Submitted:
12 March 2023
Posted:
13 March 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. C. elegans Strains
2.2. RNAi and Analysis of Protein Misfolding
2.3. GO Term Analysis of Candidate Genes
2.4. RNAi and Analysis of Neurodegeneration
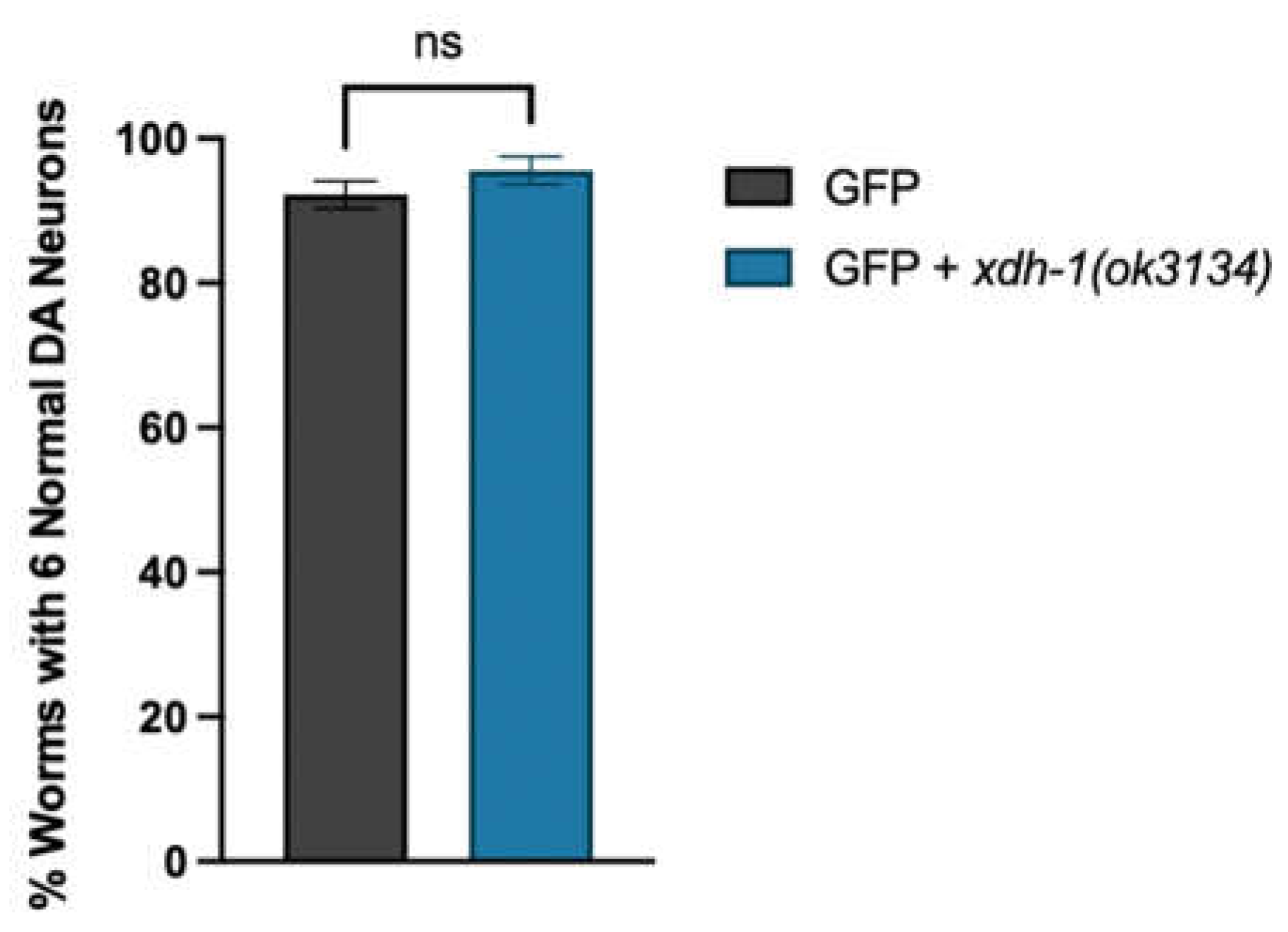
2.5. Analysis of xdh-1(ok3134) Mutants for Neurodegeneration
2.6. Transgenic line construction and analysis of neurodegeneration
2.7. Body Wall Muscle and Dopaminergic Neuron Image Acquisition
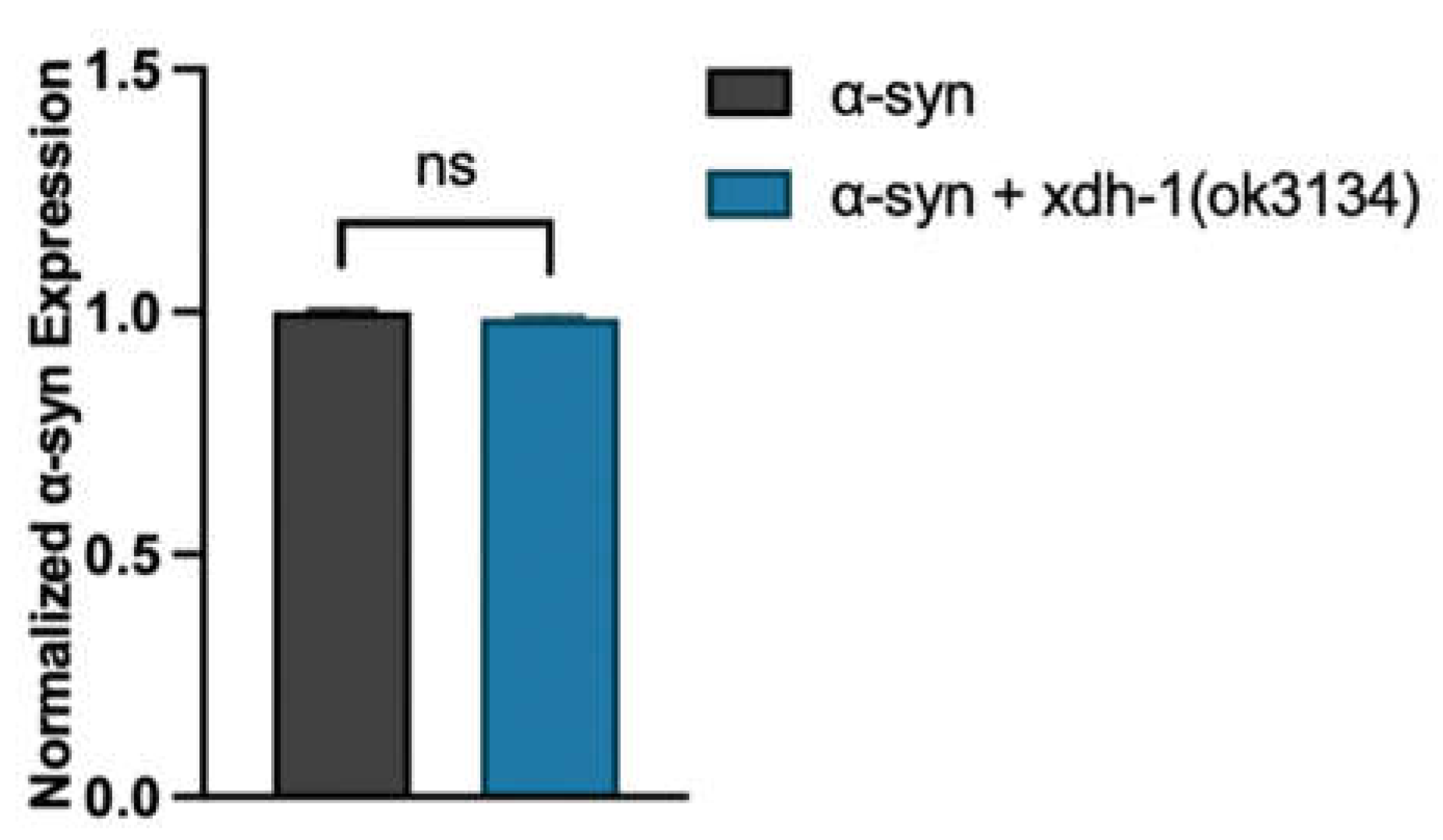
