Submitted:
27 January 2023
Posted:
28 January 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
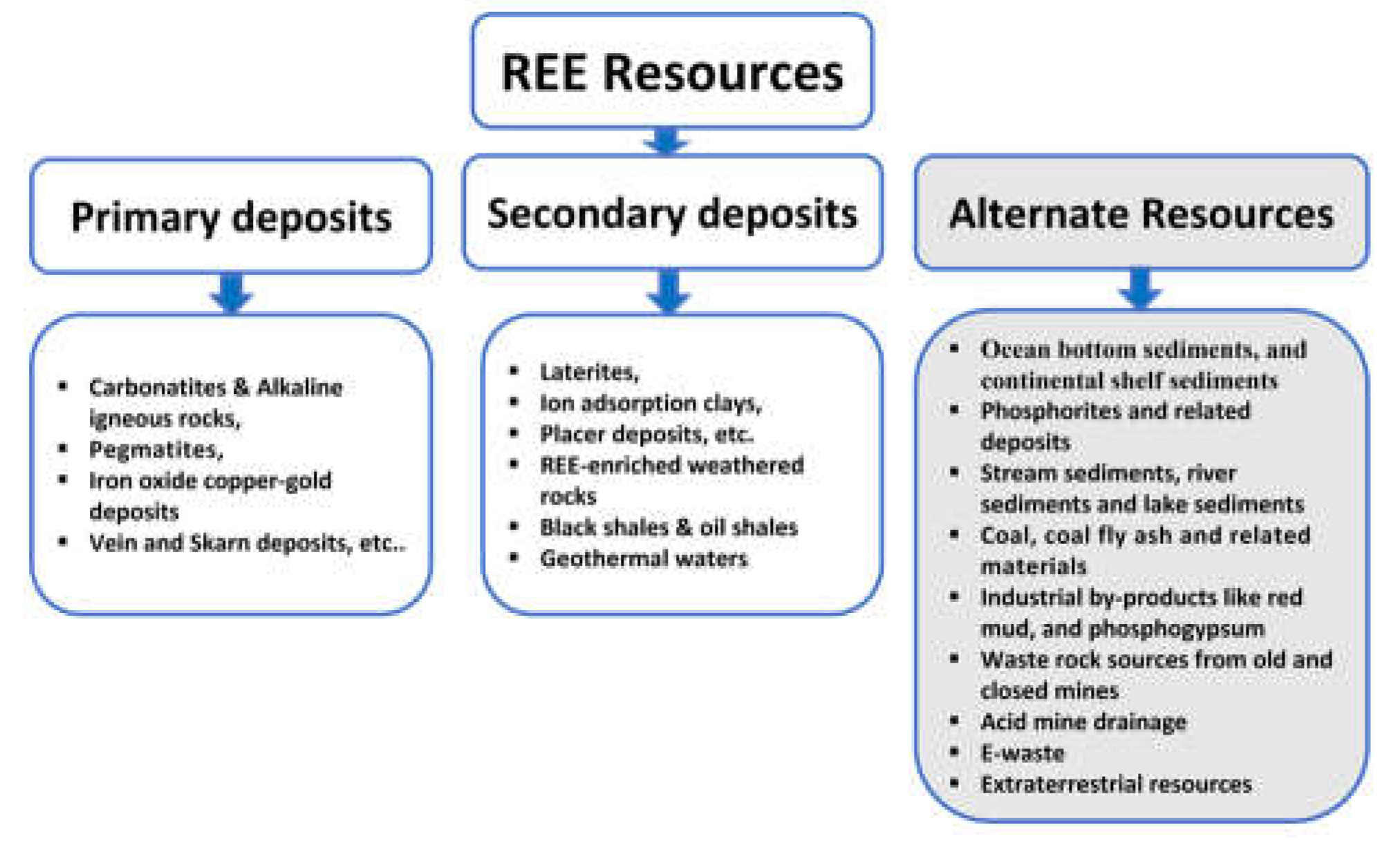
2. REE deposits
2.1. Primary deposits
2.2. Secondary deposits
2.3. Different types potential alternative deposits
2.3.1. Ocean bottom sediments, and continental shelf sediments
2.3.2. Phosphorites and related deposits
1.3.2. Stream sediments, river sediments and lake sediments
2.3.4. Coal, coal fly ash and related materials
2.3.5. Industrial by waste products like red mud, and phosphogypsum
2.3.6. Waste rock sources from old and closed mines
2.3.7. Acid mine drainage
2.3.7. Recycling of e-waste such as magnets, etc.
2.3.9. Extraterrestrial
5. Conclusions and future
Acknowledgement
References
- Zhu, S.; Yang, L.; Bai, J.; Chu, Y.; et al. Ultra-stable Pt La intermetallic compound towards highly efficient oxygen reduction reaction. Nano Research 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, J.A.C.; Vong, Y.M.; Bueno, J.J.P. Cerium and Other Rare Earth Salts as Corrosion Inhibitors—A Review. Protection of Metals and Physical Chemistry of Surfaces 2022, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaram, V. Rare Earth Elements: Sources and Applications. In Environmental Technologies to Treat Rare Earth Elements Pollution: Principles and Engineering by Arindam Sinharoy; Piet Lens, N.L., Ed.; IWA Publishers: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Raju, C.S.K.; Cossmer, A.; Scharf, H.; Panne, U.; Lück, D. Speciation of gadolinium-based MRI contrast agents in environmental water samples using hydrophilic interaction chromatography hyphenated with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry 2010, 25, 55e61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaram, V. Environmental Impact of Pt, Pd and Rh Emissions from Autocatalytic Converters – A Brief Review of the Latest Developments, Handbook of Environmental Materials Management; Hussain, C.M., Ed.; Springer Nature Switzerland AG: 2020.
- Gong, Y.; Li, H.; Li, C.; Bao, X.; Hosono, H.; Wang, J. Insight into rare-earth-incorporated catalysts: The chance for a more efficient ammonia synthesis. Journal of Advanced Ceramics 2022, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molla, S.; Farrok, O.; Islam, M.R.; Muttaqi, K.M. Application of iron nitride compound as alternative permanent magnet for designing linear generators to harvest oceanic wave energy. IET Electric Power Applications 2020, 14, 762–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavel, c.c. , Arántegui, R.L.; Marmier, A.; Schüler, D.; et al. Substitution strategies for reducing the use of rare earths in wind turbines. Resources Policy 2017, 52, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaram, V Rare Earth Elements, Resources, Extraction Technologies, Limitations, and Global Trade – A Comprehensive Review. "Treatise on Geochemistry, 3rd Edition" Section 5, Sustaining Society, Ed. Gabriel Filippelli, Editors in Chief: Ariel Anbar and Dominique Weis, Elsevier (in press), 2024.
