Submitted:
01 February 2023
Posted:
06 February 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
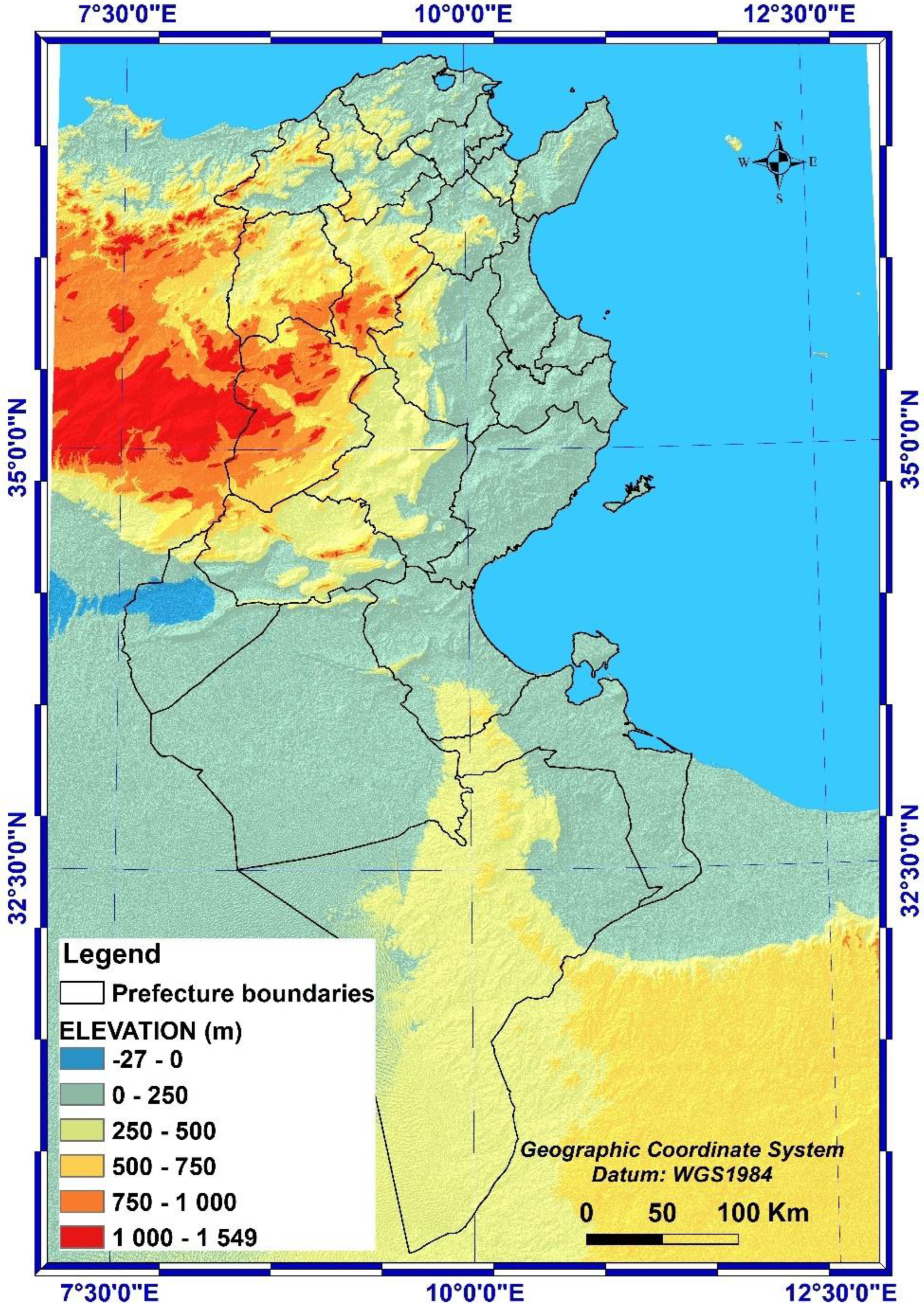
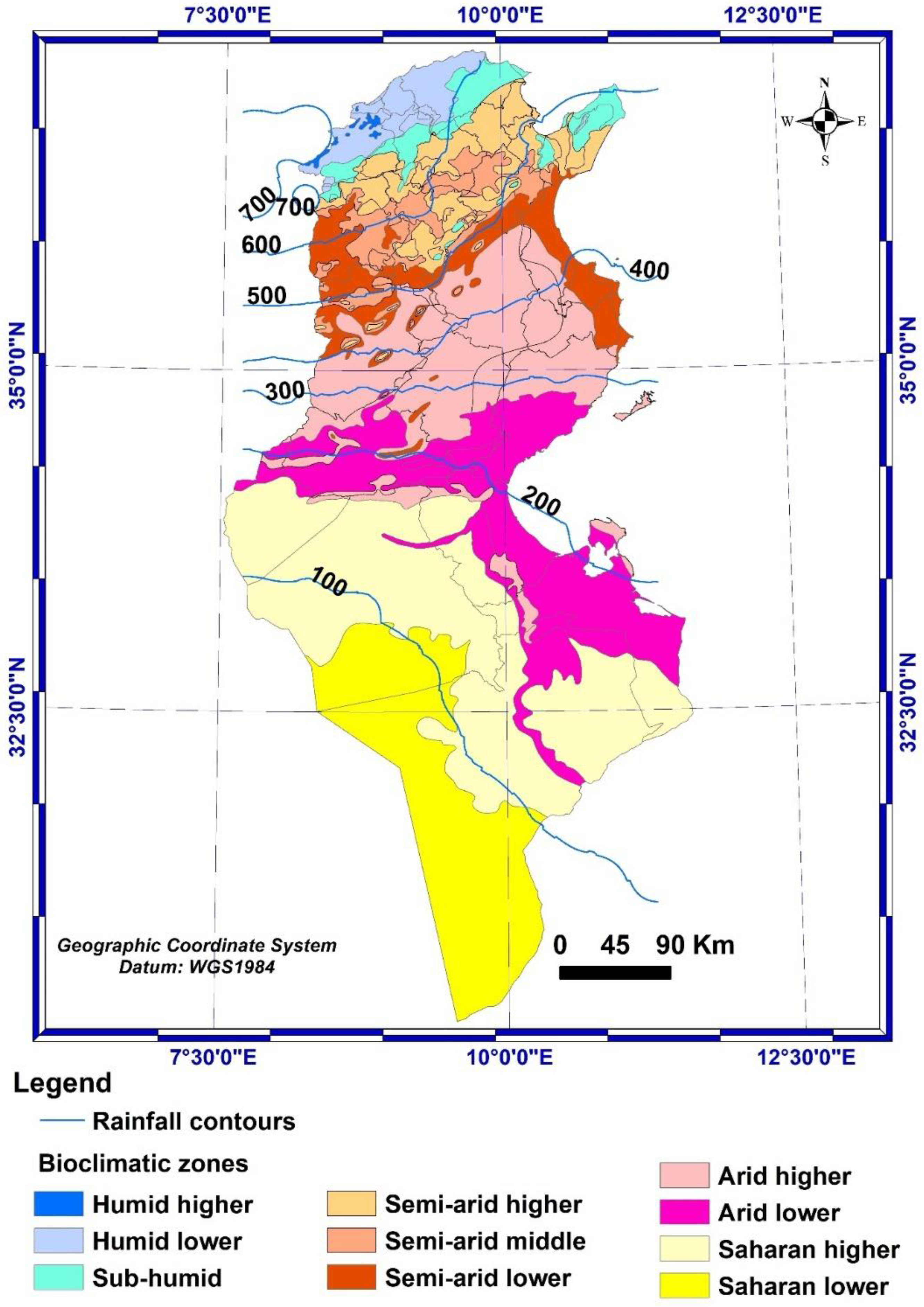
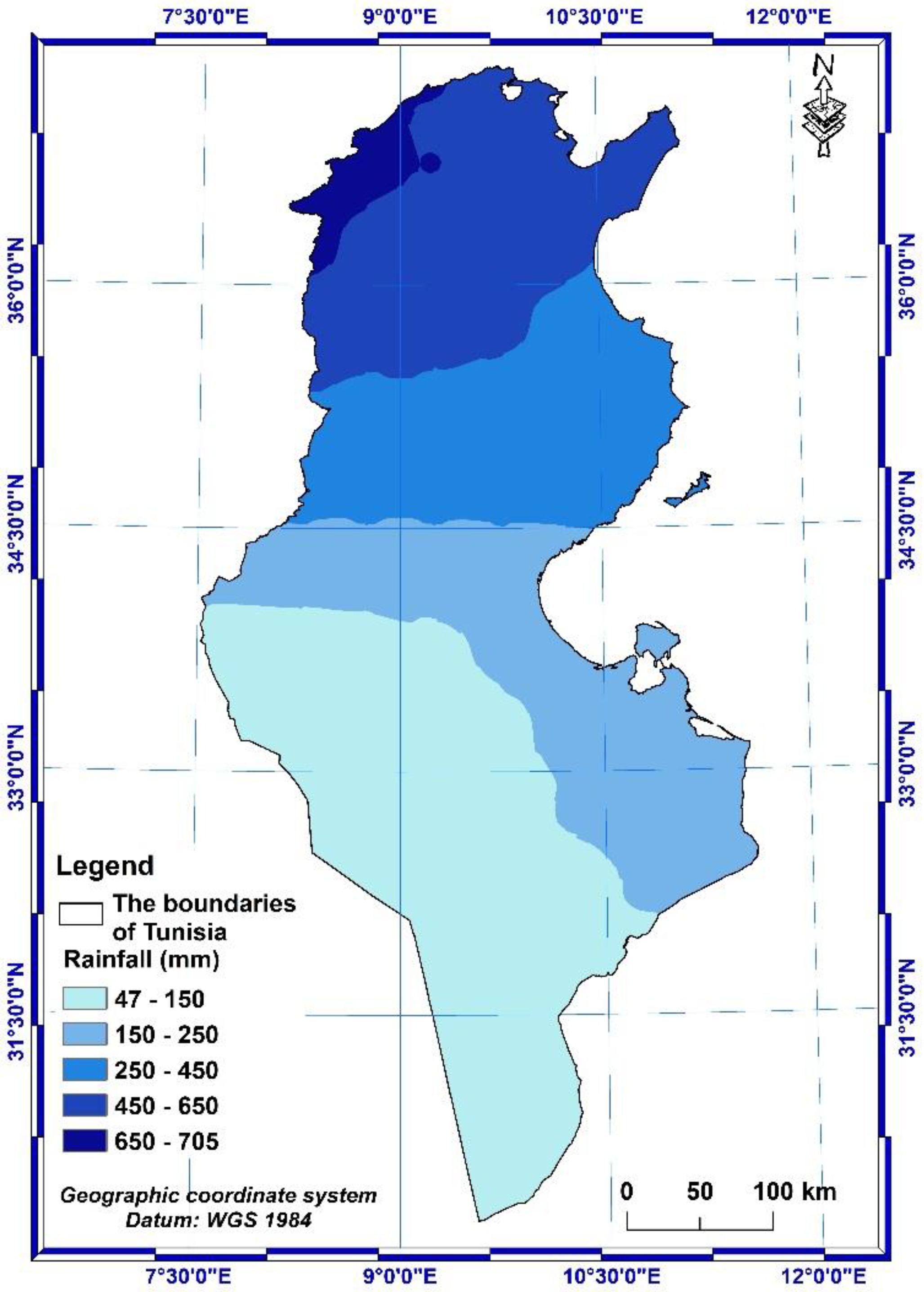
2.1. Description of the study area
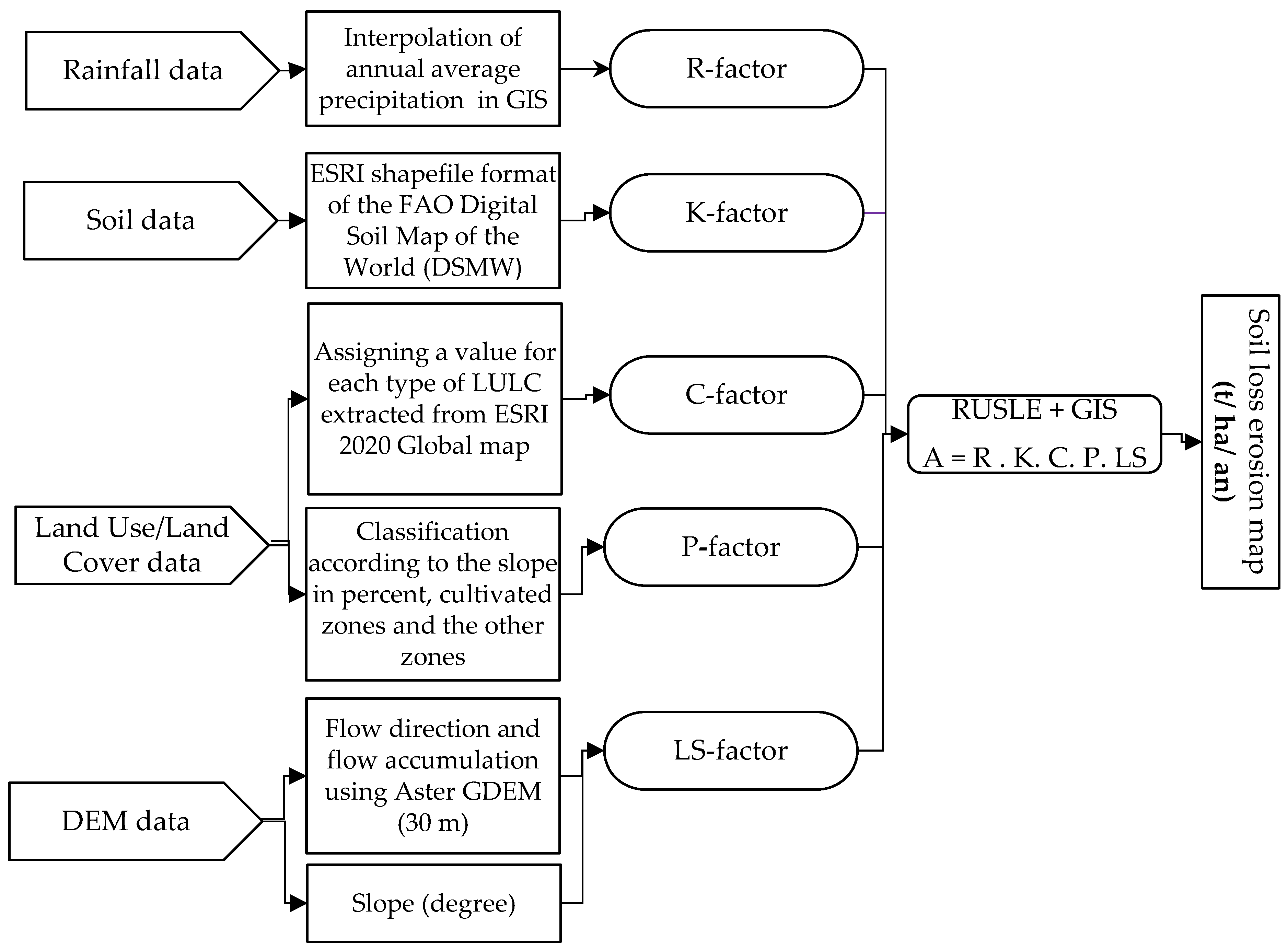
2.2. Methodology and data source processing
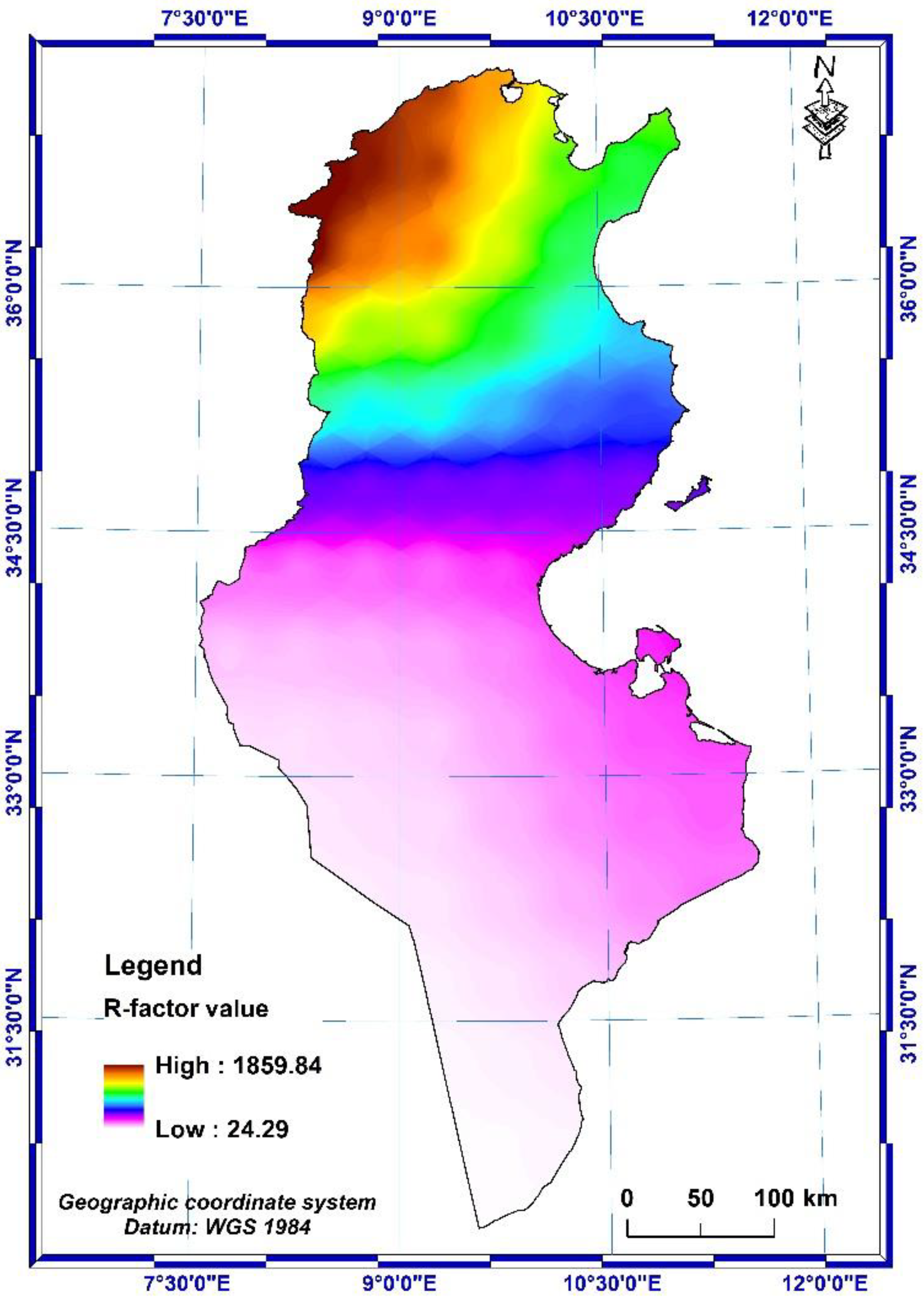
