1. Introduction
The biological and clinical importance of having readouts of the biological activity of enzymes in physiological and disease conditions, along with the possibility of non-invasive detection of their activities, high spatial resolution and great sensitivity, makes the use of fluorescent probes that penetrate inside living cells, one of the main options for detecting enzymatic activity
in vivo [
1,
2,
3].
To achieve real-time
in situ imaging of enzymes in living cells, tissues, and whole organisms, fluorescent substrates must interact with the enzyme, leading to a change in its fluorescence that allows enzyme activity to be detected. Among the fluorescent methods fluorescence microscopy has been extensively used in estimating enzyme activities in bio-molecular detection, drug distribution monitoring, image-guided surgery, preclinical research and clinical diagnosis and therapy. However, the most prominent enzymatic probes utilize one-photon microscopy (OPM) which requires UV−Vis light excitation that due to its short wavelength results in limited
in vivo depth penetration, cellular autofluorescence, and light scattering. To avoid these drawbacks, a technique can be used that consists in the excitation of the fluorophore by means of two simultaneous photons of a wavelength that doubles or exceeds that needed to excite the same fluorophore with a single photon [
4,
5,
6]. Two-photon microscopy (TPM) was predicted by Nobel laureate Maria Goeppert Mayer in 1931 [
7] and was applied by Webb in a cellular environment in 1990 [
8]. TPM uses NIR photons as excitation source of the fluorophores resulting in images of deeper layers in biological systems. Moreover, it is suitable for
in vivo enzyme activity studies with three-dimensional resolution, so that TPM is gaining immense support for clinical optical imaging applications [
9].
In addition to being excitable by two simultaneous photons, the probes should be ratiometric, as has been extensively researched and reflected in several excellent reviews on this topic [
10,
11,
12]. The quantification of a analyte using fluorescent probes emitting only one signal can be very inaccurate, since several factors independent of the analyte, such as the microenvironment around the probe, its local concentration, photobleaching, or certain instrumental parameters, interfere with correct analysis. In contrast, ratiometric fluorescent probes are based on analyte-induced changes in the intensity of two emission bands. Thus, the ratio of intensities at two wavelengths correlates directly with the concentration of the analyte providing self-calibration and correcting the analyte-independent factors listed above.
Tyrosinase (TYR), also called monophenol monooxygenase, is a cuproprotein with two copper ions in the active site, both of which are coordinated by three histidine residues (type-3 copper proteins). It catalyzes the conversion of monophenols to ortho-quinones via ortho-diphenols. TYR catalyzes the first two steps in mammalian melanogenesis, initiating melanin formation by tyrosine oxidation [
13,
14]. Although melanin primarily has a photoprotective function in human skin, the accumulation of increased amounts of melanin in specific parts of the skin results in undesirable freckles and brown spots on the human body. Additionally, it is the cause of enzymatic browning in fruits and fungi, which has a great visual impact that decreases the commercial quality and value of the products [
15]. However, even more important for human health is the abnormal expression or activation of TYR, since it is associated with several disorder such as melanoma and Parkinson's disease. Therefore, monitoring the TYR activity will help accurate diagnosis and treatment of these illnesses [
16].
The traditional colorimetric method to detect TYR activity shows very low sensitivity [
17], and was initially replaced by others methods based on electrochemistry [
18,
19] and quantum dots luminescence [
20]. Fluorescence spectroscopy has also been used to design highly sensitive TYR probes. Thus, an oligo(phenylenevinylene) containing a tyrosine moiety was synthesized as an “on/off” fluorescent probe to detect TYR activity by oxidation of tyrosine to quinone, which quenched fluorescence [
21]. A fluorescent NIR probe that incorporates tyramine (a TYR substrate) into the cyanine structure was developed by Wolfbeis’ group [
22]. Reaction with TYR in the presence of oxygen forms a quinone that quenches the fluorescence of the probe. However, to achieve high-sensitivity bioimaging in living systems by fluorescence microscopy, the most suitable approach is to develop a TYR off/on sensor. In this sense, Wu
et al. [
23] incorporated the 3-hydroxybenzyl recognition moiety into a fluorescent reporter to facilitate hydroxylation by TYR at the 4-position, and then from enzymatic oxidation to orthoquinone, which in turn undergoes a rapid intramolecular electron rearrangement that initiates cleavage of orthoquinone. In this way it is possible to eliminate the interference from reactive oxygen species.
With these ideas in mind and taking into account that a widely used strategy for obtaining ratiometric fluorescent probes is the use of molecules with electron-donor electron-acceptor (D-A) ability giving rise to an intramolecular charge transfer complex (ICT), and that one of the types of the fluorophore backbone used to design fluorescent TP probes has the structure donor-π-acceptor (D-π-A), we have developed a new DCM-based fluorescence off/on probe. The overall design strategy of the probe DCM-HBU was founded on the attachment of an enzyme active moiety 4-hydroxybenzylamine (very similar to tyrosine) to a signal reporter NIR TP chromophore dicyanomethylene-4H-pyran (DCM), perturbing the ICT effect that controls the spectral properties of DCM [
24]. By treatment with TYR, its catalytic action restores the ICT process and concomitantly the fluorescence of the DCM-NH
2 [
25], providing a ratiometric signal between the emission maxima from the dye and the probe. Due to the enzymatic reaction, color change from yellow to red, allowing colorimetric detection of TYR with the naked eye. Moreover, this fluorescent probe can be excited by two simultaneous NIR photons. This new probe has been successfully applied to the detection of TYR in solution, in living cells, tissues and in whole organisms
in vivo, using zebrafish. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of a ratiometric two photon small-molecular NIR probe for the bioimaging of TYR
in vitro/vivo.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and standards
All starting materials (reagents and solvents) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, including the enzymes TYR, dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP IV), acetylcholinesterase (AChE), lipase (PNLIP), and the enzyme inhibitor quercetin, with the highest degree of purity. Alanine aminopeptidase (ANEP) was produced and purified as previously described [
25].
2.2. Sample preparation
A 0.5 mM and 2.9 mM stock solutions of DCM-NH2 and DCM-HBU, respectively, were prepared in deuterated DMSO for purity testing by nuclear magnetic resonance. The experiments were carried out in PBS/DMSO buffer solution (7/3, v/v).
2.3. Instrumentation
UV-visible absorption spectra were collected using a Lambda 650 UV-visible spectrophotometer (PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, USA). Steady-state fluorescence and kinetics were measured by a Jasco FP-8 300 spectrofluorometer (Jasco, Tokyo, Japan). Spectrophotometry and spectrofluorimetry were performed using a temperature controller.
One-photon microscopy images were acquired with an Abberior scanning microscope (Abberior Instruments GmbH, Germany) using a pulsed excitation laser (485 nm, 40 MHz) and an objective UPlanSApo (1.4 NA, 100X) oil immersion. The pinhole size was set to 1 Airy Unit (AU) in every measurement. Two-photon microcopy images were obtained with a confocal MicroTime 200 fluorescence microscope system (PicoQuant GmbH, Berlin, Germany). The excitation source was a Chameleon Discovery NX tunable laser (Coherent Laser Group, Santa Clara, CA, USA). The intensity of the laser was controlled using a set of polarizers. Later, the excitation beam passed through an achromatic quarter-wave filter (AQWP05-M-600, Thorlabs, Jessup, MD, USA) and by an F73-705SG dichroic mirror (AHF/Chroma, Tübingen, Germany) to direct the beam to an inverted microscope system (IX-71, Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) with an oil immersion objective (1.4 NA, 100X). Fluorescence emission was acquired with a 500 nm longpass filter (AHF/Chroma, Germany) and directed to a 75 μm pinhole. Later, a 600 DCXR dichroic beam splitter (AHF/Chroma) separated the emission into two detection channels (red and green). Red channel used a bandpass filters, 685/70 (Semrock/AHF) and green channel a 520/35 filter (Semrock/AHF). The detectors used were two different single-photon avalanche diodes (SPCM-AQR 14, PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, USA).
Images of zebrafish embryos were performed on a Nikon SMZ18 fluorescent stereo microscope with a color DS-Ri2 digital camera (16.25 Mpx) using filter settings for red fluorescent protein (RFP).
2.4. Image processing
Images from two channels were exported separately as matrix data and analyzed using
Fiji Is Just ImageJ [
26]. In the image analysis, we performed a Gaussian filter (sigma = 2) to the raw images. Later, we manually selected the regions of interest (ROI) through a threshold based on the intensity. Outside the ROI a Not a Number (NaN) was assigned to pixels. These images were used to calculate the ratio value dividing both segmented channels (red and green) pixel to pixel.
2.5. Cell culture
The human melanoma primary patient-derived cell line Mel-1 comes from a malignant metastatic melanoma (stage M1a) skin biopsy and was provided by the Biobank of the Andalusian Public Health System (Spain); A-375 melanoma cell line was obtained from American Type Culture Collection (ATCC). All cell lines were cultured in Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM; Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA) supplemented with 10 % heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS) (BioWhittaker; Lonza, Basel, Switzerland), 1 % L-glutamine, 2.7 % sodium bicarbonate, 1 % Hepes buffer and with 1 % of a solution of penicillin/streptomycin (10 000 U mL-1 penicillin G and 10 mg mL-1 streptomycin; Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA) and they were maintained at 37 °C in an atmosphere containing 5 % CO2. In order to carry out the microscopy experiments, cells were seeded onto µ-Slide 8 Well IbiTreat plates at a density of 5-11×104 cells/well and then the samples were washed three times using phosphate buffered saline (PBS) 1x and bathed into DMEM buffer with 5×10-6 M of DCM-HBU.