2.8. RT-qPCR of α-syn expression
2.8. Quantification of ROS
2.9. Proteomic analysis of unedited and edited wht-2
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
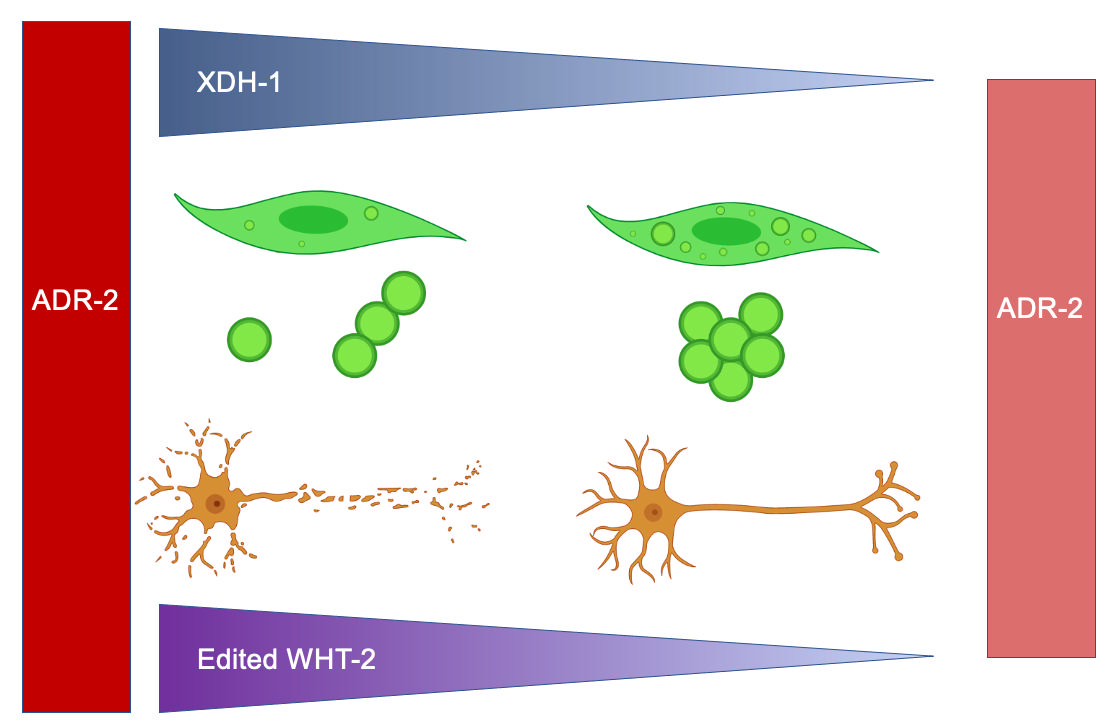
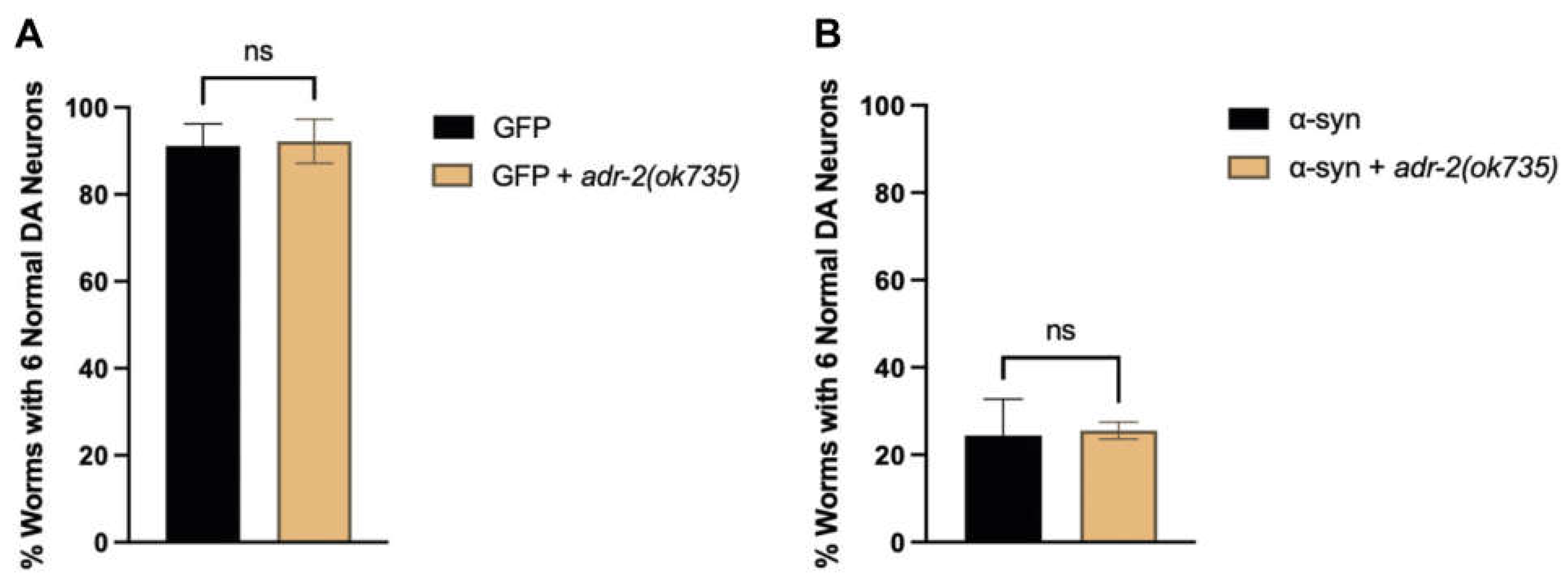
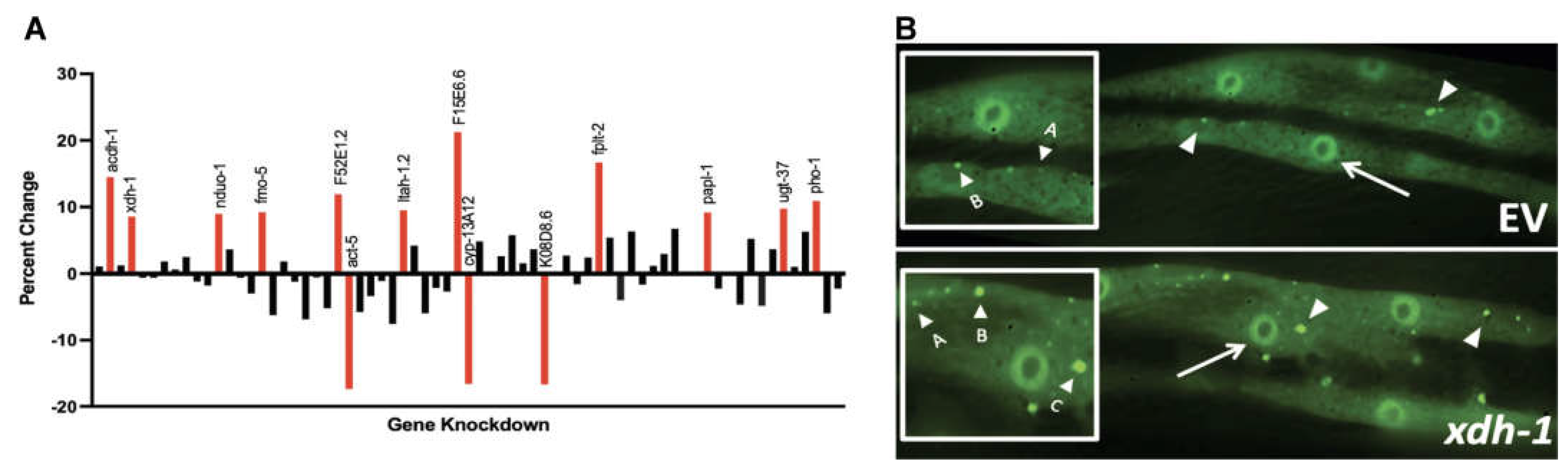
3.1. Genes Regulated by ADR-2 Alter α-syn Misfolding.
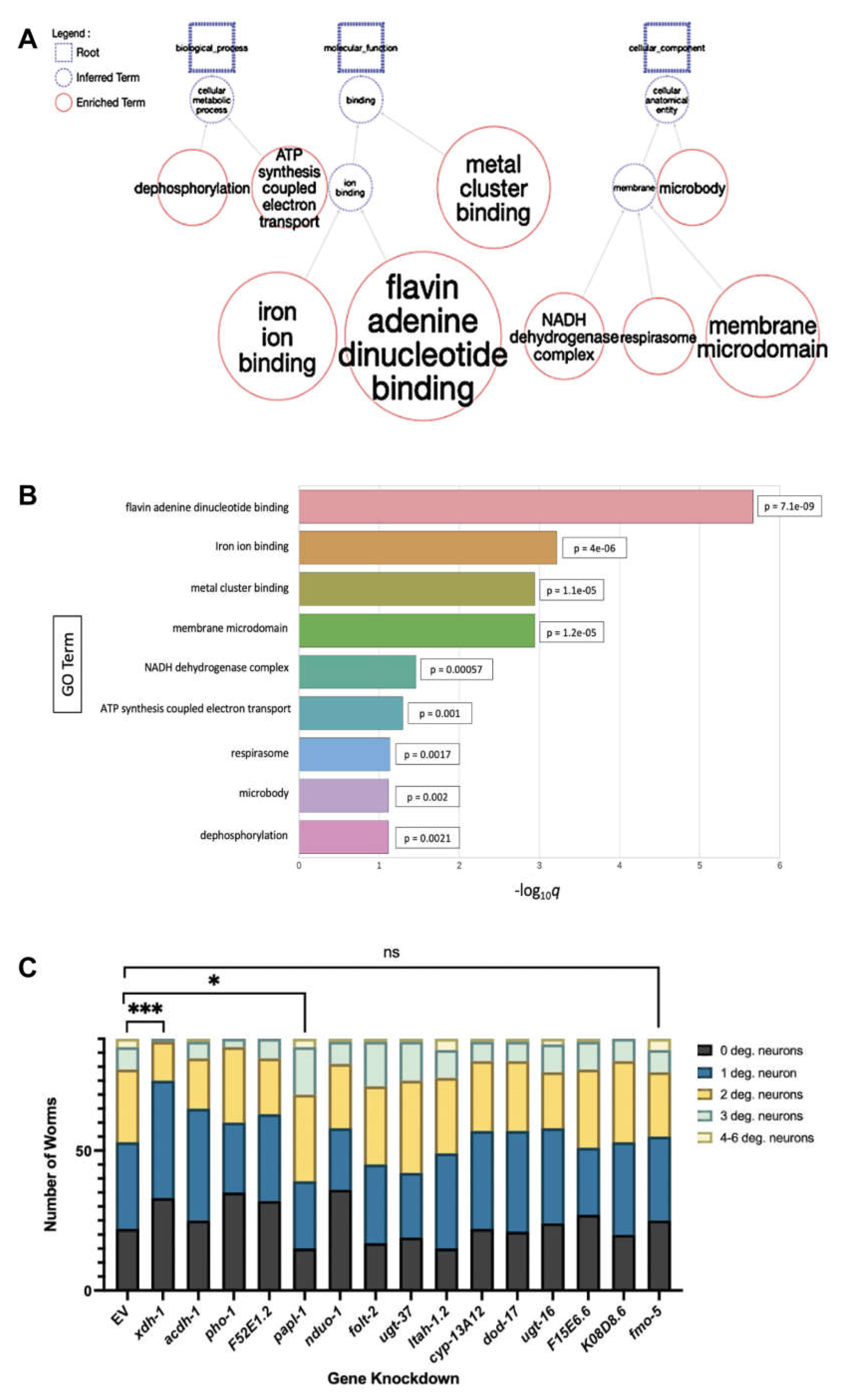
3.2. Modifiers of protein misfolding are associated with FAD and iron binding.
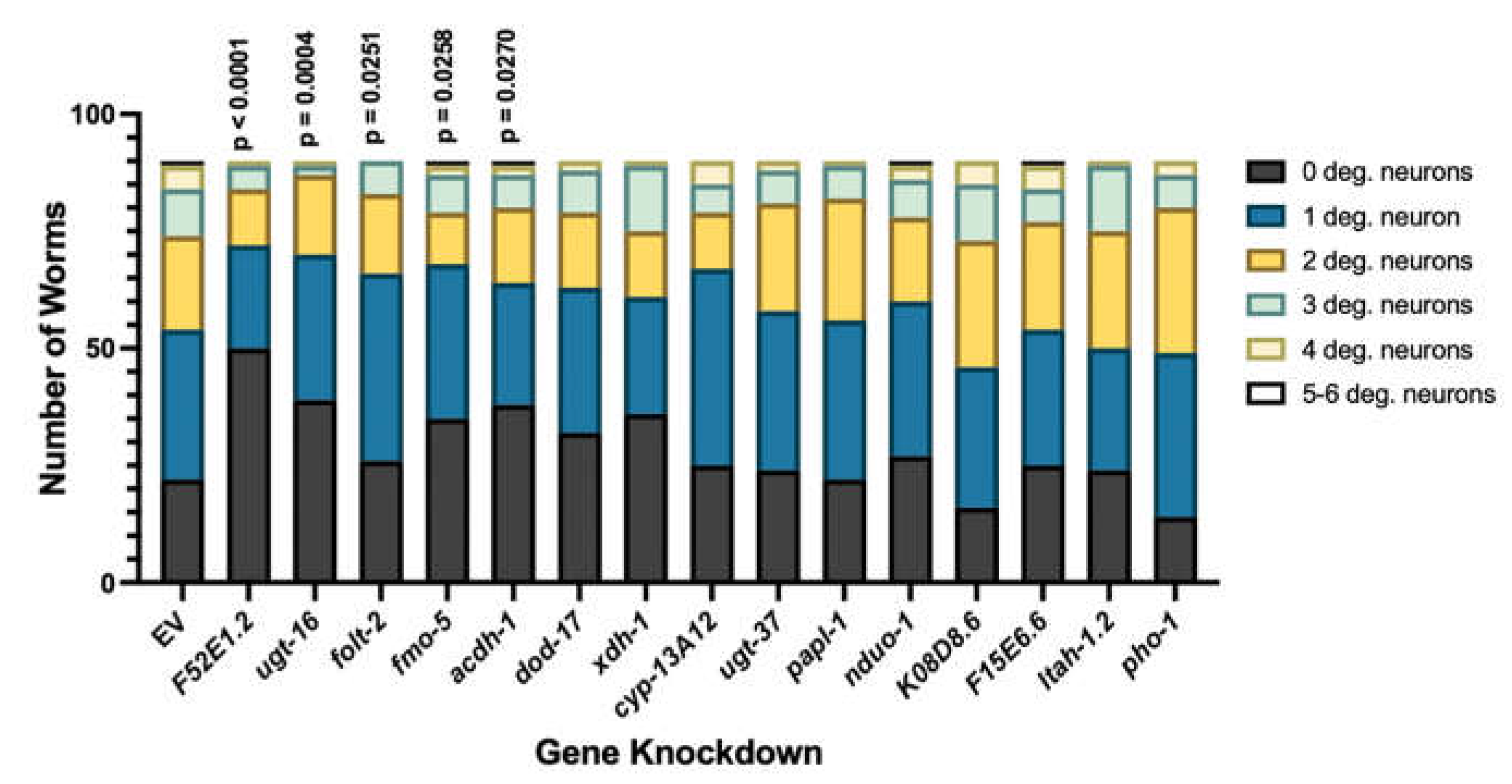
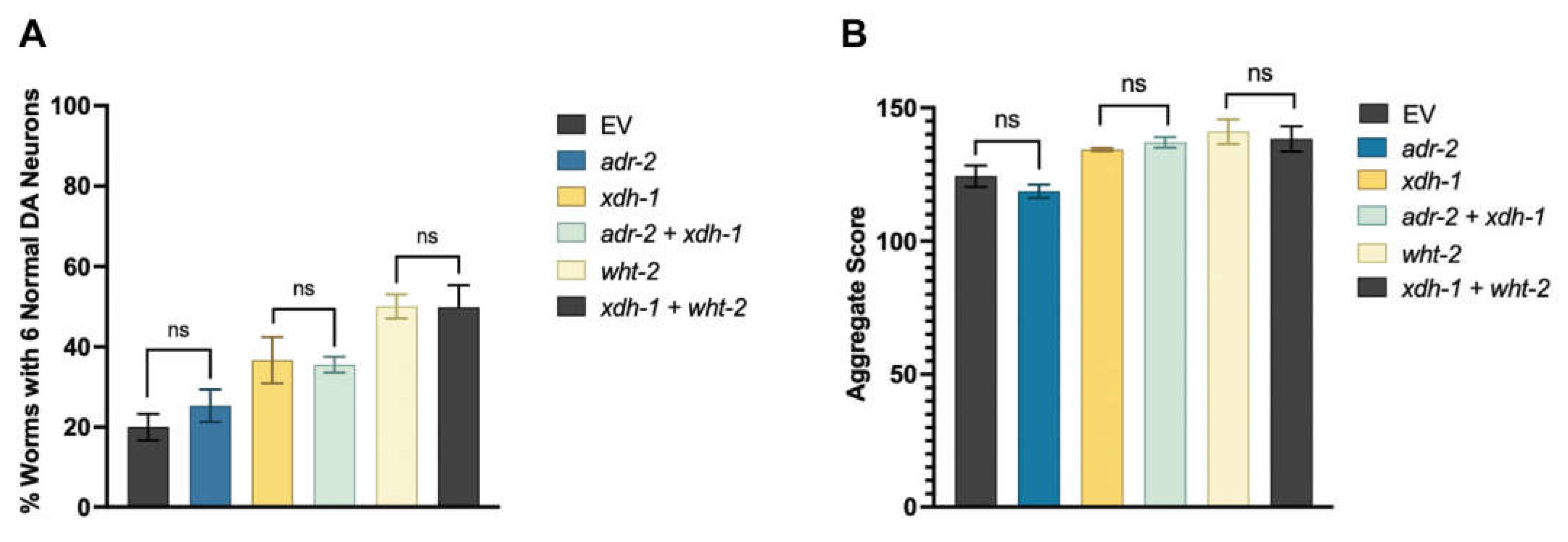
