Submitted:
02 February 2023
Posted:
07 February 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Information-Theoretic Approach Quantities
4.2. Computational Details
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Buckingham, A.D. Polarizability and hyperpolarizability. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A 1979, 293, 239–248. [Google Scholar]
- Liess, M.; Jeglinski, S.; Vardeny, Z.; Ozaki, M.; Yoshino, K.; Ding, Y.; Barton, T. Electroabsorption Spectroscopy of Luminescent and Nonluminescent π-Conjugated Polymers. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 1997, 56, 15712–15724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponder, M.; Mathies, R. Excited-State Polarizabilities and Dipole Moments of Diphenylpolyenes and Retinal. J. Phys. Chem. 1983, 87, 5090–5098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelinck, G.H.; Piet, J.J.; Wegewijs, B.R.; Müllen, K.; Wildeman, J.; Hadziioannou, G.; Warman, J.M. Measuring the Size of Excitons on Isolated Phenylene-Vinylene Chains: From Dimers to Polymers. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 2000, 62, 1489–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Haas, M.P.; Warman, J.M. Photon-Induced Molecular Charge Separation Studied by Nanosecond Time-Resolved Microwave Conductivity. Chem. Phys. 1982, 73, 35–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condon, E.U. in Handbook of Physics, ed. Condon, E.U. and Odishaw, H. McGraw-Hill, New York, 1958, pp. 4–22.
- Jackson, J.D. Classical Electrodynamics, Wiley, New York, 2nd edn, 1975, pp. 60–62.
- Dmitrieva, I.K.; Plindov, G.I. Dipole Polarizability, Radius and Ionization Potential for Atomic Systems. Phys. Scr. 1983, 27, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gough, K.M. Theoretical analysis of molecular polarizabilities and polarizability derivatives in hydrocarbons. J. Chem. Phys. 1989, 91, 2424–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laidig, K.E.; Bader, R.F.W. Properties of atoms in molecules: Atomic polarizabilities. J. Chem. Phys. 1990, 93, 7213–7224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinck, T.; Murray, J.S.; Politzer, P. Polarizability and volume. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 4305–4306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politzer, P.; Jin, P.; Murray, J.S. Atomic polarizability, volume and ionization energy. J. Chem. Phys. 2002, 117, 8197–8202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, S.A.; Thakkar, A.J. Relating polarizability to volume, ionization energy, electronegativity, hardness, moments of momentum, and other molecular properties. J. Chem. Phys. 2014, 141, 074306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, S.A.; Thakkar, A.J. Additive models for the molecular polarizability and volume. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2014, 610–611, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, K.J. Additivity Methods in Molecular Polarizability. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1990, 112, 8533–8542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, K.J. Calculation of the Molecular Polarizability Tensor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1990, 112, 8543–8551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkatchenko, A.; Scheffler, M. Accurate Molecular van der Waals Interactions from Ground-State Electron Density and Free-Atom Reference Data. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 102, 073005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabó, P.; Góger, S.; Charry, J.; Karimpour, M.R.; Fedorov, D.V.; Tkatchenko, A. Four-Dimensional Scaling of Dipole Polarizability in Quantum Systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2022, 128, 070602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McWeeny, R. Some recent advances in density matrix theory. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1960, 32, 335–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langhoff, W.; Karplus, M.; Hurst, R.P. Approximations to Hartree—Fock Perturbation Theory. J. Chem. Phys. 1966, 44, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colwell, S.M.; Murray, C.W.; Handy, N.C.; Amos, R.D. The determination of hyperpolarisabilities using density functional theory. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1993, 210, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, M.A.; Bettens, R.P. Energy-Based Molecular Fragmentation Methods. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 5607–5642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niklasson, A.M.; Challacombe, M. Density Matrix Perturbation Theory. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 92, 193001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, V.; Niklasson, A.M.N.; Challacombe, M. Ab Initio Linear Scaling Response Theory: Electric Polarizability by Perturbed Projection. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 92, 193002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grisafi, A.; Wilkins, D.M.; Csányi, G.; Ceriotti, M. Symmetry-Adapted Machine Learning for Tensorial Properties of Atomistic Systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 120, 036002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkins, D.M.; Grisafi, A.; Yang, Y.; Lao, K.U.; DiStasio, R.A., Jr.; Ceriotti, M. Accurate molecular polarizabilities with coupled cluster theory and machine learning. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 3401–3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, V.H.A.; Lunghi, A. Predicting tensorial molecular properties with equivariant machine learning models. Phys. Rev. B 2022, 105, 165131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.; Samy, H.; Küpper, J. Robust and Accurate Computational Estimation of the Polarizability Tensors of Macromolecules. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 2938–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unsöld, A. Quantentheorie des Wasserstoffmolekülions und der Born-Landéschen Abstoßungskräfte, Z. Physik 1927, 43, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simón-Manso, Y.; Fuentealba, P. On the Density Functional Relationship between Static Dipole Polarizability and Global Softness. J. Phys. Chem. A 1998, 102, 2029–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayers, P.W. The physical basis of the hard/soft acid/base principle. Faraday Discuss 2007, 135, 161–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grozema, F.C.; Telesca, R.; Jonkman, H.T.; Siebbeles, L.D.A.; Snijders, J.G. Excited State Polarizabilities of Conjugated Molecules Calculated Using Time Dependent Density Functional Theory. J. Chem. Phys. 2001, 115, 10014–10021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Improta, R.; Ferrante, C.; Bozio, R.; Barone, V. The Polarizability in Solution of Tetra-Phenyl-Porphyrin Derivatives in Their Excited Electronic States: A PCM/TD-DFT Study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2009, 11, 4664–4673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Horst, J.W.; Bobbert, P.A.; De Jong, P.H.L.; Michels, M.A.J.; Siebbeles, L.D.A.; Warman, J.M.; Gelinck, G.H.; Brocks, G. Predicting Polarizabilities and Lifetimes of Excitons on Conjugated Polymer Chains. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2001, 334, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinchliffe, A.; Sosćun, H.J. Ab Initio Studies of the Dipole Moment and Polarizability of Azulene in Its Ground and Excited Singlet States. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2005, 412, 365–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, O.; Hättig, C.; Jørgensen, P. Ground and Excited State Polarizabilities and Dipole Transition Properties of Benzene from Coupled Cluster Response Theory. Spectrochim. Acta, Part A 1999, 55, 509–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.F.; Chen, H.; Note, R.; Mizuseki, H.; Kawazoe, Y. Excess Polarizabilities Upon Excitation from the Ground State to the First Dipole-Allowed Excited State of Diphenylpolyenes. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 2007, 107, 2006–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orian, L.; Pilot, R.; Bozio, R. In Silico Stark Effect: Determination of Excited-State Polarizabilities of Squaraine Dyes. J. Phys. Chem. A 2017, 121, 1587–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.B.; Liu, S.B.; Chen, D.H. A Density Functional Theory and Information-Theoretic Approach Study of Interaction Energy and Polarizability for Base Pairs and Peptides. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.B.; Zhao, Y.L.; He, X.; Ayers, P.W.; Liu, S.B. Efficient and accurate density-based prediction of macromolecular polarizabilities. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2023, 25, 2131–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purkayastha, P.; Chattopadhyay, N. Role of rotamerisation and excited state intramolecular proton transfer in the photophysics of 2-(2′-hydroxyphenyl)benzoxazole, 2-(2′-hydroxyphenyl)benzimidazole and 2-(2′-hydroxyphenyl)benzothiazole: A theoretical study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2000, 2, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becke, A.D. A multicenter numerical integration scheme for polyatomic molecules. J. Chem. Phys. 1988, 88, 2547–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirshfeld, F.L. Bonded-Atom Fragments for Describing Molecular Charge Densities. Theoret. Chim. Acta 1977, 44, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parr, R.G.; Yang, W.T. Density Functional Theory of Atoms and Molecules; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Teale, A.M.; Helgaker, T.; Savin, A.; Adamo, C.; Aradi, B.; Arbuznikov, A.V.; Ayers, P.W.; Baerends, E.J.; Barone, V.; Calaminici, P.; et al. DFT exchange: Sharing perspectives on the workhorse of quantum chemistry and materials science. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2022, 24, 28700–28781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.H.; Li, W.; Fang, T. An Efficient Fragment-Based Approach for Predicting the Ground-State Energies and Structures of Large Molecules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 7215–7226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Li, S.H.; Jiang, Y.S. Generalized Energy-Based Fragmentation Approach for Computing the Ground-State Energies and Properties of Large Molecules. J. Phys. Chem. A 2007, 111, 2193–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.H.; Li, W.; Ma, J. Generalized Energy-Based Fragmentation Approach and Its Applications to Macromolecules and Molecular Aggregates. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 2712–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Dong, H.; Ma, J.; Li, S.H. Structures and Spectroscopic Properties of Large Molecules and Condensed-Phase Systems Predicted by Generalized Energy-Based Fragmentation Approach. Acc. Chem. Res. 2021, 54, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwerdtfeger, P.; Nagle, J.K. Table of static dipole polarizabilities of the neutral elements in the periodic table. Mol. Phys. 2018, 117, 1200–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, R.A. Theory of statistical estimation. Math. Proc. Camb. Philos. Soc. 1925, 22, 700–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.K.; Berkowitz, M.; Parr, R.G. Transcription of ground-state density-functional theory into a local thermodynamics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 8028–8031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, R.F.W.; Preston, H.J.T. The kinetic energy of molecular charge distributions and molecular stability. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 1969, 3, 327–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tal, Y.; Bader, R.F.W. Studies of the energy density functional approach. 1. Kinetic energy. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 1978, 14, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, L. Local kinetic energy in quantum mechanics. J. Chem. Phys. 1979, 70, 788–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, L. Representable local kinetic energy. J. Chem. Phys. 1984, 80, 4277–4279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.Z.; Liu, S.B.; Wang, Y.A. Uniqueness and Asymptotic Behavior of the Local Kinetic Energy. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1996, 258, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayers, P.W.; Parr, R.G.; Nagy, Á. Local kinetic energy and local temperature in the density-functional theory of electronic structure. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 2002, 90, 309–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.S.M.; Ayers, P.W.; Hernandez, J.I.R. How Ambiguous Is the Local Kinetic Energy? J. Phys. Chem. A 2010, 114, 8884–8895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkowitz, M. Exponential approximation for the density matrix and the Wigner distribution. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1986, 129, 486–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geerlings, P.; De Proft, F.; Langenaeker, W. Conceptual Density Functional Theory. Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 1793–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.A.; Bartolotti, L.J.; Ayers, P.W.; Fievez, T.; Geerlings, P. Charge density and chemical reactivity: A unified view from conceptual DFT. in Modern Charge Density Analysis, ed. Gatti, C. and Macchi, P. Springer, New York, 2012.
- Liu, S.B. Conceptual Density Functional Theory and Some Recent Developments. Acta Phys. -Chim. Sin. 2009, 25, 590–600. [Google Scholar]
- Geerlings, P.; Chamorro, E.; Chattaraj, P.K.; De Proft, F.; Gázquez, J.L.; Liu, S.B.; Morell, C.; Toro-Labbé, A.; Vela, A.; Ayers, P.W. Conceptual density functional theory: Status, prospects, issues. Theor. Chem. Acc. 2020, 139, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.B.; Rong, C.Y.; Wu, Z.M.; Lu, T. Rényi entropy, Tsallis entropy and Onicescu information energy in density functional reactivity theory. Acta Phys. -Chim. Sin. 2015, 31, 2057–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kullback, S. Information Theory and Statistics; Dover Publications: Mineola, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.B. Identity for Kullback-Leibler divergence in density functional reactivity theory. J. Chem. Phys. 2019, 151, 141103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhao, D.B.; Lu, T.; Liu, S.B.; Rong, C.Y. Quantifications and Applications of Relative Fisher Information in Density Functional Theory. J. Phys. Chem. A 2021, 125, 3802–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, C.Y.; Wang, B.; Zhao, D.B.; Liu, S.B. Information-Theoretic approach in density functional theory and its recent applications to chemical problems. WIREs Comput. Mol. Sci. 2020, 10, e1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, C.Y.; Zhao, D.B.; He, X.; Liu, S.B. Development and Applications of the Density-Based Theory of Chemical Reactivity. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2022, 13, 11191–11200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.B. Homochirality Originates from Handedness of Helices. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 8690–8696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.B. Principle of Chirality Hierarchy in Three-Blade Propeller Systems. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 8720–8725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalewajski, R.F.; Parr, R.G. Information theory, atoms in molecules, and molecular similarity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 8879–8882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayers, P.W. Information Theory, the Shape Function, and the Hirshfeld Atom. Theor. Chem. Acc. 2006, 115, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parr, R.G.; Ayers, P.W.; Nalewajski, R.F. What Is an Atom in a Molecule? J. Phys. Chem. A 2005, 109, 3957–3959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidar-Zadeh, F.; Ayers, P.W.; Verstraelen, T.; Vinogradov, I.; Vohringer-Martinez, E.; Bultinck, P. Information-Theoretic Approaches to Atoms-in-Molecules: Hirshfeld Family of Partitioning Schemes. J. Phys. Chem. A 2018, 122, 4219–4245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bader, R.F.W. Atoms in Molecules: A Quantum Theory. Oxford University Press, Oxford, England, 1990.
