Submitted:
15 February 2023
Posted:
17 February 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Yeast two-hybrid selection
2.2. Cell cultures and treatments
2.3. Transfection with siRNA and DNA constructs
2.4. Immunofluorescence
2.5. Cell lysis and sub-cellular fractionation
2.6. Co-immunoprecipitation and Western blotting
2.7. Cell viability assay
2.8. Padlock assay
2.9. RNA extraction, retrotranscription and Quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR)
2.10. Antibodies
2.11. Statistics
3. Results
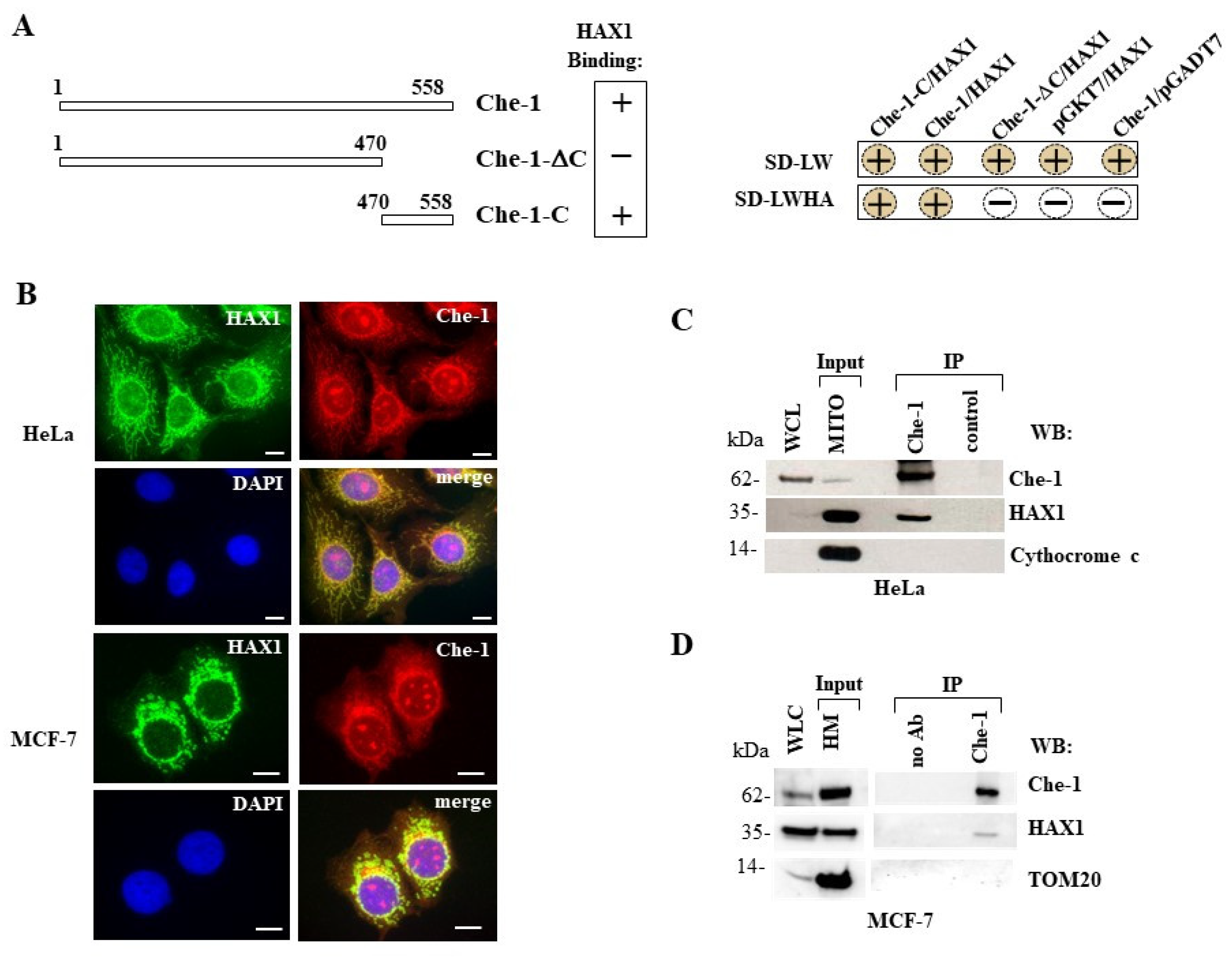
3.1. HAX1 interacts with Che-1
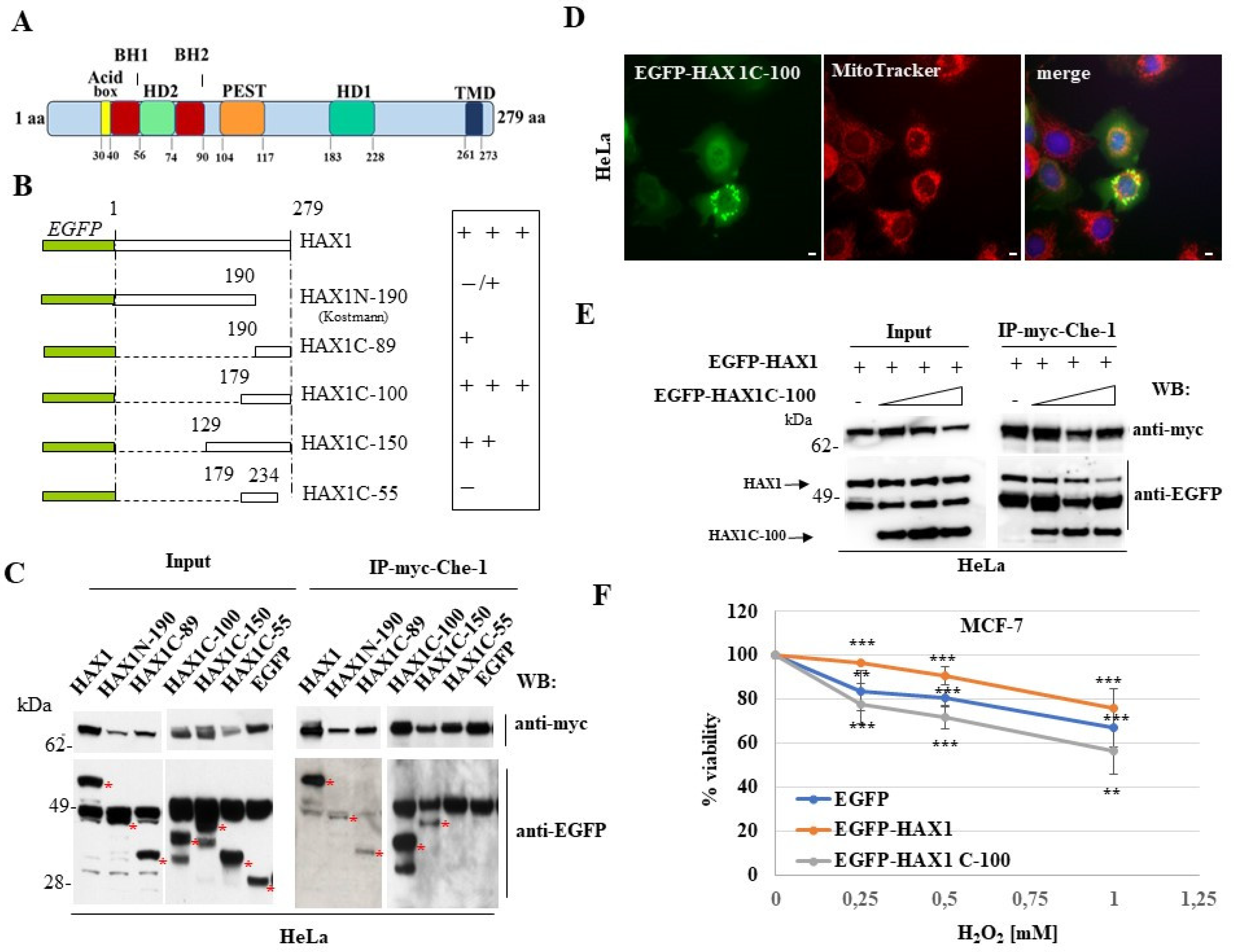
3.2. Characterization of HAX1/Che-1 interaction and dominant negative effect of HAX1 deletion construct
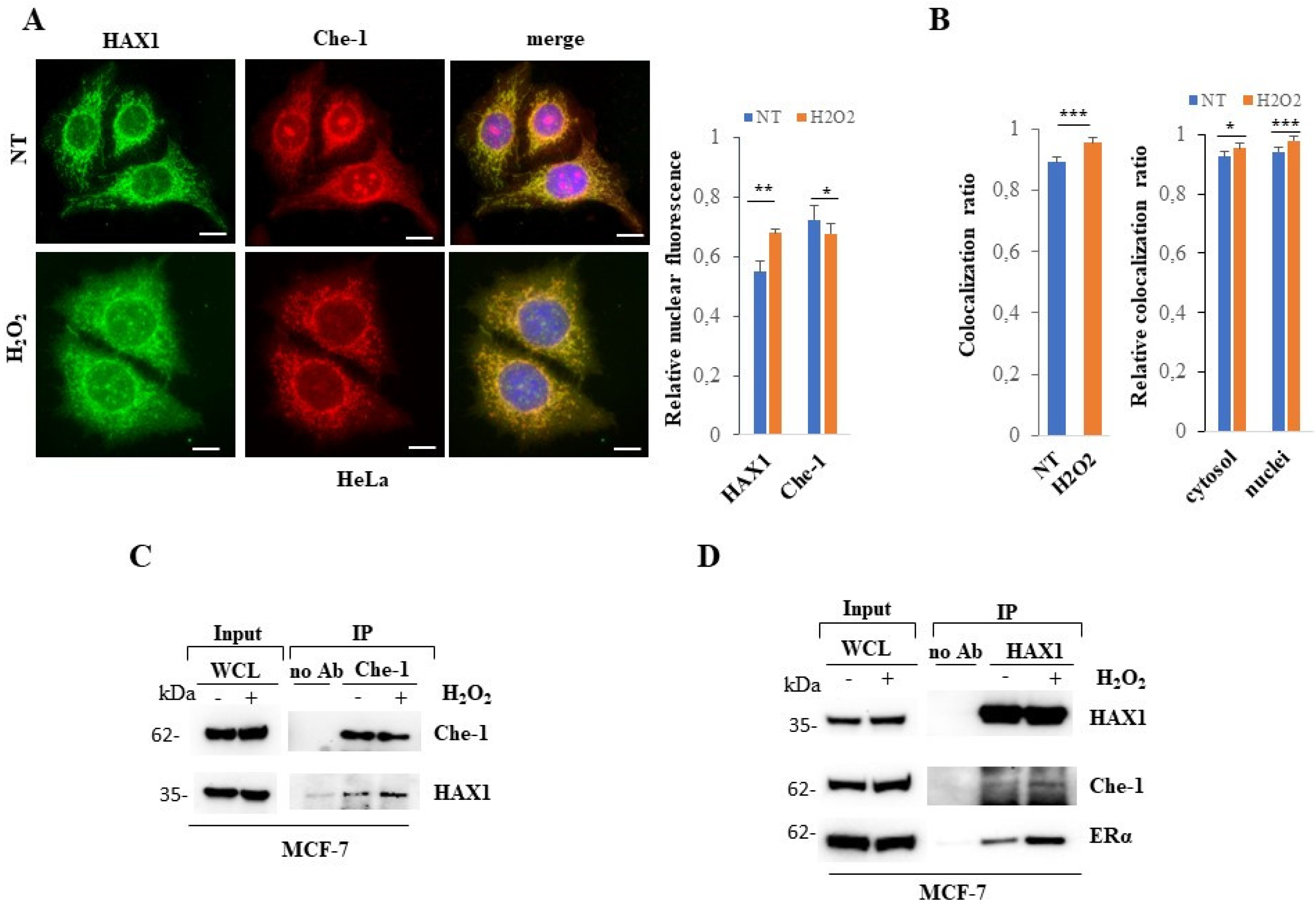
3.3. The association of HAX1 and Che-1 proteins is strengthened by oxidative stimuli
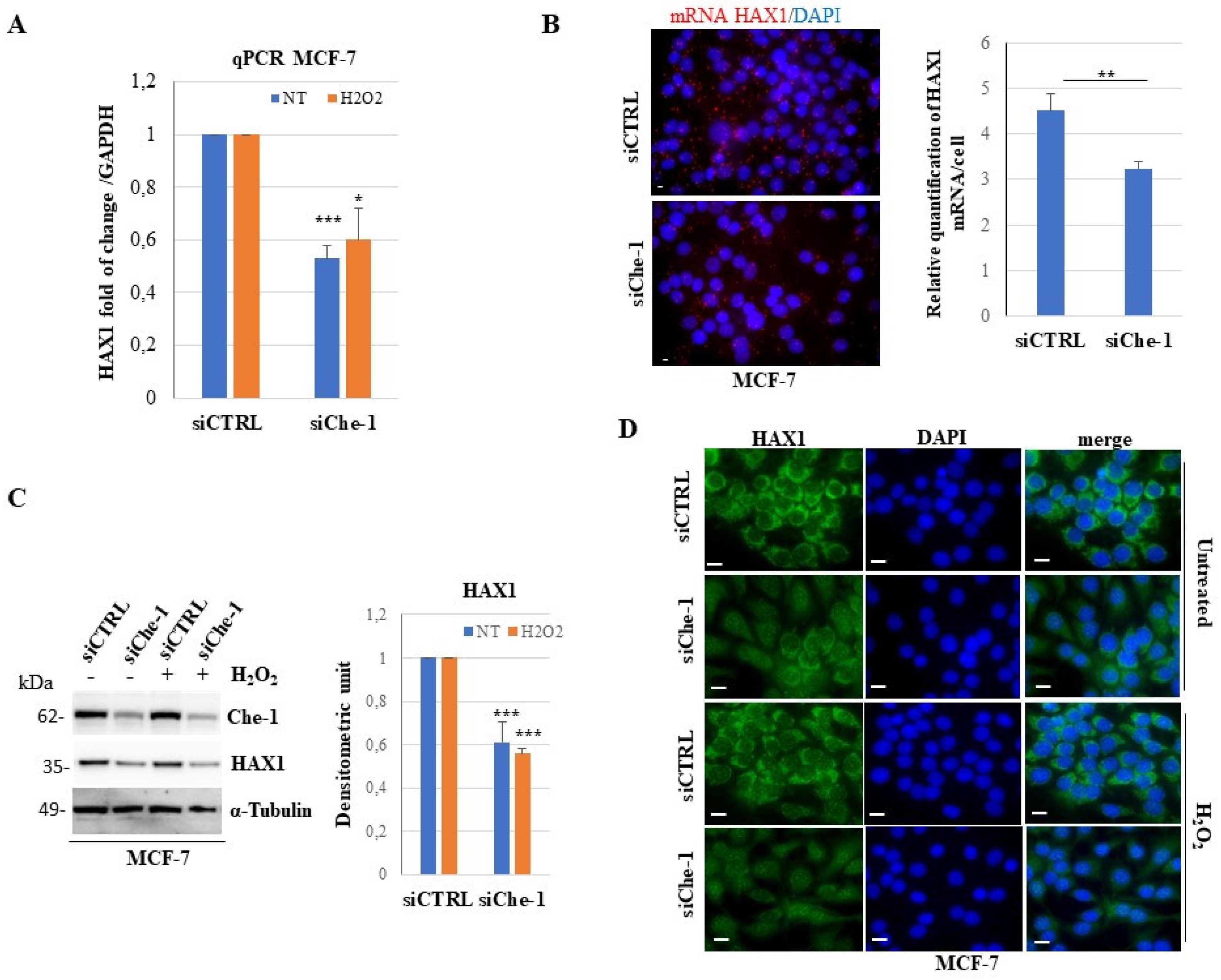
3.4. Knockdown of Che-1 induces downregulation and altered cellular distribution of HAX1
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Suzuki, Y.; Demoliere, C.; Kitamura, D.; Takeshita, H.; Deuschle, U.; Watanabe, T. HAX-1, a novel intracellular protein, localized on mitochondria, directly associates with HS1, a substrate of Src family tyrosine kinases. J Immunol 1997, 158, 2736–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trebinska, A.; Rembiszewska, A.; Ciosek, K.; Ptaszynski, K.; Rowinski, S.; Kupryjanczyk, J.; Siedlecki, J.A.; Grzybowska, E.A. HAX-1 overexpression, splicing and cellular localization in tumors. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Murgia, M.; Linder, M.I.; Mizoguchi, Y.; Wang, C.; Łyszkiewicz, M.; Ziȩtara, N.; Liu, Y.; Frenz, S.; Sciuccati, G.; et al. HAX1-dependent control of mitochondrial proteostasis governs neutrophil granulocyte differentiation. J Clin Invest 2022, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, C. Kostmann's Disease and HCLS1-Associated Protein X-1 (HAX1). J Clin Immunol 2017, 37, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Li, T.; You, B.; Shan, Y.; Shi, S.; Cao, X.; Qian, L. Expression and Function of HAX-1 in Human Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J Cancer 2015, 6, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Meng, L.