2.2.1. Rainfall and runoff erosivity factor (R-factor)
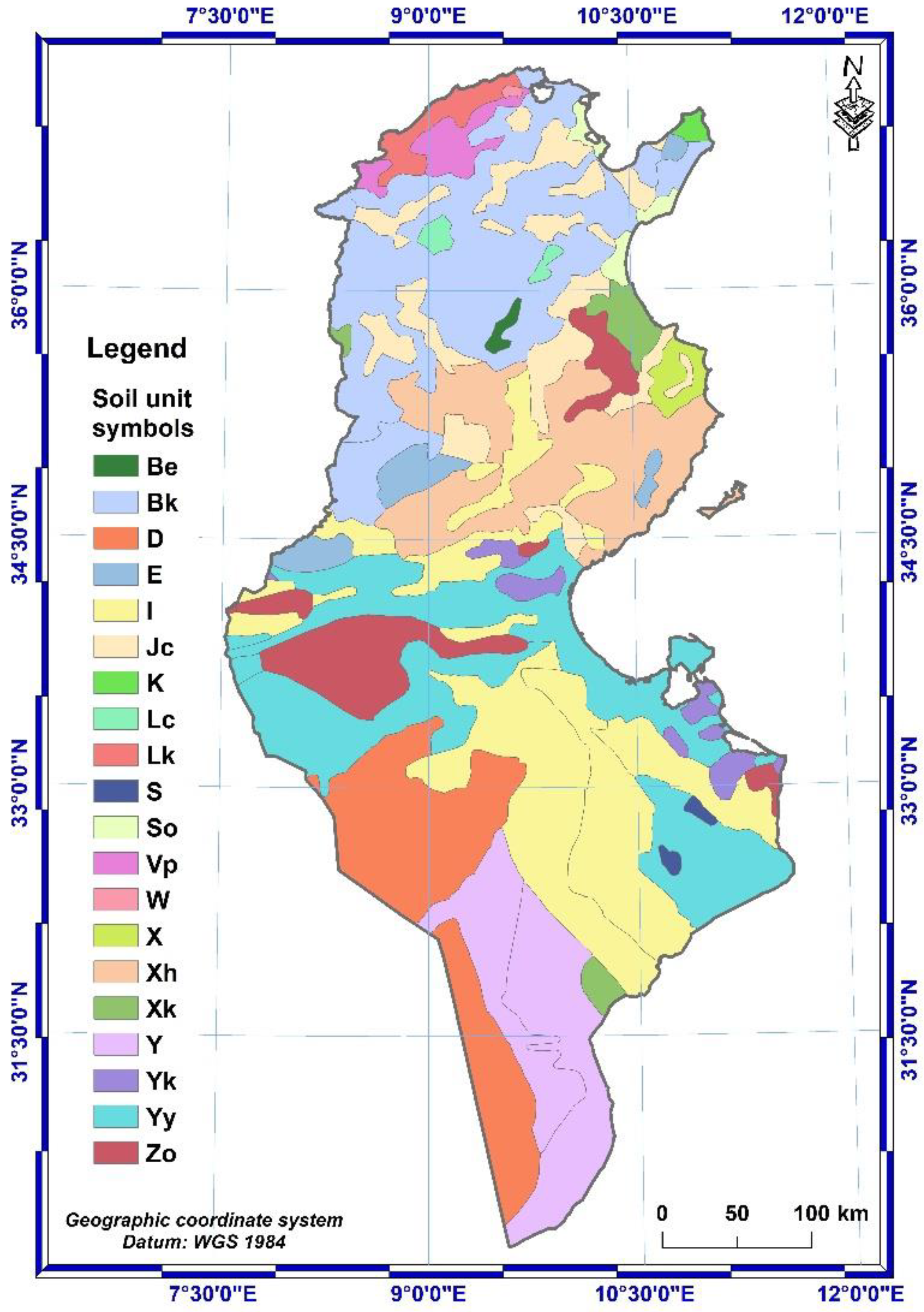
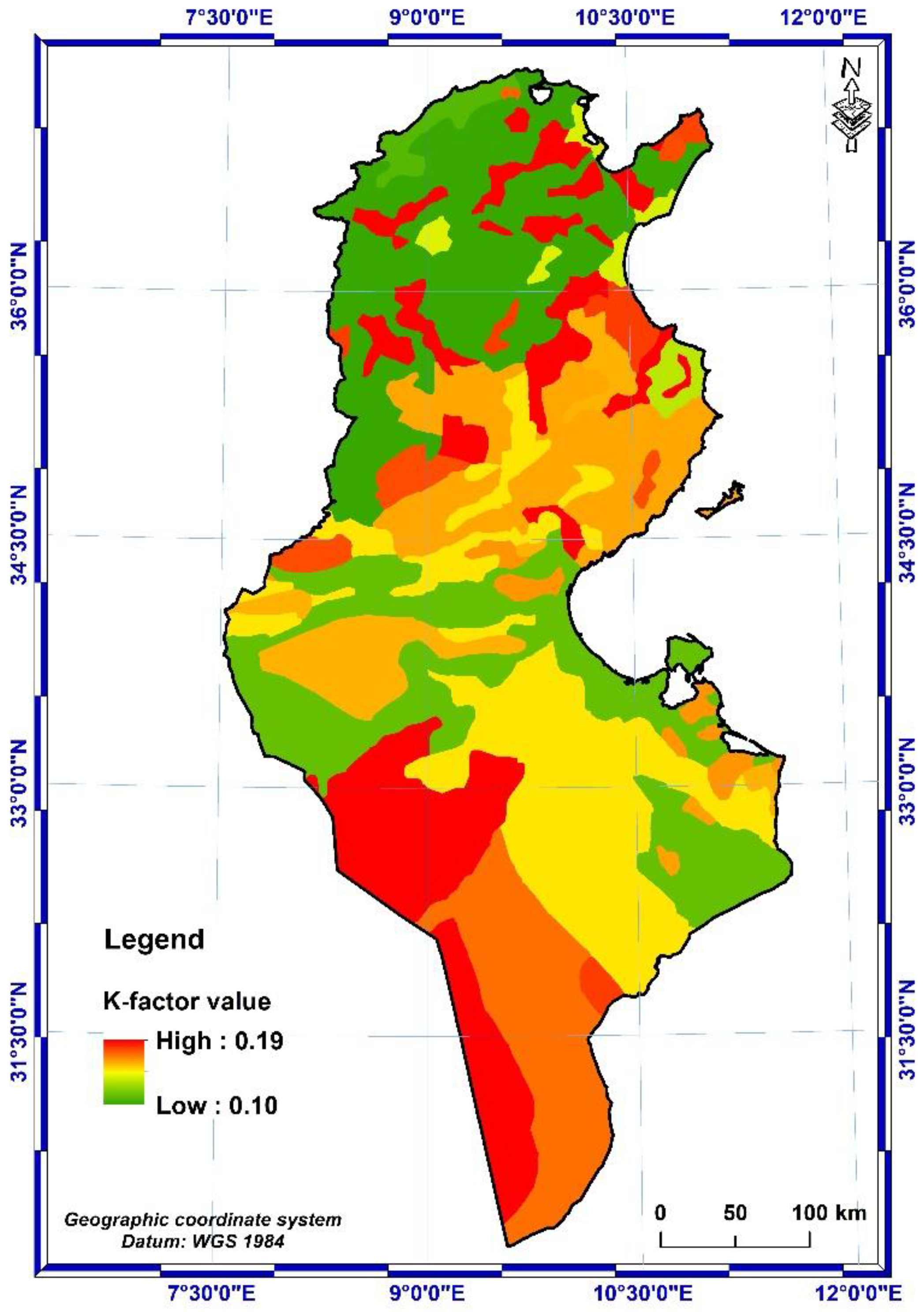
2.2.2. Soil erodibility (K-factor)
| Erodibility (K) | Type of soil |
|---|---|
| K < 0.10 | Soil highly resistant to erosion |
| 0.10 à 0.25 | Soil fairly resistant to erosion |
| 0.25 à 0.35 | Soil moderately resistant to erosion |
