1. Introduction
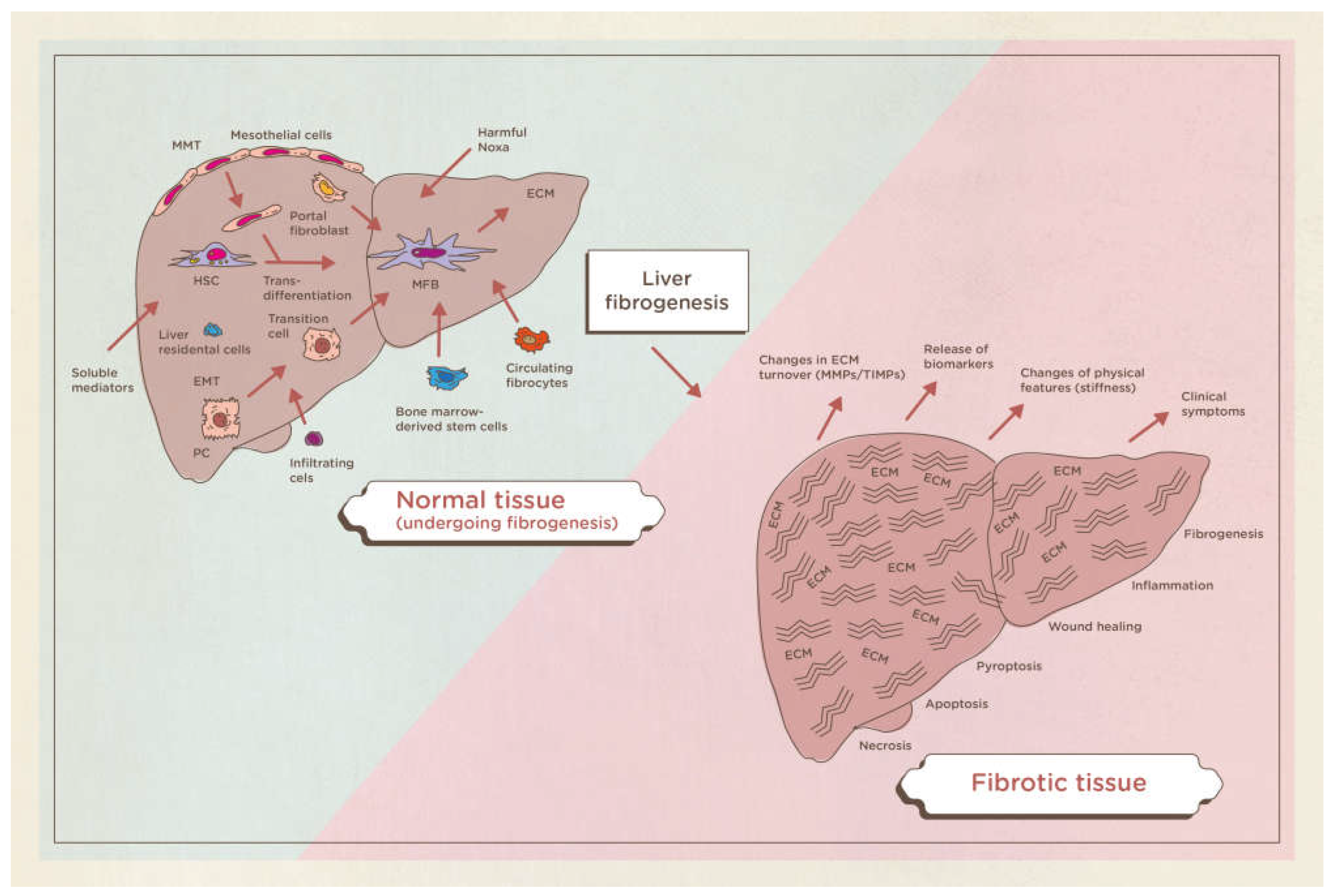
Cirrhosis is a chronic, widespread process characterized by fibrosis and the conversion of normal liver parenchyma into abnormal nodules. Although the definition is morphological (presence of cellular necrosis with nodular regeneration and fibrosis of the parenchyma), cirrhosis is always associated with a progressive deterioration of liver function. Liver fibrosis is defined as a deposition of extracellular matrix and is based on complex interactions between matrix-producing liver cells and an abundance of infiltrating cells in the liver. Various stimuli can cause liver fibrosis in humans: congenital, metabolic, inflammatory, parasitic, vascular, toxic or drugs, nevertheless the molecular mechanisms underlying this pathology are substantially the same. (
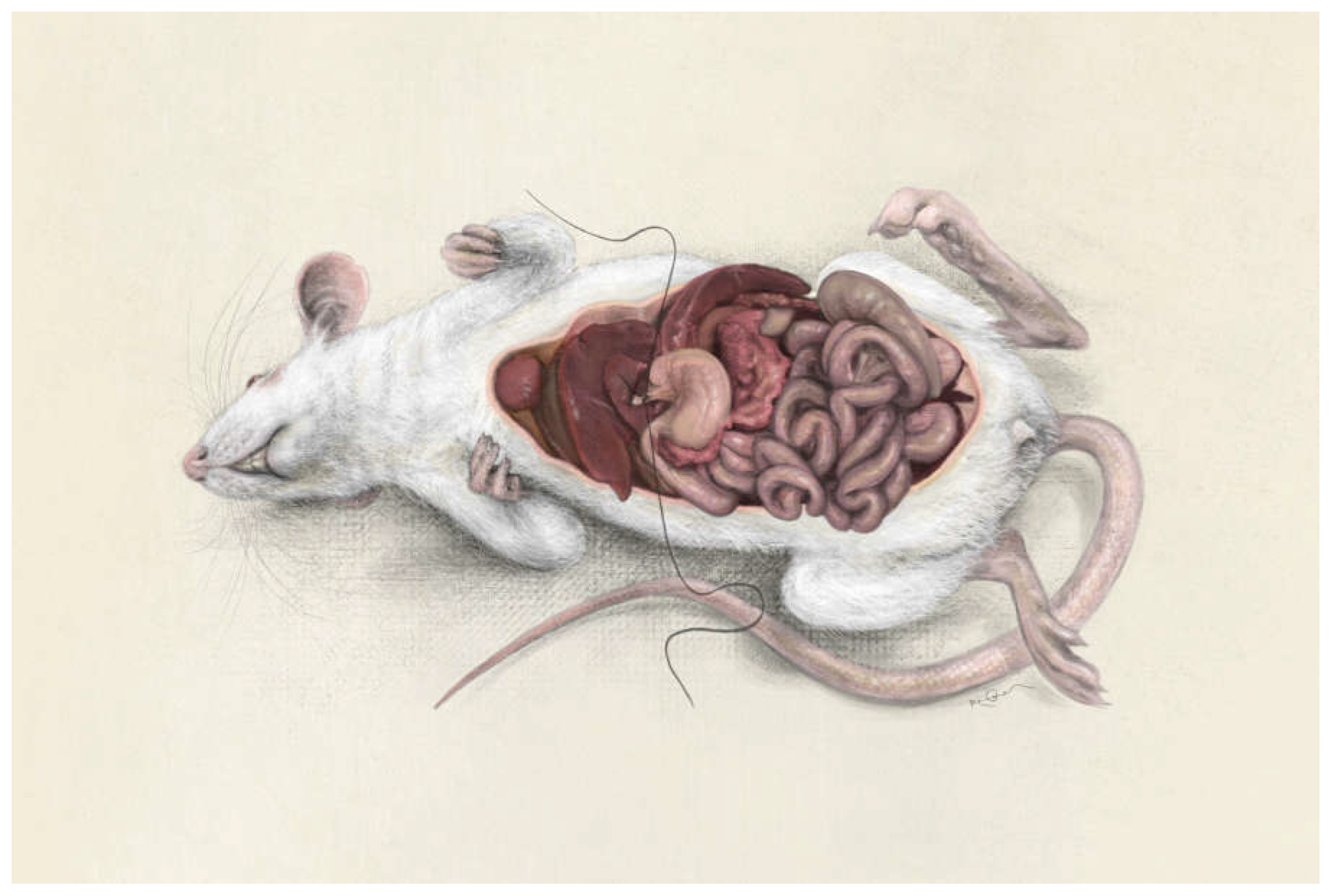
Figure 1)[
1,
2]. Double bile duct ligation (BDL) is an animal model of obstructive jaundice resulting in cholestasis. The severe hepatic and systemic repercussions of cholestasis [
3,
4] have led to the creation of many experimental surgical models in order to better understand their pathogenesis, prophylaxis and treatment. The animal model on rodents is currently the gold standard for the study of cholestasis and its hepatic and systemic repercussions (
