1. Introduction
The progressive eye disease known as DR is a direct result of having mellitus. Increases in blood glucose occur chronically in people with Diabetes Mellitus where the pancreas does not generate or release enough blood adrenaline [
1,
2]. Most diabetics go blind from DR, especially those of retirement age in low-income nations. Early identification is crucial for preventing the consequences that can arise from chronic diseases like diabetes [
3].
Retinal vasculature abnormalities are the hallmark of DR, which can progress to irreversible vision loss due to scarring or hemorrhage [
1,
4]. This may cause gradual vision impairment, and in its most severe form, blindness. It is not possible to cure the illness, thus treatment focuses on preserving the patient’s present level of eyesight [
5]. The patient’s eyesight can be maintained most successfully if DR is caught early enough. To identify DR, an ophthalmologist must manually examine photographs of the retina in a patient’s eye, which is a costly and time-consuming technique [
6]. Examining retinal images for the presence and the kind of various abnormalities has long been the standard method for detecting DR by ophthalmologists. Microaneurysms (MIA), hemorrhages (HEM), soft exudates (SOX), and hard exudates (HEX) are the four most common forms of lesions identified [
1,
7], which can be identified as the following:
A sign of earlier start DR, MIA appear as tiny, red dots on the retina due to a weakening in the vessel walls. The dots have distinct borders and a dimension of 125 micrometers or less. There are six subtypes of microaneurysms, however treatments is the same for all of them [
8,
9].
In contrast to MIA, HEM is characterized by big spots on the retina with uneven edge widths of more than 125 micrometers. A hemorrhage can be either flame or blot, according to whether the spots are on the surface or deeper in the tissue [
10,
11].
The swelling of nerve fibers causes soft exudates, which appear as white ovals on the retina as defined as SOX [
1,
7].
The yellow spots on the retina, known as HEX, are the result of plasma leakage. They extend across the periphery of the retina and also have defined borders [
1,
2].
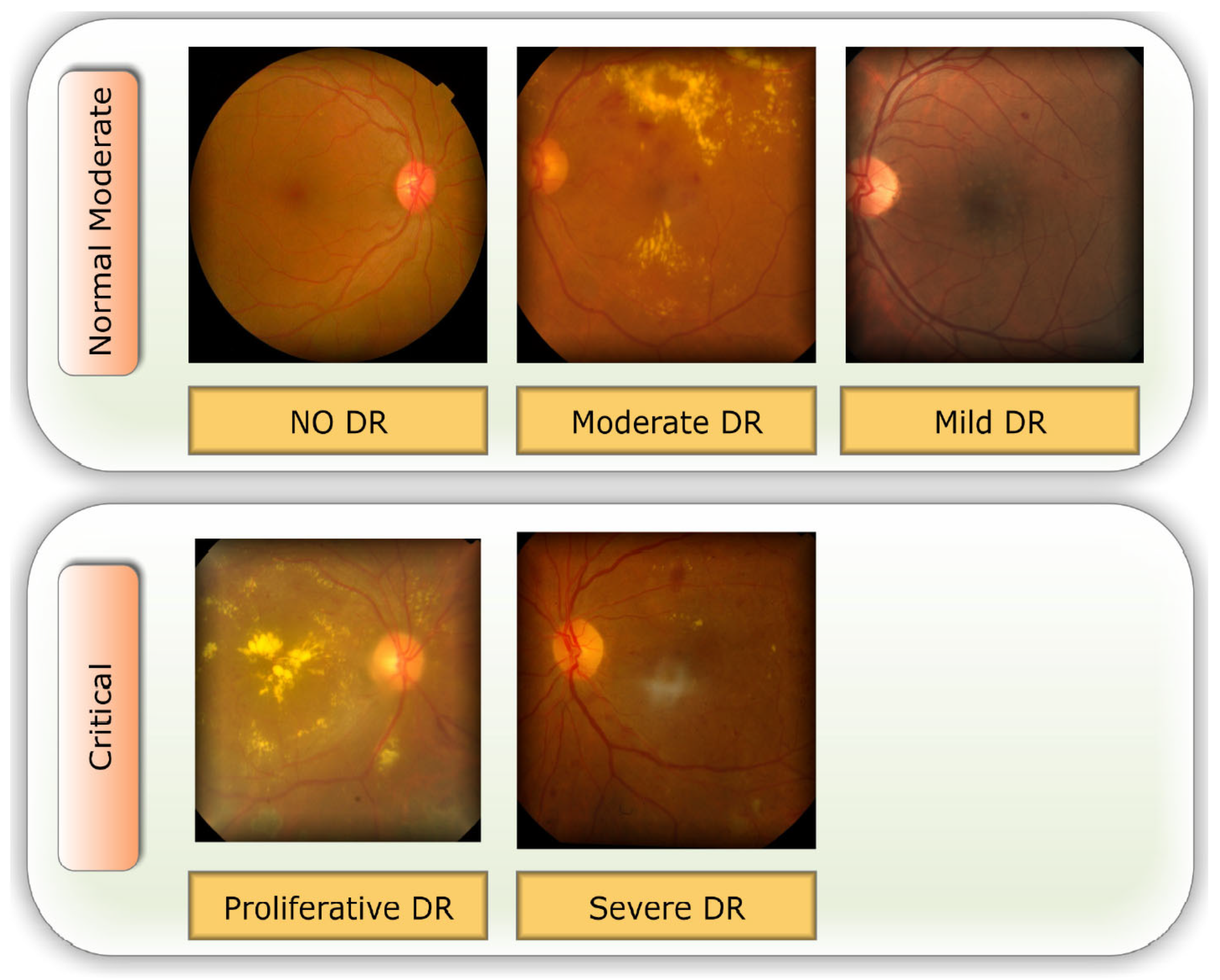
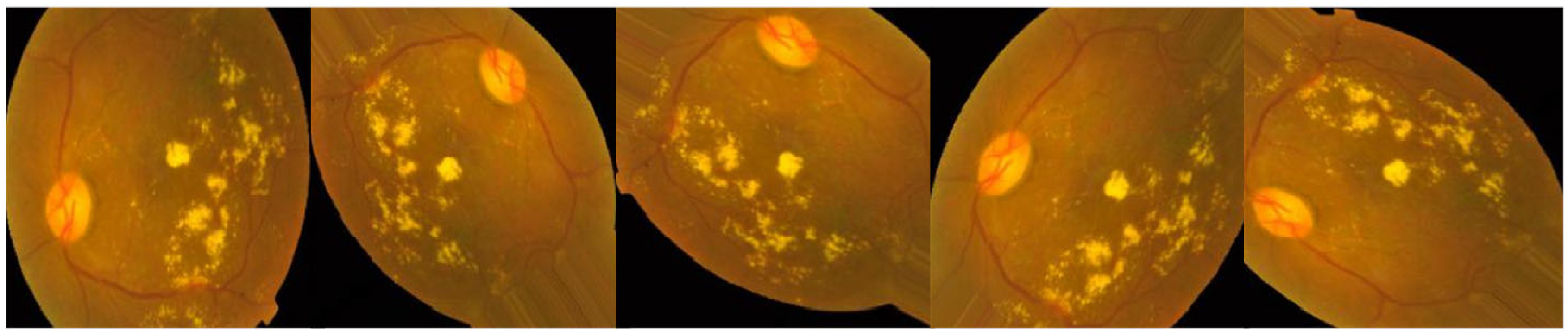
Lesions caused by MIA and HEM tend to be red, while blemishes caused by the two forms of exudates tend to be bright. There are five distinct stages of DR that can be detected: Different degrees of DR are shown in
Figure 1: none, mild, moderate, severe, and proliferative DR [
11].
