Submitted:
15 February 2023
Posted:
17 February 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
 |
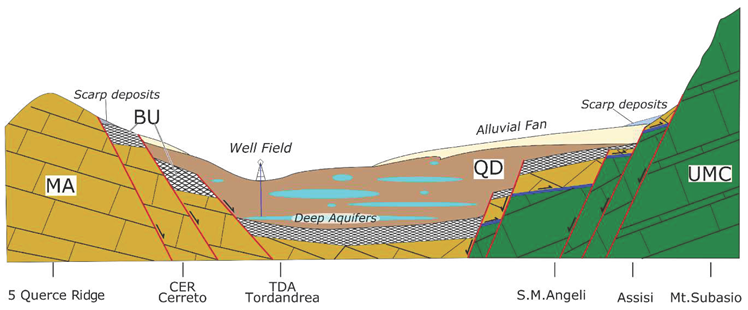
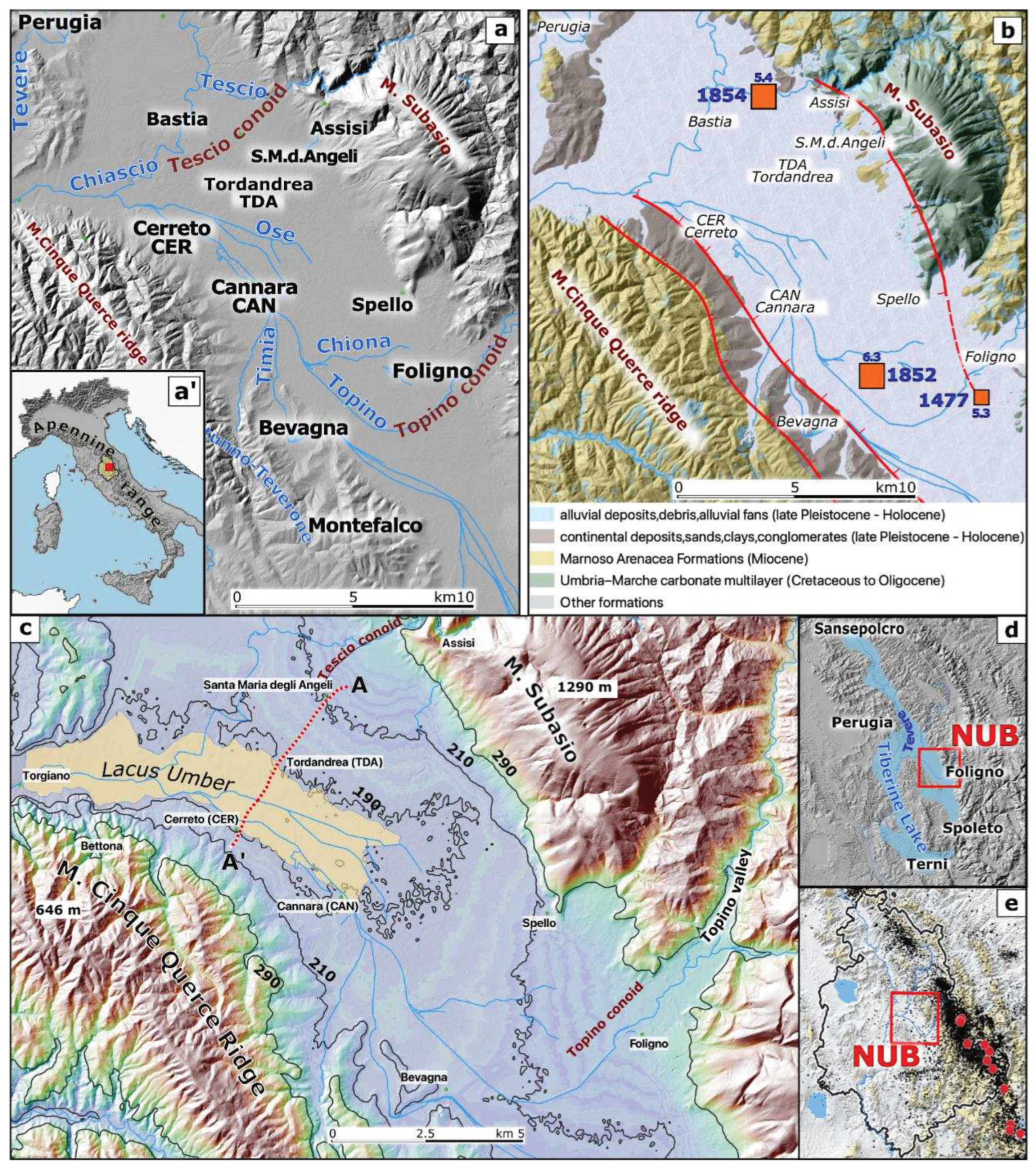
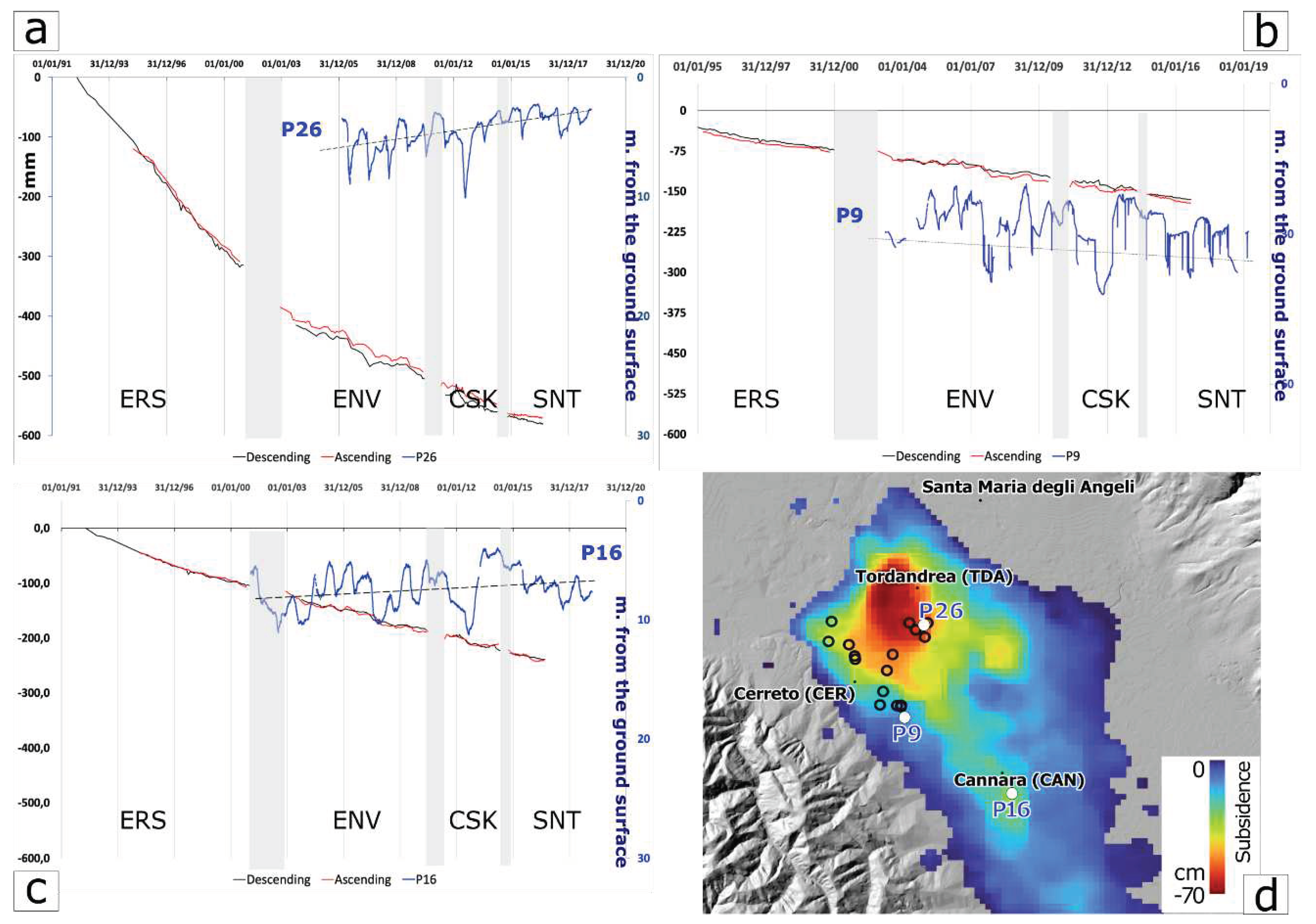
2. Case study
3. Materials and Methods
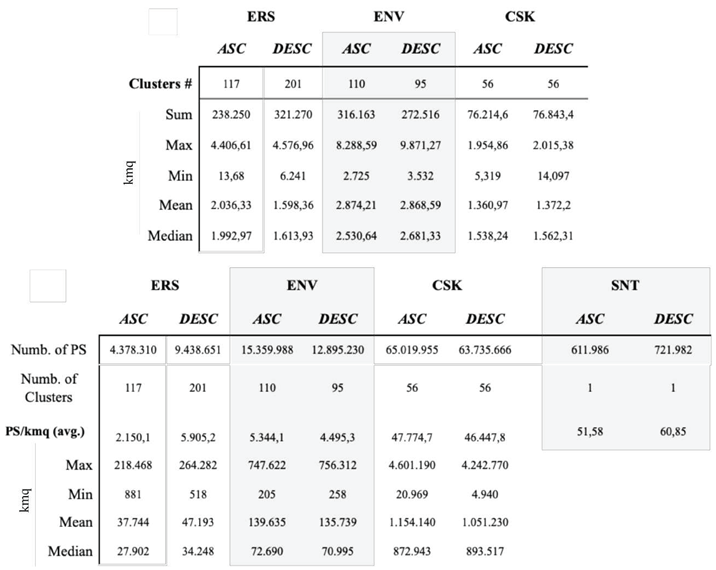
| ERS 1-2 | ENV | CSK | SNT1 | |
| Band (wavelen. cm) | C-band (5.6) | C-band (5.6) | X-Band (3.1) | C-band (5.6) |
| Operation mode | SAR/IM (1) | SAR/IM (1) | HIMAGE (Stripmap) | StripMap (HIMAGE) |
| Revisit cycle days | 35 | 35 | 16 | 12 |
| Look angle | 23° | 23° | 25°-57° | 329° |
| Swath km | 100 | 100 | 40 | 240 |
| ASC n. images | 35 | 51 | 40 | 48 |
| ASC first image | 02/04/1995 | 02/12/2002 | 09/05/2011 | 25/10/2014 |
| ASC last image | 23/10/2000 | 24/05/2010 | 30/03/2014 | 21/08/2016 |
| DESC n. images | 56 | 37 | 30 | 42 |
| DESC first image | 21/04/1992 | 10/10/2003 | 29/07/2011 | 24/10/2014 |
| DESC last image | 29/12/2000 | 25/06/2010 | 16/04/2014 | 01/09/2016 |
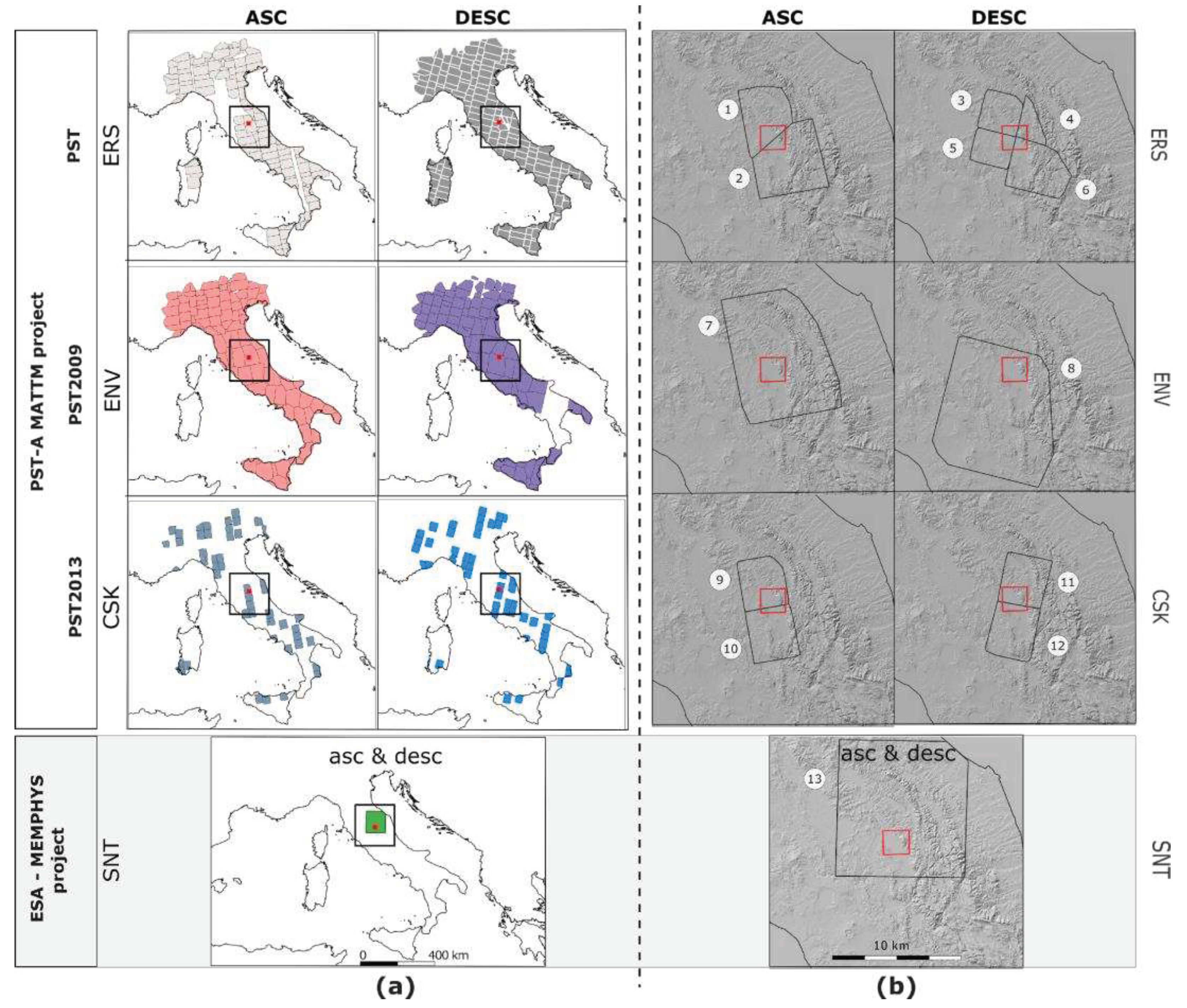
| orbit | Project ID | Cluster ID | # Fig 1b | |
| ERS 1-2 | ASC | PST | ERS_T401_F858_CL003_SPELLO ERS_T401_F858_CL004_SPOLETO |
1 2 |
| DESC | PST | ERS_T351_F2745_CL002_PERUGIA ERS_T79_F2748_CL001_GUALDO ERS_T79_F2748_CL003_SPOLETO ERS_T351_F2745_CL001_MARSCIANO |
3 4 5 6 |
|
| ENV | ASC | PST2009 | ENVISAT_T401_F858_CL001_ASSISI | 7 |
| DESC | PST2009 | ENVISAT_T351_F2745_CL001_TERNI | 8 | |
| CSK | ASC | PST2013 | CSK_F_44_PERUGIA_A_CL001 CSK_F_43_SPOLETO_A_CL001 |