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, A.; Li, X.; Wang, M. HAX1 enhances the survival and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer through the AKT/mTOR and MDM2/p53 signaling pathway. Thorac Cancer 2020, 11, 3155–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trebinska-Stryjewska, A.; Szafron, L.; Rembiszewska, A.; Wakula, M.; Tabor, S.; Sienkiewicz, R.; Owczarek, J.; Balcerak, A.; Felisiak-Golabek, A.; Grzybowska, E.A. Cytoplasmic HAX1 Is an Independent Risk Factor for Breast Cancer Metastasis. J Oncol 2019, 2019, 6375025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radhika, V.; Onesime, D.; Ha, J.H.; Dhanasekaran, N. Galpha13 stimulates cell migration through cortactin-interacting protein Hax-1. J Biol Chem 2004, 279, 49406–49413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcerak, A.; Trebinska-Stryjewska, A.; Wakula, M.; Chmielarczyk, M.; Smietanka, U.; Rubel, T.; Konopinski, R.; Macech-Klicka, E.; Zub, R.; Grzybowska, E.A. HAX1 impact on collective cell migration, cell adhesion, and cell shape is linked to the regulation of actomyosin contractility. Mol Biol Cell 2019, 30, 3024–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsay, A.G.; Keppler, M.D.; Jazayeri, M.; Thomas, G.J.; Parsons, M.; Violette, S.; Weinreb, P.; Hart, I.R.; Marshall, J.F. HS1-associated protein X-1 regulates carcinoma cell migration and invasion via clathrin-mediated endocytosis of integrin alphavbeta6. Cancer Res 2007, 67, 5275–5284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.L.; Feng, Y.; Ma, P.; Wang, F.; Huang, H.; Guo, Y.B.; Li, P.; Mao, Q.S.; Xue, W.J. HAX-1 promotes the migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through the induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the NF-κB pathway. Exp Cell Res 2019, 381, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.L.; Cai, W.F.; Wang, L.; Liu, G.S.; Paul, C.; Jiang, L.; Wang, B.; Gao, X.