Submitted:
11 February 2023
Posted:
13 February 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
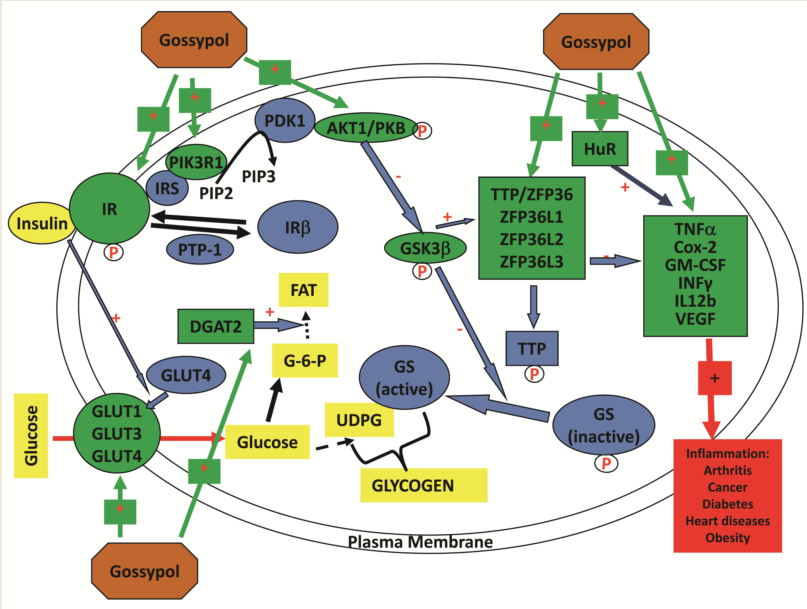
Keywords:
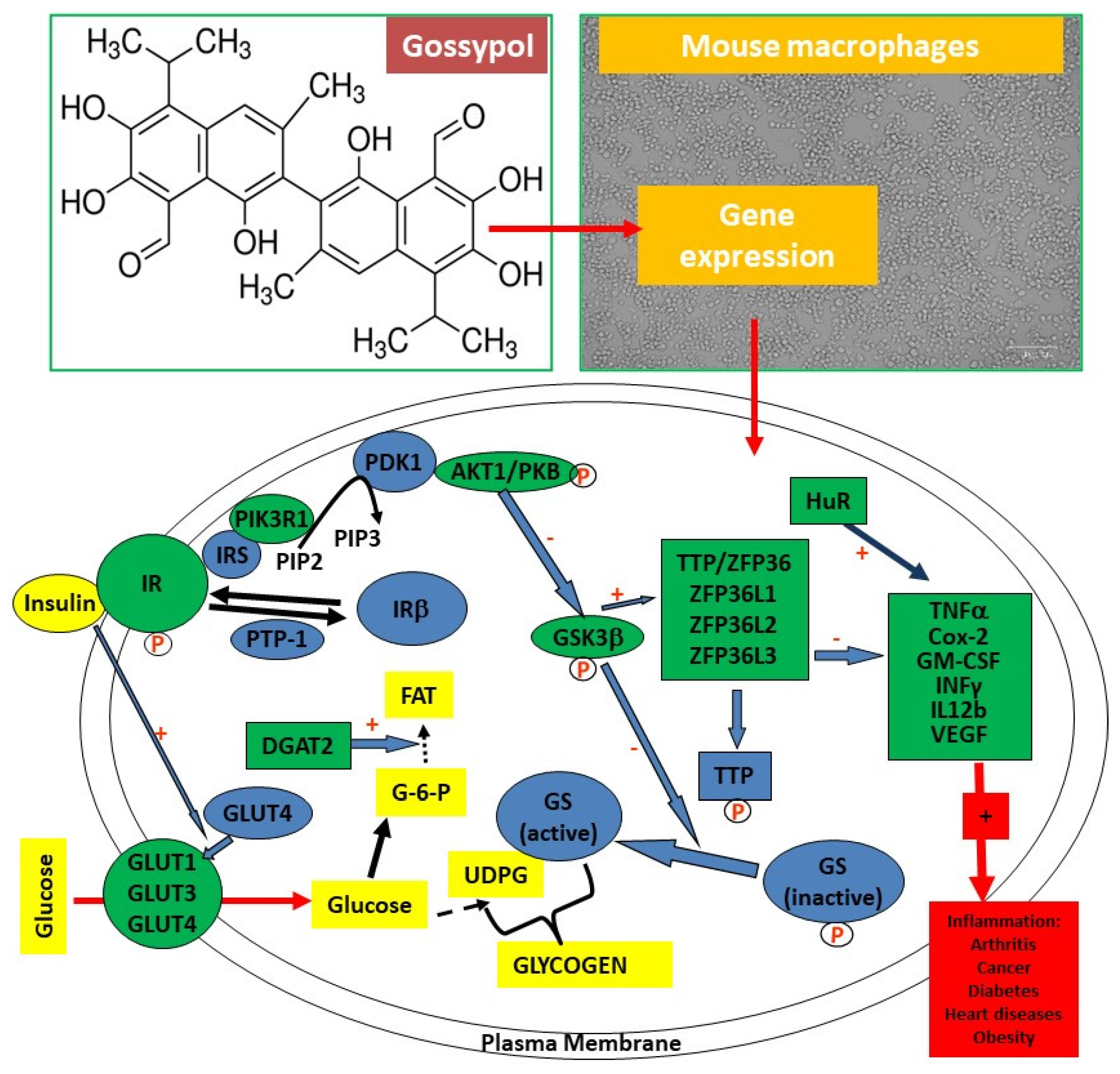
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell line, chemicals and reagents
2.2. Cell culture and treatment
2.3. Cell toxicity assay
2.4. Protein determination
2.5. RNA extraction, cDNA synthesis and real-time qPCR analysis
2.6. Statistics
3. Results
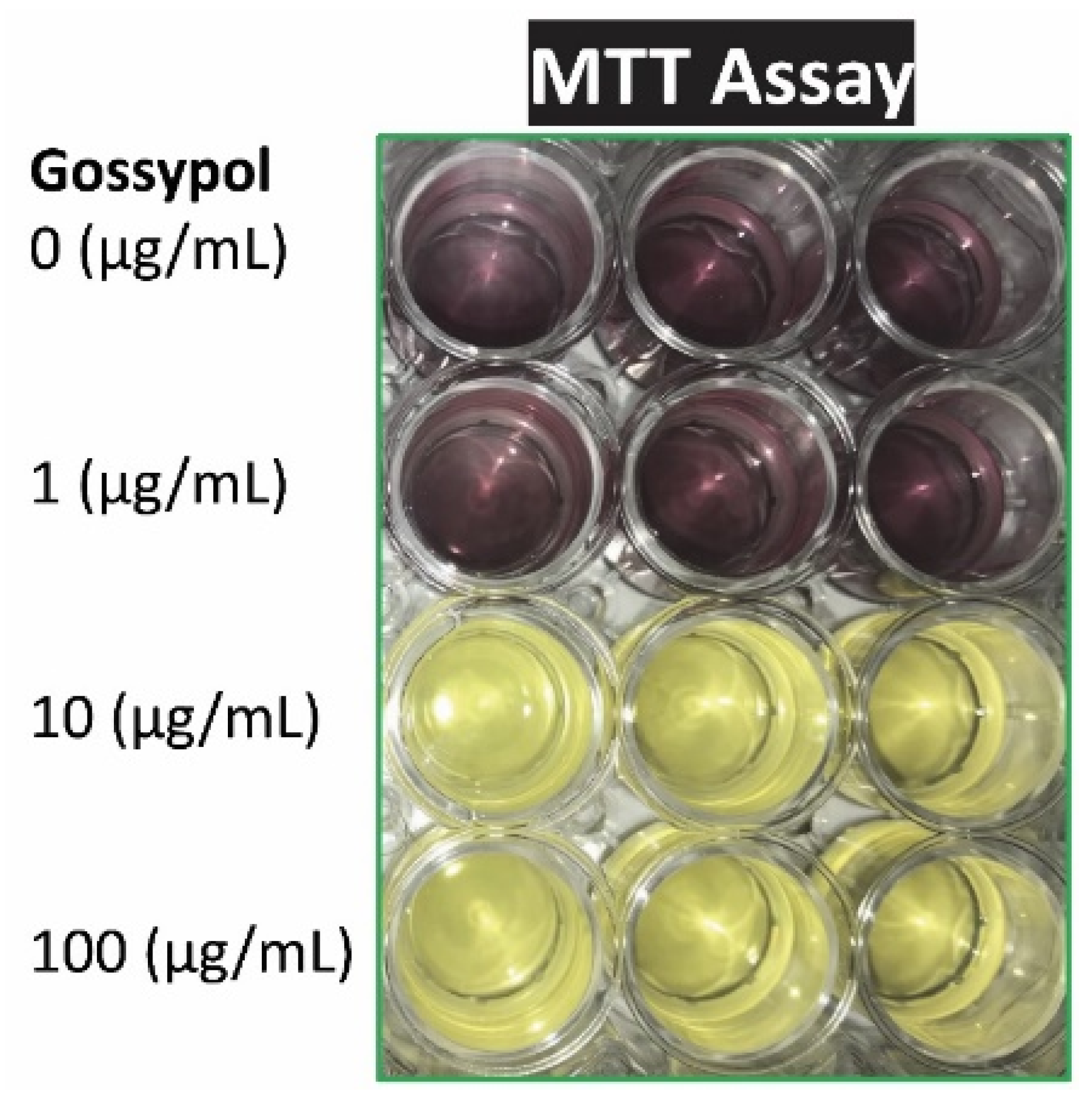
3.1. Gossypol inhibited mouse macrophages growth
3.2. Gossypol reduced soluble protein content in mouse macrophages
3.3. Relative expression levels of selected genes in mouse macrophages
| mRNA | cycle of threshold (CT ± SD) | cycle of threshold (CT) | CTTarget - Ctref (ΔCT) | ΔCTTarget - ΔCTcal (ΔΔCT ) | fold (Ttp =1 ) |
| Rpl32 | 17.82 ± 0.81 | 17.82 | 0.00 | ||
| Ttp/Zfp36/Tis11 | 24.76 ± 1.12 | 24.76 | 6.94 | 0.00 | 1.00 |
| Akt1 | 23.65 ± 1.69 | 23.65 | 5.83 | -1.11 | 2.16 |
| App | 22.51 ± 0.81 | 22.51 | 4.69 | -2.25 | 4.76 |
| Cox2 | 30.15 ± 2.38 | 30.15 | 12.33 | 5.39 | 0.02 |