9 10 |
| DESC | PST2013 | CSK_F_46_SPOLETO_D_CL001 CSK_F_45_GUALDOTADINO_D_CL001 |
11 12 |
|
| SNT | ASC | SqueeSAR | S1_T117_A_33 | 13 |
| DESC | SqueeSAR | S1_T95_D_32 | 13 |
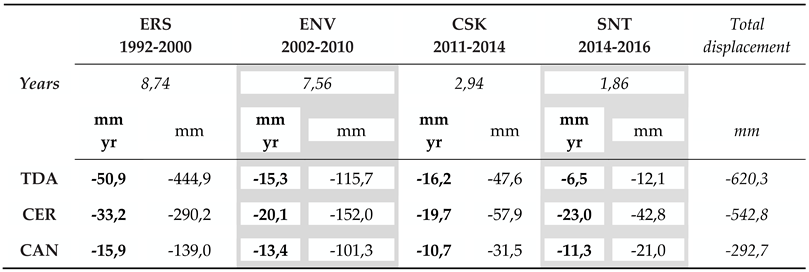 |
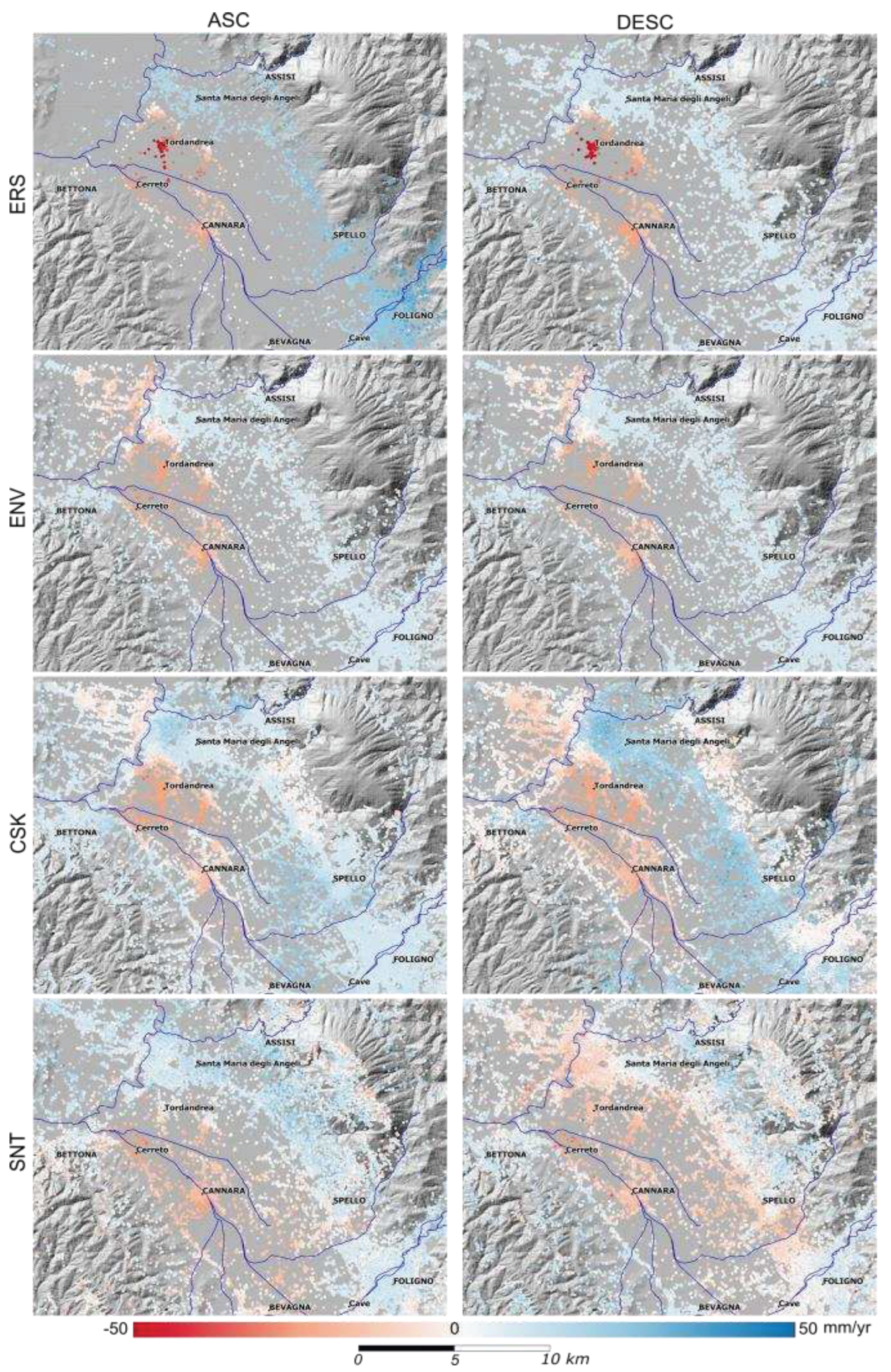
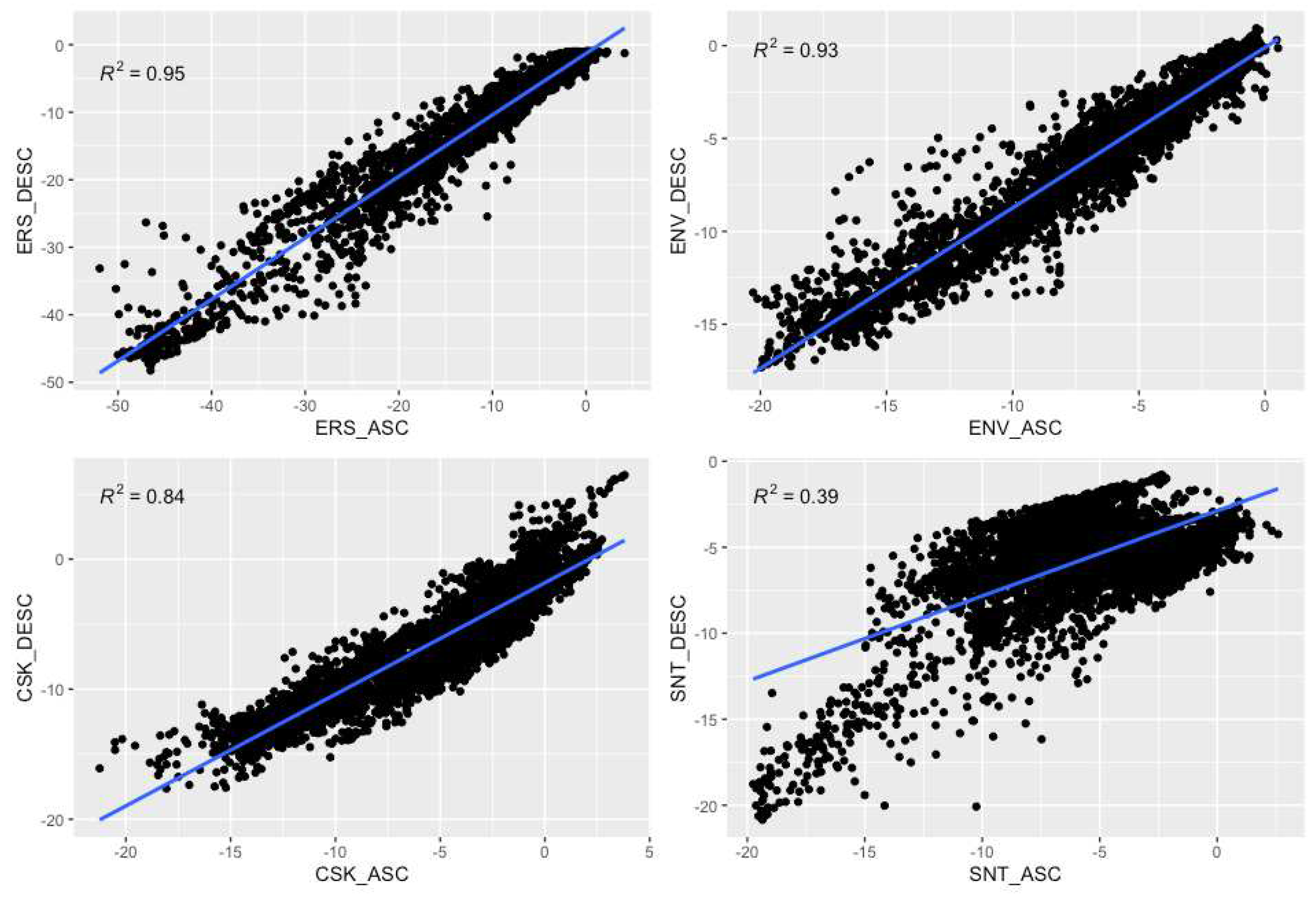
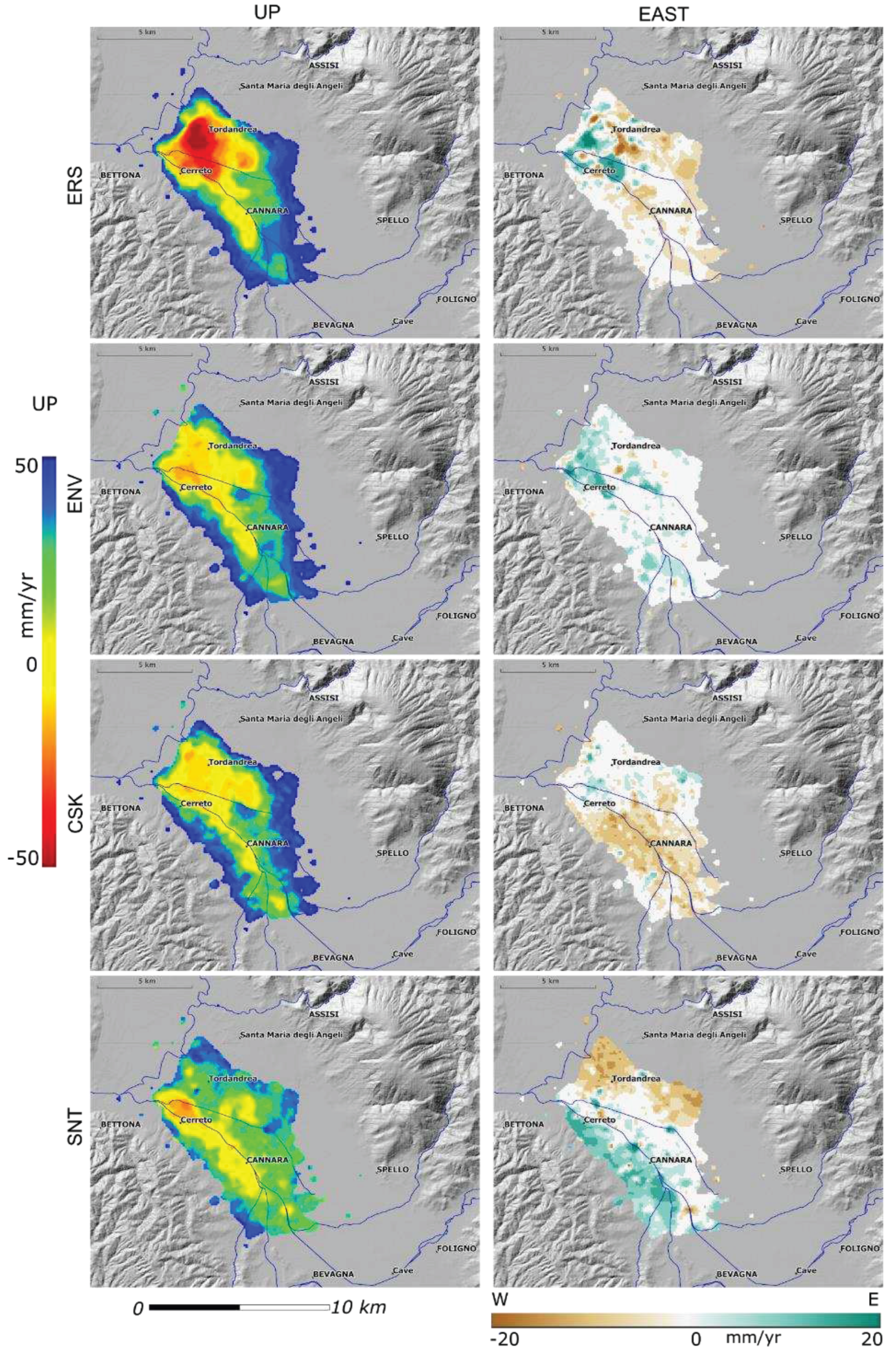
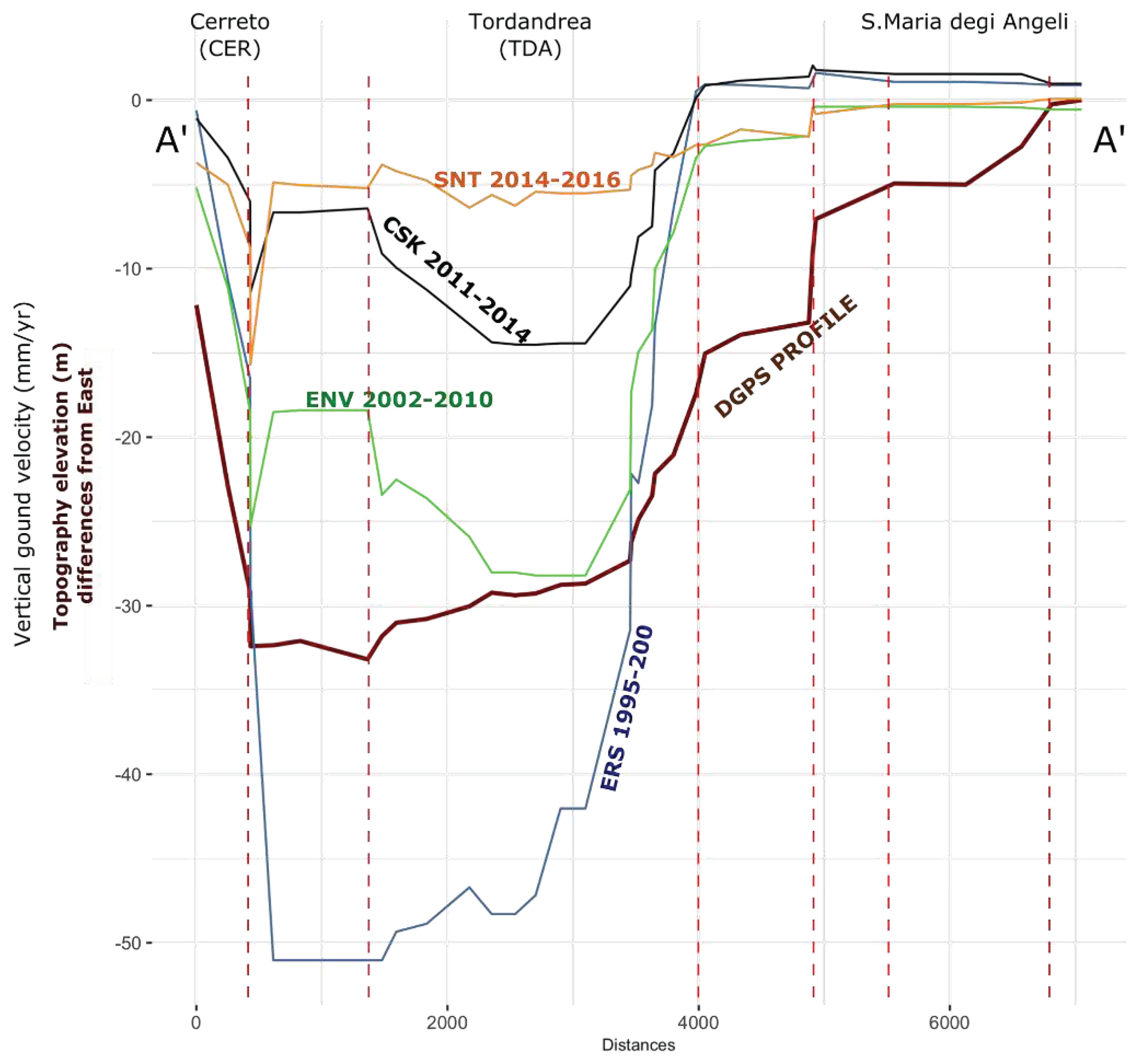
4. Discussion
2. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo H., Wang L., Chen F., Liang D. (2014). Scientific big data and Digital Earth. Chin. Sci. Bull. (2014) 59(35):5066–5073. [CrossRef]
- Guo H. (2017) Big Earth data: A new frontier in Earth and information sciences, Big Earth Data, 1:1-2, 4-20. [CrossRef]
- Casu, F. , Manunta M., Agramb P.S., Crippen R.E. Big Remotely Sensed Data: tools, applications and experiences (2017), Remote Sensing of Environment 202 (2017) 1–2. [CrossRef]
- Gurusamy, V. , Kannan S., Nandhini K. (2017). The Real-Time Big Data Processing Framework: Advantages and Limitations. Vol. 5, Issue-12 E-ISSN: 2347-2693, IJCSE. [CrossRef]
- De Luca, C. , Zinno I., Manunta M., Lanari R., Casu F., Large areas surface deformation analysis through a cloud computing P-SBAS approach for massive processing of DInSAR time series, Remote Sensing of Environment, Vol. 202, 2017, pp. 3-17. https://Doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2017.05.022.
