate gene identification for chlorophyll content in RIL rice population under drought conditions. Indonesian Journal of Natural Pigments 2021, 3, 2, 54-64. [CrossRef]
- Sahi, C.; Singh, A.; Kumar, K. Salt stress response in rice: genetics, molecular biology and comparative genomics. Funct. Integr. Genomics 2006, 6, 263–284.
- Kavitha, P.G.; Miller, A.J.; Mathew, M.K.; Maathuis, F.J.M. Rice cultivars with differing salt tolerance contain similar cation channels in their root cells. Journal of Experimental Botany 2012, 63, 8, 3289–3296. [CrossRef]
- Hoang, T.; Tran, T.; Nguyen, T.; Williams, B.; Wurm, P.; Bellairs, S.; Mundree. Improvement of Salinity Stress Tolerance in Rice: Challenges and Opportunities. Agronomy 2016, 6, 54. [CrossRef]
- Sitrarasi, R.; Nallal, U.M.; Razia, M.; Chung, W.J.; Shim, J.; Chandrasekaran, M.; Dwiningsih, Y.; Rasheed, R.A.; Alkahtani, J.; Elshikh, M.S.; Debnath, O.; Ravindran, B. Inhibition of multi-drug resistant microbial pathogens using an ecofriendly root extract of Furcraea foetida silver nanoparticles. Journal of King Saud University-Science 2022, 34, 2, 101794. [CrossRef]
- De Leon, T.B.; Linscombe, S.; Gregorio, G.; Subudhi, P.K. Genetic variation in Southern USA rice genotypes for seedling salinity tolerance. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 374. [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi-Nejad, G.; Singh, R.K.; Arzanic, A.; Rezaiec, A.M.; Sabourid, H.; Gregorio, G.B. Evaluation of Salinity Tolerance in Rice Genotypes. Int. J. Plant Prod. 2010, 4, 199–207.
- Morales, S.G.; Tellez, L.I.T.; Merino, F.C.G.; Caldana, C.; Victoria, D.E.; Cabrera, B.E.H. Growth, Photosynthetic Activity, and Potassium and Sodium Concentration in Rice Plants under Salt Stress. Acta Sci. Agron. 2012, 34, 317-324. [CrossRef]
- Dwiningsih, Y.; Thomas, J.; Kumar, A.; Gupta, C.; Gill, N.; Ruiz, C.; Alkahtani, J.; Baisakh, N.; Pereira A. Identification of QTLs and Candidate Loci Associated with Drought-Related Traits of the K/Z RIL Rice Population. Research Square 2022. [CrossRef]
- Asch, F.; Dingkuhn, M.; Dorffling, K.; Miezan, K. Leaf K/Na ratio predicts salinity induced yield loss in irrigated rice. Euphytica 2000, 113, 109–118. [CrossRef]
- Yeo, A.R.; Flowers, T.J. Salinity resistance in rice (Oryza Sativa L.) and a pyramiding approach to breeding varieties for saline soils. Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 1986, 13, 161–173. [CrossRef]
- Munns, R.; James, R.A.; Lauchli, A. Approaches to increasing the salt tolerance of wheat and other cereals. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 1025–1043. [CrossRef]
- Dwiningsih, Y.; Alkahtani, J. Genetics, Biochemistry and Biophysical Analysis of Anthocyanin in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Advance Sustainable Science, Engineering and Technology (ASSET) 2022, 4, 1. [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.J.; Azevedo, V.; Maroco, J.; Oliveira, M.M.; Santos, A.P. Salt Tolerant and Sensitive Rice Varieties Display Differential Methylome Flexibility under Salt Stress. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, 5, e0124060. [CrossRef]
- Flowers, T.J. Improving crop salt tolerance. J. Exp. Bot. 2004, 55, 307–319. [CrossRef]
- Koyama, M.L.; Levesley, A.; Koebner, R.; Flowers, T.J.; Yeo, A.R. Quantitative trait loci for component physiological traits determining salt tolerance in rice. Plant Physiol. 2001, 125, 406–422. [CrossRef]
- Gregorio, G.B.; Senadhira, D. Genetic analysis of salinity tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 1993, 86, 333–338. [CrossRef]
- Bashir, S.; Gulshan, A.B.; Iqbal, J.; Husain, A.; Alwahibi, M.S.; Alkahtani, J.; Dwiningsih, Y.; Bakhsh, A.; Ahmed, N.; Khan, M.J.; Ibrahim, M.; Diao, Z.H. Comparative role of animal manure and vegetable waste induced compost for polluted soil restoration and maize growth. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, 2021, 28, 4, 2534-2539. [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Yeasmin, L.; Gantait, S.; Goswami, R.; Chakraborty, S. Screening of rice landraces for salinity tolerance at seedling stage through morphological and molecular markers. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 2014, 20, 4, 411–423. [CrossRef]
- Flowers, T.J.; Yeo, A.R. Breeding for salinity resistance in crop plants: where next? Aust J Plant Physiol. 1995, 22, 875–884.