- Gaustad, G.; Williams, E.; Leader, A. Rare earth metals from secondary sources: Review of potential supply from waste and by-products. Resources, Conservation & Recycling 2021, 167, 105213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaram, V.; Sawant, S.S. Indicator Minerals, Pathfinder Elements, and Portable Analytical Instruments in Mineral Exploration Studies. Minerals 2022, 12, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dushyantha, N.; Batapola, N.; Ilankoon, I.M.S.K.; Rohitha, S.; Premasiri, R.; Abeysinghe, B.; Ratnayake, N.; Dissanayake, K. The story of rare earth elements (REEs): Occurrences, global distribution, genesis, geology, mineralogy and global production. Ore Geology Reviews 2020, 122, 103521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaram, V. Rare Earth Element Deposits - Sources, and Exploration Strategies. Journal of Geological Society of India 2022, 98, 1210–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dostal, J. Rare Earth Element Deposits of Alkaline Igneous Rocks. Resources 2017, 6, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakhmouradian, A.R.; Zaitsev, A.N. Rare Earth Mineralization in Igneous Rocks: Sources and Processes. Elements 2012, 8, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Z.; Jowitt, S.M.; Mudd, G.M.; Haque, N. A Detailed Assessment of Global Rare Earth Element Resources: Opportunities and Challenges. Economic Geology 2015, 110, 1925–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.A.E. ; Kotel'nikov. Geological and Geochemical exploration methods for mineral resources (skarn deposits and rare earth elements) News of the Ural State Mining University, Earth sciences 2022, 2, 7–15. [Google Scholar]
- Aali, A.A.; Khakmardan, S.; Shirazi, A.; Nazerian, H. A Review of Mineralization of Rare Earth Elements in Iran. International Journal of Science and Engineering Applications 2022, 11, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocker, M.D. Lateritic, supergene rare earth element (REE) deposits, in, Conway, F.M.; ed., Proceedings of the 48th Annual Forum on the Geology of Industrial Minerals, Phoenix, Arizona, Arizona Geological Survey Special Paper #9, 2014; Chapter 4, p. 1-18.
- Jo, J.; Shin, D. Geochemical characteristics of REE-enriched weathered anorthosite complex in Hadong district, South Korea. Geochemical Journal 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Ouyang, J.; Yang, D.; Wang, X.; Guo, Z.; Hu, K. Effect of the in situ leaching solution of ion-absorbed rare earth on the mechanical behaviour of basement rock. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering 2022, 14, 1210e1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; He, H.; Bao, W.Y.Z.; Liang, X.; Zhu, J.; Ma, L.M.; Huang, Y. Zircon texture and composition fingerprint HREE enrichment in muscovite granite bedrock of the Dabu ion-adsorption REE deposit, South China. Chemical Geology 2023, 616, 121231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Wei, G.; Zhang, J.; Liang, X.; Huang, G. Origin and distribution of rare earth elements (REEs) in the soils of Meizhou City, southern China with high abundance of regolith-hosted REEs. Applied Geochemistry 2022, 147, 105514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustos, N.; Marquardt, C.; Belmar, A.; Cordeiro, P. Regolith-hosted rare earth exploration in the Chilean Coastal Range of the Central Andes. Journal of Geochemical Exploration 2022, 234, 106934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, D.; Van Gosen, B. Placer-Type Rare Earth Element Deposits. Reviews in Economic Geology 2016, 18, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Anwar, E.A.A. ., Abdelhafiz, M.A.; Salman, S.A. Rare earth and trace elements enrichment and implications in black shales of Safaga-Qussier sector, Egypt. Journal of African Earth Sciences 2022, 188, 104482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Luo, C.; Gao, L.; Long, J.; Xu, H.; Yang, R. Anomalous concentrations and environmental implications of rare earth elements in the rock-soil-moss system in the black shale area. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 1, 135770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketris, M.P.; Yudovich, Y.E. ; Estimations of Clarkes for Carbonaceous biolithes: world averages for trace element contents in black shales and coals. International Journal of Coal Geology 2009, 78, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zierenberg, R.; Fowler, A.; Reed, M.; Palanderi, J. Maximizing REE Recovery in Geothermal Systems. Final Technical Report - DOE project DE-EE0006748 2018, 1-30.
- Kurzawa, D.K.; Wysocka, I.; Porowski, A.; Drzewicz, P.; Vassileva, A. The occurrence and distribution of rare earth elements in mineral and thermal waters in the Polish Lowlands. Journal of Geochemical Exploration 2022, 237, 106984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Liu, F.; Zhang, W. Typical geothermal waters in the Ganzi–Litang fault, western Sichuan, China: hydro chemical processes and the geochemical characteristics of rare-earth elements. Environ Earth Sci 2022, 81, 538. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Li, R.; Xue, T.; Wang, B.; et al. Characteristic and Geological Implications of Major Elements and Rare Earth Elements of Triassic Chang 7 Oil Shale in Tongchuan City, Southern Ordos Basin (China). Minerals 2018, 8, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaram, V. Recent Trends in the Instrumental Analysis of Rare Earth Elements in Geological and Industrial Materials. Trends in Analytical Chemistry 1996, 15, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaram, V. Current and emerging analytical techniques for geochemical and geochronological studies. Geological Journal 2021, 56, 2300–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palozzi, J.; Bailey, J.G.; Tran, Q.A.; Stanger, R. A characterization of rare earth elements in coal ash generated during the utilization of Australian coals. International Journal of Coal Preparation and Utilization. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Harikrishnan, S.; Ananthachar, A.; Choudhari, K.S.; George, S.D.; Chidangil, S.; Unnikrishnan, V.K. Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) for the Detection of Rare Earth Elements (REEs) in Meteorites. Minerals 2023, 13, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoggard, M.J.; Czarnota, K.; Richards, F.D. Huston, D.L.; et al. Global distribution of sediment-hosted metals controlled by craton edge stability. Nature Geoscience 2020, 13, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaram, V.; Banakar, V.K.; Subramanyam, K.S.V.; Roy, P.; Satyanarayanan, M.; Mohan, M.R.; Sawant, S.S. Yttrium and rare earth element contents in seamount cobalt crusts in the Indian Ocean. Curr. Sci. 2012, 110, 1334–1338. [Google Scholar]
- Balaram, V.; Satyanarayanan, M.; Murthy, P.K.; Mohapatra, C.; Prasad, K.L. Quantitative multi-element analysis of cobalt crust from Afanasy-Nikitin Seamount in the North Central Indian Ocean by inductively coupled plasma time-of-flight mass spectrometry. MAPAN-Journal of Metrology Society of India 2013, 28, 63–77. [Google Scholar]
- Hein, J.R.; Koschinsky, A.; Mikesell, M.; Mizell, K.; Glenn, C.R.; Wood, R. Marine Phosphorites as Potential Resources for Heavy Rare Earth Elements and Yttrium. Minerals 2016, 6, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, Y. Rare Earth Element Metallogeny in Indian Continental Shelf and Ocean Floor. J. Geol. Soc. India 2021, 97, 1396–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourret, O.; Tuduri, J. Continental shelves as potential resource of rare earth elements. Scientific Reports 2017, 7, 5857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Q.; Xue, Z.G.; Chu, F. Rare Earth Element Distributions in Continental Shelf Sediment, Northern South China Sea. Water 2020, 12, 3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattarova, V.; Astakhov, A.; Aksentov, K.; Shi, X.; et al. Geochemistry of the Laptev and East Siberian seas sediments with emphasis on rare-earth elements: Application for sediment sources and paleoceanography. Continental Shelf Research 2023, 254, 104907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaram, V. Deep-sea mineral deposits as a source of critical metals for high-and green-technology applications. Minerals and Mineral Materials.
