Submitted:
07 February 2023
Posted:
10 February 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents, Buffers, Materials, and Equipment
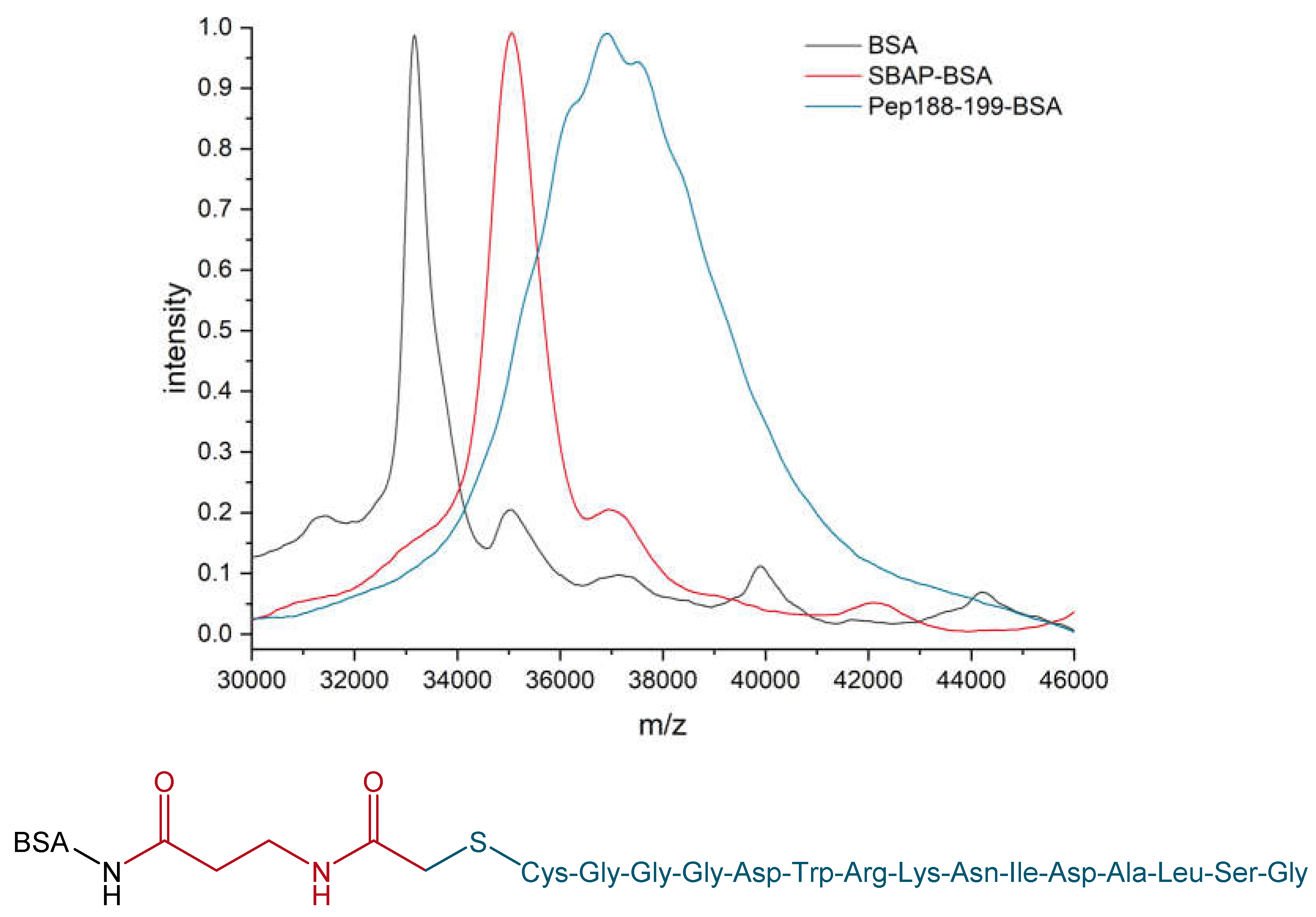
2.2. Peptide-Design and Peptide-BSA Conjugation
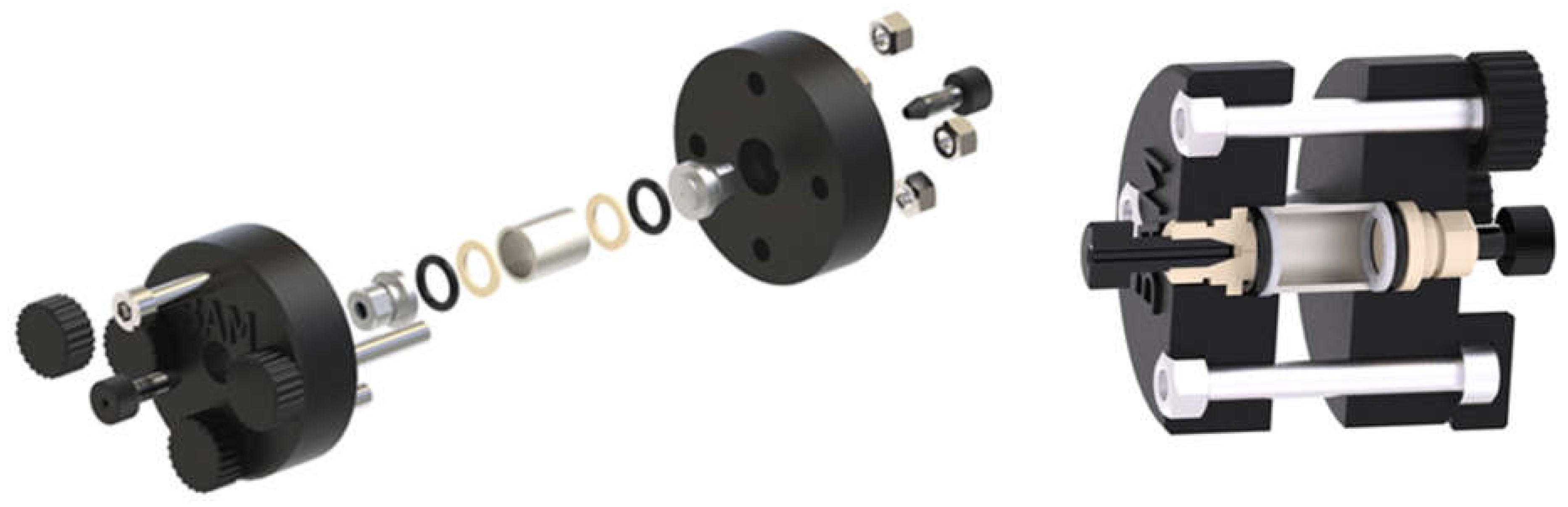
2.3. Column Preparation and Functionalization with Peptide-BSA Conjugate
2.4. Troponin Expression in E. coli and cTnI Calibration
2.4.1. Constructs and Molecular Cloning
2.4.2. Protein Expression in E.coli and Purification
2.4.3. Test Expression of the cTn Constructs
2.4.3. Large-Scale Expression
2.4.4. Protein Purification and Characterization
2.4.5. MALDI-TOF-MS of Expressed Troponins
2.4.6. Calibration of cTnI by Sandwich ELISA