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S.Z. Identification of the Functional Autophagy-Regulatory Domain in HCLS1-Associated Protein X-1 That Resists Against Oxidative Stress. DNA Cell Biol 2018, 37, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balcerak, A.; Macech-Klicka, E.; Wakula, M.; Tomecki, R.; Goryca, K.; Rydzanicz, M.; Chmielarczyk, M.; Szostakowska-Rodzos, M.; Wisniewska, M.; Lyczek, F.; et al. The RNA-Binding Landscape of HAX1 Protein Indicates Its Involvement in Translation and Ribosome Assembly. Cells 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisani, C.; Onori, A.; Gabanella, F.; Di Certo, M.G.; Passananti, C.; Corbi, N. Identification of protein/mRNA network involving the PSORS1 locus gene CCHCR1 and the PSORS4 locus gene HAX1. Exp Cell Res 2021, 399, 112471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Maghrebi, M.; Brule, H.; Padkina, M.; Allen, C.; Holmes, W.M.; Zehner, Z.E. The 3' untranslated region of human vimentin mRNA interacts with protein complexes containing eEF-1gamma and HAX-1. Nucleic Acids Res 2002, 30, 5017–5028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarnowska, E.; Grzybowska, E.A.; Sobczak, K.; Konopinski, R.; Wilczynska, A.; Szwarc, M.; Sarnowski, T.J.; Krzyzosiak, W.J.; Siedlecki, J.A. Hairpin structure within the 3'UTR of DNA polymerase beta mRNA acts as a post-transcriptional regulatory element and interacts with Hax-1. Nucleic Acids Res 2007, 35, 5499–5510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakula, M.; Balcerak, A.; Rubel, T.; Chmielarczyk, M.; Konopinski, R.; Lyczek, F.; Grzybowska, E. The interactome of multifunctional HAX1 protein suggests its role in the regulation of energy metabolism, de-aggregation, cytoskeleton organization and RNA-processing. Biosci Rep 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, S.V.; Vafiadaki, E.; Strong, J.; Kontrogianni-Konstantopoulos, A. HAX-1: a multifaceted antiapoptotic protein localizing in the mitochondria and the sarcoplasmic reticulum of striated muscle cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol 2010, 48, 1266–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.B.; Deng, X.; Wei, Y. Hematopoietic Substrate-1-Associated Protein X-1 Regulates the Proliferation and Apoptosis of Endothelial Progenitor Cells Through Akt Pathway Modulation. Stem Cells 2018, 36, 406–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szwarc, M.; Sarnowska, E.; Grzybowska, E.A. [HAX-1 protein: multifunctional factor involved in apoptosis, cell migration, endocytosis and mRNA transport]. Postepy Biochem 2007, 53, 218–227. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; Ma, C.; Cheng, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, C. HAX-1 inhibits apoptosis in prostate cancer through the suppression of caspase-9 activation. Oncol Rep 2015, 34, 2776–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, J.R.; Parganas, E.; Boyd, K.; Hong, C.Y.; Opferman, J.T.; Ihle, J.N. Hax1-mediated processing of HtrA2 by Parl allows survival of lymphocytes and neurons. Nature 2008, 452, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Chen, Y.S.; Liu, Z.; Bodyak, N.; Rigor, D.; Bisping, E.; Pu, W.T.; Kang, P.M. Overexpression of HAX-1 protects cardiac myocytes from apoptosis through caspase-9 inhibition. Circ Res 2006, 99, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, J.; Kirshenbaum, L.A. HAX-1 represses postmitochondrial caspase-9 activation and cell death during hypoxia-reoxygenation. Circ Res 2006, 99, 336–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.B.; Feng, J.; Geng, S.M.; Zhang, P.Y.; Yan, X.N.; Hu, G.; Zhang, C.Q.; Shi, B.J. Induction of apoptosis by Hax-1 siRNA in melanoma cells. Cell Biol Int 2009, 33, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, G.; Liu, W.; Dong, S.; Cai, S.; Tao, D.; Yan, Q.; Wang, J.; et al. hSav1 interacts with HAX1 and attenuates its anti-apoptotic effects in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Int J Mol Med 2011, 28, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, X.; Song, L.; Zhao, W.; Wei, Y.; Guo, X.B. HAX-1 Protects Glioblastoma Cells from Apoptosis through the Akt1 Pathway. Front Cell Neurosci 2017, 11, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Li, D.