3.3. Select modifiers of protein misfolding impact neurodegeneration when knocked down in dopamine neurons.
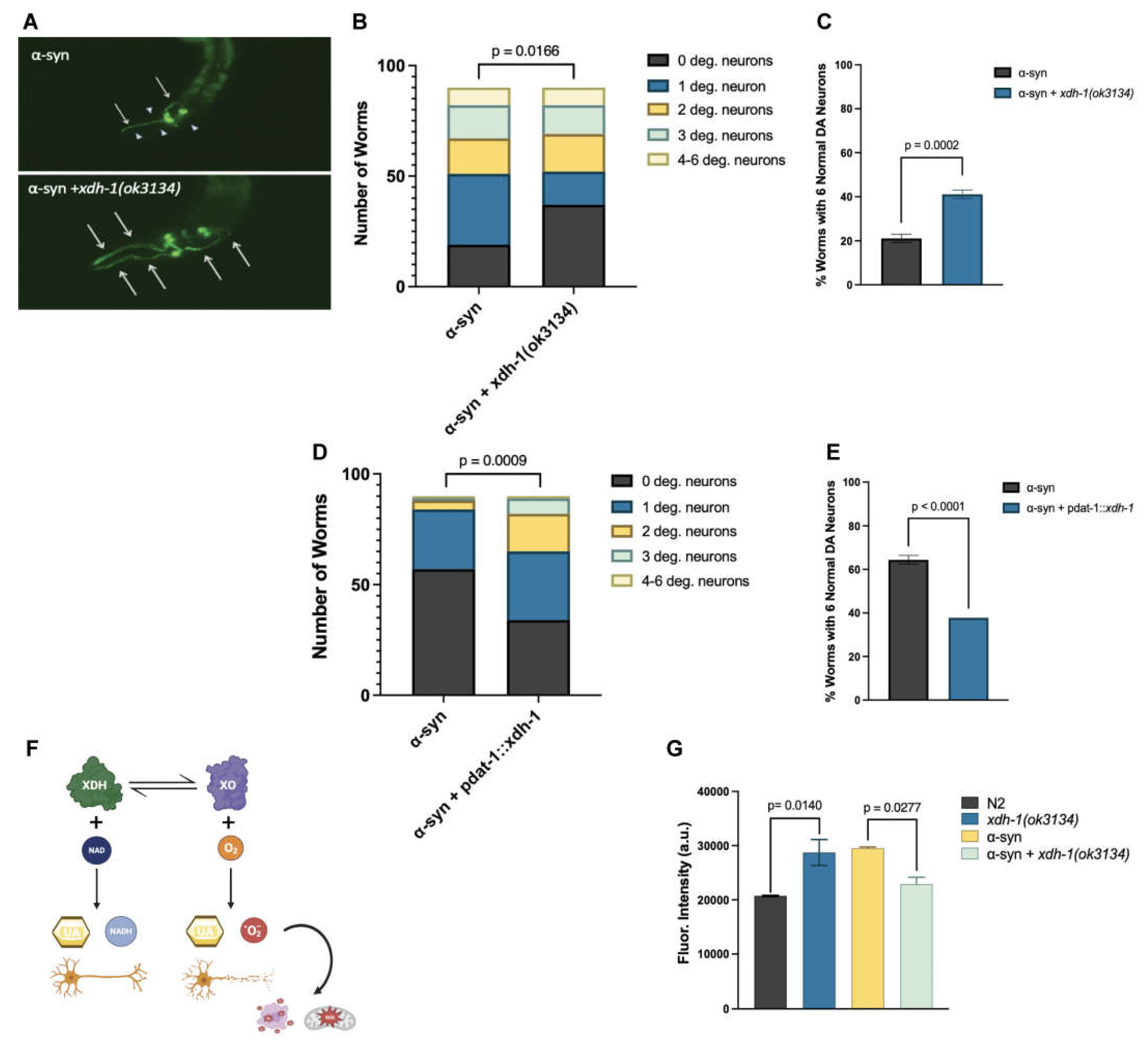
3.4. Loss of XDH leads to neuroprotection through the reduction of ROS.
| Gene Name | Human Ortholog(s) | Differential Expression in adr-2 Mutant |
Change in Protein Misfolding |
Change in Dopamine Neuron Degeneration |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| xdh-1 | XDH | Downregulated | +8.55% | Protective (p = 0.0002***) |
Catalyzes the final two steps of purine catabolism; low oxidase activity toward aldehydes; produces ROS. |
| pho-1 | ACP2, ACPT | Downregulated | +10.92% | Protective (p = 0.0198*) |
Converts orthophosphoric monoesters to alcohol and phosphate via hydrolysis; role in dephosphorylation. |
| F52E1.2 | CLEC4A, CLEC4C, CLEC4D, CLEC4E, CLEC6A, ASGR1 | Upregulated | +11.93% | Protective (p = 0.0452*) |
Promotes carbohydrate binding activity; involved in cell signaling, adhesion, glycoprotein degradation and production, inflammation, immune response. |
