Water quality is a measure of the definite state of water in terms of the requirements of several aquatic biota for optimal human use (Shah, 2017; Olalekan et al., 2022a, b; Raimi et al., 2022b, c; Raimi & Sawyerr, 2022; Stephen et al., 2023). Water quality parameters elaborate comprehensive information on the ecological impacts of lagoon water contamination due to domestic, agricultural, and industrial effluents (Odipe et al., 2018). Water is categorized into four groups based on its attribute such as infected water, contaminated water, palatable water and potable water (Chatterjee, 1996). Contaminated water comprises undesired physical, chemical, biological, and radioactive elements, making it unsafe for consumption or household purposes. Infected water is categorised due to its contamination with pathogens. Potable water has sustainable benefits such as safe consumption and domestic efficacy. Palatable water comprises the chemicals those do not risk the humans. Lagoons contain all these types of waters due to natural and the anthropogenic activities.
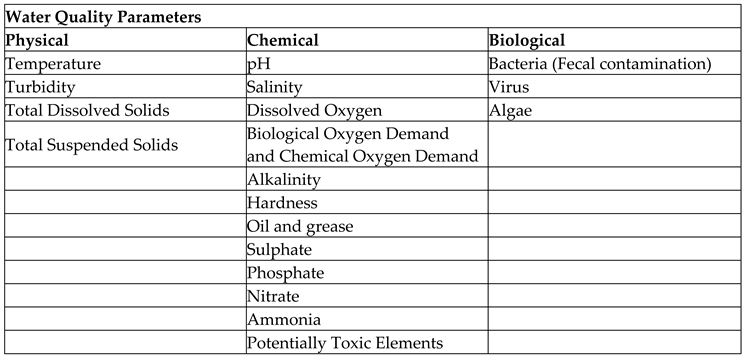
Table 1 illustrates all the physical, chemical, and biological parameters affecting the quality of lagoon water. Our research study have analysed every parameters in detail with respective to their threshold magnitudes of toxicology. Some experimental studies were also conducted using Sri Lankan lagoon water specimens using the available laboratory facilities to compare the lagoon water quality with the prerequisites mentioned for corresponding parameters in the literature sources.
2.1. Physical Parameters
2.1.1. Temperature
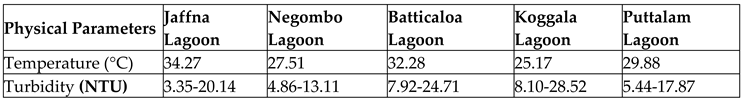
The biological activities in lagoon water are immensely influenced by temperature. It is an influential factor in terms of palatability, solubility, viscosity, odour and the biosorption of the Potentially Toxic Elements and metalloids (Abbas, Ismail, Mostafa, & Sulaymon, 2014; Olalekan et al., 2022a, b; Raimi 7 Sawyerr, 2022). It regulates metabolic activities, growth, reproduction, distribution, and migration of aquatic organisms in lagoon ecosystems (Suski, Killen, Kieffer, & Tufts, 2006; Odipe et al., 2018). Risks due to climate change impacts such as urban heat island (UHI) effect and wastewater discharge into lagoons due to anthropogenic activities all contribute to an increase in lagoon water temperature (Briciu et al., 2020). Since the majority of lagoon habitats are cold-blooded, the sudden changes in temperature due to environmental imbalances would stress the equilibrium and cause fatal results for fish species (Hall & Wazniak, 2005). Furthermore, aquatic species like fishes, phytoplanktons, zooplanktons, and insects have distinct body temperature ranges. The average temperature of five selected Sri Lankan lagoons recorded to test their nature is provided in
Table 2.
2.1.2. Turbidity
The turbidity of lagoon water is decided by the amount of suspended solids it contains. Both the light reflectivity of lagoon water and the extent of light penetration through water could be deduced by quantifying its turbidity. A turbidity test is conducted to estimate the ability of lagoon water to discharge waste corresponding to colloids (Meride & Ayenew, 2016). The content of suspensions such as clay, organic materials, planktons, silt, and other related particulates affects the amount of turbidity (Alley, 2007; Davis, 2010). These particulates due to various agricultural and industrial activities are emitted into lagoons. They serve as hotbeds for microorganisms; therefore, therefore prompted disinfection is required for the continuous supply of lagoon water for the existence of aquatic species.