| 0.35 à 0.45 | Soil with low erosion resistance |
| >0.45 | Soil with very low resistance to erosion |
2.2.3. Topographic factor (LS-factor)
2.2.4. Vegetative cover factor (C-factor)
2.2.5. Support and management practice factor (P-factor)
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Spatial distributions of RUSLE factors
3.1.1. R-factor
3.1.2. K-factor
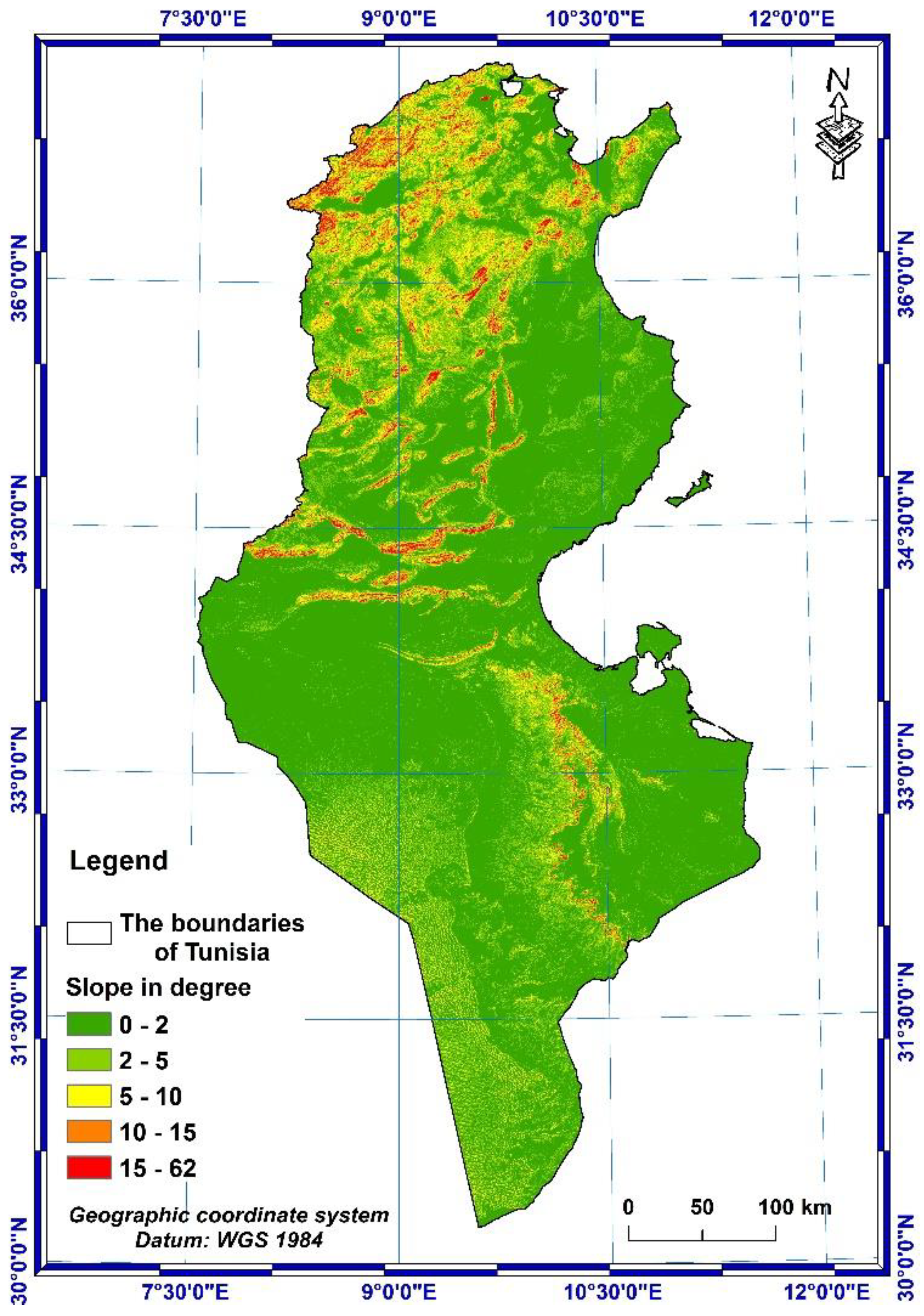
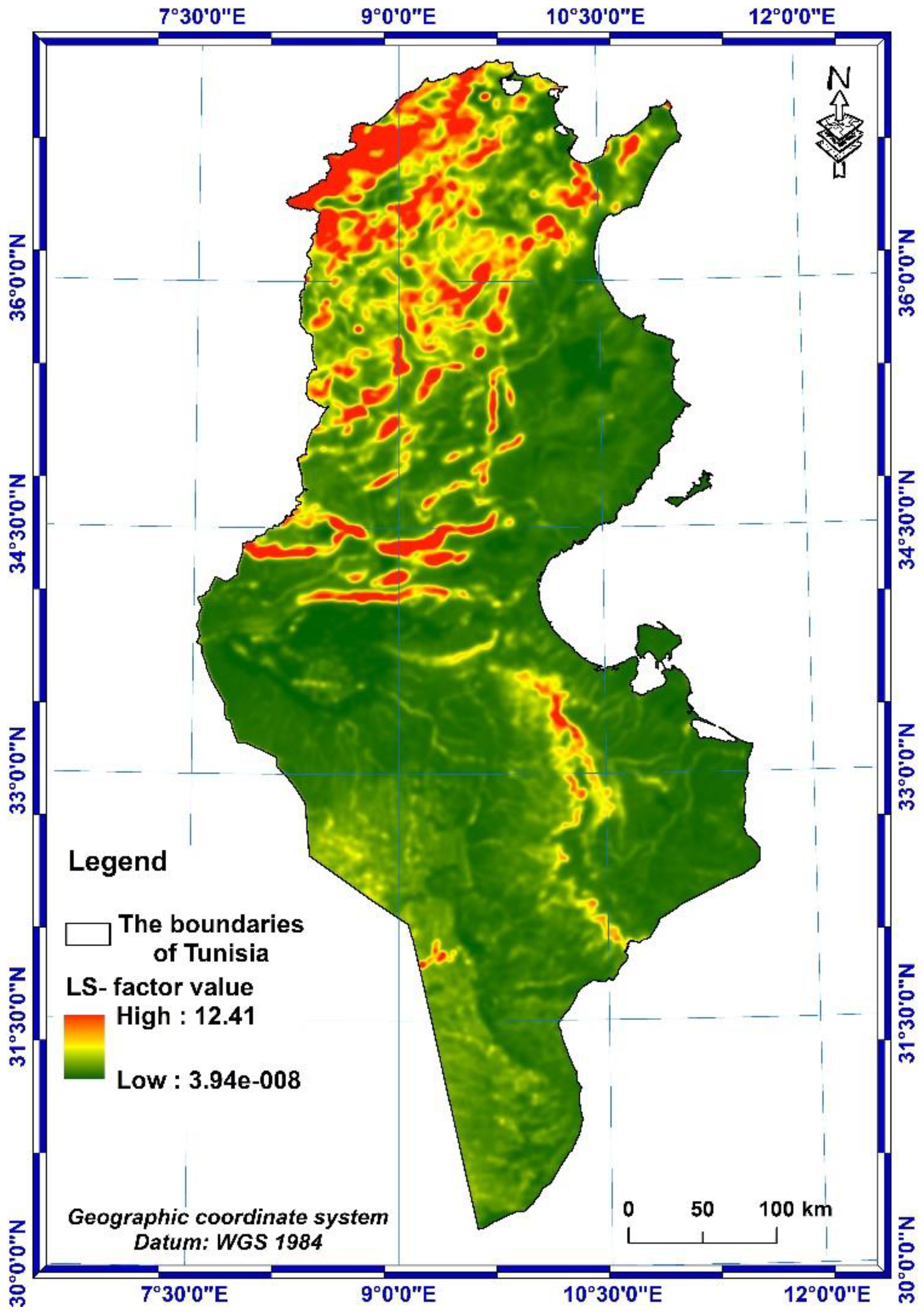
3.1.3. LS-factor
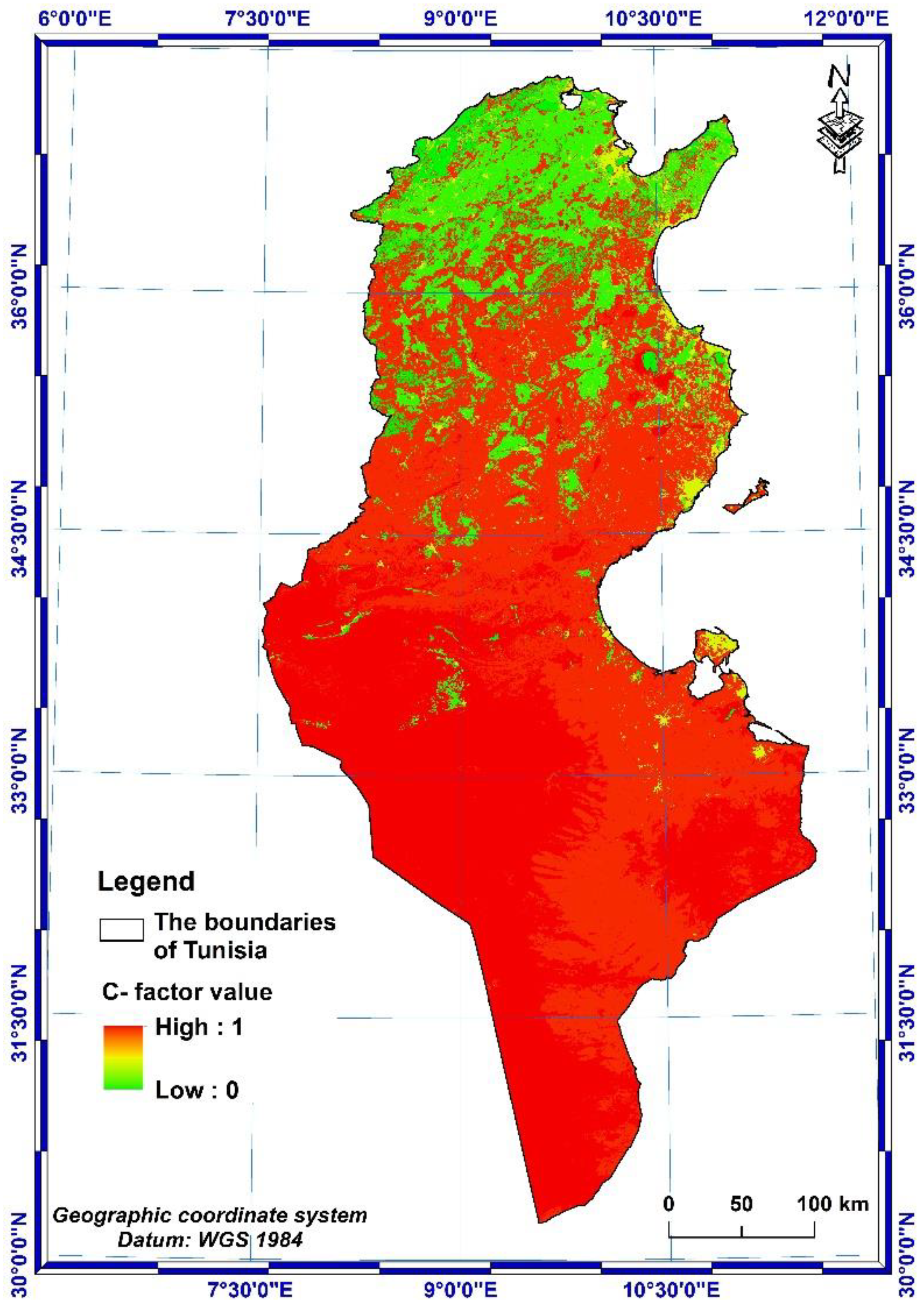
3.1.4. C-factor
3.1.5. P-factor
- The values of the erosivity factor of the rains vary from 24.29 to 1859.84 MJ.mm.h-1. ha-1. year-1 with an average of 473.73 MJ.mm.h-1. ha-1. year-1 over the whole country.