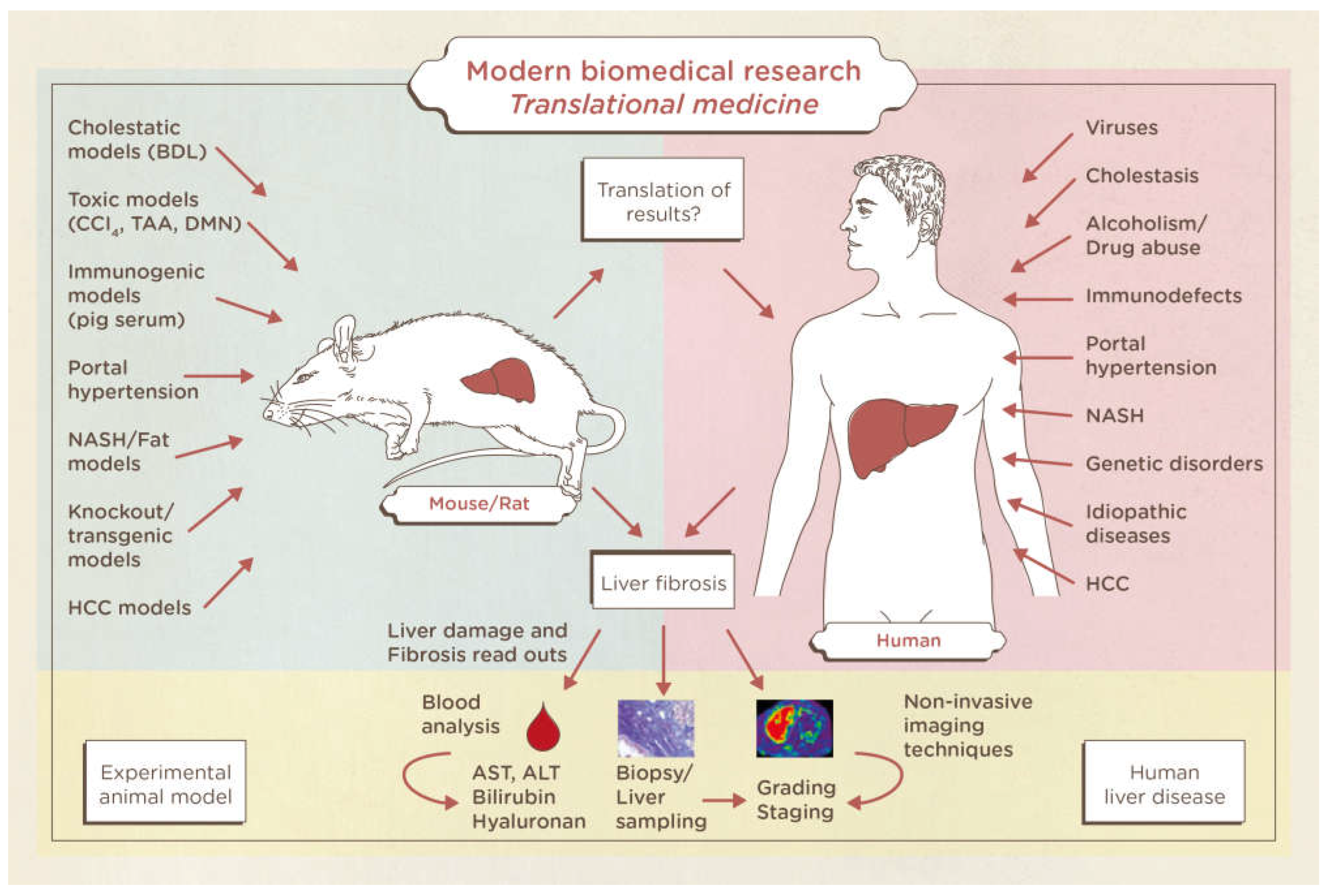
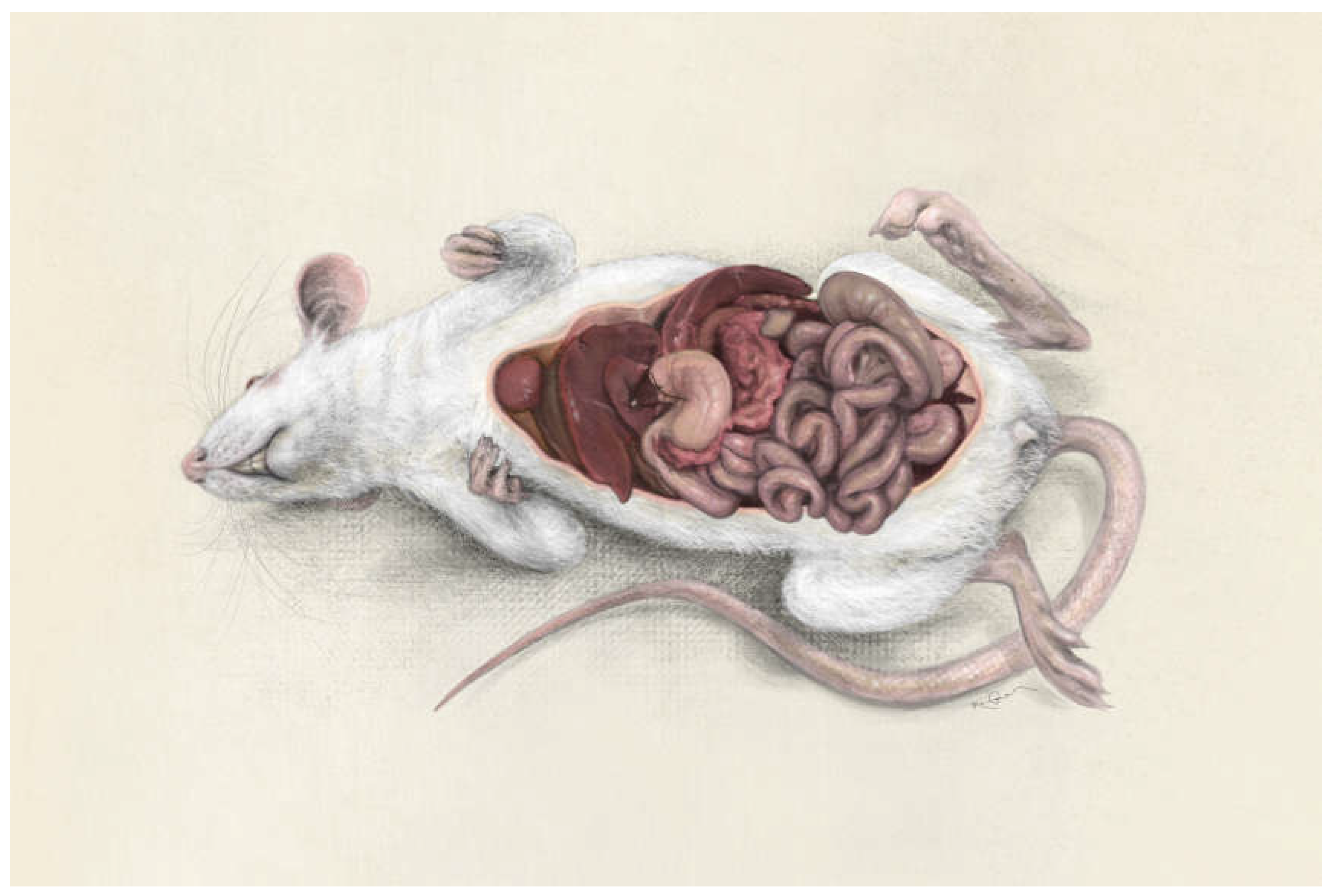
Figure 2). The results of nonclinical studies in liver fibrosis and cirrhosis are based on blood samples, organ harvesting, and liver biopsies. Furthermore, the reading systems for liver insults in animals are perfectly translatable in humans with regards to blood tests, biopsies and imaging techniques. Therefore, a gold standard publication checklist (GSPC) was recently proposed for animal studies. Such a list should reduce the number of animals used in preclinical studies and lead to more reliable results thus improving the quality of animal-based scientific articles and follow the idea of evidence-based medicine [
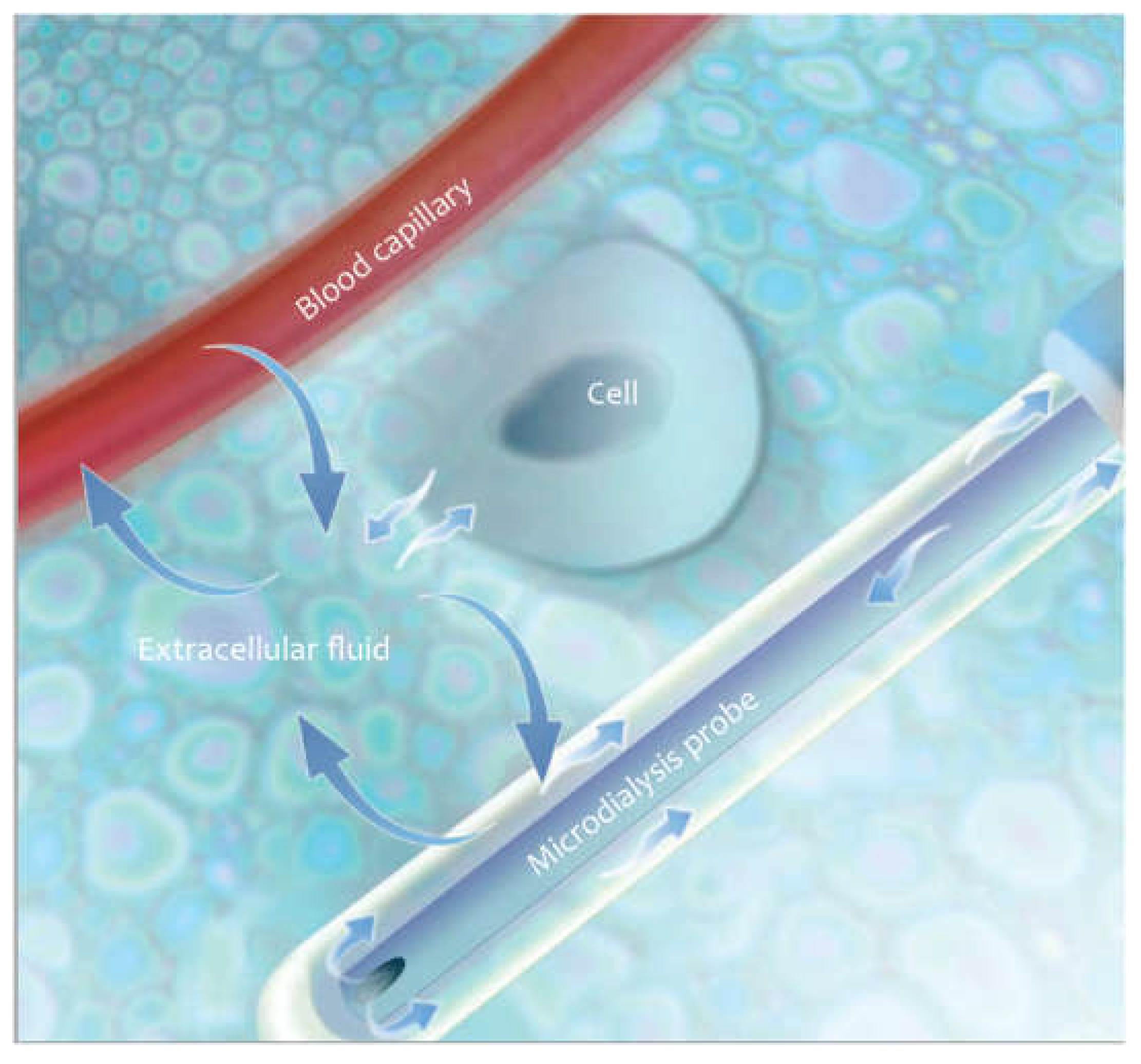
5]. it is obvious that more precise international guidelines would increase the methodological quality of animal research and reduce experimental variation, thus helping to better translate the observed results into the clinic. Serial blood draws can be used to study liver metabolism. Unfortunately, due to dilution in the systemic circulation small but significant changes in molecular concentrations can be missed. Biopsies and harvested organs provide a more accurate assessment of parenchymal concentrations of the molecules