- Sa, R.; Sun, X.; He, G.; Xu, L.; Pan, Q.; Liao, J.; … Deng, X. Enrichment of rare earth elements in siliceous sediments under slow deposition: A case study of the central North Pacific. Ore Geology Reviews 2018, 94, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Liu, J.; Ren, X.; Shi, X. Geochemistry of rare earth elements in cobalt-rich crusts from the Mid-Pacific M seamount. Journal of Rare Earths 2009, 27, 169e176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, B.N.; Balaram, V.; Sudhakar, M.; Pluger, W.L. Rare earth element geochemistry of ferromanganese deposits from the Indian Ocean. Marine Chemistry 1992, 38, 185e208. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez, F.J.; Somoza, L.; Maldonado, A.; Lunar, R.; Martinez-Frias, J.; Martin- Rubi, J.A.; Carrion, M.C. High technology elements in Co-rich ferromanganese crusts from the Scotia Sea. Revista de la Sociedad Española de Mineralogía 2010, 13, 113e114. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, Y.; Fujinaga, K.; Nakamura, K.; Takaya, Y.; Kitamura, K.; Ohta, J.; Toda, R.; Nakashima, T.; Iwamori, H. Deep-sea mud in the Pacific Ocean as a potential resource for rare-earth elements. Nature Geoscience 2011, 4, 535e539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, T.; Nakatani, N.; Arai, R.; Sekimoto, T.; Katayama, H. Combined Mining and Pulp-Lifting of Ferromanganese Nodules and Rare-Earth Element-Rich Mud around Minamitorishima Island in the Western North Pacific: A Prefeasibility Study. Minerals 2021, 11, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Zhong, C.; Javier, G.F.; Xufeng, Z.; et al. Rare earth elements and yttrium in ferromanganese deposits from the South China Sea: distribution, composition and resource considerations. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2018, 37, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasukawa, K.; Nakamura, K.; Fujinaga, K. , Machida, S.; et al. Rare-earth, major, and trace element geochemistry of deep-sea sediments in the Indian Ocean: Implications for the potential distribution of REY-rich mud in the Indian Ocean. Geochemical journal GJ 2015, 49, 621–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, L.S.; Ray, D.; Paropkari, A.L.; Mudholkar, A.V.; Satyanarayanan, M. , Balaram, V.; et al. Distribution of REEs and yttrium among major geochemical phases of marine Fe–Mn-oxides: Comparative study between hydrogenous and hydrothermal deposits. Chemical Geology, 2015; 312–313, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlu, T.K.; Kalluraya, V.K.K. Ferromanganese encrustation from Lakshadweep area, Arabia Sea. Jour. Geol. Soc. India 1997, 49, 389–394. [Google Scholar]
- Dinesh, A.C.; Nisha, N.V.; Varghese, S.; Pillai, R.; Prasad, D.; Baraik, S.; Ramesh, R.P.; Joshi, R.K.; Meitei, S.I.; Jishnu, B.K.; Manoj, R.V.; Nagasundaram, M. Extensive occurrence of Fe-Mn crusts and nodules on seamounts in the southern Andaman Sea, India. Curr. Sci. 2020, 119, 704–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.G.; Hyeong, K.; Yoo, C.M. Distribution of rare earth elements and yttrium in sediments from the Clarion-Clipperton Fracture Zone, northeastern Pacific Ocean. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems 2022, 3, e2022GC010454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Tao, C.; Ma, W.; Dias, Á.A.; Hu, S.; Shao, Y.; Yang, K.; Zhang, W. Material Source of Sediments fromWest Clarion–Clipperton Zone (Pacific): Evidence from Rare Earth Element Geochemistry and Clay Minerals Compositions. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaya, Y.; Yasukawa, K.; Kawasaki, T.; Fujinaga, K.; Ohta, J.; Usui, Y.; Nakamura, K.; Kimura, J.; Chang, Q.; Hamada, M.; Dodbiba, G.; Nozaki, T.; Iijima, K.; Morisawa, T.; Kuwahara, T.; Ishida, Y.; Ichimura, T.; Kitazume, M.; Fujita, T.; Kato, Y. The tremendous potential of deep-sea mud as a source of rare earth elements. Scientific Report 2018, 8, 5763. [Google Scholar]
- Bu, W.R.; Shi, X.F.; Peng, J.T. Geochemical characteristics of seamount ferromanganese nodules from mid-Pacific Ocean. Chinese Science Bulletin 2003, 48, 98e105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, D.Z. Rare earth elements in ferromanganese nodules and other marine phases. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 38 1974, 1007e1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milinovic, J.; Rodrigues, F.J.L.; Barriga, F.J.A.S.; Murton, B.J. Ocean-Floor Sediments as a Resource of Rare Earth Elements: An Overview of Recently Studied Sites. Minerals 2021, 11, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broom-Fendley, S.; Siegfried, P.R.; Wall, F.; O’Neill, M.; Brooker, R.A.; Fallon, E.K.; Pickles, J.R.; Banks, D.A. The origin and composition of carbonatite-derived carbonate-bearing fluorapatite deposits. Miner. Deposita 2021, 56, 863–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habashi, F. The recovery of the lanthanides from phosphate rock. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology. Chemical Technology 2007, 35, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshdy, O.E.; Haggag, E.A.; Masoud, A.M. Leaching of rare earths from Abu Tartur (Egypt) phosphate rock with phosphoric acid. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 2023, 25, 501–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buccione, R.; Kechiched, R.; Mongelli, G.; Sinisi, R. REEs in the North Africa P-Bearing Deposits, Paleoenvironments, and Economic Perspectives: A Review. Minerals 2021, 11, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.M.; Liu, M.X.; Dan, Y.; Said, N.; Wu, J.H.; Hou, M.C.; Zou, H. The origin of Ediacaran phosphogenesis event: New insights from Doushantuo Formation in the Danzhai phosphorite deposit. South Ch HinaOre Geology Review 2023, 105230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, G.; Stille, P. Diagenetic constraints on the use of cerium anomalies as palaeoseawater redox proxies: an isotopic and REE study of Cambrian phosphorites. Chemical Geology 2001, 175, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emsbo, P.; McLaughlin, P.I.; Breit, G.N.; du Bray, E.A.; Koenig, A.E. Rare earth elements in sedimentary phosphate deposits: solution to the global REE crisis? Gondwana Research 2015, 27, 776–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Yuan, Z.; Bai, G. Rare earth deposits in China. In: Jones, A.P.; Wall, Frances, Williams, C.T. (Eds.), Rare earth minerals–chemistry, origin and ore deposits. New York, Chapman and Hall, The Mineralogical Society Series 7, 1996; pp. 281–310.