2.6. Generation of tumours
In order to create subcutaneous xenograft tumours, an eight-week-old male NODSCID gamma mouse (NOD. Cg-Prkdcscid Il2rgtm1 Wjl/SzJ, NSG) was employed. Each procedure was authorized by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the University of Granada (ethical code: 03/07/2017/086). Mice were controlled at 20-24 °C, 50 % relative humidity (RH), and a 10:14 h light:dark cycle with food and water provided ad libitum. A human skin cancer cell line, A-375, was employed to generate subcutaneous xenograft tumours by injecting 1x106 cells in 0.05 mL Matrigel and 0.05 mL Roswell Park Memorial Institute (RPMI) medium using 26-gauge needles. When the tumour reached 300 mm3, the mouse was euthanised by cervical dislocation. For TPM analysis, tumours were excised, fixed in 4 % paraformaldehyde (PFA), embedded in optimal cutting temperature (OCT) compound and selected using a cryotome at 10 mm thickness for further analysis.
2.7. Zebrafish
Zebrafish (
Danio rerio) were kept at the fish facility, CIC, University of Granada, Spain, in fish tanks with constant water flow at 28.5 °C, following maintenance and breeding recommendations from the zebrafish handbook (
https://zfin.org/zf_info/zfbook/zfbk.html) and according to the European Directive 2010/63/EU assuring animal welfare. For egg lay, wild type males and females were set up in a breeding tank. Egg lay occurred shortly after the onset of light in the morning of the following day. Embryos were raised in E3 embryo medium (5 mM NaCl, 0.17 mM KCl, 0.33 mM CaCl
2, 0.33 mM MgSO
4, 10
-5 % Methylene Blue) at 28.5 °C until the desired stage. Embryos of the desired stage were incubated in E3 medium with 10 µM DCM-HBU (1:288 of stock solution at 2.9 mM in DMSO) for 3 h and then shortly washed with fresh E3 medium. For inhibition of the DCM-HBU processing tyrosine kinase, embryos were incubated with 200 µM quercetin (1:50 of stock 10 mM) for 3 h prior to adding 10 µM DCM-HBU for 3 h. Controls were incubated in E3 medium with DMSO (1:50) for 6 h. Subsequently, anesthetized (0.1 to 0.15 mg mL
-1 MS222) live embryos were imaged. Overlay images and quantification of red fluorescence intensity were done with
Fiji Is Just ImageJ [
26].
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis
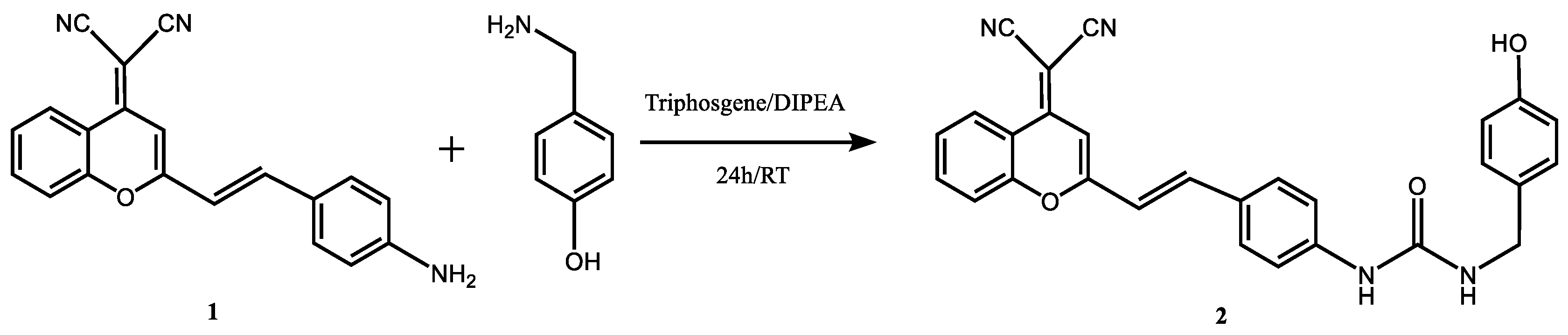
Synthesis of DCM-HBU was accomplished through a one-step route starting from ICT derivative
1, which was prepared as previously described by Sun et al. [
27]. The reaction of the aniline derivative with 4-hydroxybenzylamine provided the corresponding amide to obtain DCM-HBU
2, (
Scheme 1). The final product was characterized by
1H nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and time-of-flight mass spectrometry (TOF MS) (see the SI for more details on the synthesis and characterization).
3.2. Photophysical characterization of the enzymatic reaction
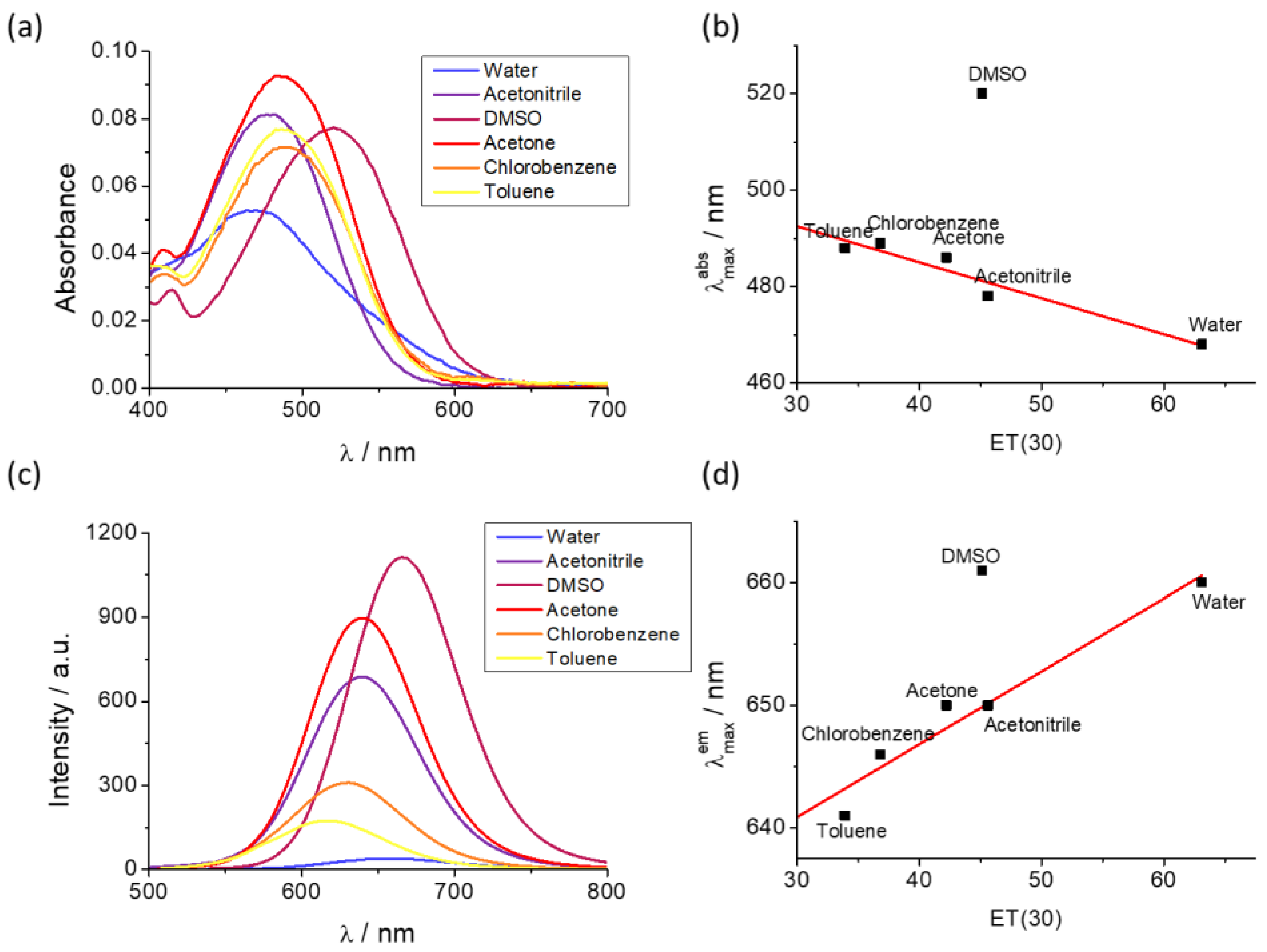
As it has been established in previous papers and can be seen in
Figure 1a, the absorption spectra show a negative solvatochromic effect (
Figure 1b), whereas the fluorescence spectra undergo a systematic red-shift with an increase in solvent ET(30) scale polarity (
Figure 1c,d). The red-shift in fluorescence is caused by the intramolecular charge transfer and linked to the increase in dipole moment upon excitation [
28]. The fluorescence lifetime was also calculated in a great number of solvents, in most of them two lifetimes were found and attributable to cis and trans isomer fluorescence. However, in DMSO the fit of the decay traces was very good using a monoexponential function and a value of 2.25 ns, higher than in other solvents, was obtained [
29], hence the DCM fluorescence decay dissolved in DMSO must be attributed to a relaxed fluorescent state. From both, previous works and our results, DMSO appears to be the best solvent for DCM in view of its longer fluorescence decay time and low photoisomerization efficiency. As a conclusion, the presence of a certain amount of DMSO in the solvent used for fluorescence studies is justified. In our previous studies using PBS buffer, the fluorescence signals decreased when less than 30 % DMSO was used, along with a rapid precipitation of the dye after dissolution [
25].
