1. Introduction
The interaction between innovation and business export performance has stimulated much academic interest in studies of the economics of innovation and in international trade studies (Altomonte et al., 2016; Bıçakcıoğlu-Peynirci et al., 2019). Innovation literature has witnessed a class of new growth models based on the idea of Schumpeterian imperfect competition, grounded on the premise that growth is the outcome of firms’ R&D effort. Empirical evidence has shown that R&D activities positively affect firms’ competitiveness. Productivity studies report a strong positive marginal return on R&D spending. Chan et al. (2001) have documented a positive association between firms’ R&D spending and both, share prices and returns.
Since R&D may give companies an advantage in terms of competitiveness, this gives them an incentive to enter international markets. This issue has been extensively studied by international trade scholars (Harris and Li, 2009; Aw et al., 2011, among others). However, unequivocal evidence of the effect of R&D on export has yet to be produced. At the same time, competition in global markets increases firms’ innovativeness through technological spillovers or “learning by exporting”. This results in reverse causality from export to R&D. It is argued that decisions on whether to engage in research and whether to export are taken concomitantly by firms (Harris and Li, 2011). This leads to simultaneity between R&D and exporting activity and a possible self-selection process on the part of firms engaged in R&D moving into international trade. The idea is that highly innovative companies expand abroad in search of returns on their investment in innovative activities.
In this study, we built upon four topics that have emerged from the debate over the past decade and conducted an empirical analysis of the effects that different types of innovation have on export intensity in a sample of European manufacturing firms, taking these aspects into account.
Our findings enabled us to design an integrated model incorporating R&D, innovation and export, in a framework of simultaneous equations which consider their mutual correlations. We studied the effect of innovation on firms’ export performance, considering that innovation intensity, in turn, depends on external and internal factors. Recent studies have emphasized that what matters for success in international markets is the output of innovation processes, rather than input (Ganotakis and Love, 2011; Tavassoli, 2018). Special emphasis is attributed to R&D efforts, which are identified as the main source of innovation in the literature (Griliches, 1979; Hall et al., 2010), and the role of the technological environment. Thus, we were able to build a bridge between literature on the R&D-innovation link and regional technological spillover studies (Jaffe, 1986; Rodríguez-Gulías et al., 2020). The regional technological environment is an important factor affecting the decision to engage in technological activities. We used this information as an instrumental variable, which we employed in the framework for the system of equations. To the best of our knowledge, our framework is the first of its kind.
Moreover, given the substantial heterogeneity in innovation, we explicitly distinguished between the following: a) process innovation; b) product innovation; c) process and product innovation; d) product innovation new to the firm; and e) product innovation new to the market. This allowed us to obtain a more focused picture about their specific effects on export and differentiates our analysis from existing studies which used generic innovation variables (among others, Ganotakis and Love, 2011; Tavassoli, 2018).
Finally, the econometric setup in our study was based on a fractional response probit model with endogenous innovation. This allowed us to take account of the bounded nature of exports, which, in our dataset, was expressed as exports over total sales.
The analysis was carried out for five European countries over the three-year period from 2007 to 2009, namely France, Germany, Italy, Spain and the UK. This also distinguishes our work from existing studies based on single-country samples. Our results may be useful for companies seeking to design technological strategies aimed at improving export performance, firm organization, synergies and growth. Our results may also be useful for policymakers designing public R&D schemes, both at national and European level. Companies ought to be especially concerned with their R&D commitment as the latter activity strongly affects innovation, which, in turn, appears to be beneficial for export performance. Moreover, innovation is systemic, embracing multiple interactions involving workers, firm organization and the external environment. Firms which can take full advantage of their technological engagement are likely to benefit more from complementary know-how in other aspects of their business. To establish and define opportunities, companies need to explore technologies and markets and build suitable capabilities (Atzeni and Carboni, 2004; 2006). Such competencies include the capability to forecast demand, understanding of the evolution of industries, and awareness of supplier and competitor possible responses. Perception of such dimensions of innovation and R&D is vital in order to increase firms’ long-term export performance.
This paper is structured as follows:
Section 2 briefly illustrates insights from recent literature on the links between innovation and exports.
Section 3 presents the methodology and describes the data used.
Section 4 presents our conclusions.
1.2. Themes in Recent Literature
It is commonly acknowledged that innovative companies have highly competitive capabilities, which help them succeed in international markets (Harris and Li, 2009; Aw et al., 2011, among others). At macro level, export is viewed as a vital factor for economic growth. According to the European Commission (2013), “[t]rade has never been more important for the European Union’s economy”, and “[b]oosting trade is one of the few ways to bolster economic growth”. European Union trade policies are designed to emphasize the interrelation between three factors through which a company’s competitiveness may support economic growth and employment: export, investment and innovation. In the following sections, we summarize four common ideas from the economic literature upon which this work was based.
1.2.1. The Innovation-Export Link
A recent insight emerging from innovation-export analysis concerns the idea that the outcome of innovation effort influences decisions about entering and being successful in international business. Tavassoli (2018) argues that focusing on input for innovative activities (measuring innovative activity on the basis of effort and resources such as R&D expenditure) can lead to an incomplete understanding of how a company’s innovation impacts on its export performance.
However, many empirical analyses have found no significant evidence of the relation between R&D and export (Harris and Li, 2009; Aw and Roberts, 2011). Conversely, other studies have used input factors of the knowledge production function as a proxy for innovation output but with inconclusive results (Van Beveren and Vandenbussche, 2010).
Few recent studies investigating factors affecting export performance have made a distinction between innovation inputs and outputs and implemented econometric setups involving models of structural equations aimed at testing the sequence of the following relations: a) R&D (along with other factors) → innovation output; and b) innovation output → export performance (Ganotakis and Love, 2011; Tavassoli, 2018).