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yao, Y.; Zhu, L.; Wang, G.F.; Liu, H.; et al. Anti-apoptotic HAX-1 suppresses cell apoptosis by promoting c-Abl kinase-involved ROS clearance. Cell Death Dis 2022, 13, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadeel, B.; Grzybowska, E. HAX-1: a multifunctional protein with emerging roles in human disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 2009, 1790, 1139–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jiang, J.; Yang, R.; Xu, X.; Hu, F.; Liu, A.; Tao, D.; Leng, Y.; Hu, J.; Gong, J.; et al. Expression of HAX-1 in colorectal cancer and its role in cancer cell growth. Mol Med Rep 2015, 12, 4071–4078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Wu, X.; Wei, M.; Guo, H.; Li, H.; Shao, Z.; Wu, Y.; Pu, J. miR-654-5p Targets HAX-1 to Regulate the Malignancy Behaviors of Colorectal Cancer Cells. Biomed Res Int 2020, 2020, 4914707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.J.; Cai, Z.Q.; He, R.M.; Wang, X.C.; Cong, L.L.; Qiu, F.H. Knockdown of Long Noncoding RNA 01124 Inhibits the Malignant Behaviors of Colon Cancer Cells via miR-654-5p/HAX-1. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2022, 2022, 1092107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, C.; Ni, Q. Expression of HAX1 and Ki-67 in breast cancer and its correlations with patient's clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis. Int J Clin Exp Med 2015, 8, 20904–20910. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kasashima, K.; Ohta, E.; Kagawa, Y.; Endo, H. Mitochondrial functions and estrogen receptor-dependent nuclear translocation of pleiotropic human prohibitin 2. J Biol Chem 2006, 281, 36401–36410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paik, S.; Shak, S.; Tang, G.; Kim, C.; Baker, J.; Cronin, M.; Baehner, F.L.; Walker, M.G.; Watson, D.; Park, T.; et al. A multigene assay to predict recurrence of tamoxifen-treated, node-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med 2004, 351, 2817–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, V.R.; Kates, R.E.; Kantelhardt, E.; Vetter, M.; Wuerstlein, R.; Fischer, T.; Schmitt, M.; Jaenicke, F.; Untch, M.; Thomssen, C.; et al. Health economic impact of risk group selection according to ASCO-recommended biomarkers uPA/PAI-1 in node-negative primary breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2013, 138, 839–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, M.P.; Zhang, M.; Le, T.P.; Wu, P.; Lainé, M.; Greene, G.L. RAC3 