Here, we highlight the original contributions of our study.
To generate high-quality images for the APTOS dataset, we used the CLAHE [
15] filtering algorithm in conjunction with ESRGAN [
16], which is the main contribution of the presented work.
By employing the technique of augmentation, we ensured that the APTOS dataset contained a consistent amount of data.
Accuracy (Acc), Confusion matrix (CM), precision (Prec), recall (Re), top n accuracy, and the F1-score (F1sc) are the indicators used in a comprehensive comparative study to determine the viability of the proposed system.
Pre-trained networks trained on the APTOS data set are fine-tuned with the use of an Inception-V3 weight-tuning algorithm.
By adopting a varied training procedure backed by various permutations of training strategies, the general reliability of the suggested method is enhanced, and overfitting is avoided (e.g., learning rate, data augmentation, batch size, and validation patience).
The APTOS dataset was used during both the training and evaluation phases of the model’s development. By employing stringent 80:20 hold-out validation, the model achieved a remarkable 98.71% accuracy of classification using enhancement techniques and 80.87% without using enhancement techniques.
This research presents two cases scenarios, in case 1 an optimal technique for DR stage enhancement using CLAHE followed by ESRGAN techniques, in case 2 no enhancement is applied to the images. Due to the class imbalance in the dataset, oversampling is required using augmentation techniques. In addition, we trained the weights of each model using Inception-V3, the results of the models have been compared using APTOS dataset images. This plan will be followed as we continue with the paper.
Section 2 provides context for the subsequent discussion of the related work.
Section 4 presents and analyzes the results of the proposed technique presented in
Section 3, and
Section 5 wraps up the research.2.
2. Related Work
There were various issues with DR picture detection when done manually. Numerous patients in underdeveloped nations face challenges due to a shortage of competence (trained ophthalmologists) and pricey tests. Because of the importance of timely detection in the fight against blindness, automated processing methods have been devised to facilitate accessibility to accurate and speedy diagnosis and treatment. Automated DR classification accuracy has recently been achieved by Machine Learning (ML) models trained on ocular fundus pictures. A lot of work has gone into developing automatic methods that are both efficient and inexpensive [
17,
18].
This means that these methods are now universally superior to their traditional counterparts. There are two main schools of thought in DR categorization research: traditional, expert-led methods, and cutting-edge, machine-learning-based methods, more in-depth analysis of these techniques is provided below. For instance, Alexandr et al. [
19] Compares a new improved structure (EfficientNet) to two extensively used traditional architectures (DenseNet, ResNet). The APTOS Symposium dataset is used to classify the retinal picture into one of five classes. Another work presented by Kazakh-British et al. [
20], performed experimental studies with relevant processing pipeline that extracted arteries from fundus pictures, after that, CNN model was trained to recognize lesions. A further method proposed by Macsik et al. [
21] proposes a new alternative of local binary CNN deterministic filter generation that can closely approximate the effectiveness of the traditional CNN with less training set and memory utilization, which can be advantageous in systems with limited memory or processing resources. They compare their binary classification of retinal fundus datasets into healthy and pathological groups to CNN and LBCNN, which use probabilistic filter sequence.
Furthermore, Al-Antary & Yasmine [
17] suggests the multi-scale attention network (MSA-Net) for DR categorization. The encoder network embeds the retina image in a high-level representational space, enriching it with mid- and high-level characteristics. A multi-scale feature pyramid describes the retinal structure in another location. On top of the high-level representation, a multi-scale attention mechanism improves feature representation discrimination. The model classifies DR severity using cross-entropy loss. The model detects healthy and unhealthy retina pictures as an extracurricular assignment using weakly annotations. This surrogate task helps the model recognize non-healthy retina pictures. EyePACS and APTOS datasets performed well with the proposed technique. Khalifa et al. [
22] examined DL models for medical DR detection. APTOS 2019 dataset was used for numerical experiments. This study used AlexNet, Res-Net18, SqueezeNet, GoogleNet, VGG16, and VGG19. These models were chosen because they have fewer layers than DenseNet and Inception-Resnet. Data augmentation improved model robustness and overfitting. A CNN-based DR detection and classification was presented by Hemanth et al. [
23]. They used HIST and CLAHE for image contrast enhancement and CNN model classification accuracy of 97% and F-measure of 94%. While, Maqsood et al. [
24] introduced a new 3D CNN model to localize hemorrhages, an early indicator of DR, using a pre-trained VGG-19 model to extract characteristics from the segmented hemorrhages. Their studies used 1509 photos from multiple datasets and averaged 97.71% accuracy. Das et al. [
25] recommended a fundus image-based CNN to classify normal and abnormal patients. Maximal principal curvature was used to recover blood vessels from pictures. Adaptive histogram equalization and morphological opening corrected incorrectly segmented sections. DIARETDB1 had 98.7% accuracy and 97.2% precision.
Table 1 summarizes the many attempts to detect DR anomalies in photos using various DL techniques [
17,
21,
26,
27,
28,
29,
30,
31,
32]. According to the results of the research into DR identification and diagnostic methods, there are still a lot of loopholes that need to be investigated. For beginning, there has been minimal emphasis on constructing and training a bespoke DL model entirely from the beginning because of the lack of a big amount of data, even though numerous researchers have obtained excellent dependability values utilizing pre-trained models using transfer-learning.
Ultimately, Training DL models with raw images instead of preprocessed images severely restricts the final classification network’s scalability, as was the case in nearly all of these studies. In order to resolve these problems, the current research creates a lightweight DR detection system by integrating multiple layers into the architecture of pre-trained models. This leads to a more efficient and effective proposed system that meets users’ expectations.