| Glut1/Slc2a1 | 27.55 ± 1.49 | 27.55 | 9.73 | 2.79 | 0.14 |
| Glut3/Slc2a3 | 26.54 ± 0.75 | 26.54 | 8.72 | 1.78 | 0.29 |
| Glut4/Slc2a4 | 34.68 ± 1.20 | 34.68 | 16.86 | 9.92 | 0.001 |
| Gm-csf | 27.58 ± 2.06 | 27.58 | 9.76 | 2.82 | 0.14 |
| Ifnγ | 27.70 ± 2.42 | 27.70 | 9.88 | 2.94 | 0.13 |
| Il12b | 28.03 ± 1.89 | 28.03 | 10.21 | 3.27 | 0.10 |
| Insr | 26.39 ± 073 | 26.39 | 8.57 | 1.63 | 0.32 |
| Lepr | 28.33 ± 2.11 | 28.33 | 10.51 | 3.57 | 0.08 |
| Pik3r1 | 26.21 ± 0.58 | 26.21 | 8.39 | 1.45 | 0.37 |
| Tnf | 29.19 ± 2.68 | 29.19 | 11.37 | 4.43 | 0.05 |
| Zfp36l1/Tis11b | 26.07 ± 0.35 | 26.07 | 8.25 | 1.31 | 0.40 |
| Zfp36l2/Tis11d | 24.61 ± 1.03 | 24.61 | 6.79 | -0.15 | 1.11 |
| Zfp36l3 | 29.20 ± 1.13 | 29.20 | 11.38 | 4.44 | 0.05 |
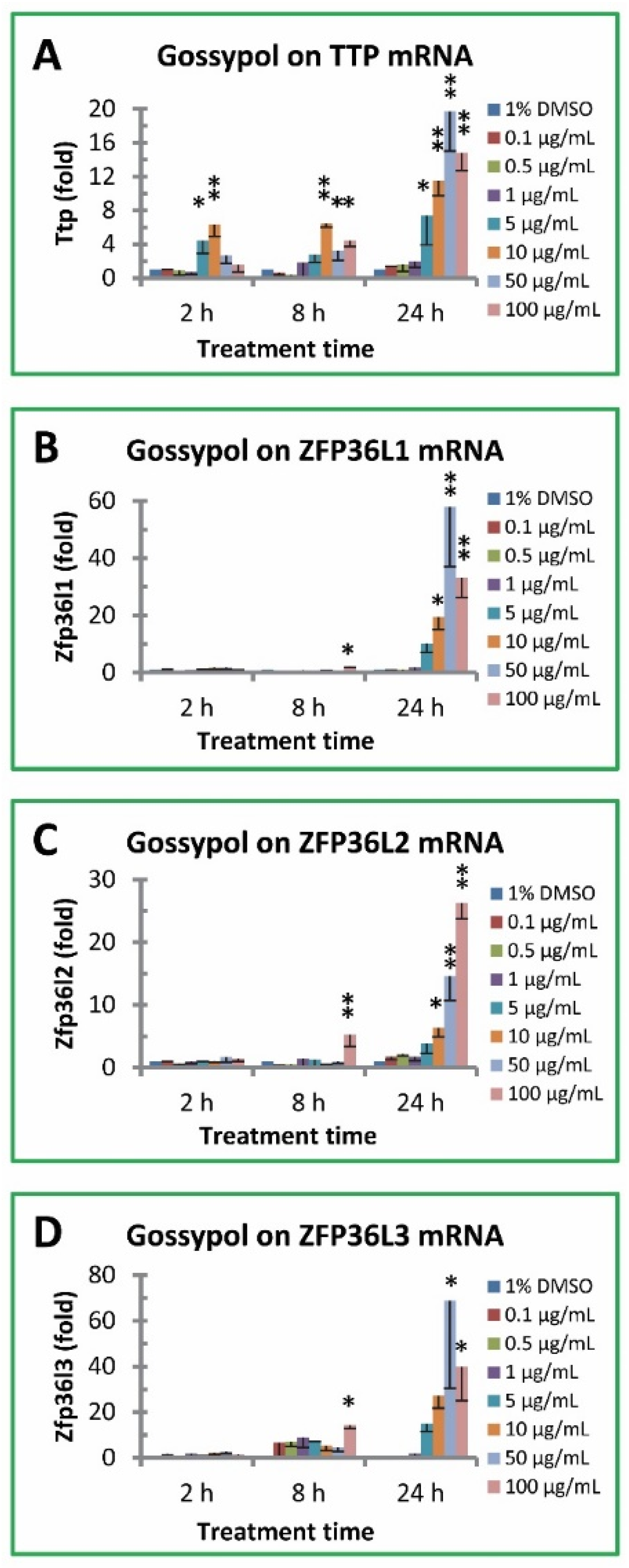
3.4. Gossypol increased TTP family gene expression in mouse macrophages
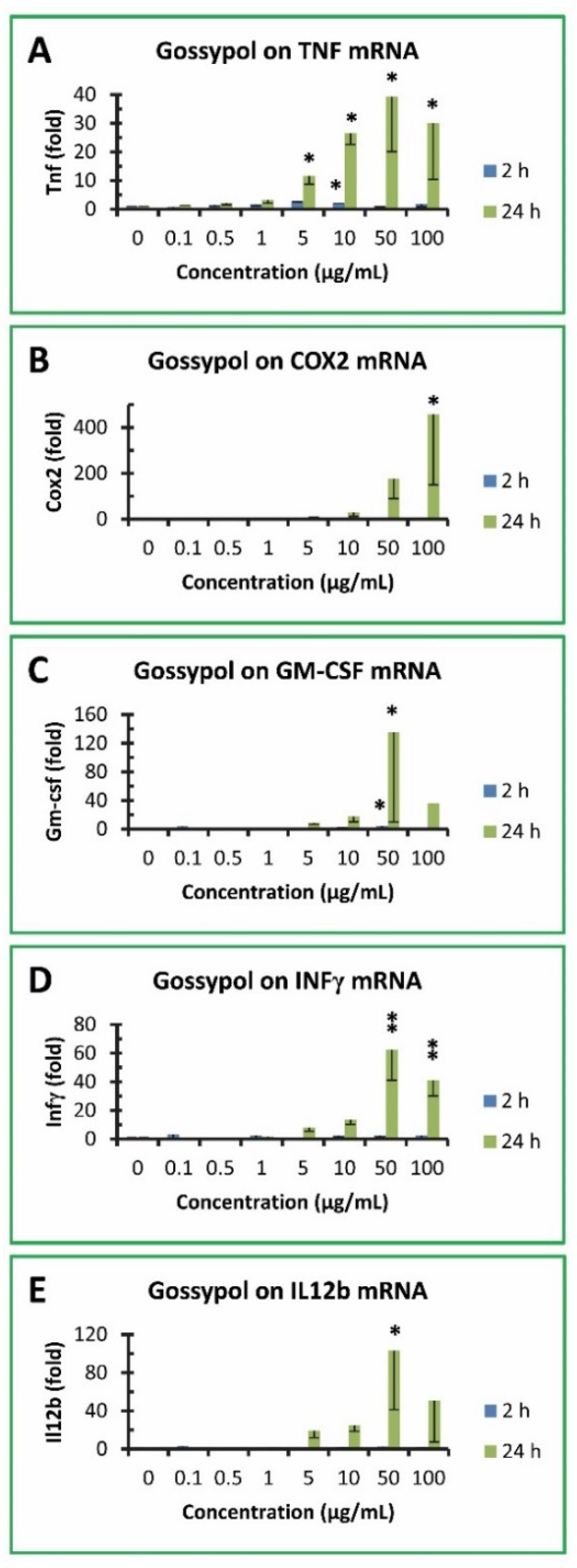
3.5. Gossypol increased proinflammatory cytokine gene expression in mouse macrophages
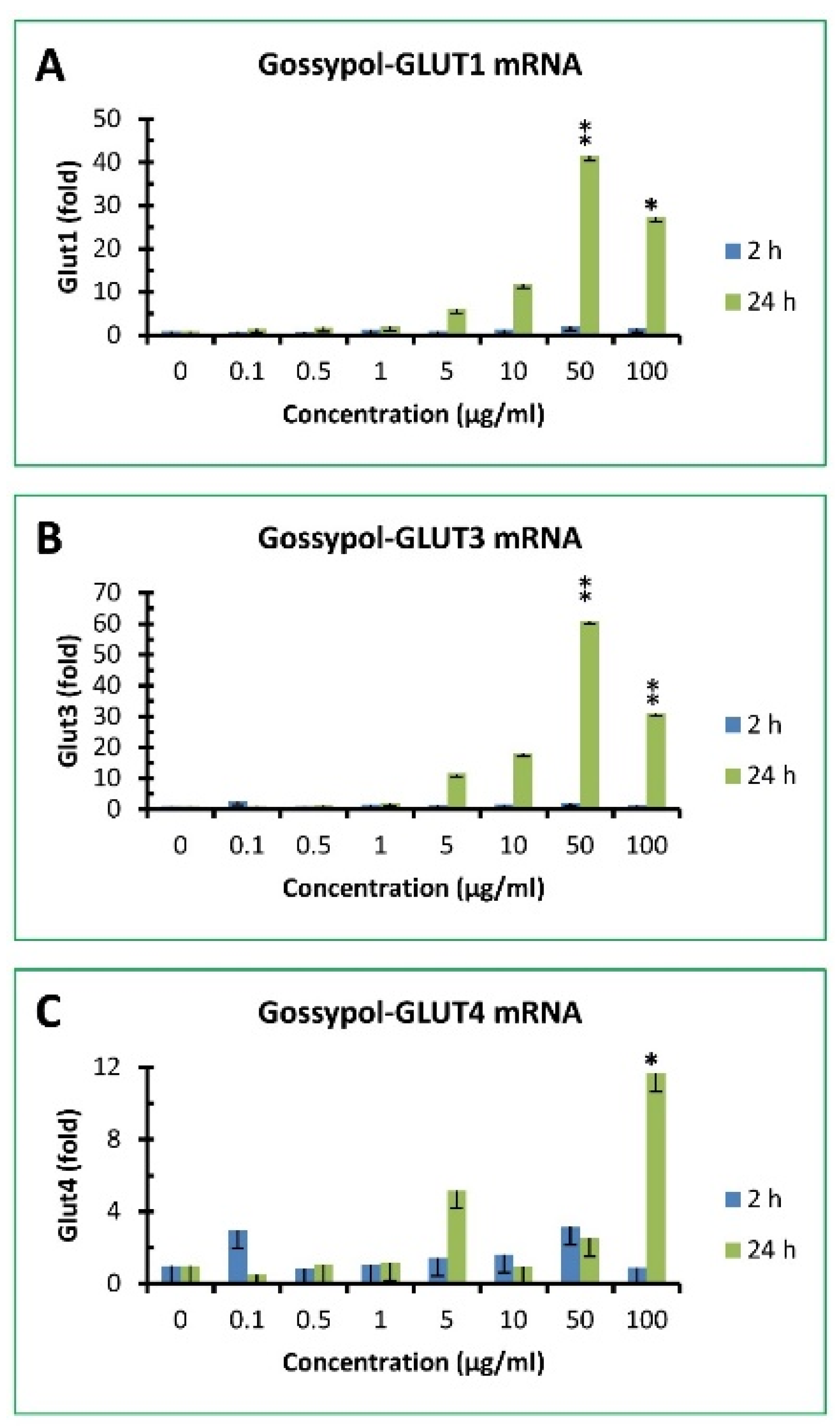
3.6. Gossypol increased GLUT family gene expression in mouse macrophages