is a pro-migratory co-activator of ERα. Oncogene 2011, 30, 1984–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, S.V.; Koontz, J.M.; Kontrogianni-Konstantopoulos, A. HAX-1: a family of apoptotic regulators in health and disease. J Cell Physiol 2011, 226, 2752–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirmohammadsadegh, A.; Tartler, U.; Michel, G.; Baer, A.; Walz, M.; Wolf, R.; Ruzicka, T.; Hengge, U.R. HAX-1, identified by differential display reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction, is overexpressed in lesional psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol 2003, 120, 1045–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorino, C.; Catena, V.; Bruno, T.; De Nicola, F.; Scalera, S.; Bossi, G.; Fabretti, F.; Mano, M.; De Smaele, E.; Fanciulli, M.; Iezzi, S. Che-1/AATF binds to RNA polymerase I machinery and sustains ribosomal RNA gene transcription. Nucleic Acids Res 2020, 48, 5891–5906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanciulli, M.; Bruno, T.; Di Padova, M.; De Angelis, R.; Iezzi, S.; Iacobini, C.; Floridi, A.; Passananti, C. Identification of a novel partner of RNA polymerase II subunit 11, Che-1, which interacts with and affects the growth suppression function of Rb. Faseb j 2000, 14, 904–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivas, A.N.; Suresh, D.; Mirshahi, F.; Santhekadur, P.K.; Sanyal, A.J.; Kumar, D.P. Emerging roles of AATF: Checkpoint signaling and beyond. J Cell Physiol 2021, 236, 3383–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iezzi, S.; Fanciulli, M. Discovering Che-1/AATF: a new attractive target for cancer therapy. Front Genet 2015, 6, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, T.; Corleone, G.; Catena, V.; Cortile, C.; De Nicola, F.; Fabretti, F.; Gumenyuk, S.; Pisani, F.; Mengarelli, A.; Passananti, C.; et al. AATF/Che-1 localizes to paraspeckles and suppresses R-loops accumulation and interferon activation in Multiple Myeloma. Embo j 2022, e109711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, R.W.J.; Erber, J.; Höpker, K.; Fabretti, F.; Müller, R.U. AATF/Che-1-An RNA