1. Introduction
The human body is home to diverse microbial communities known as the microbiota, which consist of bacteria, archaea, fungi, viruses, and protists. They residue on surfaces and niches that are directly linked or not linked to the external environment [
1]. These communities vary greatly in composition and function among different body sites and individuals. [
2]. Indeed, Techniques like 16S rRNA sequencing and statistical methods have revealed that every part of the human body is colonized with unique microbial communities that differ in composition and function based on the anatomical niche and health status of individuals. For example, the oral and nasal cavity [
3,
4], lung [
5], skin [
6], and the gastrointestinal [
7], urinary [
8,
9], and reproductive [
10] tracts harbor specific types of microbiota based on their functions and surfaces.
Traditionally, all microbiomes were thought to be pathogens and cause diseases [
11], but it is now understood that they play a crucial role in protecting against pathogens and regulating the host's inflammatory responses [
12]. However, changes (dysbiosis) of normal bacterial communities impair the normal function of microbiota as protector and modulator, and lead to disease reactions. Therefore, maintaining a healthy host microbiota community is crucial. This led to the development of microbial transfer therapy (MTT), which involves replacing diseased microbiomes with healthy ones. The most popular MTT is fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT), which has been used since the 4th century and has gained attention after its approval by the US Food and Drug Administration for treating Clostridium difficile infection in 2012 [
13]. FMT has been found to be effective and safe in treating CDI [
14], as well as gastrointestinal and psychiatric disorders such as ulcerative colitis and mental illness [
15,
16].
These successful applications of FMT inspired a new set of MTT - vaginal microbiota transplantation (VMT). VMT is an emerging experimental medical intervention that aims to restore the otherwise disbalanced vaginal microbiota by transferring vaginal microbiota from a healthy donor to the vaginal cavity of a diseased patient to restore its overall diversity, stability, normal composition and function [
17]. Recently, VMT has been successfully applied to treat bacterial vaginosis without any adverse effects [
18]. Briefly, in this clinical trial, five patients (aged 27-47 years old) suffering from symptomatic, intractable and recurrent bacterial vaginosis were treated with VMT. Among them, 80% of the patients were fully recovered during this study (5-21 months after VMT). Successful treatment results show significant symptom improvement, adherence to Amsel criteria, observation of improved vaginal fluid under a microscope, and restoration of a
Lactobacillus-dominated vaginal microbiome. However, the biggest drawback was that this study was small in sample size and uncontrolled. In order to discuss the feasibility of manipulating vaginal microbiota by VMT, Gardner and Dukes transferred
Gardnerella vaginalis from the vaginas of infected women into the vaginas of healthy volunteers who successfully developed the disease [
19]. Although these two studies have shown the possibility of manipulating vaginal microbiota in means of transplanting the entire vaginal microbiota or bacterial strain, the research and clinical applications on VMT are still in their infancy.
Studies have shown that the female reproductive tract health is not only maintained by the vaginal microbial community [
20,
21], but also heavily dependent on a healthy intestinal flora [
22]. Therefore, the potentiality of using FMT as a tool for treating female reproductive tract diseases, which aims to restore the gut microbiota, was discussed [
23]. However, compared to the gut microbiota, the vaginal microbiota is rarely explored as a MTT, which resulted in underappreciated clinical applications of VMT.
Safety concerns and lack of case-controlled studies and regulatory approvals are the main limiting factors of clinical application of VMT. For this regard, in this paper, we aimed to explore the possible mechanisms of therapeutic effect in VMT to encourage its wider clinical applications as well as future perspectives that could be a direction for further studies.
2. Normal Composition and Function of Vaginal Microbiota
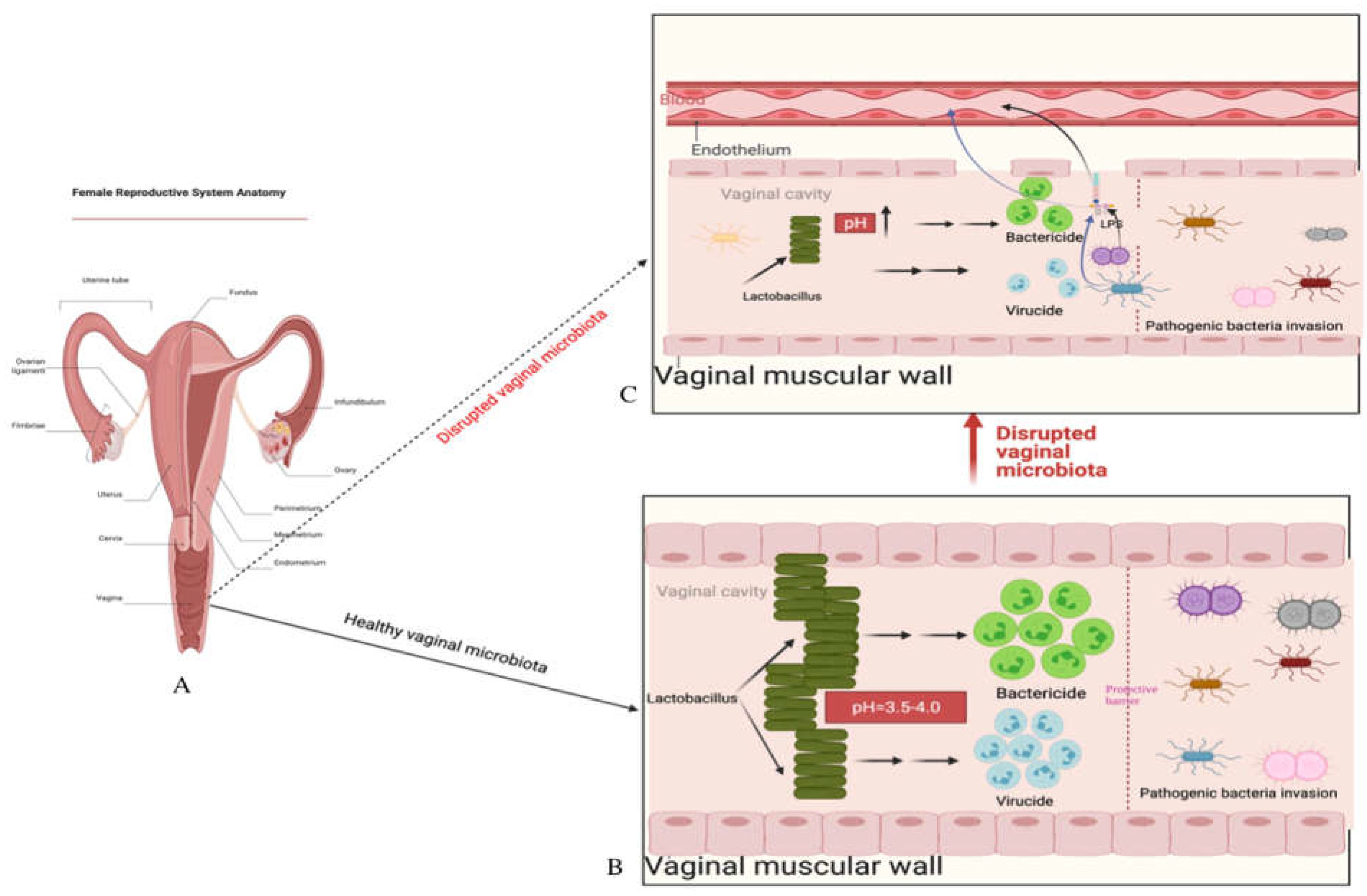
The vaginal cavity is a crucial part of the female reproductive system, extending from the cervix and uterus to the external genitalia (vulva) (
Figure 1). It is a niche in the human body that harbors a unique microbial community, predominantly composed of predominantly composed of
Lactobacillus spp. [
24], including species such as
Lactobacillus crispatus,
Lactobacillus gasseri,
Lactobacillus iners,
and Lactobacillus jensenii [
25,
26]. However, other species such as
Bacteroides spp., Fusobacterium spp., Veillonela spp., Actinomycetes spp., Bifidobacterium spp., Peptococcus spp., Peptostreptococcus spp., Propionibacterium spp., Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Streptococcus viridans, Enterococcus faecalis, Gardnerella vaginalis, and
Prevotella bivia [
25,
26,
27], also exist at low levels.
