Submitted:
06 February 2023
Posted:
08 February 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Neuropeptides
2.1. Substance P (SP)
2.2. Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone (CRH)
2.3. Neurotensin (NT)
2.4. Anti-Inflammatory IL-37
2.5. IL-38 Dumping IL-1 Induced Inflammation
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Collington, S.J.; Westwick, J.; Williams, T.J.; Weller, C.L. The Function of CCR3 on Mouse Bone Marrow-Derived Mast Cells in Vitro. Immunology 2009, 129, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, K.; Nishiyama, C. IL-10 in Mast Cell-Mediated Immune Responses: Anti-Inflammatory and Proinflammatory Roles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2021, 22, 4972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eklund, K.K.; Ghildyal, N.; Austen, K.F.; Stevens, R.L. Induction by IL-9 and Suppression by IL-3 and IL-4 of the Levels of Chromosome 14-Derived Transcripts That Encode Late-Expressed Mouse Mast Cell Proteases. Journal of Immunology (Baltimore, Md.: 1950) 1993, 151, 4266–4273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theoharides, T.C. The Impact of Psychological Stress on Mast Cells. Annals of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology: Official Publication of the American College of Allergy, Asthma, & Immunology 2020, 125, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polyzoidis, S.; Koletsa, T.; Panagiotidou, S.; Ashkan, K.; Theoharides, T.C. Mast Cells in Meningiomas and Brain Inflammation. Journal of Neuroinflammation 2015, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammendola, M.; Sacco, R.; Sammarco, G.; Luposella, M.; Patruno, R.; Gadaleta, C.D.; De Sarro, G.; Ranieri, G. Mast Cell-Targeted Strategies in Cancer Therapy. Transfusion Medicine and Hemotherapy 2016, 43, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conti, P.; Caraffa, A.; Kritas, S.K.; Ronconi, G.; Lessiani, G.; Toniato, E.; Theoharides, T.C. Mast Cell, Pro-Inflammatory and Anti-Inflammatory: Jekyll and Hyde, the Story Continues. Journal of Biological Regulators and Homeostatic Agents 2017, 31, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- de Silva, M.C.; Reid, R. Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST): C-Kit Mutations, CD117 Expression, Differential Diagnosis and Targeted Cancer Therapy with Imatinib. Pathology Oncology Research 2003, 9, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, M.; Valent, P.; Galli, S.J. KIT as a Master Regulator of the Mast Cell Lineage. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2022, 149, 1845–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, W.; O’Donnell, M.; Lutgendorf, S.; Bradley, C.; Schrepf, A.; Liu, L.; Kreder, K.; Luo, Y. Evidence for the Role of Mast Cells in Cystitis-Associated Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction: A Multidisciplinary Approach to the Study of Chronic Pelvic Pain Research Network Animal Model Study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mencarelli, A.; Gunawan, M.; Yong, K.S.M.; Bist, P.; Tan, W.W.S.; Tan, S.Y.; Liu, M.; Huang, E.K.; Fan, Y.; Chan, J.K.Y.; et al. A Humanized Mouse Model to Study Mast Cells Mediated Cutaneous Adverse Drug Reactions. Journal of Leukocyte Biology 2020, 107, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Zuani, M.; Dal Secco, C.; Tonon, S.; Arzese, A.; Pucillo, C.E.M.; Frossi, B. LPS Guides Distinct Patterns of Training and Tolerance in Mast Cells. Frontiers in Immunology 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moñino-Romero, S.; Erkert, L.; Schmidthaler, K.; Diesner, S.C.; Sallis, B.F.; Pennington, L.; Jardetzky, T.; Oettgen, H.C.; Bohle, B.; Fiebiger, E.; et al. The Soluble Isoform of Human FcɛRI Is an Endogenous Inhibitor of IgE-Mediated Mast Cell Responses. Allergy 2018, 74, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabban, S.; Ye, H.; Helm, B. Development of an in Vitro Model System for Studying the Interaction of Equus Caballus IgE with Its High-Affinity Receptor FcɛRI. Veterinary Immunology and Immunopathology 2013, 153, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asai, K.; Fujimoto, K.; Harazaki, M.; Kusunoki, T.; Korematsu, S.; Ide, C.; Ra, C.; Hosoi, S. Distinct Aggregation of β- and γ-Chains of the High-Affinity IgE Receptor on Cross-Linking. Journal of Histochemistry & Cytochemistry 2000, 48, 1705–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komi, D.E.A.; Mortaz, E.; Amani, S.; Tiotiu, A.; Folkerts, G.; Adcock, I.M. The Role of Mast Cells in IgE-Independent Lung Diseases. Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology 2020, 58, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yip, K.H.; Kolesnikoff, N.; Hauschild, N.; Biggs, L.; Lopez, A.F.; Galli, S.J.; Kumar, S.; Grimbaldeston, M.A. The Nedd4-2/Ndfip1 Axis Is a Negative Regulator of IgE-Mediated Mast Cell Activation. Nature Communications 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitroulis, I.; Alexaki, V.I.; Kourtzelis, I.; Ziogas, A.; Hajishengallis, G.; Chavakis, T. Leukocyte Integrins: Role in Leukocyte Recruitment and as Therapeutic Targets in Inflammatory Disease. Pharmacology & therapeutics 2015, 147, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wing, Michele R.; Sondek, J.; Harden, T. Kendall Molecular Cloning and Characterization of PLC‐η2. Biochemical Journal, 2005; 391, 667–676. [CrossRef]