- Cigna, F. , Tapete D. (2021) Sentinel-1 Big Data Processing with P-SBAS InSAR in the Geohazards Exploitation Platform: An Experiment on Coastal Land Subsidence and Landslides in Italy. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, M. , Ferretti A., Minati F., Falco S., Trillo F., Colombo D., Novali F., Malvarosa F., Mammone C., Vecchioli F., Rucci A., Fumagalli A., Allievi J., Ciminelli M.., Costabile S., 2017. Analysis of surface deformations over the whole Italian territory by interferometric processing of ERS, ENVISAT and COSMO-SkyMed radar data. Remote Sens. Environ. [CrossRef]
- Solari L, Del Soldato M, Bianchini S, Ciampalini A, Ezquerro P, Montalti R, Raspini F and Moretti S (2018) From ERS 1/2 to Sentinel-1: Subsidence Monitoring in Italy in the Last Two Decades. Front. Earth Sci. 6:149. [CrossRef]
- Terzaghi, K.V. Relation between soil mechanics and foundation engineering. In Proceedings of the 1936 International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering, Boston, MA, USA, 22–26 June 1936. [Google Scholar]
- Cigna, F. , Jordan H., Bateson L, McCormack H., Roberts C. (2015) Natural and Anthropogenic Geohazards in Greater London Observed from Geological and ERS-1/2 and ENVISAT Persistent Scatterers Ground Motion Data: Results from the EC FP7-SPACE PanGeo Project. Pure Appl. Geophys. 172, 2965–2995 (2015). [CrossRef]
- Dong, S. , Samsonov S., Yin H., Ye S., Cao Y. (2014) Time-series analysis of subsidence associated with rapid urbanisation in Shanghai, China measured with SBAS InSAR method. Environ Earth Sci 72, 677–691 (2014). [CrossRef]