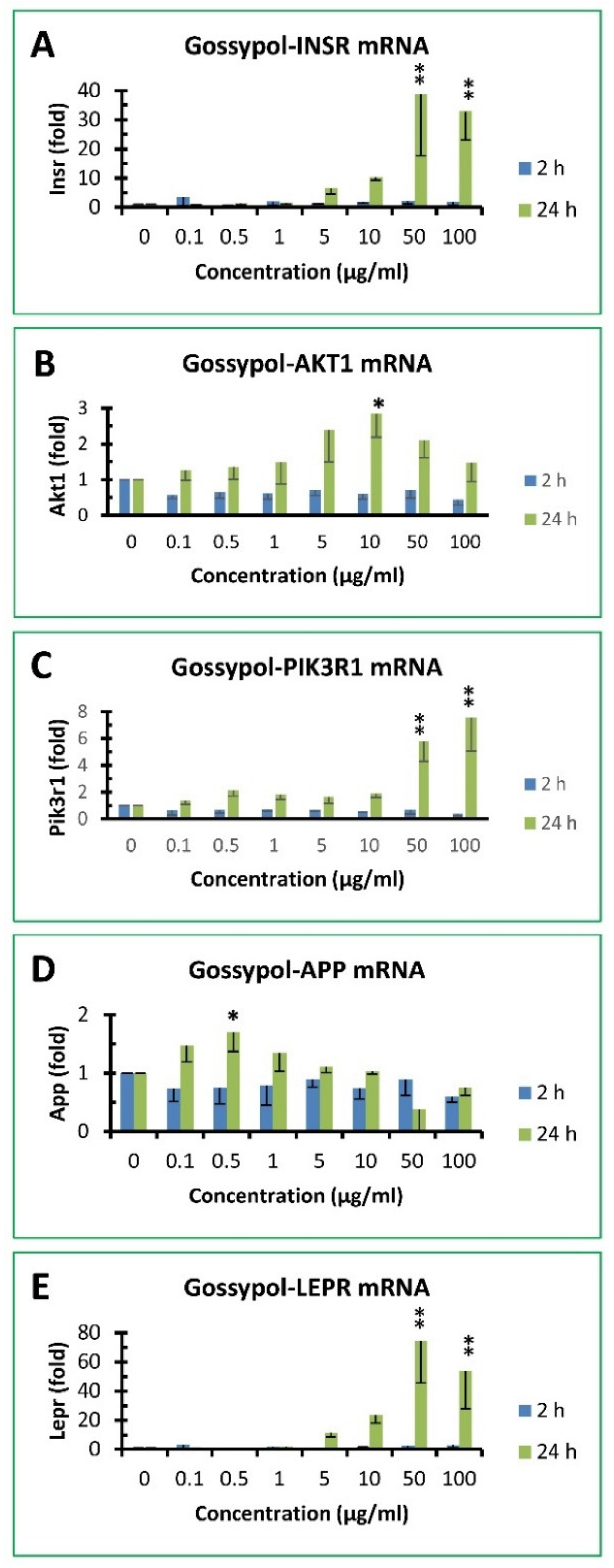
3.7. Gossypol increased insulin signaling pathway gene expression in mouse macrophages
3.8. Gossypol effect on APP and LEPR gene expression in mouse macrophages
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang CS, Landau JM, Huang MT, Newmark HL. Inhibition of carcinogenesis by dietary polyphenolic compounds. AnnuRevNutr. 2001;21:381-406. 21/1/381 [pii]. [CrossRef]
- Dixon RA, Xie DY, Sharma SB. Proanthocyanidins--a final frontier in flavonoid research? New Phytol. 2005;165(1):9-28. Epub 2005/02/22. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prior RL, Gu L. Occurrence and biological significance of proanthocyanidins in the American diet. Phytochemistry. 2005;66(18):2264-80. Epub 2005/05/21. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazafa A, Rehman KU, Jahan N, Jabeen Z. The Role of Polyphenol (Flavonoids) Compounds in the Treatment of Cancer Cells. Nutr Cancer. 2020;72(3):386-97. Epub 2019/07/10. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 5. Mileo AM, Nistico P, Miccadei S. Polyphenols: Immunomodulatory and Therapeutic Implication in Colorectal Cancer. Front Immunol. 