- Ahmed, A.H.; Aseri, A.A.; Ali, K.A. Geological and geochemical evaluation of phosphorite deposits in northwestern Saudi Arabia as a possible source of trace and rare-earth elements. Ore Geology Reviews 2022, 144, 104854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, F.; Yazdi, M.; Behzadi, M.; Yakymchuk, C.; Khoshnoodi, K. Mineralogy, geochemistry and depositional environment of phosphates in the Pabdeh Formation, Khormuj anticline, SW of Iran. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Yang, H.; Fan, H.; Xia, Y.; Meng, Q.; He, S.; Gong, X. Assessment of the Effect of Organic Matter on Rare Earth Elements and Yttrium Using the Zhijin Early Cambrian Phosphorite as an Example. Minerals 2022, 12, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, O.; Zimmermann, T.; Hildebrandt, L.; Pröfrocka, D. Technology-critical elements in Rhine sediments - A case study on occurrence and spatial distribution. Science of the Total Environment 2022, 852, 158464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramesh, R.; Ramanathan, A.; Ramesh, S.; Purvaja, R.; Subramanian, V. Distribution of rare earth elements and heavy metals in the surficial sediments of the Himalayan River system. Geochemical Journal 2000, 34, 295–319. [Google Scholar]
- Dushyantha, N.; Ratnayake, N.; Premasiri, R.; Batapola, N.; et al. Geochemical exploration for prospecting new rare earth elements (REEs) sources: REE potential in lake sediments around Eppawala Phosphate Deposit, in Sri Lanka. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences 2022, 105515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, S.S.; Ramana, R.V. V. Rao1, V.P.; Mohan, M.R.; Sawant, S.S.; Satyasree, N.; Krishna, A.K. Rare earth elements of sediments in rivers and estuaries of the east coast of India. Current Science 2021, 120, 519–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaillardet, J.; Dupre, B.; Allegre, C.J.; Negrel, P. Chemical and physical denudation in the Amazon river basin. Chem. Geol. 1997, 142, 141–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndjama, J.; Mafany, G.; Ndondo, R.G.N. ·, Belmond, B.E.; Bessa, A.Z.E. Rare earth elements in surface waters and sediments of the Mgoua watershed, south western Cameroon. Arabian Journal of Geosciences 2022, 5, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Lu, H.; Zhang, B.; Cheng, Z.; Fu, W.; Lao, C.; Xu, C. Delineating preliminary prospective areas of ion-adsorption rare earth deposits with stream sediments geochemical mapping in South China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences 2022, 105520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Gu, X.; Lian, M.; Wang, J.; et al. Occurrence, geochemical characteristics, enrichment, and ecological risks of rare earth elements in sediments of “the Yellow river−Estuary−bay” system. Environmental Pollution 2023, 319, 121025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, R.; Bank, T.L.; Roth, E.A.; Granite, E.J.; Soong, Y. Organic and inorganic associations of rare earth elements in central Appalachian coal. International Journal of Coal Geology 2017, 179, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yesenchak, R.; Sharma, S.; Maxwell, A.E. Modes of Occurrence, Elemental Relationships, and Economic Viability of Rare Earth Elements in West Virginia Coals: A Statistical Approach. Minerals 2022, 12, 1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S. Graham, I.T.; Ward, C.R. A review of anomalous rare earth elements and yttrium in coal. International Journal of Coal Geology 2016, 159, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Ma, L.; Huang, G.; Li, J.; Xu, H. Distribution and Speciation of Rare Earth Elements in Coal Fly Ash from the Qianxi Power Plant, Guizhou Province, Southwest China. Minerals 2022, 12, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, C.R. Analysis, origin and significance of mineral matter in coal: An updated review. International Journal of Coal Geology 2016, 165, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hower, J.C.; Eble, C.F.; Hopps, S.D.; Morgan, T.D. Aspects of rare earth element geochemistry of the Pond Creek coalbed, Pike County, Kentucky. International Journal of Coal Geology 2022, 104082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seredin, V.V.; Dai, S. Coal deposits as potential alternative sources for lanthanides and yttrium. International Journal of Coal Geology 2012, 94, 67–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Qin, S.; Bai, H. Geochemistry of rare earth elements and yttrium in Late Permian coals from the Zhongliangshan coalfield, southwestern China. Front. Earth Sci. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USGS. Recovery of Rare Earth Elements and Critical Materials from Coal and Coal By-products. United States Department of Energy, Washington DC; 2022; pp. 1-86.