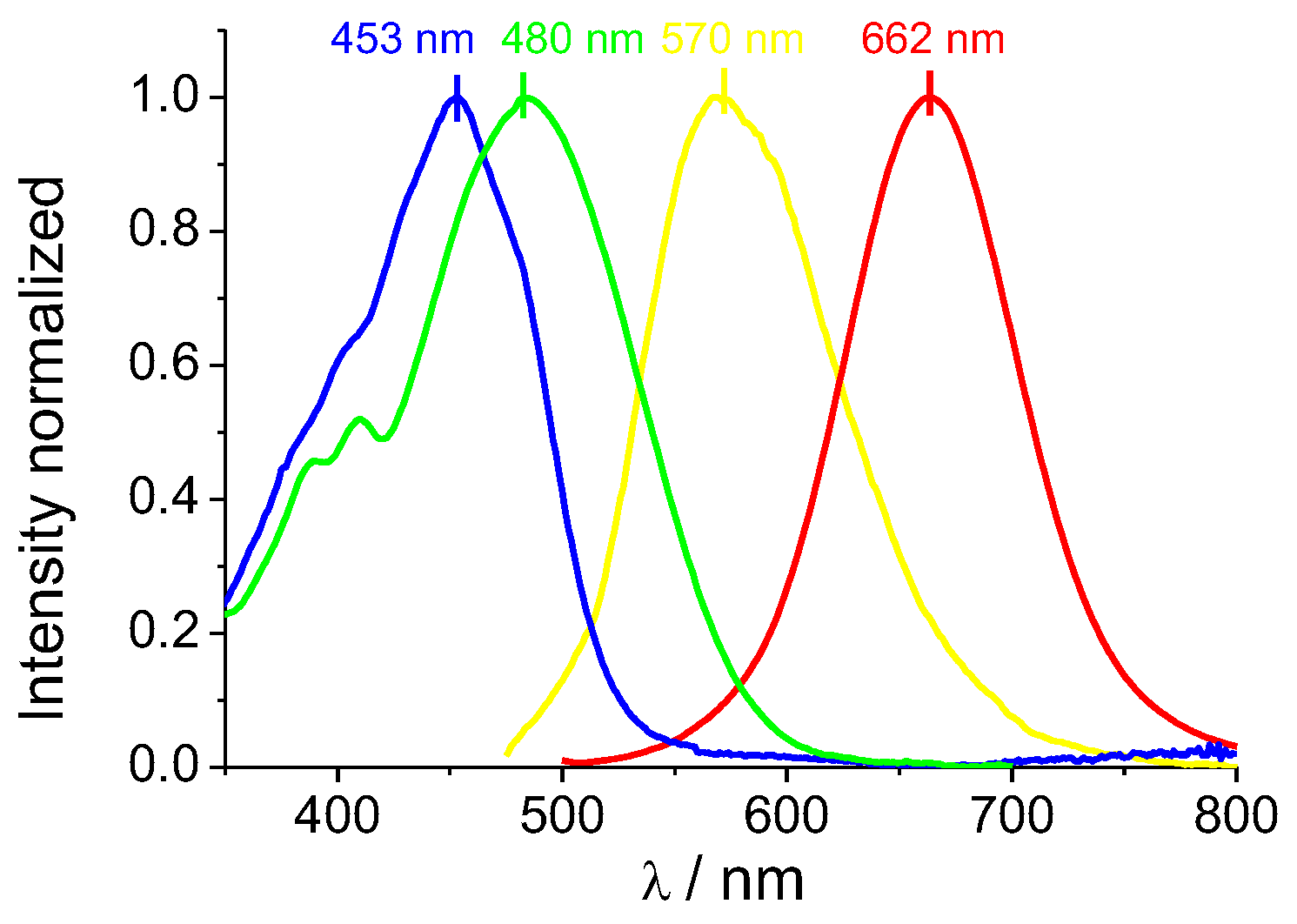
The absorption and emission spectra profiles of DCM–NH
2 and DCM-HBU in the PBS/DMSO (7/3, v/v), pH = 7.4 solution are shown in
Figure 2. The DCM-NH
2 spectrum shows an ICT absorption band around 480 nm (ε = 37 685 L mol
−1 cm
−1) in accordance with the values provided elsewhere [
25], while the band from DCM-HBU has an absorption maximum at 453 nm (ε = 5 409 L mol
−1 cm
−1; see
Figures S2 and S3). Correspondingly, the emission spectrum of DCM-HBU (
Figure 2 and
Figure S4) shows (at λ
ex = 453 nm) an emission band with its maximum around 570 nm (Φ = 7.71 %), and the DCM-NH
2 spectrum (at λ
ex = 480 nm) shows an intense emission band with its maximum at 662 nm (Φ = 16.92 %). The fluorescence lifetimes of DCM-NH
2 and DCM-HBU were 227.3 and 554.4 ps, respectively (
Figure S5).
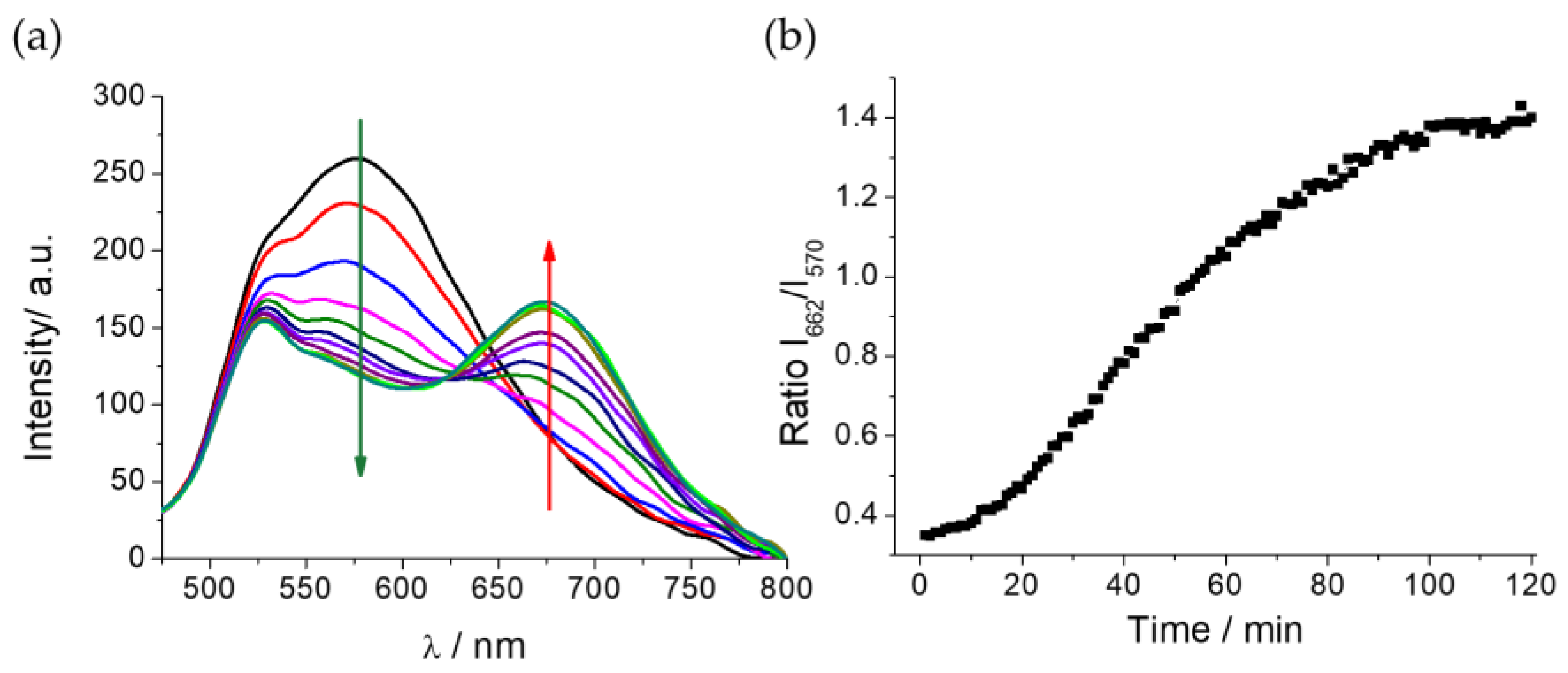
The addition of TYR (0.13 mg mL
-1) to the DCM-HBU in PBS/DMSO (7/3, v/v), 25 µM, and pH = 7.4 solution resulted in a decrease of the emission band with λ
max = 570 nm (λ
ex = 453 nm) corresponding to the probe, along with a concomitant increase of the emission band attributed to DCM-NH
2 (
Figure 3a). The kinetics was followed every minute for 2 h at 37 °C (see
Figure S6). As can be observed, the the new emission band that appears after adding the enzyme is assigned to that one shown by free DCM-NH
2. The ratio I
662/I
570 between these two fluorescence signals achieves a 4 times increase due to the addition of TYR after 100 min, remaining constant after this time (
Figure 3b). Furthermore, we tested the activity of the enzyme at different pH values and temperatures (
Figure S7), demonstrating that the best catalytic activity is at approximately pH 7.5 and 37 °C.