2.5. Antibody Labeling and Functionality Test
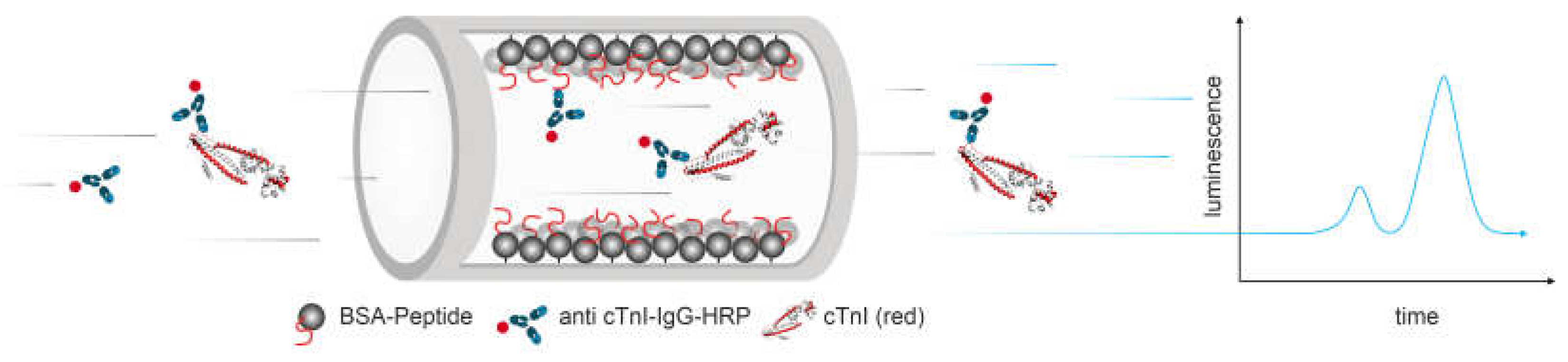
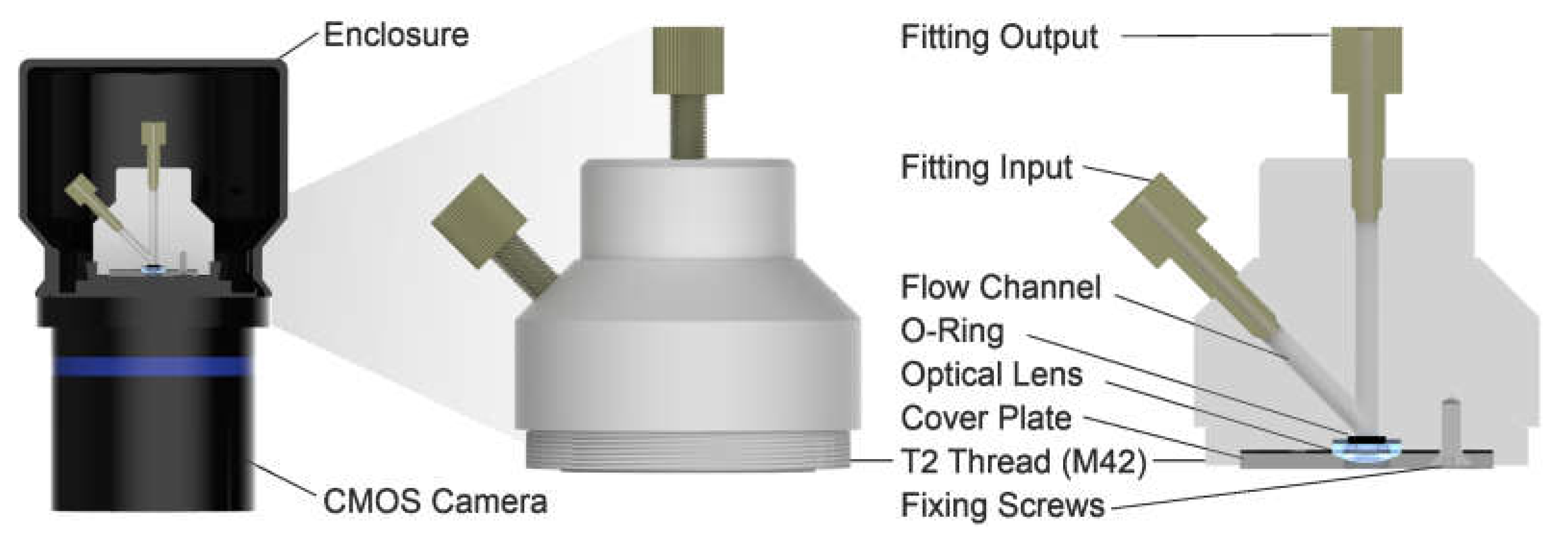
2.6. Chemiluminescence Detection
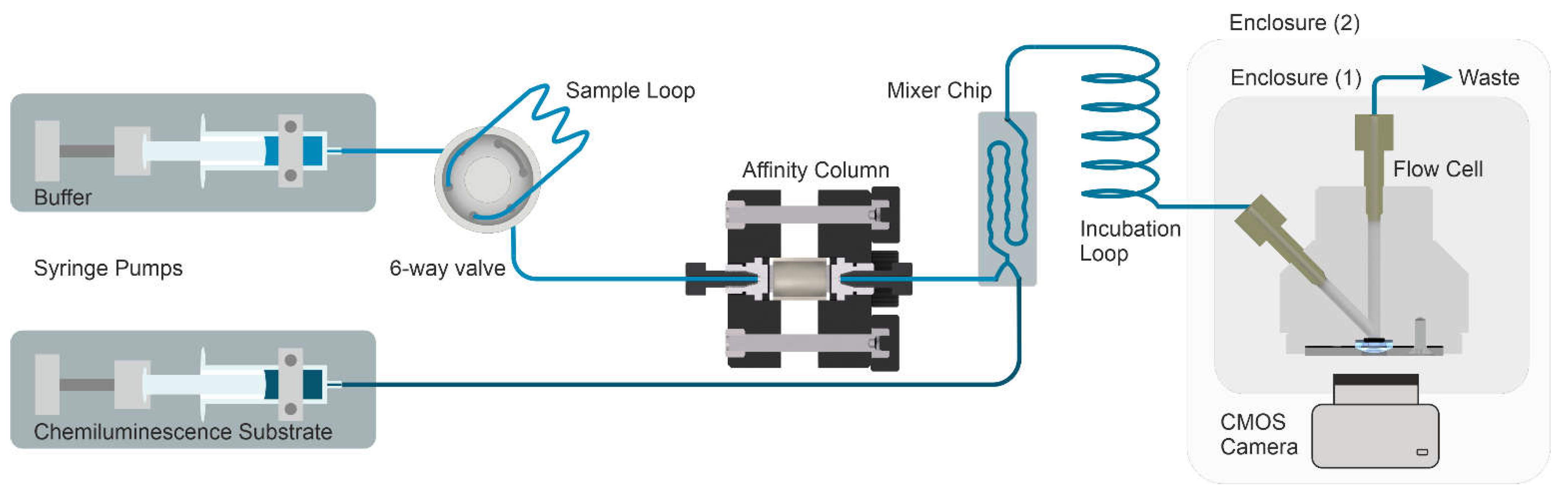
2.7. Fluidic Setup and Measurements
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Troponin Peptide-BSA Conjugation and Characterization
3.2. Expression of cTnI in E. coli and Adjustment of the Resulting Stock Solution by ELISA
3.2.1. Expression of Human Cardiac Troponins in E. coli
3.2.2. Purification and Characterization of Recombinant Cardiac Troponins
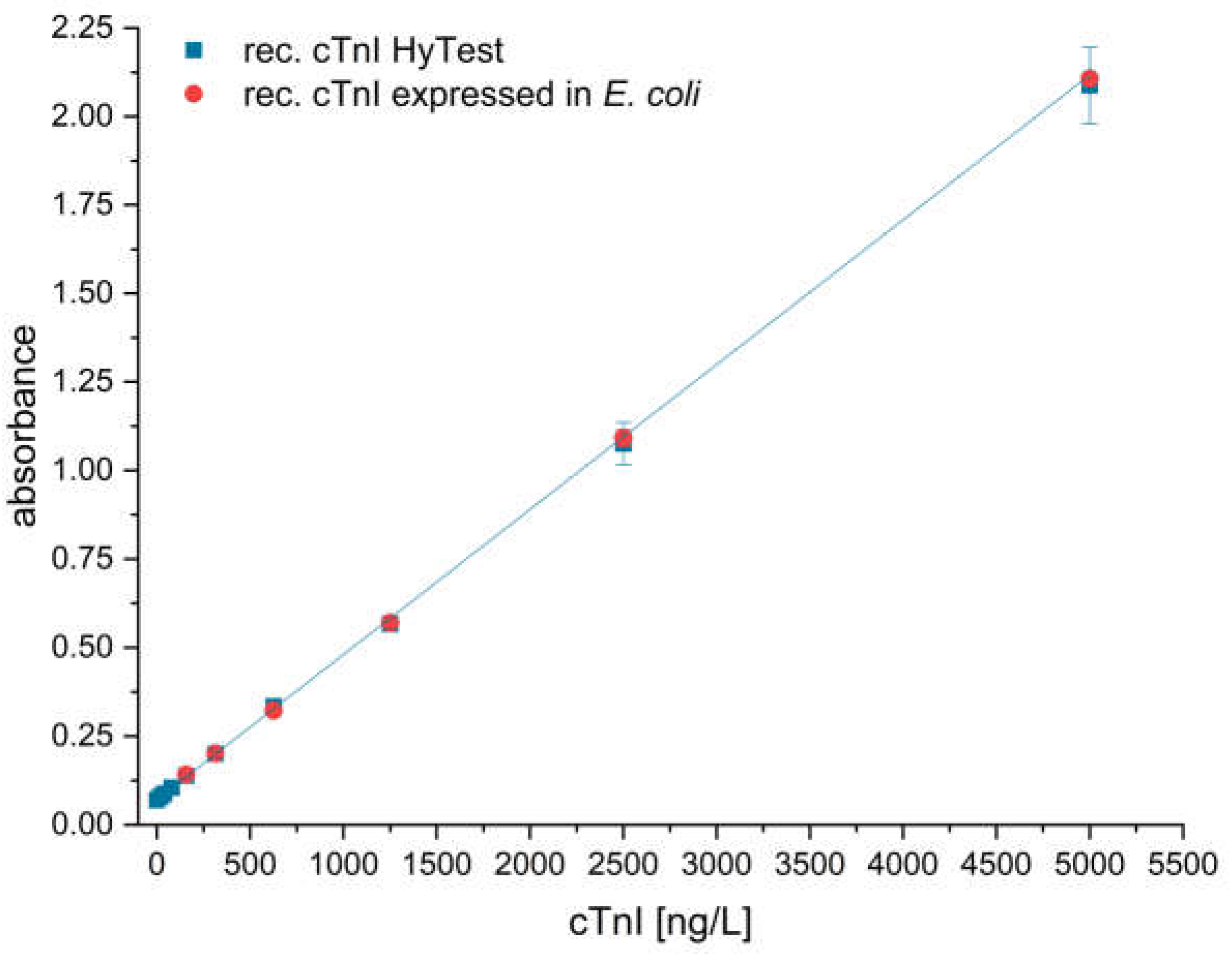
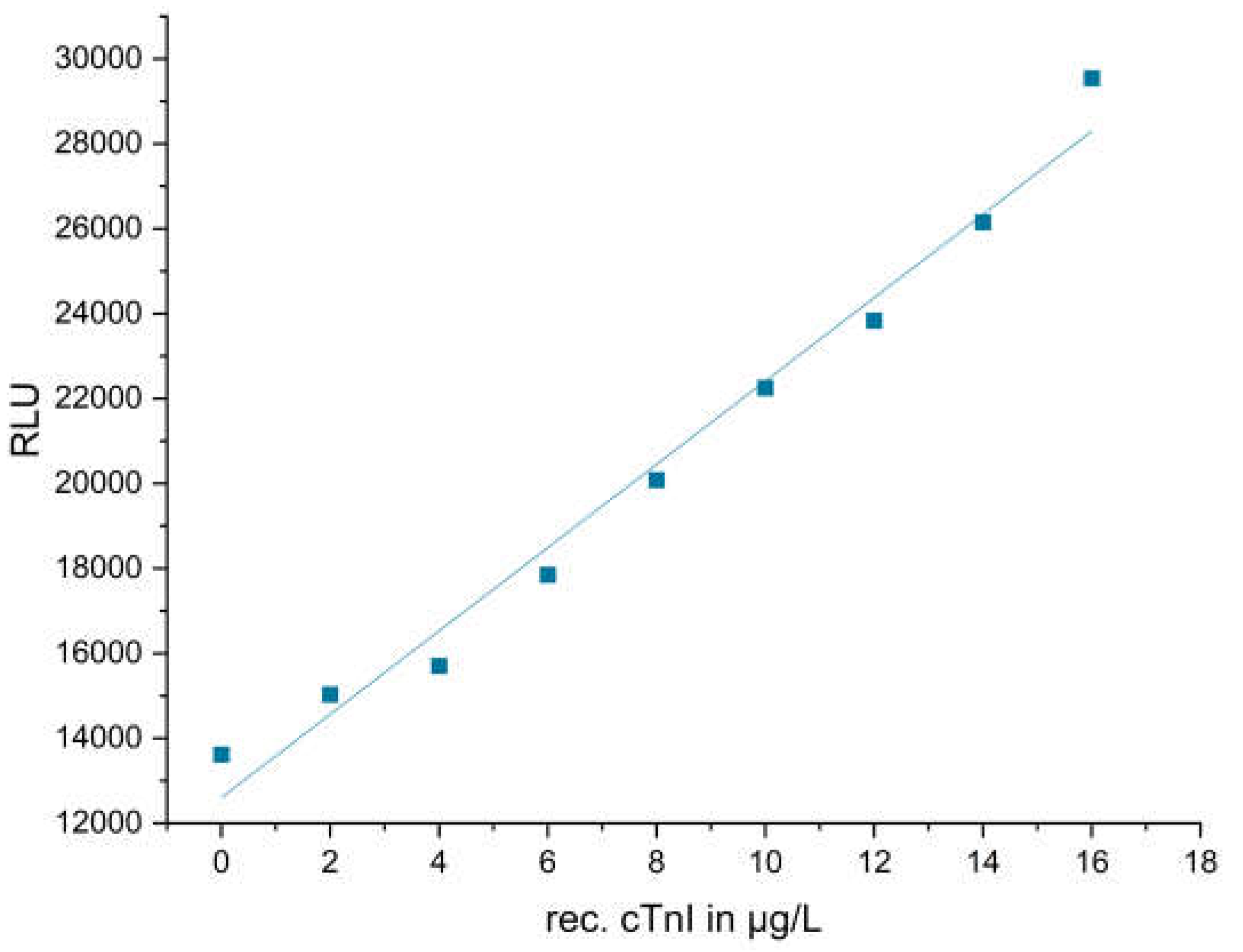