being studied, but it is not possible to follow a chain of events in the same animal without such biopsies causing serious injury. Optimally, all parameters of cirrhosis should be studied over time, with the same method, in the organ of interest, and with minimal discomfort to the animals under study. The microdialysis (μD) technique meets all of these criteria. The principle of hepatic microdialysis is based on the ability of the capillaries to recover the metabolites from the interstitium and transport them into the systemic circulation. Hepatocytes secrete metabolites into the extracellular interstitial space where these metabolites accumulate. Sinusoids and capillaries function as semipermeable membranes so the smaller molecules diffuse on the vessel walls through tiny pores, following the oncotic pressure according to concentration gradients, while the larger molecules remain in their specific compartment and maintain the oncotic pressure. (
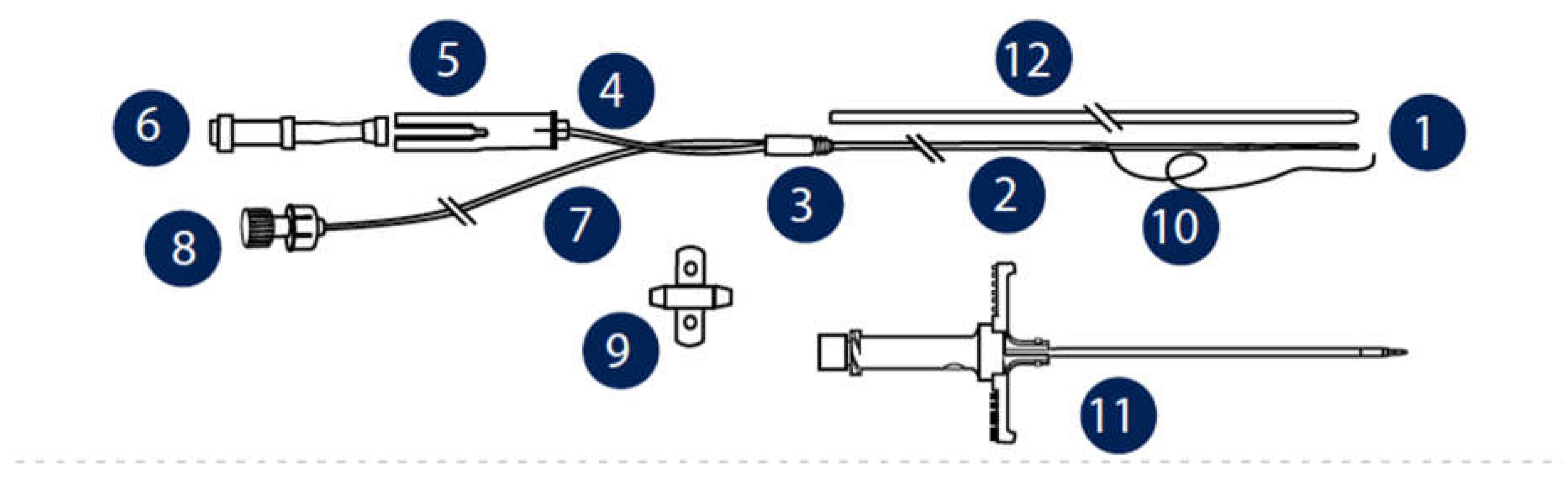
Figure 3). The aim of this work is to provide a stepwise surgical approach to resect the common bile duct and monitor hepatic metabolism in situ by hepatic microdialysis.
2. Protocol