1.2.2. The Research-Innovation Link
This aspect has been amply explored from a theoretical perspective. The notion of a knowledge production function finds its foundation in Griliches (1979), who underlined the role of transformation of technological innovation activities (input such as research and human capital) into original and economically valuable knowledge. R&D is acknowledged to be the most crucial input of the innovative process, although there is limited empirical evidence to support this. However, more recent econometric research (Conte and Vivarelli, 2014; Medda, 2020) has corroborated the beneficial impact of R&D on firms’ innovation, with diverse conclusions as to the distinction between product and process innovations. The relation between innovation and various measures of export has garnered much interest. Highly innovative firms expand in international markets, searching for a better return on their investment in innovative projects and to counterbalance sunk costs (Zhang and Zhu, 2016).
In particular, product innovation through generation of novel technology-intensive commodities and diversification of product supply can give firms an incentive to penetrate international markets or reinforce their exporting position (Cassiman and Golovko, 2011; Tavassoli, 2018). A crucial aspect of the recent insight deriving from innovation-export research is that the output of innovation activity affects the propensity to enter (and prosper in) global markets. At the same time, there is evidence that firms improve their technology as a result of exporting their products (Chen et al., 2018). Competition in the global context improves innovativeness thanks to spillovers from the wider knowledge acquired. Furthermore, companies can acquire technological knowledge by operating in a larger and richer environment, increase their reception of inputs that are not available in the home market (Aghion et al., 2018) and learn by exporting (İpek, 2019).
1.2.3. Heterogeneity in Innovation
Empirical studies have shown that one reason for fragmentation of results is the great heterogeneity in firms’ innovation activities, which relates to several factors, including variation in industrial sectors (Altomonte et al., 2016), countries’ economic and institutional environment (Ganotakis and Love, 2011) and the nature of the innovation (Dohse and Niebuhr, 2018). In particular, attempts to unravel the effect of innovation on exports by distinguishing between process, product and organizational innovation, as well as incremental or radical innovation in terms of the company or the market, have received little attention.
The outcome of innovation processes can generally be classified as product innovations or cost-reducing process innovations. These two forms differ with respect to the activities and investment required and with respect to the choice of technological partnerships, and they have different economic effects on firm performance.
According to the Oslo Manual (OECD, 2005), process innovations relate to creation of new or significantly upgraded techniques, so they are meant to promote productivity. They provide a cost advantage over potential competitors, turning into a higher markup. Product innovations concern goods or services which are new or have significantly improved characteristics, compared to comparable items on the market. Exploration of the innovation behaviour of firms has rarely focused on the direct effects of research and other factors on product and process innovation. There is often a tendency to assume that findings from literature on product innovations can be applied to process innovation (Un and Asakawa, 2015).
However, product and process innovations also influence each other. Empirical and theoretical studies are now available showing this complementarity. Hullova et al. (2016) investigated cases where cost-reducing innovation necessitates evolution of new products. In the same way, the introduction of a new product may require adjustments in the production process. Firms may choose to implement the two innovations jointly. Empirical studies have highlighted potential benefits in terms of overall innovativeness when both product and process innovations are carried out together, suggesting significant complementarity effects between the two kinds of innovations (Guisado-González et al., 2017, for Spanish firms; Carboni and Russu, 2017, for European firms).
Among the few studies that have investigated how different types of innovation affect firms’ export performance, Ayllón and Radicic (2019) find that both product and process innovation exert beneficial effects on the propensity to export, with complementary effects between the two kinds of innovation. Cassiman et al. (2010), employing a panel of Spanish manufacturing firms, found evidence that product innovation, and not process innovation, affects productivity and stimulates small non-exporting firms to enter the international market. Becker and Egger (2013) concluded that companies engaged in both process and product innovation have a higher probability of exporting than firms that do not innovate. However, when implemented alone, product innovation is more important than process innovation in firms’ exporting decisions. Dohse and Niebuhr (2018) showed that incremental product innovations speed up exports, whereas completely new products have no immediate effect.
1.2.4. Two Econometrics Aspects: The Endogeneity Issue and the Fractional Response Model
It is argued that choices about whether to engage in innovation activities and in those related to export are possibly made jointly by firms. The reverse causality (from export to innovation) has been pinpointed (Damijan et al., 2010). However, in determining the causal impact of technological activity on innovative outcomes, existing empirical research has generally not considered the endogeneity problem (Un et al., 2010; Berchicci, 2013). A key concern in literature on innovative behaviour is that the decision to commit to research projects is influenced by unobservable factors that affect other crucial firm decisions (Crepon et al., 1998). This may be a source of sizeable distortion in econometric estimates.
From the methodological perspective, this is relevant to endogeneity arguments establishing the link between innovation and exportation (Aw et al., 2011; Becker and Egger, 2013; Tavassoli, 2018). Well-established evidence shows that companies involved in innovative projects self-select into export activities. Aw et al. (2008) presented a model in which firms decide to engage in innovative activities with the aim of competing in international markets. Analysing a sample of Taiwanese companies, their results provided evidence of interactions between firms’ decision to invest in innovativeness and their export activity level.
Studies aimed at estimating the intensive innovation margin effect on export performance have considered exports as a proportion of total turnover (Bıçakcıoğlu-Peynirci et al., 2019). As a result, in these models, the dependent variable is in the range [0, 1], with a large cluster at zero, corresponding to non-exporting companies. With such cases, traditional linear models are unsuitable because of a number of methodological issues, such as inconsistency of estimates and meaningless interpretation of results (Wooldridge, 2010).
For instance, the bounded nature of such variables and the potential probability distribution accumulating at one or both boundaries prevent standard linear estimation to ensure that the predicted values of the observed variable are confined to the unit interval. Even ad hoc adjustments such as logit transformation are subject to conceptual or practical difficulties when a substantial number of observations lie at either 0 or 1, as is the case for zero-exporting sales firms in our dataset (Ramalho et al., 2011).