Higher turbidity causes suspended matters to accumulate Potentially Toxic Elements, agricultural pesticides, and organic compounds such as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) via adsorption. (Cole et al., 2000). Determining turbidity of water after a rainfall might will indicate the emergence of a new contaminant into a lagoon. Turbidity measurements must be conducted on lagoon water specimens every three to four hours under extreme care if the lagoon is proposed to be utilised for drinking water purposes (Davis & Cornwell, 2008).
Table 2 of this manuscript illustrates the Turbidity test results conducted using turbidity tubes with water samples from five Sri Lankan lagoons.
2.1.3. Total Dissolved Solids (TDS)
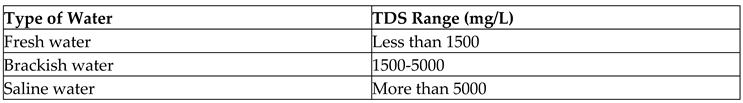
The measure of total mineral content in a lagoon water sample is described by the measure of TDS. If the lagoon water was optimum in pH and higher in TDS, the root systems of aquatic plants would be nourished further (Abinaya, Saraswathi, Rajamohan, & Mohammed, 2018; Chen et al., 2018). However, due to the agrochemical, industrial, and fuel contamination, the Sri Lankan lagoons generally contain higher pH and higher TDS. Moreover, higher chemical contamination of inland water bodies has caused drastic ecological losses in recent times in Sri Lanka (Adikaram, Pitawala, Ishiga, Jayawardana, & Eichler, 2021). It shows that the higher TDS of lagoon water could not only help on its own for enhanced aquatic biodiversity. Water can be effectively classified based on TDS as mentioned in
Table 3.
Minerals such as chlorides, bicarbonates, sulphates, potassium, magnesium, sodium and calcium are soluble after undergoing certain chemical transformations and produce detrimental changes in taste and colour of water. An extremely mineralized water sample contains excessive TDS and produces more deformations in water quality(S. A. Kader, Spalevic, & Dudic, 2022). Hard water is formed as a result of higher TDS. The most important factors in TDS are the constituents of chlorides, potassium, and sodium. These ions do not exist in higher amounts, but their presence would cause long-term effects. Most urban lagoons are contaminated due to urban runoff, pesticides, fertilizers, and construction debris, which lead to rise TDS in lagoons (Madarasinghe et al., 2020). Therefore, a comprehensive understanding of TDS using authentic past study results is compulsory to evaluate the undergoing sequences and to formulate effective solutions.
2.1.4. Total Suspended Solids (TSS)
The total amount waterborne solids with larger than 2mm particle sizes those found as suspensions are categorized into TSS (Saranga, Premarathne, & Atapattu, 2021). In contrary, total dissolved solid (TDS) are larger than 2 microns. The major constituents of TSS are inorganic compounds. Algae and bacteria are common examples for TSS. These TSS form in lagoons often by the surrounding ecosystem. Due to the water contamination by decaying organics in lagoons, silty suspended solids accumulate the water bottom and the other TSS species float on both the middle and surface. Concentration of suspended solids are inversely proportional to the clarity of water.
TSS is the standard parameter to measure the lagoon operators. It is a conventional pollutant that mostly induces the grooming of algae cells, sulphur bacteria, and protozoa (Wiley, Brenneman, & Jacobson, 2009). TSS levels beyond a certain threshold raise water temperatures and would also reduce the concentration of dissolved oxygen in lagoons. The main cause is the absorption of intense heat from solar radiation by the suspended particles in lagoon water (S. Kader, Jaufer, L., 2022; Paaijmans, Takken, Githeko, & Jacobs, 2008). Algae use carbonates and bicarbonate from the suspended solids as carbon sources and leads to high rate of algal blooms in lagoon. Furthermore, these suspended solids are clogged into fish gills and lead to their immune systems fused while declining their larval maturation, which is a serious biological effect (Kiprono, 2017; Tarras-Wahlberg, Harper, & Tarras-Wahlberg, 2003).