- Chaussard, E. , Wdowinski, S., Cabral-Cano, E.,, Amelung, F. C. (2014). Land subsidence in central Mexico detected by ALOS InSAR time series. Remote Sensing of Environment, 140, 94-106. [CrossRef]
- Murgia, F.; Bignami, C.; Brunori, C.A.; Tolomei, C.; Pizzimenti (2019), L. Ground deformations controlled by hidden faults: Multifrequency and multitemporal InSAR techniques for urban hazard monitoring. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigna, F. , & Tapete, D. (2022). Land subsidence and aquifer-system storage loss in Central Mexico: A quasi-continental investigation with Sentinel-1 InSAR. Geophysical Research Letters, 4, e2022GL098923. [CrossRef]
- Delgado Blasco, J.M.; Foumelis, M.; Stewart, C.; Hooper, A. Measuring Urban Subsidence in the Rome Metropolitan Area (Italy) with Sentinel-1 SNAP-StaMPS Persistent Scatterer Interferometry. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stramondo, S.; Saroli, M.; Tolomei, C.; Moro, M.; Doumaz, F.; Pesci, A.; Boschi, E. Surface movements in Bologna (Po Plain-Italy) detected by multitemporal DInSAR. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 110, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonellini, M. , Giambastiani B.M.S., Greggio N., Bonzi L., Calabrese L., Luciani P., Perini L., Severi P. (2019). Processes governing natural land subsidence in the shallow coastal aquifer of the Ravenna coast, Italy. Catena, 172, 76-86. [CrossRef]