- Ali, M.H.; Khan, M.I.; Bashir, S.; Azam, M.; Naveed, M.; Qadri, R.; Bashir, S.; Mehmood, F.; Shoukat, M.A.; Li, Y.; Alkahtani, J.; Elshikh, M.S.; Dwiningsih, Y. Biochar and Bacillus sp. MN54 Assisted Phytoremediation of Diesel and Plant Growth Promotion of Maize in Hydrocarbons Contaminated Soil. Agronomy 2021, 11, 9, 1795. [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Li, Y.; Huang, R. Advances and Challenges in the Breeding of Salt-Tolerant Rice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8385. [CrossRef]
- Dwiningsih Y.; Rahmaningsih M.; Alkahtani J. Development of single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers in tropical crops. Advance Sustainable Science, Engineering and Technology (ASSET) 2020, 2, 2. [CrossRef]
- Thomson, M.J.; de Ocampo, M.; Egdane, J.; Rahman, M.A.; Sajise, A.G.; Adorada, D.L.; Tumimbang-Raiz, E.; Blumwald, E.; Seraj, Z.I.; Singh, R.K.; et al. Characterizing the saltol quantitative trait locus for salinity tolerance in Rice. Rice 2010, 3, 148–160. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Khan, N.U.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wen, X.; Tang, F.; Wang, F.; Li, Z. Genetic basis and identification of candidate genes for salt tolerance in rice by GWAS. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9958. [CrossRef]
- Lekklar, C.; Pongpanich, M.; Suriya-arunroj, D.; Chinpongpanich, A.; Tsai, H.; Comai, L.; Chadchawan, S.; Buaboocha, T. Genome-wide association study for salinity tolerance at the flowering stage in a panel of rice accessions from Thailand. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 76. [CrossRef]
- Adil, M.; Bashir, S.; Bashir, S.; Aslam, Z.; Ahmad, N.; Younas, T.; Asghar, R.M.A.; Alkahtani, J.; Dwiningsih, Y.; Elshikh, M.S. Zinc oxide nanoparticles improved chlorophyll contents, physical parameters, and wheat yield under salt stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 932861. [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chen, K.; Zhao, X.Q.; Wang, X.Q.; Shen, C.C.; Zhu, Y.J.; Dai, M.L.; Qiu, X.J.; Yang, R.W.; Xing, D.Y.; et al. Identification of genes for salt tolerance and yield-related traits in rice plants grown hydroponically and under saline field conditions by genome-wide association study. Rice 2019, 12, 88. [CrossRef]
- Mansuri, R.M.; Shobbar, Z.S.; Jelodar, N.B.; Ghaffari, M.R.; Nematzadeh, G.A.; Asari, S. Dissecting molecular mechanisms underlying salt tolerance in rice: A comparative transcriptional profiling of the contrasting genotypes. Rice 2019, 12, 13. [CrossRef]
- Alkahtani, J.; Elshikh, M.S.; Dwiningsih, Y.; Rathi, M.A.; Sathya, R.; Vijayaraghavan, P. In-vitro antidepressant property of methanol extract of Bacopa monnieri. Journal of King Saud University – Science 2022, 34, 102299. [CrossRef]
- Alshiekheid, M.A.; Dwiningsih, Y.; Sabour, A.A.; Alkahtani, J. Phytochemical Composition and Antibacterial Activity of Zingiber cassumunar Roxb. against Agricultural and Foodborne Pathogens. Preprint 2022. [CrossRef]
- Pathan, M.S.; Nguyen, H.T.; Subudhi, P.K.; Courtois, B. Molecular Dissection of Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Sorghum and Rice. In: “Physiology and Biotechnology Integration for Plant Breeding”, (Eds.): H. T. Nguyen, H. T. and Blum, A. Marcel Dekker Inc., New York, USA, 2004, 525-570.