Similar to any other microbiota-residue niches (e.g., gut microbiota), the vaginal microbiota may also interact with the host immune system and act as protector and modulator against pathogenic agents and inflammatory responses in the vaginal cavity [
28]. The presence of
Lactobacillus crispatus and
Lactobacillus Jensenii in the vagina has been linked to lower levels of cellular inflammation markers and higher levels of anti-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1a and IL-8, according to a study [
29]. Another study found that higher levels of secretory leukocyte peptidase inhibitor (SLPI), an antimicrobial peptide that is typically depleted in women with conditions such as bacterial vaginosis [
31,
32], can be observed in women with high levels of
Lactobacillus iners [
30]. Doerflinger and colleagues` research suggests that while
Lactobacillus iners ATCC 5195 does activate pattern-recognition receptor (PRR) signaling pathways in human primary vaginal epithelial cells
, Lactobacillus crispatus ATCC 38820 does not significantly upregulate [
33]. These findings indicate that the composition of the vaginal microbiome plays a unique role in maintaining vaginal health.
Lactobacillus species in the vaginal play a critical role in maintaining female reproductive health through various directive and indirective anti-pathogenic mechanisms. These mechanisms include producing compounds that directly kill or inhibit pathogens, creating a microbial barrier that attaches to the epithelium and prevents pathogenic agents from adhering, and activating the host's defense mechanisms against pathogens. These functions demonstrate the unique and crucial role that the composition of the vaginal microbiome plays in maintaining a healthy reproductive system.
Furthermore, a study involving a group of asymptomatic young South African women revealed that the composition of vaginal microbiota is closely related to host genital inflammation [
34]. This study found that women with high diversity and low abundance of
lactobacillus in their vaginal microbiota experienced higher levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the genital area. This highlights the crucial role that the composition and diversity of the vaginal microbiome play in maintaining female reproductive health.
Lactobacillus species-dominated vaginal microbiota essential to female reproductive health, and its presence may protect against urological diseases such as bacterial vaginosis, yeast infections, STDs, urinary tract infections, and HIV [
35,
36,
37,
38,
39,
40,
41,
42,
43,
44,
45,
46,
47]. A healthy and diverse composition of the vaginal microbiota is important for maintaining gynaecologic wellness in women.
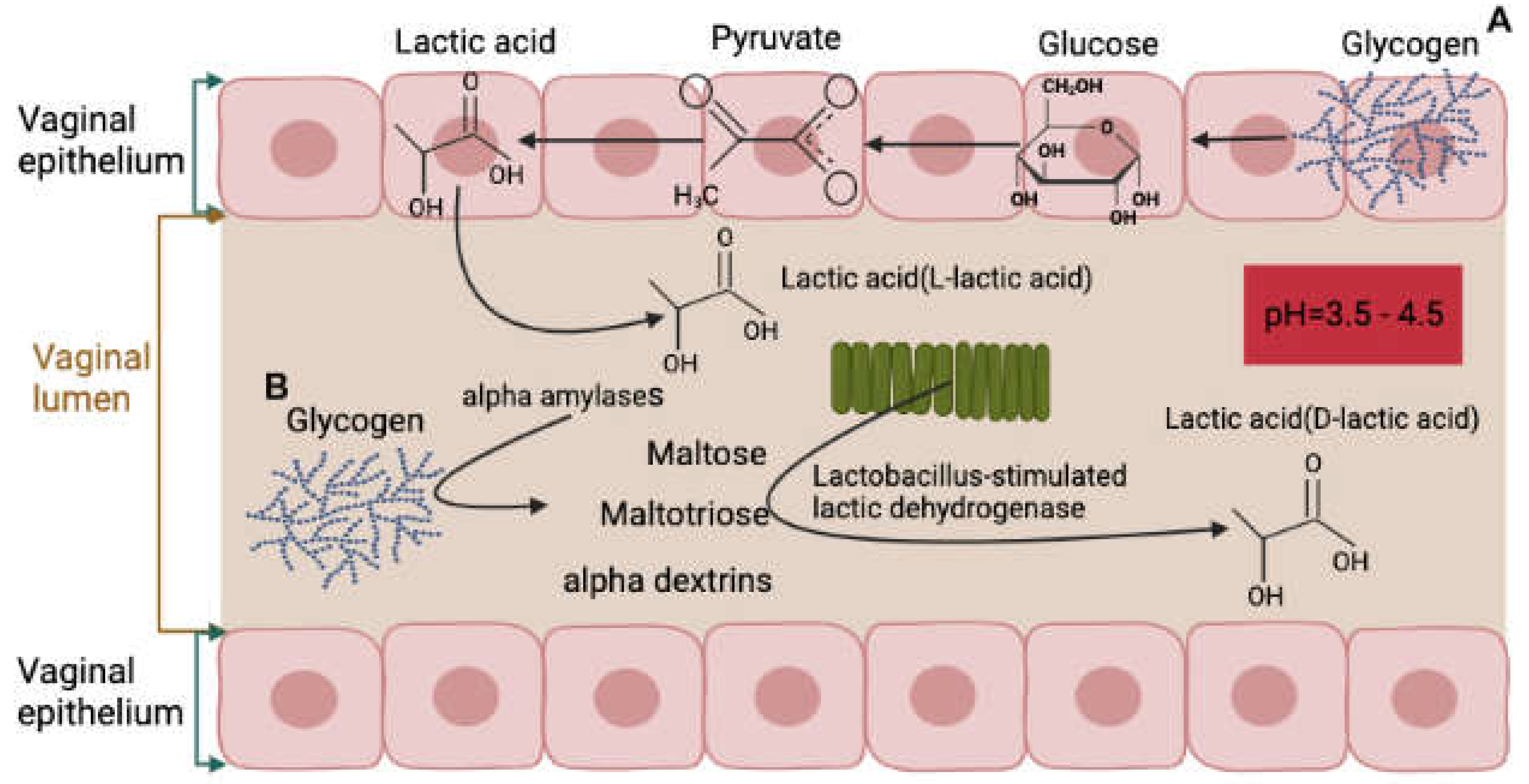
In a healthy state, the vaginal environment is maintained by a delicate balance between different elements, including lactic acid production. Lactic acid is crucial in maintaining the vaginal homeostasis and preventing the growth of pathogens. There are two sources of lactic acid in the vagina, the first being produced by the vaginal epithelium through the production of L-lactate, which accounts for 20% of total lactic acid. The second source is the vaginal microbiota, responsible for metabolizing glycogen and producing the majority of lactic acid, primarily in the form of D-lactic acid, which accounts for 80% of the total lactic acid [
48,
49] (
Figure 2).
3. Development of the Vaginal Microbiota
While the diversity of the microbiota in healthy women's vaginal cavity is relatively low, its composition undergoes a series of changes throughout the female life cycle, from childhood to the menopause stage (
Figure 3). For example, in childhood, the vaginal microbiota is most diverse and comprises gram-negative anaerobic, gram-positive anaerobic and aerobic bacteria [
54,
55]. After childhood - prepuberal, puberty and adult stages, the vaginal microbiota becomes less diverse and dominated by
Lactobacillus spp. [
55,
56]. In the menopause stage, the vaginal microbiota is also dominated by
Lactobacillus spp. but more diverse compared to the previous three stages [
57]. Although the exact purpose and function of such changes are not clear, it is possibly associated with reproductivity of a female. Therefore, the age and reproduction status of a female should be considered when carrying out clinical trials and studies regarding female healthy genitalia microbiota composition.
4. Factors related to changes of vaginal microbiota
A healthy vaginal microbiota community plays an important role not only in preventing pathogenic agents from invasion, but also in maintaining the female reproductive and gynaecologic health and overall host well-being.