- Johnson, G.L. Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Pathways Mediated by ERK, JNK, and P38 Protein Kinases. Science 2002, 298, 1911–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roux, P.P.; Blenis, J. ERK and P38 MAPK-Activated Protein Kinases: A Family of Protein Kinases with Diverse Biological Functions. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews 2004, 68, 320–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, L.; Fergusson, J.; Salimi, M.; Panse, I.; Ussher, J.E.; Hegazy, A.N.; Vinall, S.L.; Jackson, D.G.; Hunter, M.G.; Pettipher, R.; et al. Prostaglandin D2 and Leukotriene E4 Synergize to Stimulate Diverse TH2 Functions and TH2 Cell/Neutrophil Crosstalk. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2015, 135, 1358–1366e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricciotti, E.; FitzGerald, G.A. Prostaglandins and Inflammation. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology 2011, 31, 986–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arima, M.; Fukuda, T. Prostaglandin D2and TH2 Inflammation in the Pathogenesis of Bronchial Asthma. The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine 2011, 26, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peinhaupt, M.; Sturm, E.M.; Heinemann, A. Prostaglandins and Their Receptors in Eosinophil Function and as Therapeutic Targets. Frontiers in Medicine 2017, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazarinis, N.; Bood, J.; Gomez, C.; Kolmert, J.; Lantz, A.-S.; Gyllfors, P.; Davis, A.; Wheelock, C.E.; Dahlén, S.-E.; Dahlén, B. Leukotriene E4 Induces Airflow Obstruction and Mast Cell Activation through the Cysteinyl Leukotriene Type 1 Receptor. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2018, 142, 1080–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iskarpatyoti, J.A.; Shi, J.; Abraham, M.A.; Rathore, A.P.S.; Miao, Y.; Abraham, S.N. Mast Cell Regranulation Requires a Metabolic Switch Involving MTORC1 and a Glucose-6-Phosphate Transporter. Cell Reports 2022, 40, 111346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.-M.; Kim, Y.-M.; Lee, Y.M.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, J.D.; Choi, Y.; Kim, K.-W.; Lee, S.-Y.; Kwon, Y.-G. TNF-Related Activation-Induced Cytokine (TRANCE) Induces Angiogenesis through the Activation of Src and Phospholipase c (PLC) in Human Endothelial Cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2002, 277, 6799–6805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukai, K.; Tsai, M.; Saito, H.; Galli, S.J. Mast Cells as Sources of Cytokines, Chemokines, and Growth Factors. Immunological Reviews 2018, 282, 121–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
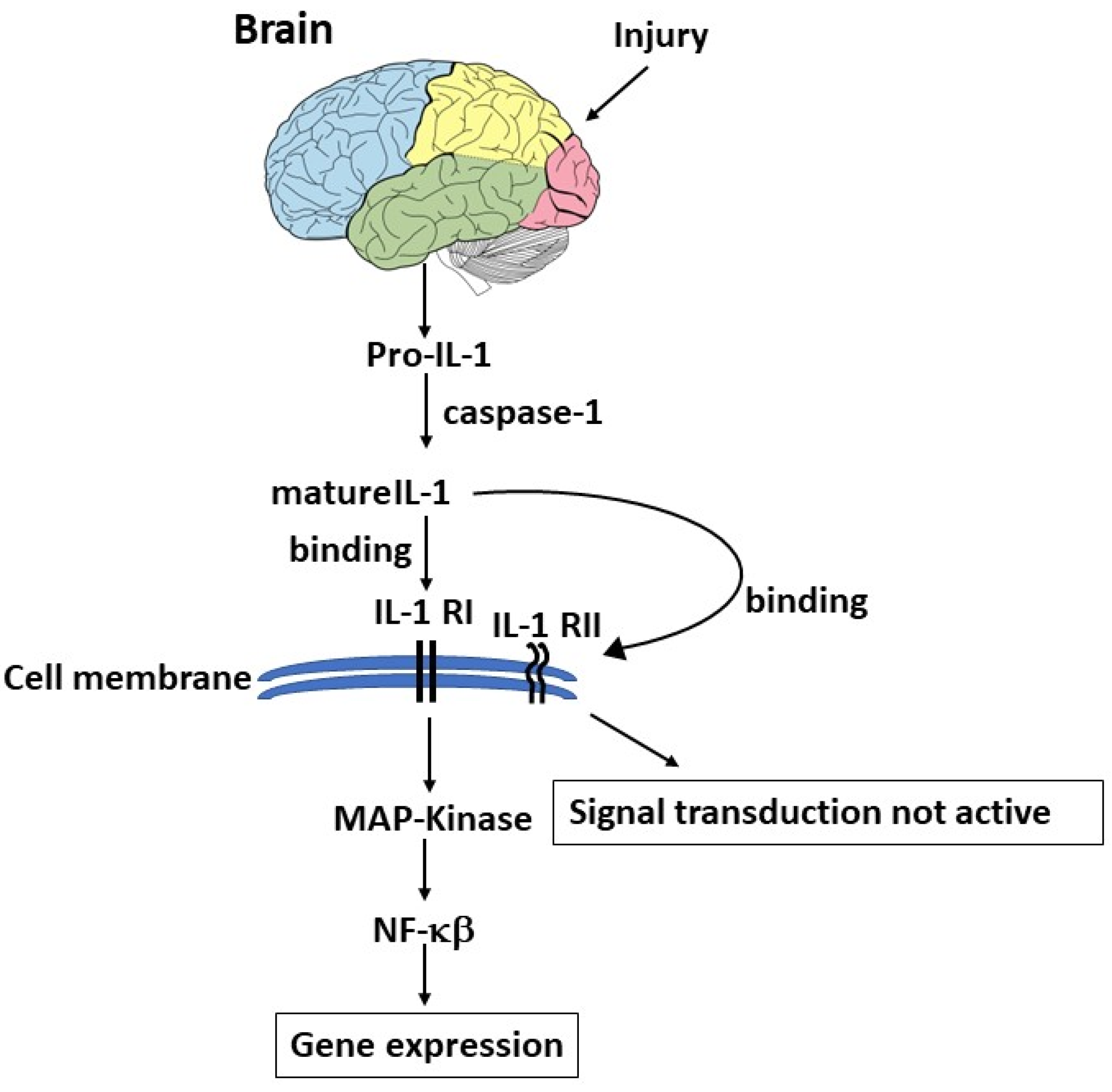
- Cartmell, T.; Luheshi, G.N.; Rothwell, N.J. Brain Sites of Action of Endogenous Interleukin-1 in the Febrile Response to Localized Inflammation in the Rat. The Journal of Physiology 1999, 518, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashaghi, A.; Marmalidou, A.; Tehrani, M.; Grace, P.M.; Pothoulakis, C.; Dana, R. Neuropeptide Substance P and the Immune Response. Cellular and molecular life sciences : CMLS 2016, 73, 4249–4264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oleszycka, E.; Kwiecien, K.; Kwiecinska, P.; Morytko, A.; Pocalun, N.; Camacho, M.; Brzoza, P.; Zabel, B.A.; Cichy, J. Soluble Mediators in the Function of the Epidermal-Immune-Neuro Unit in the Skin. Frontiers in Immunology 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.L.; Knight, Z.A. Regulation of Body Temperature by the Nervous System. Neuron 2018, 98, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsilioni, I.; Russell, I.J.; Stewart, J.M.; Gleason, R.M.; Theoharides, T.C. Neuropeptides CRH, SP, HK-1, and Inflammatory Cytokines IL-6 and TNF Are Increased in Serum of Patients with Fibromyalgia Syndrome, Implicating Mast Cells. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 2016, 356, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, B.; Peng, Y.; Zhong, C.; Cai, Y.; Zhou, S.; Chen, H.; Zhuang, J.; Zeng, H.; Xu, C.; Xu, H.; et al. Mast Cells Mediate Inflammatory Injury and Aggravate Neurological Impairment in Experimental Subarachnoid Hemorrhage through Microglial PAR-2 Pathway. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience 2021, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedict, C.; Scheller, J.; Rose-John, S.; Born, J.; Marshall, L. Enhancing Influence of Intranasal Interleukin-6 on Slowwave Activity and Memory Consolidation during Sleep. The FASEB Journal 2009, 23, 3629–3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijay, K. Toll-like Receptors in Immunity and Inflammatory Diseases: Past, Present, and Future. International Immunopharmacology 2018, 59, 391–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blomqvist, A.; Engblom, D. Neural Mechanisms of Inflammation-Induced Fever. The Neuroscientist 2018, 24, 381–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurney, J.G.; McPheeters, M.L.; Davis, M.M. Parental Report of Health Conditions and Health Care Use among Children with and without Autism. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine 2006, 160, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.M.; Leeman, S.E. Isolation of a Sialogogic Peptide from Bovine Hypothalamic Tissue and Its Characterization as Substance P. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 1970, 245, 4784–4790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theoharides, T.C.; Zhang, B.; Kempuraj, D.; Tagen, M.; Vasiadi, M.; Angelidou, A.; Alysandratos, K.-D.; Kalogeromitros, D.; Asadi, S.; Stavrianeas, N.; et al. IL-33 Augments Substance P–Induced VEGF Secretion from Human Mast Cells and Is Increased in Psoriatic Skin. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2010, 107, 4448–4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taracanova, A.; Tsilioni, I.; Conti, P.; Norwitz, E.R.; Leeman, S.E.; Theoharides, T.C. Substance P and IL-33 Administered Together Stimulate a Marked Secretion of IL-1β from Human Mast Cells, Inhibited by Methoxyluteolin. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2018, 115, E9381–E9390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinhoff, M.S.; von Mentzer, B.; Geppetti, P.; Pothoulakis, C.; Bunnett, N.W. Tachykinins and Their Receptors: Contributions to Physiological Control and the Mechanisms of Disease. Physiological Reviews 2014, 94, 265–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campo, A.; Lafont, A.-G.; Lefranc, B.; Leprince, J.; Tostivint, H.; Kamech, N.; Dufour, S.; Rousseau, K. Tachykinin-3 Genes and Peptides Characterized in a Basal Teleost, the European Eel: Evolutionary Perspective and Pituitary Role. Frontiers in Endocrinology 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, F.M.; Seda, M.; Candenas, L. Neurokinin B. xPharm: The Comprehensive Pharmacology Reference 2007, 1–4. [CrossRef]
- Conti, P.; Pregliasco, F.E.; Bellomo, R.G.; Gallenga, C.E.; Caraffa, A.; Kritas, S.K.; Lauritano, D.; Ronconi, G. Mast Cell Cytokines IL-1, IL-33, and IL-36 Mediate Skin Inflammation in Psoriasis: A Novel Therapeutic Approach with the Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines IL-37, IL-38, and IL-1Ra. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2021, 22, 8076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minnone, G.; De Benedetti, F.; Bracci-Laudiero, L. NGF and Its Receptors in the Regulation of Inflammatory Response. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2017, 18, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Kleij, H.P.M.; Ma, D.; Redegeld, F.A.M.; Kraneveld, A.D.; Nijkamp, F.P.; Bienenstock, J. Functional Expression of Neurokinin 1 Receptors on Mast Cells Induced by IL-4 and Stem Cell Factor. The Journal of Immunology 2003, 171, 2074–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.; Liu, T. Hypothalamic Inflammation: A Double-Edged Sword to Nutritional Diseases. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 2011, 1243, E1–E39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theoharides, T.C.; Alysandratos, K.-D.; Angelidou, A.; Delivanis, D.-A.; Sismanopoulos, N.; Zhang, B.; Asadi, S.; Vasiadi, M.; Weng, Z.; Miniati, A.; et al. Mast Cells and Inflammation. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 2012, 1822, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieglgänsberger, W. Substance P and Pain Chronicity. Cell and Tissue Research 2019, 375, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montana, G.; Lampiasi, N. Substance P Induces HO-1 Expression in RAW 264. 7 Cells Promoting Switch towards M2-like Macrophages. PLOS ONE 2016, 11, e0167420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Shi, X.; Li, X.; Zou, J.; Zhou, C.; Liu, W.; Shao, H.; Chen, H.; Shi, L. Neurotransmitter and Neuropeptide Regulation of Mast Cell Function: A Systematic Review. Journal of Neuroinflammation 2020, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traina, G. The Role of Mast Cells in the Gut and Brain. Journal of Integrative Neuroscience 2021, 20, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franke, K.; Wang, Z.; Zuberbier, T.; Babina, M. Cytokines Stimulated by IL-33 in Human Skin Mast Cells: Involvement of NF-ΚB and P38 at Distinct Levels and Potent Co-Operation with FcεRI and MRGPRX2. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2021, 22, 3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eissmann, M.F.; Buchert, M.; Ernst, M. IL33 and Mast Cells—the Key Regulators of Immune Responses in Gastrointestinal Cancers? Frontiers in Immunology 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taracanova, A.; Alevizos, M.; Karagkouni, A.; Weng, Z.; Norwitz, E.; Conti, P.; Leeman, S.E.; Theoharides, T.C. SP and IL-33 Together Markedly Enhance TNF Synthesis and Secretion from Human Mast Cells Mediated by the Interaction of Their Receptors. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2017, 114, E4002–E4009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murdaca, G.; Greco, M.; Tonacci, A.; Negrini, S.; Borro, M.; Puppo, F.; Gangemi, S. IL-33/IL-31 Axis in Immune-Mediated and Allergic Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2019, 20, 5856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