3. Research Methodology
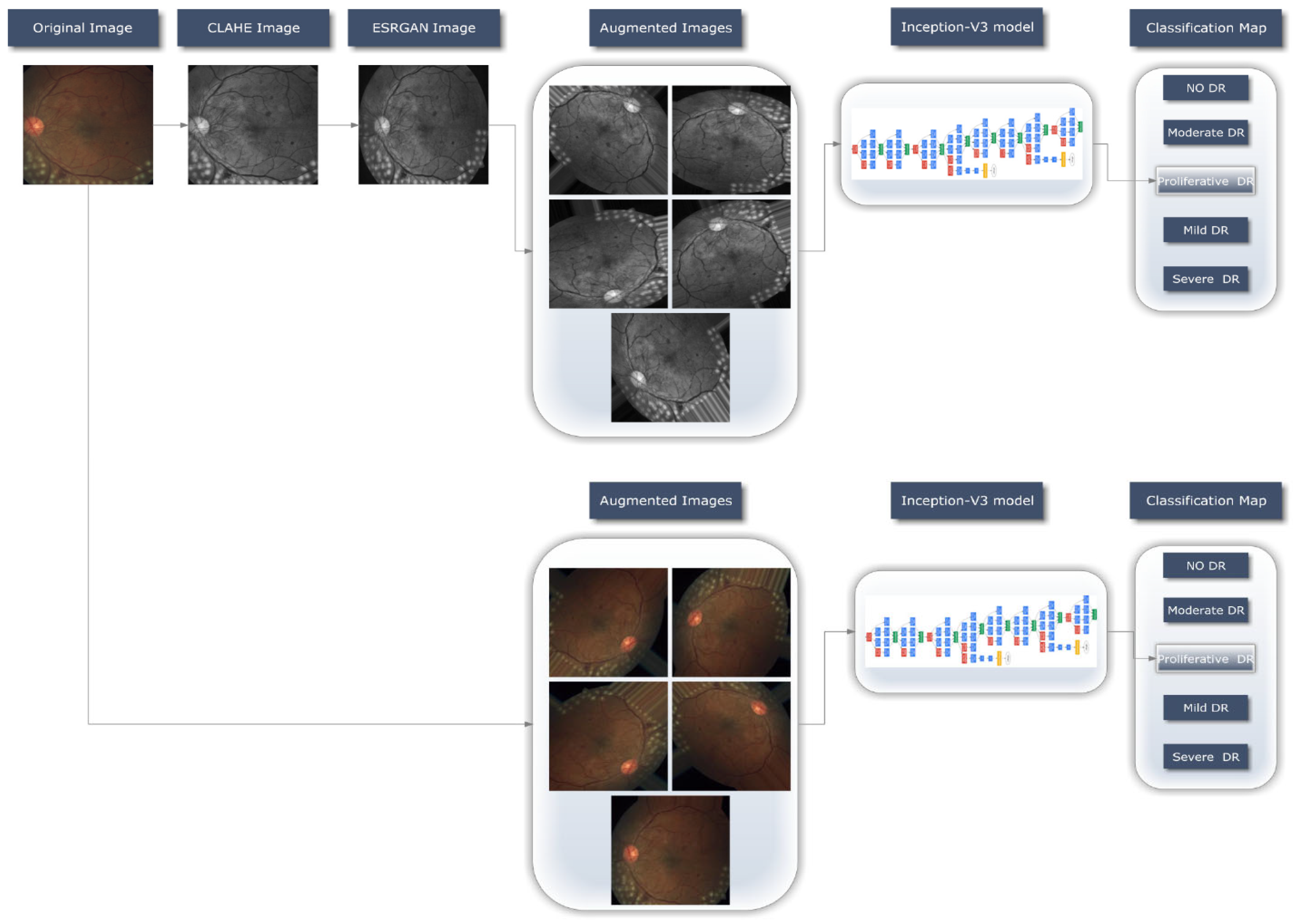
For the DR detection system to operate, as shown in
Figure 2, a transfer DL strategy (Inception-V3) have been retrained over in the image dataset in order to learn discriminative and usable feature representations. This section offers a concise summary of the method followed when working with the provided dataset. The preprocessing stage is then clearly outlined, and implementation specifics of the proposed system are covered; they include the 2 cases scenarios used in this context, the preprocessing techniques proposed, the basic design, and the training methodology for the approach that was ultimately chosen.
3.1. Data set Description
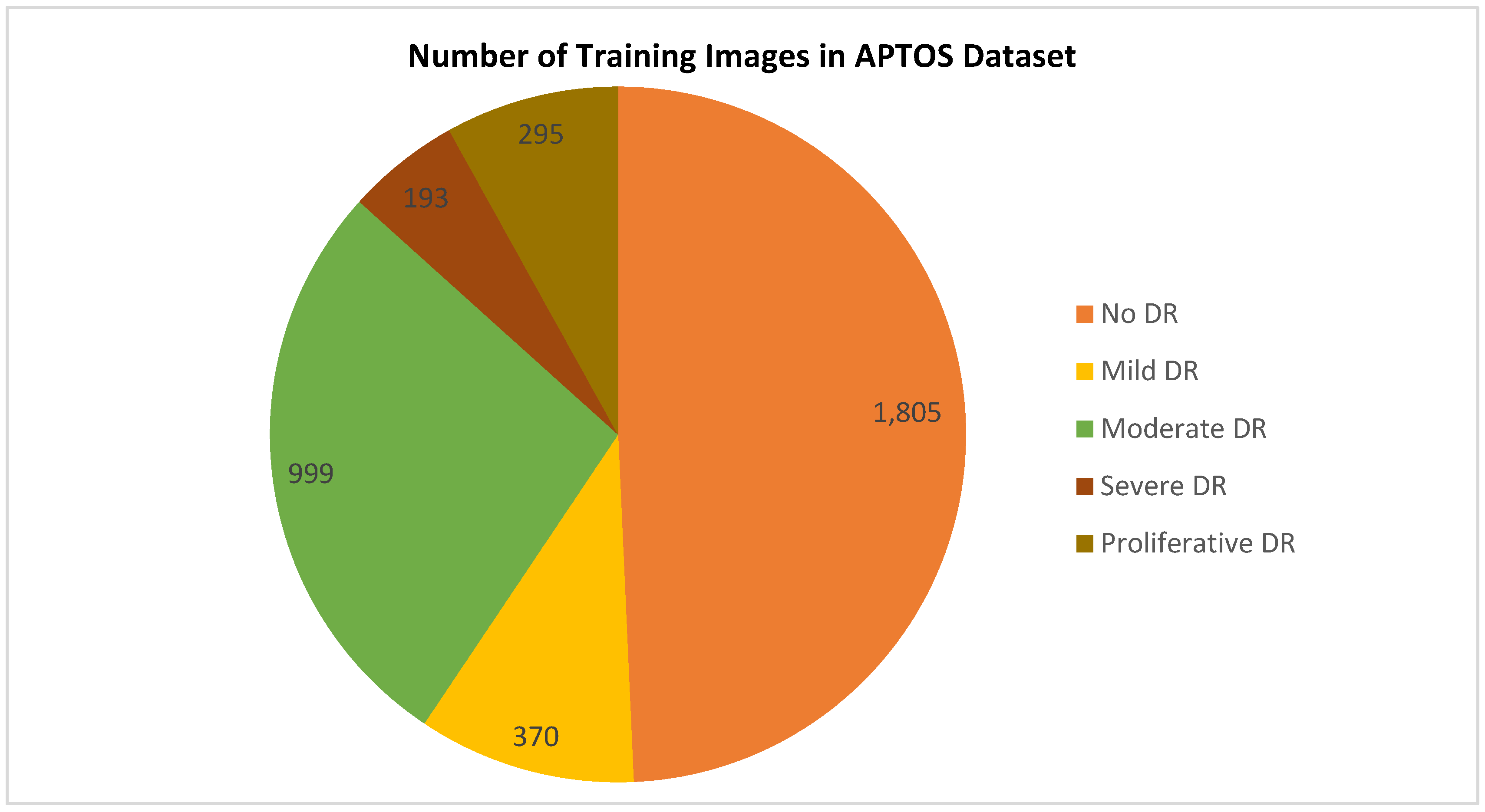
Selecting a dataset with a sufficient number of high-quality photos is crucial. This study makes use of the APTOS 2019 (Asia Pacific Tele-Ophthalmology Society) Blindness Detection Dataset [
14], a publically available Kaggle datasets that incorporates a huge number of photos. In this collection, high-resolution Retinal pictures are provided for the 5 stages of DR, classified from 0 (none) to 4 (proliferate DR), with labels 1-4 corresponding to the four levels of severity. There are 3,662 retinal pictures in total; 1,805 are from the "no DR" group, 370 are from the "mild DR" group, 999 are from the "moderate DR" group, 193 are from the "severe DR" group, and 295 are from the "proliferate DR" group as illustrated in
Table 2. Images are 3216 x 2136 pixels in size, and
Figure 1 shows some examples of these kind of pictures. There is background noise in the photographs and the labels, much like any real-world data set. It’s possible that the provided images will be flawed in some way, be it with artifacts, blurriness, improper exposure, or some other issue. The photos were collected over a long period of time from a number of different clinics using different cameras, all of which contribute to the overall high degree of diversity.