2019;10:729. Epub 2019/04/30. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Long J, Guan P, Hu X, Yang L, He L, Lin Q, et al. Natural Polyphenols as Targeted Modulators in Colon Cancer: Molecular Mechanisms and Applications. Front Immunol. 2021;12:635484. Epub 2021/03/06. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kenar JA. Reaction chemistry of gossypol and its derivatives. J Am Oil Chem Soc. 2006;83(4):269-302. [CrossRef]
- Coutinho EM. Gossypol: a contraceptive for men. Contraception. 2002;65(4):259-63. S0010782402002949 [pii]. [CrossRef]
- He Z, Zhang D, Cao H. Protein profiling of water and alkali soluble cottonseed protein isolates. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):9306. [CrossRef]
- He Z, Zhang H, Olk DC. Chemical composition of defatted cottonseed and soy meal products. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(6):e0129933. [CrossRef]
- Zhong S, Leong J, Ye W, Xu P, Lin SH, Liu JY, et al. (-)-Gossypol-enriched cottonseed oil inhibits proliferation and adipogenesis of human breast pre-adipocytes. Anticancer Res. 2013;33(3):949-55. doi: 33/3/949 [pii].
- Chien CC, Ko CH, Shen SC, Yang LY, Chen YC. The role of COX-2/PGE2 in gossypol-induced apoptosis of colorectal carcinoma cells. JCell Physiol. 2012;227(8):3128-37. [CrossRef]
- Yuan Y, Tang AJ, Castoreno AB, Kuo SY, Wang Q, Kuballa P, et al. Gossypol and an HMT G9a inhibitor act in synergy to induce cell death in pancreatic cancer cells. Cell DeathDis. 2013;4:e690. [CrossRef]
- Thakur A, Lum LG, Schalk D, Azmi A, Banerjee S, Sarkar FH, et al. Pan-Bcl-2 inhibitor AT-101 enhances tumor cell killing by EGFR targeted T cells. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(11):e47520. [CrossRef]
- Pang X, Wu Y, Wu Y, Lu B, Chen J, Wang J, et al. (-)-Gossypol suppresses the growth of human prostate cancer xenografts via modulating VEGF signaling-mediated angiogenesis. MolCancer Ther. 2011;10(5):795-805. [CrossRef]
- Huang YW, Wang LS, Dowd MK, Wan PJ, Lin YC. (-)-Gossypol reduces invasiveness in metastatic prostate cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 2009;29(6):2179-88. doi: 29/6/2179 [pii].