- The soil erodibility K-factor is classified as fairly resistant to erosion, with values varying from 0.10 to 0.19 t. h. MJ-1.mm-1.
- The value range of the topographic factor LS is between 0 and 12.41, with an average value of 1.09 over the whole country.
- The values of the vegetative cover C-factor vary from 0 to 1.
- The values of the support and management practice factor vary from 0.1 to 0.33 for agricultural land and are equal to 1 for non-agricultural land.
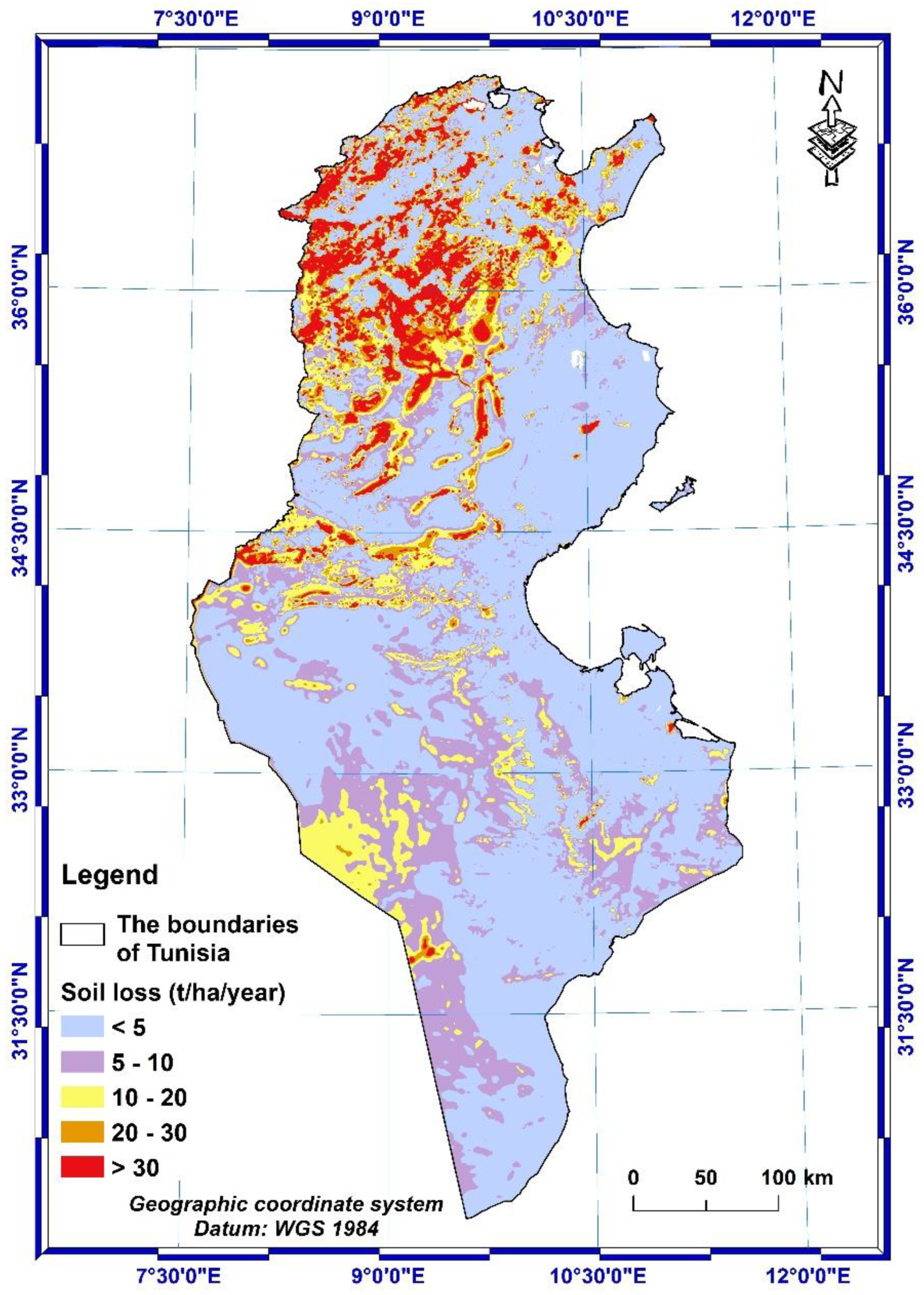
3.2. Calculation of soil loss rate and quantification of erosion
4. Conclusions
References
- Wang, B.; Zheng, F.; Römkens, M.J.M.; Darboux, F. Soil erodibility for water erosion: A perspective and Chinese experiences. Geomorphology 2013, 187, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keesstra, D.S.; Bouma, J.; Wallinga, J.; Tittonell, P.; Smith, P.; Cerdà, A.; Montanarella, L.; Quinton, J.N.; Pachepsky, Y.; van der Putten, W.H.; et al. The significance of soils and soil science towards realization of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals. Soil 2016, 2, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessel, R.; Wyseure, G.; Panagea, I.S.; Alaoui, A.; Reed, M.S.; van Delden, H.; Muro, M.; Mills, J.; Oenema, O.; Areal, F.; van den Elsen, E.; Verzandvoort, S.; Assinck, F.; Elsen, A.; Lipiec, J.; Koutroulis, A.; O’Sullivan, L.; Bolinder, M.A.; Fleskens, L.; Kandeler, E.; Montanarella, L.; Heinen, M.; Toth, Z.; Hallama, M.; Cuevas, J.; Baartman, J.E.M.; Piccoli, I.; Dalgaard, T.; Stolte, J.; Black, J.E.; Chivers, C.A. Soil-Improving Cropping Systems for Sustainable and Profitable Farming in Europe. Land 2022, 11, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J. and Wang, H. Temporal analysis on quantitative attribution of karst soil erosion: a case study of a peak-cluster depression basin in Southwest China. Catena 2018, (172): 369–377.
- Karydas, C. G.; Panagos, P. Modelling monthly soil losses and sediment yields in Cyprus, International Journal of Digital Earth 2016, Vol. 9, No. 8, 766–787.
- Buryak, Z.A.; Narozhnyaya, A.G.; Gusarov, A.V.; Beylich, A.A. Solutions for the Spatial Organization of Cropland with Increased Erosion Risk at the Regional Level: A Case Study of Belgorod Oblast, European Russia. Land 2022, 11, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wan, S.; Luo, W. Biochars Prepared from Anaerobic Digestion Residue, Palm Bark, and Eucalyptus for Adsorption of Cationic Methylene Blue Dye: Characterization, Equilibrium, and Kinetic Studies. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 140, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J. Wetland and Its Degradation in the Yellow River Source Zone. In Landscape and Ecosystem Diversity, Dynamics and Management in the Yellow River Source Zone; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2016; pp. 209–232. [Google Scholar]
- Kefi, M. ; Yoshino, K; Setiawan, Y. Assessment and mapping of soil erosion risk by water in Tunisia using time series MODIS data. Paddy Water Environ 2012, 10:59–73.