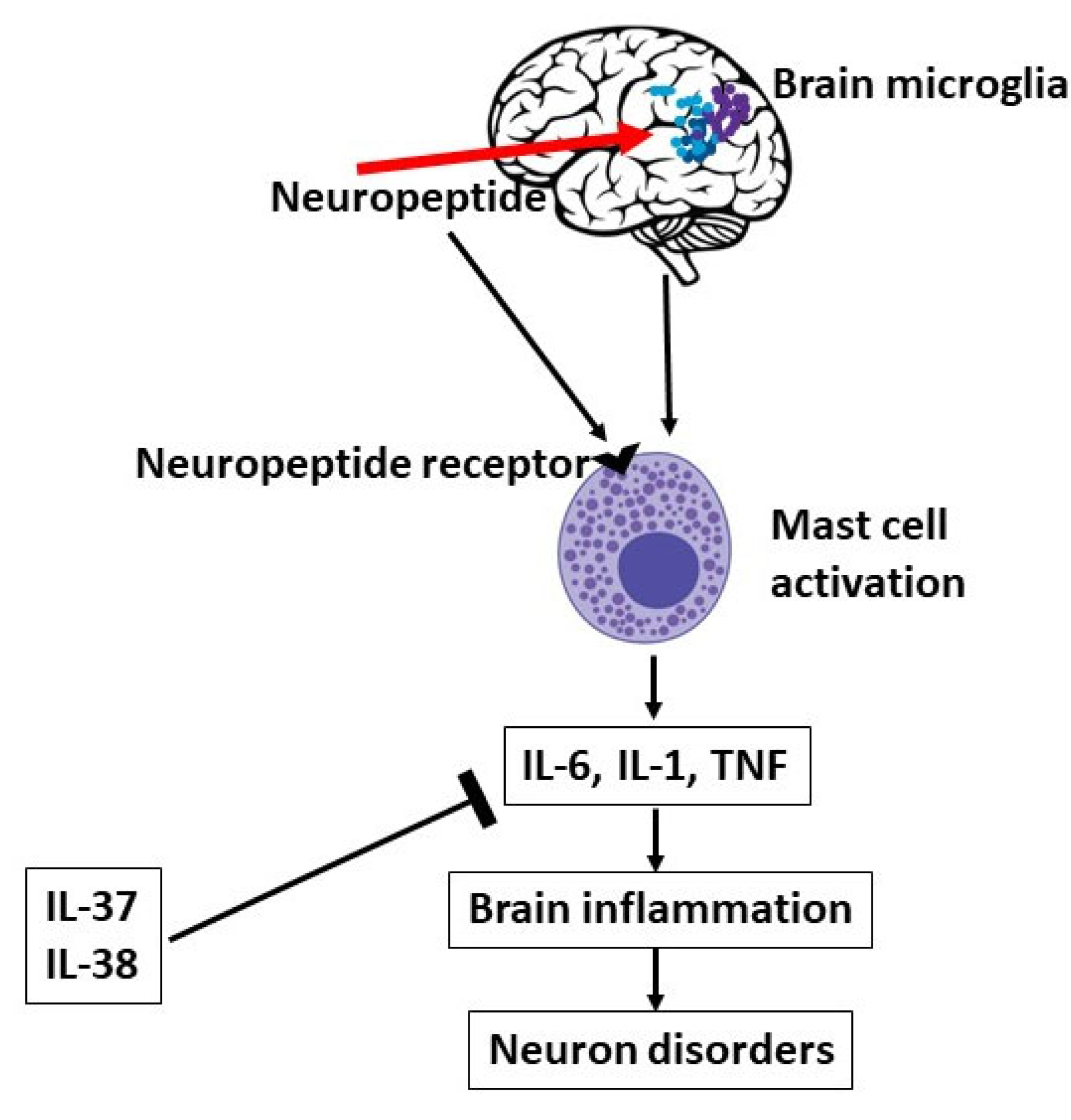
- Carniglia, L.; Ramírez, D.; Durand, D.; Saba, J.; Turati, J.; Caruso, C.; Scimonelli, T.N.; Lasaga, M. Neuropeptides and Microglial Activation in Inflammation, Pain, and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Mediators of Inflammation 2017, 2017, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theoharides, T.C.; Tsilioni, I.; Bawazeer, M. Mast Cells, Neuroinflammation and Pain in Fibromyalgia Syndrome. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience 2019, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzer, P. Local Effector Functions of Capsaicin-Sensitive Sensory Nerve Endings: Involvement of Tachykinins, Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide and Other Neuropeptides. Neuroscience 1988, 24, 739–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eglezos, A.; Giuliani, S.; Viti, G.; Maggi, C.A. Direct Evidence That Capsaicin-Induced Plasma Protein Extravasation Is Mediated through Tachykinin NK1 Receptors. European Journal of Pharmacology 1991, 209, 277–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicoletti, M.; Neri, G.; Maccauro, G.; Tripodi, D.; Varvara, G.; Saggini, A.; Potalivo, G.; Castellani, M.L.; Fulcheri, M.; Rosati, M.; et al. Impact and Neuropeptide Substance Pan Inflammatory Compound on Arachidonic Acid Compound Generation. International Journal of Immunopathology and Pharmacology 2012, 25, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maletic, V.; Raison, C. Integrated Neurobiology of Bipolar Disorder. Frontiers in Psychiatry 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okayama, Y.; Church, M.K. Comparison of the Modulatory Effect of Ketotifen, Sodium Cromoglycate, Procaterol and Salbutamol in Human Skin, Lung and Tonsil Mast Cells. International Archives of Allergy and Immunology 1992, 97, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, G.W. NEURAL CONTROL of the PITUITARY GLAND. Physiological Reviews 1948, 28, 139–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacak, K.; Palkovits, M.; Kopin, I.J.; Goldstein, D.S. Stress-Induced Norepinephrine Release in the Hypothalamic Paraventricular Nucleus and Pituitary-Adrenocortical and Sympathoadrenal Activity: In Vivo Microdialysis Studies. Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology 1995, 16, 89–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrońska, D.; Kania, B.F.; Błachuta, M. Direct Effect of Hypothalamic Neuropeptides on the Release of Catecholamines by Adrenal Medulla in Sheep – Study Ex Vivo. Polish Journal of Veterinary Sciences 2017, 20, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, M.A.; Carson, M.J.; Nair, M.G. Non-Traditional Cytokines: How Catecholamines and Adipokines Influence Macrophages in Immunity, Metabolism and the Central Nervous System. Cytokine 2015, 72, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kany, S.; Vollrath, J.T.; Relja, B. Cytokines in Inflammatory Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2019, 20, 6008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Lewis, K.A.; Perrin, M.H.; Vale, W.W. Expression Cloning of a Human Corticotropin-Releasing-Factor Receptor. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 1993, 90, 8967–8971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovenberg, T.W.; Liaw, C.W.; Grigoriadis, D.E.; Clevenger, W.; Chalmers, D.T.; De Souza, E.B.; Oltersdorf, T. Cloning and Characterization of a Functionally Distinct Corticotropin-Releasing Factor Receptor Subtype from Rat Brain. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 1995, 92, 836–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovenberg, T.W.; Chalmers, D.T.; Liu, C.; De Souza, E.B. CRF2 Alpha and CRF2 Beta Receptor MRNAs Are Differentially Distributed between the Rat Central Nervous System and Peripheral Tissues. Endocrinology 1995, 136, 4139–4142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vale, W.; Spiess, J.; Rivier, C.; Rivier, J. Characterization of a 41-Residue Ovine Hypothalamic Peptide That Stimulates Secretion of Corticotropin and Beta-Endorphin. Science (New York, N.Y.) 1981, 213, 1394–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, M.J.; Sharma, S. Physiology, Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH) Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK500031/.