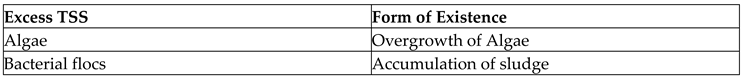
Table 4 shows the TSS types and the products in lagoon water effluents due to those corresponding TSS over existence.
2.2. Chemical Parameters
2.2.1. pH
pH is one of the important indicator for lagoon water quality. It is one of the key factors that ensures the longevity of aquatic species. pH represents the intensity of active hydrogens in water. The optimum pH magnitude for lagoon water is 7.0, while the increase beyond the optimum amount is defined as acidic and the decrementing values from 7.0 are termed alkaline (Alley, 2007; S. Kader, Chadalavada, Jaufer, Spalevic, & Dudic, 2022; Raimi et al., 2022b, c; Olalekan et al., 2022a, b; Raimi & Sawyerr, 2012). There are several natural and man-made elements that might influence the pH of lagoon water. The majority of natural changes are caused by interactions with carbonate and bicarbonate compounds, as well as other elements. Acid rain, wastewater, residential garbage, and mining discharges can all alterate the lagoon water pH. The anthropogenic activities induce variations in lagoon water CO2 concentrations and organic material decomposition intensities those passively influence the pH levels (Alam & Zohura, 2020; Raimi et al., 2022b, c; Olalekan et al., 2022a, b; Raimi & Sawyerr, 2012)). The recommended levels of pH for lagoon water is 6.5–8.5 according to the bibliographic references (Abowei, 2010; Davis & Cornwell, 2008; Organization, WHO., & Staff, 2004) for the existence of healthy ecosphere.
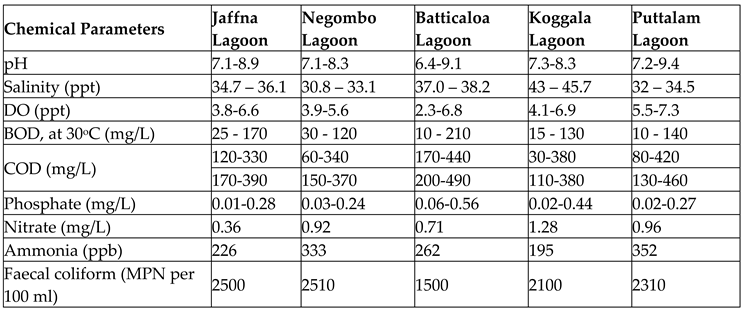
Since the majority of aquatic animals have adapted to a definite pH in aquatic ecosystems, the slight change in water pH could dearly cost its biodiversity (Cole et al., 2000). Because the fertility of fish eggs is drastically affected by the low pH of the water body due to the cell membrane being damaged by water acidity (Kiprono, 2017). Past studies have suggested that, pH below 4.0 or greater than 10.0 (i.e. pH < 4.0 or pH > 10.0) would disseminate the survival of most aquatic species including amphibians since they cannot endure the metabolic activities in such pH ranges (Abowei, 2010; Cole et al., 2000). Algal growths are heavily induced in water bodies beyond the 8.5 pH , which discrepancies the respiration of fishes (Ali, Salem, Younes, & Kaid, 2020). If the lagoon waters become more acidic, it induces the dissolving of Potentially Toxic Elements and lead to complicated level of toxicity for aquatic species. The water quality test results for pH conducted according to ASTM E70 guidelines in five different lagoons in Sri Lanka are provided in
Table 5.
