Submitted:
29 January 2023
Posted:
30 January 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods:
2.1. Introduction to MCNPX 2.6.0 Simulation Code
2.2. Assumptions of the Problem for Simulation with MCNPX
3. Results and Discussion
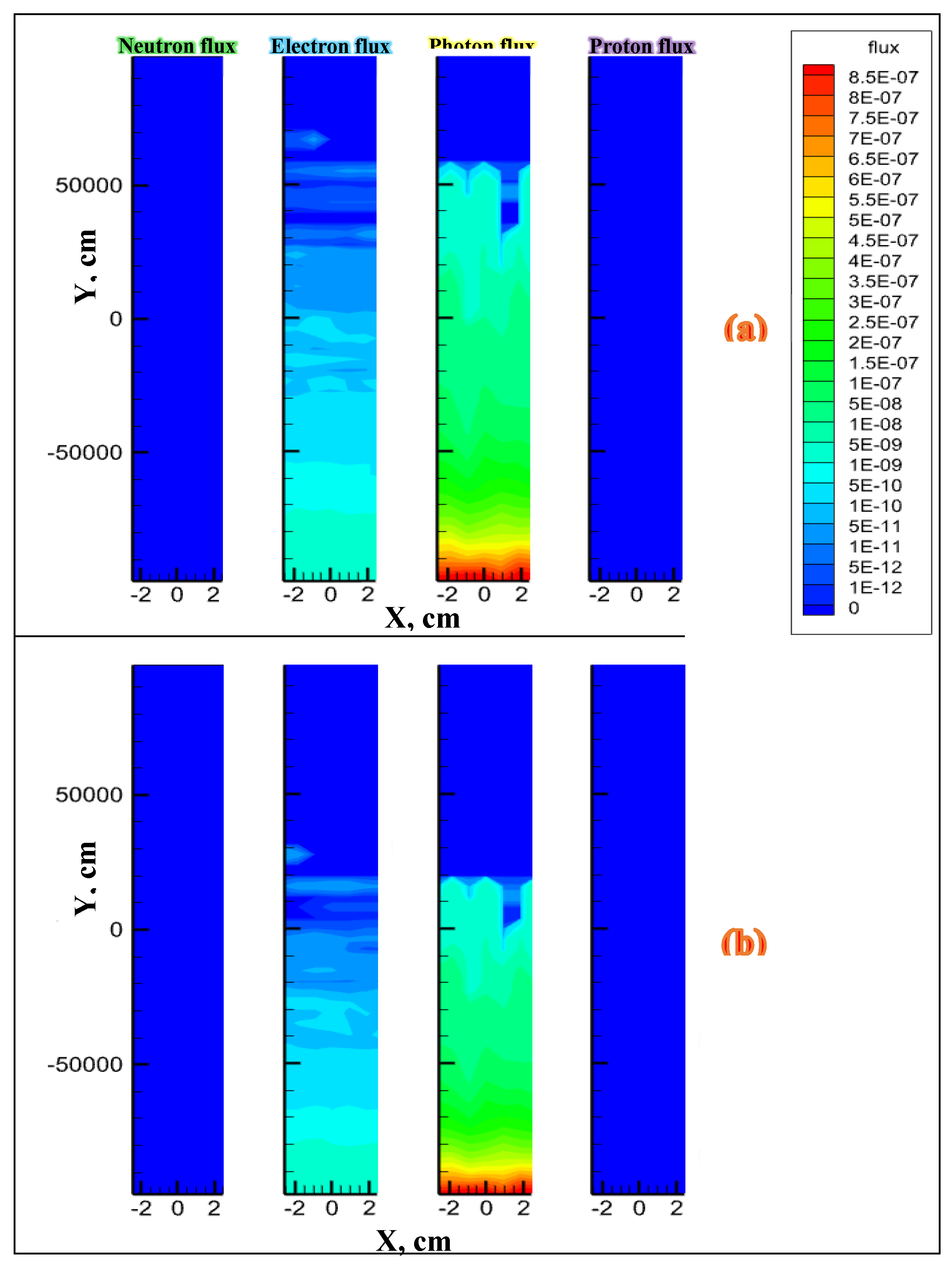
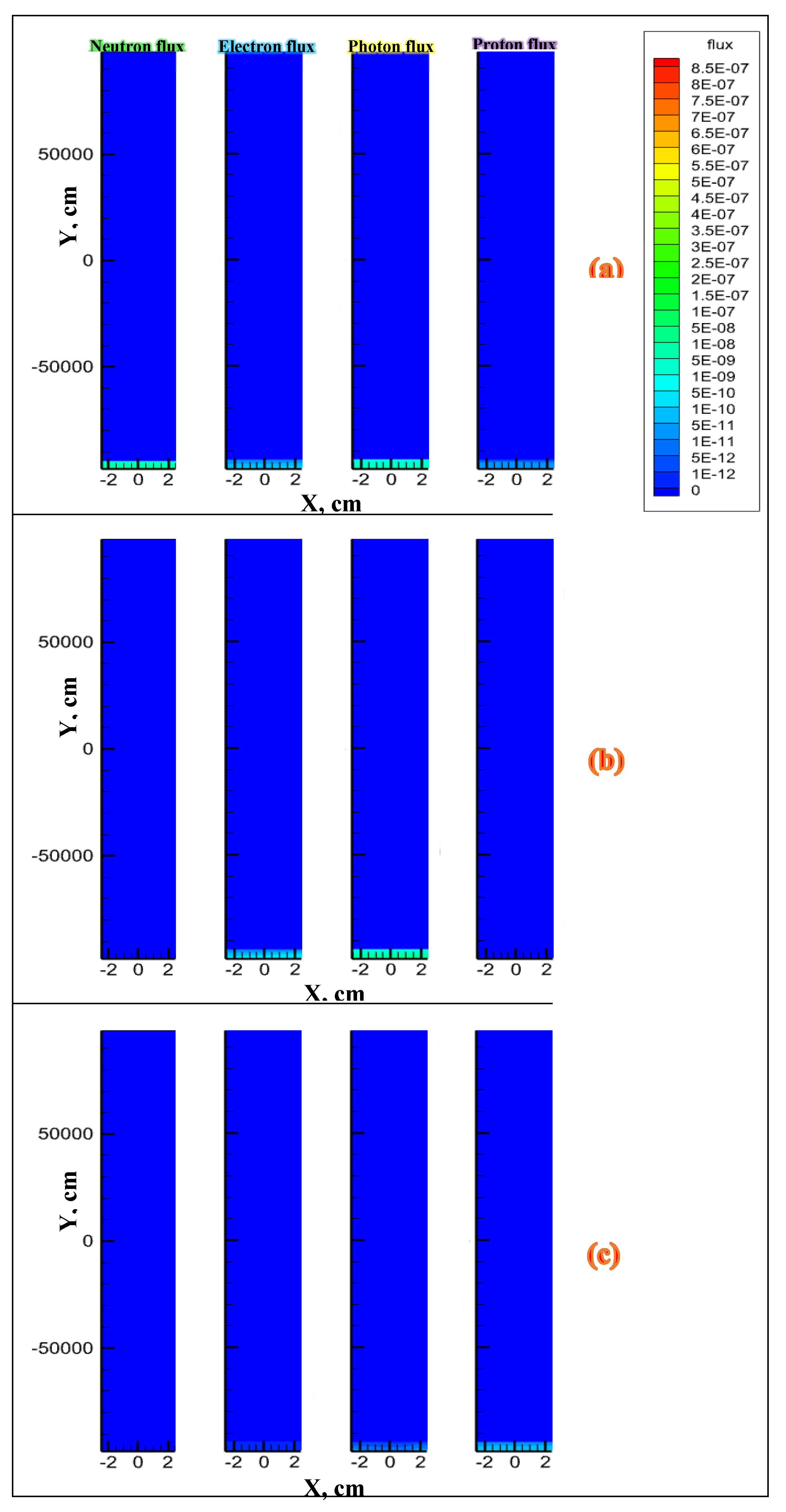
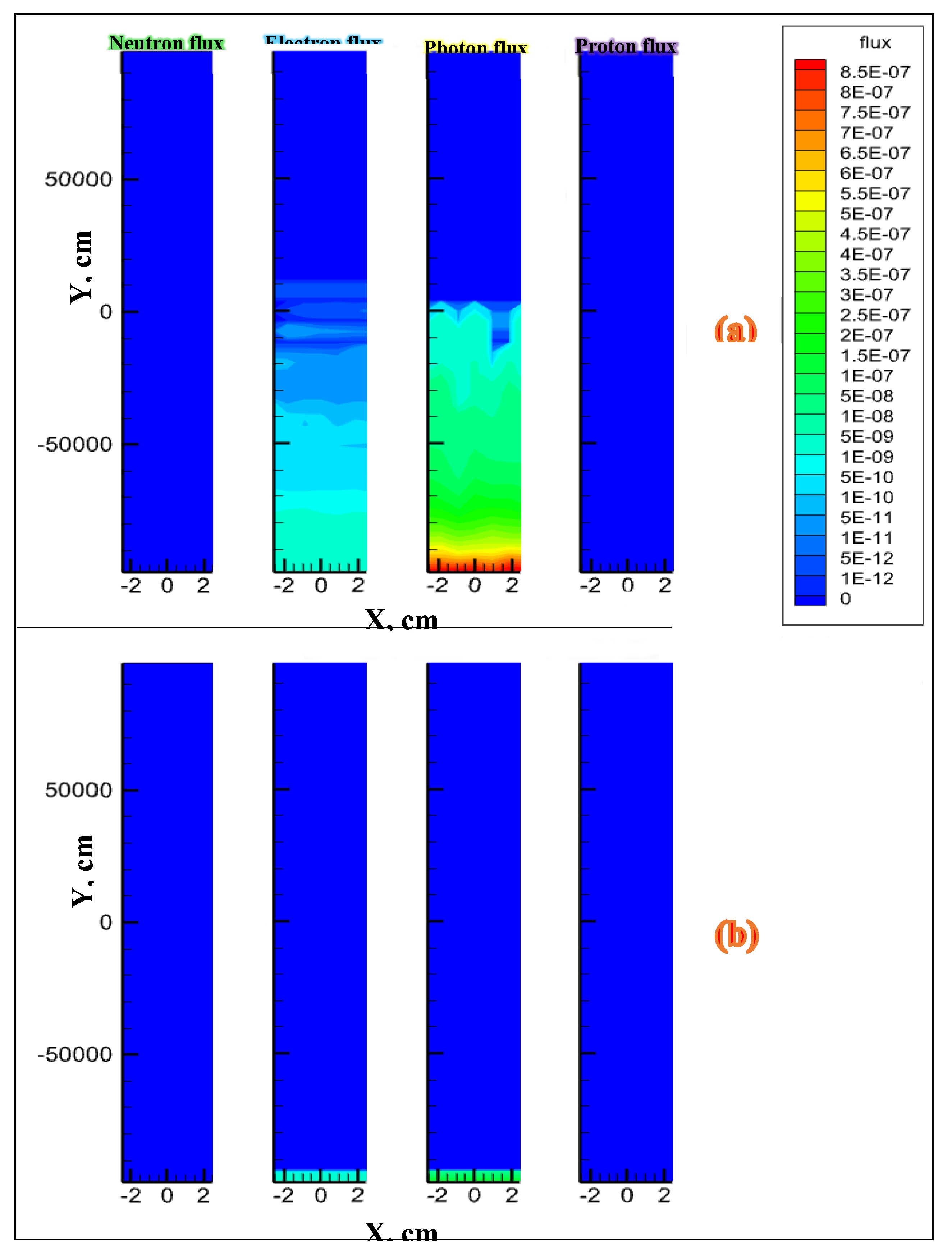
3.1. Simulation when the Fracture Is Filled with Air
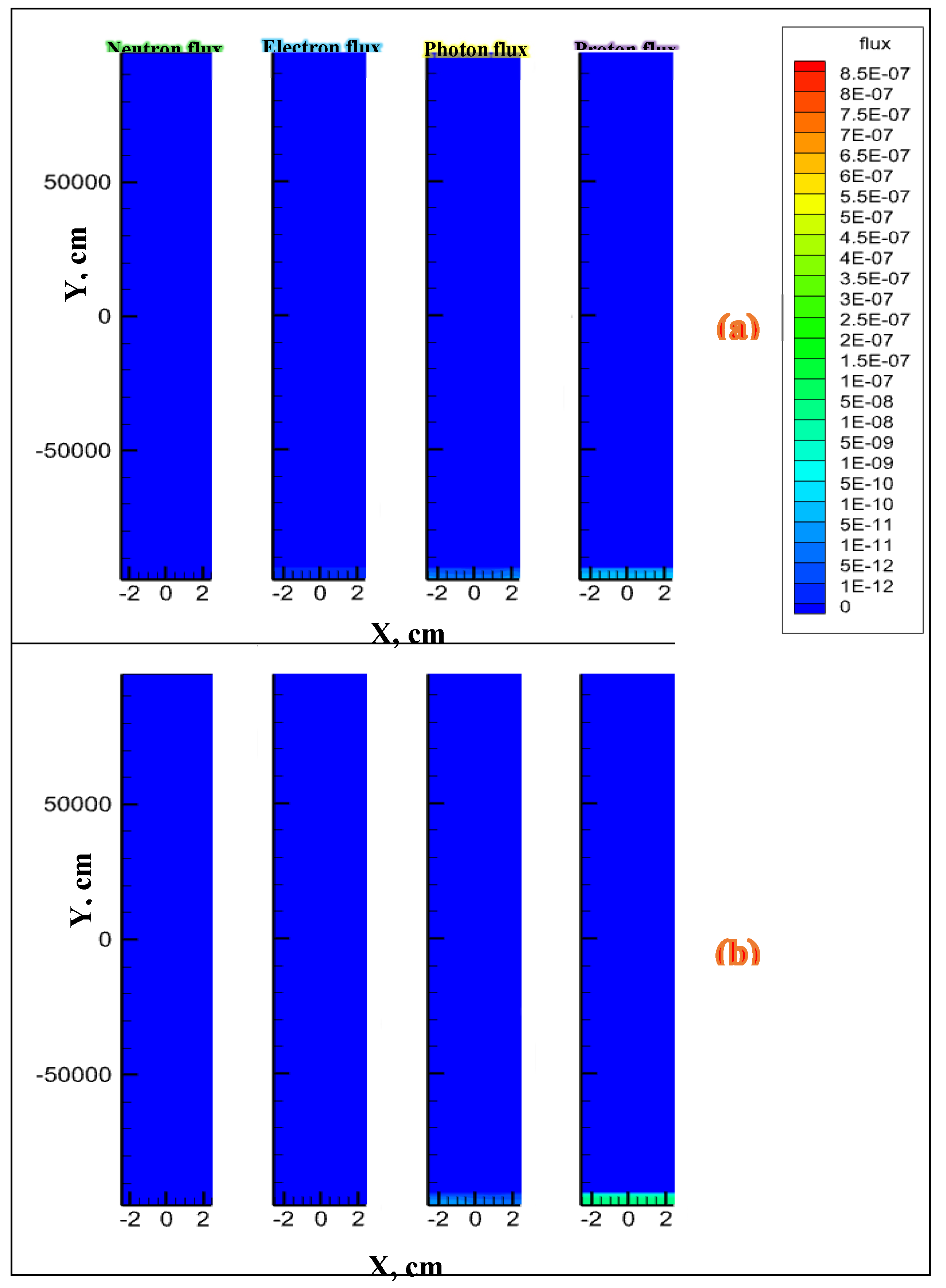
3.2. Simulation when the Fracture Is Filled with Water
3.3. Simulation when the Fracture Is Filled with CO2
4. Conclusions:
- 1-
- If we consider a rectangular-shaped fracture from the EQ hypocenter to the surface, in the case that the fracture contains vacuum (no fluid fills it), those created particles from under-stressed granitic rocks, entering into the fracture and moving alongside and parallel to the fracture walls, can pass long distances from the EQ hypocenter and reach themselves to the surface with their initial energy.
- 2-
- Using the MCNPX simulation code, we have estimated the flux of the particles inside the fractures, filled with air, water, and CO2 in different distances from the EQ hypocenter. Those particles are created from under-stressed granite rocks and also from the interactions between them and the filling fluid’s atoms/ nucleuses. It was found that inside a water-filled fracture, the particles do not show the flux far from the EQ hypocenter even if the EQ magnitude is high (more than 7 in Richter’s magnitude), but inside the fractures, filled with gases like air and CO2 with density in a normal condition, various types of particles can have a flux far from the source (more than a kilometer) and they might reach themselves to the surface when the EQ hypocenter is very shallow (0- 5 km). However, for deep EQs, it seems that the most detected atomic/ nuclear particles on the surface have been transmitted to the surface via the vacuum-filled fractures.
