Submitted:
21 February 2023
Posted:
01 March 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Operational Risk Assessment of Drone using Bayesian Network
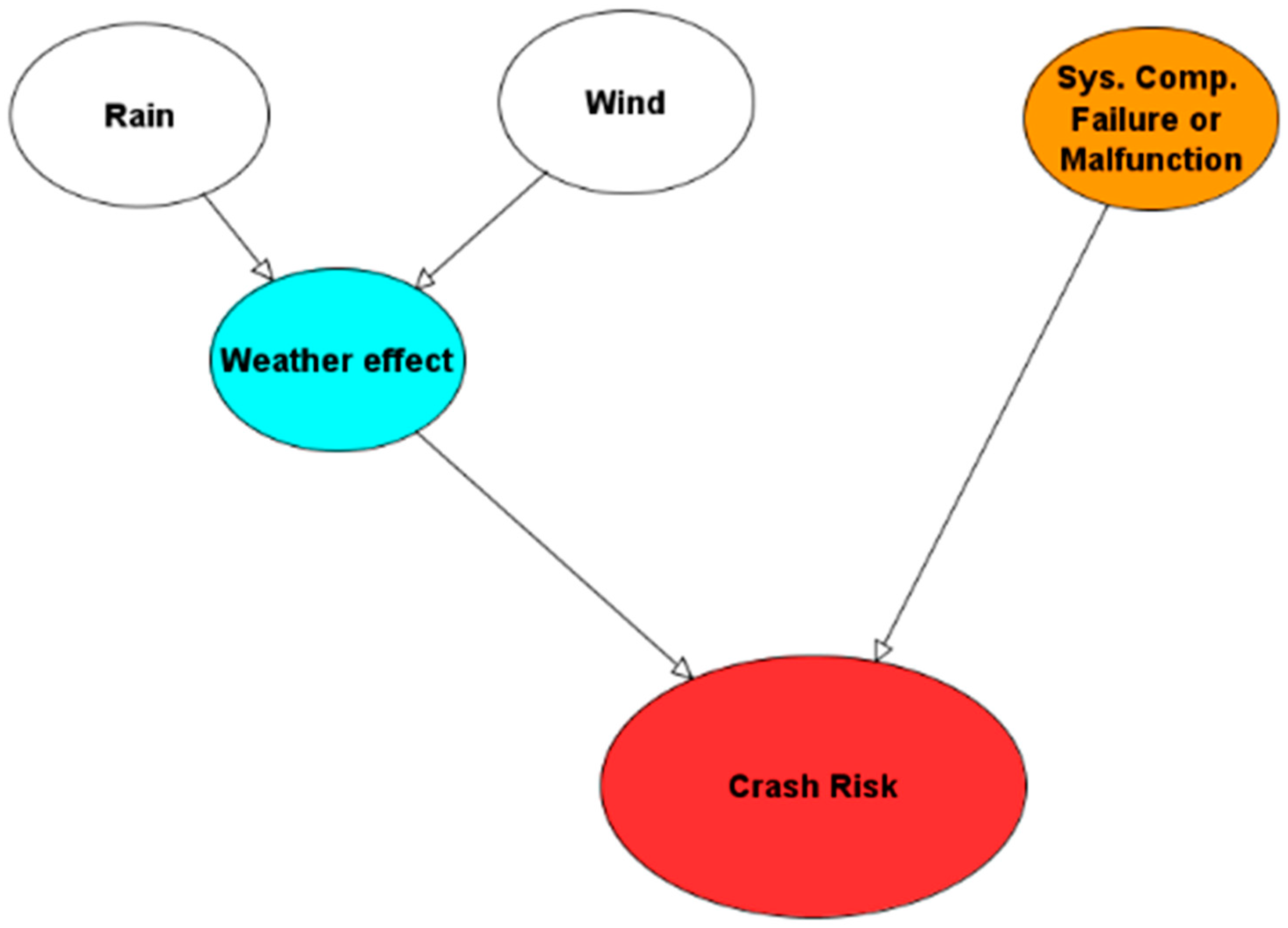
3. Drone Crash Risk Modelling using Bayesian Network
3.1. Study Area
3.2. Risk Identification and Network Building
- Catastrophic: the hazard causes harm or serious injuries or deaths to humans. The severity of such hazards is the highest considering that it affects human safety and thus must be carefully addressed and removed to avoid fatal situations.
- Critical: the event influences third parties except people, for example damaging buildings or assets in general.
- Marginal: the event causes damages to the drone system itself.
- Negligible: the event does not affect the operational capability of the drone (safe operation), or the drone doesn’t get crashed at all.