Binding Protein at the Nexus of DNA Damage Response and Ribosome Biogenesis. Front Oncol 2020, 10, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiser, R.W.J.; Ignarski, M.; Van Nostrand, E.L.; Frese, C.K.; Jain, M.; Cukoski, S.; Heinen, H.; Schaechter, M.; Seufert, L.; Bunte, K.; et al. A protein-RNA interaction atlas of the ribosome biogenesis factor AATF. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 11071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbato, C.; Corbi, N.; Canu, N.; Fanciulli, M.; Serafino, A.; Ciotti, M.; Libri, V.; Bruno, T.; Amadoro, G.; De Angelis, R.; et al. Rb binding protein Che-1 interacts with Tau in cerebellar granule neurons. Modulation during neuronal apoptosis. Mol Cell Neurosci 2003, 24, 1038–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorino, C.; Bruno, T.; Desantis, A.; Di Certo, M.G.; Iezzi, S.; De Nicola, F.; Catena, V.; Floridi, A.; Chessa, L.; Passananti, C.; et al. Centrosomal Che-1 protein is involved in the regulation of mitosis and DNA damage response by mediating pericentrin (PCNT)-dependent Chk1 protein localization. J Biol Chem 2013, 288, 23348–23357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, T.; Voss, A.K.; Petrou, P.; Gruss, P. The murine gene, Traube, is essential for the growth of preimplantation embryos. Dev Biol 2000, 227, 324–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisani, C.; Onori, A.; Gabanella, F.; Delle Monache, F.; Borreca, A.; Ammassari-Teule, M.; Fanciulli, M.; Di Certo, M.G.; Passananti, C.; Corbi, N. eEF1Bγ binds the Che-1 and TP53 gene promoters and their transcripts. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 2016, 35, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Certo, M.G.; Corbi, N.; Bruno, T.; Iezzi, S.; De Nicola, F.; Desantis, A.; Ciotti, M.T.; Mattei, E.; Floridi, A.; Fanciulli, M.; et al. NRAGE associates with the anti-apoptotic factor Che-1 and regulates its degradation to induce cell death. In J Cell Sci; England, 2007; Volume 120, pp. 1852–1858.
- Xie, J.; Guo, Q. AATF protects neural cells against oxidative damage induced by amyloid beta-peptide. In Neurobiol Dis; United States, 2004; Volume 16, pp. 150–157.