Disbalances of vaginal microbiota are associated with several adverse conditions such as preterm birth, pelvic inflammatory disease, increased risk and transmission of sexually transmitted infection, infertility, and multiple stigmatizing symptoms that impact female health [
58]. Therefore, in order to further manipulate the vaginal microbiota to a beneficial direction, it is important to understand the factors associated with changes of the vaginal microbiota community. According to previous studies there are many factors may affect the vaginal microbiota communities including but not limited to diseases (bacterial vaginosis), age and hormone physiology (new born, childhood, puberty, reproductive stage, postmenopausal stage), ethnicity, tobacco, stress, sexual activity, life style and daily practices, probiotics, diet, and exercise [
21,
22,
59,
60,
61,
62,
63,
64,
65,
66,
67,
68].
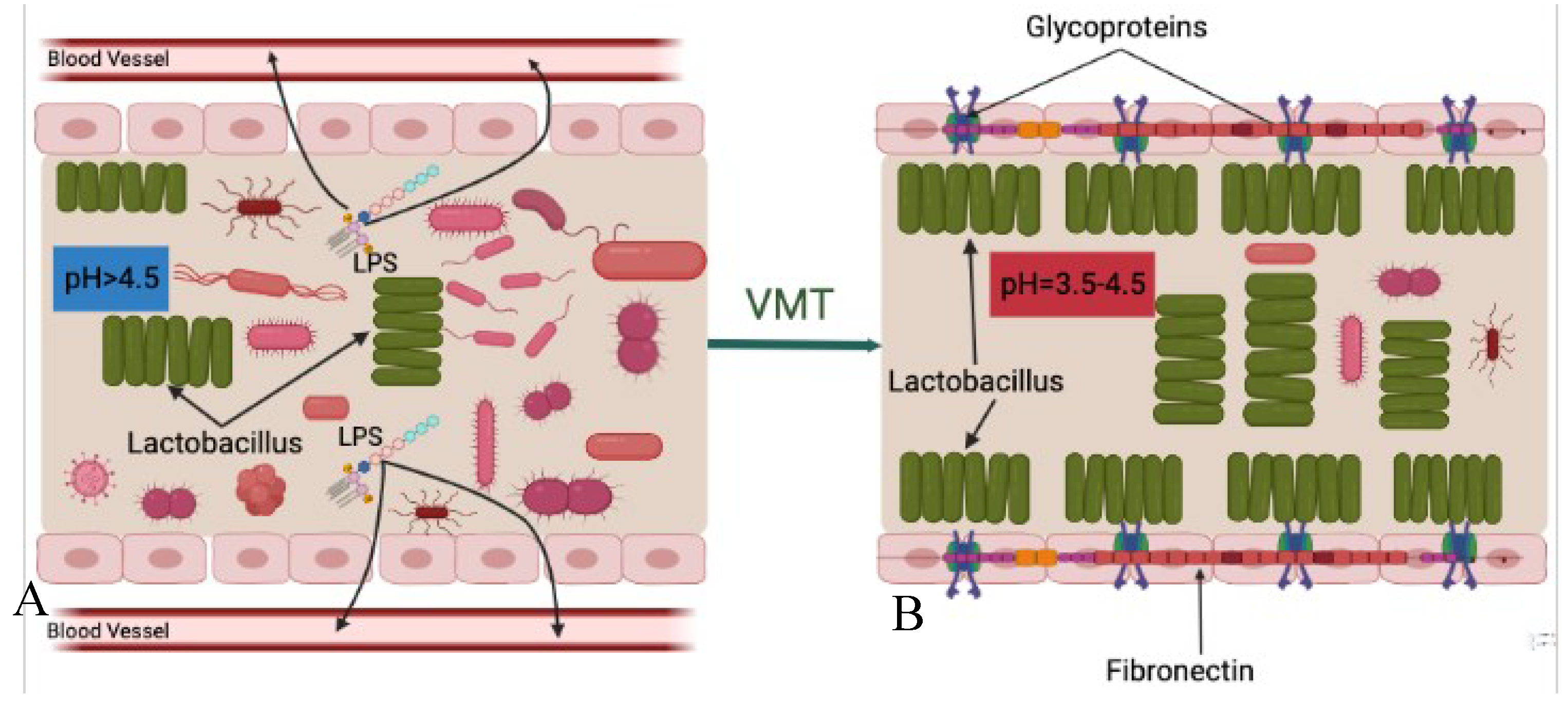
Regardless of the specific reason, a dysbiosis (imbalance) vaginal microbiota is characterized by lowered Lactobacillus spp. and increased anaerobic microorganisms in the vaginal cavity. These ultimately result in transformations of the vaginal microbiota composition from Lactobacillus spp.to potentially pathogenic facultative anaerobic bacteria and increased vaginal pH (>4.5).
A healthy vaginal microbiota community composed mainly of Lactobacillus species helps maintain female reproductive health by preventing pathogenic agents from invading. However, disruptions to this balance, caused by factors such as antibiotics, hormonal changes, and sexual activity, can lead to overgrowth of potentially pathogenic microorganisms and increase the risk of conditions such as bacterial vaginosis, aerobic vaginitis, and sexually transmitted infections, such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1), human papilloma virus (HPV) infection [
69], and
Chlamydia trachomatis infection [
70].
5. Possible Mechanisms of Vaginal Microbiota Transplantation
Here, we proposed three possible mechanisms of action involved in the VMT therapy, including increased competition for nutrition, increased production of bactericide, virucide and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and specific adhesion to epithelial cells. These are based on the role of healthy vaginal microbiota in maintaining vaginal health as well as are adapted from previous studies that discussed possible mechanisms of FMT in humans and dogs [
71,
72].
Similar to the mechanism of FMT in CDI treatment where the introduction of non-toxigenic
Clostridium difficile strains can lower the recurrence of CDI in subjects [
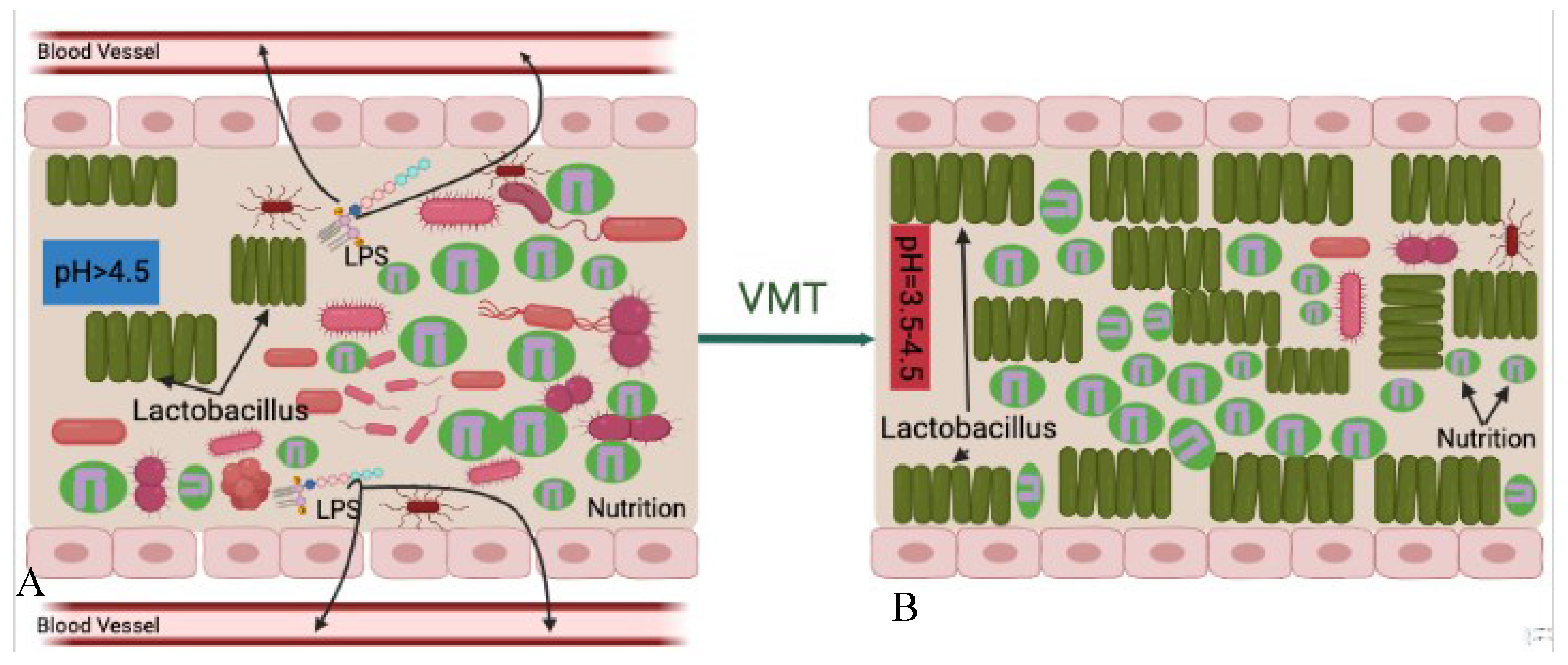
73], competition for nutrition is the first possible mechanism of VMT treatment (
Figure 4). Its main idea is that survival is the first priority of any living organism, microbiomes-healthy or pathogenic-are no exception, which requires absorbing nutrition. Under normal circumstances, although pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms exist in the vaginal cavity, compared to the healthy vaginal microbiota they are small in numbers. Therefore, the harmful microbes cannot overcome nutritional competition between the healthy vaginal microbiota. As a result, pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms are not able to overgrow or lead to disease reactions.