- Sidi Almouctar, M.A.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, F.; Dossou, J.F. Soil Erosion Assessment Using the RUSLE Model and Geospatial Techniques (Remote Sensing and GIS) in South-Central Niger (Maradi Region). Water 2021, 13, 3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganasri, B.P.; Ramesh, H. Assessment of Soil Erosion by RUSLE Model Using Remote Sensing and GIS - A Case Study of Nethravathi Basin. Geosci. Front. 2016, 7, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Jazouli, A.; Barakat, A.; Khellouk, R.; Rais, J.; El Baghdadi, M. Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques for Prediction of Land Use Land Cover Change Effects on Soil Erosion in the High Basin of the Oum Er Rbia River (Morocco). Remote. Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2019, 13, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spalevic, V.; Barovi´c, G.; Vujaˇci´c, D.; Curovi´c, M.; Behzadfar, M.; Djurovi´c, N.; Dudi´c, B.; Billi, P. The Impact of Land Use Changes on Soil Erosion in the River Basin of Miocki Potok, Montenegro. Water 2020, 12, 2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastridis, A.; Kamperidou, V. Influence of Land Use Changes on Alleviation of Volvi Lake Wetland (North Greece). Soil Water Res. 2016, 10, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall-Erosion Losses—A Guide to Conservation Planning. Agriculture Handbook No. 537; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1978; p. 58. [Google Scholar]
- Renard, K.G.; Foster, G.R.; Weesies, G.A.; McCool, D.K.; Yoder, D.C. Predicting Soil Erosion by Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE). Agricultural handbook No. 703; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1997; p. 407. [Google Scholar]
- Kirkby, M.J.; Irvine, B.J.; Jones, R.J.A.; Govers, G.; Boer, M.; Cerdan, O.; Daroussin, J.; Gobin, A.; Grimm, M.; Le Bissonnais, Y.; et al. The PESERA coarse scale erosion model for Europe. I.Model rationale and implementation. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2008, 59, 1293–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karydas, C.G.; Panagos, P. The G2 erosion model: An algorithm for month-time step assessments. Environ Res. 2018, 161:256-267.
- Morgan, R.P.C.; Quinton, J.N.; Smith, R.E.; Govers, G.; Poesen, J.W.A.; Auerswald, K.; Chisci, G.; Torri, D.; Styczen, M.E. The European Soil Ersoion Model (EUROSEM): A dynamic approach for predicting sediment transport from fields and small catchments. Earth Surf. Processes Landf. 1998, 23, 527–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrilovic, Z.; Stefanovic, M.; Milovanovic, I.; Cotric, J.; Milojevic, M. Torrent classification-Base of rational management of erosive regions. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2008, 4, 012039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragiˇcevi´c, N.; Karleuša, B.; Ožani´c, N. A. Review of the Gavrilovi´c method (erosion potential method) application. Gradevinar. 2016, 68, 715–725. [Google Scholar]
- Batista, P.V.G.; Davies, J.; Silva, M.L.N.; Quinton, J.N. On the evaluation of soil erosion models: Are we doing enough? Earth-Sci. Rev. 2019, 197, 102898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igwe, P.U.; Onuigbo, A.A.; Chinedu, O.C.; Ezeaku, I.I.; Muoneke, M.M. Soil Erosion: A Review of Models and Applications. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Res. Sci. 2017, 4, 237341. [Google Scholar]
- Karydas, C. G.; Panagos, P.; Gitas, I. Z. A Classification of Water Erosion Models According to Their Geospatial Characteristics. International Journal of Digital Earth 2014, Vol. 7, No. 3, 229–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kefi, M.; Yoshino, K.; City, T. Evaluation of the Economic Effects of Soil Erosion Risk on Agricultural Productivity Using Remote Sensing: Case of Watershed in Tunisia. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote. Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2010, 38, 930. [Google Scholar]
- Wischmeier, W.H. , Smith D.D. Predicting Rainfall-Erosion Losses from Cropland East of the Rocky Mountains: Guide for Selection of Practices for Soil and Water Conservation. Washington, D.C., USDA, Agricultural Research Service. 1965.
- Bera, A. Assessment of soil loss by universal soil loss equation (USLE) model using GIS techniques: a case study of Gumti River Basin, Tripura, India. Model Earth Syst Environ. 2017, 3:29.
- Elaloui, A.; Marrakchi, C.; Fekri, A. et al. USLE-based assessment of soil erosion by water in the watershed upstream Tessaoute (Central High Atlas, Morocco). Model Earth Syst Environ. 2017, 3:873–885.
- Pham, T.G.; Degener, J.; Kappas, M. Integrated universal soil loss equation (USLE) and geographical information system (GIS) for soil erosion estimation in A Sap basin: Central Vietnam. Int Soil Water Conserv Res. 2018, 6:99–110.
- Renard, K.G.; Foster, G.R.; Weesies, G.A.; McCool, D.K. Predicting soil erosion by water. A guide to conservation planning with the revised universal soil loss equation (RUSLE). Agric. Handbook 703. US Govt Print Office, Washington, DC. 1993.
- Maqsoom, A.; Aslam, B.; Hassan, U.; Kazmi, Z.A.; Sodangi, M.; Tufail, R.F.; Farooq, D. Geospatial Assessment of Soil Erosion Intensity and Sediment Yield Using the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) Model. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Lyu, D.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Yin, D.; Zhao, Z.; Mu, Z. Assessment of Soil Erosion Dynamics Using the GIS-Based RUSLE Model: A Case Study of Wangjiagou Watershed from the Three Gorges Reservoir Region, Southwestern China. Water 2018, 10, 1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q. , Xu, Y., Bennett, S.J., Li, Y. Assessment of soil erosion using RUSLE and GIS: a case study of the Yangou watershed in the Loess Plateau, China. Environmen. Earth Sci. 2015, 73 (4), 1715–1724.
- Ganasri, B.P.; Ramesh, H. Assessment of soil erosion by RUSLE model using remote sensing and GIS-A case study of Nethravathi Basin. Geosci. Front 2016, 7(6), 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosal, K.; Bhattacharya, S.D. A review of RUSLE Model. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2020. 1–19.
- Tzioutzios, C.; Kastridis, A. Multi-Criteria Evaluation (MCE) Method for the Management of Woodland Plantations in Floodplain Areas. Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, K.S.; Mishra, A.K.; Bhattacharyya, R. Soil Erosion Risk Assessment and Spatial Mapping Using LANDSAT-7 ETM+, RUSLE, and GIS—A Case Study. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Remortel, R.D.; Maichle, R.W.; Hickey, R.J. Computing the LS factor for the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation through array-based slope processing of digital elevation data using a C++ executable. Computers & Geosciences 2004, 30: 1043–1053.
- Efthimiou, N.; Lykoudi, E.; Psomiadis, E. Inherent Relationship of the USLE, RUSLE Topographic Factor Algorithms and Its Impact on Soil Erosion Modelling. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2020, 65, 1879–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.S.; Pani, P. Estimation of Soil Erosion Using RUSLE and GIS Techniques: A Case Study of Barakar River Basin, Jharkhand, India. Modeling Earth Syst. Environ. 2015, 4, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K. A new European slope length and steepness factor (LS-factor) for modeling soil erosion by water. Geosciences 2015, 5 (2), pp. 117-126.
- Yang, Q.; Guo, M.; Li, Z.; Wang, C. Extraction and analysis of China soil erosion topographic factor Soil Water Convers. China 2013, pp. 17-21.
- National Institute of Meteorology. Climatological Report for summer 2021 in Tunisia: Hottest summer on record since 1950. Climate Product Department-Deputy Direction of Climatology 2021, pp. 1-16. Available online: https://www.meteo.tn/ (accessed on 18 September 2022).
- Sadiki, A.; Bouhlassa, S.; Auajjar, J.; Faleh, A.; Macaire, J.J. Utilisation d’un SIG pour l’évaluation et la cartographie des risques d’érosion par l’Equation universelle des pertes en sol dans le Rif oriental (Maroc): cas du bassin versant de l’oued Boussouab. Bull l’Inst Sci Rabat Sect Sci Terre 2004, 26:69–79.
- Renard, K.G.; Freimund, J.R. Using Monthly Precipitation Data to Estimate the R Factor in the Revised USLE. Journal of Hydrology 1994, 157, 287–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pangali Sharma, T.P.; Zhang, J.; Khanal, N.R.; Prodhan, F.A.; Nanzad, L.; Zhang, D.; Nepal, P. A Geomorphic Approach for Identifying Flash Flood Potential Areas in the East Rapti River Basin of Nepal. Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, P. Spatial Estimation of Soil Erosion Using RUSLE Modeling: A Case Study of Dolakha District, Nepal. Env. Syst. Res. 2020, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hage Hassan, H. Les apports d'un SIG dans la connaissance des évolutions de l'occupation du sol et de la limitation du risque érosif dans la plaine de la Bekaa (Liban): exemple d'un secteur du Bekaa el Gharbi. 2011. Doctoral thesis. Orleans.
- Bolline, A.; Rousseau, P. Erodibilité des sols de moyenne en haute Belgique. Utilisation d’une méthode de calcul du facteur K de l’équation universelle de perte en terre. Bull. Soc. Géogr. de Liège 1978, 14, 4. pp. 127–140. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, J.R. Chapter 25: The EPIC model. In V.P. Singh (ed.) Computer models of watershed hydrology. Water Resources Publications 1995, p. 909-1000.
- Moore, I.D.; Wilson, J.P. Length-slope factors for the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation: Simplified method of estimation. Journal of soil and water conservation 1992, Sep 1;47(5):423-428.
- Moore, I.D.; Burch, G. J. Physical Basis of the Length Slope Factor in the Universal Soil Loss Equation. Soil Science Society America Journal 1986, 50: 1294–1298.