2.2.2. Salinity
Salinity is the measure of mineral salt concentration in water. It is calculated using the freshwater discharge, evaporation, surface runoff, and precipitation classifications. Low salinity in lagoon water could result in ammonia toxicity in lagoon water, which could lead to eutrophication (Valencia-Castañeda, Frías-Espericueta, Vanegas-Pérez, Chávez-Sánchez, & Páez-Osuna, 2019). Along with temperature, salinity is a key determinant of the productivity of organisms in lagoons, and variations in salinity have affected the breeding rates of aquatic fishes (Lawson, 2011; Perera & Priyadarshana, 2015). The salinity of lagoon water mainly depends on two factors, namely rainfall and proximity to the sea. It increases the salinity of lagoon water because of the incoming saline water from the sea. Due to the higher rate of evaporation, salinity in lagoon water will be comparatively higher in dry season. The global salinity of lagoon water exists within 33-37 ppt at 30°C (Huber et al., 2000). In the context of the overall sustainability of aquatic ecosystems, a proper level of salinity maintenance is highly preferable. However, high salinity is a favoured habitat for prawns (Sugirtharan, Pathmarajah, & Mowjood, 2015), and the ample salinity for the dwelling for prawn species was 4-25 ppt (Banerjee, 2008). Salinity test results for the Sri Lankan lagoon water samples are provided in
Table 5.
2.2.3. Dissolved Oxygen
Due to the necessity of oxygen for survival, DO has a distinguished value among the other water quality parameters since it has a direct influence on the longevity of aquatic biodiversity. Dynamic models are designed in field experiments for estimating the waste assimilating capacity (WAC) for organic wastes need to be deposited into a body of water in order to maintain ideal DO conditions in lagoons respective to natural and anthropogenic activities in the ecosystem (Hendriarianti et al., 2019). In lagoons, the atmosphere and aquatic plants are the main suppliers of oxygen. Plant decays, faecal excretes, domestic wastes, oil leakage from boats, industrial and agricultural aspects are all inhibitors of DO levels in lagoons. The increase of DO in water would raise the pH. Furthermore, atmospheric pressure of oxygen gas, temperature, and salinity are the main influencers in determining the DO levels in lagoon waterbodies (Lawson, 2011). In
Table 5, the mean magnitude ranges of dissolved oxygen in the selected Sri Lankan lagoon water specimens are provided.
2.2.4. Biochemical Oxygen Demand
Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) is the quantity of oxygen consumption by bacteria and fellow microorganisms when decomposing organic material under aerobic environment at a certain temperature. It is a statistic for determining water quality. BOD measurements are being utilised to remediate polluted lagoons. BOD has an effect on the quantity of dissolved oxygen in streams and rivers. The pH, microbe intensity, temperature, organic materials, and trace materials in lagoon water all influence the levels of oxygen by aquatic species (Tawalbeh et al., 2020; Afolabi & Raimi, 2021). It is also critical to understand that high BOD levels have similar impacts as low dissolved oxygen (DO) levels.
Bacteria and other microorganisms consume organic substances during fermentation. The broken organics were converted into simple compounds consisting of CO
2 and H
2O. The released energy is used up by microbes for their reproduction and growth. Water is considered to be contaminated at BOD levels exceeding 4mg/L. Tolerance range of BOD is between 5 and 6 mg/L in relation to Sri Lankan Central Environment Standards which is the governing body of water quality and maintenance in the inland water body of country (Piyasiri, 2009; Afolabi & Raimi, 2021).
Table 5 illustrates the BOD measured in five Sri Lankan lagoons using the manometric method.
2.2.5. Chemical Oxygen Demand
In terms of lagoon water ecosystem, Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) is the amount of oxygen consumed in the lagoon water for chemical oxidation in organic substances. Elevated COD levels result the depletion of oxygen content due to high microbial decomposition. It leads to detrimental aquatic life. COD serves in the lagoon as an indicating parameter for biodegradable and non-biodegradable organic content from its channels. The study related to municipal wastewater hydrodynamics using lagoon systems shows that redox potential (ORP) and COD show proportionality between the two parameters (García-Martínez et al., 2017; Raimi et al., 2022b, c; Olalekan et al., 2022a, b; Raimi & Sawyerr, 2012). High ORP due to more oxygen requirements for organic oxidations caused high concretions of COD in the field study. Furthermore, COD parameters seem to always be higher than the BOD of a particular sample (Metcalf, Eddy, & Tchobanoglous, 1991).