However, when the vaginal microbiota is disrupted, the vagina creates a suitable microenvironment for surviving and proliferation of pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms. This kind of disruption further leads to decrease of relative abundance of healthy vaginal microbiota that lose advantages for nutritional competition. After the disease-leading microorganisms became the predominant species in the vagina, they absorb most of the nutrition, grow and cause disease.
There are some situations when vaginal microbiota donor strains may compete for the same available nutrition in the vaginal cavity more successfully than the recipient's pathogenic strains. Transferring healthy vaginal microbiota that predominated by Lactobacillus spp from a healthy donor increases the relative abundance of the healthy microbial community in the vaginal cavity. The increased overall number of healthy microbiota after VMT procedure gives the advantage of competing nutrition between harmful microorganisms. In this situation, the healthy vaginal donor strains may compete for the same nutrition that is available in the vaginal cavity more successfully than the recipient`s pathogenic strains. This leads to a decrease in relative abundance of pathogenic agents to a level at which they no longer are able to cause disease reactions. This also indicates healthy Lactobacillus spp. offered by VMT can prevent harmful microorganisms from absorbing nutrition. However, this is a slow process and repeated treatments may be needed for successful outcomes.
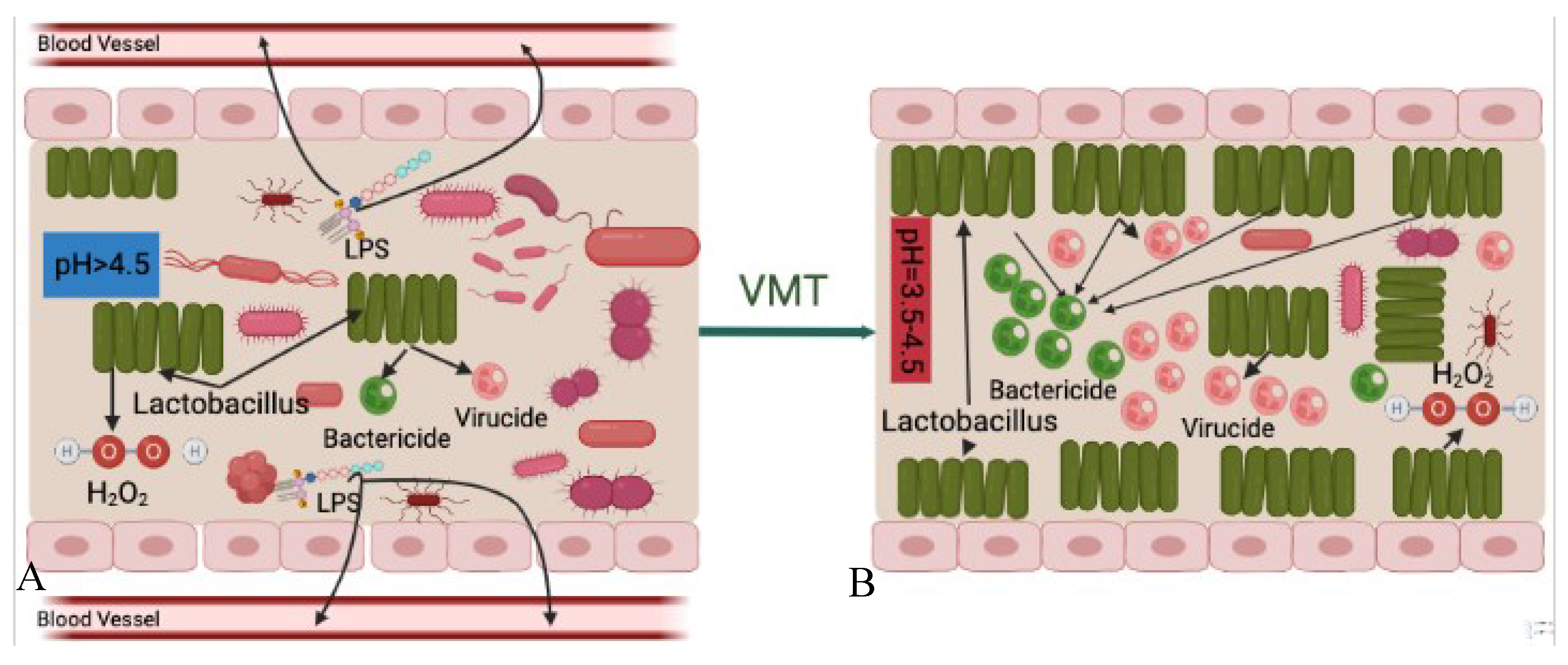
Another possible mechanism of VMT is increased bactericidal and virucidal products. As previously stated [
74], it is hypothesized that the predominated vaginal microbiota,
Lactobacillus spp., plays an important protective role in the vagina by producing bactericides and virucides, including lactic acid and bacteriocins, which prevent the overgrowth of pathogens and other opportunistic microorganisms. In addition, a previous study also suggested that hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) produced by
lactobacilli plays a secondary role in the vaginal microbiota [
75].
Under normal situations, the volume of bactericidal, virucidal and H2O2 compounds produced by Lactobacillus spp. are enough to inhabit invaded pathogens from proliferation and causing diseases. However, after the vaginal microbiota is disrupted, Lactobacillus spp. become less abundant which consequently result in decreasing production of such disease-inhabiting agents. Decreased volume of these products, the vaginal cavity becomes more susceptible to disease reactions caused by pathogens and opportunistic microorganisms.
After the patient receives vaginal microbiota from a healthy donor, which is rich in
Lactobacillus spp., the relative abundance of
Lactobacilli in the vaginal cavity increases, followed by increasing production of bactericides and virucides, and H2O2 which consequently inhabit and/or slow down colonization and proliferation of harmful microorganisms (
Figure 5).
Lactobacillus spp. can inhibit the attachment and colonization of pathogenic agents by producing compounds that directly kill or inhibit pathogens, creating a microbial barrier on the epithelium, and stimulating host defense mechanisms. Additionally, several in vitro studies have shown that
Lactobacillus spp. can prevent the attachment of pathogens on the surface of epithelial cells, including
E.coli,
Gradnerella vaginalis,
Klebsiella pneumonia,
Pseudomonas aeruginosa,
Staphylococcus aureus,
group B streptococci, and
Trichomonas vaginalis [
76,
77,
78,
79,
80](
Figure 6).
All of these three mechanisms are closely related to the Lactobacillus species community in the vagina and its pH level. The pH is a very important parameter for bacterial survival. Various niches located in different parts of the human body have different pH features which create ideal living environments for the resident bacterial communities. The presence of lactic acid in the vagina helps maintain its acidic environment with a pH level of around 3.5-4.5, which is crucial for the health and balance of the vaginal microbiota.