- 3-
- By running the simulation code on a CO2-filled fracture, it was concluded that the more density of the fracture’s filling fluid, the less distance that the particles can have a flux.
- 4-
- The fracture’s geometry and size, specially the width of the fracture, the moving direction of the source particles, the type and density of the filling fluid, are amongst the important factors, affecting on how much the particles can reach themselves to the surface.
- 5-
- Due to the photon’s wave- particle duality, low energy photons like ULF waves can pass long distances of solids/ fluids and be detected on the surface. However, the wave properties of photon can not be simulated with MCNPX and it must be simulated with other simulators.
- 6-
- We have considered the “average energy” of the particles for each EQ magnitude. However, some of the interactions in which the particles are created have higher energies than the average and therefore, created particles from those interactions can pass longer distances inside a fluid-filled fracture.
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
5. References
- Fu, C.C. et al., “Temporal variation of gamma rays as a possible precursor of EQ in the Longitudinal Valley of eastern Taiwan”, Journal of Asian Earth Sciences 2015, 114, 362. [CrossRef]
- Maksudov, A.U., Zufarov, M.A., “Measurement of neutron and charged particle fluxes toward EQ prediction”, EQ Sci. 2017, 30, 283. [CrossRef]
- Volodichev, N.N.; et al. “Sun-Moon-Earth connections: the neutron intensity splashes and seismic activity”. Astron. Vestnik. 2000, 34, 188. [Google Scholar]
- Sigaeva, E.; et al. , “Thermal neutrons’ observations before the Sumatra EQ”, Geophys. Res. Abstr. 2006, 8, 00435. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X., Yan, J., Wang, Q., “Monitoring of gamma radiation in aseismic region and its response to seismic events”, Journal of Environmental Radioactivity 2020, 213, 106119. [CrossRef]
- Carpinteri, A., Cardone, F., Lacidogna, G. “Piezonuclear neutrons from brittle fracture: early results of mechanical compression tests”, Strain 2009, 45:332. [CrossRef]
- Cardone, F., Carpinteri, A., Lacidogna, G., “Piezonuclear neutrons from fracturing of inert solids”, Phys. Lett. A 2009, 373:4158. [CrossRef]
- Carpinteri, A., Cardone, F., Lacidogna, G., “Energy emissions from failure phenomena: mechanical, electromagnetic, nuclear”, Exp. Mech. 2010, 50:1235. [CrossRef]
- Carpinteri, A.; et al. Neutron emissions in brittle rocks during compression tests: monotonic vs cyclic loading. Phys. Mesomech. 2010, 13, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpinteri, A. et al., “Energy emissions from brittle fracture: neutron measurements and geological evidences of piezonuclear reactions”, Strength, Fract. Complexity 2011, 7, 13-31. [CrossRef]
- Manuello, A., Grosso, B., Ricciu, R., “Anisotropic and impulsive neutron emissions from brittle rocks under mechanical load”, Meccanica 2014, 50 (5). [CrossRef]
- Freund, F. et al., “Highly mobile hole charge carriers in minerals: Key to the enigmatic electrical EQ phenomena?”, in Electromagnetic Phenomena Related to EQ Prediction, F. Fujimori and M. Hayakawa eds., Terra Sci. Publ. Co., Tokyo, 1994; pp. 271-292.
- Freund, F., Takeuchi, A., and Lau, B.W.S., “Electric current streaming out of stressed igneous rocks—A step towards understanding pre-EQ low frequency EM emissions”, Phys. Chem. Earth, Parts ABC 2006, 31, 389–396. [CrossRef]
- Freund, F., and Sornette, D., “Electro-magnetic EQ bursts and critical rupture of peroxy bond networks in rocks”, Tectonophysics 2007, 431, 33–47. [CrossRef]
- Bahari et al., “Simulation with Monte Carlo Methods to Find Relationships between Accumulated Mechanical Energy and Atomic/Nuclear Radiation in Piezoelectric Rocks with Focus on Earthquakes”, Radiation effects and defects in solids 2022, 177, 743-767. [CrossRef]
- Berryman, J. Seismic waves in rocks with fluids and fractures. Geophys. J. Int. 2007, 171, 954–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weeks, E.P. , “Effect of topography on gas flow in unsaturated fractured rock: concepts and observations, in flow and transport through unsaturated fractured rock”. Geophys. Monogr. Ser. 2001, 42, 53–59. [Google Scholar]
- Weisbrod et al., “Falling through the cracks: The role of fractures in Earth-atmosphere gas exchange”, Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L02401. [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.R., “Air circulation in deep fractures and the temperature field of an alpine rock slope”, Earth Surface Processes and Landforms 2011, 36, 1985-1996. [CrossRef]
- Laurie, S.W. et al., “The MCNPX Monte Carlo radiation transport code”, AIP Conf. Proc. 2007, 896, 81. [CrossRef]
- Los Alamos National Laboratory, “Monte Carlo Methods, codes, & applications group”, https://mcnp.lanl.gov/.