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 16 Revision C.01; Gaussian Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yanai, T.; Tew, D.; Handy, N. A new hybrid exchange-correlation functional using the Coulomb-attenuating method (CAM-B3LYP). Chem. Phys. Lett. 2004, 393, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, A.D.; Chandler, G.S. Contracted Gaussian-basis sets for molecular calculations. 1. 2nd row atoms, Z=11-18. J. Chem. Phys. 1980, 72, 5639–5648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauernschmitt, R.; Ahlrichs, R. Treatment of electronic excitations within the adiabatic approximation of time dependent density functional theory. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1996, 256, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furche, F.; Ahlrichs, R. Adiabatic time-dependent density functional methods for excited state properties. J. Chem. Phys. 2002, 117, 7433–7447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liang, W. Analytical Hessian of electronic excited states in time-dependent density functional theory with Tamm-Dancoff approximation. J. Chem. Phys. 2011, 135, 014113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Chen, F.W. Multiwfn: A multifunctional wavefunction analyzer. J. Comput. Chem. 2012, 33, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
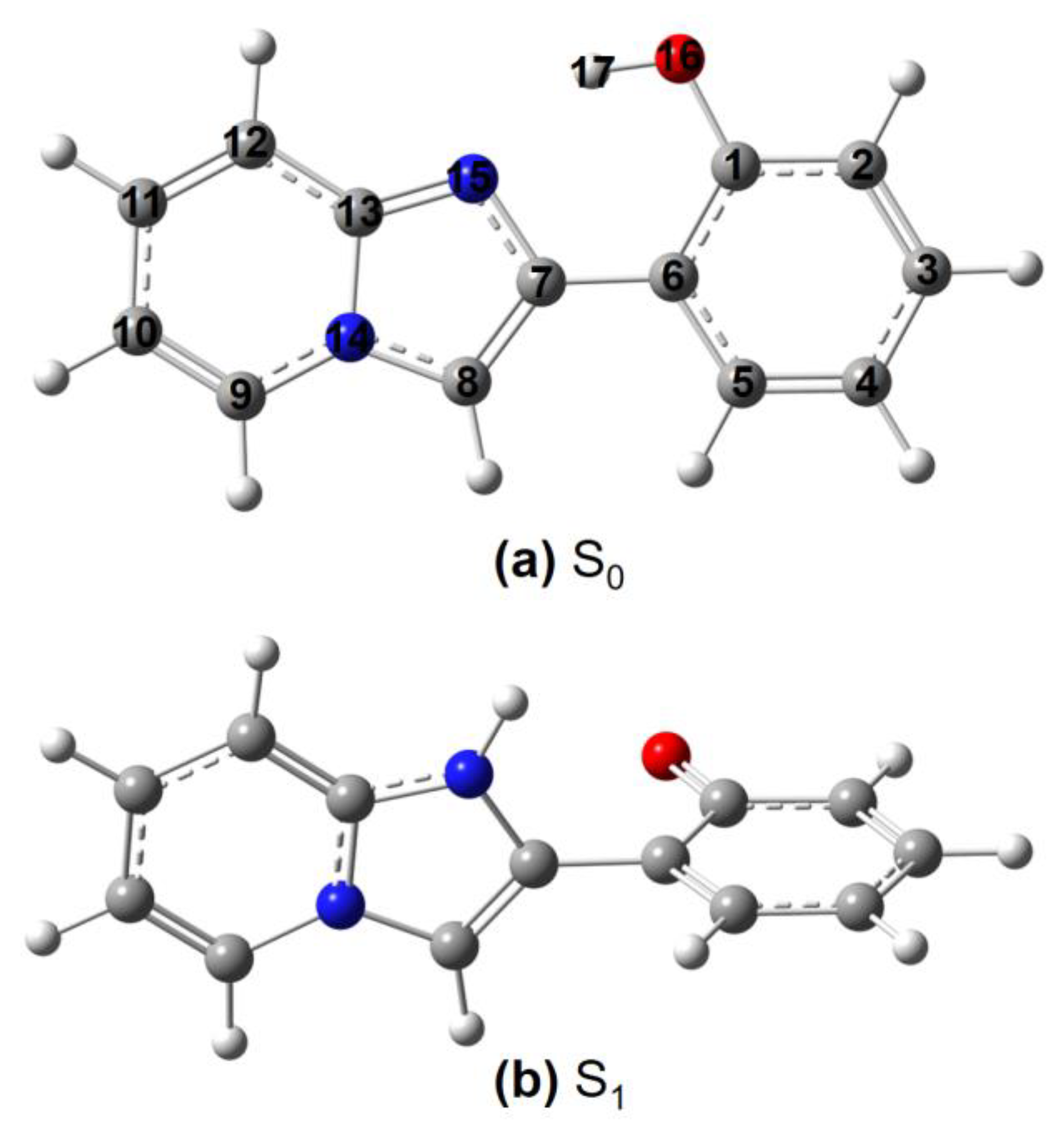
| Index | αiso | SS | IF | SGBP | rR2 | rR3 | IG | G1 | G2 | G3 | Vol | Θiso |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 175.68 | 96.35 | 4343.89 | 746.75 | 112.64 | 117.78 | 1.38 | ‒35.34 | 24.07 | 139.78 | 1715.75 | ‒87.39 |
| 2 | 200.87 | 20.66 | 13967.27 | 973.91 | 146.61 | 151.68 | 1.36 | ‒34.93 | 23.70 | 141.74 | 2073.70 | ‒103.29 |
| 3 | 237.32 | 142.90 | 5692.80 | 1016.86 | 154.03 | 161.91 | 2.10 | ‒50.98 | 35.00 | 196.05 | 2441.40 | ‒115.43 |
| 4 | 182.97 | 97.74 | 4793.46 | 801.56 | 120.76 | 126.07 | 1.45 | ‒34.44 | 22.49 | 147.78 | 1855.73 | ‒91.79 |
| 5 | 197.76 | 107.94 | 5045.63 | 855.45 | 129.06 | 135.01 | 1.60 | ‒39.10 | 25.75 | 159.82 | 1886.74 | ‒95.32 |
| 6 | 175.11 | 92.94 | 4917.98 | 801.81 | 120.62 | 125.71 | 1.37 | ‒34.55 | 22.69 | 144.27 | 1765.67 | ‒93.87 |
| 7 | 188.87 | 81.70 | 6524.29 | 855.22 | 128.61 | 133.70 | 1.37 | ‒34.93 | 22.13 | 142.27 | 1959.26 | ‒100.99 |