COD test determines the quantity of oxygen required for the chemical oxidation of organic compounds and mineral salts in water such as the ammonia and nitrates (S. Kader, Novicevic, & Jaufer, 2022). Unlike BOD, COD determines the extent of oxygen need to be removed from an organic substance after absorbing water due to bacterial activities. COD test is built upon the concept that a strong oxidising agent has heavy potential under an acidic medium to completely oxidise any organic substance into carbon dioxide (Meng et al., 2020; Raimi et al., 2022b, c; Olalekan et al., 2022a, b; Raimi & Sawyerr, 2012). After this oxidation, the intensity of organic substances at specimen is estimated by determining the oxidants. Titration with an indicator solution is typically used. COD is measured in milligrammes per litre of solution and represents the mass of oxygen used per litre of solutions. Unlike the BOD test, which takes 5 days, the COD test takes only 2-3 hours.
Table 5 shows the COD results obtained from the selected Sri Lankan lagoon waters.
2.2.6. Alkalinity
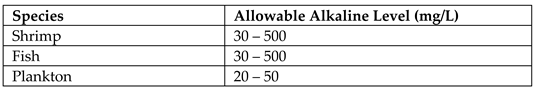
Alkalinity is the ability of aqueous solutions to neutralise strong acids. The presence of calcium, sodium, and potassium carbonates, bicarbonates, and hydroxides causes lagoons to be alkaline (Patil & Patil, 2010). The sources of these compounds are salt sediments, industrial wastes, and dissolved rocks. An experimental study based on Malala lagoon in Hambanota, Sri Lanka, has identified its alkalinity as 2.14 mmol/L with a tolerance of 0.59 mmol/L (Titus, Deepananda, & Cumaranatunga, 2017). The ambient alkaline levels for shrimp, fish, and planktons breeding in lagoon water were extracted from literature source (Boyd, 2019) and illustrated by
Table 6. The excessive alkalinity may disrupt the dynamic nature of the lagoon ecosystem and lead to the destruction of its biodiversity.
Alkalinity contributes to aquatic species through buffering the pH alterations that indirectly reduce the vulnerability of acid rain (Apau, Appiah, & Marmon-Halm, 2012). This buffering against acidity protects the aquatic species from undergoing a sudden pH change in their surroundings (Omer, 2020). Alkalinity does not change at the top, middle, or bottom of water columns in lagoons (Titus et al., 2017) but the decrease in alkalinity leads to eutrophication effects in water bodies (Verspagen et al., 2014). Therefore, the increment in the alkaline or acidic nature of lagoon water is also an indicator of chemical pollution.
2.2.7. Hardness
The extent of mineralization in lagoon water is often described by its hardness. Lagoon water gets hardened mainly due to the increased concentration of calcium ions (Ca2+), magnesium ions (Mg2+), or due to the increment of both ions (Patil & Patil, 2010; Spellman, 2008; Raimi et al., 2022b, c; Olalekan et al., 2022a, b; Raimi & Sawyerr, 2012). The existence of these metal ions during rock formation is a substantial cause of water hardness in lagoon water. Most common example is the deposition of limestone near the water bodies (Nadiri et al., 2022). Common forms of these ions are bicarbonates, chlorides, nitrates, and sulphates (Davis & Cornwell, 2008). Ions like barium (Ba2+), strontium (Sr2+) and iron (Fe2+) have negligible contributions to water hardness.
Water hardness is categorised into temporary and permanent hardness. Temporary hardness is the result of carbonates and bicarbonates, while permanent hardness is due to chlorides and sulphates (Metcalf et al., 1991). Generally, water hardness is given as total calcium and magnesium contents in water, given in milligrammes per litre of CaCO3. (Omer, 2020). The occupation of toxic elements like As, Cd, Pb, and nitrate compounds cause hardness in lagoon water. However, most countries including Sri Lanka do not have predetermined policies regulations regarding the thresholds for hardness. Therefore, they are not comparable incomparable since some literary sources offer a suggested range while others mandate minimum or maximum limit levels. Our conclusion upon the water hardness is well supported by data analytical study focused on water hardness in European Union member countries (Kozisek, 2020).