NOTE: This protocol was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of the University of Salerno based on animal use and care; agrees with the practices and principles of the European Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals, in accordance with the ethical guidelines of the European Community Council Directive (86/609/EEC). Rats are housed in specific pathogen-free conditions according to the guidelines of the Federation for Laboratory Animal Science Associations (FELASA).
2.1. Animals
The model should be performed on 50 male Wistar rats weighing an average of 200 g and aged between 8 and 10 weeks.
One week before the experiment, the animals must be housed for acclimatization at a temperature of 22 ± 2 °C, humidity 55 ± 10% and light/dark cycles for 12 h.
They must have free access to water and food pellets.
2.2. Anesthetic protocol
Animals should be premedicated by intramuscular injection of tiletamine/zolazepam (Zoletil) at a dose of 20 mg/kg.
They must then be relocated to the original house, maintain a quiet environment with soft light until the animals reach a state of deep sedation.
The achievement of a deep anesthesia level must be maintained by gaseous anesthesia: the rat, under sedation, must be placed on a heated carpet and a mask must be applied to the animal's muzzle for the administration of a mixture of oxygen, air and 2% isoflurane.
During anesthesia, the heart rate and body temperature must be monitored by special equipment (in our case: Indus Instruments-Visualsonic), the maintenance of anesthesia must be followed by the veterinarian through the evaluation of clinical parameters such as increased breathing and heart rate.
At the end of the procedure, recovery should be obtained by interrupting the administration of isoflurane.
The animal must then be placed in a special heated room with soft light where it will be followed by the veterinarian until it is fully awakened.
The anesthetic procedures for animals to be subjected to bile duct ligation must be integrated with analgesic therapy by administering Carprofen (Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug) 5 mg/kg, performed immediately after the end of the operation and every 24 hours for two days, and antibiotic therapy with the administration of Enrofloxacin at a dose of 5 mg/kg diluted in 0.5 ml of physiological solution every 24 hours for 5 days.
2.3. Euthanasia
Animals to be subjected to euthanasia must be placed under general anesthesia, then administer intracardiac Tanax (embutramide, mebenzonium iodide and tetracaine hydrochloride) at a dose of 2 ml/400 g.
2.4. Ligature of the Common Bile Duct
Bile duct ligation surgeries are performed under deep anesthesia.