3.2. Proposed Methodology
An automatic DR classification model was developed using the dataset referenced in this paper, and its general process is demonstrated in
Figure 2. It demonstrates two different scenarios, case one in which preprocessing step is performed using CLAHE followed by ESRGAN is used and case 2 in which neither step is performed, while using augmentation of the images to prevent overfitting in both scenarios. Lastly, images are sent into the Inception-V3 model for classification step.
3.2.1. Preprocessing Using CLAHE and ESRGAN
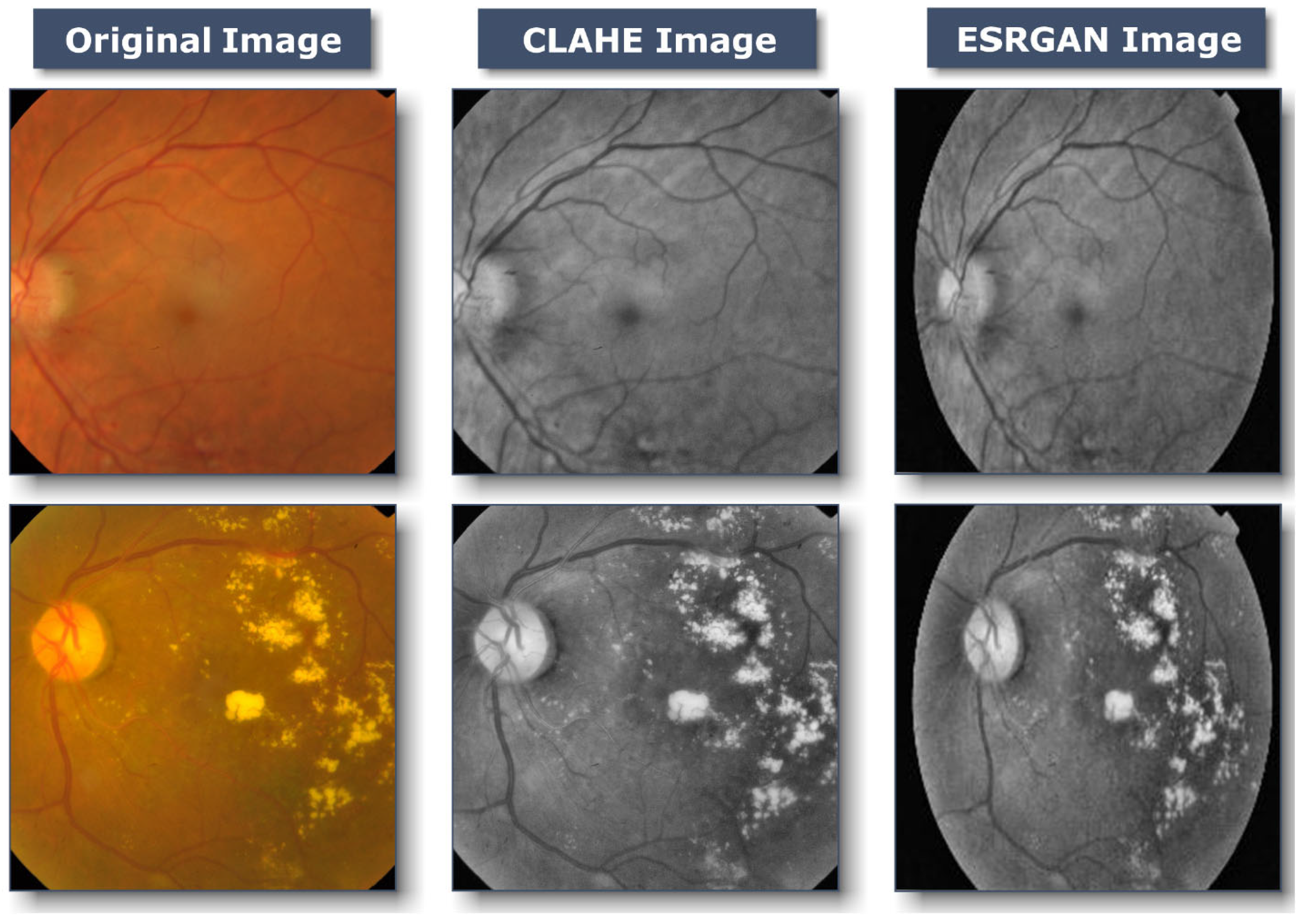
Images of the retinal fundus are often taken from several facilities using various technologies. Consequently, given the high intensity variation in the photographs used by the proposed method, it was crucial to enhance the quality of DR images and get rid of various types of noise. All images in case 1, undergo a preliminary preprocessing phase prior to augmentation and training necessitated various stages:
Figure 3b shows that first, CLAHE was used to improve the DR image’s fine details, textures, and low contrast by redistributing the input image’s lightness values [
33]. This was accomplished by separating the image into numerous non-overlapping sections of almost identical size. Therefore, this technique improves the local contrast enhancement while also making borders and slopes more apparent. Following this, all photos are scaled to suit the input of the learning model, which is 224*224*3.
Figure 3c depicts the subsequent application of ESRGAN on the output of the preceding stage. ESRGAN pictures can more closely mimic image artifacts’ sharp edges [
34]. Intensity differences between images can be rather large, thus images are normalized so that their intensities fall within the range [−1] to [1]; this keeps the data within acceptable bounds and gets rid of any noise. As a result of normalization, the model is less sensitive to variations in weights, making it easier to tune. As a result, the approach depicted in
Figure 3 enhances the appearance of the image’s borders and arcs while also increasing the image’s contrast, resulting in more precise results when utilizing this method.
3.2.3. Data Augmentation
Data augmentation was implemented on the training set to increase the number of images and alleviate the issue of an imbalanced dataset before exposing Inception-V3 to the dataset images. In most cases, deeper learning models perform better when given more data to learn from. We can utilize the characteristics of DR photos by applying several modifications to each image. If the image is magnified, flipped horizontally or vertically, or rotated by a specified number of degrees, the deep neural network (DNN) is unaffected. Data augmentations (i.e., shifting, rotating, and zooming) are utilized to regulate the data, reduce overfitting, and address the issue of dataset imbalance. The horizontal shift augmentation is one of the transformations utilized in this study; it horizontally shifts the image pixels while keeping the image’s aspect ratio, a number between 0 and 1 indicates the step size for this operation. Rotation is another transformation; after selecting a rotation angle between 0 and 180, the image is rotated at random. To create fresh samples for the network, all prior alterations to the training set’s images are applied.