| 8 | 197.51 | 20.60 | 13967.06 | 973.87 | 146.60 | 151.67 | 1.36 | ‒34.95 | 23.67 | 141.84 | 1850.09 | ‒101.48 |
| 9 | 194.07 | 102.37 | 4928.42 | 829.28 | 124.78 | 130.18 | 1.46 | ‒36.68 | 23.12 | 151.22 | 1897.41 | ‒106.85 |
| 10 | 189.36 | 106.46 | 4595.48 | 800.72 | 120.93 | 126.64 | 1.53 | ‒39.13 | 25.97 | 150.98 | 1931.31 | ‒93.18 |
| 11 | 194.81 | 107.96 | 5045.77 | 855.48 | 129.06 | 135.02 | 1.60 | ‒39.13 | 23.71 | 159.81 | 1994.38 | ‒95.26 |
| 12 | 191.68 | 81.72 | 6524.35 | 855.23 | 128.60 | 133.66 | 1.36 | ‒34.98 | 22.67 | 142.29 | 1957.16 | ‒105.11 |
| 13 | 200.29 | 20.66 | 13967.37 | 973.93 | 146.60 | 151.67 | 1.36 | ‒35.01 | 22.86 | 141.85 | 1980.91 | ‒111.96 |
| 14 | 198.88 | 102.42 | 4928.71 | 829.32 | 124.77 | 130.16 | 1.45 | ‒36.79 | 23.62 | 151.19 | 1696.49 | ‒112.11 |
| 15 | 190.18 | 106.46 | 4595.43 | 800.71 | 120.93 | 126.64 | 1.53 | ‒39.12 | 24.61 | 151.02 | 1842.17 | ‒94.41 |
| 16 | 191.22 | 96.42 | 6318.70 | 965.73 | 144.80 | 150.24 | 1.46 | ‒37.81 | 23.40 | 165.13 | 2064.71 | ‒117.92 |
| 17 | 255.95 | 135.18 | 5826.22 | 1017.73 | 153.69 | 160.90 | 1.92 | ‒52.71 | 36.65 | 192.16 | 2401.28 | ‒125.79 |
| 18 | 246.58 | 135.11 | 5826.00 | 1017.67 | 153.68 | 160.90 | 1.92 | ‒52.74 | 36.93 | 192.52 | 2494.60 | ‒119.81 |
| 19 | 277.67 | 146.79 | 6528.00 | 1126.45 | 170.10 | 178.13 | 2.14 | ‒56.48 | 38.53 | 212.18 | 2819.11 | ‒137.35 |
| 20 | 295.24 | 153.19 | 7225.20 | 1222.09 | 184.32 | 192.76 | 2.25 | ‒58.90 | 39.85 | 226.76 | 2761.18 | ‒154.13 |
| 21 | 268.01 | 146.71 | 6527.76 | 1126.38 | 170.10 | 178.12 | 2.14 | ‒56.47 | 39.11 | 212.53 | 2467.93 | ‒128.04 |
| 22 | 283.05 | 153.12 | 7225.00 | 1222.03 | 184.32 | 192.76 | 2.25 | ‒58.93 | 39.71 | 227.00 | 2913.80 | ‒139.45 |
| 23 | 205.46 | 91.83 | 6775.95 | 909.20 | 136.89 | 142.52 | 1.51 | ‒38.70 | 26.44 | 153.26 | 1963.41 | ‒110.94 |
| 24 | 205.03 | 106.53 | 6570.28 | 1019.70 | 153.09 | 159.11 | 1.61 | ‒41.55 | 26.57 | 176.20 | 2201.13 | ‒123.83 |
| 25 | 327.20 | 173.93 | 7308.31 | 1288.65 | 194.73 | 204.01 | 2.46 | ‒70.08 | 50.17 | 244.74 | 3066.91 | ‒156.33 |
| 26 | 320.10 | 190.84 | 7330.19 | 1328.47 | 201.30 | 211.70 | 2.76 | ‒74.61 | 52.80 | 255.30 | 3332.26 | ‒160.67 |
| 27 | 175.19 | 82.72 | 6640.05 | 966.86 | 144.50 | 149.36 | 1.31 | ‒32.94 | 20.03 | 158.50 | 3218.41 | ‒108.98 |
| R2 | 1.000 | 0.581 | 0.005 | 0.859 | 0.868 | 0.883 | 0.927 | 0.959 | 0.955 | 0.931 | 0.618 | 0.869 |