- William, S. et al., “Measuring the size of an earthquake”, Earthquakes and Volcanoes 1989, 21, 58-63.
- Miller, S.A. et al., “Aftershocks driven by a high-pressure CO2 source at depth”, Nature 2004, 427, 724-7. [CrossRef]
- Engineering ToolBox. “Carbon dioxide - Density and Specific Weight vs. Temperature and Pressure”. [online] Available at: https://www.engineeringtoolbox.com/carbon-dioxide-density-specific-weight-temperature-pressure-d_2018.html, (2018).
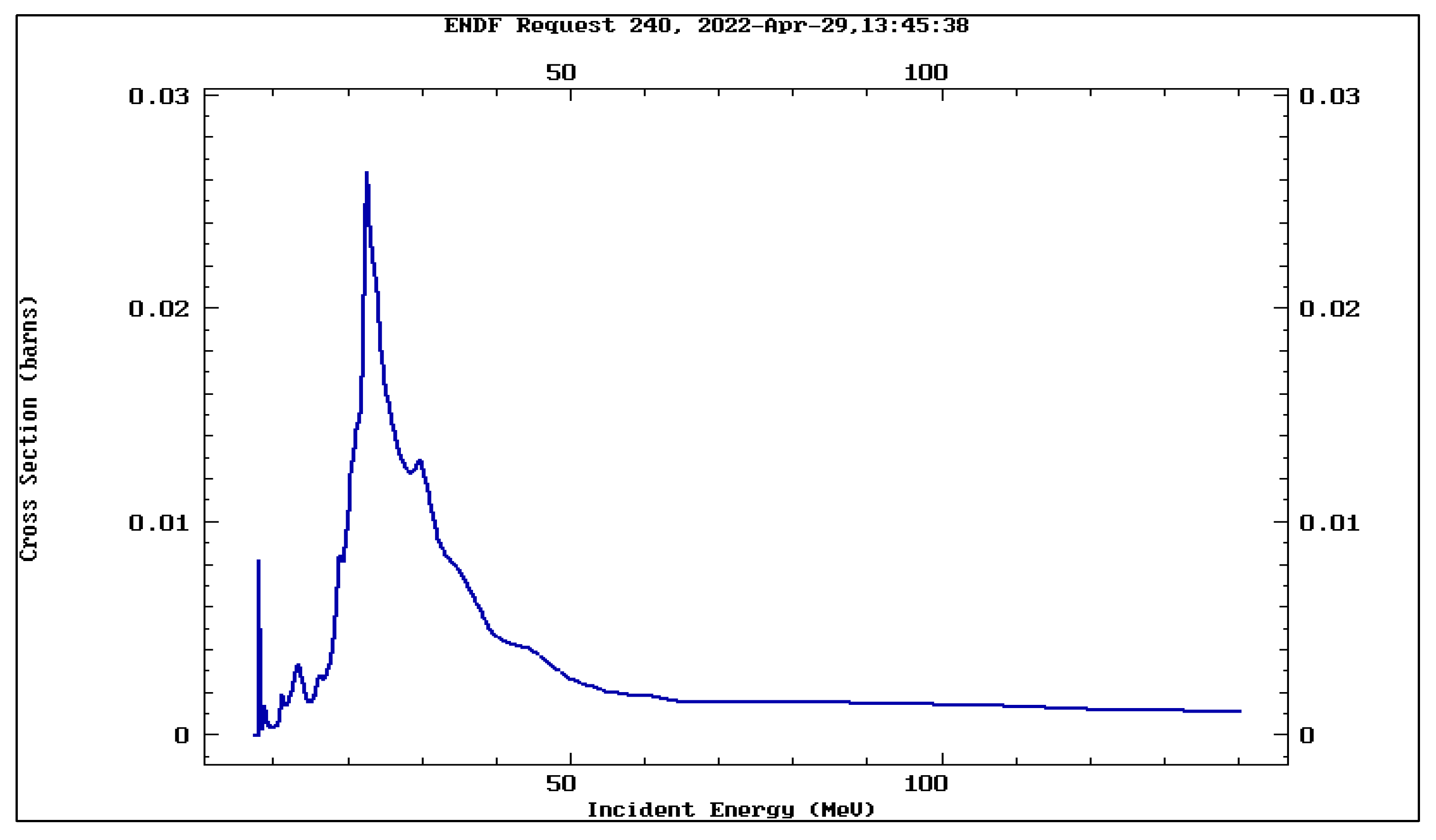
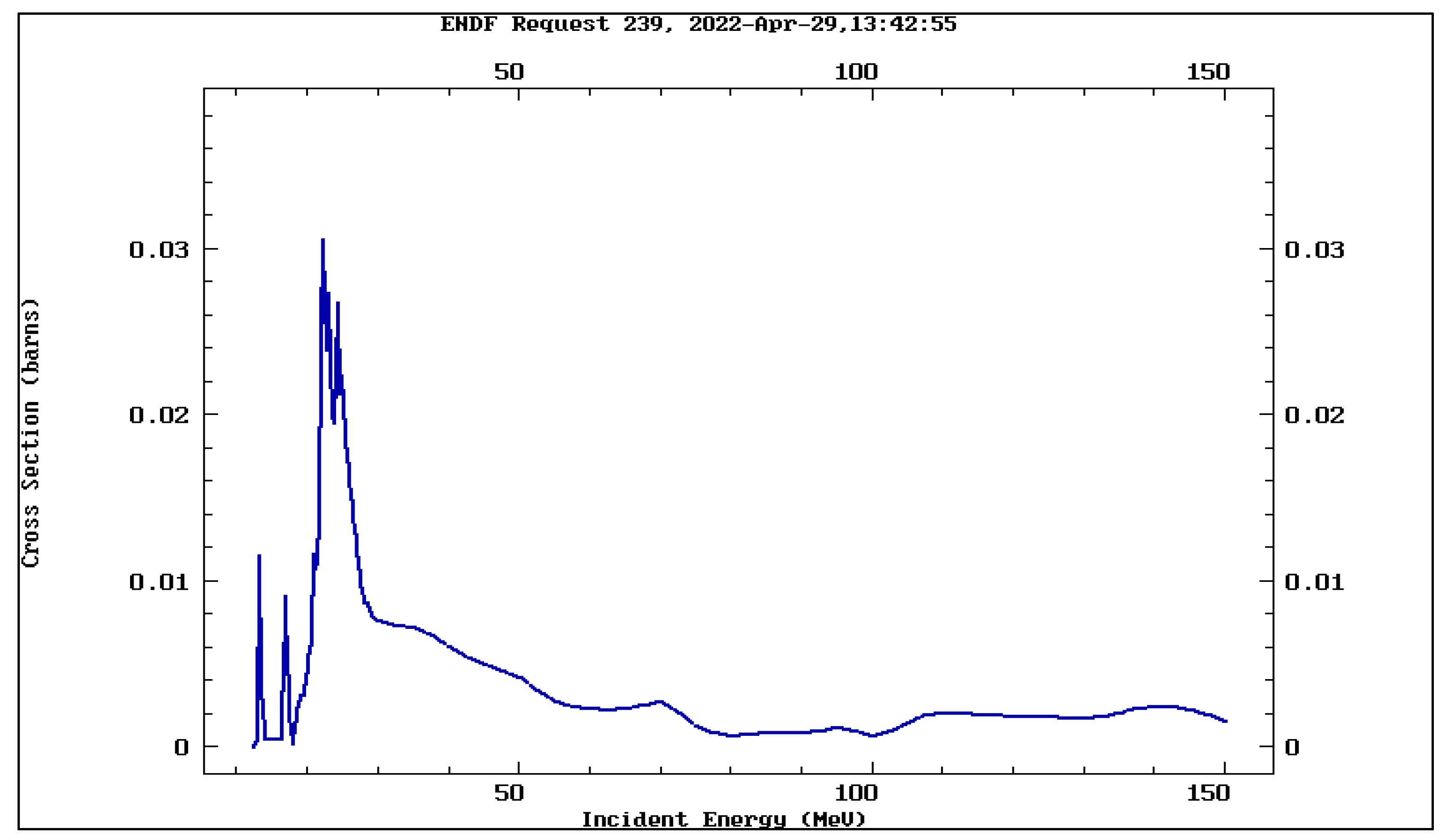
- International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), “Evaluated Nuclear Data File (ENDF)”: https://www-nds.iaea.org/exfor/endf.htm, database version of: (2022-04-22).