- Yoshida, S.; Forno, D.A.; Cock, J.H.; Gomez, K.A. Laboratory manual for physiological studies of rice. IRRI, Las Banos, Laguna, 1976, 83.
- Yildirim, B.; Yaser, F.; Ozpay, T.; Ozpay, D.; Turkozu, D.; Terziodlu, O.; Tamkoc, A. Variations in response to salt stress among field pea genotypes (Pisum sativum sp. arvense L.). J Anim Vet Adv. 2008, 7, 907–910.
- Raza, S.H.; Athar, H.U.R.; Ashraf, M. Influence of exogenously applied glycinebetaine on the photosynthetic capacity of two differently adapted wheat cultivars under salt stress. Pak J Bot. 2006, 38, 341–351.
- Mukhtar, E.; Siddiqi, K.; Bhatti, K.H.; Nawaz, K.; Hussain, K. Gas exchange attributes can be valuable selection criteria for salinity tolerance in canola cultivars (Brassica napus L.). Pak J Bot. 2013, 45, 35–40.
- Siddiqi, E.H.; Ashraf, M.; Hussain, M.; Jamil, A. Assessment of intercultivar variation for salt tolerance in safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) using gas exchange characteristics as selection criteria. Pak J Bot. 2009, 41, 2251–2259.
- Mano, Y.; Takeda, K. Diallel analysis of salt tolerance at germination and the seedling stage in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Breeding Sci. 1997, 47, 203-209. [CrossRef]
- Jamil, M.; Lee, K.B.; Jung, K.Y.; Lee, D.B.; Han, M.S.; Rha, E.S. Salt stress inhibits germination and early seedling growth in cabbage (Brassica oleracea capitata L.). Pakistan J. Biol. Sci. 2007, 10, 6, 910-914. [CrossRef]
- Guan, B.; Yu, J.; Lu, Z.; Japhet, W.; Chen, X.; Xie, W. Salt tolerance in two Suaeda species: seed germination and physiological response. Asian J. Plant Sci. 2010, 9, 4, 194-199. [CrossRef]
- Dwiningsih, Y.; Alkahtani, J. Phenotypic Variations, Environmental Effects and Genetic Basis Analysis of Grain Elemental Concentrations in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) for Improving Human Nutrition. Preprints 2022, 2022090263. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Hussain, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wei, H.; Gao, P.; Dai, Q. Comprehensive Evaluation of Salt Tolerance in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Germplasm at the Germination Stage. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1569. [CrossRef]
- Dwiningsih, Y.; Alkahtani, J. Rojolele: a Premium Aromatic Rice Variety in Indonesia. Preprints 2022, 2022100373. [CrossRef]
- Ponnamperuma, F.N. Role of cultivar tolerance in increasing rice production in saline lands. In: Staples RC, Toenniessen GH (eds) Salinity tolerance in plants. Strategies for crop improvement. Wiley-Interscience, New York, 1984, 255–271.