| papl-1 | ACP7 | Downregulated | +9.195% | Enhanced (p = 0.0361*) |
Promotes acid phosphatase activity; enables metal ion binding. |
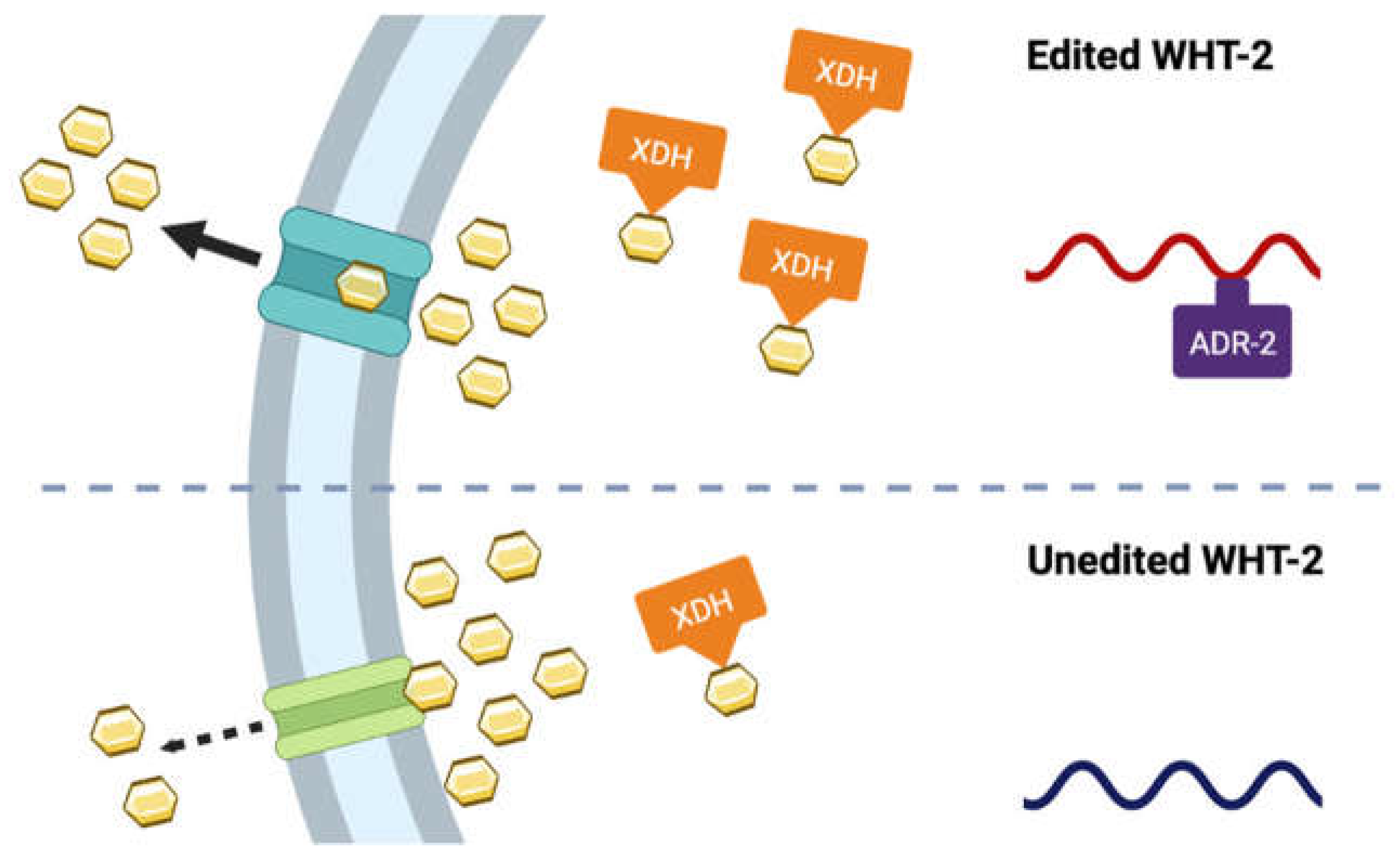
3.5. A target of ADR-2 editing, wht-2, interacts in a network with xdh-1 to mediate PD-associated pathologies.
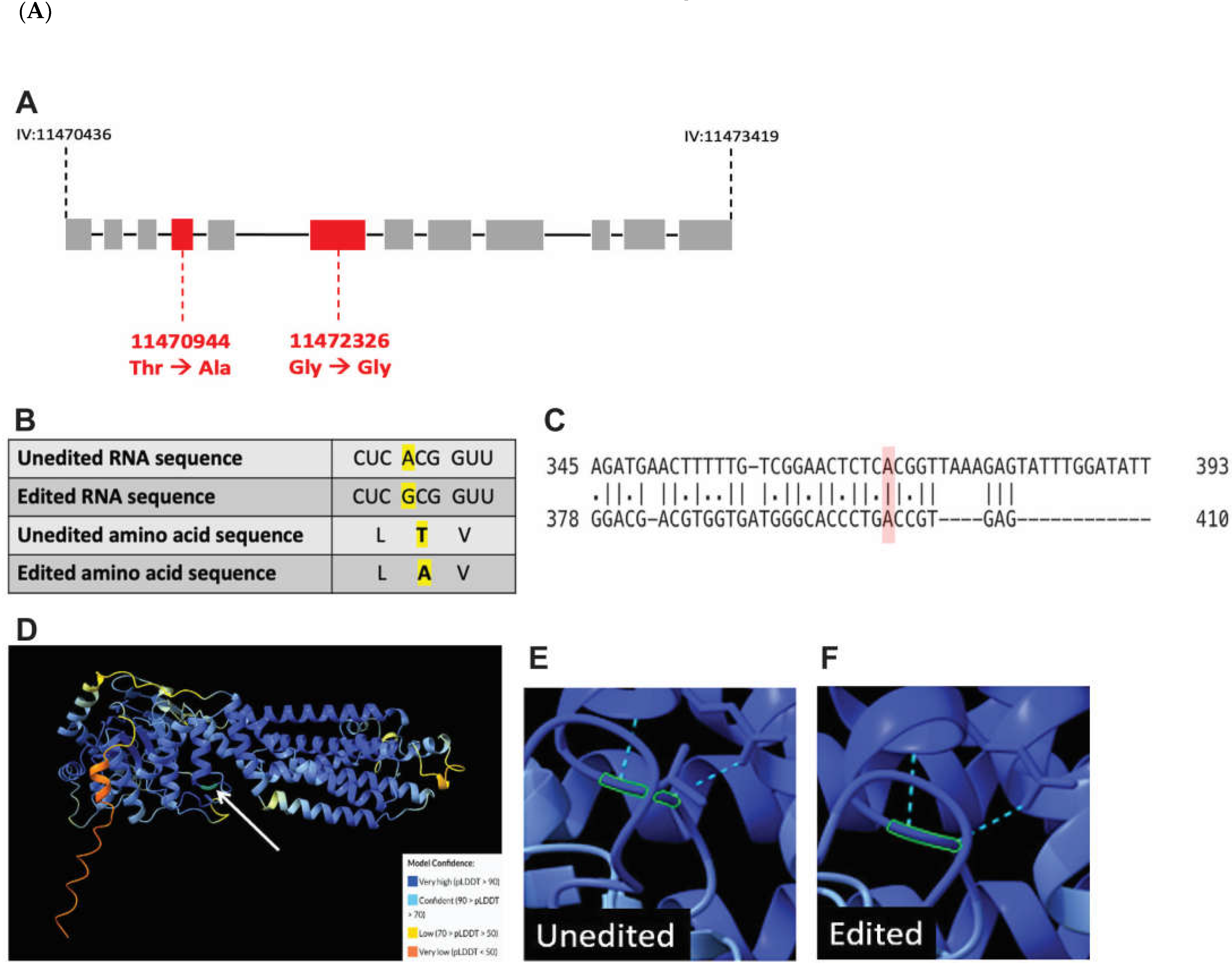
3.6. A-to-I RNA editing of wht-2 is predicted to alter WHT-2 protein structure.
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Healy, D.G.; Falchi, M.; O’Sullivan, S.S.; Bonifati, V.; Durr, A.; Bressman, S.; Brice, A.; Aasly, J.; Zabetian, C.P.; Goldwurm, S.; et al. Phenotype, Genotype, and Worldwide Genetic Penetrance of LRRK2-Associated Parkinson’s Disease: A Case-Control Study. The Lancelet Neurology 2008. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mythri, R.B.; Jagatha, B.; Pradhan, N.; Andersen, J.; Bharath, M.M.S. Mitochondrial Complex I Inhibition in Parkinson’s Disease: How Can Curcumin Protect Mitochondria? Antioxidants and Redox Signaling 2007, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blesa, J.; Trigo-Damas, I.; Quiroga-Varela, A.; Jackson-Lewis, V. Oxidative Stress and Parkinson’s Disease. Frontiers in Neuroanatomy 2015. [CrossRef]
- Cook, C.; Stetler, C.; Petrucelli, L. Disruption of Protein Quality Control in Parkinson’s Disease. Cold Spring Harbor Perspective Medicine 2012. [CrossRef]
- Hattori, N.; Tanaka, M.; Ozawa, T.; Mizuno, Y. Immunohistochemical Studies on Complexes I, II, III, and IV of Mitochondria in Parkinson’s Disease. Annals of Neurology 1991. [CrossRef]
- Hattingen, E.; Magerkurth, J.; Pilatus, U.; Mozer, A.; Seifried, C.; Steinmetz, H.; Zanella, F.; Hilker, R. Phosphorus and Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Demonstrates Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Early and Advanced Parkinson’s Disease. Brain 2009. [CrossRef]
- Sveinbjornsdottir, S. The Clinical Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease. Journal of Neurochemistry 2016. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Jia, C.; Li, T.; Le, W. Hot Topics in Recent Parkinson’s Disease Research: Where We Are and Where We Should Go. Neuroscience Bulletin 2021. [CrossRef]
- Mhyre, T.R.; Boyd, J.T.; Hamill, R.W.; KA, M.-Z. Parkinson’s Disease; Subcellular Biochemistry, 2012;
- Wang, I.X.; So, E.; Devlin, J.L.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, M.; Cheung, V.G. ADAR Regulates RNA Editing, Transcript Stability, and Gene Expression. Cell Reports 2013, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, D.P.; Tyc, K.M.; Bass, B.L. C. C. elegans ADARs Antagonize Silencing of Cellular DsRNAs by the Antiviral RNAi Pathway. Genes and Development 2018. [CrossRef]
- Morse, D.P.; Aruscavage, P.J.; Bass, B.L. RNA Hairpins in Noncoding Regions of Human Brain and Caenorhabditis elegans mRNA Are Edited by Adenosine Deaminases That Act on RNA. PNAS 2002. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Okada, S.; Sakurai, M. Adenosine-to-Inosine RNA Editing in Neurological Development and Disease. RNA Biology 2021. [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, M.; Maas, S.; Single, F.N.; Hartner, J.; Rozov, A.; Burnashev, N.; Feldmeyer, D.; Sprengel, R.; Seeburg, P.H. Point Mutation in an AMPA Receptor Gene Rescues Lethality in Mice Deficient in the RNA-Editing Enzyme ADAR2. Nature 2000, 406, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Paro, S.; McGurk, L.; Sambrani, N.; Hogg, M.C.; Brindle, J.; Pennetta, G.; Keegan, L.P.; O’Connell, M.A. Membrane and Synaptic Defects Leading to Neurodegeneration in Adar Mutant Drosophila Are Rescued by Increased Autophagy. BMC Biology 2020, 18, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozdyshev, D.V.; Zharikova, A.A.; Medvedeva, M.V.; Muronetz, V.I. Differential Analysis of A-to-I mRNA Edited Sites in Parkinson’s Disease. Genes 2021, 13, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calahorro, F.; Ruiz-Rubio, M. Caenorhabditis elegans as an Experimental Tool for the Study of Complex Neurological Diseases: Parkinson’s Disease, Alzheimer’s Disease and Autism Spectrum Disorder. Invertebrate Neuroscience 2011, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldwell, K.A.; Willicott, C.W.; Caldwell, G.A. Modeling Neurodegeneration in Caenorhabditis elegans. Disease Models & Mechanisms 2020, 13, dmm046110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towlson, E.K.; Vértes, P.E.; Ahnert, S.E.; Schafer, W.R.; Bullmore, E.T. The Rich Club of the C. elegans Neuronal Connectome. Journal of Neuroscience 2013, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonkin, L.A.; Saccomanno, L.; Morse, D.P.; Brodigan, T.; Krause, M.; BL, B. RNA Editing by ADARs Is Important for Normal Behavior in Caenorhabditis elegans. EMBO Journal 2002. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Washburn, M.C.; Kakaradov, B.; Sundararaman, B.; Wheeler, E.; Hoon, S.; Yeo, G.W.; HA, H. The DsRBP and Inactive Editor ADR-1 Utilizes DsRNA Binding to Regulate A-to-I RNA Editing across the C. elegans Transcriptome. elegans Transcriptome. Cell Reports 2014. [CrossRef]