2.2.8. Oil and Grease
The lagoon environment endures significant pollution due to oil and grease by the effluents from petroleum-related disciplines such as transportation, industrial and municipal solid wastes, urban runoff, offshore effluents, and sediment erosion (Nadiri et al., 2022). The probable reasons for oil and grease contamination are unplanned infrastructure development thus causing hindrance to human benefits. Oil sediments in lagoon water surround the gills of fishes under low and high oil concentrations, causing suffocation for respiration. Oil pollution is responsible for the destruction of coral reefs and lead to the increased erosion of the lagoon coast. It also provides a passive contribution to the destruction of mangroves (Tong, Goh, Abdulah, Tahir, & Wang, 1999; Raimi & Sabinus, 2017; Olalekan et al., 2018; Raimi et al., 2021; Raimi et al., 2022b, c; Olalekan et al., 2022a, b; Raimi & Sawyerr, 2012).
In the Sri Lankan context, the main mode of oil contamination in lagoon waters are the transportation of engine boats in lagoons. Tolerance limits for oil and grease within the discharged effluents according to Sri Lankan standards is up to 20 mg/L (Najim & Kithsiri, 2021). However, a recent study have indicated that the oil and grease levels in Sri Lankan lagoons is getting exceeded beyond the allowable limits due to the existence of sea ports in the territories (Kanchana, Chandrasekara, Weerasinghe, Pathirana, & Piyadasa, 2021).
2.2.9. Sulphates
Sulphates are common pollutants in lagoons. The concentration of sulphates and their complex accumulation are directly influenced by the leaching of natural deposits, atmospheric deposition, and human discharges. In general, industrial activities like tanneries, textile mills, paper mills, mines, agricultural runoffs and smeltings release sulphates into lagoons (Meays, Nordin, Protection, & Branch, 2013). However, high sulphate concentrations are of particular concern to the mining industry. The most common forms of sulphates are gypsum (CaSO4.2H2O), barites (BaSO4) and epsomites (MgSO4.7H2O) and water contact in these kind of forms will pollute lagoons with sulphates (Greenwood & Earnshaw, 2012). Compounds such as Na2SO4, K2SO4 and MgSO4 have high solubility in water during the sulphur compound contaminations, while CaSO4, BaSO4 and the other cationic sulphates exhibit low solubility (Delisle & Schmidt, 1977).
Elevated sulphate concentrations in lagoon water cause long-term consequences for aquatic life. Maximum sulphate content in lagoon water should not exceed 2,700 mg/L (S. Kader, Jaufer, Shiromi, & Asmath, 2021; Meays et al., 2013). Turbidimetric experiments quantify the sulphate content in lagoon water. This test consider the reaction of sulphate ions with aqueous barium chloride is induced in an acidic medium to study the resulting turbidity (Hatiboruah, Talukdar, Ahamad, & Nath, 2021). The passive outcome of turbidimetric test is that the turbidity would be proportional to the sulphate concentration in the water specimen.
2.2.10. Phosphates
Agricultural runoff, detergents, home and industrial untreated sewage are all causes of phosphate pollution in the lagoon. For healthy aquatic life, the maximum permitted phosphate content is 0.4 mg/L (Bama, Thushyanthy, Alvappillai, & Pirabhaharan, 2013). Higher phosphate content would cause eutrophication, which gives both short-term and long-term BOD in lagoons. The maximum phosphate limit that a lagoon could buffer without eutrophication is 0.1 mg/L (Muthucumaran, Pathmarajah, & Mowjood, 2015). Phosphates are one of the most important constituents required in lagoon water since they significantly contribute for the formation and propagation of aquatic plant root systems. But they should not exceed their threshold limits.