3.2.5. Calibration of the Stock Solution of Recombinant cTnI by ELISA
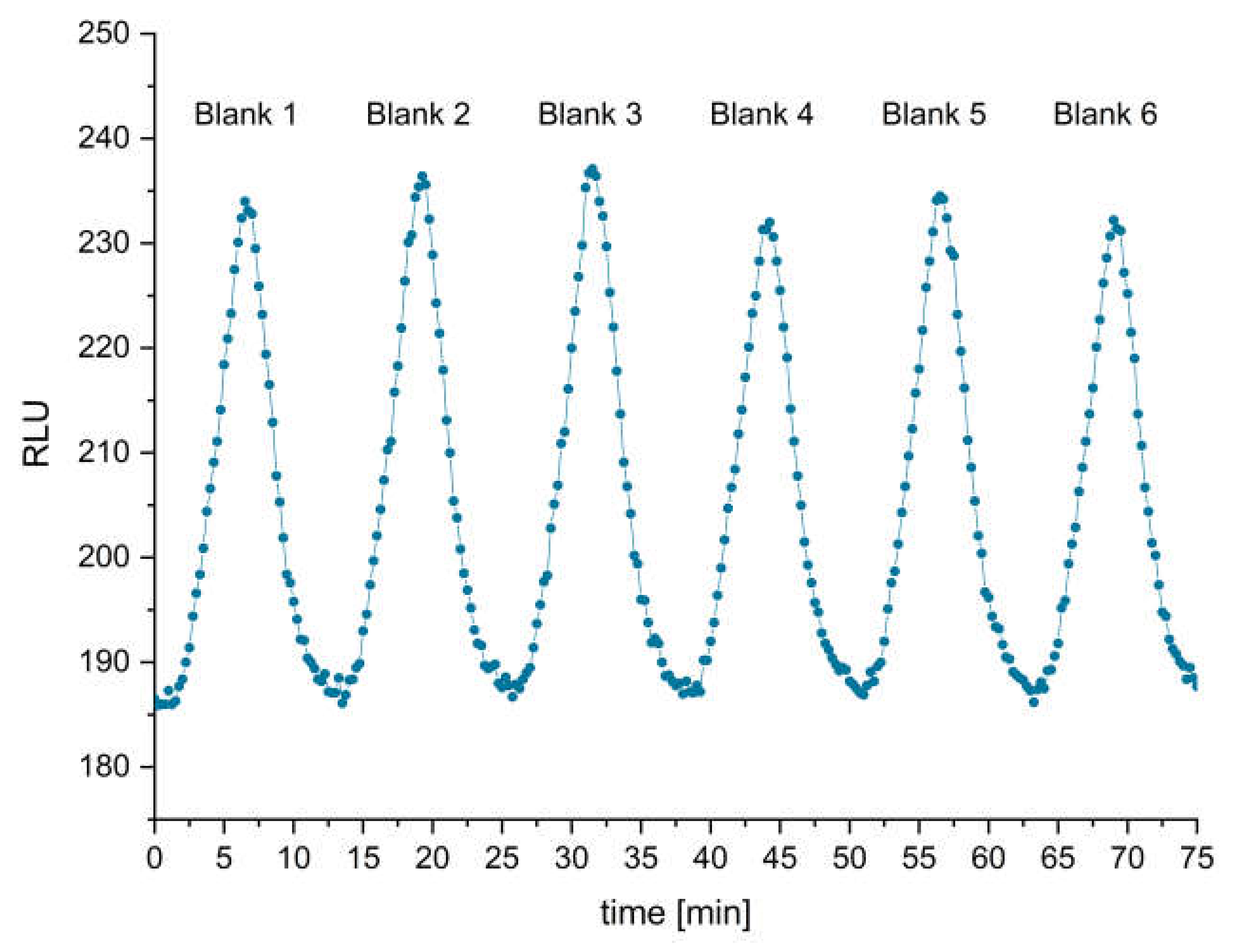
3.3. Performance of Peptide-BSA Column and Blank Measurement
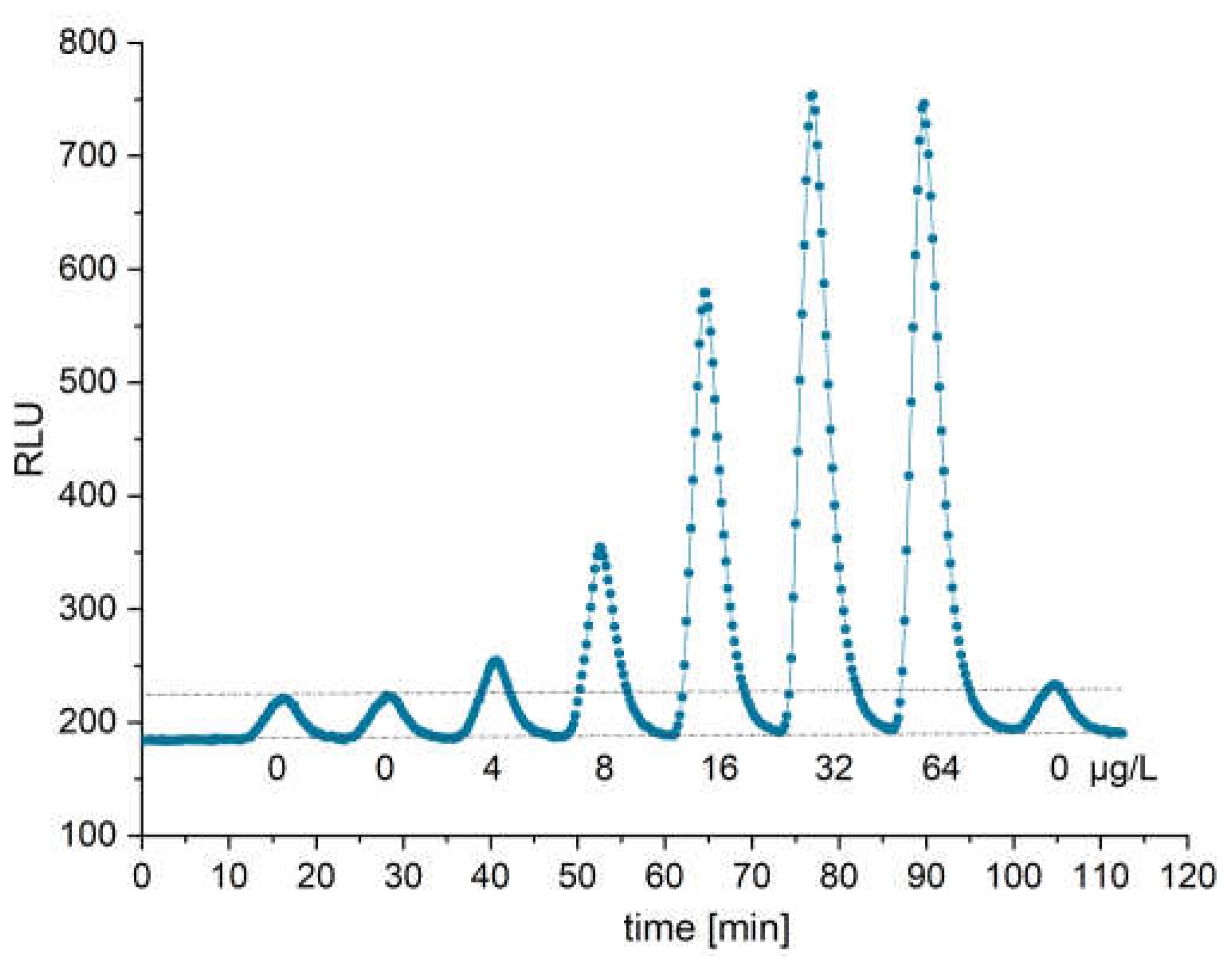
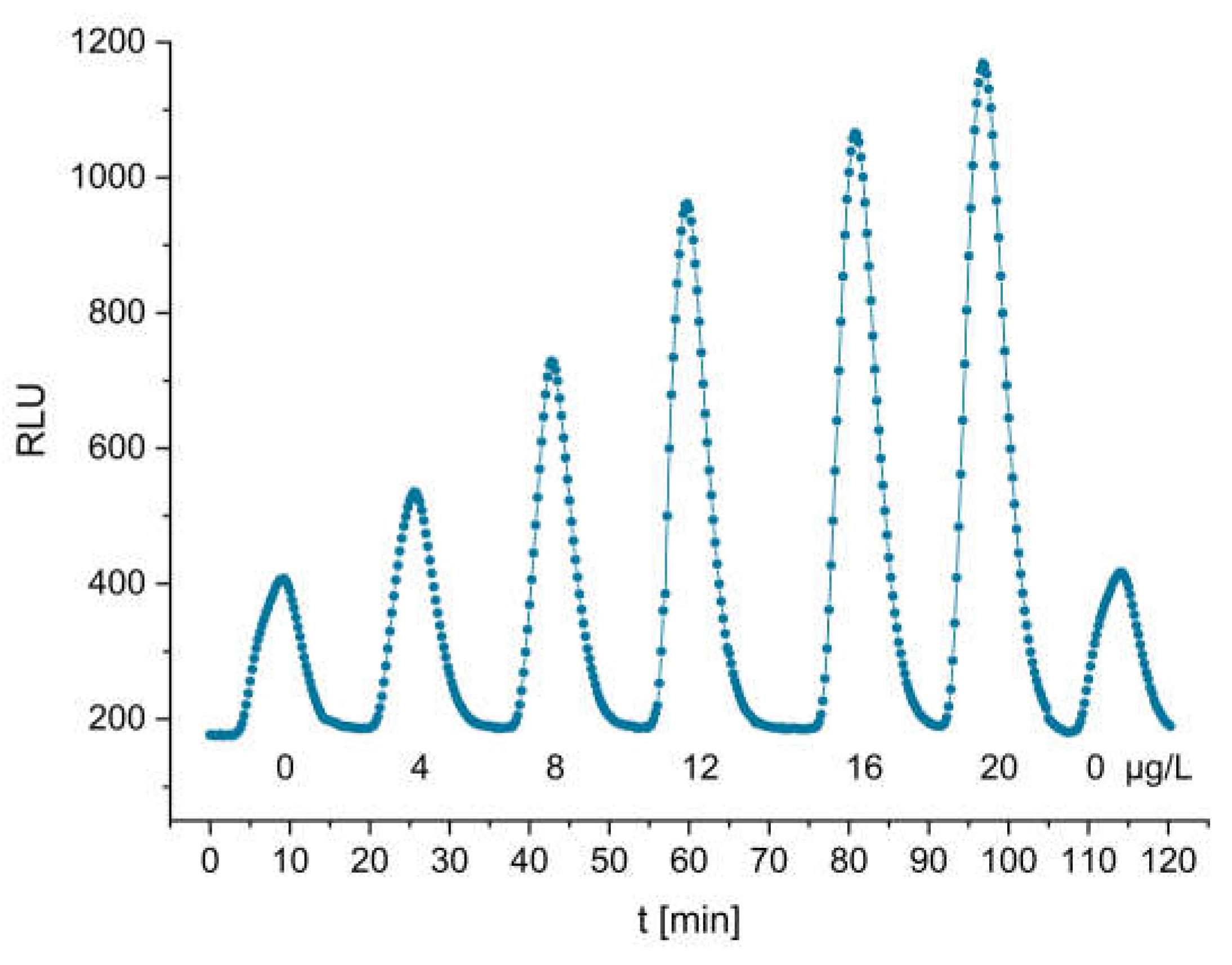
3.4. cTnI Measurement
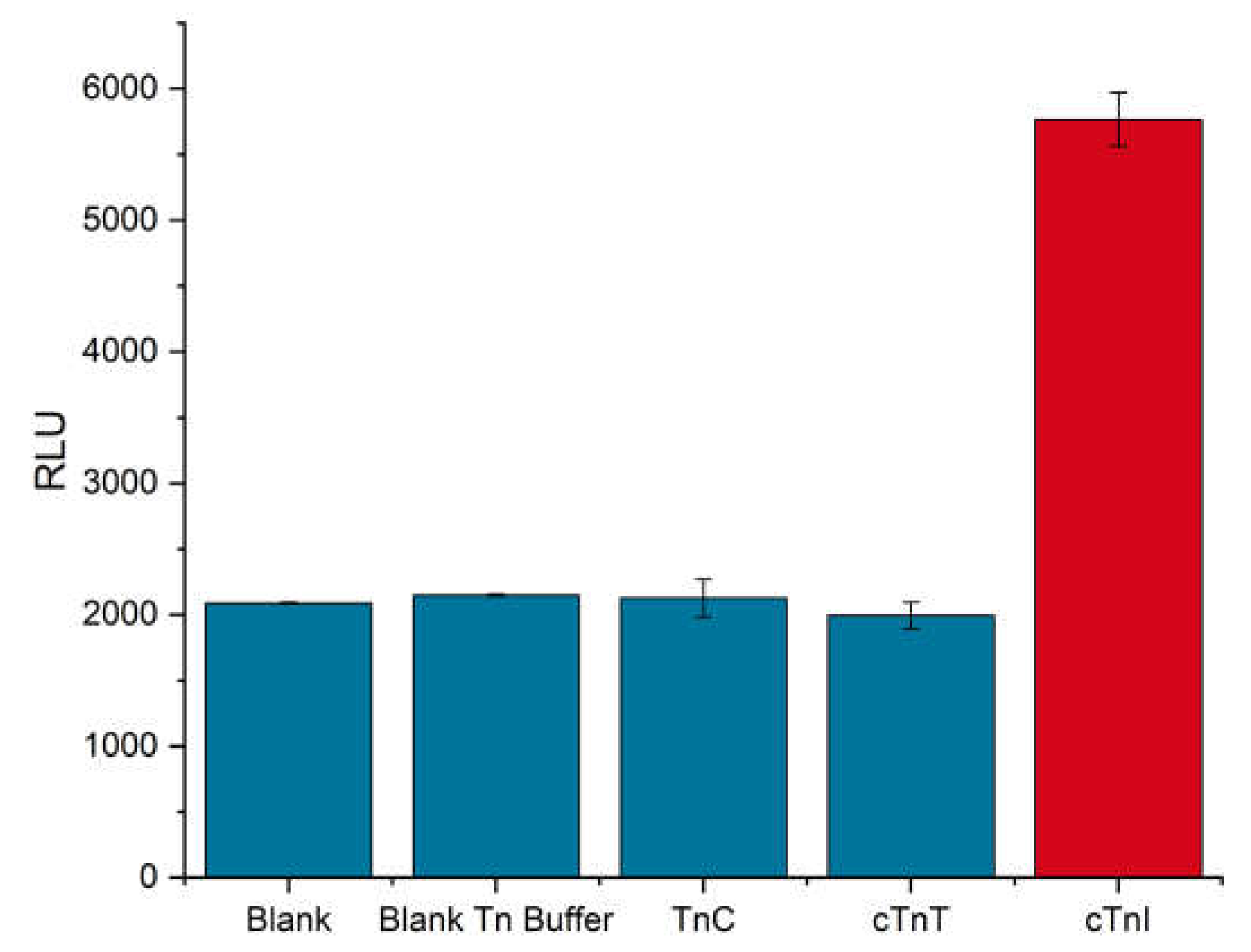
3.5. Test of Specificity (Cross-Reactivity)
3.6. Linearity of cTnI Measurement in PBST-BSA Running Buffer
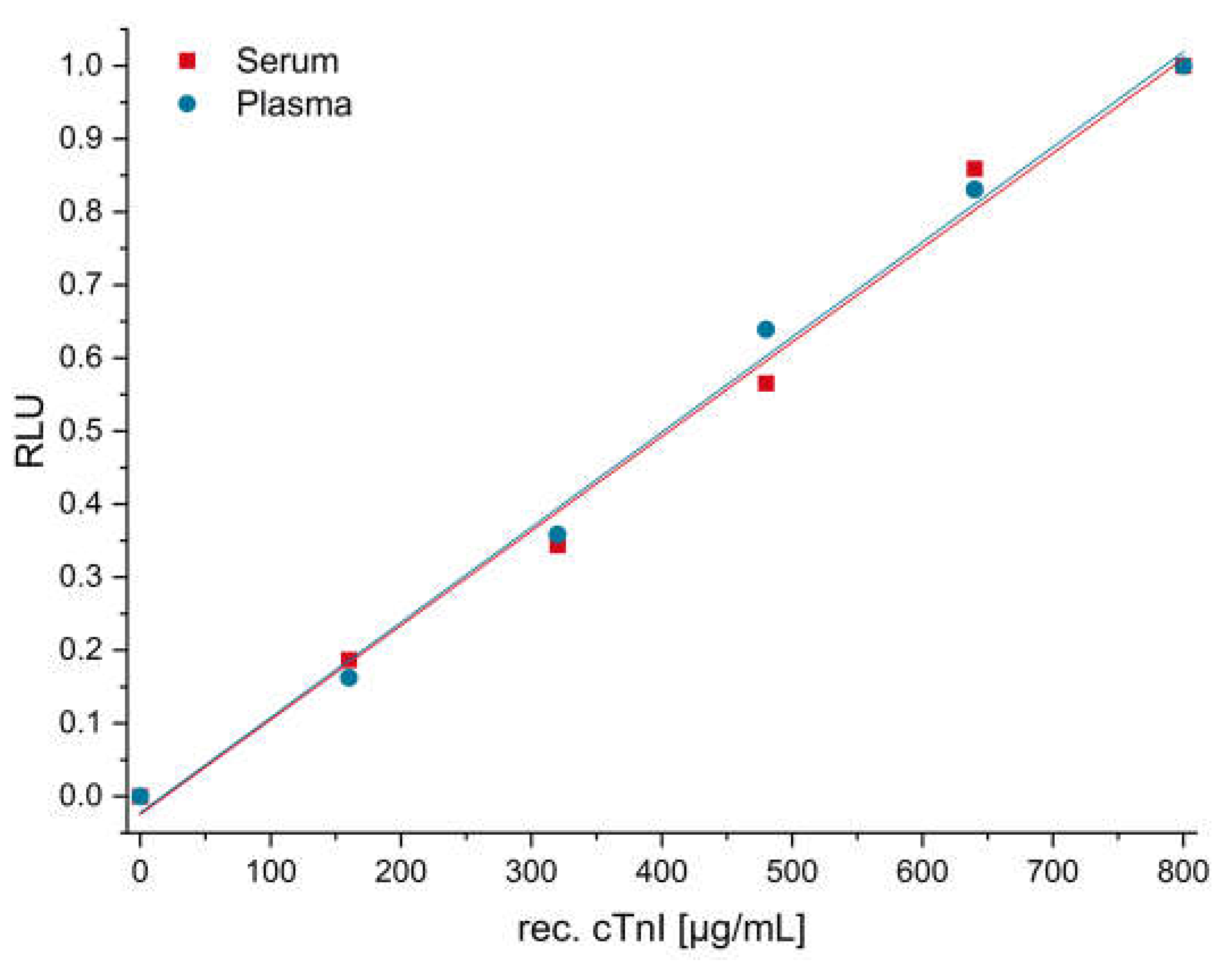
3.7. cTnI Measurement in Human Plasma and Serum
4. Discussion and Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elizabeth Wilkins, L.W., Kremlin Wickramasinghe, Prachi Bhatnagar, Jose Leal, Ramon Luengo-Fernandez, R Burns, Mike Rayner, Nick Townsend. European Cardiovascular Disease Statistics 2017. 2017. 2017.