- Miller, T.; Gibbison, B.; Russell, G.M. Hypothalamic–Pituitary–Adrenal Function during Health, Major Surgery, and Critical Illness. BJA Education 2017, 17, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, M.N.; Pearce, B.D.; Biron, C.A.; Miller, A.H. Immune Modulation of the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal (HPA) Axis during Viral Infection. Viral Immunology 2005, 18, 41–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wamsteeker Cusulin, J.I.; Füzesi, T.; Watts, A.G.; Bains, J.S. Characterization of Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone Neurons in the Paraventricular Nucleus of the Hypothalamus of Crh-IRES-Cre Mutant Mice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, A.V.; Latchford, K.J.; Samson, W.K. The Paraventricular Nucleus of the Hypothalamus – a Potential Target for Integrative Treatment of Autonomic Dysfunction. Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Targets 2008, 12, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emeric-Sauval, E. Corticotropin-Releasing Factor (CRF) — a Review. Psychoneuroendocrinology 1986, 11, 277–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OELKERS, W.; BOELKE, T.; BÄHR, V.; EXNER, P.; FAUST, B.; HARENDT, H. Dose-Response Relationships between Plasma Adrenocorticotropin (ACTH), Cortisol, Aldosterone, and 18-Hydroxycorticosterone after Injection of ACTH-(1–39) or Human Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone in Man*. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 1988, 66, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCann, S.M.; Antunes-Rodrigues, J.; Franci, C.R.; Anselmo-Franci, J.A.; Karanth, S.; Rettori, V. Role of the Hypothalamic Pituitary Adrenal Axis in the Control of the Response to Stress and Infection. Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research 2000, 33, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieseler-Frank, J.; Jekich, B.M.; Mahoney, J.H.; Bland, S.T.; Maier, S.F.; Watkins, L.R. A Novel Immune-To-CNS Communication Pathway: Cells of the Meninges Surrounding the Spinal Cord CSF Space Produce Proinflammatory Cytokines in Response to an Inflammatory Stimulus. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity 2007, 21, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuoka, H.; Shichi, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Takahashi, Y. The Mechanisms Underlying Autonomous Adrenocorticotropic Hormone Secretion in Cushing’s Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2020, 21, 9132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Lu, M.; Yuan, H.; Chen, T.; Han, X. Mast Cell-Mediated Neuroinflammation May Have a Role in Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (Review). Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine 2020, 20, 714–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DESIMONE, R. Nerve Growth Factor Released into the Bloodstream Following Intraspecific Fighting Induces Mast Cell Degranulation in Adult Male Mice. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity 1990, 4, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theoharides, T.C.; Kempuraj, D.; Marchand, J.; Tzianoumis, L.; Vasiadi, M.; Katsarou-Katsari, A.; Makris, M.; Kalogeromitros, D. Urticaria Pigmentosa Associated with Acute Stress and Lesional Skin Mast-Cell Expression of CRF-R1. Clinical and Experimental Dermatology 2009, 34, e163–e166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Dong, H.-Q.; Liu, Y.-H.; Ji, M.-H.; Zhang, X.; Dai, H.-Y.; Sun, Z.-C.; Liu, L.; Zhou, J.; Sha, H.-H.; et al. Laparotomy-Induced Peripheral Inflammation Activates NR2B Receptors on the Brain Mast Cells and Results in Neuroinflammation in a Vagus Nerve-Dependent Manner. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience 2022, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, I.; Inoue, Y.; Shimada, T.; Aikawa, T. Brain Mast Cells Act as an Immune Gate to the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis in Dogs. Journal of Experimental Medicine 2001, 194, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Papadopoulou, N.; Kempuraj, D.; Boucher, W.S.; Sugimoto, K.; Cetrulo, C.L.; Theoharides, T.C. Human Mast Cells Express Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone (CRH) Receptors and CRH Leads to Selective Secretion of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor. The Journal of Immunology 2005, 174, 7665–7675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Majid, R.M.; Marshall, J.S. Prostaglandin E2 Induces Degranulation-Independent Production of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor by Human Mast Cells. The Journal of Immunology 2004, 172, 1227–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeman, S.E.; Mroz, E.A. Substance P. Life Sciences 1974, 15, 2033–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
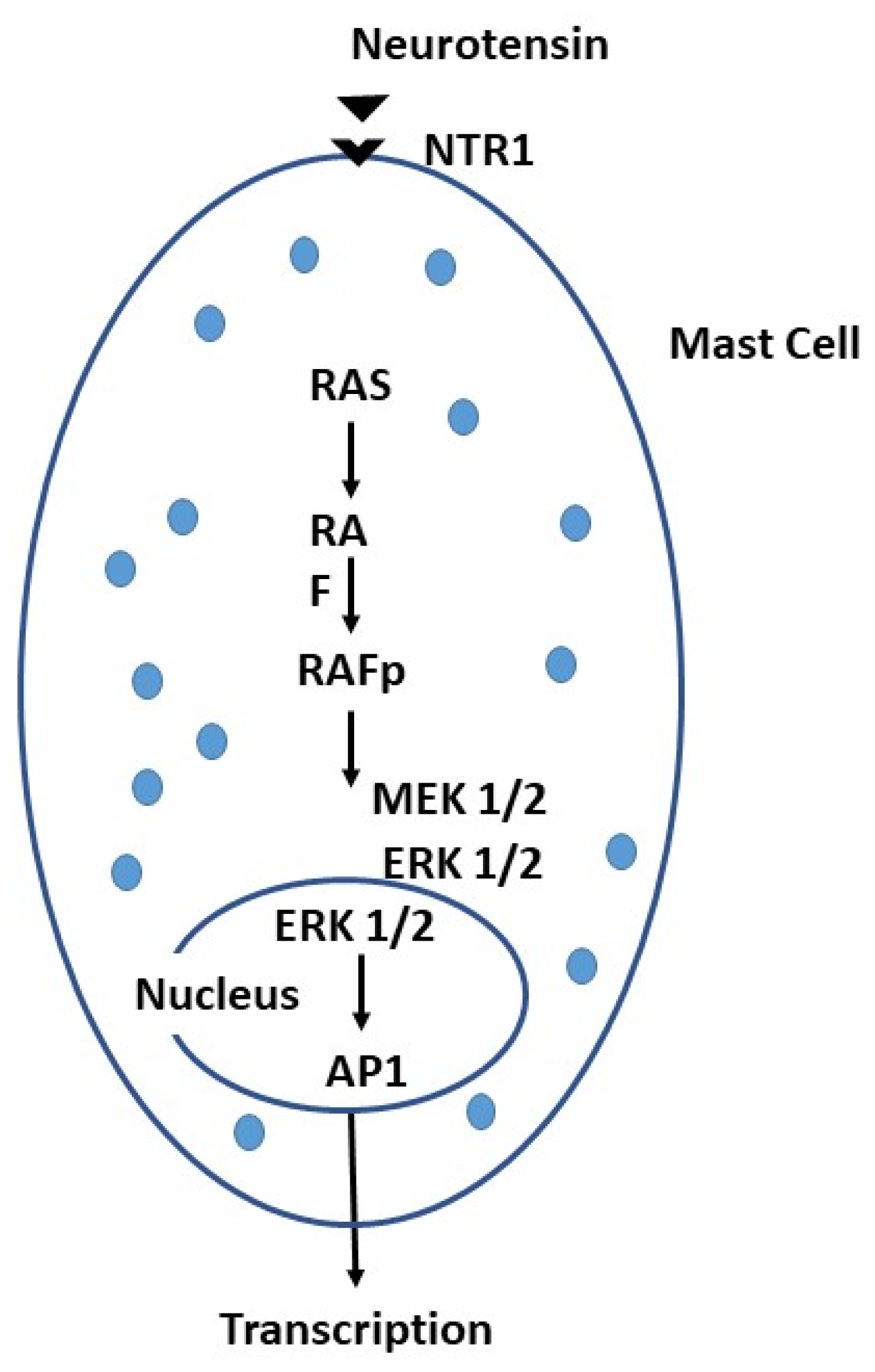