In some cases, Tobit models have been used. However, the Tobit approach may lead to inconsistent results when a dependent variable is limited on both the left and right side and, most importantly, the limited dependent nature of variables analysed in these models is assumed by a censoring mechanism; that is, the researchers do not observe values beyond certain boundaries. This is not the case when a variable is a fraction which is, by nature, confined to the 0–1 limit. A better alternative is a fractional response model, which is more appropriate for dealing with dependent variables specified as proportions (Papke and Wooldridge, 1996; Wulff and Villadsen, 2020).1
2. Data and Methods
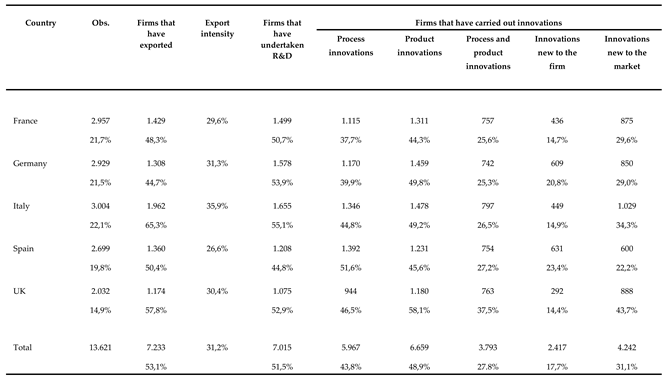
The data employed in this study covered five countries (France, Germany, Italy, Spain and the UK) and derive from the EU-EFIGE/Bruegel survey, which collected qualitative and quantitative data on the characteristics and activities of companies relative to the three-year period from 2007 to 2009. The final sample included responses from 13,621 European firms (
Table 1), 22.1% of which were from Italy, 21.5% from Germany, 21.7% from France, 19.8% from Spain and 14.9% from the UK.
2
The variable of observation in this study was exports over sales. Over half of the firms in the survey (53.1%) declared sales to other countries of some (or all) of their own products/services in 2008, with the maximum proportion in Italy (65.3%) and the minimum in Germany (44.7%). The average export intensity recorded for exporting firms was 31.2%, with the maximum, again, found in Italian firms (35.9%) and the minimum pertaining to Spanish companies (26.6%). Just over half of the companies were engaged in research, while 27.8% carried out both process and product innovation (43.8% and 48.9%, respectively). Product innovation was rated as “new to the firm” for 17.7% and “new to the market” for 31.1% of the companies. In the following section, we describe the variables employed in the analysis and provide the theoretical background.
2.1. Estimation Strategy
The analysis considered innovation as endogenous and determined by R&D through a process influenced by the role of the regional technological context. In the following section, we describe an integrated model incorporating R&D, innovation and export, in a framework of simultaneous equations which consider their mutual correlations. The objective of our estimation design was to provide an empirical analysis of the complex R&D-innovation and export link, emphasizing the potential non-linear form of this relation. We argue that simultaneity may be at the base of such decisions. We regard firms’ decisions to undertake R&D as an endogenous process and examined the factors which may influence firms’ propensity for R&D commitment. An interesting aspect in investigation of firms’ knowledge production function is that innovation output may be affected by unobservable factors that also affect firms’ R&D. Moreover, endogeneity issues also arise in the innovation-export relation: several studies have shown that choices about whether to engage in innovation activities and in those related to export are made jointly by firms (Aw et al., 2011; Becker and Egger, 2013). However, in their survey of empirical literature, Wu et al. (2022) found that less than half of innovation-export empirical analysis accounts for endogeneity, claiming that this approach may lead to contrasting estimates of the magnitude and direction of the effect of innovation on companies’ export performance.
We considered endogeneity in the relation between R&D and innovation by studying factors that may affect firms’ propensity for R&D, with a particular focus on the role of the regional technological environment. In doing so, we identified the regional (NUTS-2 level) technological environment as a determining component in incentivizing firms to engage in research.
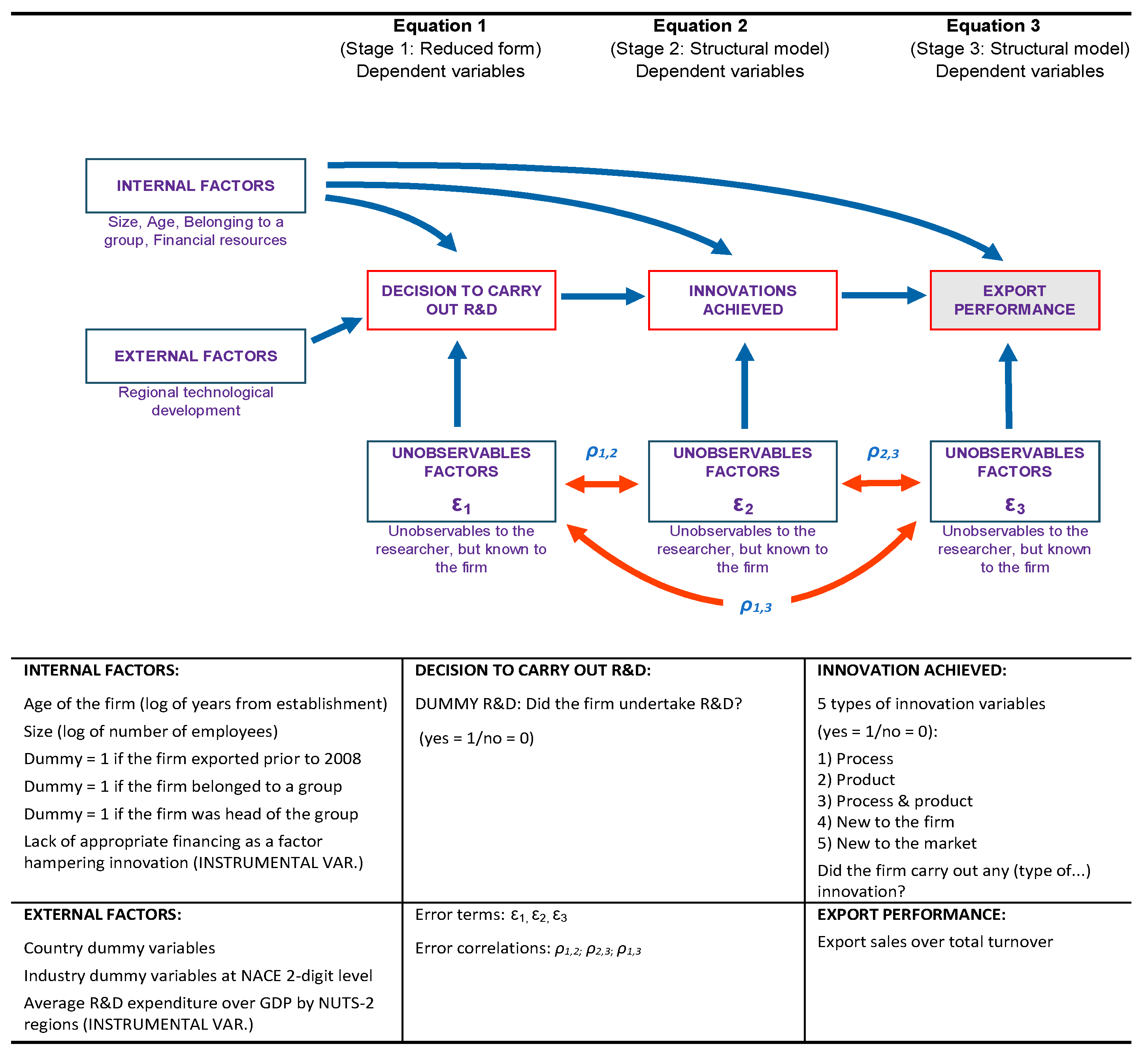
The econometric strategy of this study considered the themes in literature discussed above and employed a three-equation model, as follows: (1) estimation where the dummy innovation variables were endogenous and dependent on R&D and other controls. R&D (employed as the main input in the innovative activity process) was determined by the regional technological context, proxied by the regional R&D/Pil ratio; (2) estimation of the impact on export intensity of output from firms’ innovative activities; and finally (3) analysis of the nature of the export intensity dependent variable, which was a proportion with bounds [0, 1]. Thus, as suggested by Wooldridge (2010) and Wulff and Villadsen (2020), we employed a fractional probit response model.