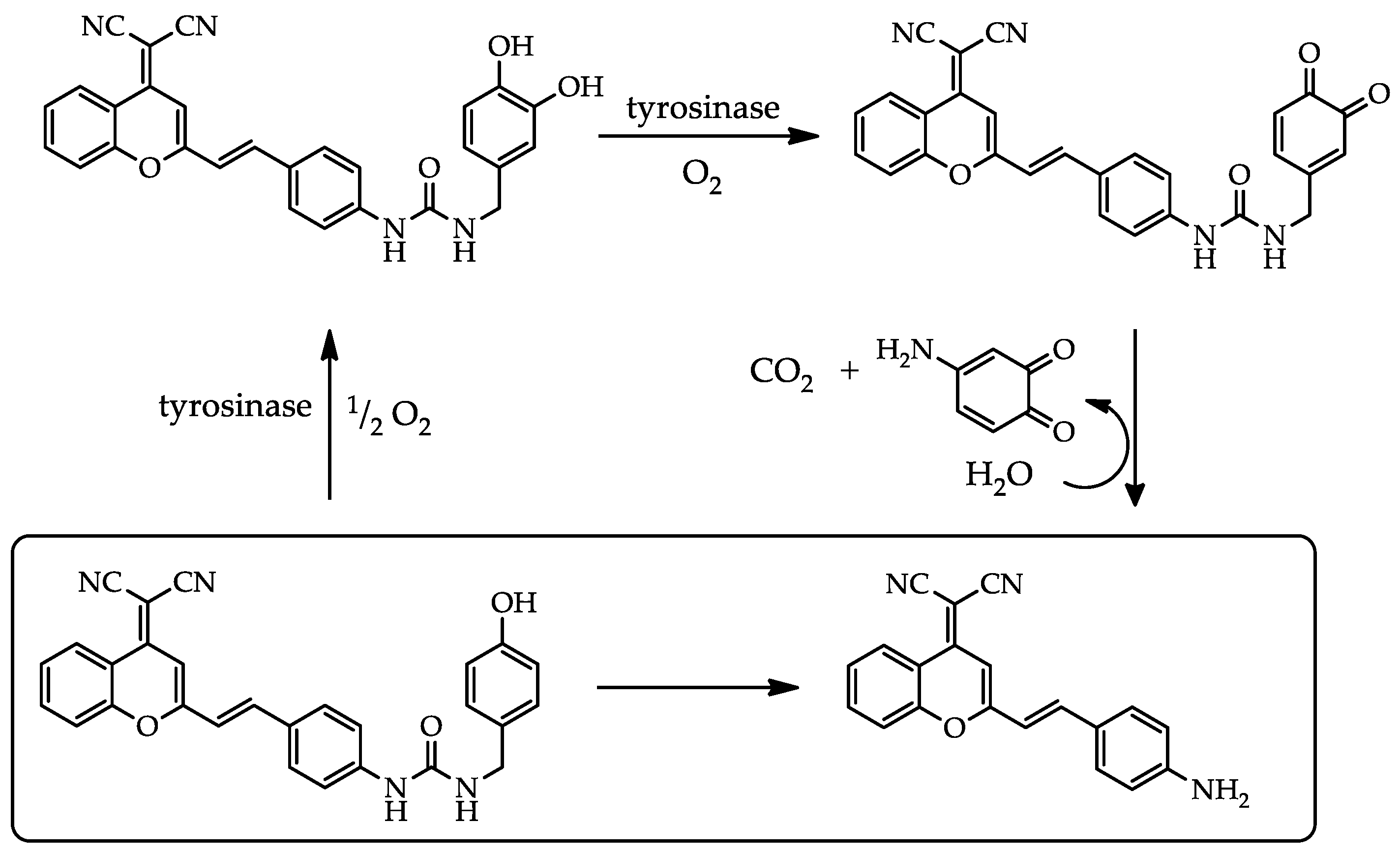
3.3. Proposed mechanism for TYR response
According to the reaction mechanism of the tyrosinase catalysis proposed by Ma et al [
23], the
Scheme 2 shows the necessary steps for sensing TYR by the new probe DCM-HBU. As further test of the proposed mechanism, the IR spectra of the dye and the probe (both dissolved in DMSO) along with a sample of the reaction mixture after 2h reacting (PBS/DMSO as solvent) have been recorded and are shown in
Figure S8. Among the most prominent signals in the spectrum from the reaction sample are the intense band in the region of hydrogen tension due to solvent water and a band of medium intensity assignable to the presence of C = O groups that is consistent with the presence of ketones.
3.4. Sensitivity of the probe towards TYR.
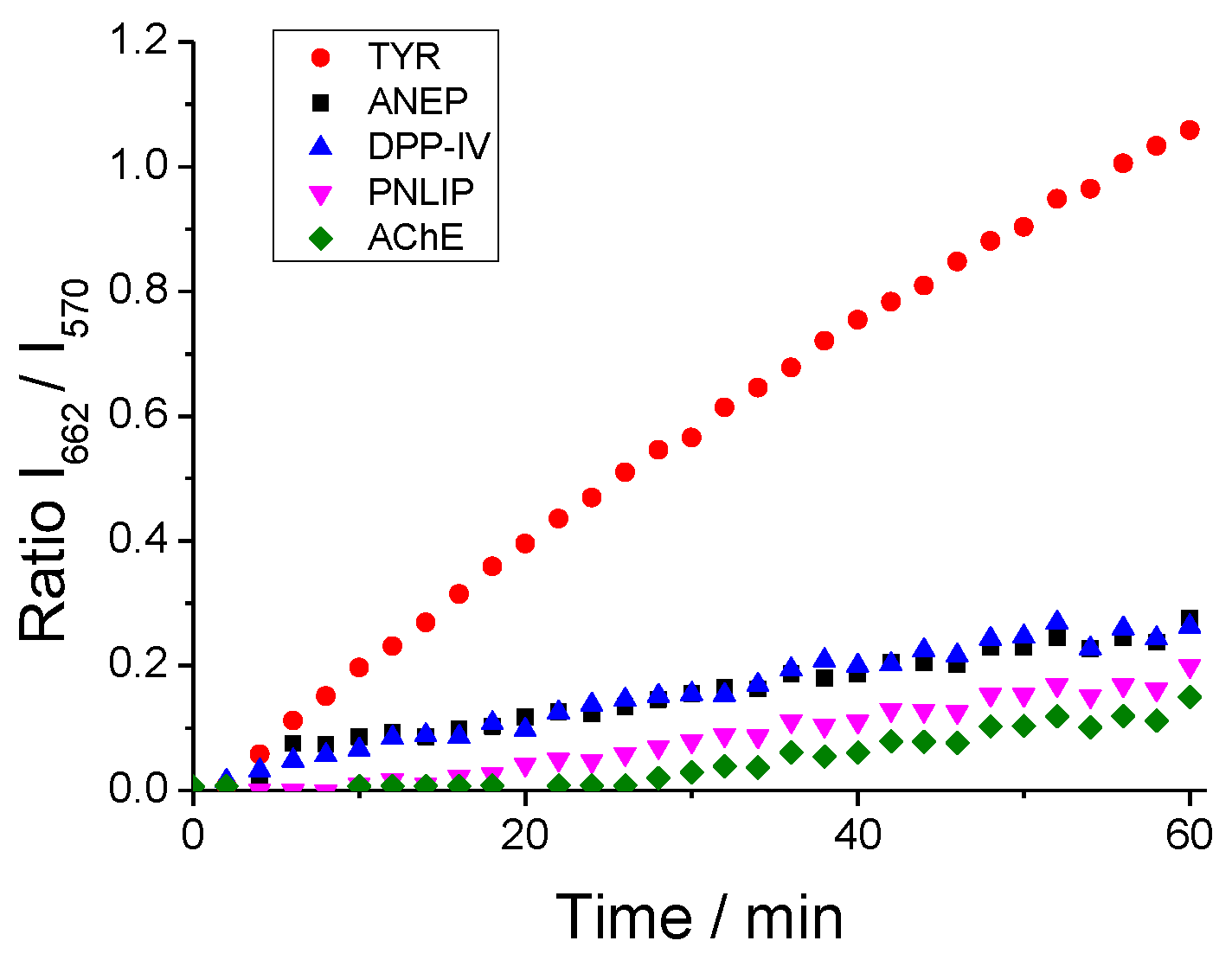
To show unambiguously that DCM-HBU senses only TYR we have investigated the specificity of the probe. In the
Figure 4 the fluorescence I
662/I
570 ratio of the DCM-HBU in the presence of TYR is compared to the same fluorescence ratio recorded when the probe was incubated in the presence of other related enzymes such as ANEP, DPP IV, AChE, and PNLIP. The results demonstrate the very high specificity of DCM-HBU towards the enzymatic action of TYR.
3.5. Ratiometric monitoring of TYR activity in tumour cells and tissues
After photophysical characterization in solution, the study was carried out on tumour cells by single-photon excitation microscopy. Moreover, we measured the TYR activity in melanoma cells and in ex vivo tissues under two-photon excitation.