- Christou, N.; Blondy, S.; David, V.; Verdier, M.; Lalloué, F.; Jauberteau, M.-O.; Mathonnet, M.; Perraud, A. Neurotensin Pathway in Digestive Cancers and Clinical Applications: An Overview. Cell Death & Disease 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Martinez-Fong, D.; Trédaniel, J.; Forgez, P. Neurotensin and Its High Affinity Receptor 1 as a Potential Pharmacological Target in Cancer Therapy. Frontiers in Endocrinology 2013, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, L.E.; Leinninger, G.M. Role of Central Neurotensin in Regulating Feeding: Implications for the Development and Treatment of Body Weight Disorders. Biochimica et biophysica acta 2018, 1864, 900–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- St-Gelais, F.; Jomphe, C.; Trudeau, L.-É. The Role of Neurotensin in Central Nervous System Pathophysiology: What Is the Evidence? Journal of Psychiatry and Neuroscience 2006, 31, 229–245. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Servonnet, A.; Minogianis, E.-A.; Bouchard, C.; Bédard, A.-M.; Lévesque, D.; Rompré, P.-P.; Samaha, A.-N. Neurotensin in the Nucleus Accumbens Reverses Dopamine Supersensitivity Evoked by Antipsychotic Treatment. Neuropharmacology 2017, 123, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuladhar, A.M.; de Leeuw, F.-E. Thalamus: A Key Player in Alcohol Use Disorder and Korsakoff’s Syndrome. Brain 2019, 142, 1170–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carabotti, M.; Scirocco, A.; Maselli, M.A.; Severi, C. The Gut-Brain Axis: Interactions between Enteric Microbiota, Central and Enteric Nervous Systems. Annals of gastroenterology 2015, 28, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boules, M.; Li, Z.; Smith, K.; Fredrickson, P.; Richelson, E. Diverse Roles of Neurotensin Agonists in the Central Nervous System. Frontiers in Endocrinology 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theoharides, T.C.; Kempuraj, D.; Tagen, M.; Conti, P.; Kalogeromitros, D. Differential Release of Mast Cell Mediators and the Pathogenesis of Inflammation. Immunological Reviews 2007, 217, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustain, W.C.; Rychahou, P.G.; Evers, B.M. The Role of Neurotensin in Physiologic and Pathologic Processes. Current Opinion in Endocrinology, Diabetes & Obesity 2011, 18, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Asadi, S.; Weng, Z.; Sismanopoulos, N.; Theoharides, T.C. Stimulated Human Mast Cells Secrete Mitochondrial Components That Have Autocrine and Paracrine Inflammatory Actions. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsilioni, I.; Patel, A.B.; Pantazopoulos, H.; Berretta, S.; Conti, P.; Leeman, S.E.; Theoharides, T.C. IL-37 Is Increased in Brains of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder and Inhibits Human Microglia Stimulated by Neurotensin. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2019, 116, 21659–21665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.-M.; An, J. Cytokines, Inflammation, and Pain. International Anesthesiology Clinics 2007, 45, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrea Predonzani, B.C.; Andrielly HR Agnellini, B.M. Spotlights on Immunological Effects of Reactive Nitrogen Species: When Inflammation Says Nitric Oxide. World Journal of Experimental Medicine 2015, 5, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wink, D.A.; Hines, H.B.; Cheng, R.Y.S.; Switzer, C.H.; Flores-Santana, W.; Vitek, M.P.; Ridnour, L.A.; Colton, C.A. Nitric Oxide and Redox Mechanisms in the Immune Response. Journal of Leukocyte Biology 2011, 89, 873–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theoharides, T.C.; Stewart, J.M.; Taracanova, A.; Conti, P.; Zouboulis, C.C. Neuroendocrinology of the Skin. Reviews in Endocrine & Metabolic Disorders 2016, 17, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marek-Jozefowicz, L.; Czajkowski, R.; Borkowska, A.; Nedoszytko, B.; Żmijewski, M.A.; Cubała, W.J.; Slominski, A.T. The Brain–Skin Axis in Psoriasis—Psychological, Psychiatric, Hormonal, and Dermatological Aspects. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2022, 23, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redegeld, F.A.; Yu, Y.; Kumari, S.; Charles, N.; Blank, U. Non-IgE Mediated Mast Cell Activation. Immunological Reviews 2018, 282, 87–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, A.; Lal, G. Neurokinin Receptors and Their Implications in Various Autoimmune Diseases. Current Research in Immunology 2021, 2, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulenwider, H.D.; Smith, B.M.; Nichenko, A.S.; Carpenter, J.M.; Nennig, S.E.; Cheng, K.; Rice, K.C.; Schank, J.R. Cellular and Behavioral Effects of Lipopolysaccharide Treatment Are Dependent upon Neurokinin-1 Receptor Activation. Journal of Neuroinflammation 2018, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aich, A.; Afrin, L.B.; Gupta, K. Mast Cell-Mediated Mechanisms of Nociception. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2015, 16, 29069–29092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Fonseca, A.C.C.; Matias, D.; Garcia, C.; Amaral, R.; Geraldo, L.H.; Freitas, C.; Lima, F.R.S. The Impact of Microglial Activation on Blood-Brain Barrier in Brain Diseases. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience 2014, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damsker, J.M.; Hansen, A.M.; Caspi, R.R. Th1 and Th17 Cells. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 2010, 1183, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.B.; Tsilioni, I.; Leeman, S.E.; Theoharides, T.C. Neurotensin Stimulates Sortilin and MTOR in Human Microglia Inhibitable by Methoxyluteolin, a Potential Therapeutic Target for Autism. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2016, 113, E7049–E7058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Mu, R.; Wei, X. The Roles of IL-1 Family Cytokines in the Pathogenesis of Systemic Sclerosis. Frontiers in Immunology 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutet, M.-A.; Nerviani, A.; Pitzalis, C. IL-36, IL-37, and IL-38 Cytokines in Skin and Joint Inflammation: A Comprehensive Review of Their Therapeutic Potential. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2019, 20, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Li, Y.; Guo, C.; Wang, L.; Chu, H.; Zhu, F.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, W.; et al. IL-37 Isoform D Downregulates Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Expression in a Smad3-Dependent Manner. Cell Death & Disease 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Amo-Aparicio, J.; Neff, C.P.; Tengesdal, I.W.; Azam, T.; Palmer, B.E.; López-Vales, R.; Bufler, P.; Dinarello, C.A. Role for Nuclear Interleukin-37 in the Suppression of Innate Immunity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2019, 116, 4456–4461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nold-Petry, C.A.; Lo, C.Y.; Rudloff, I.; Elgass, K.D.; Li, S.; Gantier, M.P.; Lotz-Havla, A.S.; Gersting, S.W.; Cho, S.X.; Lao, J.C.; et al. IL-37 Requires the Receptors IL-18Rα and IL-1R8 (SIGIRR) to Carry out Its Multifaceted Anti-Inflammatory Program upon Innate Signal Transduction. Nature Immunology 2015, 16, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parihar, A.; Eubank, T.D.; Doseff, A.I. Monocytes and Macrophages Regulate Immunity through Dynamic Networks of Survival and Cell Death. Journal of Innate Immunity 2010, 2, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Tao, X. Current Understanding of IL-37 in Human Health and Disease. Frontiers in Immunology 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, X.; Wei-min, L.; Tong, Y.; Dong, N.; Sheng, Z.; Yao, Y. Expression of IL-37 Contributes to the Immunosuppressive Property of Human CD4+CD25+ Regulatory T Cells. Scientific Reports 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonnemann, N.; Hosseini, S.; Ohm, M.; Geffers, R.; Hiller, K.; Dinarello, C.A.; Korte, M. IL-37 Expression Reduces Acute and Chronic Neuroinflammation and Rescues Cognitive Impairment in an Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Model. eLife 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, S.; Li, L.; Huang, Z.; Ma, K. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of IL-37-Producing T-Cell Population in DSS-Induced Chronic Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2018, 19, 3884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinarello, C.A.; Nold-Petry, C.; Nold, M.; Fujita, M.; Li, S.; Kim, S.; Bufler, P. Suppression of Innate Inflammation and Immunity by Interleukin-37. European Journal of Immunology 2016, 46, 1067–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, G.; Tengesdal, I.W.; Gresnigt, M.; Nemkov, T.; Arts, R.J.W.; Domínguez-Andrés, J.; Molteni, R.; Stefanoni, D.; Cantoni, E.; Cassina, L.; et al. The Anti-Inflammatory Cytokine Interleukin-37 Is an Inhibitor of Trained Immunity. Cell Reports 2021, 35, 108955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Neff, C.P.; Barber, K.; Hong, J.; Luo, Y.; Azam, T.; Palmer, B.E.; Fujita, M.; Garlanda, C.; Mantovani, A.; et al. Extracellular Forms of IL-37 Inhibit Innate Inflammation in Vitro and in Vivo but Require the IL-1 Family Decoy Receptor IL-1R8. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2015, 112, 2497–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.-T.; Zhu, D.; Mou, T.; Guo, Z.; Pu, J.-L.; Chen, Q.-S.; Wei, X.-F.; Wu, Z.-J. IL-37 Induces Autophagy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells by Inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/MTOR Pathway. Molecular Immunology 2017, 87, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.R.; Nold, M.F.; Tang, S.