- Dwiningsih, Y.; Al-Kahtani, J. Genome-Wide Association Study of Complex Traits in Maize Detects Genomic Regions and Genes for Increasing Grain Yield and Grain Quality. Advance Sustainable Science Engineering and Technology 2022, 4, 2, 0220209. [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.; Harris, P. Photosynthesis under stressful environments: an overview. Photosynthetica 2013, 51, 163–190. [CrossRef]
- Khafagy, M.A.; Arafa, A.A.; El-Banna, M.F. Glycinebetaine and ascorbic acid can alleviate the harmful effects of NaCl salinity in sweet pepper. Aust J Crop Sci. 2009, 3, 257–267.
- Santos, V.C. Regulation of chlorophyll biosynthesis and degradation by salt stress in sunflower leaves. Sci Hortic. 2004, 130, 93–99.
- Lone, J.; Shikari, A.; Sofi, N.; Ganie, S.; Sharma, M.; Sharma, M.; Kumar, M.; Saleem, M.H.; Almaary, K.S.; Elshikh, M.S.; Dwiningsih, Y. Screening technique based on seed and early seedling parameters for cold tolerance of selected F2-derived F3 rice genotypes under controlled conditions. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14, 8447. [CrossRef]
- Kishor, P.B.; Sangam, S.; Amrutha, R.N. Regulation of proline biosynthesis, degradation, uptake and transport in higher plants: its implications in plant growth and abiotic stress tolerance. Curr Sci. 2005, 88, 424–438.
- Dwiningsih, Y.; Kumar, A.; Thomas, J.; Gupta, C.; Ruiz, C.; Alkahtani, J.; Baisakh, N.; Pereira, A. Identification and expression of abscisic acid-regulated genes in US RIL rice population under drought conditions. In 82nd Meeting of Southern Section of the American Society of Plant Biologists. 2021.
- Ghosh, N.; Adak, M.K.; Ghosh, P.D.; Gupta, S.; Sen Gupta, D.N.; Mandal, C. Differential responses of two rice varieties to salt stress. Plant Biotechnol Rep. 2011, 5, 89–103. [CrossRef]
- Fariduddin, Q.; Khalil, R.R.A.E.; Mir, B.A.; Yusuf, M.; Ahmad, A. 24-Epibrassinolide regulates photosynthesis, antioxidant enzyme activities and proline content of Cucumis sativus under salt and/ or copper stress. Environ Monit Assess. 2013, 185, 7845–7856.
- Saha, P.; Chatterjee, P.; Biswas, A.K. NaCl pretreatment alleviates salt stress by enhancement of antioxidant defense system and osmolyte accumulation in mungbean (Vigna radiata L. Wilczek). Indian J Exp Biol. 2010, 48, 593–600.
- Dwiningsih, Y.; Kumar, A.; Thomas, J.; Yingling, S.; Pereira, A. Identification of QTLs associated with drought resistance traits at reproductive stage in K/Z RILs rice population. In 5th Annual Meeting of the Arkansas Bioinformatics Consortium AR-BIC. 2020.
- Abu-Muriefah, S.S. Effect of sitosterol on growth, metabolism and protein pattern of pepper (Capsicum Annuum L.) plants grown under salt stress conditions. Int J Agric Crop Sci. 2015, 8, 94–106.
- Azuma, R.; Ito, N.; Nakayama, N.; Suwa, R.; Nguyen, N.T.; Larrinaga Mayoral, J.A.; Esaka, M.; Fujiyama, H.; Saneoka, H. Fruits are more sensitive to salinity than leaves and stems in pepper plants (Capsicum annuum L.). Sci Hortic. 2010, 125, 171–178. [CrossRef]
- Dwiningsih, Y.; Kumar, A.; Thomas, J.; Yingling, S.; Pereira, A. Molecular genetic analysis of drought resistance and productivity in K/Z RIL rice population. Arkansas Bioinformatics Consortium. 2019.