- Page, G.; Lödige, I.; Kögel, D.; Scheidtmann, K.H. AATF, a novel transcription factor that interacts with Dlk/ZIP kinase and interferes with apoptosis. FEBS Lett 1999, 462, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Guo, Q. Apoptosis antagonizing transcription factor protects renal tubule cells against oxidative damage and apoptosis induced by ischemia-reperfusion. J Am Soc Nephrol 2006, 17, 3336–3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desantis, A.; Bruno, T.; Catena, V.; De Nicola, F.; Goeman, F.; Iezzi, S.; Sorino, C.; Ponzoni, M.; Bossi, G.; Federico, V.; et al. Che-1-induced inhibition of mTOR pathway enables stress-induced autophagy. Embo j 2015, 34, 1214–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruno, T.; Desantis, A.; Bossi, G.; Di Agostino, S.; Sorino, C.; De Nicola, F.; Iezzi, S.; Franchitto, A.; Benassi, B.; Galanti, S.; et al. Che-1 promotes tumor cell survival by sustaining mutant p53 transcription and inhibiting DNA damage response activation. Cancer Cell 2010, 18, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desantis, A.; Bruno, T.; Catena, V.; De Nicola, F.; Goeman, F.; Iezzi, S.; Sorino, C.; Gentileschi, M.P.; Germoni, S.; Monteleone, V.; et al. Che-1 modulates the decision between cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by its binding to p53. Cell Death Dis 2015, 6, e1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folgiero, V.; Sorino, C.; Pallocca, M.; De Nicola, F.; Goeman, F.; Bertaina, V.; Strocchio, L.; Romania, P.; Pitisci, A.; Iezzi, S.; et al. Che-1 is targeted by c-Myc to sustain proliferation in pre-B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. EMBO Rep 2018, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, M. Apoptosis-antagonizing transcription factor (AATF) gene silencing: role in induction of apoptosis and down-regulation of estrogen receptor in breast cancer cells. Biotechnol Lett 2013, 35, 1561–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabanella, F.; Onori, A.; Ralli, M.; Greco, A.; Passananti, C.; Di Certo, M.G. SMN protein promotes membrane compartmentalization of ribosomal protein S6 transcript in human fibroblasts. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 19000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindfors, K.; Halttunen, T.; Huotari, P.; Nupponen, N.; Vihinen, M.; Visakorpi, T.; Mäki, M.; Kainulainen, H. Identification of novel transcription factor-like gene from human intestinal cells. In Biochem Biophys Res Commun; 2000 Academic Press.: United States, 2000; Volume 276, pp. 660–666. [Google Scholar]
- Grzybowska, E.A.; Zayat, V.; Konopinski, R.; Trebinska, A.; Szwarc, M.; Sarnowska, E.; Macech, E.; Korczynski, J.; Knapp, A.; Siedlecki, J.A. HAX-1 is a nucleocytoplasmic shuttling protein with a possible role in mRNA processing. Febs j 2013, 280, 256–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobley, J.A.; Brueggemeier, R.W. Estrogen receptor-mediated regulation of oxidative stress and DNA damage in breast cancer. Carcinogenesis 2004, 25, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazmeen, A.; Maiti, S. Redox Regulation of Estrogen Signaling in Human Breast Cancer.
- Wang, D.; Chen, T.Y.; Liu, F.J. Che-1 attenuates hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis by upregulation of Nrf2 signaling. In Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci; Italy, 2018; Volume 22, pp. 1084–1093.
- Ishigaki, S.; Fonseca, S.G.; Oslowski, C.M.; Jurczyk, A.; Shearstone, J.R.; Zhu, L.J.; Permutt, M.A.; Greiner, D.L.; Bortell, R.; Urano, F. AATF mediates an antiapoptotic effect of the unfolded protein response through transcriptional regulation of AKT1. Cell Death Differ 2010, 17, 774–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Yang, J.; Yi, J. Nucleolar Stress: hallmarks, sensing mechanism and diseases. Cell Stress 2018, 2, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapio, R.T.; Burns, C.J.; Pestov, D.G. Effects of Hydrogen Peroxide Stress on the Nucleolar Redox Environment and Pre-rRNA Maturation. Front Mol Biosci 2021, 8, 678488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shcherbik, N.; Pestov, D.G. The Impact of Oxidative Stress on Ribosomes: From Injury to Regulation. Cells 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassa, G.; Giurato, G.; Salvati, A.; Gigantino, V.; Pecoraro, G.; Lamberti, J.; Rizzo, F.; Nyman, T.A.; Tarallo, R.; Weisz, A. The RNA-mediated estrogen receptor α interactome of hormone-dependent human breast cancer cell nuclei. Sci Data 2019, 6, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leister, P.; Burgdorf, S.; Scheidtmann, K.H. Apoptosis antagonizing transcription factor AATF is a novel coactivator of nuclear hormone receptors. Signal Transduction 2003, 3, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Huangyang, P.; Wang, Y.; Xue, L.; Devericks, E.; Nguyen, H.G.; Yu, X.; Oses-Prieto, J.A.; Burlingame, A.L.; Miglani, S.; Goodarzi, H.; Ruggero, D. ERα is an RNA-binding protein sustaining tumor cell survival and drug resistance. Cell 2021, 184, 5215–5229.e5217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