- Polcari M, lbano M, Montuori A, Bignami C, Tolomei C, Pezzo G, Falcone S, La Piana C, Doumaz F, Salvi S, Stramondo S. (2018) InSAR Monitoring of Italian Coastline Revealing Natural and Anthropogenic Ground Deformation Phenomena and Future Perspectives. Sustainability. 2018; 10(9):3152. [CrossRef]
- Fiaschi, S. , Fabris M., Floris M, Achilli V. (2018) Estimation of land subsidence in deltaic areas through differential SAR interferometry: the Po River Delta case study (Northeast Italy), International Journal of Remote Sensing, 39:23, 8724-8745. [CrossRef]
- Teatini, P. , Tosi L., Strozzi T., Carbognin L., Cecconi G., Rosselli R., Libardo S. (2010) Resolving land subsidence within the Venice Lagoon by persistent scatterer SAR interferometry. J. Phys. Chem. Earth. [CrossRef]
- Solari, L.; Ciampalini, A.; Raspini, F.; Bianchini, S.; Moretti, S. PSInSAR analysis in the pisa urban area (Italy): A case study of subsidence related to stratigraphical factors and urbanization. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raspini, F. , Cigna F., Moretti S. (2012) Multi-temporal mapping of land subsidence at basin scale exploiting Persistent Scatterer Interferometry: case study of Gioia Tauro plain (Italy), Journal of Maps, 8:4, 514-524. [CrossRef]
- Cianflone, G. , Tolomei, C., Brunori, C. A., Dominici, R. (2016). InSAR time series analysis of natural and anthropogenic coastal plain subsidence: the case of Sibari (Southern Italy). Remote Sens. 7, 16004–16023. [CrossRef]