- Frank L. J. Visseren, F.M., Yvo M. Smulders, David Carballo, Konstantinos C Koskinas, Maria Bäck, Athanase Benetos, Alessandro Biffi, José-Manuel Boavida, Davide Capodanno, Bernard Cosyns, Carolyn Crawford, Constantinos H. Davos, Ileana Desormais, Emanuele Di Angelantonio, Oscar H Franco, Sigrun Halvorsen, F D Richard Hobbs, Monika Hollander, Ewa A Jankowska, Matthias Michal, Simona Sacco, Naveed Sattar, Lale Tokgozoglu, Serena Tonstad, Konstantinos P Tsioufis, Ineke van Dis, Isabelle C. van Gelder, Christoph Wanner, Bryan Williams. 2021 ESC Guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice. European Heart Journal 2022, 43, 4468. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collet, J.P.; Thiele, H.; Barbato, E.; Barthelemy, O.; Bauersachs, J.; Bhatt, D.L.; Dendale, P.; Dorobantu, M.; Edvardsen, T.; Folliguet, T.; et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes in patients presenting without persistent ST-segment elevation. European Heart Journal 2021, 42, 1289–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apple, F.S.; Sandoval, Y.; Jaffe, A.S.; Ordonez-Llanos, J.; Bio-Markers, I.T.F.o.C.A.o.C. Cardiac Troponin Assays: Guide to Understanding Analytical Characteristics and Their Impact on Clinical Care. Clinical Chemistry 2017, 63, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachuba, S.; Salmon, A.; Zhelev, Z.; Pitt, M. Redesigning the diagnostic pathway for chest pain patients in emergency departments. Health Care Manag Sci 2018, 21, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, J.J.; Jin, J.P. Gene regulation, alternative splicing, and posttranslational modification of troponin subunits in cardiac development and adaptation: a focused review. Frontiers in Physiology 2014, 5, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssens, J.V.; Ma, B.; Brimble, M.A.; Van Eyk, J.E.; Delbridge, L.M.D.; Mellor, K.M. Cardiac troponins may be irreversibly modified by glycation: novel potential mechanisms of cardiac performance modulation. Scientific Reports 2018, 8, 16084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vylegzhanina, A.V.; Kogan, A.E.; Katrukha, I.A.; Koshkina, E.V.; Bereznikova, A.V.; Filatov, V.L.; Bloshchitsyna, M.N.; Bogomolova, A.P.; Katrukha, A.G. Full-Size and Partially Truncated Cardiac Troponin Complexes in the Blood of Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction. Clinical Chemistry 2019, 65, 882–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 18HLT10 CardioMet - Providing the measurement infrastructure to allow quantitative diagnostic methods for biomarkers of coronary heart diseases. Available online: https://www.ptb.de/empir2019/cardiomet/home/ (accessed on 11 August 2022).