- Rajendren, S.; Manning, A.C.; Al-Awadi, H.; Yamada, K.; Takagi, Y.; HA, H. A Protein-Protein Interaction Underlies the Molecular Basis for Substrate Recognition by an Adenosine-to-Inosine RNA-Editing Enzyme. Nucleic Acids Research 2018. [CrossRef]
- Deffit, S.N.; Yee, B.A.; Manning, A.C.; Rajendren, S.; Vadlamani, P.; Wheeler, E.C.; Domissy, A.; Washburn, M.C.; Yeo, G.W.; HA, H. The C. elegans neural editome reveals an ADAR target mRNA required for proper chemotaxis. eLife 2017. [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.Y.; Baek, B.S.; Song, S.H.; Kim, M.S.; Huh, J.I.; Shim, K.H.; Kim, K.W.; Lee, K.H. Xanthine dehydrogenase/xanthine oxidase and oxidative stress 1997, 20, 127-140. [CrossRef]
- Bortolotti, M.; Polito, L.; Battelli, M.G.; Bolognesi, A. Xanthine Oxidoreductase: One Enzyme for Multiple Physiological Tasks. Redox Biology 2021, 41, 101882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishino, T.; Okamoto, K.; Eger, B.T.; Pai, E.F.; Nishino, T. Mammalian Xanthine Oxidoreductase - Mechanism of Transition from Xanthine Dehydrogenase to Xanthine Oxidase. FEBS Journal 2008, 275, 3278–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuhashi, M. New Insights into Purine Metabolism in Metabolic Diseases: Role of Xanthine Oxidoreductase Activity. American Journal of Physiology - Endocrinology and Metabolism 2020, 319, E827–E834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.S.; Weickert, C.S.; Garner, B. Role of ATP-Binding Cassette Transporters in Brain Lipid Transport and Neurological Disease; Journal of Neurochemistry, 2008, 104,1145-1166. [CrossRef]
- Kobuchi, H.; Moriya, K.; Ogino, T.; Fujita, H.; Inoue, K.; Shuin, T.; Yasuda, T.; Utsumi, K.; Utsumi, T. Mitochondrial Localization of ABC Transporter ABCG2 and Its Function in 5-Aminolevulinic Acid-Mediated Protoporphyrin IX Accumulation. PLOS One 2012. [CrossRef]
- Kukal, S.; Guin, D.; Rawat, C.; Bora, S.; Mishra, M.K.; Sharma, P.; Paul, P.R.; Kanojia, N.; Grewal, G.K.; Kukreti, S.; et al. Multidrug Efflux Transporter ABCG2: Expression and Regulation. Cell and Molecular Life Sciences 2021. [CrossRef]
- Stiernagle, T. Maintenance of C. elegans. WormBook : the online review of C. elegans biology 2006. [CrossRef]
- Angeles-Albores, D.; Ryn, L.; Chan, J.; PW, S. Tissue Enrichment Analysis for C. elegans Genomics. elegans Genomics. BMC Bioinformatics 2016. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmons, L.; Court, D.L.; Fire, A. Ingestion of Bacterially Expressed dsRNAs Can Produce Specific and Potent Genetic Interference in Caenorhabditis elegans. Gene 2001, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrington, AJ; Knight, AL; Caldwell, GA; Caldwell, KA. Caenorhabditis elegans as a Model System for Identifying Effectors of α-Synuclein Misfolding and Dopaminergic Cell Death Associated with Parkinson’s Disease. Methods 53, 220–225. [CrossRef]
- Tournayre, J.; Reichstadt, M.; Parry, L.; Fafournoux, P.; Jousse, C. “Do My QPCR Calculation”, a Web Tool. Bioinformation 2019, 15, 369–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueroa, D.; Asaduzzaman, M.; Young, F. Real Time Monitoring and Quantification of Reactive Oxygen Species in Breast Cancer Cell Line MCF-7 by 2′,7′–Dichlorofluorescin Diacetate (DCFDA) Assay. Journal of Pharmacological and Toxicological Methods 2018, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, B.; Agranat-Tamir, L.; Light, D.; Ben-Naim Zgayer, O.; Fishman, A.; Lamm, A.T. A-to-I RNA Editing Promotes Developmental Stage–Specific Gene and LncRNA Expression. Genome Research 2017, 27, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice EMBOSS: The European Molecular Biology Open Software Suite (2000) Rice, P. Longden, I. and Bleasby, A. Trends in Genetics. 16, pp. 276--277.