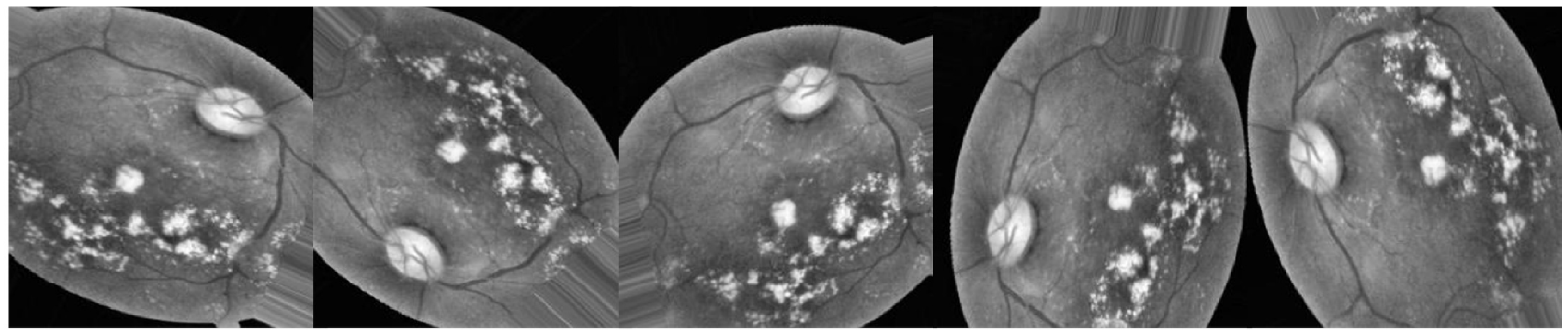
In this study, two scenarios were utilized to train Inception-V3: the first was to apply augmentation to the enhanced images, as depicted in
Figure 4, and the second was to apply augmentation to the raw images, as depicted in
Figure 5. Data augmentation, depicted in
Figure 4 and
Figure 5, aims to increase the volume of data by adding slightly modified copies of existing data or newly synthesized data derived from the existing data using the same parameters for both scenarios (
Figure 4 and
Figure 5), with the same total number of images in both cases.
In a second use of data augmentation techniques, the issue of inconsistent sample sizes and complicated classifications was resolved. As seen in
Table 2, the APTOS dataset exemplifies the "imbalanced class," because the samples are not distributed evenly throughout the several classes. After applying augmentation techniques to the dataset, the classes are obviously balanced for both scenarios as depicted in
Figure 6.
3.2.4. Learning Model (Inception-V3)
In this section, the approach’s fundamental theory is outlined and explained. Inception-v3 [
11,
12] is one of transfer learning pretrained models, it is a succeeding of the original architecture for Inception-v1 [
35] and Inception-v2 [
36]. The Inception-v3 model is trained using the ImageNet datasets [
37,
38], which contain the information required for identifying one thousand classes. The error rate for the top five in ImageNet is 3.5%, while the error rate for the top one has lowered to 17.3%.
Inception was influenced in particular by Serre et al. [
39] technique, which may process information in several stages. By adopting Lin et al. [
40] method, the developers of Inception were able to improve the model precision of the neural networks, making them a significant design requirement. As a result of the dimension reduction to 1*1 convolutions, this had also protected them from computing constraints. Researchers were able to significantly reduce the amount of time and effort spent on DL picture classification using Inception [
41]. Using only the theoretical explanations offered by Arora et al. [
42], they emphasized discovering an optimal spot between the typical technique of improving performance—increasing both depth and size—and layer separability. When utilized independently, both procedures might be computationally expensive. This was the fundamental goal of the 22-layer architecture employed by the Inception DL system, in which all filters are learned. On the basis of Arora et al. [
42] research, a correlation statistical analysis was developed to generate highly associated categories that were input into the subsequent layer. The 1*1 layer, the 3*3 layer, and the 5*5 convolution layer were all inspired by the concept of multiscale processing of visual data. Each of these layers eventually becomes a set of 1*1 convolutions [
41] following a process of dimension reduction.
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Instruction and Setup of Inception-V3
To demonstrate the effectiveness of the deployed DL system and to compare results to industry standards, tests were carried out on the APTOS dataset. The dataset has been divided into three categories in accordance with the suggested training method: Eighty percent of the data was utilized for training (9,952 photographs), ten percent for testing (1012 photos), and the remaining ten percent was randomly selected and used as a validation set (1025 photos) to evaluate performance and save the best weight combinations. All photographs were reduced in size during the training process to a 224*224*3 pixel resolution. We tested the proposed system’s TensorFlow Keras implementation on a Linux desktop equipped with a GPU RTX3060 and 8GB of RAM.
Using the Adam optimizer and a method that slows down training when learning has stalled for too long, the proposed framework was first trained on the APTOS dataset (i.e., validation patience). Throughout the entirety of the training process, the following hyperparameters were input into the Adam optimizer: In this simulation, we used a range of 1E^3 to 1E^5 for the learning rate, 2–64 for the batch size (with an increase of 2x the previous value), 50 epochs, 10 for patience, and 0.90 for momentum. Our arsenal of anti-infectious measures is completed by a method known as "batching" for the dissemination of infectious forms.
4.2. Evaluative Parameters
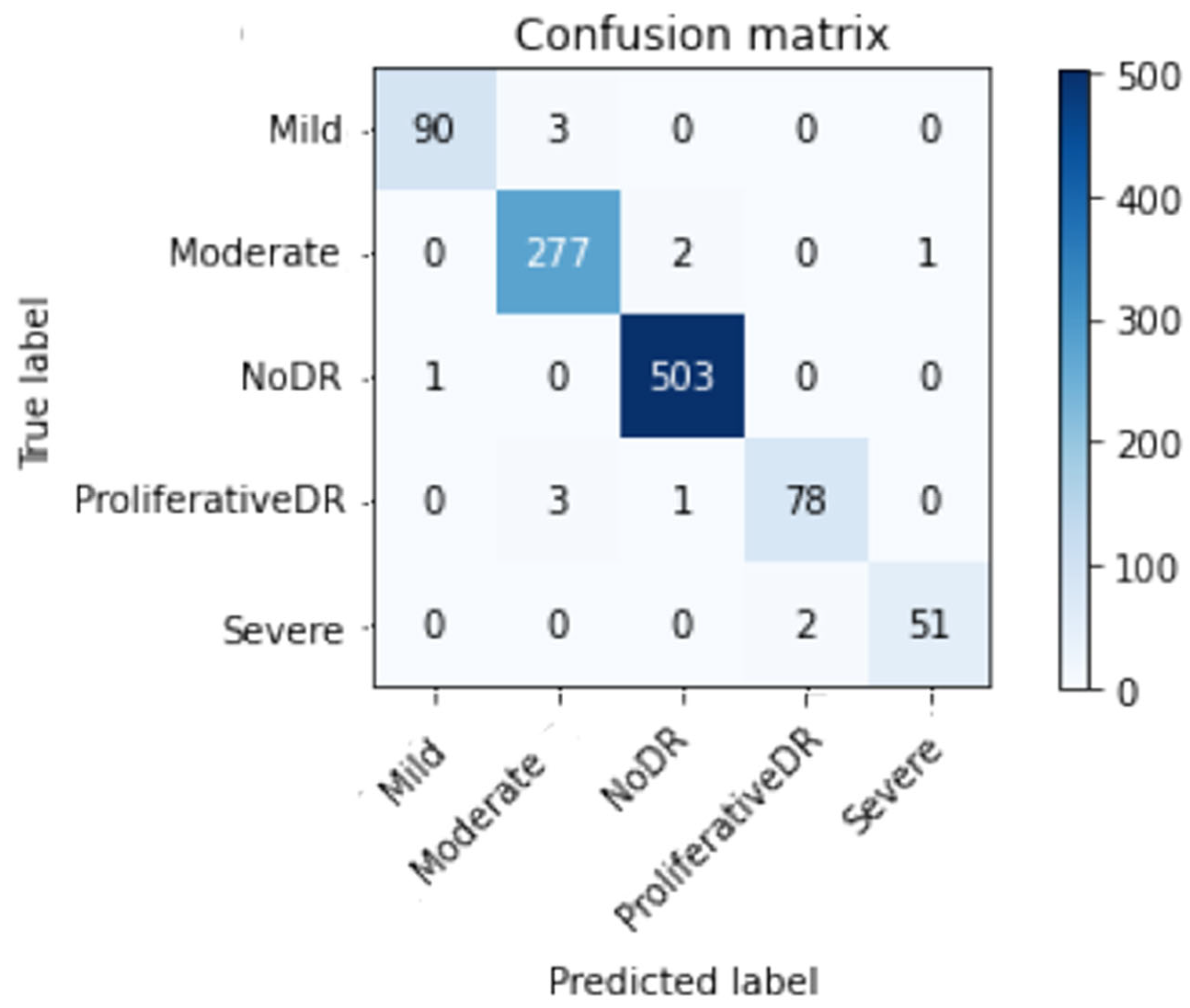
This study describes the evaluation methods and their results. Classifier accuracy (Acc) is a standard performance measure. It is determined by dividing the number of successfully categorized instances (images) by the total number of examples in the dataset (equation (1)). Picture categorization systems are often evaluated using precision (Prec) and recall (Re). As demonstrated in equation (2), precision improves with the number of accurately labeled photos, whereas recall is the ratio of properly categorized images in the dataset to those related numerically (3). The F1-score also shows that the system is more accurate at predicting the future than one with a lower value. Equation (4) calculates the F1-score (F1sc). This study’s final criterion, top N accuracy, requires model N’s highest probability answers to match the expected softmax distribution. If one of N predictions matches the intended label, the classification is accurate.