- Moore, I.D.; Gessler, P.E.; Nielsen, G.A.; Peterson, G.A. Soil attribute prediction using terrain analysis. Soil science society of america journal 1993, Mar;57(2):443-52.
- Jain, M.K.; Kothyari, U.C. Estimation of soil erosion and sediment yield using GIS. Hydrological Sciences Journal. 2000, Oct 1;45(5):771-86.
- Van der Knijff, J. M.; Jones, R.J.A.; Montanarella, L. Soil erosion risk: assessment in Europe. 2000.
- Garouani, A.; Chen, H.; Lewis, L.; Triback, A.; Abahrour, M. Cartographie de l'utilisation du sol et de l'érosion à partir d'images satellitaires et du SIG IDRISI au Nord Est du Maroc, Télédétection 2008, vol 8, n°3, p 193-201.
- Negese, A.; Fekadu, E.; Getnet, H. Potential Soil Loss Estimation and Erosion-Prone Area Prioritization Using RUSLE, GIS, and Remote Sensing in Chereti Watershed, Northeastern Ethiopia. Air, Soil and Water Research 2021,14.
- Karydas, C.G.; Sekuloska, T.; Silleos, G.N. Quantification and site-specification of the support practice factor when mapping soil erosion risk associated with olive plantations in the Mediterranean island of Crete. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 2009, Feb;149:19-28.
- Lazzari, M.; Gioia, D.; Piccarreta, M.; Danese, M.; Lanorte, A. Sediment yield and erosion rate estimation in the mountain catchments of the Camastra artificial reservoir (Southern Italy): a comparison between different empirical methods. Catena 2015, p323–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatandaşlar, C.; Yavuz, M. Modeling cover management factor of RUSLE using very high-resolution satellite imagery in a semiarid watershed. Environmental Earth Sciences 2017, Jan;76:1-21.
- Borrelli, P.; Marker, M.; Panagos, P.; Schutt, B. Modeling Soil Erosion and River Sediment Yield for an Intermountain Drainage Basin of the Central Apennines, Italy. Catena 2014, 114: 45–58.
- Sekiyama, A.; Mihara, M. Determining C factor of universal soil loss equation (USLE) based on remote sensing. International Journal of Environmental and Rural Development. 2016, p72. [Google Scholar]
- Shawul, A.A.; Chakma, S. Spatiotemporal detection of land use/land cover change in the large basin using integrated approaches of remote sensing and GIS in the Upper Awash basin, Ethiopia. Environmental Earth Sciences 2019, vol. 78, no. 5.
- Sewnet, A. Land use/cover change at Infraz watershed by using GIS and remote sensing techniques, northwestern Ethiopia. International Journal of River Basin Management 2015, vol. 14, no. 2, pp. 133–142.
- Chakilu, G.G.; Moges, M.A. Assessing the land use/cover dynamics and its impact on the low flow of Gumara watershed, upper Blue Nile basin, Ethiopia. Hydrology: Current Research 2017, vol. 8, no. 1.
- Guo, Q.K.; Liu, B.Y.; Yun, X.I.E.; Liu, Y.N.; Yin, S.Q. Estimation of USLE crop and management factor values for crop rotation systems in China. Journal of Integrative Agriculture 2015, 14(9), 1877–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurni, H. Erosion-productivity-conservation systems in Ethiopia.1985, 654-674.
- Tiruneh, G.; Ayalew, M. Soil loss estimation using geographic information system in enfraz watershed for soil conservation planning in highlands of Ethiopia. International Journal of Agricultural Research, Innovation and Technology (IJARIT). 2015, 5(2355-2020-1587):21-30.
- Ewunetu, A.; Simane, B.; Teferi, E.; Zaitchik, B.F. Land cover change in the blue nile river headwaters: farmers’ perceptions, pressures, and satellite-based mapping. Land 2021, 10(1), 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdogan, H.E.; Erpul, G.; Bayramin, I. Use of USLE/GIS methodology for predicting soil loss in a semiarid agricultural watershed. Turkey: Department of Soil Science, University of Ankara 2006.