- Stepien, P.; Klobus, G. Antioxidant defense in the leaves of C3 and C4 plants under salinity stress. Physiol Plantarum 2005, 125, 31–40. [CrossRef]
- Sudhakar, C.; Lakshmi, A.; Giridarakumar, S. Changes in the antioxidant enzyme efficacy in two high yielding genotypes of mulberry (Morus alba L.) under NaCl salinity. Plant Sci. 2001, 161, 613–619. [CrossRef]
- Meloni, D.A.; Oliva, M.A.; Martinez, C.A.; Cambraia, J. Photosynthesis and activity of superoxide dismutase, peroxidase and glutathione reductase in cotton under salt stress. Environ Exp Bot. 2003, 49, 69–76. [CrossRef]
- Dwiningsih, Y.; Thomas, J.; Kumar, A.; Gupta, C.; Crowley, E.; Ruiz, C.; Pereira, A. Drought stress response in US recombinant inbred line of rice population. In National Science Foundation (NSF) 26th National Conference 2019, 26, 76, 127.
- Chang, J.; Cheong, B.; Natera, S.; Roessner, U. Morphological and metabolic responses to salt stress of rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars which differ in salinity tolerance. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2019, 144, 427–435. [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Yang, Z.Z.; Li, F.; Yan, C.R.; Zhong, X.L.; Liu, Q.; Xia, X.; Li, H.R.; Zhao, L. Comparative metabolic responses and adaptive strategies of wheat (Triticum aestivum) to salt and alkali stress. BMC Plant Biol. 2015, 15. [CrossRef]
- Dwiningsih, Y.; Thomas, J.; Kumar, A.; Gupta, C.; Yingling, S.; Basu, S.; Pereira, A. Circadian expression patterns of the HYR gene. Arkansas Bioinformatics Consortium 2018, 7, 11, 34.
- Rock, W.R.L. Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Arkansas (AR). 2020.
- Ismanto, A.; Hadibarata, T.; Widada, S.; Indrayanti, E.; Ismunarti, D.; Safinatunnajah, N.; Kusumastuti, W.; Dwiningsih, Y.; Alkahtani, J. Groundwater contamination status in Malaysia: level of heavy metal, source, health impact, and remediation technologies. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering 2022. [CrossRef]
- Dwiningsih, Y.; Kumar, A.; Thomas, J.; Pereira, A. Identification drought-tolerance rice variety for reducing climatic impacts on rice production. In Fulbright Enrichment Seminar Climate Change, Estes Park, Colorado, USA. 2017.
- Peng, S.; Cassman, K.G.; Virmani, S.S.; Sheehy, J.; Khush, G.S. Yield potential trends of tropical rice since the release of IR8 and the challenge of increasing rice yield potential. Crop Sci. 1999, 39, 1552-1559. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Li, P.; Wang, L.X.; Hu, Z.L.; Zhu, L.H.; Zhu, Y.G. Genetic dissection of the relationships of biomass production and partitioning with yield and yield related traits in rice. Plant Sci. 2004, 167, 1-8.
- Dwiningsih, Y.; Alkahtani, J. Agronomics, Genomics, Breeding and Intensive Cultivation of Ciherang Rice Variety. Preprints 2022, 2022110489. [CrossRef]
- Dwiningsih, Y.; Alkahtani, J. Potential of Pigmented Rice Variety Cempo Ireng in Rice Breeding Program for Improving Food Sustainability. Preprints 2023, 2023020039. [CrossRef]
- IRRI [International Rice Research Institute]. Annual report for 1967. Manila (Philippines): International Rice Research Institute 1967, 308.
- Dwiningsih, Y.; Kumar, A.; Thomas, J.; Gupta, C.; Ruiz, C.; Baisakh, N.; Pereira, A. QTLs analysis and identification of candidate genes for flag leaf characteristics related to grain yield in US RIL rice population under drought conditions. In ASA, CSSA, SSSA International Annual Meeting. ASA-CSSA-SSSA. 2021.