As a model of melanoma, we selected MEL1 (a primary cell line) and A-375 (a well- established cell line). Firstly, we performed a study to confirm that our probe is sensitive to intracellular TYR enzymatic activity. For this purpose, images of both cell lines were collected for 30 min after adding DCM-HBU (5 µM) in PBS/DMSO (7/3, v/v). The results reveal that in both cell lines red fluorescence increases over time, while green fluorescence remains almost constant, which leads to a progressive increase in the value of the image ratio (
Figure S9). This increase is very likely to be caused by the release of the DCM-NH
2 product due to the action of the tyrosinase enzyme on the probe. Interestingly, we observed a faster increase in the ratio values of MEL1 versus A-375 cells. This fact suggests a higher enzymatic activity in this human primary cell line (
Figure S10).
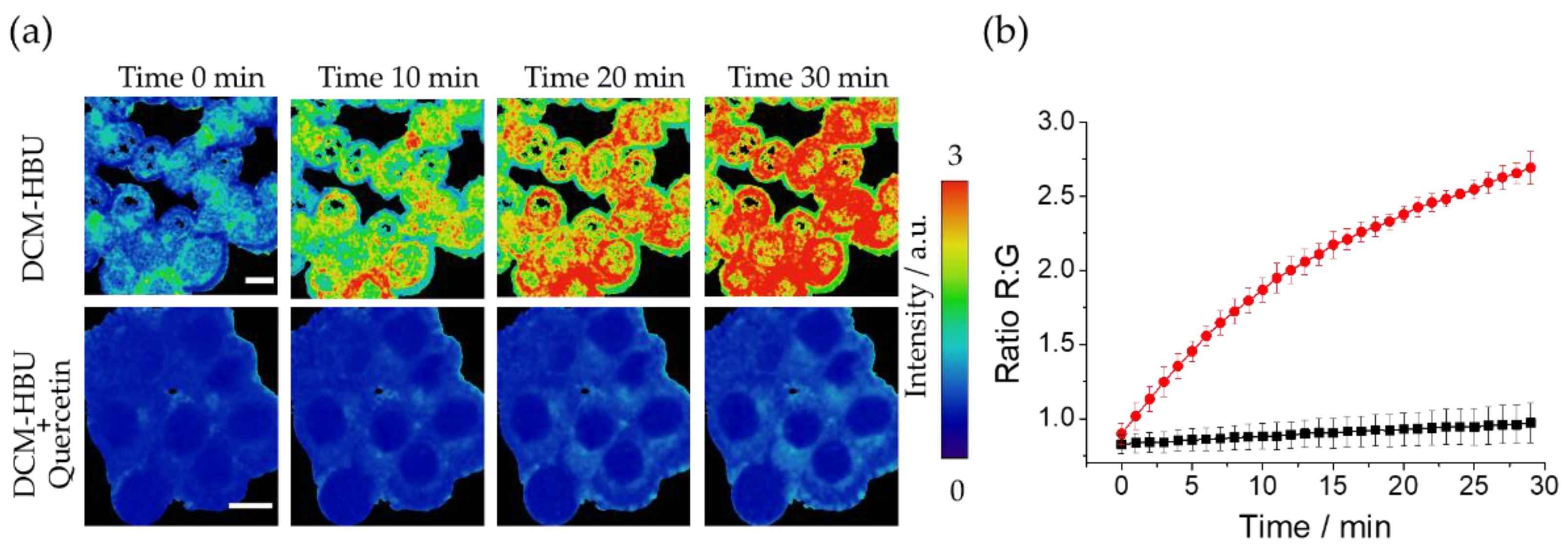
In order to demonstrate that the increase in NIR emission and, consequently, in the ratio values, is mainly due to TYR enzymatic activity, MEL1 was also measured under the same previous conditions but in the presence of the TYR inhibitor quercetin [
30,
31] (
Figure 5a). The ratio values were plotted as a function of time for both cells without quercetin and those exposed to the inhibitor (
Figure 5b), in which a great increase on the fluorescent signal in the red channel is clearly observed when the inhibitor is absent, while in the presence of quercetin the enzymatic reaction is virtually inhibited. This experiment confirms that in this cell line TYR is the main responsible of the conversion of the DCM-HBU probe to DCM-NH
2.
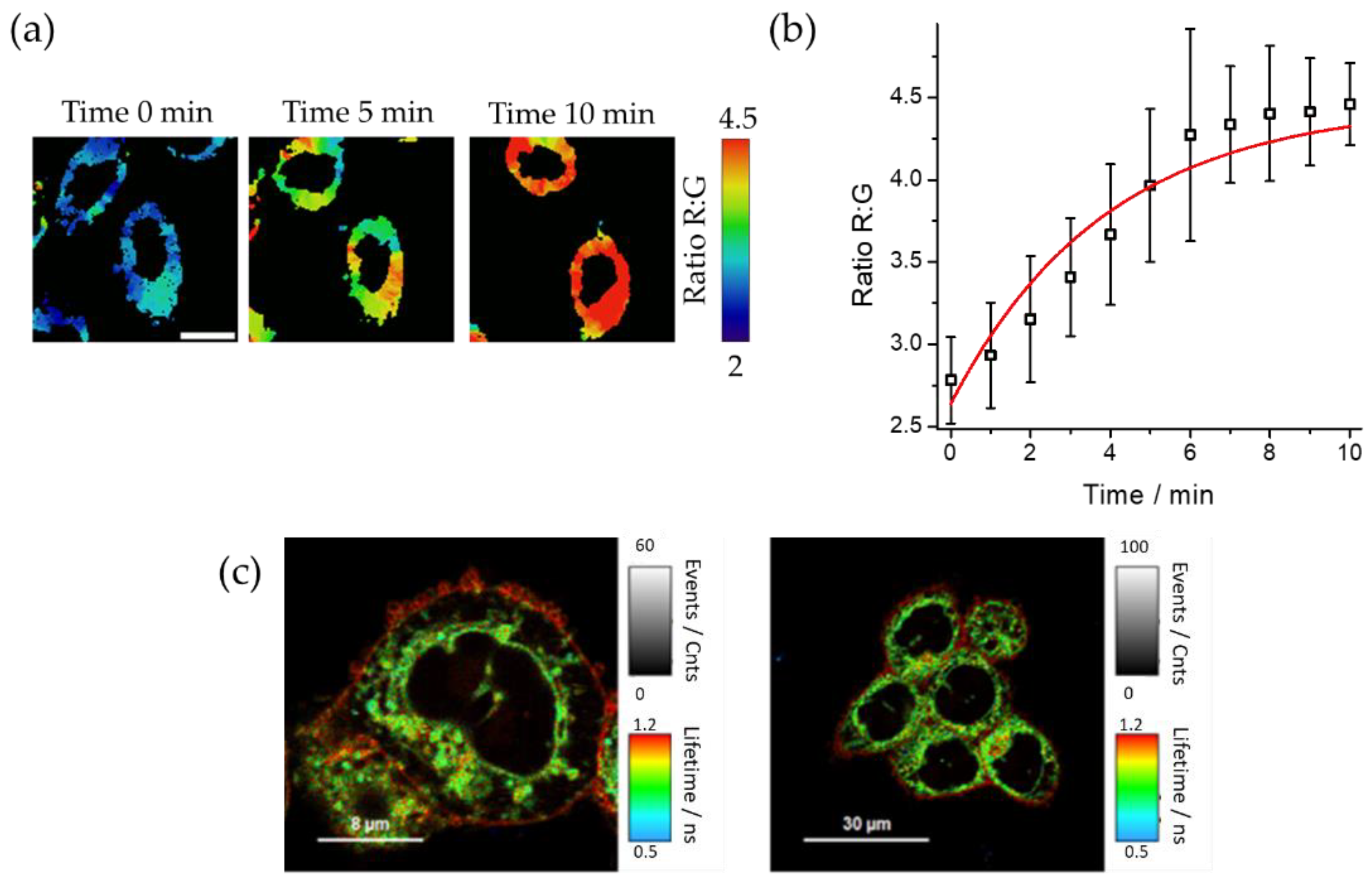
Next, in order to confirm the probe´s ability to be excited by two photons that double or exceed the wavelength of excitation the same fluorophore with a single photon, the A-375 cell line was excited with a wavelength of 800 nm.
Figure 6a shows representative two-photon excitation images obtained, where an increase in the R:G ratio value after 10 min of incubation can be observed. The kinetics of the R:G ratio increase is shown in
Figure 6b and Video S1, representing R:G ratios values versus time. The results show an increase of the ratio values during the first 10 min of incubation. In
Figure 6c, fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy (FLIM) of the fluorophore revealed on live A-375 cells that the dye has a longer lifetime (above 1.2 ns) in the cell periphery, compatible with its presence at the cytoplasmic membrane, one of the cellular structures with higher lipophilia. However, the greater polarity of other structures in the cytoplasm causes a faster deexcitation that correspond to a lower fluorescence lifetime (around 0.9 ns). The fluorescence lifetime of DCM-NH
2 was previously studied in different solvents [
25], and although the changes in its fluorescence lifetime can be caused by polarity differences in the probe´s microenvironment, more experiments should be performed to determine if additional causes exit. The images obtained also show the typical accumulation pattern of DCM-NH
2 in cells, mainly in lysosomes as previously was indicated [
32]. The pattern of accumulation as well as the difference in fluorescence lifetime in the different structures of DCM-NH
2, are promising behaviors to perform deeper fluorescence lifetime imaging studies of organelles isolation and internal lipophilia through changes in the fluorescence lifetime.