4. Result
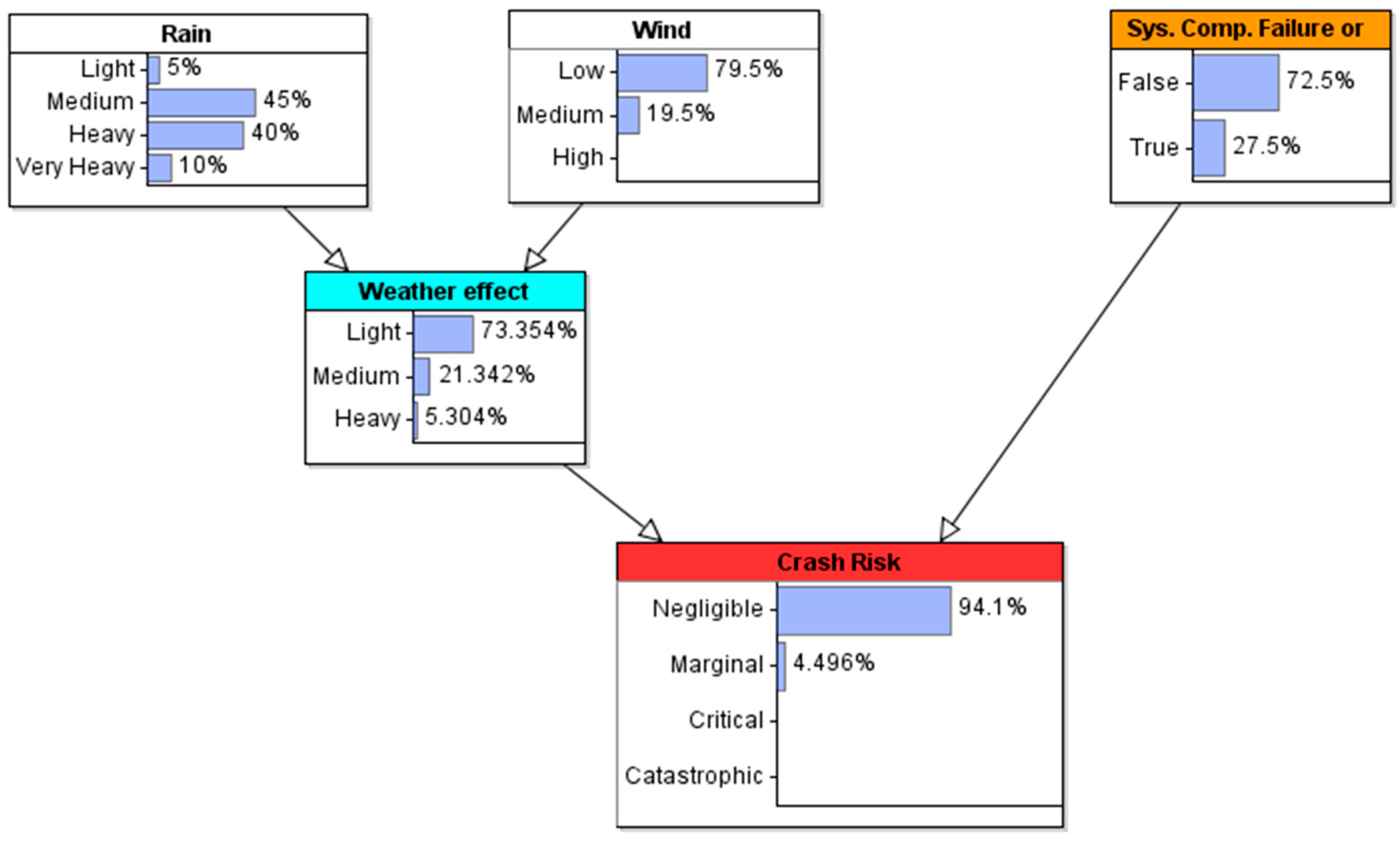
4.1. Prior Probability
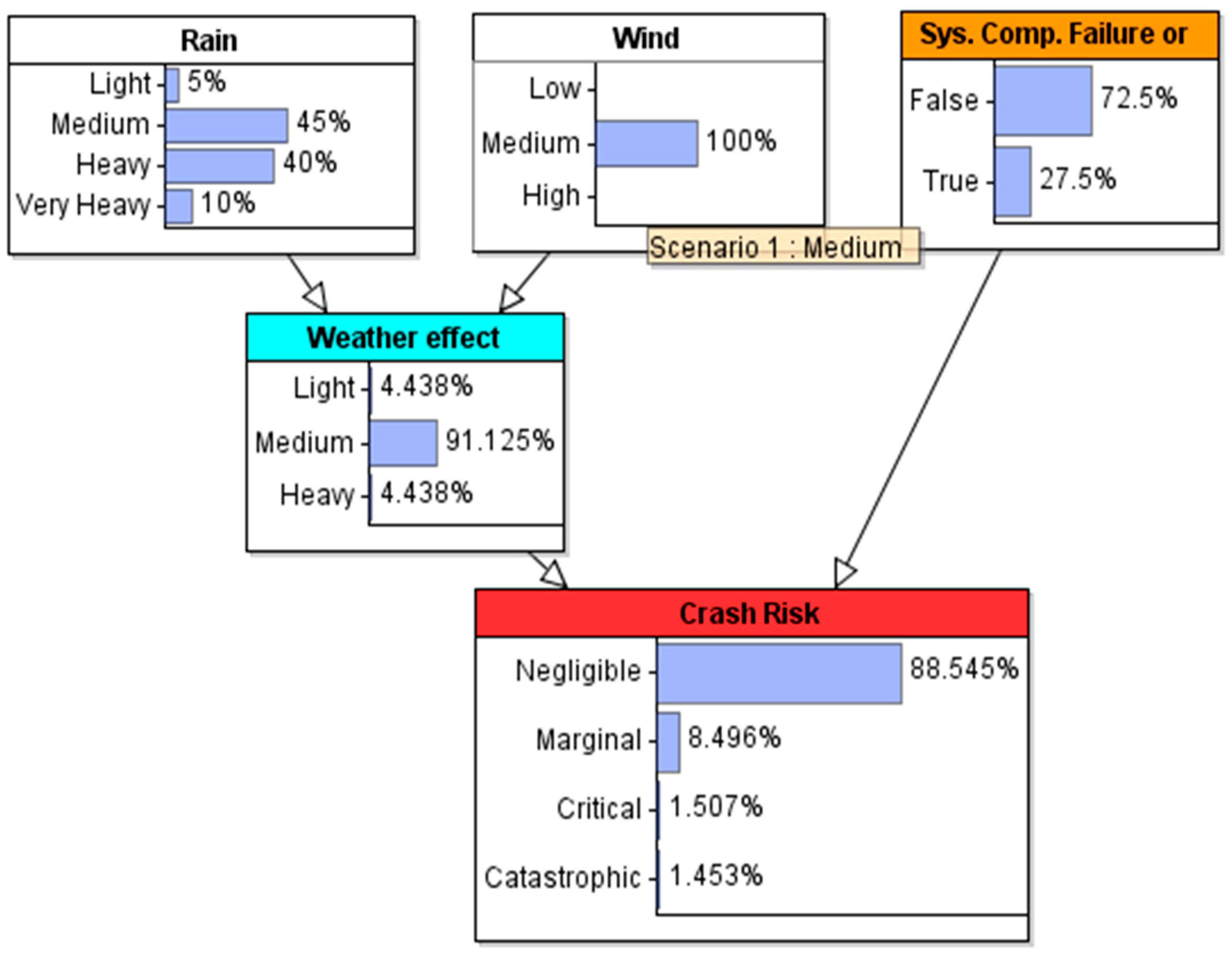
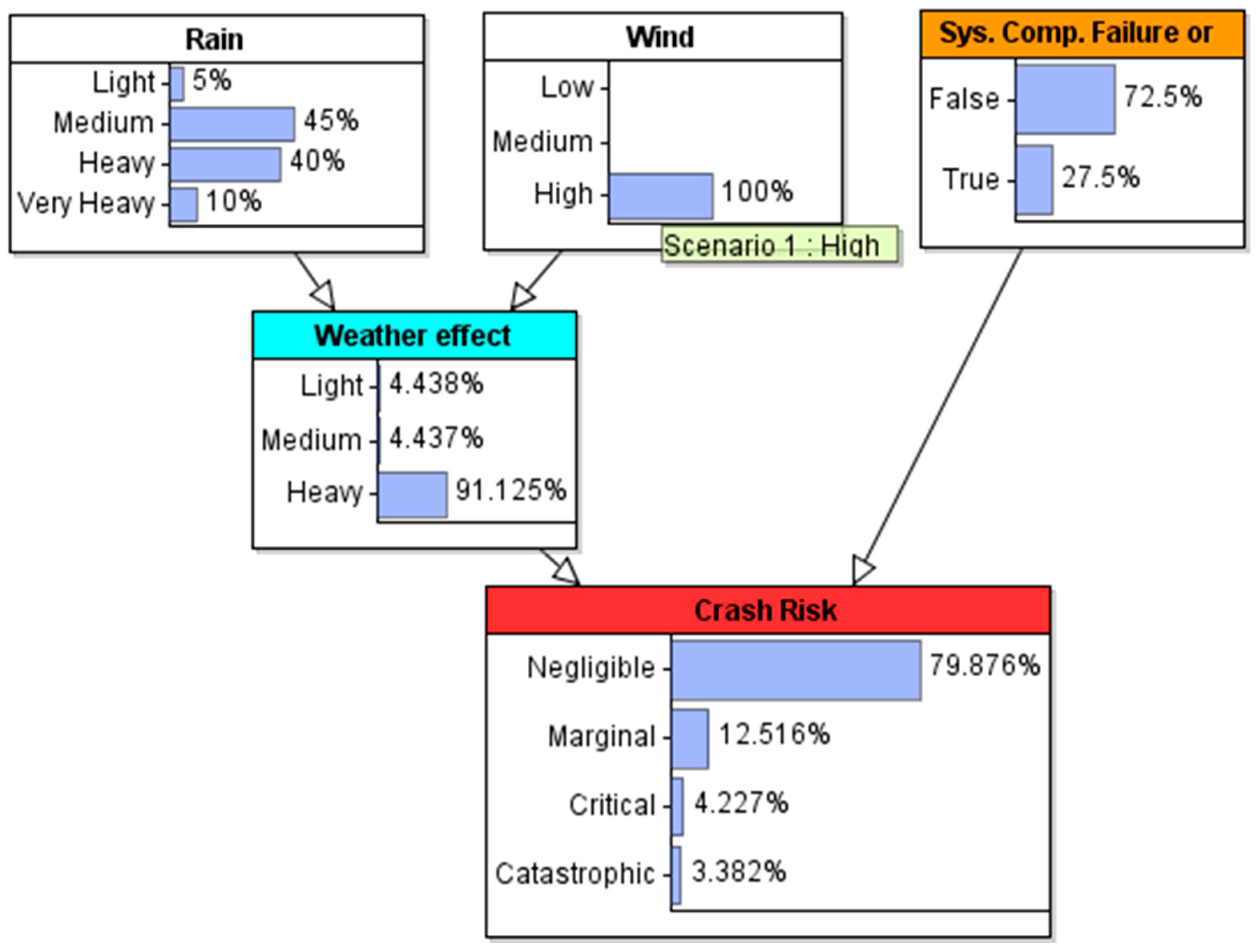
4.2. Scenario Analyses
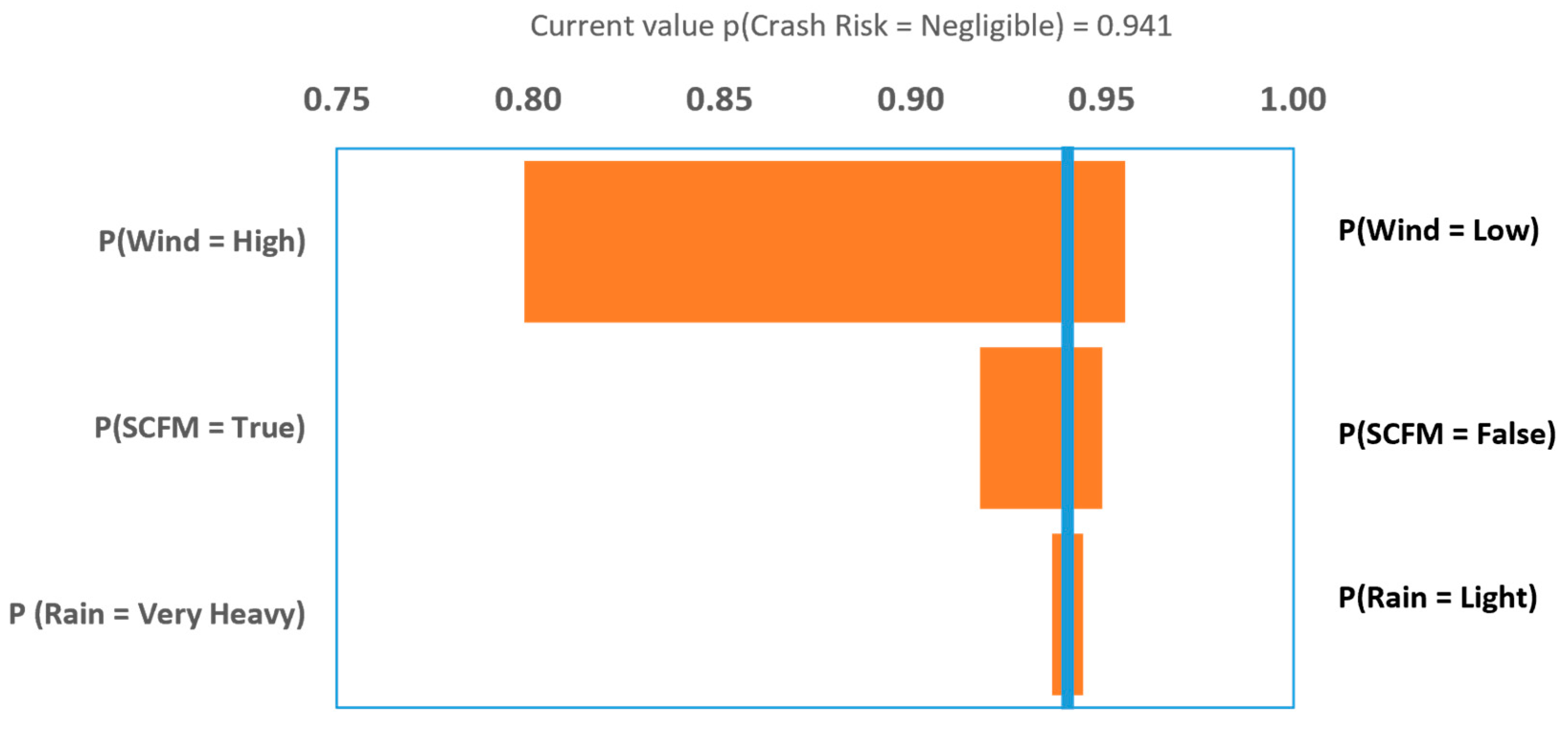
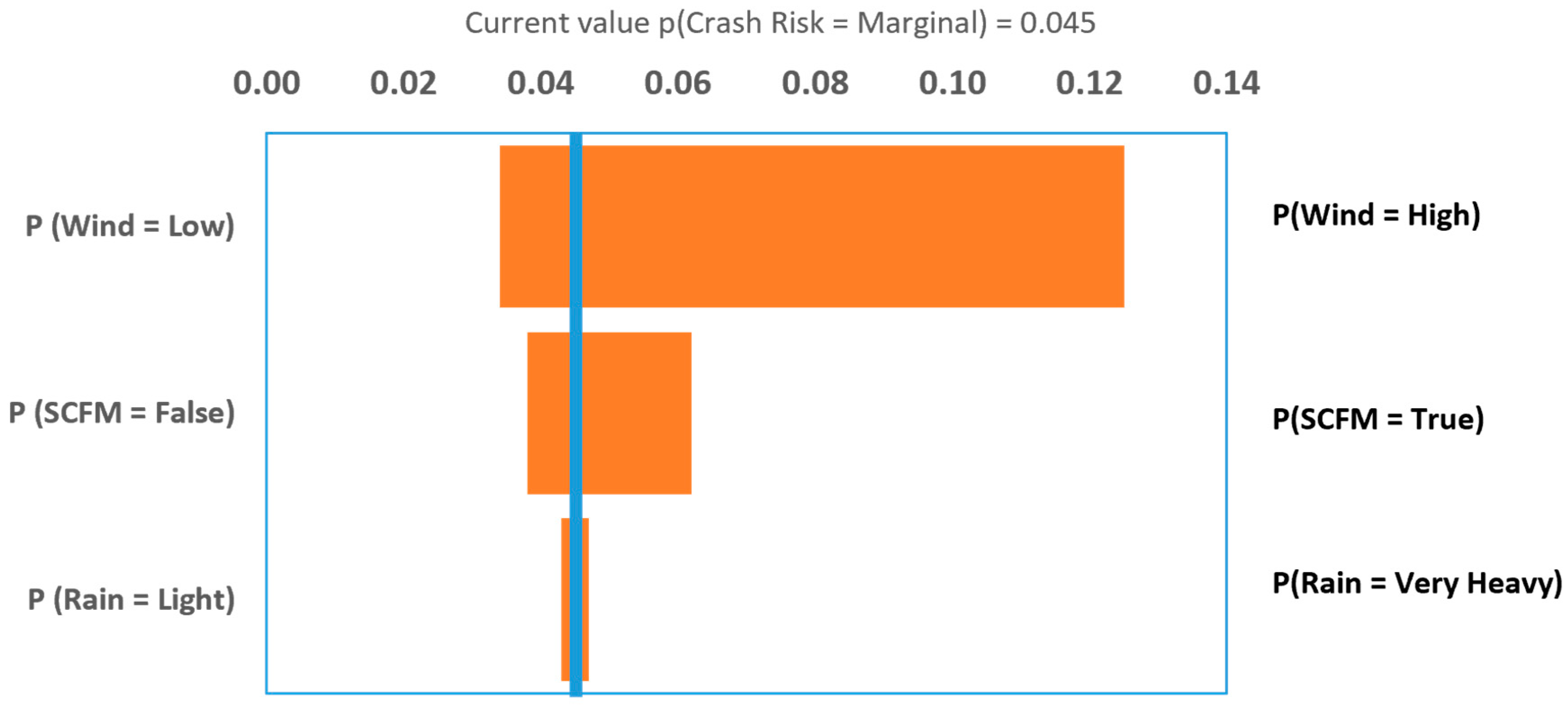