- Pearson, G.A.; Ayers, S.D.; Eberhard, D.L. Relative salt tolerance of rice during germination and early seedling development. Soil Sci. 1966, 102, 151-156. [CrossRef]
| # | Rice Varieties | Country | Sub-population |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Karang Serang | Indonesia | TRJ |
| 2 | Rojolele | Indonesia | TRJ |
| 3 | Cempo Ireng | Indonesia | TRJ |
| 4 | Ciherang | Indonesia | IND |
| 5 | Mayang Khang | Indonesia | IND |
| 6 | Sipirasikkam | Indonesia | TRJ |
| 7 | Mitak | Indonesia | TRJ |
| 8 | Dara | Indonesia | AUS |
| 9 | B805D-Mr-16-8-3 | Indonesia | IND |
| 10 | Tia Bura | Indonesia | TRJ |
| 11 | C 5560 | Thailand | TEJ/TRJ |
| 12 | Nam Dawk Mai | Thailand | IND |
| 13 | Bkn 6987-68-14 | Thailand | IND |
| 14 | Td 70 | Thailand | IND |
| 15 | Cntlr80076-44-1-1-1 | Thailand | IND |
| 16 | Nahng Sawn | Thailand | IND |
| 17 | Quinimpol | Philippines | TRJ |
| 18 | TCCP 266 | Philippines | IND |
| 19 | IR 4482-5-3-9-5 | Philippines | IND |
| 20 | IR 45427 | Philippines | IND |
| 21 | IR 9660-48-1-1-2 | Philippines | IND |
| 22 | IR 238 | Philippines | IND |
| 23 | IR 2061-214-2-3 | Philippines | IND |
| 24 | IR 2462 | Philippines | IND |
| 25 | IR 58614-B-B-8-2 | Philippines | IND |
| 26 | Pakkali | Philippines | ARO |
| 27 | IR64 | Philippines | IND |
| 28 | IR58 | Philippines | IND |
| 29 | IR29 | Philippines | IND |
| 30 | Taichu Mochi 59 | Taiwan | TRJ |
| 31 | Ai Chueh Ta Pai Ku | Taiwan | IND |
| 32 | Ragasu | Taiwan | TEJ/TRJ |
| 33 | Tobura | Taiwan | TEJ/TRJ |
| 34 | Kao Chio Lin Chou | Taiwan | IND |
| 35 | Taino 38 | Taiwan | IND/AUS |
| 36 | Nanton No. 131 | Taiwan | TRJ/(admix) |
| 37 | Hsin Hsing Pai Ku | Taiwan | IND |
| 38 | Tainung 45 | Taiwan | IND |
| 39 | Ao Chiu 2 Hao | China | IND |
| 40 | Chun 118-33 | China | IND |
| 41 | Kin Shan Zim | China | IND |
| 42 | Pan Ju | China | IND |
| 43 | Kechengnuo No. 4 | China | IND |
| 44 | 4484 | China | IND |
| 45 | 4595 | China | IND |
| 46 | You-I B | China | IND |
| 47 | Chunjiangzao No. 1 | China | TEJ |
| 48 | Shimizu Mochi | Japan | TEJ |
| 49 | Norin 11 | Japan | TEJ |
| 50 | Tamanishiki | Japan | TEJ |
| 51 | Niwahutaw Mochi | Japan | TEJ |
| 52 | Somewake | Japan | TEJ |
| 53 | A 5 | Japan | TEJ |
| 54 | C.B. Ii | Japan | AUS |
| 55 | Fujisaka 5 | Japan | IND |
| 56 | Nipponbare | Japan | TEJ |
| 57 | Khao Phoi | Laos | TEJ/TRJ |
| 58 | Khao Luang | Laos | TRJ/(admix) |
| 59 | Padi Pohon Batu | Malaysia | TRJ |
| 60 | Acheh | Malaysia | IND |