| Index | αiso | SS | IF | rR2 | rR3 | G2 | G3 | Vol | Θiso |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 166.08 | 96.94 | 4345.68 | 112.73 | 118.02 | 23.88 | 138.16 | 1784.17 | ‒89.93 |
| 2 | 189.81 | 21.28 | 13969.19 | 146.67 | 151.87 | 23.61 | 140.08 | 1956.89 | ‒114.26 |
| 3 | 224.23 | 143.51 | 5694.61 | 154.12 | 162.16 | 34.15 | 194.24 | 2519.29 | ‒126.71 |
| 4 | 174.81 | 98.36 | 4795.23 | 120.83 | 126.27 | 22.33 | 146.07 | 1862.89 | ‒96.38 |
| 5 | 187.84 | 108.57 | 5047.40 | 129.14 | 135.22 | 25.53 | 158.13 | 1983.35 | ‒101.96 |
| 6 | 166.88 | 93.55 | 4919.65 | 120.68 | 125.87 | 22.56 | 142.61 | 1809.41 | ‒97.69 |
| 7 | 182.88 | 82.29 | 6525.95 | 128.66 | 133.83 | 23.33 | 140.53 | 1948.71 | ‒105.58 |
| 8 | 188.20 | 21.19 | 13968.88 | 146.65 | 151.80 | 22.97 | 140.28 | 1945.05 | ‒110.07 |
| 9 | 182.03 | 103.04 | 4930.44 | 124.83 | 130.34 | 24.17 | 149.51 | 1945.30 | ‒110.22 |
| 10 | 178.88 | 107.05 | 4597.05 | 121.02 | 126.88 | 26.58 | 149.31 | 1919.82 | ‒96.99 |
| 11 | 182.81 | 108.54 | 5047.21 | 129.14 | 135.22 | 25.57 | 158.15 | 1992.00 | ‒99.73 |
| 12 | 178.54 | 82.29 | 6526.00 | 128.69 | 133.90 | 23.14 | 140.43 | 1905.76 | ‒103.35 |
| 13 | 186.41 | 21.24 | 13968.99 | 146.69 | 151.92 | 23.40 | 139.90 | 1961.97 | ‒105.81 |
| 14 | 185.73 | 102.96 | 4930.10 | 124.85 | 130.37 | 24.33 | 149.38 | 1959.21 | ‒111.23 |
| 15 | 179.03 | 107.06 | 4597.29 | 121.01 | 126.87 | 26.78 | 149.25 | 1938.52 | ‒94.93 |
| 16 | 178.64 | 96.95 | 6320.18 | 144.88 | 150.45 | 23.97 | 163.21 | 2040.58 | ‒111.79 |
| 17 | 240.42 | 135.77 | 5827.95 | 153.76 | 161.09 | 36.81 | 190.49 | 2466.79 | ‒117.96 |
| 18 | 253.40 | 135.66 | 5827.52 | 153.75 | 161.08 | 36.75 | 190.81 | 2411.54 | ‒120.97 |
| 19 | 260.31 | 147.38 | 6529.77 | 170.17 | 178.31 | 39.03 | 210.40 | 2664.07 | ‒124.40 |
| 20 | 280.48 | 153.76 | 7226.84 | 184.39 | 192.94 | 40.08 | 225.02 | 2822.78 | ‒136.33 |
| 21 | 267.99 | 147.29 | 6529.43 | 170.17 | 178.33 | 38.50 | 210.79 | 2665.63 | ‒128.47 |
| 22 | 327.99 | 153.50 | 7225.08 | 184.32 | 192.78 | 39.42 | 226.35 | 2798.30 | ‒138.46 |
| 23 | 190.90 | 92.40 | 6777.37 | 136.99 | 142.77 | 25.46 | 151.82 | 2091.13 | ‒110.61 |
| 24 | 191.30 | 107.05 | 6571.54 | 153.18 | 159.32 | 26.69 | 174.50 | 2213.23 | ‒119.08 |
| 25 | 331.10 | 174.16 | 7307.99 | 194.72 | 204.02 | 48.71 | 244.76 | 3050.07 | ‒168.67 |