2.2.11. Nitrate
Nitrates are soluble compounds those washed into ground water and gradually into lagoons. It is the primary source of algal blooms. The maximum contaminant level for nitrates is 10 mg/L (Boyer, 2014). Nitrogen polluted water appears grey colour and results health impacts including dizziness, fatigue and cardiac problems to aquatic organism (Davis, 2002; Raimi & Sabinus, 2017; Olalekan et al., 2018; Raimi et al., 2021; Raimi et al., 2022b, c, d; Olalekan et al., 2022a, b; Raimi & Sawyerr, 2012). Nitrates reach lagoons through faecal matters, solid waste deposits, septic tanks, agro fertilizers and wastewater sewages (Odipe et al., 2018). The main sources of nitrates are the municipal wastes, domestic wastes and the agricultural effluents.
Thermal treatment for nitrates is irrelevant since nitrates cannot evaporate like water. Nitrate pollution would cause higher carbon emissions due to greenhouse gas production (Kader, Chadalavada, et al., 2022) The total dissolved inorganic nitrogen is the sum of nitrates (NO
3), nitrites (NO
2) and ammonium (NH
4). Nitrification of lagoon waters can be explained as follows:
| NH3 + O2 + Nitrosomonas sp bacteria |
 |
NO2
|
| NO2 + O2 + Nitrobactor sp bacteria |
 |
NO3
|
2.2.12. Ammonia
Ammonia exists in lagoon water due to the microbial activities involving nitrogen-containing compounds and sewage effluents. Ammonia pollution in lagoons occur primarily due to wastewater effluents from anthropogenic activities like industries, public services like hospitals and due to the improper solid waste disposals by dumping besides lagoons (Vesilind & Morgan, 2004). The reduction of these nitrogen compounds results in ammonia in small amounts in water bodies. The existence of ammonia levels beyond 0.1mg/L Nitrogen indicates the water contamination. The maximum allowable ammonia limit in lagoon water surface is 0.8 mg/L (800 ppb). (Buijs & Toader, 2007). Excessive sewage pollution causes pathogenic offspring in lagoons. In terms of health issues, the presence of ammonia should be seriously considered to prevent the possibility of sewage pollution due to microorganisms in lagoons (Vesilind & Morgan, 2004). Water temperature, DO and algal concentrations in lagoons have an undisputed influence on the effluent rates of ammonia and nitrogen. Therefore, it can be inferred that the maintenance of DO and algal blooms under the tolerance limit is essential to prevent any contamination due to ammonia breeding in the lagoon.
Table 5 shows the ammonia levels measured using chemical titration on selected lagoons.
2.2.13. Potentially Toxic Elements
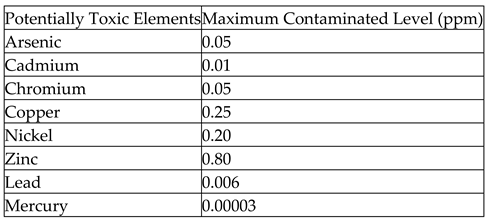
Human activities are the main contributors to the Potentially Toxic Element contamination in lagoons. Both agricultural and industrial effluents due to the toxic chemicals used in all those scenarios could accelerate Potentially Toxic Element contamination in lagoon water (Renu, Agarwal, & Singh, 2017). Lagoons accumulate highly concentrated Potentially Toxic Elements due to their biochemical nature. Environmental toxicity of Potentially Toxic Elements due to anthropogenic pressure in ecosystems has dwindle the lagoon water quality, decline the existence of lagoon species, and lead to destruction of resources. The presence of Potentially Toxic Elements beyond allowable range could challenge the health since they are carcinogenic and non-biodegradable (Qasem, Mohammed, & Lawal, 2021), thus causing the aquatic fishes to be inconsumable due to their intake of Potentially Toxic Element contaminated water. Commonly found Potentially Toxic Elements in lagoons are Lead (Pb), Arsenic (As), Zinc (Zn), Cadmium (Cd), Mercury (Hg), Nickel (Ni), Chromium (Cr) and Copper (Cu). Potentially Toxic Elements induce hatching delays, deformities, and mortality in fish (Sfakianakis, Renieri, Kentouri, & Tsatsakis, 2015; Raimi & Sabinus, 2017; Olalekan et al., 2018; Raimi et al., 2021; Raimi et al., 2022b, c; Olalekan et al., 2022a, b; Raimi & Sawyerr, 2012). The toxicity of Potentially Toxic Elements could vary according to their type, compound formation, and the quantity of deposition (Lawson, 2011). The maximum contaminated level standards for those Potentially Toxic Elements established by the USEPA are summarised in
Table 7.