True positives, represented by the symbol (Tp), are successfully anticipated positive cases, and true negatives (Tn) are effectively predicted negative scenarios. False positives (Fp) are falsely predicted positive situations, whereas false negatives (Fn) are falsely projected negative situations.
Evaluation Considering a Variety of Other Methodologies
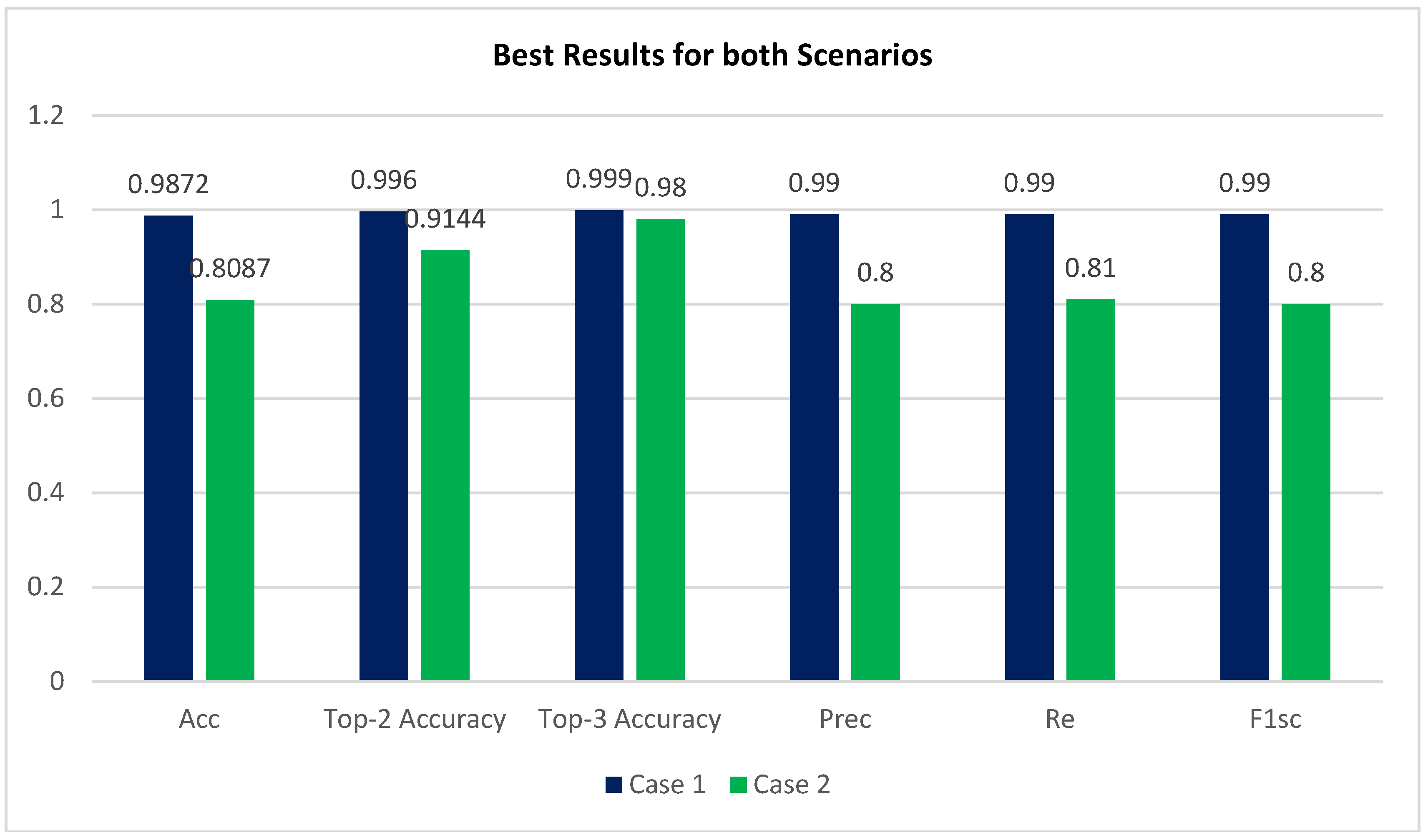
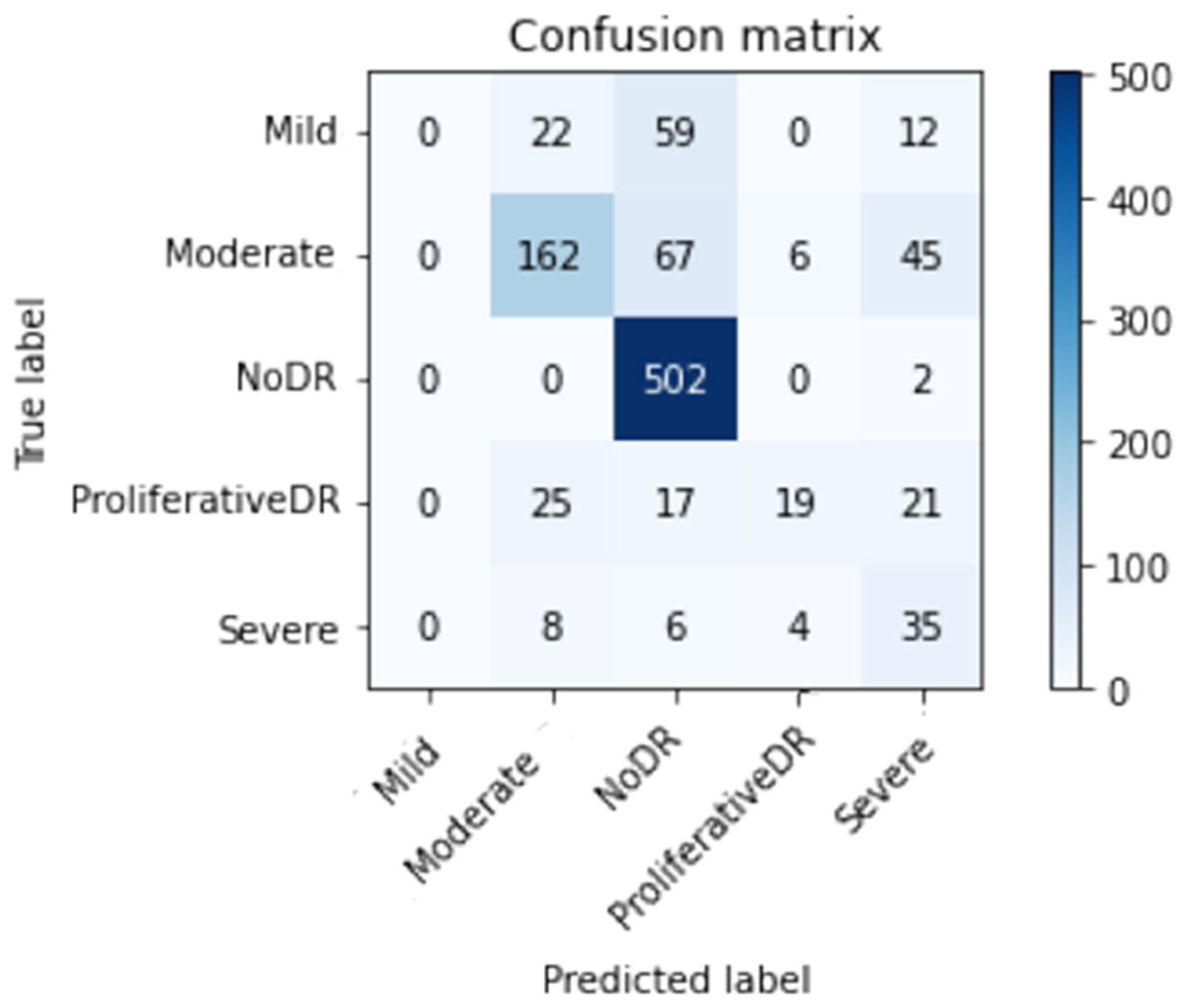
Effectiveness is compared to that of other methods. According to
Table 7, our method exceeds other alternatives in terms of effectiveness and performance. The proposed inception model achieves an overall accuracy rate of 98.7%, surpassing the present methods.
5. Discussion
Based on CLAHE and ESRGAN, a novel DR categorization scheme was presented in this research. The developed model was tested on the DR images founded in APTOS 2019 dataset. Consequently, there are two training scenarios, case 1 with CLAHE + ESRGAN applied to the APTOS dataset and case 2 without CLAHE + ESRGAN. Through 80:20 hold-out validation, the model attained a 5-class accuracy rate of 98.7% for Case 1 and 80.87% for Case 2. The proposed method classified both cases scenarios using the pretrained Inception-V3 infrastructure. Throughout model construction, we evaluated the classification performance of two distinct scenarios and found that enhancement techniques produced the best results (
Figure 7). The main contributing element in our methodology is the general resolution enhancement of CLAHE + ESRGAN, which we prove with evidence that it is responsible for great improvement in the accuracy.
6. Conclusions
By identifying retinal images displayed in the APTOS dataset, researchers have established a strategy for quickly and accurately diagnosing five distinct forms of cancer. The proposed method employs two scenarios: case 1 using image enhancement (using CLAHE and ESRGAN) and case 2 without using enhancement. Case 1 scenario employs four-stage picture enhancement techniques in order to increase the image’s luminance and eliminate noise. CLAHE and ESRGAN are the two stages with the best impact on accuracy, as demonstrated by experimental results. The state-of-the-art in preprocessed medical imagery was employed to learn Inception-V3 with augmentation techniques that helped reduce overfitting and raised the entire competencies of the suggested methodology. This proposed solution claims that when using Inception-V3, the conception model achieves a correctness of 98.7% ≈ 99% for case 1 scenario and 80.87% ≈ 81% for case 2 scenario, both of which are on line with the accuracy of trained ophthalmologists. The usage of CLAHE and ESRGAN in the preprocessing step further contributes to the study’s novelty and significance. The proposed methodology outperforms the current establishment models, as evidenced by a comparison of their respective strengths and weaknesses. To prove the effectiveness of the proposed method, it must be tested on a sizable and intricate dataset, ideally consisting of a significant number of potential DR instances soon. In the future, new datasets may be analyzed using DenseNet, VGG, or ResNet as well as additional augmentation approaches.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Walaa Gouda; Data curation, Walaa Gouda; Formal analysis, Ghadah Alwakid and Walaa Gouda; Funding acquisition, Ghadah Alwakid; Methodology, Ghadah Alwakid and Mamoona Humayun; Project administration, Mamoona Humayun; Supervision, Mamoona Humayun; Writing – original draft, Walaa Gouda; Writing – review & editing, Mamoona Humayun.