Shave the abdominal wall of the animals and disinfect the skin with chlorhexidine solution (0.5%).
Make a midline abdominal incision (approximately 5 cm long) to expose the xiphoid process.
Retract the severed abdominal wall bilaterally (laparotomy) using double-curved forceps to hold the peritoneal cavity open and expose the liver.
Using a saline-moistened cotton tip, gently pull down on the middle lobe of the liver and cut the falciform ligament using curved microsurgical scissors.
Pull the duodenum to the left with a saline-moistened cotton tip to visualize the hepatic hilum.
Using the microdissection forceps, place a 5-0 silk thread around the common bile duct (
Figure 4).
Make a second ligature at a distance of about 1 cm (
Figure 5).
Use the microsurgical curved scissors to cut the common bile duct between the two ligatures (
Figure 6).
Carefully reposition the middle and left lateral lobes to their anatomical position using moistened cotton swabs.
Gently return the intestinal loops to the abdominal cavity.
Close the muscle layer of the abdominal wall using a running suture with a 3-0 polyglycatin suture and needle holder.
Close the skin incision using a running stitch with a 4-0 silk suture.
After closing the abdominal cavity, clean the skin around the suture with chlorhexidine.
Administer 1 ml of saline (0.9%) subcutaneously.
Place the animal in a heated recovery chamber for 15 minutes.
2.5. Blood Sampling
Anesthetize the animals and place them in sternal recumbency.
Place a pre-heparinized 24G peripheral venous catheter into the lateral tail vein. This procedure is facilitated by a tourniquet at the base of the tail.
Collect a 600 μl blood sample in a tube with a separating gel.
Then centrifuge the sample at 2700 rpm for 15 minutes at 4°C.
Aliquot the collected plasma in 2 ml Eppendorf and use it for the determination of GOT, GPT and total bilirubin.
2.6. Microdialysis
Anesthetize the animals and place them on the operating table in dorsal recumbency.
Proceed with trichotomy of the abdominal region with a special clipper, then disinfect the skin with surgical betadine.
Make an incision along the linea alba proceeding in the craniocaudal direction for a length of approximately 2 cm, involving the skin, subcutaneous tissue, muscle and peritoneum.
Once in the abdominal cavity, use a special abdominal retractor for proper visualization of the cavity bodies.
Then proceed to remove the intestine from the liver parenchyma.
Into the left and right lobes of the liver insert two CMA20 Elite microdialysis probes (CMA / Microdialysis AB, Stockholm, Sweden) and perfuse them at a rate of 1.0 mL/min with T1 perfusion fluid (147 mM Na, K 4 mM, 2, 3 mm Ca, 156 mM Cl, pH 6, osmolality 290 mOsm/kg) (CMA/Microdialysis AB, Stockholm, Sweden) via a microdialysis pump (CMA/Microdialysis AB). (
Figure 7)
Subsequently secure the probes to the muscular component of the abdominal wall using a 3/0 Vicryl suture (
Figure 8).
Collect two samples at 30 minute intervals.
Use the Iscus CMA analyzer microdialysis for glucose, glycerol, lactate and pyruvate analysis.
Finally, restore the planes by surgical suturing from the muscle and skin using a 3/0 vicryl suture.
3. Representative Results
When the previously described technique is performed correctly, no mortality is observed.
In a typical trial, BDL will have been performed on 50 Wistar rats. In this model all animals were blood sampled preoperatively and 14 days postoperatively. During our experiments using this model, the stages of liver fibrosis were classified according to Scheuer's staging system: no fibrosis (stage 0) fibrosis confined to the portal tracts (stage 1); periportal or portal fibrosis with intact architecture (stage 2); septal fibrosis with structural distortion but no obvious cirrhosis (stage 3); probable or certain cirrhosis (stage 4).
Serum bilirubin in the cirrhotic group (BDL) was significantly higher (6.41 mg/dl) than in the control group (0.13 mg/dl). The same results occurred for the values of serum GOT activity (320 IU/L in the BDL group compared to 56.12 IU/L in the control group) and serum GPT activity (67.16 IU/L in the BDL group compared to 36 IU/L in the control group). (
Table 1).
Glucose concentrations in the microdialysate of intact rats were significantly higher than in cirrhotic rats. There was a moderate decrease in glucose microdialysate concentrations in all compartments during anesthesia in rats after BDL. Microdialysate lactate concentrations in intact rats exhibited similar dynamic changes. There were significant differences in interstitial lactate concentration between intact rats and rats with hepatic insufficiency. The groups with impaired liver function had lower interstitial liver glycerol concentrations than the intact rats (
Table 2).