- Varadi, M.; Anyango, S.; Deshpande, M.; Nair, S.; Natassia, C.; Yordanova, G.; Yuan, D.; Stroe, O.; Wood, G.; Laydon, A.; et al. AlphaFold Protein Structure Database: Massively Expanding the Structural Coverage of Protein-Sequence Space with High-Accuracy Models. Nucleic Acids Research 2022, 50, D439–D444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Meng, E.C.; Couch, G.S.; Croll, T.I.; Morris, J.H.; Ferrin, T.E. UCF ChimeraX: Structure Visualization for Researchers, Educators, and Developers. Protein Science 2021, 30, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamamichi, S.; Rivas, R.N.; Knight, A.L.; Cao, S.; Caldwell, K.A.; Caldwell, G.A. Hypothesis-Based RNAi Screen Identifies Neuroprotective Genes in a Parkinson’s Disease Model. PNAS 2008, 105, 728–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larosa, V.; Remacle, C. Insights into the Respiratory Chain and Oxidative Stress. Bioscience Reports 2018, 38, BSR20171492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolfi-Donegan, D.; Braganza, A.; Sruti Shiva, S. Mitochondrial Electron Transport Chain: Oxidative Phosphorylation, Oxidant Production, and Methods of Measurement. Redox Biology 2020, 37, 101674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, V.; Junn, E.; Mouradian, M. The Role of Oxidative Stress in Parkinson’s Disease. 2013, 3, 461-491. [CrossRef]
- Mash, D.C.; Pablo, J.; Buck, B.E.; Sanchez-Ramos, J., Weiner, W.J. Distribution and Number of Transferrin Receptors in Parkinson’s Disease and in MPTP-Treated Mice. Experimental Neurology 1991. 114, 73-81. [CrossRef]
- Song, N.; Wang, J.; Jiang, H.; Xie, J. Ferroportin 1 but Not Hephaestin Contributes to Iron Accumulation in a Cell Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Free Radical Biology & Medicine 2010, 48, 332–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, D.; Xu, C.; Nagarajan, S.; Liu, Z.; Hemphill, W.O.; Shi, R.; Uversky, V.N.; Caldwell, G.A.; Caldwell, K.A.; Witt, S.N. Alpha-Synuclein Inhibits Snx3–Retromer-Mediated Retrograde Recycling of Iron Transporters in S. cerevisiae and C. elegans Models of Parkinson’s Disease. Human Molecular Genetics 2018, 27, 1514–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Corte, E.; Stirpe, F. The Regulation of Rat Liver Xanthine Oxidase. Involvement of thiol groups in the conversion of the enzyme activity from dehydrogenase (type D) into oxidase (type O) and purification of the enzyme 1972, 2, 83-84. [CrossRef]
- Shaye, D.D.; Greenwald, I. Ortholist: A Compendium of C. elegans Genes with Human Orthologs. PLoS ONE 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, F.; Allen, J.E.; Allen, J.; Alvarez-Jarreta, J.; Amode, M.R.; Armean, I.M.; Austine-Orimoloye, O.; Azov, A.G.; Barnes, I.; Bennett, R.; et al. Ensembl 2022. Nucleic Acids Research 2022, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, K.; Davis, P.; Paulini, M.; Tuli, M.A.; Williams, G.; Yook, K.; Durbin, R.; Kersey, P.; Sternberg, P.W. WormBase. Worm 2012, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deffit, S.N.; Yee, B.A.; Manning, A.C.; Rajendren, S.; Vadlamani, P.; Wheeler, E.C.; Domissy, A.; Washburn, M.C.; Yeo, G.W.; Hundley, H.A. The C. elegans Neural Editome Reveals an ADAR Target MRNA Required for Proper Chemotaxis. eLife 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, W.; Sternberg, P.W. Genome-Wide Prediction of C. elegans Genetic Interactions. Science 2006, 311, 1481–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalbeth, N.; Gosling, A.L.; Gaffo, A.; Abhishek, A. Gout. The Lancet 2021, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Cowley, A.; Uludag, M.; Gur, T.; McWilliam, H.; Squizzato, S.; Park, Y.M.; Buso, N.; Lopez, R. The EMBL-EBI Bioinformatics Web and Programmatic Tools Framework. Nucleic Acids Research 2015, 43, W580–W584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podoly, E.; Hanin, G.; Soreq, H. Alanine-to-Threonine Substitutions and Amyloid Diseases: Butyrylcholinesterase as a Case Study. Chemico-Biological Interactions 2010, 187, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Jongchan, L.; Mok, K.H.; Lee, J.H.; Han, K.H. Salient Features of Monomeric Alpha-Syn Revealed by NMR Spectroscopy. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dohgu, S.; Takata, F.; Matsumoto, J.; Kimura, I.; Yamauchi, A.; Kataoka, K. Monomeric α-Synuclein Induces Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction through Activated Brain Pericytes Releasing Inflammatory Mediators in Vitro. Microvascular Research, 2019, 124, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascherio, A.; Schwarzschild, M.A. The Epidemiology of Parkinson’s Disease: Risk Factors and Prevention. Lancet Neurology 2016, 15, 1257–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.F.; Bruce-Keller, A.J.; Goodman, Y.; Mattson, M.P. Uric Acid Protects Neurons against Excitotoxic and Metabolic Insults in Cell Culture, and against Focal Ischemic Brain Injury in Vivo. Journal of Neuroscience Research 1998, 53, 613–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghio, A.J.; Kennedy, T.P.; Stonehuerner, J.; Carter, J.D.; Skinner, K.A.; Parks, D.A.; Hoidal, J.R. Iron Regulates Xanthine Oxidase Activity in the Lung. American Journal of Physiology - Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology 2002, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Investigators, S.-P.-. 3 Effect of Urate-Elevating Inosine on Early Parkinson Disease Progression: The SURE-PD3 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2021, 326, 926–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devos, D.; Cabantchik, Z.I.; Moreau, C.; Daniel, V.; Mahoney-Sanchez, L.; Bouchaoui, H.; Gouel, F.; Rolland, A.S.; Duce, J.A.; Devedijan, J.C.; et al. Conservative Iron Chelation for Neurodegenerative Diseases Such as Parkinson’s Disease and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Journal of Neural Transmission 2020, 27, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, T.; Buaas, F.W.; Simons, A.K.; Ackert-Bicknell, C.L.; Braun, R.E.; Hibbs, M.A. Canonical A-to-I and C-to-U RNA Editing Is Enriched at 3’UTRs and MicroRNA Target Sites in Multiple Mouse Tissues. PLOS ONE 2012, 7, e33720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- To, K.; Zhan, Z.; Litman, T.; Bates, S.E. Regulation of ABCG2 Expression at the 3’ Untranslated Region of Its MRNA through Modulation of Transcript Stability and Protein Translation by a Putative MicroRNA in the S1 Colon Cancer Cell Line. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 28, 5147-5161. [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Kay, M. How Do miRNAs Mediate Translational Repression? Silence 2010, 1, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emin, D.; Zhang, Y.P.; Lobanova, E.; Miller, A.; Li, X.; Xia, Z.; Dakin, H.; Sideris, D.I.; Lam, J.Y.; Ranasinghe, R.T.; et al. Small Soluble α-Synuclein Aggregates Are the Toxic Species in Parkinson’s Disease. Nature Communications 2022, 13, 5512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mougenot, A.-L.; Nicot, S.; Bencsik, A.; Morignat, E.; Verchère, J.; Lakhdar, L.; Legastelois, S.; Baron, T. Prion-like Acceleration of a Synucleinopathy in a Transgenic Mouse Model. Neurobiology of Aging 2012, 33, 2225–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Gao, J.; Wang, J.; Xie, A. Prion-Like Mechanisms in Parkinson’s Disease. Frontiers in Neuroscience 2019, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Wen, Q.; Ren, J.; Hendricks, M.; Gershow, M.; Qin, Y.; Greenwood, J.; Soucy, E.R.; Klein, M.; Smith-Parker, H.K.; et al. Dynamic Encoding of Perception, Memory, and Movement in a C. elegans Chemotaxis Circuit. Neuron 2014, 82, 1115–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdmann, E.A.; Mahapatra, A.; Mukherjee, P.; Yang, B.; Hundley, H.A. To Protect and Modify Double-Stranded RNA – the Critical Roles of ADARs in Development, Immunity and Oncogenesis. Critical Reviews in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2021, 56, 54–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaeta, A.L.; Caldwell, K.A.; Caldwell, G.A. Found in Translation: The Utility of C. elegans Alpha-Synuclein Models of Parkinson’s Disease. Brain Sciences 2019, 9, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mew, M.; Caldwell, K.A.; Caldwell, G.A. From Bugs to Bedside: Functional Annotation of Human Genetic Variation for Neurological Disorders Using Invertebrate Models. Human Molecular Genetics 2022, 31, R37–R46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- P.A. Kropp; R. Bauer; I. Zafra; Golden, A. Caenorhabditis elegans for Rare Disease Modeling and Drug Discovery: Strategies and Strengths. Disease Models & Mechanisms 2021, 14, dmm049010. [CrossRef]
| Strain | Genotype | Strains Crossed |
| UA455 | xdh-1(ok3134); baIn11[Pdat-1::α-syn, Pdat-1 ::GFP] | RB2379 x UA44 |
| UA456 | xdh-1(ok3134); vtIs7 [Pdat-1::GFP] | RB2379 x BY250 |
| UA457 | adr-2(ok735); vtIs7[Pdat-1::α-syn, Pdat-1 ::GFP] | RB886 x BY250 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