- Madhusmita, M.; Sahu, S.K.; Poonam, M.; Gufran, B. Assessment of hazardous radionuclide emission due to fly ash from fossil fuel combustion in industrial activities in India and its impact on public. Journal of Environmental Management 2023, 328, 116908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, R.; Raja, P.; Malpe, D.; Subramanyam, K.S.V.; Balaram, V. Radio elemental characterization of fly ash from Chandrapur Super Thermal Power Station, Maharashtra, India. Current Science 2011, 100, 1880–1883. [Google Scholar]
- Sreenivas, T.; Serajuddin, M.; Moudgil, R.; Anand Rao, K. Developments in characterization and mineral processing of coal Fly ash for recovery of rare earth elements. In: Jyothi, R.K., Parhi, P.K. (Eds.), Clean Coal Technologies: Beneficiation, Utilization, Transport Phenomena and Prospective. Springer International Publishing, Cham. 2021; pp. 431–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franus, W.; Motykam, M.M.W.; Wdowin, M. Coal fly ash as a resource for rare earth elements. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2015, 22, 9464–9474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, J.; Long, X.; Zhang, L.; Shoppert, A.; Valeev, D.; Zhou, C.; Liu, X. The Discrepancy between Coal Ash from Muffle, Circulating Fluidized Bed (CFB), and Pulverized Coal (PC) Furnaces, with a Focus on the Recovery of Iron and Rare Earth Elements. Materials 2022, 15, 8494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, K.A.; Serajuddin, M. , Devi, G.R.; Thakurta, S.G.; Sreenivas, T. On the characterization and leaching of rare earths from a coal fly ash of Indian origin. Separation Science and Technology 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, H.B.; Kim, S.; Lee, J. Recovery of rare earth elements from coal fly ash using enrichment by sodium hydroxide leaching and dissolution by hydrochloric acid. Geosystem Engineering 2022, 25, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hower, J.C.; Ruppert, L.F.; Eble, C.F. Lanthanide, Yttrium, and Zirconium anomalies in the Fire Clay coal bed, Eastern Kentucky. Int. J. Coal Geol 1999, 39, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.A.; Karan, R.; Babu, J.M.; Devi, G.R.; Sreenivas, T. Development of process scheme for recovery of rare earths from leachate of coal fly ash. Cleaner Chemical Engineering 2022, 4, 100078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, S.; Yang, J.; Stuckman, M.; Verba, C. Rare Earth Element (REE) and Critical Mineral Fractions of Central Appalachian Coal-Related Strata Determined by 7-Step Sequential Extraction. Minerals 2022, 12, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klauber, C.; Gräfe, M.; Power, G. Bauxite residue issues: II: Options for residue utilization. Hydrometallurgy 2011, 108, 11–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, B.; Lee, C.G.; Park, J.R. Assessment of bauxite residue as secondary resource for rare earth metal and valorization challenges: A perspective. Resources. Conservation & Recycling Advances 2022, 14, 200078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archambo, M.; Kawatra, S.K. Red Mud: Fundamentals and New Avenues for Utilization. Mineral Processing and Extractive Metallurgy Review. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Abaka-Wood, G.B.; Johnson, B.; Addai-Mensah, J.; Skinner, W. Recovery of Rare Earth Elements Minerals in Complex Low-Grade Saprolite Ore by Froth Flotation. Minerals 2022, 12, 1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dushyantha, N.; Ilankoon, I.M.S.K.; Ratnayake, N.P.; Premasiri, H.M.R.; Dharmaratne, P.G.R.; Abeysinghe, A.M.K.B.; Rohitha, L.P.S.; Chandrajith, R.; Ratnayake, A.S.; Dissanayake, D.M.D.O.K.; et al. Recovery Potential of Rare Earth Elements (REEs) from the Gem Mining Waste of Sri Lanka: A Case Study for Mine Waste Management. Minerals 2022, 12, 1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiegiel, K.; Miśkiewicz, A.; Koniecko, I.H.; Gajda, D.; Kołtuniewicz, G.Z. Perspective of Obtaining Rare Earth Elements in Poland}, Chapter 2, Lanthanides, editor = {Nasser S. Awwad and Ahmed T. Mubarak}, IntechOpen. [CrossRef]
- Baron, R. Results of Pilot Research Work on the Content of Rare Earth Elements in Metallurgical Wastes from Nowa Huta. Journal of the Polish Mineral Engineering Society 2022, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaram, V. Rare earth elements: A review of applications, occurrence, exploration, analysis, recycling, and environmental impact. Geoscience Frontiers 2019, 10, 1285–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujaczki E, Feigl V, Molnar M, Cusack P, Curtin T, Courtney R, O’Donoghue L, Davris P, Hugi C, Evangelou M, Balomenos, E, and Lenz, M. Re-using bauxite residues: benefits beyond (critical raw) material recovery. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology 2018, 93, 2498–2510. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W. Y. Pranolo, and C.Y. Cheng. Recovery of scandium from synthetic red mud leach solutions by solvent extraction with D2EHPA. Separation and Purification Technology 2013, 108, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botelho, A.B.; Costa, R.H.; Espinosa, D.C.R.; Soares, T.J.A. Recovery of scandium by leaching process from Brazilian red mud. In Rare Metal Technology. G.; Azimi, H., Kim, S., Ala, T., Neelameggham Ouch, N.R., Baba, A.A., Eds.; Sprnger: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Abhilash, A.; Sinha, S.; Sinha, M.K.; Pandey, B.D. Extraction of lanthanum and cerium from Indian red mud. International Journal of Mineral Processing 2014, 127, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, U.; Thawrani, S.A.; Ansari, M.S.; Puttewar, S.P.; Agnihotri, A. Studies on beneficiation and leaching characteristics of rare earth elements in Indian red mud. Russian Journal of Non-Ferrous Metals 2019, 60, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, R.P.; Kazantzis, N.K.; Emmert, M.H. Process for scandium recovery from Jamaican bauxite residue: A probabilistic economic assessment. Materials Today: Proceedings 2019, 9, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borra, C.R.; Pontikes, Y.; Binnemans, K.; Van Gerven, T. Leaching of rare earths from bauxite residue (red mud). Minerals Engineering 2015, 76, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vind, J.A. ; Malfliet, B.; Blanpain, P.E.; Tsakiridis, A.H.; Tkacyk, V. Vassiliadou, and D. Panias. Rare earth element phases in bauxite residue. Minerals 2018, 8, 77. [Google Scholar]
- Deady, E.A.E. ; Mouchos, K.; Goodenough, B.J. Williamson, and F. Wall. A review of the potential for rare-earth element resources from European red muds: Examples from Seydişehir, Turkey and Parnassus-Giona, Greece. Mineralogical Magazine 2016, 80, 43–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petropulu, M.O.; Tyberopulu, T. , Parissakis, G. Direct determination of lanthanides, yttrium and scandium in bauxites and red mud from alumina production. Anal Chim Acta 1994, 296, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujaczki, E. ; Y.-S.; Zimmerman, V. Feigl, and M. Lenz. Recovery of rare Earth elements from Hungarian red mud with combined acid leaching and liqud-liquid extraction. Proceedings of the Bauxite Residue Valorization and Best Practices Conference, Leuven, Belgium, 2015; pp. 1–7.
- Martoyan, G.A. ; G.G. Karamyan, and G.A. Vardan. New technology of extracting the amount of rare earth metals from the red mud. IOP conference series: Materials Science and Engineering, Altay, Russia, 2016; p. 112.