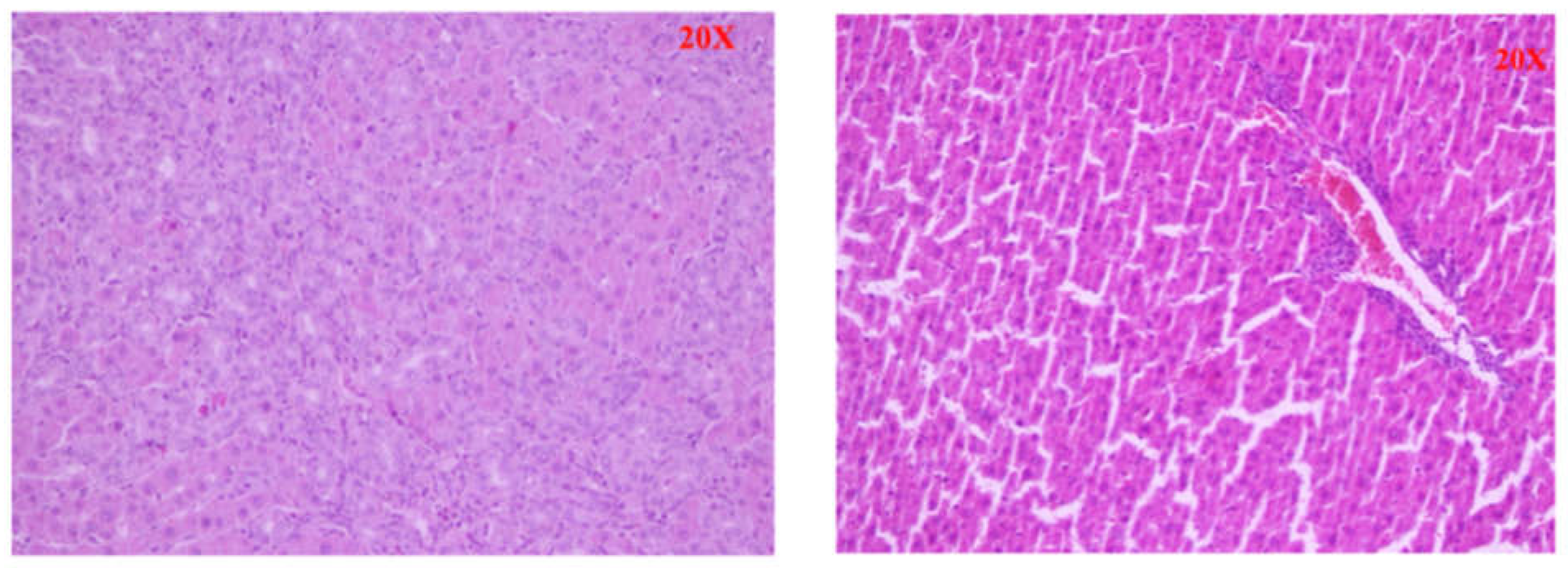
In the control group we found preserved intact liver parenchyma. The lobular architecture was intact without any changes (Scheuer stage 0). In the BDL group we found established micronodular cirrhosis of the liver parenchyma and severe fibrosis. The hepatocytes showed dystrophic changes and the presence of apoptotic cells and edema, some hepatocytes showed an oncocytic transformation (Scheuer stage 2-3).(
Figure 9).
Table 1.
GOT, GPT and Bilirubin serum levels in BDL and Control Groups.
Table 1.
GOT, GPT and Bilirubin serum levels in BDL and Control Groups.
| |
GOT (UI/L) |
GPT (UI/L) |
Bilirubin (mg/dl) |
| Control |
56.12 ± 11.3 |
36 ± 9.4 |
0.13 ± 0.07 |
| BDL |
320 ± 47.58 |
67.16 ± 25.8 |
6.41 ± 1.37 |
Table 2.
Liver microdialysis results.
Table 2.
Liver microdialysis results.
| |
Glucose (mM) |
Lactate (mM) |
Glycerol (μM) |
| Control |
1.11± 0.38 |
0.45 ± 0.18 |
1.83 ± 0.70 |
| BDL |
0.95 ± 0.41 |
0.52 ± 0.21 |
1.00 ± 0.70 |
4. Discussion
Bile duct ligation (BDL) is a surgically created animal model developed by Cameron and Oakley in 1932 which consists of the ligation or excision of the common bile duct [
6]. BDL represents the most useful animal model to study cholestatic disease and has been used to study portal hypertension and hepatopulmonary syndrome because it allows for long-term follow-up. The BDL model was mainly performed on adult rats [
7,
8]. The experiments that have used the microdialysis technique have instead been performed in various organs such as the brain, skin, muscles and recently also in the liver. The first studies using liver microdialysis were aimed at monitoring metabolism in rodent transplantation models [
9].
Critical steps in the Protocol
Animals: All rats should be between 8 and 10 weeks of age and weigh 200-250g.
Procedure:
- -
step 4.5: it is not necessary to cut it up to the superior vena cava, the risk is to cut the diaphragm or the superior vena cava causing bleeding and/or pneumothorax.
- -
step 4.8/4.9: maintain the proximal ligation of the common bile duct at a height of 4-5 cm to allow for subsequent upward dissection without damaging it.
- -
point 4.10: Avoid damaging the liver parenchyma during the dissection of the common bile duct. The dissection space is very small, so it is very easy to injure the middle lobe parenchyma and cause bleeding.
Modifications and Troubleshooting of the Method
Analgesia: A side effect of tiletamine/zolazepam is the ingestion of sawdust or wood chips that make up the litter, in which case the gastric obstruction can be severe enough to cause death. For this reason it is recommended to house animals in cages with a grid floor for a short time after surgery.
step 4.8/4.9: The first ligature should be as close as possible to the base of the lobe and the second ligature at a distance of 1 cm. If part of the biliary branch remains free, a biliary pseudocyst may form during the postoperative period. These biliary pseudocysts are easily infected by bacteria that translocate from the intestines and the rats could suffer from sepsis and premature death. To prevent this complication, inspect all ligatures before closing the abdominal cavity. If a long section of a lobular biliary branch emerges from the liver parenchyma, a second ligature should be placed at the base of the biliary stump.
step 4.10: If the hepatic artery is injured during the dissection of the common bile duct, it may cause intrahepatic biliary ischemia. Consequently, cholangitis would be induced, invalidating the experimental model of extrahepatic cholestasis.
step 4.11: If there is bile flow from one of the biliary stumps, make another ligature around the biliary stump closest to the liver parenchyma.