| 61 | Mahsuri | Malaysia | IND |
| 62 | Padi Tarab Arab | Malaysia | TRJ |
| 63 | Nc 1/536 | Pakistan | AUS |
| 64 | Red | Pakistan | AUS/(Admix) |
| 65 | Santhi 990 | Pakistan | IND/AUS |
| 66 | Daudzai Field Mix | Pakistan | AUS |
| 67 | Jp 5 | Pakistan | IND/AUS |
| 68 | Won Son Zo No. 11 | Korea | IND |
| 69 | Daegudo | Korea | TEJ |
| 70 | Guweoldo | Korea | TEJ |
| 71 | Namyang 7 | Korea | TEJ |
| 72 | Yong Chal Byo | Korea_ South | TEJ |
| 73 | Thang 10 | Vietnam | IND |
| 74 | Cm1_ Haipong | Vietnam | IND |
| 75 | Nang Bang Bentre | Vietnam | AUS |
| 76 | Lua Chua Chan | Vietnam | TRJ |
| 77 | Soc Nau | Vietnam | IND |
| 78 | Heo Trang | Vietnam | IND |
| 79 | Pd 46 | Sri Lanka | IND |
| 80 | Bakiella 1 | Sri Lanka | IND |
| 81 | Gallawa | Sri Lanka | AUS |
| 82 | Ittikulama | Sri Lanka | AUS |
| 83 | Karayal | Sri Lanka | AUS |
| 84 | Amane | Sri Lanka | IND |
| 85 | Thavalu | Sri Lanka | AUS |
| 86 | Patnai 6 | Myanmar | AUS |
| 87 | Buphopa | Myanmar | TEJ/TRJ |
| 88 | Kaukkyi Ani | Myanmar | TRJ |
| 89 | A100943-R | Myanmar | AUS |
| 90 | Nsgc 5953 | Myanmar | IND |
| 91 | A 36-3 | Myanmar | IND |
| 92 | Jumli Dhan | Nepal | TEJ/TRJ |
| 93 | N-2703 | Nepal | AUS |
| 94 | Bhim Dhan | Nepal | TEJ/TRJ |
| 95 | Juppa | Nepal | IND |
| 96 | Tauli | Nepal | AUS |
| 97 | Darmali | Nepal | TEJ/ARO |
| 98 | Dhan | Nepal | IND |
| 99 | Tchampa | Iran | AUS |
| 100 | Phudugey | Bhutan | AUS |
| 101 | Jyanak | Bhutan | TEJ/TRJ |
| 102 | Wir 3039 | Tajikistan | TEJ |
| 103 | Ak Tokhum | Azerbaijan | ARO |
| 104 | Gasym Hany | Azerbaijan | ARO |
| 105 | Celiaj | Azerbaijan | TEJ |
| 106 | Shimla Early | Iraq | IND/AUS |
| 107 | A 152 | Bangladesh | IND/TRJ |
| 108 | Dnj 179 | Bangladesh | AUS |
| 109 | Dj 24 | Bangladesh | AUS |
| 110 | Dj 102 | Bangladesh | AUS |
| 111 | Dnj 121 | Bangladesh | AUS |
| 112 | Aswina 330 | Bangladesh | AUS |
| 113 | Tranoeup Beykher | Cambodia | IND |
| 114 | Srav Prapay | Cambodia | IND |
| 115 | Simpor | Brunei | TRJ |
| 116 | Pokkali | India | IND |
| Score | Observation | Tolerance |
|---|---|---|
| 1 3 5 7 9 |
Normal growth, no leaf symptoms Nearly normal growth, but leaf tips or few leaves whitish and rolled Growth severely retarded; most leaves rolled; only a few are elongating Complete cessation of growth; most leaves dry; some plants dying Almost all plants dead or dying |
Highly tolerant Tolerant Moderately tolerant Susceptible Highly susceptible |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