In detail, the model we propose is as follows:
The DUMMY_R&D variable indicates whether a firm has carried out R&D. DUMMY_INNOVATION is a set of dummy variables indicating whether different kinds of innovation have been undertaken, namely process, product innovation, both product and process innovation together, and finally, product innovation new to the company or new to the market. EXPORT_INTENSITY expresses the percentage of annual turnover represented by export activities. REGIONAL_TECH_CONTEXT is measured by Eurostat statistics on regional (NUTS-2 level) R&D spending over GDP. CONTROLS features conventional variables used to capture the significant heterogeneity in companies’ characteristics (Altomonte et al., 2016; Coad, 2018).
As suggested by Wooldridge (2010), equations (1) and (2) do not need to be correctly specified and are estimated by linear models, while equation (3) is analysed using a fractional probit response design. We assumed (and tested) the following:
We employed the Stata conditional mixed-process estimator (CMP) command (Roodman, 2011) and used the delta method to compute average marginal effects. The econometric methodology applied in this work was supported by tests, revealing the presence of unobservable factors that affect export intensity, innovation and R&D.
Chart 1 following illustrates the econometric setup. The methodology and mechanism by which regional effects entered the estimation strategy are then specifically described.
3.2. Control Variables
There is a consensus that export performance by firms is positively correlated with age. Given the strong heterogeneity in production systems, size may be important for understanding differences in the behaviour of firms. Firm size is also a crucial factor in determining innovativeness and access to financial resources devoted to physical investment. We considered firm size as the logarithm of the number of employees.
The age of firms (expressed in years since their foundation) was also included in the model. The rationale is that older firms may have accumulated valuable business experience, giving them a possible market advantage. The age of firms was also considered as a factor influencing the innovative inclination of companies, on the grounds that young dynamic firms put more effort into R&D than older companies, although the evidence for this is mixed (García-Quevedo et al., 2014).
A binary variable, indicating whether firms had exported before 2008, was also considered. The key role of experience in international business is commonly recognized. Returns from exports can be employed to finance internal investment. This may be crucial if firms depend heavily on their own financing. Being active in international markets may also affect firms in relation to their innovativeness: exporting firms are asked to stress efficiency up to international level. Furthermore, international trade fosters a firm’s potential to acquire technological spillovers from abroad (Altomonte et al., 2013).
Two variables (equal to one if the firm was part of a group and if the firm was the head of a group) were also included (Wu et al., 2021). Being part of a group may enable companies to internalize externalities from R&D activities, and may alleviate financial constraints (Guzzini and Iacobucci, 2014).
An indicator of financial constraints was also included in the model. Financial constraints provide an approximate proxy of credit market efficiency and are generally good at explaining under-investment in technology. They are commonly considered to be one of the major factors constraining innovation (Hall et al., 2016; Chen et al., 2018; Nemlioglu and Mallick, 2020; Kou et al., 2020). A shortage of financial resources may hamper or delay a company’s decision about whether to implement R&D projects. The rationale is that having access to internal resources facilitates investment by limiting the risks that arise when firms use external sources of finance. This strongly impacts on the costs of financing. R&D investment is arguably riskier in general. Sunk costs and other forms of market failures are commonly associated with this idea. Credit constraints have also been found to impact on exports negatively (Aristei and Franco, 2014). In light of this, we included lack of appropriate financing as a variable (equal to 1 if the firm acknowledged a shortage of finance as the major factor constraining innovation, 0.5 if this shortage was rated as the second factor and 0 otherwise).
We controlled for internal heterogeneity of firms’ innovative activity between regions. The spatial technological context was proxied by the regional average R&D spending over gross domestic product (similar to Rodríguez-Gulías et al., 2020, and Carboni and Medda, 2021). This variable was built using Eurostat data from 2007 and was matched to the EFIGE dataset. We followed the idea that the technological context plays an important role in encouraging companies to engage in research and has an impact on the level of intensity of this. Consolidated literature starting with Jaffe (1986) has shown the existence of localized technological spillover and that firms benefit from neighbours’ innovative activities (Bengoa et al., 2017; Lòpez-Bazo and Motellòn, 2018; Coad, 2019; Rodríguez-Gulías et al., 2020). This information represented our instrumental variable in the econometric estimates.
The R&D dichotomy variable was constructed according to the information contained in the survey about companies’ research activity in the triennium 2007–2009. Research activity refers to four different modes: (1) invested in R&D; (2) acquired R&D from companies within the same group; (3) acquired R&D from other firms/consultants; and (4) acquired R&D from universities and research centres.