- Brunori, C.A. , Bignami C. Albano M., Zucca F. Samsonov S., Groppelli G. Norini G. Saroli M., Stramondo S. (2015), Land subsidence, Ground Fissures and Buried Faults: InSAR Monitoring of Ciudad Guzmán (Jalisco, Mexico). Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 8610–8630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Hernández, M. I. , Tomás, R., Lopez-Sanchez, J. M., Cárdenas-Tristán, A., & Mallorquí, J. J. (2020). Spatial analysis of land subsidence in the San Luis Potosí valley induced by aquifer overexploitation using the coherent pixels technique (CPT) and sentinel-1 insar observation. Remote Sensing, 12(22), 3822. [CrossRef]
- Gourmelen, N. , Amelung F., Casu F., Manzo M., Lanari R.. (2007) Mining-related ground deformation in Crescent Valley, Nevada: implications for sparse GPS networks Geophys. Res. Lett., 34 (9) (2007), Article L09309. [CrossRef]
- Cianflone, G. , Tolomei C., Brunori C.A., Monna S., Dominici R. (2018) Landslides and Subsidence Assessment in the Crati Valley (Southern Italy) Using InSAR Data. Geosciences 2018, 8 (2), 67. [CrossRef]
- Hu, L. , Dai K., Xing C., Li Z., Tomás R., Clark B., Shi X., Chen M., Zhang R., Qiu Q., Lu Y. (2019) Land subsidence in Beijing and its relationship with geological faults revealed by Sentinel-1 InSAR observations. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation. 82. [CrossRef]
- Guzzetti, F. , Manunta M., Ardizzone F., Pepe A., Cardinali M., Zeni G., Reickenbach P., Lanari R. (2009), Analysis of ground deformation detected using the SBAS-DInSAR technique in Umbria, Central Italy. Pure Appl. geophys. 166 (2009) 1425–1459, 0033–4553/09/081425–35. [CrossRef]