- Huo M, Gao R, Jiang L, Cui X, Duan L, Deng X, et al. Suppression of LPS-induced inflammatory responses by gossypol in RAW 264.7 cells and mouse models. IntImmunopharmacol. 2013;15(2):442-9. [CrossRef]
- Oskoueian E, Abdullah N, Hendra R, Karimi E. Bioactive compounds, antioxidant, xanthine oxidase inhibitory, tyrosinase inhibitory and anti-inflammatory activities of selected agro-industrial by-products. IntJMolSci. 2011;12(12):8610-25. ijms-12-08610 [pii]. [CrossRef]
- Fu M, Blackshear PJ. RNA-binding proteins in immune regulation: a focus on CCCH zinc finger proteins. NatRevImmunol. 2017;17(2):130-43. nri.2016.129 [pii]. [CrossRef]
- Patial S, Blackshear PJ. Tristetraprolin as a Therapeutic Target in Inflammatory Disease. Trends PharmacolSci. 2016;37(10):811-21. S0165-6147(16)30079-7 [pii]. [CrossRef]
- Carballo E, Lai WS, Blackshear PJ. Feedback inhibition of macrophage tumor necrosis factor-alpha production by tristetraprolin. Science. 1998;281(5379):1001-5. [CrossRef]
- Lai WS, Carballo E, Thorn JM, Kennington EA, Blackshear PJ. Interactions of CCCH zinc finger proteins with mRNA. Binding of tristetraprolin-related zinc finger proteins to Au-rich elements and destabilization of mRNA. JBiolChem. 2000;275(23):17827-37. [CrossRef]
- Phillips K, Kedersha N, Shen L, Blackshear PJ, Anderson P. Arthritis suppressor genes TIA-1 and TTP dampen the expression of tumor necrosis factor alpha, cyclooxygenase 2, and inflammatory arthritis. ProcNatlAcadSciUSA. 2004;101(7):2011-6. [CrossRef]
- Taylor GA, Carballo E, Lee DM, Lai WS, Thompson MJ, Patel DD, et al. A pathogenetic role for TNF alpha in the syndrome of cachexia, arthritis, and autoimmunity resulting from tristetraprolin (TTP) deficiency. Immunity. 1996;4(5):445-54. [CrossRef]
- Sauer I, Schaljo B, Vogl C, Gattermeier I, Kolbe T, Muller M, et al. Interferons limit inflammatory responses by induction of tristetraprolin. Blood. 2006;107(12):4790-7. [CrossRef]
- Cao H, Hininger-Favier I, Kelly MA, Benaraba R, Dawson HD, Coves S, et al. Green tea polyphenol extract regulates the expression of genes involved in glucose uptake and insulin signaling in rats fed a high fructose diet. JAgricFood Chem. 2007;55(15):6372-8. [CrossRef]
- Cao H, Kelly MA, Kari F, Dawson HD, Urban JF, Jr., Coves S, et al. Green tea increases anti-inflammatory tristetraprolin and decreases pro-inflammatory tumor necrosis factor mRNA levels in rats. JInflamm(Lond). 2007;4(1):1. [CrossRef]
- Cao H, Polansky MM, Anderson RA. Cinnamon extract and polyphenols affect the expression of tristetraprolin, insulin receptor, and glucose transporter 4 in mouse 3T3-L1 adipocytes. ArchBiochemBiophys. 2007;459(2):214-22. [CrossRef]
- Cao H, Graves DJ, Anderson RA. Cinnamon extract regulates glucose transporter and insulin-signaling gene expression in mouse adipocytes. Phytomedicine. 2010;17(13):1027-32. [CrossRef]
- Cao H, Urban JF, Jr., Anderson RA. Cinnamon polyphenol extract affects immune responses by regulating anti- and proinflammatory and glucose transporter gene expression in mouse macrophages. J Nutr. 2008;138(5):833-40. [CrossRef]
- Cao H, Anderson RA. Cinnamon polyphenol extract regulates tristetraprolin and related gene expression in mouse adipocytes. JAgricFood Chem. 2011;59(6):2739-44. [CrossRef]
- Blackshear PJ. Tristetraprolin and other CCCH tandem zinc-finger proteins in the regulation of mRNA turnover. BiochemSocTrans. 2002;30(6):945-52. [CrossRef]
- Blackshear PJ, Phillips RS, Ghosh S, Ramos SB, Richfield EK, Lai WS. Zfp36l3, a rodent X chromosome gene encoding a placenta-specific member of the tristetraprolin family of CCCH tandem zinc finger proteins. BiolReprod. 2005;73(2):297-307. [CrossRef]
- Cha HJ, Lee HH, Chae SW, Cho WJ, Kim YM, Choi HJ, et al. Tristetraprolin downregulates the expression of both VEGF and COX-2 in human colon cancer. Hepatogastroenterology. 2011;58(107-108):790-5.