The following types of innovation were considered: a) process innovation; b) product innovation; c) process and product innovation; d) product innovation new to the firm; and e) product innovation new to the market; the dummy variable was constructed according to the information contained in the survey.
The analysis included country controls to account for unobserved country-specific effects, and industry controls (manufacturing sectors, defined by two-digit NACE Rev. 1 codes) were employed to check for potential sectoral systematic differences in research, innovation and export decisions.
3.3. The Role of Regional Innovation
Consolidated literature since Jaffe (1986) has demonstrated the existence of localized technological spillover (Lòpez-Bazo and Motellòn, 2018; Coad, 2019; Audretsch and Belitski, 2020). Firms benefit from the innovative activities of neighbouring companies and adjust their R&D decisions on the basis of the local technological environment and opportunities (Bengoa et al., 2017). Even though we could not deepen the analysis of themes relating to geographical aspects, we controlled for significant internal heterogeneity in firms’ innovative activity between regions (countries).
In accordance with regional technological innovation literature, we hypothesized that territorial conditions have a role in influencing firms’ R&D decisions (a relevant condition for instrumental variables; Ketokivi and Mcintosh, 2017; Angrist and Krueger, 2001), but they are not correlated with the error term of the structural equation with each firm’s export intensity as a dependent variable. The regional context impacts on companies’ innovation output through its influence on each firm’s internal R&D (exclusion condition), as well as on other inputs in firms’ knowledge production function (Griliches, 1979). In other words, we separated inputs from the outputs of firms’ innovative activity (Hagedoorn and Cloodt, 2003; Ganotakis and Love, 2011), considering the local technological environment as a crucial factor (Roper and Love, 2017 ; Holl, Peters, and Rammer, 2022).
The spatial technological context was proxied by total regional R&D spending over gross domestic product (Rodríguez-Gulías et al., 2020, and Carboni and Medda, 2021). This information represented our instrumental variable (IV). It is worth noting that our framework required the instrumental variable to be excluded from the structural equation. Finally, we checked the validity of our instrumental variable following the guidelines proposed by Ketokivi and McIntosh (2017), although (as argued in the work of Angrist and Krueger, 2001) the assumption beyond the exclusion restriction is formally untestable. In the second step, we estimated the structural equation where R&D was included to test its effect on innovation outcomes.
3. Results
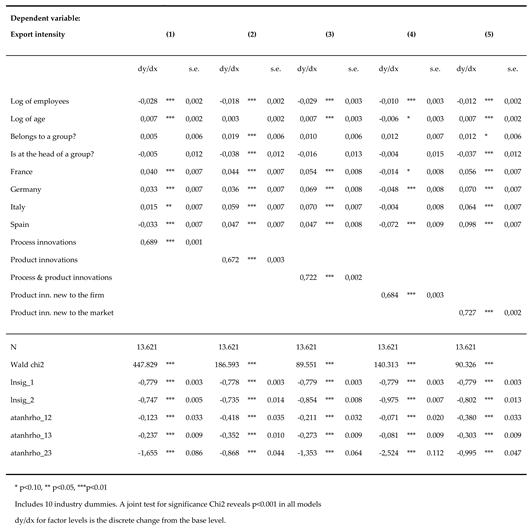
The estimated results of equation (3) are given in
Table 2. All estimates confirmed our hypothesis that innovation has a positive and highly significant impact on exports. The average marginal effect of innovations on export intensity of any kind among the firms studied here was between 67.2% (for the general product innovation dummy) and 72.7% (for the new-to-the-market product innovation dummy). The average effect on export intensity from carrying out process innovation was larger than that found for product innovation, except for cases where the product was new to the market.
It is worth noting that the effect was highest in the case of product innovations new to the market (0.727). Moreover, in line with Ayllón and Radicic (2019), a complementarity effect was found between product and process innovation: when product and process innovations occur together, the effect on exports (0.722) is greater than when they are carried out alone (0.689 and 0.672, respectively). This might be a sign that firms performing both types of innovations are tout court technology-oriented and, for this very reason, more related to international markets. This somewhat contradicts conventional wisdom that product innovation has a major role in export performance (Becker and Egger, 2013). However, Bıçakcıoğlu-Peynirci et al. (2019) argue that process innovation can significantly improve productivity, which is a crucial factor in international markets. Furthermore, in accordance with Aw, Roberts and Xu (2008), exporting companies invest in product innovations which have a stronger link with international market exposure.
Being part of a business group has positive effects in the case of product innovation. This might suggest that the interaction between these two aspects has a role to play, probably due to the presence of internal spillovers within the group. The coefficient is non-significant in the case of process innovation and product and process innovation. Size generally has a negative impact on exportation. This is also corroborated by the negative coefficient for firms that are the head of a group (which are commonly large in size). It is worth noting that the period covered by the dataset coincided with financial crises where large exporting firms suffered the most. Concerning the age of firms, our estimations did not supply clear evidence.