- Zhang, S.; Zhao, F.; Liu, D.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, X.; Lin, J.; Dong, H.; Zhao, S.; Liu, X.; Zan, M. Modes of Occurrence of Critical Metal Elements (Li, REEs and Other Critical Elements) in Low-Grade Bauxite from Southern Shanxi Province, China. Minerals 2022, 12, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamaletsos, P.N.; Godelitsas, A.; Filippidis, A.; et al. The Rare Earth Elements Potential of Greek Bauxite Active Mines in the Light of a Sustainable REE Demand. J. Sustain. Metall. 2019, 5, 20–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amidi, A.; Razif, S.A.M.; Jabit, N.A.; Ariffin, K.S. Characterization of rare earth elements (REE) from industrial REE waste resources. Materials Today: Proceedings 2022, 66, 3140–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, S.; Tam, J.; Yang, M.; Azimi, G. Technospheric Mining of Rare Earth Elements from Bauxite Residue (Red Mud): Process Optimization, Kinetic Investigation, and Microwave Pretreatment. Scientific Reports 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echeverry-Vargas, L.; Ocampo-Carmona, L.M. Recovery of Rare Earth Elements from Mining Tailings: A Case Study for Generating Wealth from Waste. Minerals 2022, 12, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoppert, A.; Loginova, I.; Napol’skikh, J.; Kyrchikov, A.; Chaikin, L.; Rogozhnikov, D.; Valeev, D. Selective Scandium (Sc) Extraction from Bauxite Residue (RedMud) Obtained by Alkali Fusion-Leaching Method. Materials 2022, 15, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, R.M.; Ounoughene, G.; Borra, C.R.; Binnemans, K.; Van Gerven, T. Neutralisation of bauxite residue by carbon dioxide prior to acidic leaching for metal recovery. Minerals Engineering 2017, 112, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenzhaliyev, B.K.; Surkova, T.Yu. , Yessimova, D.M. Concentration of rare-earth elements by sorption from sulphate solutions. Complex Use of Mineral Resources. [CrossRef]
- Rychkov, V.N.; Kirillov, E.V.; Kirillov, S.V.; Semenishchev, V.S.; Bunkov, G.M.; Botalov, M.S.; … Malyshev, A.S. Recovery of rare earth elements from phosphogypsum. Journal of Cleaner Production 2018, 196, 674–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, J.D.; Diwa, R.R.; Palattao, B.L.; Haneklaus, N.H.; et al. Rare earths in Philippine phosphogypsum: Use them or lose them. The Extractive Industries and Society 2022, 10, 101082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasatkina, E.A. ; Shumilov,O.I.; Kirtsideli, I.Y.; Makarov, D.V. Bioleaching Potential of Microfungi Isolated from Arctic Loparite Ore Tailings (Kola Peninsula, Northwestern Russia). Geomicrobiology Journal. [CrossRef]
- Abaka-Wood, G.B.; Ehrig, K.; Addai-Mensah, J.; Skinner, W. Recovery of Rare Earth Elements Minerals from Iron-Oxide-Silicate-Rich Tailings: Research Review. Eng. 2022, 3, 259–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, G.C.; Bertoli, A.C.; Duarte, H.A.; Ladeira, A.C.Q. Recovery of rare earth elements from sulfate-rich acid mine water: Looking through the keyhole the exchange reaction for cationic resin. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering 2022, 10, 108715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vass, C.R.; Noble, A.; Ziemkiewicz, P.F. The Occurrence and Concentration of Rare Earth Elements in Acid Mine Drainage and Treatment By-products: Part 1—Initial Survey of the Northern Appalachian Coal Basin. Mining, Metallurgy & Exploration 2019, 36, 903–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vass, C.R.; Noble, A.; Ziemkiewicz, P.F. The Occurrence and Concentration of Rare Earth Elements in Acid Mine Drainage and Treatment Byproducts. Part 2: Regional Survey of Northern and Central Appalachian Coal Basins. Mining Metall. Explor. 2019, 36, 917–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyrgaki, K.; Gemeni, V.; Karkalis, C.; Koukouzas, N.; Koutsovitis, P.; Petrounias, P. Geochemical Occurrence of Rare Earth Elements in Mining Waste and Mine Water: A Review. Minerals 2021, 11, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larochelle, T.; Noble, A.; Strickland, K.; Ahn, A.; Ziemkiewicz, P.; Constant, J.; Hoffman, D.; Glascock, C. Recovery of Rare Earth Element from Acid Mine Drainage Using Organo-Phosphorus Extractants and Ionic Liquids. Minerals 2022, 12, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, P.; Valente, T.; Marques, R.; Prudencio, M.I.; Pamplona, J. Rare earth elements - Source and evolution in an aquatic system dominated by mine-Influenced waters. Journal of Environmental Management 2022, 322, 116125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wu, P. Geochemical characteristics of dissolved rare earth elements in acid mine drainage from abandoned high-As coal mining area, southwestern China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 2017, 24, 20540–20555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jyothi, R.K.; Thenepalli, T.; Ahn, J.W.; Parhi, P.K.; Chung, K.W.; Lee, J.-Y. Review of rare earth elements recovery from secondary resources for clean energy technologies: Grand opportunities to create wealth from waste. Journal of Cleaner Production 2020, 122048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.; Ahmed, T.; Awual, M.R.; Rahman, A.; et al. Advances in sustainable approaches to recover metals from e-waste-A review. Journal of Cleaner Production 2020, 244, 118815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukowiak, A.; Zur, L.; Tomala, R.; LamTran, T.N.; et al. Rare earth elements and urban mines: Critical strategies for sustainable development, Ceramics International 2020, 46, 26247-26250. [CrossRef]
- Jowitt, S.M.; Werner, T.T.; Weng, Z.; Mudd, G.M. Recycling of the rare earth elements. Current Opinion in Green and Sustainable Chemistry 2018, 13, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguli, R.; Cook, D.R. Rare earths: A review of the landscape. MRS Energy & Sustainability: A Review Journal. [CrossRef]
- Rizos, V.; Righetti, E.; Kassab, A. Developing a supply chain for recycled rare earth permanent magnets in the EU CEPS in-depth analysis. INSPIRES CEPS, 2022; 1–57. [Google Scholar]
- Constantine, J.; Lie, J.; Liu, J.C. Recovery of rare earth elements from spent NiMH batteries using subcritical water extraction with citric acid. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering 2022, 10, 108000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Tian, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, W.; Li, B.; Gong, Y.; Zuo, T. Recycling rare earth elements from waste cathode ray tube phosphors: Experimental study and mechanism analysis. Journal of Cleaner Production 2018, 205, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yin, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, W.; Mu, X. The recycling of rare earths from waste tricolor phosphors in fluorescent lamps: A review of processes and technologies. Resources, Conservation and Recycling 2014, 88, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-Z.; Hsieh, Y.-H.; Tang, Y.-C.; Shen, Y.-H. Separation of Cobalt, Samarium, Iron, and Copper in the Leaching Solution of Scrap Magnets. Metals 2023, 13, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patcharawit, T.; Kritsarikan, W.; Yingnakorn, T.; Khumkoa, S. Comparative Study of Manufacturing NdFeB Magnet Wastes Recycling: Oxidative Roasting-Selective Leaching and Whole Leaching Routes. Recycling 2022, 7, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucey, P.; et al. Understanding the Lunar Surface and Space-Moon Interactions. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry 2006, 60, 83–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASA. 2022 NASA's Centennial Challenges: Space Robotics Challenge, NationalAeronautics and Space Administration. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/directorates/spacetech/centennial_challenges/space_robotics/about.html.