The Significance of the Method with Respect to Existing/Alternative Methods
In recent years, several studies have highlighted the differences in the cholestatic response after bile duct ligation between adult and young animals [
10,
11]. However, operating on rat pups is technically difficult because they have small biliary structures. Furthermore, rat pups easily die during anesthesia or after surgery. Some authors reported a high mortality (18.1-77.5%) after BDL even in adult rats due to complications such as sepsis and multiple abscesses [
8,
12]. In our study, the survival rate of rats was higher than in literature studies. Appropriate choice of anesthetic agent and prevention of hypothermia probably resulted in a higher survival rate of the animals. In our protocol, we have suggested isoflurane as an anesthetic agent because induction and recovery are faster than other volatile agents and because it induces less myocardial depression. Furthermore, maintaining the proper depth of anesthesia is easily maintained by adjusting the percentage of isoflorane delivered. Finally, it should not be underestimated that only a small percentage of isoflurane is metabolized in the liver.
Microdialysis has many advantages over traditional methods such as blood or tissue sampling. In fact it is performed in the liver parenchyma without systemic dilution and can be performed without additional needle punctures. Liver microdialysis is especially valuable when studying metabolic events over time, as sampling is performed continuously while the catheters remain in the study object. This reduces the discomfort for animals not needing repetitive biopsies and the number of experimental animals sacrificed.
Future Applications or Directions of the Method
In the present study, we found progressive liver fibrosis after BDL surgery, with massive fibrosis in the second postoperative week. These results demonstrate that the BDL model in rats clearly reproduces the liver histological features of liver cirrhosis and specifically recreates what is observed in human pathology. Ligation of the bile duct in rats produces progressive cholestatic damage, leading to liver fibrosis and related complications. All surgical protocols can be quickly learned by other scientists even if they are not experts. Ligation of the bile duct in rats is a good animal model to study therapeutic approaches against liver fibrosis as well as for common complications of liver cirrhosis such as hepatic encephalopathy and hepatic cardiomyopathy.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Valentina Iovane and Luigi De Lucia for their help in preparing the experiments and photographs.
References
- Kisseleva T, Brenner D. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of liver fibrosis and its regression. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 Mar;18(3):151-166. [CrossRef]
- G. Scarpati, E. De Robertis, C. Esposito, O. Piazza, Hepatic encephalopathy and cirrhotic cardiomyopathy in Intensive Care Unit. Minerva Anestesiologica 2018 August;84(8):970-9. 9: Minerva Anestesiologica 2018 August;84(8). [CrossRef]
- Cho SJ, Kim GE. A practical approach to the pathology of neonatal cholestatic liver disease. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2019 Nov;36(6):375-388. [CrossRef]
- Baker A, Kerkar N, Todorova L, Kamath BM, Houwen RHJ. Systematic review of progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2019 Feb;43(1):20-36. Erratum in: Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2020 Feb;44(1):115. [CrossRef]
- Chitnis KR, Shah AC, Jalgaonkar SV. A Study to Assess the Quality of Reporting of Animal Research Studies Published in PubMed Indexed Journals: A Retrospective, Cross-Sectional Content Analysis. Cureus. 2022 Jan 19;14(1):e21439. [CrossRef]
- Van Campenhout S, Van Vlierberghe H, Devisscher L. Common Bile Duct Ligation as Model for Secondary Biliary Cirrhosis. Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1981:237-247. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bebiashvili IS, Kakabadze MS, Gvidiani SM, Tsomaia KB, Gusev SA, Kordzaia DJ. Features of Ductular Reaction in Rats with Extrahepatic Cholestasis. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2022 Apr;172(6):770-774. [CrossRef]
- Raevens S, Fallon MB. Potential Clinical Targets in Hepatopulmonary Syndrome: Lessons From Experimental Models. Hepatology. 2018 Nov;68(5):2016-2028. [CrossRef]
- Tian YH, Schafer T, Sckell A, Schilling MK. Adenosine deaminase inhibition attenuates reperfusion low flow and improves graft survival after rat liver transplantation. Transplantation. 2000 Jun 15;69(11):2277-81.
- orbi LE, Tannuri ACA, de Aro Braz MJ, Paes VR, Sbragia L, Figueira RL, da Costa KM, Coelho MCM, Gonçalves JO, Serafini S, Tannuri U. Does Biliodigestive Anastomosis Have Any Effect on the Reversal of Hepatopulmonary Syndrome in a Biliary Cirrhosis Experimental Model? Dig Dis Sci. 2019 Nov;64(11):3192-3202. [CrossRef]
- Cicero L, Fazzotta S, Palumbo VD, Cassata G, Lo Monte AI. Anesthesia protocols in laboratory animals used for scientific purposes. Acta Biomed. 2018 Oct 8;89(3):337-342. [CrossRef]
- Kikalishvili L, Jandieri K, Turmanidze T, Jandieri L. MORPHOLOGICAL CHANGES OF THE HEPATIC PORTAL TRACTS IN EXPERIMENTALLY INDUCED CHOLESTASIS. Georgian Med News. 2022 Mar;(324):183-187. [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).