- Paul, M.; Tannenberg, R.; Tscheuschner, G.; Ponader, M.; Weller, M.G. Cocaine Detection by a Laser-Induced Immunofluorometric Biosensor. Biosensors (Basel) 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, M.; Tscheuschner, G.; Herrmann, S.; Weller, M.G. Fast Detection of 2,4,6-Trinitrotoluene (TNT) at ppt Level by a Laser-Induced Immunofluorometric Biosensor. Biosensors (Basel) 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christenson, R.H.; Duh, S.H.; Apple, F.S.; Bodor, G.S.; Bunk, D.M.; Panteghini, M.; Welch, M.J.; Wu, A.H.; Kahn, S.E. Toward standardization of cardiac troponin I measurements part II: assessing commutability of candidate reference materials and harmonization of cardiac troponin I assays. Clinical Chemistry 2006, 52, 1685–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panteghini, M.; Bunk, D.M.; Christenson, R.H.; Katrukha, A.; Porter, R.A.; Schimmel, H.; Wang, L.; Tate, J.R.; I, I.W.G.o.S.o.T. Standardization of troponin I measurements: an update. Clinical Chemistry 2008, 46, 1501–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohmann, K.; Westerdorf, B.; Maytum, R.; Geeves, M.A.; Jaquet, K. Overexpression of human cardiac troponin in Escherichia coli: its purification and characterization. Protein Expr Purif 2001, 21, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straceski, A.J.; Nakouzi, A.S.; Malhotra, A. Expression of regulated cardiac troponin I in Escherichia coli. J Mol Cell Cardiol 1994, 26, 1565–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, T.; Vogtherr, M.; Elshorst, B.; Betz, M.; Schieborr, U.; Saxena, K.; Schwalbe, H. NMR backbone assignment of a protein kinase catalytic domain by a combination of several approaches: application to the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Chembiochem 2004, 5, 1508–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medix Biochemica: Anti-h cTnI 9707 SPTN-5. Available online: https://www.medixbiochemica.com/anti-h-ctni-9707-100180.html (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- Bayoumy, S.; Martiskainen, I.; Heikkila, T.; Rautanen, C.; Hedberg, P.; Hyytia, H.; Wittfooth, S.; Pettersson, K. Sensitive and quantitative detection of cardiac troponin I with upconverting nanoparticle lateral flow test with minimized interference. Scientific Reports 2021, 11, 18698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilke, M.; Röder, B.; Paul, M.; Weller, M. Sintered Glass Monoliths as Supports for Affinity Columns. Separations 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golovanov, A.P.; Hautbergue, G.M.; Wilson, S.A.; Lian, L.Y. A simple method for improving protein solubility and long-term stability. J Am Chem Soc 2004, 126, 8933–8939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troponins Booklet. Available online: https://hytest.fi/resources/technotes/cardiac-troponin-i-booklet (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- Roche, M.; Rondeau, P.; Singh, N.R.; Tarnus, E.; Bourdon, E. The antioxidant properties of serum albumin. FEBS Lett 2008, 582, 1783–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagababu, E.; Rifkind, J.M. Reaction of hydrogen peroxide with ferrylhemoglobin: superoxide production and heme degradation. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 12503–12511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taverna, M.; Marie, A.L.; Mira, J.P.; Guidet, B. Specific antioxidant properties of human serum albumin. Ann Intensive Care 2013, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apple, F.S.; Sandoval, Y.; Jaffe, A.S.; Ordonez-Llanos, J.; Bio-Markers, I.T.F.o.C.A.o.C. Cardiac Troponin Assays: Guide to Understanding Analytical Characteristics and Their Impact on Clinical Care. Clin Chem 2017, 63, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- High-Sensitivity* Cardiac Troponin I and T Assay Analytical Characteristics Designated by Manufacturer IFCC Committee on Clinical Applications of Cardiac Bio-Markers (C-CB) v012019. Available online: https://www.ifcc.org/media/477656/high-sensitivity-cardiac-troponin-i-and-t-assay-analytical-characteristics-designated-by-manufacturer-v012019.pdf (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- Lovgren, U.; Kronkvist, K.; Backstrom, B.; Edholm, L.E.; Johansson, G. Design of non-competitive flow injection enzyme immunoassays for determination of haptens: application to digoxigenin. J Immunol Methods 1997, 208, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, R.; Clavering, C.; Hutchinson, A. Electrochemiluminescence enzyme immunoassays for TNT and pentaerythritol tetranitrate. Anal Chem 2003, 75, 4244–4249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, J.P.; Vilaplana, L.; Marco, M.P. Nanobody: outstanding features for diagnostic and therapeutic applications. Anal Bioanal Chem 2019, 411, 1703–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liang, J.; Li, H.; Li, M.; Chen, L.; Dong, H.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Li, B.; Jiang, G.; et al. Immunosensor for rapid detection of human cardiac troponin I, a biomarker for myocardial infarction. Microchemical Journal 2022, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julian, M.C.; Li, L.; Garde, S.; Wilen, R.; Tessier, P.M. Efficient affinity maturation of antibody variable domains requires co-selection of compensatory mutations to maintain thermodynamic stability. Scientific Reports 2017, 7, 45259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanes, J.; Schaffitzel, C.; Knappik, A.; Pluckthun, A. Picomolar affinity antibodies from a fully synthetic naive library selected and evolved by ribosome display. Nat Biotechnol 2000, 18, 1287–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