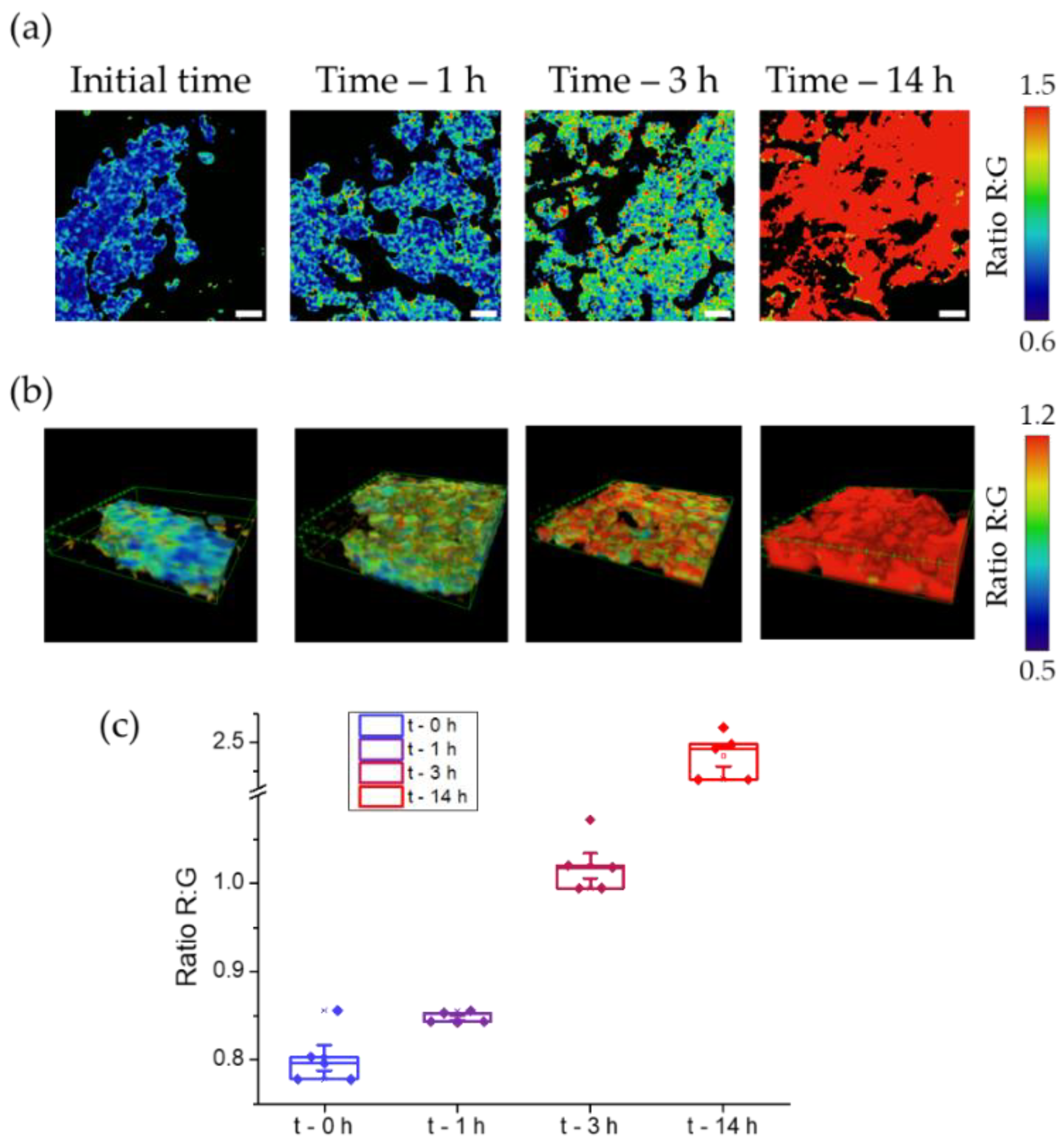
As we mentioned, the potential use in two photon excitation is the key for its employment in more complex biological structures including tissues or even in whole body animals. In this context, our first approach was to detect the enzyme TYR in tissues through the sensor. For this purpose, we selected A-375 derived tumours as a model of human melanoma for the study. The use of an excitation wavelength of 800 nm lowers autofluorescence to nearly undetectable levels (see
Figure S11), a fundamental advantage in the ratiometric based sensors.
We incubated these tissues with a solution of DCM-HBU (5 μM), and measured the green and NIR emission at four time points (initial time, 1, 3 and 14 h). From this data we calculated the ratio images (see
Figure 7a) at different z positions that also allowed us to reconstruct 3D images (see
Figure 7b and Video S2). Once the compound was added, the NIR fluorescence intensity increased over time, reaching its maximum value at 14 h (
Figure 7c). On the other hand, green fluorescence, remained almost constant, without significant changes (see
Figures S11 and S12). This resulted in an increase in the value of the R:G ratio from 0.8 to 2.5, as can be seen in the
Figure 7c. It follows, therefore, that the activity of the enzyme TYR causes the cleavage of the DCM-HBU sensor, releasing the DCM-NH
2 product, which is responsible for the NIR fluorescence.
3.6. In Vivo Imaging of TYR in Zebrafish.
In a recent study, TYR activity was found in zebrafish larvae, however, its activity was determined only qualitatively [
23]. Here we have gone further and we have completed, for first time to our knowledge, a deeper study quantifying the differences in TYR activity
in vivo in zebrafish larvae and embryos at different days post fertilization (dpf) in the absence or presence of an inhibitor (quercetin).
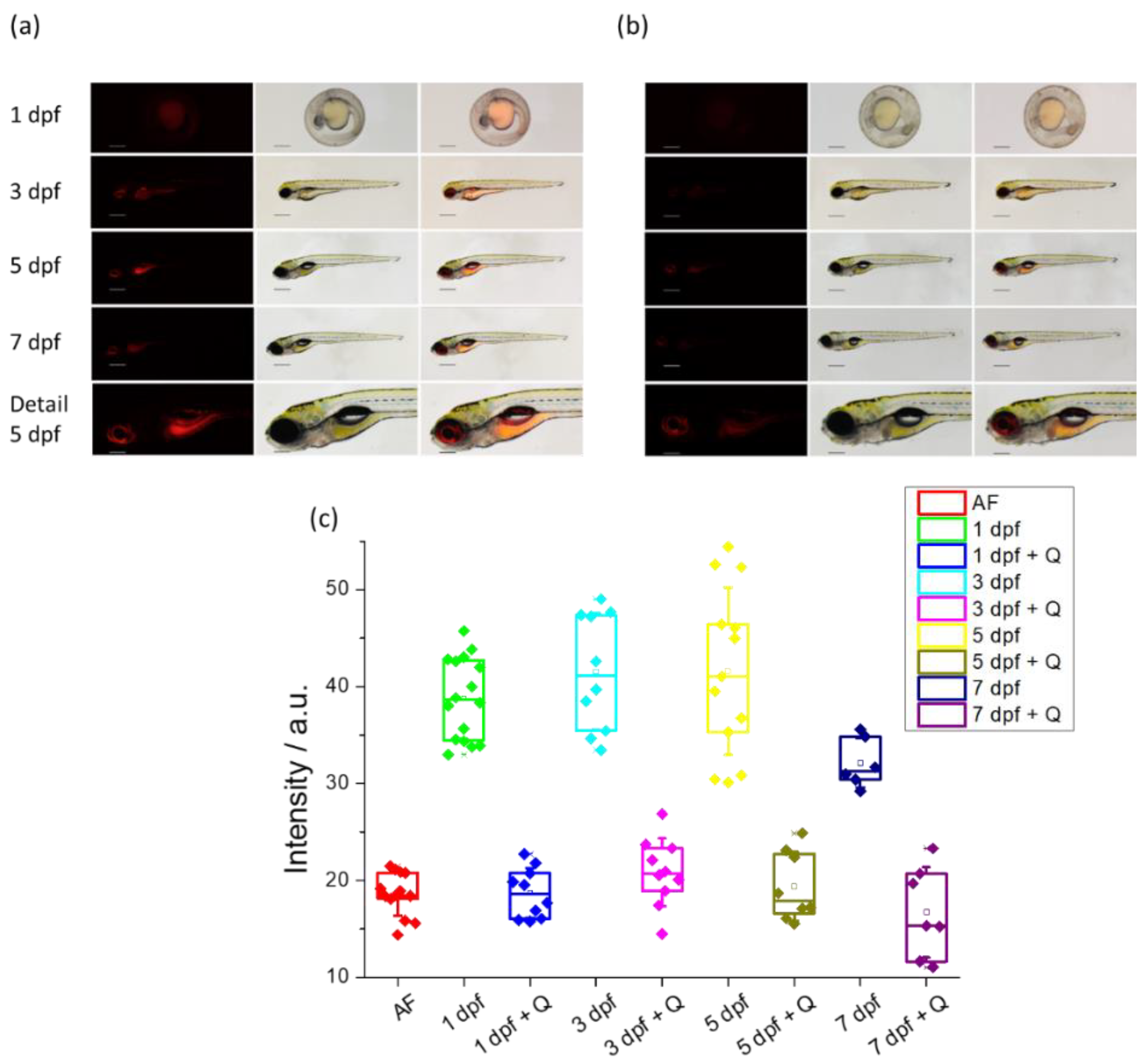
Zebrafish embryos and larvae of different dpf, when incubated with the DCM-HBU probe, show the characteristic NIR fluorescence indicating the release of the DCM-NH
2 compound due to the action of the TYR enzyme in yolk sac and larval tissues (
Figure 8a). Both the eye and the central nervous system (CNS) are the tissues where most enzymatic activity is observed, while skin and muscles do not show strong NIR fluorescence. Control zebrafish incubated with DMSO display a low level of autofluorescence (
Figure S14). In order to demonstrate that the NIR fluorescence observed with DCM-HBU is due to the action of the TYR enzyme, a co-inhibition study was performed at every time point. In the presence of the known TYR inhibitor quercetin [
30,
31], DCM-HBU was not processed to DCM-NH
2 and NIR fluorescence was almost completely suppressed, demonstrating the specificity of the sensor (
Figure 8b).