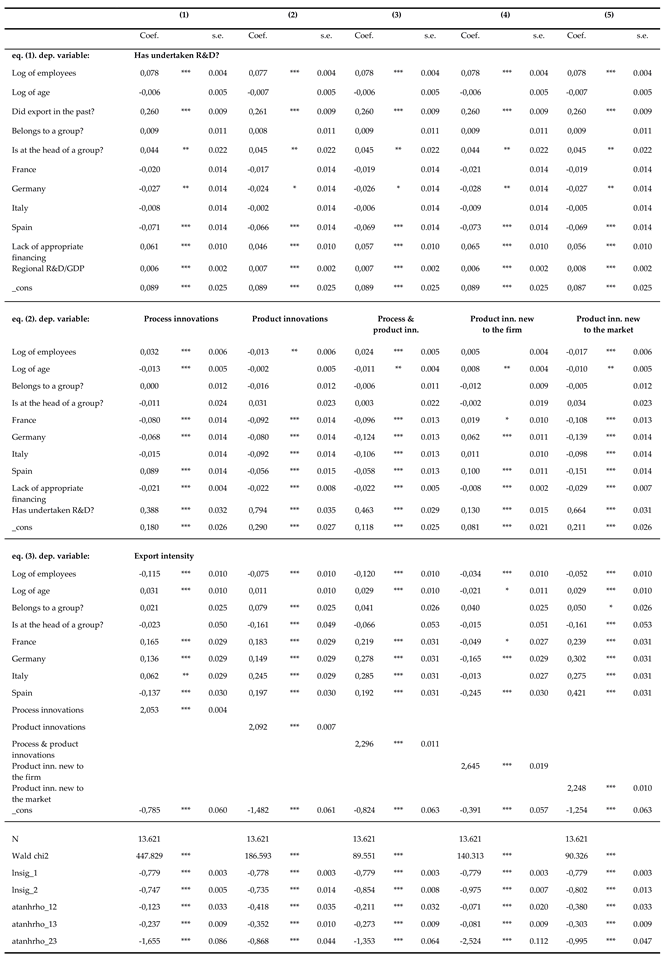
Table 3 shows the results for the three-equation system estimation. In the first stage (eq. (1) at the top of the table), the binary R&D decision was the dependent variable. It is worth noting that the technological regional context variable was found to have a positive effect on R&D, suggesting the relevance of geographical spillovers. The size of firms asserts a positive impact on decisions to carry out R&D, particularly for those at the head of a group. It also emerges that being part of a group itself does not have a significant effect on research. Having exported in the past has a positive impact on R&D. However, it is not easy to state whether this is due to structurally persistent characteristics of firms which push them to enter and remain in the international market, or whether it is the result of reverse causality between export and innovation.
The second stage (eq. (2)) involved the five different types of innovation as dependent variables. From the estimations, it emerged that small firms are more innovative in terms of products, while in terms of process, large firms appear to be more performant. Concerning the research variable, the results suggest that commitment to R&D impacts overall on the probability of performing product innovations (the coefficient was double that for process innovation). This is not surprising given that in order to create innovations in the process of production, along with the intensity of research commitment, it is also important to realize organizational changes. The latter are widely acknowledged as being crucial to maintaining a competitive advantage in a changing environment and also beneficial for efficient implementation of technical product and process innovations (Carboni and Russu, 2017). The results also confirm the relevance of financial resources in the innovation process (Hall et al., 2016; Nemlioglu and Mallick, 2020).
In the third panel of
Table 3 (eq. (3) at the bottom of the table), the variable of observation is export intensity, and the five types of innovation are the explanatory variables. All types of innovation exert a positive and highly significant effect on export intensity. The estimated effect of size was negative overall, while belonging to a group or being at the head of a group was found to have positive effects on export intensity in the product innovation equation only. Significant industry-specific effects were detected. In the same manner, country fixed effects suggest the presence of structural differences among countries, possibly related to the specific legal system, and the national economic and institutional environment that firms belong to.
Finally, tests of the model’s validity corroborated the approach used: the atanhrho statistics were all highly significant, revealing correlations between the error terms of pairs of equations. These values were different from zero in all the specifications, thus allowing rejection of the hypothesis of exogeneity of the R&D variable.
The excluded instrumental variable (regional technological opportunities) was shown to assert a highly significant and positive impact on R&D propensities, as reported in equation (1) and (2) regressions. This finding is aligned with studies that stress the geographical dimension as a cause of the considerable heterogeneity in firms’ innovation outcomes (Lychagin et al., 2016; Hu et al., 2020) and confirms the crucial role of local public commitment to promoting innovation (García-Vega and Vicente-Chirivella, 2020; Carboni and Medda, 2021). This result corroborates the validity of our instrument, which was also confirmed by highly significant chi-square tests. The latter enabled us to reject the null hypothesis of variable coefficients jointly equal to zero. Although this does not represent a full resolution, we reasonably believe that the analysis supports the conclusion that the endogeneity bias was sensibly mitigated.
4. Discussion and Conclusions
In this work, we investigated the nexus between export performance and innovation. Given the marked heterogeneity associated with innovation, we explicitly distinguished between a) process innovation; b) product innovation; c) process and product innovation; d) product innovation new to the firm; and e) product innovation new to the market. Such heterogeneity relates to several internal and external factors, including industrial sectors and the economic and institutional environment.
The empirical analysis was based upon a large and representative sample of European manufacturing firms in Germany, France, Italy, Spain and the UK. This is an important target, particularly considering the lack of unequivocal evidence available and considering the European Union’s trade policy, which stresses the role of research and innovation for economic growth and employment.
We developed an integrated model incorporating R&D, innovation and export, in a framework of simultaneous equations which consider their mutual correlations. We considered firms’ decisions to engage in research as an endogenous process and analysed factors which may affect firms’ propensity for R&D commitment. Moreover, it is possible that choices about whether to engage in research and innovation activities and in those related to export are made jointly by firms. Hence, we employed a recursive system of regression equations. This meant that the analysis could consider whether firms make different decisions about R&D, innovation and export simultaneously.
We also considered the fact that firms may benefit from neighbouring companies’ technological activity and adapt their R&D decisions to the surrounding knowledge opportunities. For this purpose, we used total regional R&D spending over regional gross domestic product as a proxy for the geographical technological context. This information represented our instrumental variable in the econometric setting. Finally, given the bounded nature of the dependent variable and the possibility of values at the boundaries, we made use of the fractional specification. Only a limited number of empirical investigations have considered this specific issue, potentially leading to biased estimates.
Although the cross-sectional nature of the data did not allow long-term effects to be estimated, the analysis produced some valuable insights, such as the nexus between export performance and product and process innovation. What differentiates our results from previous literature is that we found process innovation to have a larger average effect on export intensity than on product innovation. However, when product innovations are new to the market, their effect is stronger, and this is also the case when they are carried out together with process innovations, in which case significant complementarity effects arise.
The importance of innovation and its interaction with R&D in the export process has clear policy implications. Firms ought to capitalize upon R&D and, while trying to improve their export performance, focus on innovative activities which are strictly linked to research activity. This circular process embraces several crucial internal and external aspects. The innovation process is, in fact, systemic and has complex interactions involving workers, the organization of firms and the external environment. Firms capable of taking full advantage of their technological efforts are likely to benefit from complementary expertise in other areas of their business. Awareness of such dimensionality is crucial and may help firms develop better export strategies.