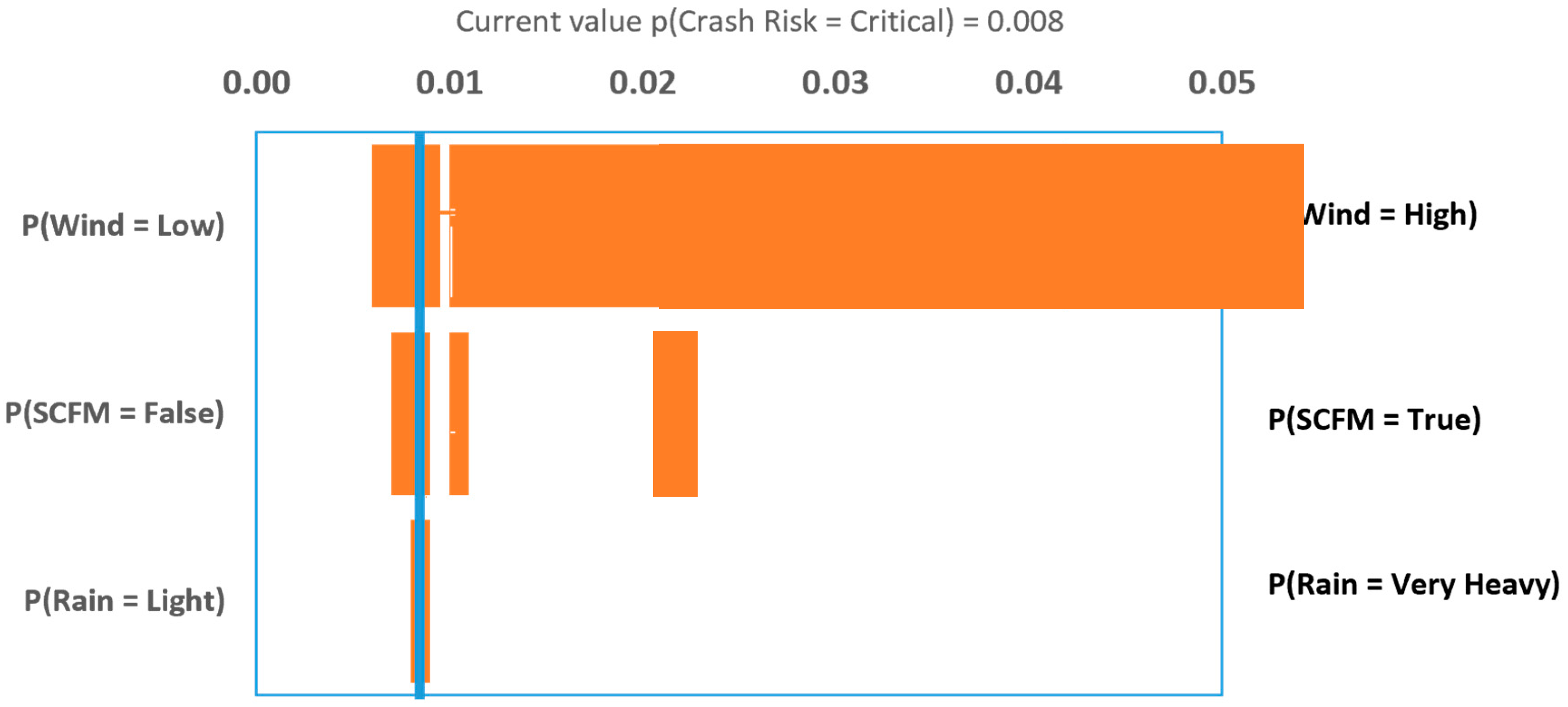
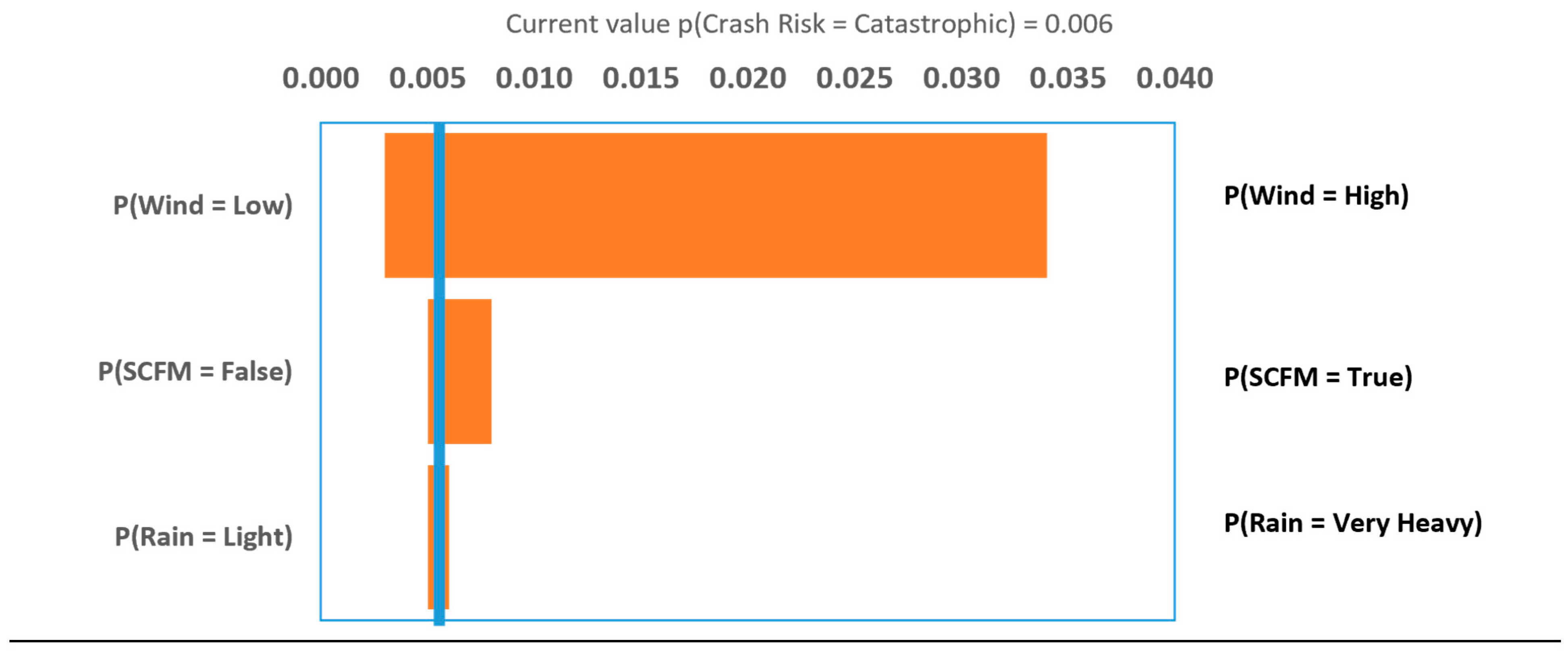
4.3. Sensitivity Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kornatowski, P.M.; Mintchev, S.; Floreano, D. An Origami-Inspired Cargo Drone. IEEE Int. Conf. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2017, 2017-Septe, 6855–6862. [CrossRef]
- Euchi, J. Do Drones Have a Realistic Place in a Pandemic Fight for Delivering Medical Supplies in Healthcare Systems Problems ? Chinese J. Aeronaut. 2021, 34, 182–190. [CrossRef]
- Ackerman, E.; Strickland, E. Medical Delivery Drones Take Flight in East Africa. IEEE Spectr. 2018, 55, 34–35. [CrossRef]
- Kementerian Desa, Pembangunan Daerah Tertinggal, dan T. Petunjuk Pelaksanaan (Juklak) Identifikasi Masalah-Masalah Ketertinggalan Kabupaten Daerah Tertinggal. 2016, 31.