- Scarsella, F. (1951) - Un raggruppamento di pieghe dell’Appennino umbro-marchigiano. La catena M. Nerone-M. Catria-M. Cucco-M. Penna-Colfiorito-M. Serano. Bollettino del Servizio Geologico d’Italia, 73, 309-20.
- Lavecchia, G. , Barchi, M., Brozzetti, F., & Menichetti, M. (1994). Sismicità e tettonica nell’area umbro-marchigiana. Boll. Soc. Geol. It, 113, 483-500.
- Barchi, M.R. , Lemmi M. (2015). NOTE ILLUSTRATIVE della CARTA GEOLOGICA D’ITALIA alla scala 1:50.000, Foglio 324 Foligno. ISPRA-Servizio Geologico d'Italia https://www.isprambiente.gov.it/Media/carg/note_illustrative/324_Foligno.
- Tarquini S., I. Isola, M. Favalli, A. Battistini, G. Dotta (2023). TINITALY, a digital elevation model of Italy with a 10 meters cell size (Version 1.1). Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia (INGV). [CrossRef]
- Camerieri, P. , Manconi D. (2008), “Le centuriazioni della Valle Umbra da Spoleto a Perugia”, in XVII International Congress of Classical Archaeology, Roma 22-26 Sept. Poster Session: Landscape Archaeology / Archeologia del Paesaggio, Bollettino di Archeologia on line.
- Conti M., A. & Girotti O. (1977) - Il Villafranchiano nel «lago tiberino », ramo sud-occidentale: schema stratigrafico e tettonico. Geol. Romana, 16, 67-80, 13 fl., 1 tab.
- Ambrosetti, P. , Carboni M.G., Conti M.A., Esu D., Girotti O., La Monica G.B., Landini B., Parisi G. (1987) - Il Pliocene ed il Pleistocene inferiore del bacino del Fiume Tevere nell'Umbria meridionale. Geogr. Fis. Dinam. Quat., 10, 10-33.