2.3. Biological Parameters
2.3.1. Faecal Contamination
Intestinal guts of warm-blooded species produce faecal coliforms (Seo, Lee, & Kim, 2019). The existence of faecal coliforms is an indicator of the quality of water to be used for drinking purpose. These coliforms survive longer in water than most pathogenic bacteria. Total coliforms contain both faecal bacteria and non-faecal bacteria. When effluents from laundry sinks, domestic and industrial wastewater enter the lagoon, coliform bacteria enter via pastures, a faulty septic system, and animal waste. The existence of faecal coliforms in lagoon water could change its odour and cause some health-related effects on the living organisms.
Despite their pathogenic properties, their main advantage is that they can be used as a reliable and easy indicator of faecal pollution. The main sources of faecal bacteria are sewage. Surface water class II standard values for faecal coliform and total coliform are 14 and 70 MPN/100 mL, while class III standards for surface water are 200 and 1000 MPN per 100 mL (Consultants, 1994). The total coliforms and faecal coliforms were measured via membrane filtration (Munasinghe-Arachchige, Delanka-Pedige, Abeysiriwardana-Arachchige, Zhang, & Nirmalakhandan, 2019) and the results of the experiment are presented in Table 9.
2.3.2. Virus
Lagoons are becoming the predominant breeding places for viruses in recent times. The adverse effect of viral contamination of lagoons is the spread of diseases that affect the environmental balance. Impacts of viruses on the lagoon's water quality lead to harmful drawbacks in biological and economic aspects. Lagoons have been identified as a primitive source of mosquito-borne diseases in several case studies. Viruses of the genus Culex annulirostris and Orbivirus have been found in stretch lagoons in Australia, causing blue tongue disease in sheep, cattle, donkeys, and horses (Cowled et al., 2009). Studies conducted in the urban lagoons of Rio de Janeiro determined the breeding of rotavirus, norovirus, and human adenovirus within the surface water of the lagoon (Vieira et al., 2012). Shrimp farming in Sri Lanka in 1990 was heavily destroyed by the spread of the Monodan baculo virus and white spot syndrome virus in Puttalam lagoon (Arthur, 1998).
In the statistical sources of Sri Lankan context, it is evident that the country had suffered an enormous loss of 1 billion Sri Lankan rupees due to white spot disease in fishery exports (Senarath & Visvanathan, 2001). Moreover, the brood stocks in Sri Lanka's Puttalam lagoon region were affected by yellow head disease back in 1998, which coincided with white spot disease and resulted in a whopping 70% drop in shrimp exports (Munasinghe, Stephen, Abeynayake, & Abeygunawardena, 2010). The reasons for the viral contamination of lagoons are the destruction of mangrove habitats and paddy cultivation at surrounding locations.
2.3.3. Algae
Algal blooms in lagoon water bodies are a common occurrence due to nutrient enrichment by wastewater, agricultural waste, and storm water drainage. Overgrowth of algae causes high TSS and BOD in lagoon ecosystems, which causes problems for aquatic organisms (Lapointe, Herren, Debortoli, & Vogel, 2015). Furthermore, overgrowth of algae species releases toxic substances into lagoon waters, depletes deep water oxygen, decreases water column transparency, reduces health and size of corals, mitigates the overall aesthetic value in lagoons, conceals economic repercussions, and declines the existence, biomass, and diversity of aquatic plants (Smith, 2003). When the effluent discharges to the lagoon are in high intensity, algal blooms happen more in the offshores compared to the lagoon water (Hsieh et al., 2021) due to high turbidity of interior lagoon water and because of the short residence time of algae.