| Elements | O | Si | Al | K | Na | Ca | Fe | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Percentage, % | 62 | 22.5 | 9 | 3 | 2 | 0.5 | 1 | 100 |
| Block dimensions,m3 | ML | Initial runaway electrons’ energy, MeV | Average energy of the created particles, MeV | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neutrons | Photons | Electrons | Protons | |||
| 4003 | 5.79 | 885 | 10.4 | 1.81 | 0.03 | 9.38 |
| 40003 | 7.67 | 8858 | 24.6 | 3.05 | 0.04 | 20 |
| ML | Material | Fracture dimensions, m3 | Source particle | Average Energy (MeV) | Source position | Source direction | No. of particles (NPS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.67 | Air | 2000×1000×0.1 | n | 24.6 | bottom surface | From bottom to top surface | 100’000 |
| NPS=100’000 | Created particles’ characteristics | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fracture filling material | ML | Source particle | Source particle’s Energy, MeV | Particles | No. | Average energy, MeV | Mean free path (mfp), cm | Average time of capture or escape, s |
| Air | 7.67 | Neutron | 24.6 | Neutron | 112686 | 2.31E+01 | 1.33E+04 | 2.68E-04 |
| Electron | 94389550 | 1.59E-02 | 2.05E+01 | ….. | ||||
| Photon | 1207243 | 9.24E-01 | 1.58E+04 | 1.87E-04 | ||||
| Proton | 42362 | 5.07E+00 | 3.65E+00 | ….. | ||||
| Air | 7.67 | Photon | 3.05 | Neutron | 0 | 0.00E+00 | 0.00E+00 | 0 |
| Electron | 27029959 | 1.56E-02 | 2.45E+01 | ….. | ||||
| Photon | 329562 | 9.49E-01 | 2.34E+04 | 7.60E-07 | ||||
| Proton | 0 | 0.00E+00 | 0.00E+00 | …. | ||||
| Air | 7.67 | Proton | 20 | Neutron | 31 | 3.49E+00 | 8.34E+03 | 3.35E-04 |
| Electron | 250243 | 1.59E-02 | 9.24E+00 | ….. | ||||
| Photon | 3098 | 9.53E-01 | 1.86E+04 | 3.48E-05 | ||||
| Proton | 100783 | 1.99E+01 | 1.26E+01 | ….. | ||||
| Air | 5.79 | Neutron | 10.4 | Neutron | 100000 | 1.04E+01 | 1.41E+04 | 2.21E-04 |
| Electron | 75862285 | 1.60E-02 | 2.10E+01 | ….. | ||||
| Photon | 965231 | 9.31E-01 | 1.81E+04 | 1.90E-04 | ||||
| Proton | 6366 | 3.49E+00 | 6.94E-01 | ….. | ||||
| Air | 5.79 | Photon | 1.81 | Neutron | 0 | 0.00E+00 | 0.00E+00 | 0 |
| Electron | 16646303 | 1.47E-02 | 1.36E+01 | ….. | ||||
| Photon | 132001 | 7.88E-01 | 1.77E+04 | 5.75E-07 | ||||
| Proton | 0 | 0.00E+00 | 0.00E+00 | …. | ||||
| Air | 5.79 | Proton | 9.38 | Neutron | 0 | 0.00E+00 | 0.00E+00 | 0.00E+00 |
| Electron | 30057 | 1.53E-02 | 6.09E+00 | ….. | ||||
| Photon | 386 | 8.89E-01 | 1.58E+04 | 1.22E-08 | ||||
| Proton | 105 | 9.37E+00 | 2.88E+00 | ….. | ||||
| ML | Material | Fracture dimensions, m3 | Source particle | Average Energy (MeV) | Source position | Source direction | No. of particles (NPS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.67 | Water | 2000×1000×0.1 | N | 24.6 | bottom surface | From bottom to top surface | 100’000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