The vaginal cavity, being directly connected to the external environment, is highly susceptible to the invasion of pathogenic bacteria. However, the presence of
Lactobacillus spp. that produce lactic acid helps to maintain a low and acidic vaginal pH of around 3.5-4.5, creating a protective environment for the mucosa that limits the growth of pathogenic microorganisms, including uropathogenic
E.coli,
Neisseria gonorrhoeae, and
Chlamydia trachomatis [
28,
81,
82,
83,
84,
85].
A disrupted vaginal microbiota can lead to an increase in vaginal pH, making the environment more susceptible to diseases. For example, Brotman and colleagues have shown that a higher vaginal pH of more than 4.6 is highly associated with increased risk of trichomonal, gonococcal, and chlamydial infections, as opposed to a lower pH of less than 4.0 [
86].
In conclusion, a healthy vaginal microenvironment characterized as rich in Lactobacillus spp. and low at pH, which collectively create a protective barrier against pathogen invasion is of utmost importance for maintaining female reproductive health. Therefore, transferring healthy vaginal microbiota from a donor, which restores the healthy vaginal cavity that is predominated by Lactobacillus spp. and lower pH that negatively impact survival of pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms, and also reconstructs the protective barrier and prevents harmful bacteria from continuing invasion.
However, it should be noted that although we explored the possible mechanisms of VMT treatment individually aimed to better understand, the therapeutic effect of VMT is a result of combined effort that includes increased competition for nutrition, decreased pH level, and increased production of bactericides and virucides at the same time.
6. Risks and Limitations
The main risk of VMT is the possible transmission of pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms. Indeed, considering such risks, safety issues are the main limitations in VMT therapy in clinics. Therefore, careful screening of the donors for VMT is utmost important to avoid exposure to infectious agents. For example, as previously mentioned, pathogenic bacteria can be transmitted by VMT procedure and cause disease pathogenesis [
19].
Presently, the donor selection process is focused on safety by excluding as many risky elements as possible to obtain relatively ‘healthy’ vaginal microbiota, which is characterized as high abundance of Lactobacillus spp.
In addition, the healthy vaginal microbiota is also composed of fungi and viruses [
87,
88,
89,
90], such as
Candida albicans, double stranded DNA viruses, undefined viruses, and a small proportion of single stranded DNA viruses. Without doubt they have an impact on VMT efficacy. However, current research is mainly focused on bacteria, more studies are needed to explore the roles of fungi and viruses on the efficacy of VMT treatment. At the same time, other bacterial species that are in low abundance may play a certain role in maintaining vaginal health. However, in current studies they are mostly ignored. In the future studies, the role of such microorganisms could be deeper studied, it is also a way of increasing safety and efficacy of VMT treatment.
There is no guarantee that VMT can treat all vaginal disorders. For example, present VMT treatment is limited to bacterial vaginosis [
18]. It is unknown if VMT is effective for treating viral vaginosis. Therefore, the medical specialists should offer detailed explanation of risks and limitations that may involve VMT treatment before the procedure.
7. Future Perspectives
In the future, VMT will be more widely used for treating diseases such as bacterial vaginosis as more studies are being conducted to explore its efficacy and safety. In addition, other issues such as HIV, HPV, and sexually transmitted diseases are reported to be able to alter vaginal microbiota communities [
34,
35]. Based on these, restoring the vaginal microbiota in means of VMT may prevent such diseases from further damaging to reproductive health.
Similar to FMT treatment, selecting the most suitable donor is the most important part of VMT therapy. Except for regular examinations, such as blood examination and possibility of various virus infractions, we are now able to choose the donor one step further based on the vaginal microbiota content with the help of 16S rRNA sequencing technology. The most suitable donor, in theory, not only healthy, but also has the most abundant Lactobacillus spp. which plays a crucial role in maintaining vaginal health. In this way the VMT treatment would be safer and more efficient.
In FMT, studies explored the efficacy and safety of readily available and capsulized fecal materials in treating CDI and observed promising results [
91]. The most important parameter in storing bacteria is temperature. For example, Burz and colleagues found that fecal microbiota can be stored at 4 °C for 24h and don't lose their viability [
92]. However, -80°C is more suitable for long-term (over 3 months) stool storage. The bacterial viability may diminish dramatically especially in gram negative bacterial communities when stored at room temperatures for more than 8h. Therefore, the storage conditions for preserving the most viable bacteria are an important part of microbiota transplant therapy.
In the future, VMT may become a widely available treatment option similar to FMT, which may be followed by increased demand that requires more easily accessible vaginal microbiota. Therefore, preparing a vaginal microbiota bank similar to stool banks may be an innovative approach for future studies. However, as stated, the optimal temperature that can preserve the most viability of Lactobacillus spp. should be prioritized for building vaginal microbiota banks.
In clinics, when treating CDI with FMT, doctors use laxatives to clear the intestine microbiota, this is not only to increase visual in endoscopic delivery, but also increases the colonization of newly transplanted fecal microbiota to the gastrointestinal tract. Other studies also showed that antibiotic administration prior to CDI treatments could significantly increase FMT efficacy. Although it is impossible to use laxatives for getting rid of the vaginal microbiota, it may enhance the efficiency of VMT if a vaginal douche is applied before transplanting microbiota. However, studies are needed before such methods are adapted to clinical applications.
At the same time, studies also found that there are distinct microbial communities between healthy and women with reproductive problems. For example, a recent study involving 31 female participants revealed that they have different vaginal microbiota compositions [
93]. Another recent study also indicated that the composition of vaginal microbiota but not of seminal microbiota is associated with successful intrauterine insemination in couples with idiopathic infertility, where the domination of
lactobacillus crispatus was strongly associated with successful pregnancy [
94]. Although we cannot overlook the fact that these women may have other issues that induce their infertility, the distinct differences between vaginal microbiota communities may offer theoretical bases for exploring whether transferring vaginal microbiota from a healthy fertile donor leads to reconstruction of vaginal microbiota in an infertile woman and further leads to increased pregnancy rate. But, again, such a hypothesis needs a series of studies to validate its efficiency and safety before recommending it as a therapeutic option.
In addition, a recent study found that vaginal samples with positive in vitro fertilization (IVF) clinical outcome were significantly colonized by
Lactobacillus gasseri, and less colonized by
Bacteroides and
Lactobacillus iners [
95]. This result may suggest the possibility of increasing the pregnancy rate by replenishing
Lactobacillus in the vaginal cavity before IVF treatment by means of VMT.
Regulations and oversights, in FMT treatment, regarding donor selection, stool storage, recipient preparation, and delivery methods are becoming more sophisticated and generally accepted [
71]. With more studies conducted, future VMT studies and clinical applications would be more regulated in donor selection, bacterial storage and delivery methods.
8. Conclusion
After years of successful experience of FMT therapy, in recent years VMT is becoming an available option for treatment for female reproductive issues, such as vaginosis. However, VMT is still in its infancy. Based on our understanding of the therapeutic potentiality of FMT, we can assume that the application of VMT may become a regular choice for treating and preventing many more female reproductive tract disorders. At the same time, due to the role of vaginal microbiota in successful pregnancy, VMT may exert a potential role in increasing reproductive rate. Therefore, VMT may become a popular choice of treatment in female patients with various issues.
The success of vaginal microbiota transplantation (VMT) is largely dependent on choosing an appropriate donor. An ideal vaginal microbiota composition is crucial in regulating disrupted microbiota in the recipient. Advancements in technology that enable the identification of suitable donors based on bacterial communities, combined with increasing research on the safety and efficacy of VMT, as well as established regulations and guidelines, can make the VMT process safer.
To make VMT more widely used in clinical therapy, it is important to have case-controlled studies as guidelines and regulatory approvals to ensure safety. Additionally, doctors and patients need clear and simple explanations on how VMT works. This paper provides information on the mechanisms involved in VMT treatment and future prospects for improving its clinical usage.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: M.T; Supervision: N.Z, Y.F; Visualization: M.T; Writing - original draft: M.T; Writing-review & editing: X.H and S.L.