- Schenkelberg, F. How Reliable Does a Delivery Drone Have to Be? Proc. - Annu. Reliab. Maintainab. Symp. 2016, 2016-April. [CrossRef]
- Custers, B. The Future of Drone Use Opportunities and Threats from Ethical and Legal Perspectives; Springer Link, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Erceg, A.; Činčurak Erceg, B.; Vasilj, A. Unmanned Aircraft Systems in Logistics – Legal Regulation and Worldwide Examples toward Use in Croatia. Bus. Logist. Mod. Manag. 2017, 0, 43–62.
- Liu, Z.; Cai, K.; Zhu, Y. Civil Unmanned Aircraft System Operation in National Airspace: A Survey from Air Navigation Service Provider Perspective Target Level of Safety. Chinese J. Aeronaut. 2021, 34, 200–224. [CrossRef]
- Sanz, D.; Valente, J.; Del Cerro, J.; Colorado, J.; Barrientos, A. Safe Operation of Mini UAVs: A Review of Regulation and Best Practices. Adv. Robot. 2015, 1221–1233. [CrossRef]
- Standard ISO/IEC Guide 51:2014 Safety Aspects_Guidelines for Their Inclusion in Standards; 1999.
- Torben, J. Ensuring Compliance with the EU Directives. In Risk Assessments and Safe Machinery; Springer Cham ISBN 978-3-319-81022-5.
- Balador, A.; Kouba, A.; Cassioli, D.; Foukalas, F.; Severino, R.; Stepanova, D.; Agosta, G.; Xie, J.; Pomante, L.; Mongelli, M.; et al. Wireless Communication Technologies for Safe Cooperative Cyber Physical Systems. Sensors 2018, 18, 1–27. [CrossRef]
- Rajagopalan, R.P.; Krishna, R. Drones: Guidelines, Regulations, and Policy Gaps in India; 2018; ISBN 9789387407794.
- Sah, B.; Gupta, R.; Bani-Hani, D. Analysis of Barriers to Implement Drone Logistics. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Waibel, Markus; Augugliaro, F. Drone Shows: Creative Potential and Best Practices. 2017. [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, P.; Sobral, J.; Ferreira, L.A. Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Safety Assessment Modelling through Petri Nets ☆. 2017, 167, 2016–2018. [CrossRef]
- Belcastro, C.M.; Newman, R.L.; Evans, J.K.; Klyde, D.H.; Barr, L.C.; Ancel, E. Hazards Identification and Analysis for Unmanned Aircraft System Operations. 17th AIAA Aviat. Technol. Integr. Oper. Conf. 2017 2017. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.; Choley, J. SafeSysE: A Safety Analysis Integration In Systems Engineering Approach. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Washington, DC, U.T.N.; Press, A. Assessing the Risks of Integrating Unmanned Aircraft Systems (UAS) into the National Airspace System Available online: https://www.nap.edu/%0Acatalog/25143/assessingtherisksofintegratingunmannedaircraftsystemsuasintothenationalairspacesystem%0A.
- Newman, R.L.; Systems, C.; Ancel, E.; Evans, J. Preliminary Risk Assessment for Small Unmanned Aircraft Systems Preliminary Risk Assessment for Small Unmanned Aircraft Systems. 2017. [CrossRef]
- Neff, P.; Garman, K.E. Identifying and Mitigating Human Factors Errors in Unmanned Aircraft Systems. In Proceedings of the AIAA; 2016.
- Shankar Sankararaman Towards a Computational Framework for Autonomous Decision-Making in Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. In Proceedings of the AIAA; 2017.
- Automotive, H.; Peter, I. Probabilistic Safety Assessment Using Quantitative Analysis Techniques. 2011.