-C.; Bui, C.B.; Nold, C.A.; Arumugam, T.V.; Drummond, G.R.; Sobey, C.G.; Kim, H.A. IL-37 Increases in Patients after Ischemic Stroke and Protects from Inflammatory Brain Injury, Motor Impairment and Lung Infection in Mice. Scientific Reports 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCurdy, S.; Liu, C.A.; Yap, J.; Boisvert, W.A. Potential Role of IL-37 in Atherosclerosis. Cytokine 2019, 122, 154169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Tan, S.; Wu, D. IL-37 as a Potential Biotherapeutics of Inflammatory Diseases. Current Drug Targets 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Quan, N. Microglia and CNS Interleukin-1: Beyond Immunological Concepts. Frontiers in Neurology 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pringle, A.K.; Gardner, C.R.; Walker, R.J. Reduction of Cerebellar GABAA Responses by Interleukin-1 (IL-1) through an Indomethacin Insensitive Mechanism. Neuropharmacology 1996, 35, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, P.; Goldstein, J.D.; Mermoud, L.; Diaz-Barreiro, A.; Palmer, G. IL-1 Family Antagonists in Mouse and Human Skin Inflammation. Frontiers in Immunology 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeilzadeh, A.; Bahmaie, N.; Nouri, E.; Hajkazemi, M.J.; Zareh Rafie, M. Immunobiological Properties and Clinical Applications of Interleukin-38 for Immune-Mediated Disorders: A Systematic Review Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2021, 22, 12552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; Peng, X.; Li, Y.; Li, M. Role of IL-38 and Its Related Cytokines in Inflammation. Mediators of Inflammation 2015, 2015, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Huang, Z.; Li, H.; Liu, X.; Zheng, S.; Su, W. IL-38: A New Player in Inflammatory Autoimmune Disorders. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.-D.; Huang, A.-F. Role of Interleukin-38 in Chronic Inflammatory Diseases: A Comprehensive Review. Frontiers in Immunology 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Veerdonk, F.L.; Stoeckman, A.K.; Wu, G.; Boeckermann, A.N.; Azam, T.; Netea, M.G.; Joosten, L.A.B.; van der Meer, J.W.M.; Hao, R.; Kalabokis, V.; et al. IL-38 Binds to the IL-36 Receptor and Has Biological Effects on Immune Cells Similar to IL-36 Receptor Antagonist. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2012, 109, 3001–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brevi, A.; Cogrossi, L.L.; Grazia, G.; Masciovecchio, D.; Impellizzieri, D.; Lacanfora, L.; Grioni, M.; Bellone, M. Much More than IL-17A: Cytokines of the IL-17 Family between Microbiota and Cancer. Frontiers in Immunology 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waisman, A.; Hauptmann, J.; Regen, T. The Role of IL-17 in CNS Diseases. Acta Neuropathologica 2015, 129, 625–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelderblom, M.; Weymar, A.; Bernreuther, C.; Velden, J.; Arunachalam, P.; Steinbach, K.; Orthey, E.; Arumugam, T.V.; Leypoldt, F.; Simova, O.; et al. Neutralization of the IL-17 Axis Diminishes Neutrophil Invasion and Protects from Ischemic Stroke. Blood 2012, 120, 3793–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichols, J.R.; Aldrich, A.L.; Mariani, M.M.; Vidlak, D.; Esen, N.; Kielian, T. Toll-like Receptor 2 (TLR2) Deficiency Leads to Increased Th17 Infiltrates in Experimental Brain Abscesses. Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2009, 182, 7119–7130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milovanovic, J.; Arsenijevic, A.; Stojanovic, B.; Kanjevac, T.; Arsenijevic, D.; Radosavljevic, G.; Milovanovic, M.; Arsenijevic, N. Interleukin-17 in Chronic Inflammatory Neurological Diseases. Frontiers in Immunology 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siffrin, V.; Radbruch, H.; Glumm, R.; Niesner, R.; Paterka, M.; Herz, J.; Leuenberger, T.; Lehmann, S.M.; Luenstedt, S.; Rinnenthal, J.L.; et al. In Vivo Imaging of Partially Reversible Th17 Cell-Induced Neuronal Dysfunction in the Course of Encephalomyelitis. Immunity 2010, 33, 424–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliorini, P.; Italiani, P.; Pratesi, F.; Puxeddu, I.; Boraschi, D. The IL-1 Family Cytokines and Receptors in Autoimmune Diseases. Autoimmunity Reviews 2020, 19, 102617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
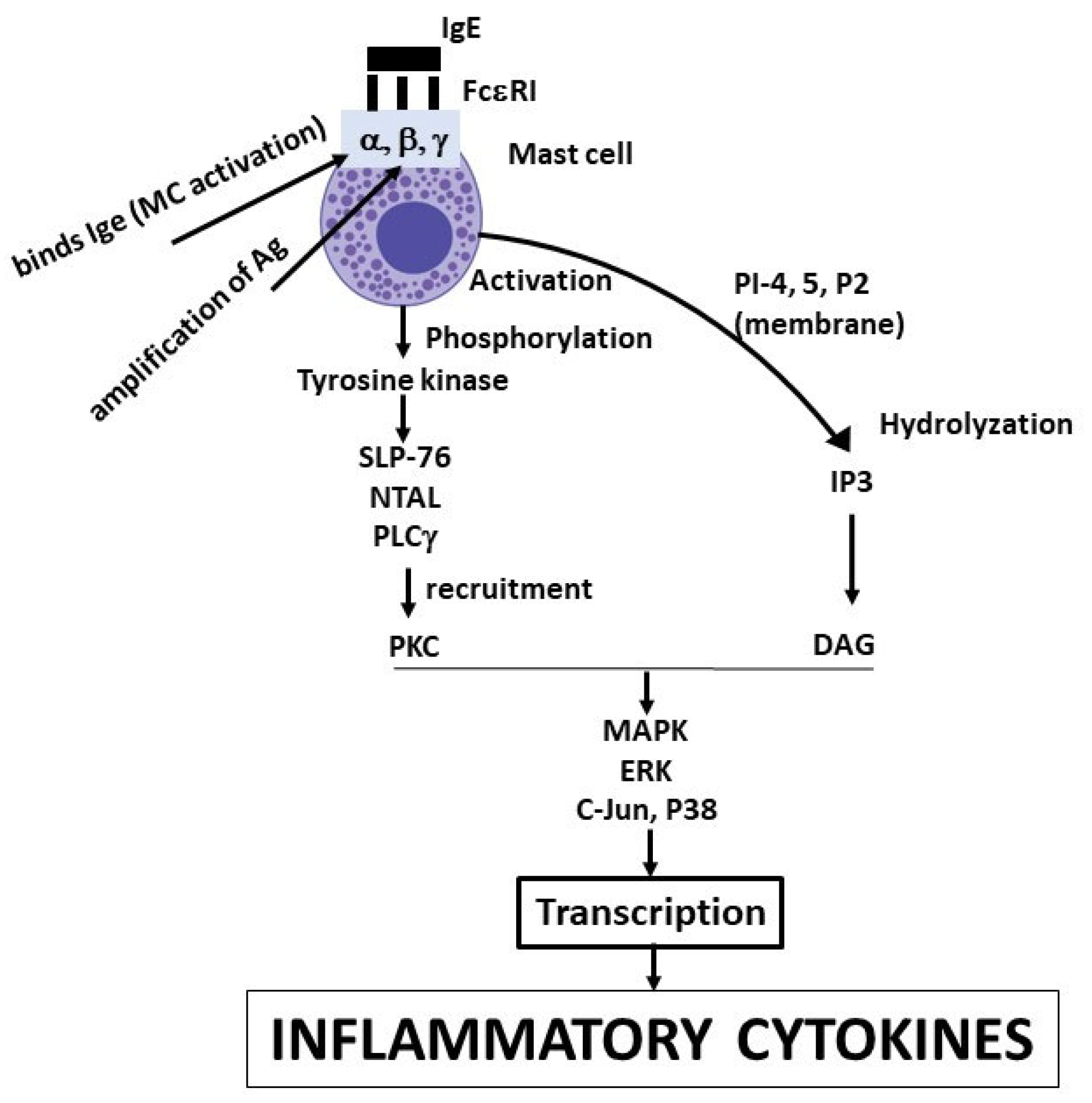
| Compound de novo synthesis: IL-1, IL-2, IL-3, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-10, IL-13, TNF, NO, VEGF.Arachidonic acid products: prostaglandin PGD2, leukotriene LTB4, LTC4, Chemokines: IL-8 (CXCL8), MCP-1 (CCL2), MCP-3 (CCL7), MCP-4, RANTES (CCL5), Eotaxin (CCL11) |
| Prestored mediators: chymase, tryptase, CRH, GM-CSF, SCF, NGF, TGF-β, chondroitin, heparin, histamine, serotonin, β-endorphin, SP, VIP, NT |
| IL-6, TNF or VEGF, NT (neurotensin), CRH (corticotropin releasing hormone), LPS (lipopolysaccharide), VIP (vasoactive intestinal peptide), PACAP (pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide), PCBs (polychlorinated biphenols), PTH (parathyroid hormone), SP (substance P) |
| Heavy metals: Aluminum, Cadmium, Mercury |
| Peptide | Function |
| Neurotensin | Digestive tract and cardiovascular regulation |
| Substance P | Inflammation, pain |
| Kinins (bradykinin) | Inflammation, pain, vasodilation |
| Corticotropin-releasing hormone | Inflammation: vasodilation |
| VEGF | Neovascularization, vasodilation |
| Angiogenin | Neovascularization |
| Endorphins | Analgesia |
| Endothelin | Sepsis |
| Renin | Angiotensin synthesis |
| Urocortin | Inflammation, vasodilation |
| Vasoactive intestinal peptide | Vasodilation, mast cell activation |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