To identify and frame opportunities, firms need to constantly explore technologies, markets and customers, and create appropriate capabilities and competences. This, in turn, means commitment to technological research, understanding the evolution of demand, industries, markets and competitors. Constructing (and progressively honing) these skills helps firms to make appropriate decisions and achieve better long-term export performance. This is particularly true as product innovation contributes to the renewal of a company through its dynamic and mutual relationship with capacity, which, in turn, is strongly determined by R&D activity.
One limit of this study is that we only analysed a cross-section of companies (although the dataset was large and related to multiple countries). As new data become available, future enquiries should concentrate on the dynamic sequence of firms’ choices regarding R&D, innovation, export entry (and exit) and export performance. This would provide a clearer picture of exporting strategies from a sequence-of-events perspective. Another limit of this research is that we did not consider the role of public policies aimed at promoting exports (such as trade liberalization) or policies aimed at encouraging innovation through tax reforms. Further investigation can study how reduction of trade tariffs can impact on firms’ success in global markets.
Author Contributions
O.A.C.: writing-original draft, conceptualization, investigation, data curation, methodology, writing-review and editing, supervision. G.M., conceptualization, writing-original draft, software, data curation, formal analysis. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded with the support of University of Sassari ‘Fondo di Ateneo per la Ricerca 2022’; ‘Fondazione Banco di Sardegna’ and ‘Fondo progetto di eccellenza DISEA, University of Sassari’.
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank University of Sassari ‘Fondo di Ateneo per la Ricerca 2022’; ‘Fondazione Banco di Sardegna’ and ‘Fondo progetto di eccellenza DISEA, University of Sassari’ for financial support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results”.
| 1 |
When the observations at one or both boundaries display too large a frequency, it may be preferable to use two-part models. |
| 2 |
The original dataset also contains information about Austria and Hungary, however given the numerous missing observations that prevented us from generating our core variables, these two countries have been excluded from the study. |
References
- Aghion, P.; Bergeaud, A.; Lequien, M.; Melitz, M.J. The impact of exports on innovation: Theory and evidence. NBER working paper No. w24600. Nber Inc. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Altomonte, C.; Aquilante, T.; Békés, G.; Ottaviano, G. Internationalization and innovation of firms: Evidence and policy. Economic Policy 2013, 28, 663–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altomonte, C.; Gamba, S.; Mancusi, M.L.; Vezzulli, A. R&D investments, financing constraints, exporting and productivity. Economics of Innovation and New Technology 2016, 25, 283–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angrist, J.D.; Krueger, A.B. Instrumental variables and the search for identification: from supply and demand to natural experiments. Journal of Economic Perspectives 2001, 15, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aristei, D.; Franco, C. The role of credit constraints on firms’ exporting and importing activities. Industrial and Corporate Change 2014, 23, 1493–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzeni, G.E.; Carboni, O.A. ICT Productivity and Human Capital: The Italian North-South Duality. RISEC (International Review of Economics and Business) 2004, 51, 265–284. [Google Scholar]
- Atzeni, G.E.; Carboni, O.A. The effects of subsidies on investment: an empirical evaluation on ICT in Italy. Revue de l’OFCE 2006, 5, 279–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audretsch, D.; Belitski, M. The role of R&D and knowledge spillovers in innovation and productivity. European Economic Review 2020, 123, 103391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aw, B.Y.; Roberts, M.J.; Xu, D.Y. R&D investments, exporting, and the evolution of firm productivity. American Economic Review 2008, 98, 451–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aw, B.Y.; Roberts, M.J.; Xu, D.Y. R&D Investments, Exporting, and Productivity Dynamics. American Economic Review 2011, 101, 1312–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayllón, S.; Radicic, D. Product innovation, process innovation and export propensity: persistence, complementarities and feedback effects in Spanish firms. Applied Economics 2019, 51, 3650–3664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, S.; Egger, P. Endogenous product versus process innovation and a firm’s propensity to export. Empirical Economics 2013, 44, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengoa, M.; Román, V.M.; Pérez, P. Do R&D activities matter for productivity? A regional spatial approach assessing the role of human and social capital. Economic Modelling 2017, 60, 448–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berchicci, L. Towards an open R&D system: Internal R&D investment, external knowledge acquisition and innovative performance. Research Policy 2013, 42, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bıçakcıoğlu-Peynirci, N.; Hizarci-Payne, A.K.; Özgen, Ö.; Madran, C. Innovation and export performance: a meta-analytic review and theoretical integration. European Journal of Innovation Management 2019, 23, 789–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carboni, O.; Russu, P. Complementarity in product, process, and organizational innovation decisions: Evidence from European firms. R&D Management 2017, 48, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carboni, O.A.; Medda, G. Innovative activities and investment decision: evidence from European firms. Journal of Technology Transfer 2021, 46, 172–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassiman, B.; Golovko, E.; Martínez-Ros, E. Innovation, exports and productivity. International Journal of Industrial Organization 2010, 28, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassiman, B.; Golovko, E. Innovation and Internationalization Through Exports. Journal of International Business Studies 2011, 42, 56–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, L.K.; Lakonishok, J.; Sougiannis, T. The stock market valuation of research and development expenditures. The Journal of Finance 2001, 56, 2431–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Chen, X.; Wanga, C.; Xiang, X. Export behaviour and firm innovation: New method and evidence. Economics Letters 2018, 170, 76–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coad, A. Firm age: a survey. Journal of Evolutionary Economics 2018, 28, 13–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coad, A. Persistent heterogeneity of R&D intensities within sectors: evidence and policy implications. Research Policy 2019, 48, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, A.; Vivarelli, M. Succeeding in innovation: key insights on the role of R&D and technological acquisition drawn from company data. Empirical Economics 2014, 47, 1317–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crépon, B.; Duguet, E.; Mairesse, J. Research, innovation and productivity: an econometric analysis at the firm level. Economic of Innovation and New Technology 1998, 7, 115–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damijan, J.P.; Kostevc, Č.; Polanec, S. From Innovation to Exporting or Vice Versa? The World Economy 2010, 33, 374–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohse, D.; Niebuhr, A. How different kinds of innovation affect exporting, Economics Letters 2018, 163, 182–185. 163. [CrossRef]
- European Commission. (2013). Trade, growth and jobs. Contribution from the Commission to the February 2013 European Council Debate on Trade, Growth and Jobs, 1–20. http://trade.ec.europa.eu/doclib/docs/2013/april/tradoc_151052.pdf.