- Carballo E, Lai WS, Blackshear PJ. Evidence that tristetraprolin is a physiological regulator of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor messenger RNA deadenylation and stability. Blood. 2000;95(6):1891-9. [CrossRef]
- Kontoyiannis D, Boulougouris G, Manoloukos M, Armaka M, Apostolaki M, Pizarro T, et al. Genetic dissection of the cellular pathways and signaling mechanisms in modeled tumor necrosis factor-induced Crohn's-like inflammatory bowel disease. J Exp Med. 2002;196(12):1563-74. [CrossRef]
- Molle C, Zhang T, Ysebrant de LL, Gueydan C, Andrianne M, Sherer F, et al. Tristetraprolin regulation of interleukin 23 mRNA stability prevents a spontaneous inflammatory disease. JExpMed. 2013;210(9):1675-84. jem.20120707 [pii]. [CrossRef]
- Gamelli RL, Liu H, He LK, Hofmann CA. Augmentations of glucose uptake and glucose transporter-1 in macrophages following thermal injury and sepsis in mice. J Leukoc Biol. 1996;59(5):639-47. Epub 1996/05/01. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sala-Vila A, Barbosa VM, Calder PC. Olive oil in parenteral nutrition. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2007;10(2):165-74. Epub 2007/02/08. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puschel GP, Klauder J, Henkel J. Macrophages, Low-Grade Inflammation, Insulin Resistance and Hyperinsulinemia: A Mutual Ambiguous Relationship in the Development of Metabolic Diseases. J Clin Med. 2022;11(15). Epub 2022/08/13. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cao H, Sethumadhavan K, Bland JM. Isolation of cottonseed extracts that affect human cancer cell growth. SciRep. 2018;8(1):10458. [CrossRef]
- Cao H, Sethumadhavan K, Cao F, Wang TTY. Gossypol decreased cell viability and down-regulated the expression of a number of genes in human colon cancer cells. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):5922. Epub 2021/03/17. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cao H, Sethumadhavan K. Identification of Bcl2 as a Stably Expressed qPCR Reference Gene for Human Colon Cancer Cells Treated with Cottonseed-Derived Gossypol and Bioactive Extracts and Bacteria-Derived Lipopolysaccharides. Molecules. 2022;27(21):7560. Epub 2022/11/12. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cao H, Tuttle JS, Blackshear PJ. Immunological characterization of tristetraprolin as a low abundance, inducible, stable cytosolic protein. JBiolChem. 2004;279(20):21489-99. [CrossRef]
- Cao H. Expression, purification, and biochemical characterization of the antiinflammatory tristetraprolin: a zinc-dependent mRNA binding protein affected by posttranslational modifications. Biochemistry. 2004;43(43):13724-38. [CrossRef]
- Bustin SA, Benes V, Garson JA, Hellemans J, Huggett J, Kubista M, et al. The MIQE guidelines: minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. ClinChem. 2009;55(4):611-22. [CrossRef]
- Cao H, Shockey JM. Comparison of TaqMan and SYBR Green qPCR methods for quantitative gene expression in tung tree tissues. J AgricFood Chem. 2012;60(50):12296-303. [CrossRef]
- Cao H, Sethumadhavan K. Cottonseed extracts and gossypol regulate diacylglycerol acyltransferase gene expression in mouse macrophages. JAgricFood Chem. 2018;66(24):6022-30. [CrossRef]
- Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 2001;25(4):402-8. [CrossRef]
- Cao H, Cao F, Roussel AM, Anderson RA. Quantitative PCR for glucose transporter and tristetraprolin family gene expression in cultured mouse adipocytes and macrophages. In Vitro Cell DevBiolAnim. 2013;49(10):759-70. [CrossRef]
- Fukuzumi M, Shinomiya H, Shimizu Y, Ohishi K, Utsumi S. Endotoxin-induced enhancement of glucose influx into murine peritoneal macrophages via GLUT1. Infect Immun. 1996;64(1):108-12. Epub 1996/01/01. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cao H, Sethumadhavan K. Gossypol but not cottonseed extracts or lipopolysaccharides stimulates HuR gene expression in mouse cells. Journal of Functional Foods. 2019;59:25-9. [CrossRef]
- Cao H, Sethumadhavan K, Wu X, Zeng X. Cottonseed-derived gossypol and ethanol extracts differentially regulate cell viability and VEGF gene expression in mouse macrophages. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):15700. Epub 2021/08/05. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Deng S, Yuan H, Yi J, Lu Y, Wei Q, Guo C, et al. Gossypol acetic acid induces apoptosis in RAW264.7 cells via a caspase-dependent mitochondrial signaling pathway. J VetSci. 2013;14(3):281-9. jvs.2013.046 [pii]. [CrossRef]