- Xu, F. The approach to sustainable space mining: issues, challenges, and solutions. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering 2020, 738, 012014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvis M, Krolikowski A, Milligan, T. Concentrated lunar resources: imminent implications for governance and justice. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2021, 379, 20190563. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Ocean | Matrix | ΣREE range (µg/g) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| East Siberian Arctic Shelf | Bottom sediments | 104 to 220 | [44] |
| Central North Pacific Ocean | Siliceous sediments | 810.4 | [46] |
| Afanasy Niktin Seamount (ANS) in the Eastern Equatorial Indian Ocean. | Cobalt crust | 1727 – 2511 | [38,39] |
| Mid-Pacific seamount | Cobalt-rich crusts | 2085 | [47] |
| Indian Ocean | Ferromanganese crust | 928 - 1570 | [48] |
| Scotia Sea | Ferromanganese crust | 3400 | [49] |
| Eastern South Pacific | Deep sea mud | 1000 – 2230 | [50] |
| North Pacific (east & west of Hawaiian Islands) | Deep sea mud | 400 – 1000 | |
| Minamitorishima Island in the Western North Pacific | REE-Rich Mud | >1446.2 (REE+Y) | [51] |
| South China Sea | Ferromanganese nodule deposits | 1460 (avg) | [52] |
| Indian Ocean | REY-rich mud | > 400 | [53] |
| Marine sediments | 585 - 920 | ||
| Andaman Sea, Indian Ocean | Ferromanganese crust, summit of southern seamount |
1139 | [54] |
| Ferromanganese crust within the two peaks of the same seamount. | 2285 | ||
| Lakshadweep Sea, Indian Ocean | Ferromanganese crust, | La (200) & Y (150) | [55] |
| West Sewell Ridge, Andaman Sea, Indian Ocean | Ferromanganese crust | 1600 | [56] |
| Manganese nodules | 1186 | ||
| Clarion-Clipperton Fracture Zone, North-eastern Pacific Ocean |
Deep-sea sediments | >700 | [57] |
| West Clarion–Clipperton Zone, Pacific Ocean | Marine sediments | 454.7 (REE+Y) | [58] |
| North Pacific Ocean near Minamitorishima Island, Japan | Deep-sea mud | > 5,000 (REE+Y) | [60] |
| Mid Pacific Ocean | Fe-Mn nodules | 1178 - 1434 | [60] |
| Pacific Ocean | Deep nodules | 1326 | [61] |
| Shallow nodules | 1398 | ||
| Pacific Ocean | ocean-floor sediments | 22,000 | [62] |
| Ocean | Phosphorites | Average concentration (µg/g) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pacific and northeast Atlantic | Seamount phosphorites | 727 (∑REE+ Y) | [40] |
| Continental margin phosphorites | 161 (∑REE+ Y) | ||
| Doushantou Formation, South China | Danzhai phosphorite deposit | 21 to 447 (∑REE) | [67] |
| Meishucun excavation sites, South China | Cambrian phosphorites | 99.1 - 709.7 (∑REE) | [68] |
| Sedimentary Abu Tartur phosphate ore, Egypt | Phosphate ore | 0.05-0.20 wt. % (∑REE) | [65] |
| Mississippian phosphorites, USA | Phosphorite ore | 18,000 (∑REE) | [69] |
| Mountain Pass phosphorites, USA |
Phosphorite ore | ||
| Chinese clay-type Phosphorite deposits | Phosphorite ore | 500 to 2000 (∑REE) | [70] |
| Hazm Al-Jalamis Phosphorites, Saudi Arabia | Phosphorites | <121.8 (∑REE+ Y) | [71] |
| Pabdeh Formation, Khormuj anticline, SW of Iran | Phosphorites | 48 to 682 ∑REE | [72] |
| Northern African phosphorite deposits (Morocco, Algeria and Tunisia) | 39.2 to 1759.4 ∑REE | [66] | |
| South China | Phosphorus-bearing dolomites |
330 ∑REY | [73] |
| Phosphorus dolomites | 676 ∑REY | ||
| Phosphorites | 1477 ∑REY |
| Country | Type of sediment | ∑REE | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Indigirka River, in the Laptev Sea | River sediments | 124 to 197 | [44] |
| Rhine river sediments, Europe | Upper Rhine | 136.07 | [74] |
| Middle Rhine | 215.32 | ||
| Lower Rhine | 340.45 | ||
| Tributaries | 291.39 | ||
| Himalayan river system sediments | Brahmaputra | 95 | [75] |
| Ganges | 97 | ||
| Megna | 107 | ||
| Padma | 131 | ||
| Jamuna | 152 | ||
| Yamuna | 100 | ||
| Rivers of the east coast of India | Cauvery | 171 | [77] |
| Pennar | 203 | ||
| Krishna | 131 | ||
| Godavari-Vasista | 194 | ||
| Godavari-Gauthami | 290 | ||
| Mahanadi | 270 | ||
| Hooghly | 167 | ||
| South America | Amazon sediments | 217 | [78] |
| The Mgoua watershed, Cameroon, Africa | Sediments | 282 to 728 Average 550 |
[79] |
| China | Stream sediments | 212 | [80] |
| Catchment sediments | 187 | ||
| Soils | 190 | ||
| Sri Lanka | Lake sediments* | 1011 | [74] |
| Yellow River, China | River sediment | 149 | [81] |
| Estuary | 165 | ||
| Laizhou Bay | 173 |
| Place & Country | Material | ∑REE (µg/g) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| World average | Fly ash | 450 | [93] |
| 404 | [84] | ||
| Poland | Fly ash | 101 - 543 | [94] |
| Faer power plant in Guizhou Province, China | Fly ash | 240.20 to 520.27 | [95] |
| lignite coal-based thermal power plants, India | Fly ash | 2100 | [96] |
| Collie Basin, Western Australia | Fly ash | 0.21% ∑REO | [35] |
| Pond Creek coalbed, Pike County, Kentucky, US | Coal | <300 to >1000 | [87] |
| World hard coal | Coal | 69 | [84] |
| World low-rank coal | 65 | ||
| World coal | 68 | ||
| US coal | 62 | ||
| China | 138 | ||