- Allouch, A.; Koubaa, A.; Khalgui, M.; Abbes, T. Qualitative and Quantitative Risk Analysis and Safety Assessment of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles Missions over the Internet. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 53392–53410. [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.C.; Alves Lima, G.B. Probabilistic Risk Analysis in Manufacturing Situational Operation: Application of Modelling Techniques and Causal Structure to Improve Safety Performance. Int. J. Prod. Manag. Eng. 2015, 3, 33. [CrossRef]
- Fenton, N.; Neil, M. Decision Support Software for Probabilistic Risk Assessment Using Bayesian Networks. IEEE Softw. 2014, 31, 21–26. [CrossRef]
- Morais, C.; Moura, R.; Beer, M.; Patelli, E. Human Reliability Analysis—Accounting for Human Actions and External Factors through the Project Life Cycle. Saf. Reliab. - Safe Soc. a Chang. World - Proc. 28th Int. Eur. Saf. Reliab. Conf. ESREL 2018 2018, 329–338. [CrossRef]
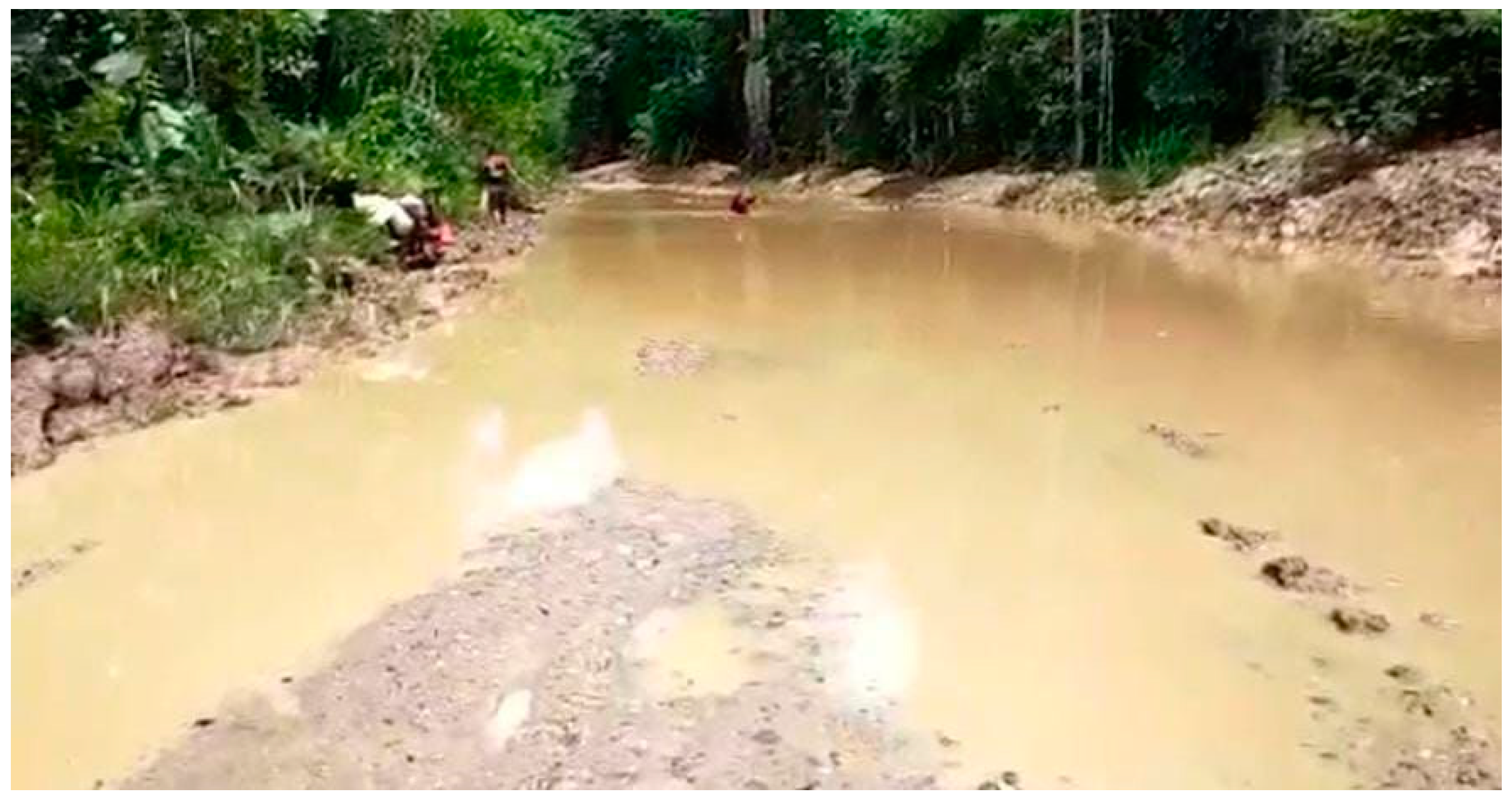
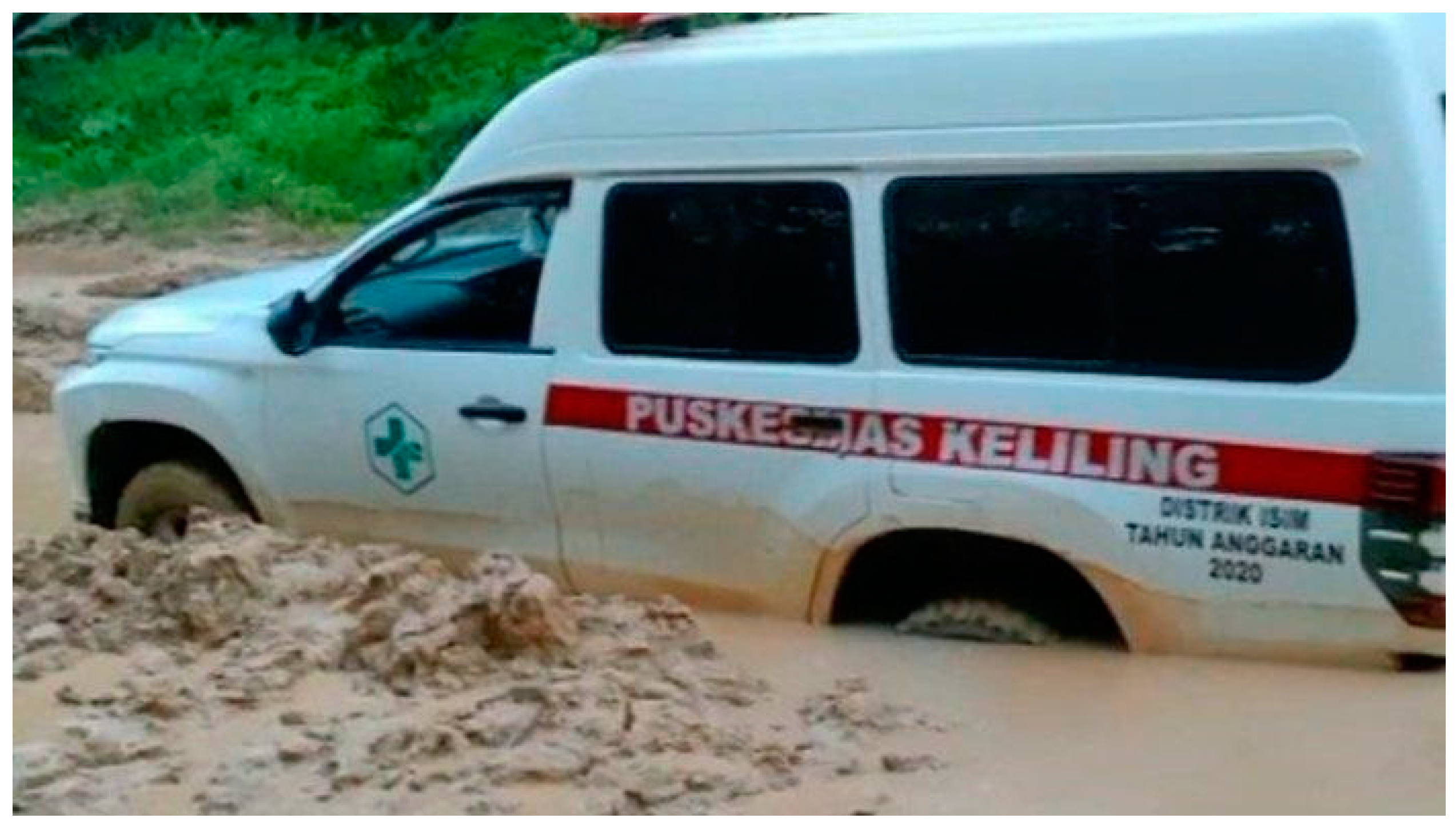
- Arief, H. Ini Yang Membuat Warga Keluhkan Akses Jalan Manokwari Selatan Ke Distrik Isim Available online: https://www.penabicara.com/nusantara/pr-2063108763/ini-yang-membuat-warga-keluhkan-akses-jalan-manokwari-selatan-ke-distrik-isim (accessed on 8 June 2022).