- Lin QR, Li CG, Zha QB, Xu LH, Pan H, Zhao GX, et al. Gossypol induces pyroptosis in mouse macrophages via a non-canonical inflammasome pathway. ToxicolApplPharmacol. 2016;292:56-64. S0041-008X(15)30173-3 [pii]. [CrossRef]
- Lai WS, Stumpo DJ, Blackshear PJ. Rapid insulin-stimulated accumulation of an mRNA encoding a proline-rich protein. JBiolChem. 1990;265(27):16556-63. [CrossRef]
- DuBois RN, McLane MW, Ryder K, Lau LF, Nathans D. A growth factor-inducible nuclear protein with a novel cysteine/histidine repetitive sequence. JBiolChem. 1990;265(31):19185-91. [CrossRef]
- Varnum BC, Lim RW, Kujubu DA, Luner SJ, Kaufman SE, Greenberger JS, et al. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and tetradecanoyl phorbol acetate induce a distinct, restricted subset of primary- response TIS genes in both proliferating and terminally differentiated myeloid cells. MolCellBiol. 1989;9(8):3580-3. [CrossRef]
- Cousins RJ, Blanchard RK, Popp MP, Liu L, Cao J, Moore JB, et al. A global view of the selectivity of zinc deprivation and excess on genes expressed in human THP-1 mononuclear cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(12):6952-7. Epub 2003/05/21. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Taddeo B, Zhang W, Roizman B. The U(L)41 protein of herpes simplex virus 1 degrades RNA by endonucleolytic cleavage in absence of other cellular or viral proteins. ProcNatlAcadSciUSA. 2006;103(8):2827-32. [CrossRef]
| mRNA | accession no. | amplicon (bp) | forward primer (5´ to 3´) | reverse primer (5´ to 3´) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TTP family | ||||
| Ttp/Zfp36/Tis11 | NM_011756 | 70 | GGTACCCCAGGCTGGCTTT | ACCTGTAACCCCAGAACTTGGA |
| Zfp36l1/Tis11b | NM_007564 | 60 | TGCGAACGCCCACGAT | CTTCGCTCAAGTCAAAAATGG |
| Zfp36l2/Tis11d | NM_001001806 | 77 | GAGGGCACCTCCCAACCT | TGACAGAAGTGTGGTCGACATTT |
| Zfp36l3 | NM_001009549 | 70 | CGAACTGCGTACCCTGTCAAG | GCCAACGCTGTGGAAGGT |
| Cytokines | ||||
| Gm-csf/Csf2 | NM_009969 | 71 | CACCCGCTCACCCATCAC | GGAGGTTCAGGGCTTCTTTGA |
| Cox2/Ptgs2 | NM_011198 | 106 | CCACCTCTGCGATGCTCTTC | CATTCCCCACGGTTTTGACATG |
| Ifnγ | NM_008337 | 81 | TGGCATAGATGTGGAAGAAAAGAG | TGCAGGATTTTCATGTCACCAT |
| Il12b | NM_008352 | 79 | GACCAGAGACATGGAGTCATAGG | TGTACTGGCCAGCATCTAGAAACT |
| Tnf/Tnfα | NM_013693 | 74 | GCTGTCGCTACATCACTGAACCT | TGACCCGTAGGGCAATTACA |
| GLUT family | ||||
| Glut1 (Slc2a1) | M13979 | 123 | CGTGCTTATGGGTTTCTCCAAA | GACACCTCCCCCACATACATG |
| Glut2 (Slc2a2) | NM_012879 | 80 | TTTGCAGTAGGCGGAATGG | GCCAACATGGCTTTGATCCTT |
| Glut3 (Slc2a3) | NM_017102 | 112 | TGAAGCCATGAGCTTTGTCTGT | GCCCTGGCTGAAGAGTTCAG |
| Glut4 (Slc2a4) | NM_012751 | 87 | CAACTGGACCTGTAACTTCATCGT | ACGGCAAATAGAAGGAAGACGTA |
| Insulin signaling | ||||
| Insr | NM_017071 | 137 | CAAAAGCACAATCAGAGTGAGTATGAC | ACCACGTTGTGCAGGTAATCC |
| Akt1/Pkb | NM_033230 | 90 | TGGACTACTTGCACTCCGAGAA | TTATCTTGATATGCCCGTCCTT |
| GSK3β | NM_032080 | 106 | TTAAGGAAGGAAAAGGTGAATCGA | CCAAAAGCTGAAGGCTGCTG |
| Pik3r1 | NM_013005 | 118 | CCTCTCCTTATAAAGCTCCTGGAA | GATCACAATCAAGAAGCTGTCGTAA |
| Other mRNA | ||||
| App | NM_007471 | 70 | GTTGCCTAGTTGGTGAGTTTGT | TCCTGGTGTAGGAACTTGCACTTG |
| Lepr | NM_146146 | 92 | TGACCAGTGTAACAGTGCTAACTTCTC | CATATTTAACTGAGGGTTGTCTCTGACA |
| Rpl32 (reference) | NM_172086 | 66 | AACCGAAAAGCCATTGTAGAAA | CCTGGCGTTGGGATTGG |
| gossypol concentration (µg/mL). | A570 nm ± SD (2 h) (% of control) | A570 nm ± SD (24 h) (% of control) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 100.0 ± 8.1 | 100.0 ± 18.5 |
| 0.1 | 110.2 ± 9.0 | 92.8 ± 3.2 |
| 0.5 | 93.6 ± 4.8 | 90.4 ± 5.5 |
| 1 | 99.2 ± 1.3 | 88.3 ± 11.5 |
| 5 | 92.7 ± 4.9 | 7.6 ± 0.4 ** |
| 10 | 85.7 ± 7.4 * | 7.6 ± 0.4 ** |
| 50 | 69.3 ± 2.4 ** | 8.6 ± 0.5 ** |
| 100 | 20.0 ± 0.6 ** | 8.5 ± 3.2 ** |
| treatment | time (h) | supernatant protein | pellet protein | total protein | |||||
| concentration (µg/µL) | amount (mg) | ratio (%) | concentration (µg/µL) | amount (mg) | ratio (%) | amount (mg) | ratio (%) | ||
| control | 2 | 7.78 ± 0.36 | 3.89 | 100 | 22.05 ± 0.21 | 1.1 | 100 | 4.99 | 100 |
| gossypol | 2 | 6.56 ± 0.39 * | 3.28 | 84 | 23.67 ± 0.22 ** | 1.18 | 107 | 4.47 | 90 |
| gossypol | 4 | 6.45 ± 0.38 * | 3.22 | 83 | 31.47 ± 0.15 ** | 1.57 | 143 | 4.80 | 96 |
| gossypol | 8 | 4.85 ± 0.32 ** | 2.42 | 62 | 34.21 ± 0.45 ** | 1.71 | 155 | 4.13 | 83 |
| gossypol | 24 | 0.21 ± 0.18 ** | 0.11 | 3 | 22.12 ± 0.45 | 1.11 | 101 | 1.22 | 24 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