| South Korea | Fly ash | 267 to 556 | [97] |
| Coal bed, Eastern Kentucky, US | Fire clay | 1965–4198 | [98] |
| Qianxi coal-fired power plant, Guizhou province, China | Fly ash | 630.51 | [73] |
| Thermal Power Station II (TS II) of Neyveli Lignite Corporation (NLC), Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India | Fly ash | 2160 (∑REE) 300 (Y) |
[99] |
| Central Appalachian Coal-Related Strata, West Virginia (WV) and Central Pennsylvania (PA), US | WV MKT underclay | 297 | [100] |
| WV MKT coarse coal refuse |
345 | ||
| Central PA LKT underclay |
221 | ||
| Central PA MKT underclay |
728 |
| Location | REE (µg/g) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Yb | Y | Sc | |
| Average in Earth’s crust [108] | 39 | 66 | 9 | 41 | 7 | - | 6 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 33 | 22 |
| Chinalco, China [109] | 416 | 842 | 95 | 341 | 64 | - | 56 | 184 | 48 | 25 | 28 | 28 | 266 | 158 |
| Australia [110] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 68 | 54 |
| Brazil [111] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 24 | 43 |
| India [112] | 110 | 70 | 0.5 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | 5 |
| India [113] | 58 | 98 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 48 |
| India [109] | 112 | 191 | 18 | 48 | 9 | - | 7 | - | 4 | - | 1 | 2 | 13 | 58 |
| Jamaica [114] | 287 | 366 | 74 | 69 | 0 | - | 37 | 0 | 37 | 5 | 21 | 16 | 373 | 55 |
| Greece [115] | 114 | 386 | 28 | 98 | 21 | - | 22 | - | 16 | 4 | 13 | 4 | 75 | 121 |
| Alumine de Greece, Greece [116] | 130 | 480 | 29 | 107 | 19 | - | 22 | 3 | 20 | 4 | 13 | 13 | 108 | - |
| Greece [117] | 127 | 409 | 28 | 103 | 20 | - | 18 | 2 | 19 | 3 | 11 | 13 | 98 | - |
| Greece [118] | 149 | 418 | 26 | 115 | 29 | 5.0 | 23 | - | 1 | 4.3. | 17 | 16 | 91. | |
| Ajka, Hungary [119] | 114 | 368 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 68 | - |
| Turkey [117] | 169 | 480 | 47 | 161 | 32 | - | 4 | 26 | 23 | 4 | 13 | 14 | 113 | - |
| Russian Federation [120] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 53 | 25 |
| Russian Federation [109] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 90 |
| Iran [120] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | 19 |
| Country | Industrial waste | ∑REE | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Poland | Uranium mine tailings, Sudety region | 64.9- 109.8 µg/g | [106] |
| Southern Shanxi Province, China | Low-grade bauxite | 1539 µg/g | [121] |
| Greece | Bauxite | 192 to 1109 (avg. 463) ΣREE + Y+Sc | [122] |
| Australia | Low–grade saprolite ore | 1.14% (∑REE oxides) |
[104] |
| Poland | Metallurgical industry waste. | >140 µg/g | [107] |
| Malaysia | Water Leach Purification (WLP) residue | 88367 µg/g with Gd as the most abundant element | [123] |
| Canada | Red Mud | 0.03 wt% | [124] |
| Jamaica | Red Mud | >1303 (REE+Y+Sc) | [114] |
| Alumine de Greece, Greece | Red Mud | >948 (REE+Y) | [116] |
| Turkey | Red Mud | > 1086 (REE+Y) | [117] |
| Sri Lanka | Gem Mine | 0.3% (∑REE oxides) | [105] |
| Bagre-Nechí mining district, Colombia | Mine waste (mostly gold mine residue and monazite waste) | 2.19% (Ce, La, Nd & Pr) | [125] |
| Russia | Different types of red mud | Sc (> 100 µg/g) | [126] |
| Greece | Bauxite residue (Red mud) | 0.1% (∑REE+Y+Sc) | [115] |
| Agios Nikolaos, Greece | Bauxite residue | ∑REE 260 & Sc 120 | [127] |
| SARECO LLP, Kazakhstan | Mineral formations (TMF) from the processing of phosphate uranium ores | 5% | [127] |
| Russia | Phosphogypsum | 0.43 - 0.52% | [129] |
| Philippine | Phosphogypsum | 266 µg/g | [130] |
| Name and location of the mine | Type | Concentration of ∑REE | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Minas Gerais, Brazil | AMD | 130 ng/ml | [133] |
| Staszic post-mining, Poland | Uranium mine | 993.3 µg/ml | [106] |
| Northern and Central Appalachian Coal Basins, US | Coal mine | 282 ng/ml | [134,135] |
| Treated precipitate | 517 µg/g | ||
| Coal mine, Treated AMD | 724 µg/g | ||
| Central Appalachian AMD source, US | Pregnant leach solution | 132.02 µg/g ∑REE+Y+Sc |
[137] |
| Sao Domingo mining complex, Iberian Pyrite Belt, Portugal | AMD | <221.8 ng/ml | [138] |
| Xingren coalfield, China | AMD | 118 to 926 ng/ml | [139] |
| E-waste item | REE | Concentration per unit | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nickel metal hydride (NiMH) battery | ∑REE | 5–25% | [146] |
| Cathode-ray tube (CRT) phosphor (as a coating on the panel. | ∑REE | 1–7 g | [147] |
| Fluorescent lamp | ∑REE + Y | 301.2 mg/1 g powder | [148] |
| Cathode-ray tube (CRT) | 265 mg/1 g powder | ||
| Navy submarines | ∑REE | 3636 kg | [144] |
| Navy surface ships | ∑REE | 1818 kg | |
| Lockheed-Martin F-35 | ∑REE | 416 kg | |
| Toyota Prius | ∑REE | 15 kg | |
| Air conditioner | ∑REE | 120 g | |
| Mobile phone | ∑REE | 0.5 g | |
| Wind turbine that generates 3.5 MW Electricity | ∑REE | 600 Kg | [3] |
| Fly and bottom ash | ∑REE | 0.9-1.3% | [10] |
| SmCo5 magnet | Sm | 21.94% | [149] |
| NdFeB magnet | Nd & Pr | 64.5% & 17.32% | [150] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