- Tribun-Papua Ambulans Terjebak Lumpur, Ibu Hamil Di Manokwari Selatan Terpaksa Melahirkan Di Dalam Kendaraan. Available online: https://papua.tribunnews.com/2022/04/02/ambulans-terjebak-lumpur-ibu-hamil-di-manokwari-selatan-terpaksa-melahirkan-di-dalam-kendaraan (accessed on 8 June 2022).
- BMKG Climate Information. Available online: https://www.bmkg.go.id/?lang=EN (accessed on 8 May 2022).


| No | Event | Crash? (Y/N) | Drone Type | Operation | Location | Factors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Operator 1 | ||||||
| 1 | Drone: Hitting Tree | Yes | Fixed-Wing | LIDAR Survey | Sorong, West Papua | 1) GPS Loss or Inaccuracy (GIL), 2) Inability to avoid collision (IAC) |
| 2 | Drone: Hitting Terrain | Yes | Multirotor | LIDAR Survey | Morogiri, Papua | 1) GPS Loss or Inaccuracy (GIL), 2) Inability to avoid collision (IAC), 3) Weather effect (WE) |
| 3 | Drone: Crash | Yes | Multirotor | LIDAR Survey | Gunung Abang, Bali | 1) Pilot Error (PE), 2) Weather Effect (WE), 3) Loss of UAV electrical power (LEP) |
| 4 | Drone: Lost | Yes | Multirotor | N/A | Lampung | 1) Weather Effect (WE) |
| 5 | Drone: Landing Failure | Yes | N/A | Flight Testing | Bandung, West Java | 1) Weather Effect (WE), 2) Autopilot controller module failure (ACMF) |
| Operator 2 | ||||||
| 1 | Drone: Attacked by Eagle | Yes | Fixed-Wing | N/A | Palu, Central Sulawesi | 1) Loss of UAV electrical power (LEP), 2) Animal Attack (AA) |
| 2 | Drone: run out of battery | Yes | N/A | N/A | N/A | 1) Loss of UAV electrical power (LEP) |
| 3 | Drone: crash | Yes | N/A | N/A | N/A | 1) Pilot Error (PE) |
| Operator 3 | ||||||
| 1 | Drone: crash | Yes | Fixed-Wing | Mapping | 1) Pilot Error (PE) | |
| 2 | Drone: signal lost | No | N/A | Mapping | West Java | 1) Degraded communication quality (DCQ) |
| 3 | Drone: effected by downwash | Yes | N/A | N/A | Jambi | 1) Pilot Error (PE), 2) Weather Effect (WE) |
| 4 | Drone: entered a windstorm | No | N/A | N/A | Irian Jaya | 1) Weather Effect (WE) |
| 5 | Drone: attacked by an eagle | No | Fixed-Wing | N/A | N/A | 1) Animal Attack (AA) |
| Rank | Wind Speed Category | Range Value (Fixed Wing) | Range Value (Quadrotor) | Definition |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Low | 0 m/s - 5 m/s | 0 m/s - 3 m/s | Wind speed have no significant effect to drone operation |
| 2 | Medium | 5 m/s - 10 m/s | 3 m/s - 8 m/s | Wind speed can cause drone to deviate from desired flight path |
| 3 | High | > 10 m/s | > 8 m/s | Wind speed can cause drone to be lost controlled |
| “Rain” Node | Light | Medium | Heavy | Very Heavy | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| “Wind” Node | Low | Med. | High | Low | Med. | High | Low | Med. | High | Low | Med. | High |
| Light | 0.95 | 0.025 | 0.025 | 0.925 | 0.0375 | 0.0375 | 0.9 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.875 | 0.0625 | 0.0625 |
| Med. | 0.025 | 0.95 | 0.025 | 0.0375 | 0.925 | 0.0375 | 0.05 | 0.9 | 0.05 | 0.0625 | 0.875 | 0.0625 |
| Heavy | 0.025 | 0.025 | 0.95 | 0.0375 | 0.0375 | 0.925 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.9 | 0.0625 | 0.0625 | 0.875 |
| Total Score | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Weather Effect | Light | Medium | Heavy | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sys. Comp. Failure or Malfunction (SCFM) | FALSE | TRUE | FALSE | TRUE | FALSE | TRUE |
| Negligible | 0.975 | 0.95 | 0.9 | 0.85 | 0.8 | 0.75 |
| Marginal | 0.02 | 0.045 | 0.08 | 0.1 | 0.125 | 0.15 |
| Critical | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.01 | 0.025 | 0.040 | 0.06 |
| Catastrophic | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.01 | 0.025 | 0.035 | 0.04 |
| Total Score | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Crash Severity Category | Frequency in 2021 | Relative Frequency (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Negligible | 1670 | 99.4 |
| Marginal | 9 | 0.5 |
| Critical | 1 | 0.1 |
| Catastrophic | 0 | 0.0 |
| Total | 1780 | 100.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