Funding
No external funding available in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
None of the authors have a financial interest in any of the products, devices, or Materials mentioned in this manuscript. The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
References
- Marchesi, J.R.; Ravel, J. The Vocabulary of Microbiome Research: A Proposal. Microbiome 2015, 3, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Human Microbiome Project Consortium Structure, Function and Diversity of the Healthy Human Microbiome. Nature 2012, 486, 207–214. [CrossRef]
- Bassis, C.M.; Tang, A.L.; Young, V.B.; Pynnonen, M.A. The Nasal Cavity Microbiota of Healthy Adults. Microbiome 2014, 2, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arweiler, N.B.; Netuschil, L. The Oral Microbiota. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 902, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommariva, M.; Le Noci, V.; Bianchi, F.; Camelliti, S.; Balsari, A.; Tagliabue, E.; Sfondrini, L. The Lung Microbiota: Role in Maintaining Pulmonary Immune Homeostasis and Its Implications in Cancer Development and Therapy. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 2739–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egert, M.; Simmering, R. The Microbiota of the Human Skin. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 902, 61–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieterich, W.; Schink, M.; Zopf, Y. Microbiota in the Gastrointestinal Tract. Med Sci (Basel) 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, E.R.; Wolfe, A.J.; Brubaker, L. Female Urinary Microbiota. Curr. Opin. Urol. 2017, 27, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, J.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Huang, W.; Zhong, J.; Zeng, J. Corrigendum: Profiling the Urinary Microbiota in Male Patients With Bladder Cancer in China. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, I.; Simon, C. Deciphering the Effect of Reproductive Tract Microbiota on Human Reproduction. Reprod. Med. Biol. 2019, 18, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowden, G.H.W. Actinomyces, Propionibacterium Propionicus, and Streptomyces. Medical Microbiology. 4th edition 1996.
- Wirusanti, N.I.; Baldridge, M.T.; Harris, V.C. Microbiota Regulation of Viral Infections through Interferon Signaling. Trends Microbiol. 2022, 30, 778–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicco, C.; Paule, A.; Konturek, P.; Edeas, M. From Donor to Patient: Collection, Preparation and Cryopreservation of Fecal Samples for Fecal Microbiota Transplantation. Diseases 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baunwall, S.M.D.; Lee, M.M.; Eriksen, M.K.; Mullish, B.H.; Marchesi, J.R.; Dahlerup, J.F.; Hvas, C.L. Faecal Microbiota Transplantation for Recurrent Clostridioides Difficile Infection: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. EClinicalMedicine 2020, 29–30, 100642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, S.; Li, J.; Zhao, K.; Li, X.; Wen, X.; Li, X.-A. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation for Ulcerative Colitis: A Prospective Clinical Study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2019, 19, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinna Meyyappan, A.; Forth, E.; Wallace, C.J.K.; Milev, R. Effect of Fecal Microbiota Transplant on Symptoms of Psychiatric Disorders: A Systematic Review. BMC Psychiatry 2020, 20, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLong, K.; Zulfiqar, F.; Hoffmann, D.E.; Tarzian, A.J.; Ensign, L.M. Vaginal Microbiota Transplantation: The Next Frontier. J. Law Med. Ethics 2019, 47, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lev-Sagie, A.; Goldman-Wohl, D.; Cohen, Y.; Dori-Bachash, M.; Leshem, A.; Mor, U.; Strahilevitz, J.; Moses, A.E.; Shapiro, H.; Yagel, S.; et al. Vaginal Microbiome Transplantation in Women with Intractable Bacterial Vaginosis. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1500–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, H.L.; Dukes, C.D. Haemophilus Vaginalis Vaginitis: A Newly Defined Specific Infection Previously Classified Non-Specific Vaginitis. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1955, 69, 962–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lu, Y.; Chen, T.; Li, R. The Female Vaginal Microbiome in Health and Bacterial Vaginosis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 631972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punzón-Jiménez, P.; Labarta, E. The Impact of the Female Genital Tract Microbiome in Women Health and Reproduction: A Review. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2021, 38, 2519–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chadchan, S.B.; Singh, V.; Kommagani, R. Female Reproductive Dysfunctions and the Gut Microbiota. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2022, 69, R81–R94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaranta, G.; Sanguinetti, M.; Masucci, L. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation: A Potential Tool for Treatment of Human Female Reproductive Tract Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anahtar, M.N.; Gootenberg, D.B.; Mitchell, C.M.; Kwon, D.S. Cervicovaginal Microbiota and Reproductive Health: The Virtue of Simplicity. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravel, J.; Gajer, P.; Abdo, Z.; Schneider, G.M.; Koenig, S.S.K.; McCulle, S.L.; Karlebach, S.; Gorle, R.; Russell, J.; Tacket, C.O.; et al. Vaginal Microbiome of Reproductive-Age Women. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2011, 108 Suppl 1, 4680–4687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Wijgert, J.H.H.M.; Borgdorff, H.; Verhelst, R.; Crucitti, T.; Francis, S.; Verstraelen, H.; Jespers, V. The Vaginal Microbiota: What Have We Learned after a Decade of Molecular Characterization? PLoS One 2014, 9, e105998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Song, X.; Wei, W.; Zhong, H.; Dai, J.; Lan, Z.; Li, F.; Yu, X.; Feng, Q.; Wang, Z.; et al. The Microbiota Continuum along the Female Reproductive Tract and Its Relation to Uterine-Related Diseases. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, J.A.; Lievens, E.; Hummelen, R.; van der Westen, R.; Reid, G.; Petrova, M.I. Women and Their Microbes: The Unexpected Friendship. Trends Microbiol. 2018, 26, 16–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyongo, J.K.; Jespers, V.; Goovaerts, O.; Michiels, J.; Menten, J.; Fichorova, R.N.; Crucitti, T.; Vanham, G.; Ariën, K.K. Searching for Lower Female Genital Tract Soluble and Cellular Biomarkers: Defining Levels and Predictors in a Cohort of Healthy Caucasian Women. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaitchouk, N.; Andersch, B.; Falsen, E.; Strömbeck, L.; Mattsby-Baltzer, I. The Lower Genital Tract Microbiota in Relation to Cytokine-, SLPI- and Endotoxin Levels: Application of Checkerboard DNA-DNA Hybridization (CDH). APMIS 2008, 116, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balkus, J.; Agnew, K.; Lawler, R.; Mitchell, C.; Hitti, J. Effects of Pregnancy and Bacterial Vaginosis on Proinflammatory Cytokine and Secretory Leukocyte Protease Inhibitor Concentrations in Vaginal Secretions. Journal of Pregnancy 2010, 2010, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dezzutti, C.S.; Hendrix, C.W.; Marrazzo, J.M.; Pan, Z.; Wang, L.; Louissaint, N.; Kalyoussef, S.; Torres, N.M.; Hladik, F.; Parikh, U.; et al. Performance of Swabs, Lavage, and Diluents to Quantify Biomarkers of Female Genital Tract Soluble Mucosal Mediators. PLoS One 2011, 6, e23136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doerflinger, S.Y.; Throop, A.L.; Herbst-Kralovetz, M.M. Bacteria in the Vaginal Microbiome Alter the Innate Immune Response and Barrier Properties of the Human Vaginal Epithelia in a Species-Specific Manner. The Journal of Infectious Diseases 2014, 209, 1989–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anahtar, M.N.; Byrne, E.H.; Doherty, K.E.; Bowman, B.A.; Yamamoto, H.S.; Soumillon, M.; Padavattan, N.; Ismail, N.; Moodley, A.; Sabatini, M.E.; et al. Cervicovaginal Bacteria Are a Major Modulator of Host Inflammatory Responses in the Female Genital Tract. Immunity 2015, 42, 965–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donders, G.G.; Bosmans, E.; Dekeersmaecker, A.; Vereecken, A.; Van Bulck, B.; Spitz, B. Pathogenesis of Abnormal Vaginal Bacterial Flora. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2000, 182, 872–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.; Stapleton, A.E.; Hooton, T.M.; Roberts, P.L.; Fennell, C.L.; Stamm, W.E. Inverse Association of H2O2-Producing Lactobacilli and Vaginal Escherichia Coli Colonization in Women with Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections. J. Infect. Dis. 1998, 178, 446–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pybus, V.; Onderdonk, A.B. Microbial Interactions in the Vaginal Ecosystem, with Emphasis on the Pathogenesis of Bacterial Vaginosis. Microbes Infect. 1999, 1, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherpes, T.L.; Meyn, L.A.; Krohn, M.A.; Lurie, J.G.; Hillier, S.L. Association between Acquisition of Herpes Simplex Virus Type 2 in Women and Bacterial Vaginosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2003, 37, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, H.L.; Richardson, B.A.; Nyange, P.M.; Lavreys, L.; Hillier, S.L.; Chohan, B.; Mandaliya, K.; Ndinya-Achola, J.O.; Bwayo, J.; Kreiss, J. Vaginal Lactobacilli, Microbial Flora, and Risk of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 and Sexually Transmitted Disease Acquisition. J. Infect. Dis. 1999, 180, 1863–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobel, J.D. Is There a Protective Role for Vaginal Flora? Current Infectious Disease Reports 1999, 1, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watts, D.H.; Fazzari, M.; Minkoff, H.; Hillier, S.L.; Sha, B.; Glesby, M.; Levine, A.M.; Burk, R.; Palefsky, J.M.; Moxley, M.; et al. Effects of Bacterial Vaginosis and Other Genital Infections on the Natural History of Human Papillomavirus Infection in HIV-1-Infected and High-Risk HIV-1-Uninfected Women. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 191, 1129–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiesenfeld, H.C.; Hillier, S.L.; Krohn, M.A.; Landers, D.V.; Sweet, R.L. Bacterial Vaginosis Is a Strong Predictor of Neisseria Gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia Trachomatis Infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2003, 36, 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.K.; Hida, K.; Shukair, S.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Figueiredo, A.; Cone, R.; Hope, T.J.; Hanes, J. Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Is Trapped by Acidic but Not by Neutralized Human Cervicovaginal Mucus. Journal of Virology 2009, 83, 11196–11200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, T.E.; Hoover, D.R.; Dallabetta, G.A.; Kumwenda, N.I.; Mtimavalye, L.A.; Yang, L.P.; Liomba, G.N.; Broadhead, R.L.; Chiphangwi, J.D.; Miotti, P.G. Bacterial Vaginosis and Disturbances of Vaginal Flora: Association with Increased Acquisition of HIV. AIDS 1998, 12, 1699–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryckman, K.K.; Simhan, H.N.; Krohn, M.A.; Williams, S.M. Predicting Risk of Bacterial Vaginosis: The Role of Race, Smoking and Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone-Related Genes. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2009, 15, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobel, J.D. Bacterial Vaginosis. Annu. Rev. Med. 2000, 51, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brotman, R.M. Vaginal Microbiome and Sexually Transmitted Infections: An Epidemiologic Perspective. J. Clin. Invest. 2011, 121, 4610–4617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.B.; Ravel, J. The Vaginal Microbiota, Host Defence and Reproductive Physiology. J. Physiol. 2017, 595, 451–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boskey, E.R.; Cone, R.A.; Whaley, K.J.; Moench, T.R. Origins of Vaginal Acidity: High d/l Lactate Ratio Is Consistent with Bacteria Being the Primary Source. Human Reproduction 2001, 16, 1809–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mossop, H.; Linhares, I.M.; Bongiovanni, A.M.; Ledger, W.J.; Witkin, S.S. Influence of Lactic Acid on Endogenous and Viral RNA-Induced Immune Mediator Production by Vaginal Epithelial Cells. Obstet. Gynecol. 2011, 118, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartner, L.P.; Hiatt, J.L.; Samperio, J.O. Texto Atlas de Histología; McGraw-Hill Interamericana, 2008.
- Amabebe, E.; Anumba, D.O.C. The Vaginal Microenvironment: The Physiologic Role of Lactobacilli. Frontiers in Medicine 2018, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrientos-Durán, A.; Fuentes-López, A.; de Salazar, A.; Plaza-Díaz, J.; García, F. Reviewing the Composition of Vaginal Microbiota: Inclusion of Nutrition and Probiotic Factors in the Maintenance of Eubiosis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dei, M.; Di Maggio, F.; Di Paolo, G.; Bruni, V. Vulvovaginitis in Childhood. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2010, 24, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranđelović, G.; Mladenović, V.; Ristić, L.; Otašević, S.; Branković, S.; Mladenović-Antić, S.; Bogdanović, M.; Bogdanović, D. Microbiological Aspects of Vulvovaginitis in Prepubertal Girls. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2012, 171, 1203–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Zhou, X.; Williams, C.J.; Hochwalt, A.; Forney, L.J. Bacterial Populations in the Vaginas of Healthy Adolescent Women. Journal of Pediatric and Adolescent Gynecology 2009, 22, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Baghdadi, O.; Ewies, A.A.A. Topical Estrogen Therapy in the Management of Postmenopausal Vaginal Atrophy: An up-to-Date Overview. Climacteric 2009, 12, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrova, M.I.; Lievens, E.; Malik, S.; Imholz, N.; Lebeer, S. Lactobacillus Species as Biomarkers and Agents That Can Promote Various Aspects of Vaginal Health. Front. Physiol. 2015, 6, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackwell, A.; Phillips, I.; Fox, A.; Barlow, D. ANAEROBIC VAGINOSIS (NON-SPECIFIC VAGINITIS): CLINICAL, MICROBIOLOGICAL, AND THERAPEUTIC FINDINGS. The Lancet 1983, 322, 1379–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donders, G.G.G.; Bellen, G.; Grinceviciene, S.; Ruban, K.; Vieira-Baptista, P. Aerobic Vaginitis: No Longer a Stranger. Res. Microbiol. 2017, 168, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, I.; Blaser, M.J. The Human Microbiome: At the Interface of Health and Disease. Nature Reviews Genetics 2012, 13, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, G.B. The Microbiology of Bacterial Vaginosis. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1993, 169, 450–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, A.C.; Chaban, B.; Bocking, A.; Rocco, M.; Yang, S.; Hill, J.E.; Money, D.M. VOGUE Research Group The Vaginal Microbiome of Pregnant Women Is Less Rich and Diverse, with Lower Prevalence of Mollicutes, Compared to Non-Pregnant Women. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, R.; Hassan, S.S.; Gajer, P.; Tarca, A.L.; Fadrosh, D.W.; Nikita, L.; Galuppi, M.; Lamont, R.F.; Chaemsaithong, P.; Miranda, J.; et al. Correction: The Composition and Stability of the Vaginal Microbiota of Normal Pregnant Women Is Different from That of Non-Pregnant Women. Microbiome 2014, 2, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuriel-Ohayon, M.; Neuman, H.; Koren, O. Microbial Changes during Pregnancy, Birth, and Infancy. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Hansmann, M.A.; Davis, C.C.; Suzuki, H.; Brown, C.J.; Schütte, U.; Pierson, J.D.; Forney, L.J. The Vaginal Bacterial Communities of Japanese Women Resemble Those of Women in Other Racial Groups. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 58, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brotman, R.M.; He, X.; Gajer, P.; Fadrosh, D.; Sharma, E.; Mongodin, E.F.; Ravel, J.; Glover, E.D.; Rath, J.M. Association between Cigarette Smoking and the Vaginal Microbiota: A Pilot Study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, A.; da Silva, A.P.; Medeiros, R.; Bicho, M.; Bicho, M.C. Microenvironment in Vagina as a Key-Player on Cervical Cancer: Interaction of Polymorphic Genetic Variants and Vaginal Microbiome as Co-Factors. Cervical Cancer - Screening, Treatment and Prevention - Universal Protocols for Ultimate Control 2018.