Additionally, a quantitative analysis of NIR emission has been carried out. The amount of the fluorescent signal obtained after incubation with 10µM DCM-HBU is similar during all larval time points studied (1 dpf, 3 dpf, and 5 dpf), with the exception of a slightly smaller difference observed in 7-day-old zebrafish, when compared to the autofluorescence control. Quercetin inhibition leads to a strong reduction of the fluorescent signal down to autofluorescence levels or below (day 7). Importantly, the fluorescent signal differences between the experimental and the quercetin-inhibited conditions are similar at all time points. This suggests that the levels of enzyme available at different stages of animal development are virtually identical to each other (see
Figure 8c).
4. Discussion
By assembling the HBU enzyme recognition cluster on the DCM-NH
2 fluorophore, we have synthesized an extremely specific TYR fluorescent substrate. Based on the existing bibliography [
23] and with the experimental results obtained, it has been possible to establish the mechanism by which the enzymatic catalysis of the DCM-HBU probe-substrate occurs. By the action of TYR, the probe is hydroxylated, followed by enzymatic oxidation to orthoquinone, which after a rapid intramolecular electronic rearrangement, initiates the cleavage of quinone, as indicated in
Scheme 2. The IR spectrum of the reaction sample supports the proposed reaction mechanism since shows a new band at 1 680 cm
−1 in the C = O region that is consistent with the appearance of the ketone in the proposed mechanism.
The release of the recognition group allows that the typical ICT of the DCM-NH2 fluorophore to be restored, resulting in NIR emission spectrum that generates the possibility of collecting a ratiometric fluorescence signal between the green fluorescence intensity of the probe and the NIR DCM-NH2 fluorescence.
As TYR activity has an important interest in diagnosis and biomedical research, we study the application of the DCM-HBU probe in cells. Since melanoma is one of the medical issues with anomalous TYR activity, we selected MEL1 and A-375 cell lines as
in vitro melanoma models to perform live cell studies. Once added the probe, both cell lines showed an increase in the R:G ratio value over time. As the initial rate of this increase is dependent on TYR activity, the measure of the slope in the initial stage can be used to determine the activity of the enzymatic reaction. From a comparative study between both cell lines, we detected a higher TYR activity in the MEL1 primary cell line than in A-375. On the other hand, the ratiometric R:G values from MEL1 melanoma cells plotted in
Figure 5b as a function of time for cells without quercetin inhibitor and another one exposed to the inhibitor, show a large increase in the R:G ratio when the inhibitor is not present, while in the presence of quercetin the increase in the R:G ratio is negligible. All these results clearly show that the probe is sensitive to the action of TYR and when this enzyme is inhibited, the substrate does not suffer alteration in its photophysical properties. Moreover, our results show that both the substrate and DCM-NH
2 can be excited by one green photon or two NIR photons. In both experiments we found a measurable increase in the ratio values that is useful in the determination of TYR activity in cells through fluorescence microscopy. Excitation by NIR radiation has been widely used to prevent or reduce autofluorescence of cells and tissues, as well as the absorption and scattering of excitation light, which allows obtaining sharper images at greater depths, although its use is limited in the range of wavelength of higher transmittance in biological samples [
6].
Two photon excitation microscopy is a technique of special importance in the measurement of highly scattering samples, as happen in biological tissues, firstly because NIR wavelengths scatter less than blue/green light, secondly, because there is lack of absorption outside the focus, and thirdly, two photon excitation prevents or reduces autofluorescence of biological samples. Two photon excitation is especially relevant for imaging of structures that extend into the specimen, for avoiding UV excitation, for
in vivo measurements or when a localized photochemistry is important [
33]. All these features encouraged us to apply it to fluorescence imaging of tumour tissues at different depths. Our data allowed us to reconstruct 3D ratiometric images after two photon excitation and the results in
Figure 7b show the ratio value at different depth measured at every incubation time. That demonstrates the potential use of this probe in biological tissues under two photon excitation. Comparing the top and bottom slice of the tissues in the 3D images (
Figure S13), it is possible to observe a higher ratio value in the upper plane than in the lower one. This could be due to a faster penetration in this level. So, the probe should cross the whole tissue to reach the lower plane.
From the high levels of NIR fluorescence obtained in zebrafish larvae at different dpf incubated with the DCM-HBU probe, enzymatic TYR is predicted to be active in the yolk sac, eye, CNS and inner organs. In addition, the quantification of the intensity of emission NIR in the recovered images from the incubation with DCM-HBU + quercetin showed only basic levels of autofluorescence indicating that quercetin inhibits TYR activity in whole organisms. The use of this fluorescent probe together with the imaging techniques allow us to measure TYR activity in vivo in zebrafish. Our results suggest a similar activity during the first seven dpf, that is during all early developmental stages.
5. Conclusions
By the assembly of the enzyme-recognizing group 4-hydroxybenzylamine on the fluorophore dicyanomethylene-4H-pyran derivative, we synthesized the corresponding amide to obtain DCM-HBU a TYR-sensitive and highly specific fluorescent substrate. After a TYR-mediated oxidation followed by hydrolysis of the urea linkage, the donor-acceptor DCM-NH2 system is restored, showing the NIR characteristic ICT emission spectrum along with a large Stokes shift, which allows us to obtain a ratiometric fluorescence output between the green fluorescent signal of the substrate and the NIR signal of DCM-NH2. In addition, both the substrate and probe are capable of being excited by two NIR photons, which has made it possible to eliminate the green and red bands of autofluorescence. Owing to the possibility of being excited by two simultaneous photons, the applicability of this new probe as an intracellular in vivo sensor of TYR, as well as its ability to obtain clear fluorescence microscopy images of tumor tissues, has been confirmed. Finally, the probe is useful for the quantitative sensing of TYR activity in vivo, as demonstrated in zebrafish larvae at different stages. This new two-photon ratiometric NIR fluorescent probe is expected to be useful for the accurate detection of TYR in complex biosystems at greater depths than other one-photon excited fluorescent probes.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org. Figure S1: synthesis of compound DCM-HBU; mass and NMR spectra; Figure S2: absorption spectra of the DCM-HBU at different concentrations; Figure S3: molar absorptivity coefficient calculation; Figure S4: emission spectra of the DCM-HBU at different concentrations; Quantum yield calculation; Figure S5: fluorescence decays of DCM-NH2 and DCM-HBU; Figure S6: evolution of the emission spectra of DCM−HBU with TYR; Figure S7: influence of pH and temperature on enzyme activity; Figure S8: IR spectra; Figure S9: representative images of the green and red intensity channels and R:G ratio images of A-375 and MEL1 cells after adding DCM-HBU; Figure S10: increase in the value of the ratio versus time of the images of MEL1 and A-375 cells; Figure S11: representative images of the green and red intensity channels of A-375 tumours after adding DCM-HBU using two-photon microscopy; Figure S12: 3D red and green intensity images of A-375 tumours after adding DCM-HBU using two-photon microscopy; Figure S13: top and bottom planes of 3D ratiometric images; Figure S14: images of living zebrafish embryos and larvae incubated with DMSO; Video S1: fluorescence microscopy R:G ratio maps of live A-375 cell line after adding DCM-HBU and representation of the R:G ratio values over time, by two-photon excitation; Video S2: 3D ratiometric images of A-375 tumours.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.M.T., J.M.A-P., J.M.P., and J.A.M.; methodology, E.M.T., J.M.A-P., J.M.P., T.J.W., J.V-P., M.E.G-R., C.G-L., and J.A.M.; formal analysis, J.V-P., J.M.P., T.J.W., M.E.G-R., C.G-L., and S.L-M.; investigation, J.V-P., J.M.P., T.J.W., M.E.G-R., C.G-L., and S.L.M.; resources, E.M.T.; J.A.M., M.E.G-R., C.G-L., and J.V-P.; writing—original draft preparation, E.M.T., J.M.P., J.M.A-P., J.V-P., T.J.W., and C.G-L.; writing—review and editing, E.M.T., J.M.P., J.M.A-P., J.V-P., T.J.W., and J.A.M.; visualization, J.M.P., J.V-P., M.E.G-R., S.L-M., T.J.W., and C.G-L.; supervision, E.M.T., J.M.A-P., and J.M.P.; project administration, E.M.T., J.M.P., J.M.A-P., funding acquisition, E.M.T., and J.A.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript. The manuscript was written through contributions of all authors. All authors have given approval to the final version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work has been supported by the Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación (MCIN/AEI/10.13039/501100011033/FEDER) under grants PID2020-114256RB-I00, PID2020-113059GB-C21 and RTI2018-101309-B-C22; and by FEDER/Junta de Andalucía-Consejería de Transformación Económica, Industria, Conocimiento y Universidades/Proyecto A-FQM-230-UGR20 and by the Consejería de Economía, Conocimiento, Empresas y Universidad de la Junta de Andalucía (European Regional Development Fund ) under grant P18-FR-2470 and by the Chair “Doctors Galera-Requena in cancer stem cell research”. J.V-P. is supported by a FPU fellowship (FPU17/04749). T.J.W. is financed by a senior postdoctoral stipend of the Consejería de Salud y Familias (CSyF) of the Regional Government of Andalusia, Spain (RH-0019-2020). C.G-L. acknowedges the posdoctoral fellowship from Plan Andaluz de Investigación, Desarrollo e Innovación (PAIDI 2021-FEDER funds-POSTDOC_21_638).