- Basilici, G. (1997) - Sedimentary facies in an extensional and deep-lacustrine depositional system: the Plio-cene Tiberino Basin, Central Italy. Sedimentary Geology, 109(1-2), 73-94. [CrossRef]
- Coltorti, M. , Pieruccini P., 1997. Middle-Upper Pliocene ‘compression’ and Middle Pleistocene ‘extention’ in the modelling of the East Tiber Basin (Central Italy): from ‘perched’ to ‘extentional basin in the Northern Apennines. Il Quaternario 10(2) 521-528.
- Bucci, F. , Mirabella, F., Santangelo, M., Cardinali, M., Guzzetti, F. (2016). Photogeology of the Montefalco Quaternary basin, Umbria, Central Italy. Journal of Maps, ISSN: 1744-5647. [CrossRef]
- Ge.Mi.Na. (1962). Ligniti e torbe dell’Italia continentale. Geomineraria nazionale, 1–319 (Italian).
- Cardinali, M. , Antonini, G., Reichenbach, P., Guzzetti, F. (2001), Photo-geological and landslide inventory map for the Upper Tevere River basin. CNR, Gruppo Nazionale per la Difesa dalle Catastrofi Idrogeologiche, Publication n. 2154, scale 1:100,000. http://geomorphology.irpi.cnr.it/publications/repository/public/maps/UTR-data.
- Martinetto, E. , Bertini, A., Basilici, G., Baldanza, A., Bizzarri, R., Cherin, M., Gentili, S., & Pontini, M. R. (2014). THE PLANT RECORD OF THE DUNAROBBA AND PIETRAFITTA SITES IN THE PLIO-PLEISTOCENE PALAEOENVIRONMENTAL CONTEXT OF CENTRAL ITALY. Alpine and Mediterranean Quaternary, 27(1), 29–72. Retrieved from https://amq.aiqua.it/index.
- Mutti, E. ,Ricci Lucchi F. (1978). 2: Turbidites of the northern Apennines: introduction to facies analysis, International Geology Review, 20; :2. [CrossRef]
- Centamore, E. , Deiana G., Micarelli A., Potetti M. (1986) - Il Trias-Paleogene delle Marche. Studi Geologici Camerti, Vol. Spec. “La geologia delle Marche”: 9-27.
- Cresta, S. , Monechi S., Parisi G., Baldanza A., Reale V. (1989) - Stratigrafia del Mesozoico e Cenozoico nell’area umbro-marchigiana. Itinerari geologici sull’Appennino Umbro-marchigiano. Mem. Descr. della Carta Geol. d’It., 39.
- Barchi, M. (2010). The Neogene-quaternary evolution of the Northern ApeREFines: Crustal structure, style of deformation and seismicity. In M. Beltrando, A. Peccerillo, M. Matte, S. Conticelli, & C. Doglioni (Eds.), The geology of Italy, Journal of the Virtual Explorer, Electronic Edition, 36, paper 10.
- Pucci, S. , Mirabella, F., Pazzaglia, F., Barchi, M. R., Melelli, L., Tuccimei, P., et al. (2014). Interaction between regional and local tectonic forcing along a complex Quaternary extensional basin: Upper Tiber Valley, Northern Apennines, Italy. Quaternary Science Reviews, 102, 111–132. [CrossRef]
- Malinverno, A. and Ryan, W.B.F. (1986) Extension in the Tyrrhenian Sea and Shortening in the Apennines as Result of Arc Migration Driven by Sinking of the Lithosphere. Tectonics, 5, 227-245. [CrossRef]
- Martini, I.P. and Sagri, M. (1993) Tectono-Sedimentary Characteristics of Late Miocene Quaternary Extensional Basins of the Northern Apennines, Italy. Earth-Science Reviews, 34, 197-133. [CrossRef]
- Famiani, D. , Brunori C.A., Pizzimenti L., Cara F., Caciagli M., Melelli L., Mirabella F., Barchi M. R. (2020). Geophysical reconstruction of buried geological features and site effects estimation of the Middle Valle Umbra basin (central Italy). Engineering Geology, 105543. [CrossRef]
- Rovida, A. , Locati M., Camassi R., Lolli B., Gasperini P., Antonucci A. (eds), 2021. Italian Parametric Earthquake Catalogue (CPTI15), version 3.0. Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia (INGV). [CrossRef]
- Vetturini E. (1995). Terre e acque in valle Umbra, Bastia, 1995, pag. 74.
- Ferretti, A. , Fumagalli A., Novali F., Prati C., Rocca F, Rucci O. (2011), A new algorithm for processing interferometric data-stacks: SqueeSAR IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 49 (9), 3460-3470. [CrossRef]
- Costantini, M. , Falco S., Malvarosa F., Minati F., Trillo F., Vecchioli F. (2014). Persistent Scatterer Pair Interferometry: Approach and Application to COSMO-SkyMed SAR Data. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics In Applied Earth Observations And Remote Sensing, vol. 7, no. 7. [CrossRef]
- Costantini, M. , Falco S., Malvarosa F., Minati F., Trillo F. (2009). Method of persistent scatterer pairs (PSP) and high resolution SAR interferometry. 2009 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Cape Town, South Africa, 2009, pp. III-904-III-907. [CrossRef]
- Dalla Via, G. , Crosetto M., Crippa B. (2012), Resolving vertical and east-west horizontal motion from differential interferometric synthetic aperture radar: The L’Aquila earthquake: resolving z and e-w motion from D-InSAR. J. Geophys.: Solid Earth, vol 117, 2012. [CrossRef]
- Fuhrmann, T. , Garthwaite M. C. (2019). Resolving three-dimensional surface motion with InSAR: Constraints from multi-geometry data fusion. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepe, A.; Solaro, G.; Calò, F.; Dema, C. A Minimum Acceleration Approach for the Retrieval of Multiplatform InSAR Deformation Time Series. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 3883–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beretta, G. P. , Avanzini, M., Marangoni, T., Burini, M., Schirò, G., Terrenghi, J., & Vacca, G. (2018). Groundwater modelling of the withdrawal sustainability of Cannara artesian aquifer (Umbria-Italy). ACQUE SOTTERRANEE, 7(3), 47-60. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