- Di Paola, M.; Sani, C.; Clemente, A.M.; Iossa, A.; Perissi, E.; Castronovo, G.; Tanturli, M.; Rivero, D.; Cozzolino, F.; Cavalieri, D.; et al. Characterization of Cervico-Vaginal Microbiota in Women Developing Persistent High-Risk Human Papillomavirus Infection. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balle, C.; Lennard, K.; Dabee, S.; Barnabas, S.L.; Jaumdally, S.Z.; Gasper, M.A.; Maseko, V.; Mbulawa, Z.Z.A.; Williamson, A.-L.; Bekker, L.-G.; et al. Endocervical and Vaginal Microbiota in South African Adolescents with Asymptomatic Chlamydia Trachomatis Infection. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.C.; Kamm, M.A.; Yeoh, Y.K.; Chan, P.K.S.; Zuo, T.; Tang, W.; Sood, A.; Andoh, A.; Ohmiya, N.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Scientific Frontiers in Faecal Microbiota Transplantation: Joint Document of Asia-Pacific Association of Gastroenterology (APAGE) and Asia-Pacific Society for Digestive Endoscopy (APSDE). Gut 2020, 69, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuniyazi, M.; Hu, X.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, N. Canine Fecal Microbiota Transplantation: Current Application and Possible Mechanisms. Veterinary Sciences 2022, 9, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullish, B.H.; Quraishi, M.N.; Segal, J.P.; McCune, V.L.; Baxter, M.; Marsden, G.L.; Moore, D.; Colville, A.; Bhala, N.; Iqbal, T.H.; et al. The Use of Faecal Microbiota Transplant as Treatment for Recurrent or Refractory Clostridium Difficile Infection and Other Potential Indications: Joint British Society of Gastroenterology (BSG) and Healthcare Infection Society (HIS) Guidelines. Journal of Hospital Infection 2018, 100, S1–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boskey, E.R.; Telsch, K.M.; Whaley, K.J.; Moench, T.R.; Cone, R.A. Acid Production by Vaginal Flora in Vitro Is Consistent with the Rate and Extent of Vaginal Acidification. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 5170–5175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajawat, A.S.; Shrivastava, V.; Shrivastava, A.; Singh, V. In Vitro Evaluation of Inhibitory Activity of Probiotic Lactobacilli against Candida Species Isolated from the Vaginal Flora of Immunocompro-Mised Patients. South Asian Journal of Experimental Biology 2014, 3, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osset, J.; Bartolomé, R.M.; García, E.; Andreu, A. Assessment of the Capacity of Lactobacillus to Inhibit the Growth of Uropathogens and Block Their Adhesion to Vaginal Epithelial Cells. J. Infect. Dis. 2001, 183, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastromarino, P.; Brigidi, P.; Macchia, S.; Maggi, L.; Pirovano, F.; Trinchieri, V.; Conte, U.; Matteuzzi, D. Characterization and Selection of Vaginal Lactobacillus Strains for the Preparation of Vaginal Tablets. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2002, 93, 884–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zárate, G.; Nader-Macias, M.E. Influence of Probiotic Vaginal Lactobacilli on in Vitro Adhesion of Urogenital Pathogens to Vaginal Epithelial Cells. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 43, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phukan, N.; Parsamand, T.; Brooks, A.E.S.; Nguyen, T.N.M.; Simoes-Barbosa, A. The Adherence of Trichomonas Vaginalis to Host Ectocervical Cells Is Influenced by Lactobacilli. Sex. Transm. Infect. 2013, 89, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karczewski, J.; Troost, F.J.; Konings, I.; Dekker, J.; Kleerebezem, M.; Brummer, R.-J.M.; Wells, J.M. Regulation of Human Epithelial Tight Junction Proteins by Lactobacillus Plantarum in Vivo and Protective Effects on the Epithelial Barrier. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2010, 298, G851-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Luna, Y.; Yu, P.; Fan, H. Lactobacilli Inactivate Chlamydia Trachomatis through Lactic Acid but Not H2O2. PLoS One 2014, 9, e107758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juárez Tomás, M.S.; Ocaña, V.S.; Wiese, B.; Nader-Macías, M.E. Growth and Lactic Acid Production by Vaginal Lactobacillus Acidophilus CRL 1259, and Inhibition of Uropathogenic Escherichia Coli. J. Med. Microbiol. 2003, 52, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graver, M.A.; Wade, J.J. The Role of Acidification in the Inhibition of Neisseria Gonorrhoeae by Vaginal Lactobacilli during Anaerobic Growth. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2011, 10, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukair, S.A.; Allen, S.A.; Cianci, G.C.; Stieh, D.J.; Anderson, M.R.; Baig, S.M.; Gioia, C.J.; Spongberg, E.J.; Kauffman, S.M.; McRaven, M.D.; et al. Human Cervicovaginal Mucus Contains an Activity That Hinders HIV-1 Movement. Mucosal Immunol. 2013, 6, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hanlon, D.E.; Moench, T.R.; Cone, R.A. Vaginal PH and Microbicidal Lactic Acid When Lactobacilli Dominate the Microbiota. PLoS One 2013, 8, e80074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyva-Gómez, G.; Prado-Audelo, M.L.D.; Ortega-Peña, S.; Mendoza-Muñoz, N.; Urbán-Morlán, Z.; González-Torres, M.; González-Del Carmen, M.; Figueroa-González, G.; Reyes-Hernández, O.D.; Cortés, H. Modifications in Vaginal Microbiota and Their Influence on Drug Release: Challenges and Opportunities. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekaboruah, E.; Suryavanshi, M.V.; Chettri, D.; Verma, A.K. Human Microbiome: An Academic Update on Human Body Site Specific Surveillance and Its Possible Role. Arch. Microbiol. 2020, 202, 2147–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursell, L.K.; Metcalf, J.L.; Parfrey, L.W.; Knight, R. Defining the Human Microbiome. Nutr. Rev. 2012, 70 Suppl 1, S38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtoranta, L.; Hibberd, A.A.; Yeung, N.; Laitila, A.; Maukonen, J.; Ouwehand, A.C. Characterization of Vaginal Fungal Communities in Healthy Women and Women with Bacterial Vaginosis (BV); a Pilot Study. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 161, 105055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsen, R.R.; Haahr, T.; Humaidan, P.; Jensen, J.S.; Kot, W.P.; Castro-Mejia, J.L.; Deng, L.; Leser, T.D.; Nielsen, D.S. Characterization of the Vaginal DNA Virome in Health and Dysbiosis. Viruses 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youngster, I.; Russell, G.H.; Pindar, C.; Ziv-Baran, T.; Sauk, J.; Hohmann, E.L. Oral, Capsulized, Frozen Fecal Microbiota Transplantation for Relapsing Clostridium Difficile Infection. JAMA 2014, 312, 1772–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burz, S.D.; Abraham, A.-L.; Fonseca, F.; David, O.; Chapron, A.; Béguet-Crespel, F.; Cénard, S.; Le Roux, K.; Patrascu, O.; Levenez, F.; et al. A Guide for Ex Vivo Handling and Storage of Stool Samples Intended for Fecal Microbiota Transplantation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.; Patel, N.; Patel, S.; Nathani, N.; Pandit, R.; Patel, M.; Patel, N.; Joshi, C.; Parekh, B. Distinct Gut and Vaginal Microbiota Profile in Women with Recurrent Implantation Failure and Unexplained Infertility.
- Amato, V.; Papaleo, E.; Pasciuta, R.; Viganò, P.; Ferrarese, R.; Clementi, N.; Sanchez, A.M.; Quaranta, L.; Burioni, R.; Ambrosi, A.; et al. Differential Composition of Vaginal Microbiome, but Not of Seminal Microbiome, Is Associated With Successful Intrauterine Insemination in Couples With Idiopathic Infertility: A Prospective Observational Study. Open Forum Infectious Diseases 2020, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okwelogu, S.I.; Ikechebelu, J.I.; Agbakoba, N.R.; Anukam, K.C. Microbiome Compositions From Infertile Couples Seeking In Vitro Fertilization, Using 16S RRNA Gene Sequencing Methods: Any Correlation to Clinical Outcomes? Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).