Funding
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deputyship for Research & Innovation, Ministry of Education in Saudi Arabia for funding this research work through the project number 223202.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not Applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not Applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Will be furnished on request.
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deputyship for Research & Innovation, Ministry of Education in Saudi Arabia for funding this research work through the project number 223202.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Atwany, M.Z., A.H. Sahyoun, and M. Yaqub, Deep learning techniques for diabetic retinopathy classification: A survey. IEEE Access, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Amin, J., M. Sharif, and M. Yasmin, A review on recent developments for detection of diabetic retinopathy. Scientifica, 2016. 2016. [CrossRef]
- Kharroubi, A.T. and H.M. Darwish, Diabetes mellitus: The epidemic of the century. World journal of diabetes, 2015. 6(6): p. 850. [CrossRef]
- Alex, S.A., Jhanjhi, N.Z., Humayun, M., Ibrahim, A.O. and Abulfaraj, A.W., 2022. Deep LSTM Model for Diabetes Prediction with Class Balancing by SMOTE. Electronics, 11(17), p.2737. [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R. and D. Batey, Handbook of retinal screening in diabetes: diagnosis and management. 2012: John Wiley & Sons.
- Alyoubi, W.L., W.M. Shalash, and M.F. Abulkhair, Diabetic retinopathy detection through deep learning techniques: A review. Informatics in Medicine Unlocked, 2020. 20: p. 100377. [CrossRef]
- Dubow, M., et al., Classification of human retinal microaneurysms using adaptive optics scanning light ophthalmoscope fluorescein angiography. Investigative ophthalmology & visual science, 2014. 55(3): p. 1299-1309. [CrossRef]
- Mazhar, K., et al., Severity of diabetic retinopathy and health-related quality of life: the Los Angeles Latino Eye Study. Ophthalmology, 2011. 118(4): p. 649-655. [CrossRef]
- Willis, J.R., et al., Vision-related functional burden of diabetic retinopathy across severity levels in the United States. JAMA ophthalmology, 2017. 135(9): p. 926-932. [CrossRef]
- Vora, P. and S. Shrestha, Detecting diabetic retinopathy using embedded computer vision. Applied Sciences, 2020. 10(20): p. 7274. [CrossRef]
- Humayun, Mamoona, Muhammad Ibrahim Khalil, Saleh Naif Almuayqil, and Noor Zaman Jhanjhi. "Framework for Detecting Breast Cancer Risk Presence Using Deep Learning." Electronics 12, no. 2 (2023): 403. [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C., et al. Inception-v4, inception-resnet and the impact of residual connections on learning. in Thirty-first AAAI conference on artificial intelligence. 2017.