| 26 | 309.58 | 191.50 | 7332.09 | 201.39 | 211.92 | 53.05 | 253.29 | 3379.72 | ‒164.60 |
| 27 | 190.21 | 83.28 | 6640.35 | 144.47 | 149.29 | 19.82 | 157.57 | 1894.17 | ‒115.25 |
| R2 | 1.000 | 0.560 | 0.004 | 0.861 | 0.874 | 0.884 | 0.917 | 0.908 | 0.831 |
| αiso | SS | IF | SGBP | rR2 | rR3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | 0.941 | 0.561 | 0.004 | 0.855 | 0.862 | 0.874 |
| IG | G1 | G2 | G3 | Vol | Θiso | |
| R2 | 0.876 | 0.906 | 0.896 | 0.914 | 0.688 | 0.814 |
| R2 | SS | IF | SGBP | rR2 | rR3 | IG | G1 | G2 | G3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| αiso@S0 | 0.580 | 0.005 | 0.859 | 0.868 | 0.883 | 0.927 | 0.959 | 0.955 | 0.932 |
| αiso@S1 | 0.561 | 0.004 | 0.855 | 0.862 | 0.874 | 0.873 | 0.907 | 0.897 | 0.914 |
| Index | Ground-state (S0) | Excited-state (S1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Becke | Hirshfeld | avg. | Becke | Hirshfeld | avg. | |
| 1 | 119.84 | 176.99 | 148.41 | 121.05 | 176.63 | 148.84 |
| 2 | 228.99 | 281.15 | 255.07 | 228.53 | 279.36 | 253.95 |
| 3 | 167.92 | 250.19 | 209.05 | 169.26 | 249.87 | 209.56 |
| 4 | 122.82 | 182.28 | 152.55 | 124.20 | 182.08 | 153.14 |
| 5 | 132.97 | 197.56 | 165.27 | 134.35 | 197.34 | 165.84 |
| 6 | 119.40 | 177.07 | 148.24 | 120.98 | 177.15 | 149.06 |
| 7 | 170.42 | 224.86 | 197.64 | 170.23 | 223.53 | 196.88 |
| 8 | 229.52 | 281.83 | 255.67 | 227.91 | 279.02 | 253.46 |
| 9 | 129.98 | 189.98 | 159.98 | 131.48 | 190.06 | 160.77 |
| 10 | 129.77 | 192.41 | 161.09 | 131.17 | 192.26 | 161.72 |
| 11 | 132.81 | 197.40 | 165.11 | 134.35 | 197.35 | 165.85 |
| 12 | 169.65 | 224.32 | 196.98 | 172.04 | 224.59 | 198.32 |
| 13 | 227.44 | 279.92 | 253.68 | 231.41 | 281.70 | 256.56 |
| 14 | 130.12 | 190.12 | 160.12 | 131.17 | 189.61 | 160.39 |
| 15 | 129.85 | 192.48 | 161.16 | 131.10 | 192.26 | 161.68 |
| 16 | 130.63 | 194.40 | 162.51 | 131.24 | 193.58 | 162.41 |
| 17 | 167.50 | 248.17 | 207.83 | 168.68 | 247.78 | 208.23 |
| 18 | 167.20 | 248.13 | 207.66 | 168.36 | 247.93 | 208.14 |
| 19 | 180.67 | 268.74 | 224.70 | 181.79 | 268.33 | 225.06 |
| 20 | 190.15 | 282.83 | 236.49 | 191.24 | 282.39 | 236.82 |
| 21 | 180.36 | 268.73 | 224.55 | 181.54 | 268.42 | 224.98 |
| 22 | 189.86 | 282.78 | 236.32 | 190.76 | 283.63 | 237.19 |
| 23 | 179.61 | 239.76 | 209.69 | 182.19 | 240.24 | 211.21 |