- Swarnkar, S.; Malini, A.; Tripathi, S.; Sinha, R. Assessment of uncertainties in soil erosion and sediment yield estimates at ungauged basins: an application to the Garra River basin, India. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences 2018, Apr 24;22(4):2471-85.
- Lufafa, A.; Tenywa, M.M.; Isabirye, M.; Majaliwa, M.J.G.; Woomer, P.L. Prediction of soil erosion in a Lake Victoria basin catchment using a GIS-based Universal Soil Loss model. Agricultural systems 2003, 76(3), 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The ASTER Global Digital Elevation Model V003. Available online: https://search.earthdata.nasa.gov/downloads (accessed on 12 February 2022).
- FAO. Digital Soil Map of the World (DSMW)|Land & Water|Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Land & Water|Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Available online: http://www.fao.org/land-water/land/landgovernance/land-resources-planning-toolbox/category/details/en/c/1026564/ (accessed on 2 April 2022).
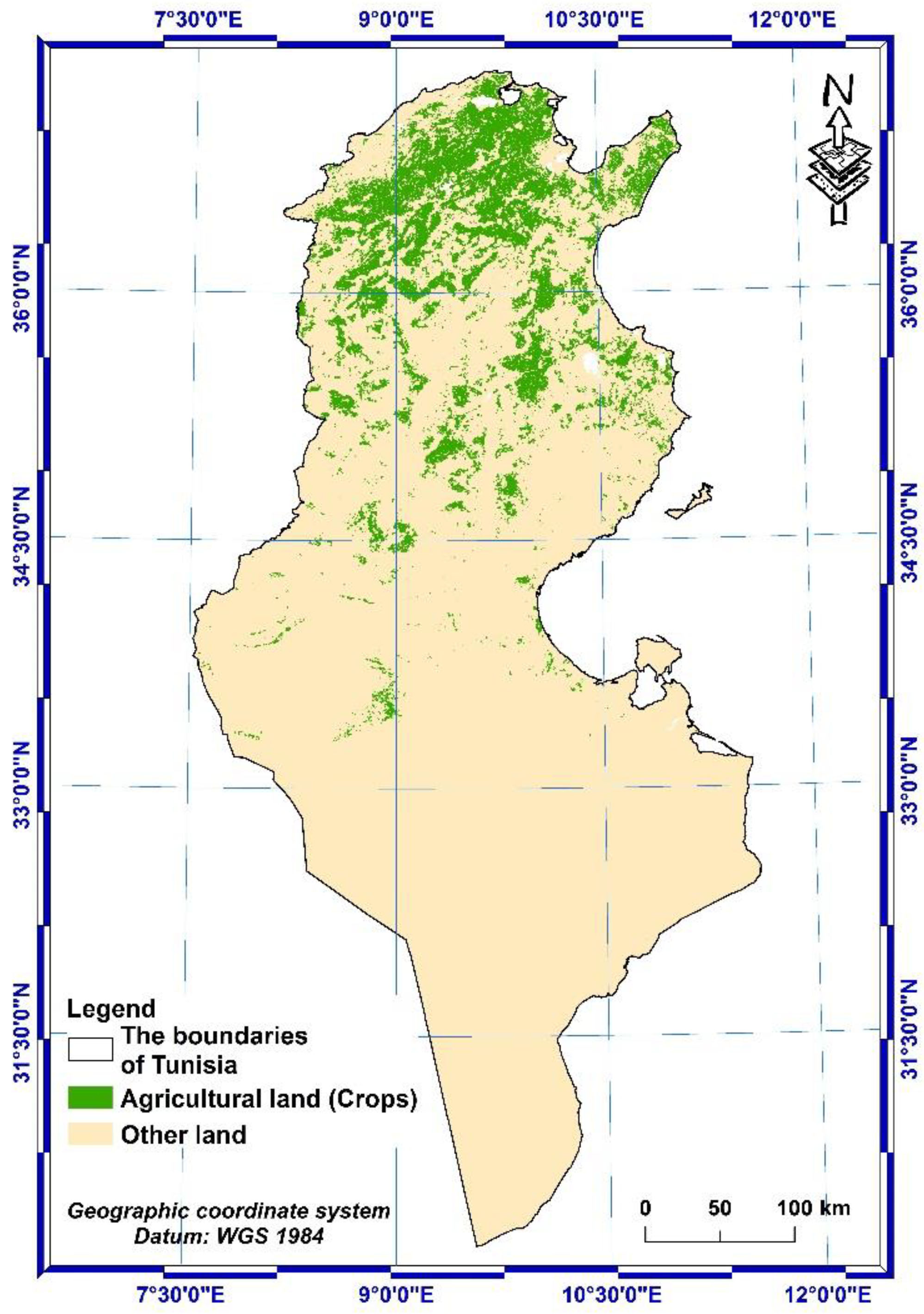
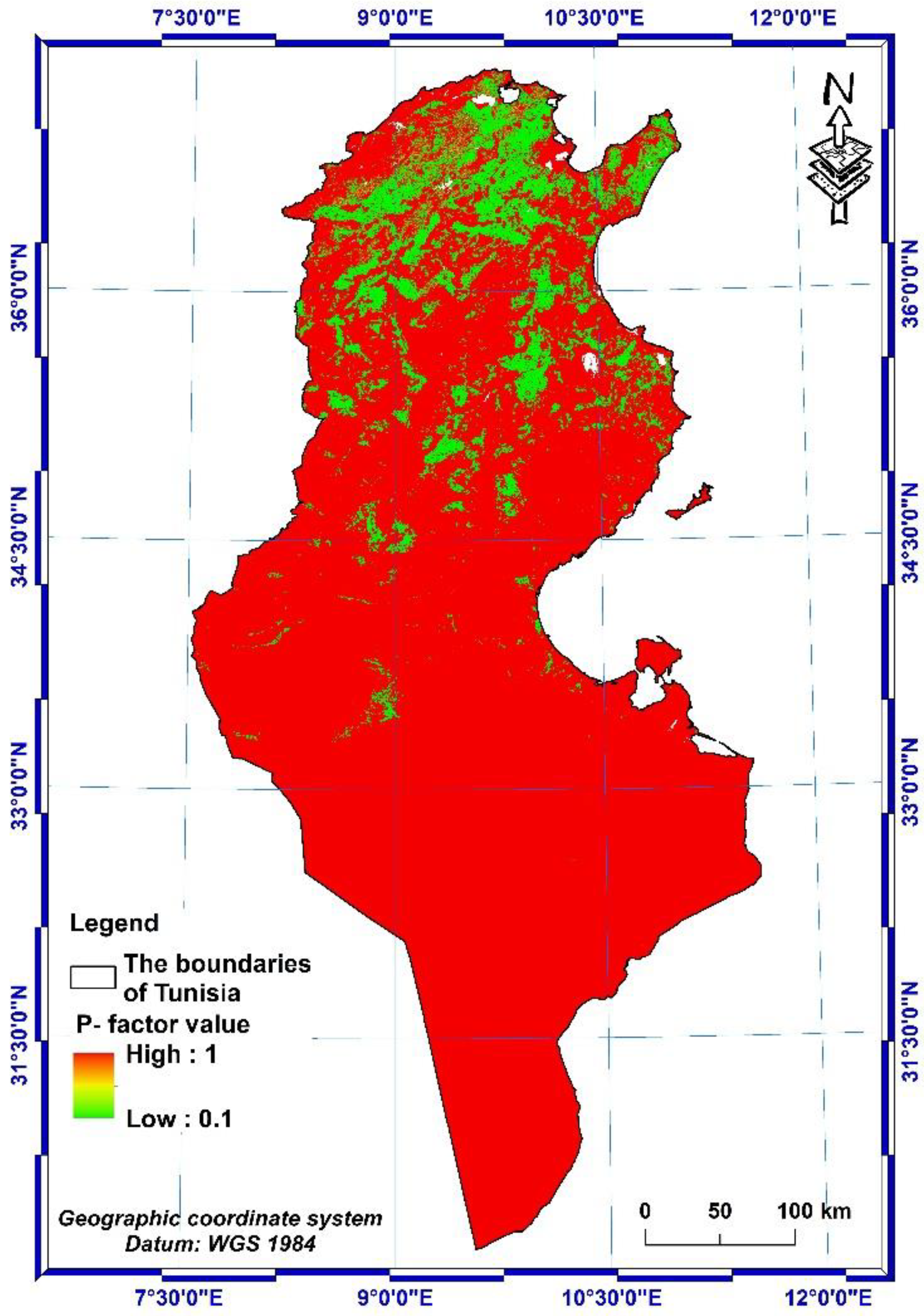
| N° | Type of Data | Data description | Name of the service that provide the data | Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Rainfall data | Monthly and annual precipitation data derived from NASA's Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM)-CSV file format | National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Prediction of Worldwide Energy Resources (POWER project) | https://power.larc.nasa.gov/data-access-viewer/ |
| 2 | Soil data | FAO Digital Soil Map of the World (DSMW)-ESRI shapefile format | Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations | https://data.apps.fao.org/map/catalog/srv/eng/catalog.search#/home |
| 3 | DEM data | Terra Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer-Global Digital Elevation Model (ASTER-GDEM)-Version 3-Grid format at 30m resolution | NASA’s Earth Observing System Data and Information System (EOSDIS) | https://search.earthdata.nasa.gov/download/ |
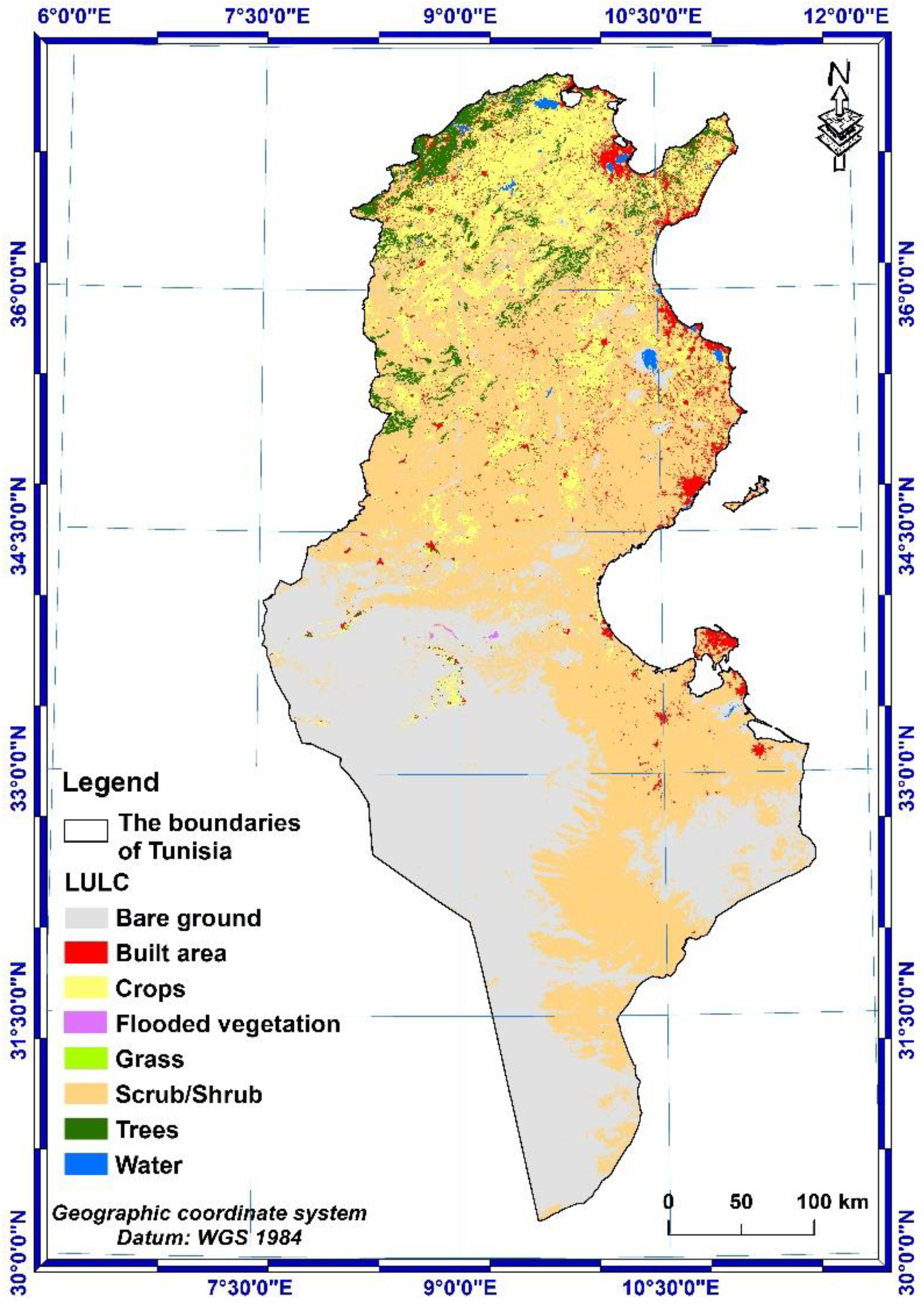
| 4 | LULC data | ESRI 2020 Global Land Use Land Cover from Sentinel-2 (TIF file format) | The map is derived from ESA Sentinel-2 imagery at 10 m resolution. | https://livingatlas.arcgis.com/landcover/ |
| LULC type | C-factor | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Cropland | 0.24 | Guo et al., 2015 [66] |
| Forest (Dense) | 0.01 | Hurni, 1985 [67] |
| Grassland | 0.05 | Tiruneh and Ayalew, 2015 [68] |
| Shrubland | 0.2 | Tiruneh and Ayalew, 2015 [68] |
| Bare land | 0.6 | Ewunetu et al., 2021 [69] |
| Waterbody | 0 | Erdogan et al., 2006 [70]; Swarnkar el al., 2018 [71] |
| Settlement | 0.15 | Hurni, 1985 [67] |
| Slope (%) | P- Factor | |
|---|---|---|
| Agricultural land | 0 – 5 | 0.1 |
| 5 – 10 | 0.12 | |
| 10 – 20 | 0.14 | |
| 20 – 30 | 0.19 | |
| 30 – 50 | 0.25 | |
| 50 – 100 | 0.33 | |
| Other land | All | 1 |
| Score scale | Soil loss class (t/ha/year) | Area (km2) | Area percentage (%) | Indicator |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | < 5 | 87559,33 | 56,34 | Very low |
| 2 | 5 - 10 | 32854,00 | 21,14 | Low |
| 3 | 10 - 20 | 18471,60 | 11,89 | Moderate |
| 4 | 20 - 30 | 6535,03 | 4,21 | High |
| 5 | > 30 | 9989,66 | 6,43 | Very high |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