- Ganotakis, P.; Love, J.H. R&D, product innovation, and exporting: evidence from UK new technology-based firms. Oxford Economic Papers 2011, 63, 279–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Vega, M.; Vicente-Chirivella, Ó. Do university technology transfers increase firms' innovation? European Economic Review 2020, 123, 103388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griliches, Z. Issues in Assessing the Contribution of Research and Development to Productivity Growth. Bell Journal of Economics 1979, 10, 92–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guisado-González, M.; Wright, L.; Guisado-Tato, M. Product–process matrix and complementarity approach. The Journal of Technology Transfer 2017, 42, 441–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzzini, E.; Iacobucci, D. Business group affiliation and R&D. Industry and Innovation 2014, 21, 20–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagedoorn, J.; Cloodt, M. Measuring innovative performance: is there an advantage in using multiple indicators? Research Policy 2003, 32, 1365–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, B.H.; Moncada-Paternó-Castello, P.; Montresor, S.; Vezzani, A. Financing constraints, R&D investments and innovative performances: new empirical evidence at the firm level for Europe. Economics of Innovation and New Technology 2016, 25, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, R.; Li, Q.C. Exporting, R&D, and absorptive capacity in UK establishments. Oxford Economic Papers 2009, 61, 74–103. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, R.; Li, Q.C. Participation in export markets and the role of R&D: establishment-level evidence from the UK Community Innovation Survey 2005. Applied Economics 2011, 43, 3007–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holl, A.; Peters, B.; Rammer, C. ; Local knowledge spillovers and innovation persistence of firms. Economics of Innovation and New Technology. [CrossRef]
- Hullova, D.; Trott, P.; Simms, C.D. Uncovering the reciprocal complementarity between product and process innovation. Research policy 2016, 45, 929–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İpek, İ. Organizational Learning in Exporting: A Bibliometric Analysis and Critical Review of the Empirical Research. International Business Review 2019, 28, 544–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, A.B. Technological opportunity and spillovers of R&D: evidence from firms' patents, profits, and market Value. American Economic Review 1986, 76, 984–1001. [Google Scholar]
- Ketokivi, M.; McIntosh, C.N. Addressing the endogeneity dilemma in operations management research: theoretical, empirical, and pragmatic considerations. Journal of Operation Management 2017, 52, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, M.; Yang, Y.; Chen, K. The impact of external R&D financing on innovation process from a supply-demand perspective. Economic Modelling 2020, 92, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Bazo, E.; Motellón, E. Innovation, heterogeneous firms and the region: evidence from Spain. Regional Studies 2018, 52, 673–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lychagin, S.; Pinkse, J.; Slade, M.E.; Van Reenen, J. Spillovers in space: does geography matter? Journal of Industrial Economics 2016, 64, 295–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medda, G. External R&D, product and process innovation in European manufacturing companies. Journal of Technology Transfer 2020, 45, 339–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemlioglu, I.; Mallick, S. Do innovation-intensive firms mitigate their valuation uncertainty during bad times? Journal of Economic Behavior and Organization 2020, 177, 913–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. 2015. STAN R&D: Research and Development Expenditure in Industry - ISIC Rev. 4. 2015 ed. STAN: OECD Structural Analysis Statistics (database).
- Papke, L.E.; Wooldridge, J.M. Econometric methods for fractional response variables with an application to 401(k) plan participation rates. Journal of Applied Economics 1996, 11, 619–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, E.A.; Ramalho, J.; Murteira, M.R. Alternative estimating and testing empirical strategies for fractional regression models. Journal of Economic Surveys 2011, 25, 19–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Gulías, M.J.; Rodeiro-Pazos, D.; Fernández-López, S. The effect of regional resources on innovation: a firm-centered approach. Journal of Technology Transfer 2020, 46, 760–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roodman, D. Fitting fully observed recursive mixed-process models with cmp. Stata Journal 2011, 11, 159–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roper, S; Love, J. H.; Bonner, K. Firms’ knowledge search and local knowledge externalities in innovation performance. Research Policy 2017, 46, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavassoli, S. The Role of Product Innovation on Export Behaviour of Firms: Is It Innovation Input or Innovation Output That Matters? European Journal of Innovation Management 2018, 21, 294–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Un, C.A.; Cuervo-Cazurra, A.; Asakawa, K. R&D Collaborations and Product Innovation. Journal of Product Innovation Management 2010, 27, 673–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Un, C.A.; Asakawa, K. Types of R&D collaborations and process innovation: The benefit of collaborating upstream in the knowledge chain. Journal of Product Innovation Management 2015, 32, 138–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Beveren, I.; Vandenbussche, H. Product and process innovation and firms' decision to export. Journal of Economic Policy Reform 2010, 13, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooldridge, J.M. 2010. Econometric Analysis of Cross Section and Panel Data. MIT Press Books, The MIT Press, edition 2.
- Wu, L.; Wei, Y.; Wang, C. Disentangling the effects of business groups in the innovation-export relationship. Research Policy 2021, 50, 104093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulff, J.N.; Villadsen, A.R. Keeping it within bounds: Regression analysis of proportions in international business. Journal of International Business Studies 2020, 51, 244–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, M. Market Orientation, Product Innovation and Export Performance: Evidence from Chinese Manufacturers. Journal of Strategic Marketing 2016, 24, 377–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Chart 1.
Estimation models scheme and variables
Chart 1.
Estimation models scheme and variables
Table 1.
Descriptive statistics.
Table 1.
Descriptive statistics.
Table 2.
Innovation and export.
Table 2.
Innovation and export.
Table 3.
Three equation model
Table 3.
Three equation model
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).