| 24 | 140.56 | 209.82 | 175.19 | 141.35 | 209.19 | 175.27 |
| 25 | 214.86 | 319.29 | 267.08 | 214.84 | 321.13 | 267.99 |
| 26 | 226.85 | 337.95 | 282.40 | 228.26 | 337.38 | 282.82 |
| 27 | 119.65 | 177.97 | 148.81 | 121.63 | 179.51 | 150.57 |
| MUE (%)a | –24.90 | 6.62 | –9.14 | –21.21 | 10.82 | –5.19 |
| MSE (%)b | 28.14 | 8.10 | 16.00 | 26.07 | 12.63 | 15.23 |
| Index | Ground-state (S0) | Excited-state (S1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Becke | Hirshfeld | avg. | Becke | Hirshfeld | avg. | |
| 1 | 119.84 | 176.99 | 148.41 | 121.05 | 176.63 | 148.84 |
| 2 | 228.99 | 281.15 | 255.07 | 228.53 | 279.36 | 253.95 |
| 3 | 167.92 | 250.19 | 209.05 | 169.26 | 249.87 | 209.56 |
| 4 | 122.82 | 182.28 | 152.55 | 124.20 | 182.08 | 153.14 |
| 5 | 132.97 | 197.56 | 165.27 | 134.35 | 197.34 | 165.84 |
| 6 | 119.40 | 177.07 | 148.24 | 120.98 | 177.15 | 149.06 |
| 7 | 170.42 | 224.86 | 197.64 | 170.23 | 223.53 | 196.88 |
| 8 | 229.52 | 281.83 | 255.67 | 227.91 | 279.02 | 253.46 |
| 9 | 129.98 | 189.98 | 159.98 | 131.48 | 190.06 | 160.77 |
| 10 | 129.77 | 192.41 | 161.09 | 131.17 | 192.26 | 161.72 |
| 11 | 132.81 | 197.40 | 165.11 | 134.35 | 197.35 | 165.85 |
| 12 | 169.65 | 224.32 | 196.98 | 172.04 | 224.59 | 198.32 |
| 13 | 227.44 | 279.92 | 253.68 | 231.41 | 281.70 | 256.56 |
| 14 | 130.12 | 190.12 | 160.12 | 131.17 | 189.61 | 160.39 |
| 15 | 129.85 | 192.48 | 161.16 | 131.10 | 192.26 | 161.68 |
| 16 | 130.63 | 194.40 | 162.51 | 131.24 | 193.58 | 162.41 |
| 17 | 167.50 | 248.17 | 207.83 | 168.68 | 247.78 | 208.23 |
| 18 | 167.20 | 248.13 | 207.66 | 168.36 | 247.93 | 208.14 |
| 19 | 180.67 | 268.74 | 224.70 | 181.79 | 268.33 | 225.06 |
| 20 | 190.15 | 282.83 | 236.49 | 191.24 | 282.39 | 236.82 |
| 21 | 180.36 | 268.73 | 224.55 | 181.54 | 268.42 | 224.98 |
| 22 | 189.86 | 282.78 | 236.32 | 190.76 | 283.63 | 237.19 |
| 23 | 179.61 | 239.76 | 209.69 | 182.19 | 240.24 | 211.21 |
| 24 | 140.56 | 209.82 | 175.19 | 141.35 | 209.19 | 175.27 |
| 25 | 214.86 | 319.29 | 267.08 | 214.84 | 321.13 | 267.99 |
| 26 | 226.85 | 337.95 | 282.40 | 228.26 | 337.38 | 282.82 |
| 27 | 119.65 | 177.97 | 148.81 | 121.63 | 179.51 | 150.57 |
| MUE (%)a | –28.40 | 6.77 | –10.82 | –24.74 | 11.05 | –6.84 |
| MSE (%)b | 39.16 | 15.48 | 26.74 | 37.89 | 16.21 | 26.41 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