- Xia, X., C. Xu, and B. Nan. Inception-v3 for flower classification. in 2017 2nd international conference on image, vision and computing (ICIVC). 2017. IEEE.
- APTOS 2019 Blindness Detection. 2019, Kaggle.: Kaggle.
- Pizer, S.M., et al., Adaptive histogram equalization and its variations. Computer vision, graphics, and image processing, 1987. 39(3): p. 355-368. [CrossRef]
- Ledig, C., et al. Photo-realistic single image super-resolution using a generative adversarial network. in Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2017.
- Al-Antary, M.T. and Y. Arafa, Multi-scale attention network for diabetic retinopathy classification. IEEE Access, 2021. 9: p. 54190-54200. [CrossRef]
- Gargeya, R. and T. Leng, Automated identification of diabetic retinopathy using deep learning. Ophthalmology, 2017. 124(7): p. 962-969. [CrossRef]
- Pak, A., et al., Comparative analysis of deep learning methods of detection of diabetic retinopathy. Cogent Engineering, 2020. 7(1): p. 1805144. [CrossRef]
- Kazakh-British, N.P., A. Pak, and D. Abdullina. Automatic detection of blood vessels and classification in retinal images for diabetic retinopathy diagnosis with application of convolution neural network. in Proceedings of the 2018 international conference on sensors, signal and image processing. 2018.
- Macsik, P., et al., Local Binary CNN for Diabetic Retinopathy Classification on Fundus Images. Acta Polytechnica Hungarica, 2022. 19(7). [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, N.E.M., et al., Deep transfer learning models for medical diabetic retinopathy detection. Acta Informatica Medica, 2019. 27(5): p. 327. [CrossRef]
- Hemanth, D.J., O. Deperlioglu, and U. Kose, An enhanced diabetic retinopathy detection and classification approach using deep convolutional neural network. Neural Computing and Applications, 2020. 32(3): p. 707-721. [CrossRef]
- Maqsood, S., R. Damaševičius, and R. Maskeliūnas, Hemorrhage detection based on 3D CNN deep learning framework and feature fusion for evaluating retinal abnormality in diabetic patients. Sensors, 2021. 21(11): p. 3865. [CrossRef]
- Das, S., et al., Deep learning architecture based on segmented fundus image features for classification of diabetic retinopathy. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2021. 68: p. 102600. [CrossRef]
- Saranya, P., et al. Red Lesion Detection in Color Fundus Images for Diabetic Retinopathy Detection. in Proceedings of International Conference on Deep Learning, Computing and Intelligence. 2022. Springer.
- Thomas, N.M. and S. Albert Jerome, Grading and Classification of Retinal Images for Detecting Diabetic Retinopathy Using Convolutional Neural Network, in Advances in Electrical and Computer Technologies. 2022, Springer. p. 607-614.
- Crane, A. and M. Dastjerdi, Effect of Simulated Cataract on the Accuracy of an Artificial Intelligence Algorithm in Detecting Diabetic Retinopathy in Color Fundus Photos. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, 2022. 63(7): p. 2100–F0089-2100–F0089.
- Majumder, S. and N. Kehtarnavaz, Multitasking deep learning model for detection of five stages of diabetic retinopathy. IEEE Access, 2021. 9: p. 123220-123230. [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, A. and J. Pardhi, Automated detection of Diabetic Retinopathy using VGG-16 architecture. International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology, 2021. 8(03).
- Yadav, S., P. Awasthi, and S. Pathak, RETINA IMAGE AND DIABETIC RETINOPATHY: A DEEP LEARNING BASED APPROACH.
- Kobat, S.G., et al., Automated Diabetic Retinopathy Detection Using Horizontal and Vertical Patch Division-Based Pre-Trained DenseNET with Digital Fundus Images. Diagnostics, 2022. 12(8): p. 1975. [CrossRef]
- Reza, A.M., Realization of the contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization (CLAHE) for real-time image enhancement. Journal of VLSI signal processing systems for signal, image and video technology, 2004. 38(1): p. 35-44. [CrossRef]
- Jolicoeur-Martineau, A. The relativistic discriminator: a key element missing from standard GAN. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.00734. [Google Scholar]
- Humayun, M. and Alsayat, A., 2022. Prediction Model for Coronavirus Pandemic Using Deep Learning. Comput. Syst. Sci. Eng., 40(3), pp.947-961. [CrossRef]
- Hamza, M., Tehsin, S., Humayun, M., Almufareh, M.F. and Alfayad, M., 2022. A Comprehensive Review of Face Morph Generation and Detection of Fraudulent Identities. Applied Sciences, 12(24), p.12545. [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A., I. Sutskever, and G.E. Hinton, Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Advances in neural information processing systems, 2012. 25.
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Serre, T., et al., Robust object recognition with cortex-like mechanisms. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence, 2007. 29(3): p. 411-426. [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Chen, Q.; Yan, S. Network in network. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1312.4400. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C., et al. Going deeper with convolutions. in Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2015.
- Arora, S., et al. Provable bounds for learning some deep representations. in International conference on machine learning. 2014. PMLR.
- Maqsood, Z. and M.K. Gupta, Automatic Detection of Diabetic Retinopathy on the Edge, in Cyber Security, Privacy and Networking. 2022, Springer. p. 129-139.
- Lahmar, C. and A. Idri, Deep hybrid architectures for diabetic retinopathy classification. Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering: Imaging & Visualization, 2022: p. 1-19. [CrossRef]
- Oulhadj, M., et al., Diabetic retinopathy prediction based on deep learning and deformable registration. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2022: p. 1-19. [CrossRef]
- Gangwar, A.K. and V. Ravi, Diabetic retinopathy detection using transfer learning and deep learning, in Evolution in Computational Intelligence. 2021, Springer. p. 679-689.
- Lahmar, C. and A. Idri, On the value of deep learning for diagnosing diabetic retinopathy. Health and Technology, 2022. 12(1): p. 89-105. [CrossRef]
- Canayaz, M., Classification of diabetic retinopathy with feature selection over deep features using nature-inspired wrapper methods. Applied Soft Computing, 2022. 128: p. 109462. [CrossRef]
- Escorcia-Gutierrez, J., et al. Analysis of Pre-trained Convolutional Neural Network Models in Diabetic Retinopathy Detection Through Retinal Fundus Images. in International Conference on Computer Information Systems and Industrial Management. 2022. Springer.
- Salluri, D.K., V. Sistla, and V.K.K. Kolli, HRUNET: Hybrid Residual U-Net for automatic severity prediction of Diabetic Retinopathy. Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering: Imaging & Visualization, 2022: p. 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S. and P. Awasthi, DIABETIC RETINOPATHY DETECTION USING DEEP LEARNING AND INCEPTION-V3 MODEL.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).