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Razgulin, A.; Ma, N.; Rao, J.H. Strategies for in vivo imaging of enzyme activity: An overview and recent advances. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 4186–4216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.F.; Shi, W.; Li, X.H.; Ma, H.M. Recognition moieties of small molecular fluorescent probes for bioimaging of enzymes. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 1892–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J.; Chai, X.Z.; He, X.P.; Kim, H.J.; Yoon, J.; Tian, H. Fluorogenic probes for disease-relevant enzymes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 683–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juvekar, V.; Lee, H.W.; Kim, H.M. Two-photon fluorescent probes for detecting enzyme activities in live tissues. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 2957–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.W.; Liu, Y.C.; Wang, P.; Zhang, X.B. Molecular engineering of two-photon fluorescent probes for bioimaging applications. Methods Appl. Fluoresc. 2017, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, P.A.; Forsyth, E.; Haseeb, F.; Yang, S.; Bradley, M.; Klausen, M. Two-photon absorption: An open door to the NIR-II biological window? Front Chem 2022, 10, 921354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göppert-Mayer, M. Über elementarakte mit zwei quantensprüngen. Annalen der Physik 1931, 401, 273–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denk, W.; Strickler, J.; Webb, W. Two-photon laser scanning fluorescence microscopy. Science 1990, 248, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragan, T.; Kadiri, L.R.; Venkataraju, K.U.; Bahlmann, K.; Sutin, J.; Taranda, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Kim, Y.; Seung, H.S.; Osten, P. Serial two-photon tomography for automated ex vivo mouse brain imaging. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, R.J.; Jin, H.; Bu, X.N.; Fu, Y.X.; Wang, Z.H.; Liu, Q.Y. Recent advances in dual-emission ratiometric fluorescence probes for chemo/biosensing and bioimaging of biomarkers. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 383, 82–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.H.; Kim, J.S.; Sessler, J.L. Small molecule-based ratiometric fluorescence probes for cations, anions, and biomolecules. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 4185–4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.H.; Kwon, N.; Lee, J.H.; Yoon, J.; Shin, I. Synthetic ratiometric fluorescent probes for detection of ions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 143–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decker, H.; Schweikardt, T.; Tuczek, F. The first crystal structure of tyrosinase: All questions answered? Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 4546–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solem, E.; Tuczek, F.; Decker, H. Tyrosinase versus catechol oxidase: One asparagine makes the difference. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 2884–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artes, F.; Castaner, M.; Gil, M.I. Review: Enzymatic browning in minimally processed fruit and vegetables. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 1998, 4, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.W.; Zhan, Q.; Du, S.B.; Ding, Y.; Fang, B.; Du, W.; Wu, Q.; Yu, H.D.; Li, L.; Huang, W. Catalysis-based specific detection and inhibition of tyrosinase and their application. J. Pharm. Anal. 2020, 10, 414–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espin, J.C.; Morales, M.; Varon, R.; Tudela, J.; Garciacanovas, F. A continuous spectrophotometric method for determining the monophenolase and diphenolase activities of apple polyphenol oxidase. Anal. Biochem. 1995, 231, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Gill, R.; Freeman, R.; Willner, I. Probing of enzyme reactions by the biocatalyst-induced association or dissociation of redox labels linked to monolayer-functionalized electrodes. Chem. Commun. 2006, 5027–5029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, H.B.; Freeman, R.; Gill, R.; Willner, I. Electrochemical, photoelectrochemical, and piezoelectric analysis of tyrosinase activity by functionalized nanoparticles. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 2811–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, R.; Freeman, R.; Xu, J.P.; Willner, I.; Winograd, S.; Shweky, I.; Banin, U. Probing biocatalytic transformations with CdSe-ZnS QDs. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 15376–15377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.L.; Feng, F.D.; Yu, M.H.; He, F.; Xu, Q.L.; Tang, H.W.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.L.; Zhu, D.B. Synthesis of a new water-soluble oligo(phenylenevinylene) containing a tyrosine moiety for tyrosinase activity detection. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 5369–5372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Shi, W.; Chen, S.M.; Jia, J.; Ma, H.M.; Wolfbeis, O.S. A near-infrared fluorescent probe for monitoring tyrosinase activity. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 2560–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.F.; Li, L.H.; Shi, W.; Gong, Q.Y.; Ma, H.M. Near-infrared fluorescent probe with new recognition moiety for specific detection of tyrosinase activity: Design, synthesis, and application in living cells and zebrafish. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 14728–14732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.T.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Tang, Y.H.; Zhu, M.Q.; Wang, Y.L. Progress of dicyanomethylene-4H-pyran derivatives in biological sensing based on ict effect. Front. Chem. 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valverde-Pozo, J.; Paredes, J.M.; Salto-Giron, C.; Herrero-Foncubierta, P.; Giron, M.D.; Miguel, D.; Cuerva, J.M.; Alvarez-Pez, J.M.; Salto, R.; Talavera, E.M. Detection by fluorescence microscopy of N-aminopeptidases in bacteria using an ICT sensor with multiphoton excitation: Usefulness for super-resolution microscopy. Sensors Actuators B: Chem. 2020, 128487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B. , et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Fan, J.L.; Hu, C.; Cao, J.F.; Zhang, H.; Xiong, X.Q.; Wang, J.Y.; Cui, S.; Sun, S.G.; Peng, X.J. A two-photon fluorescent probe with near-infrared emission for hydrogen sulfide imaging in biosystems. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 3890–3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, M.; Mialocq, J.C. Ground-state and singlet excited-state of laser-dye DCM - dipole-moments and solvent induced spectral shifts. Opt. Commun. 1987, 64, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, M.; Mialocq, J.C.; Rougée, M. Fluorescence lifetime measurements of the two isomers of the laser dye DCM. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1988, 150, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.H.; Zhang, G.W.; Hu, X.; Xu, X.M.; Gong, D.M. Quercetin as a tyrosinase inhibitor: Inhibitory activity, conformational change and mechanism. Food Res. Int. 2017, 100, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.X.; Kubo, I. Kinetics of mushroom tyrosinase inhibition by quercetin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 4108–4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, X.J.; Qi, Y.M.; Zhang, Y.M. Highly photostable fluorescent tracker with pH-insensitivity for long-term imaging of lysosomal dynamics in live cells. ACS Sensors 2021, 6, 786–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ustione, A.; Piston, D.W. A simple introduction to multiphoton microscopy. J. Microsc. 2011, 243, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Scheme 1.
Synthetic route of DCM-HBU (compound 2).
Scheme 1.
Synthetic route of DCM-HBU (compound 2).
Figure 1.
(a) Absorption spectra of the compound DCM-NH2, 1.7 µM in different solvents. (b) Maxima absorption wavelength in function of the ET(30) scale polarity. (c) Emission spectra of the compound DCM-NH2, 1.7 µM in different solvents. (d) Maxima emission wavelength in function of the ET(30) scale polarity.
Figure 1.
(a) Absorption spectra of the compound DCM-NH2, 1.7 µM in different solvents. (b) Maxima absorption wavelength in function of the ET(30) scale polarity. (c) Emission spectra of the compound DCM-NH2, 1.7 µM in different solvents. (d) Maxima emission wavelength in function of the ET(30) scale polarity.
Figure 2.
Normalized absorption spectra of the pure compounds DCM-HBU (blue line) and DCM−NH2 (green line); normalized emission spectra of the pure compounds DCM-HBU (yellow line) and DCM-NH2 (red line) by excitation at 453 nm and 480 nm, respectively.
Figure 2.
Normalized absorption spectra of the pure compounds DCM-HBU (blue line) and DCM−NH2 (green line); normalized emission spectra of the pure compounds DCM-HBU (yellow line) and DCM-NH2 (red line) by excitation at 453 nm and 480 nm, respectively.
Figure 3.
(a) Evolution of the emission spectra of DCM-HBU (25 μM) with TYR (0.13 mg mL-1) observed every 10 min for 2 h by excitation at 450 nm at 37 °C; (b) Ratiometric measurements of fluorescence signals of I662 / I570 at different times.
Figure 3.
(a) Evolution of the emission spectra of DCM-HBU (25 μM) with TYR (0.13 mg mL-1) observed every 10 min for 2 h by excitation at 450 nm at 37 °C; (b) Ratiometric measurements of fluorescence signals of I662 / I570 at different times.
Scheme 2.
Proposed sensing mechanism of DCM-NH2 release by TYR.
Scheme 2.
Proposed sensing mechanism of DCM-NH2 release by TYR.
Figure 4.
Ratiometric measurements of fluorescence signals of I662/I570 of DCM-HBU (10 µM) over time in the presence of different related enzymes at the same concentration (5 µg mL−1) by excitation at 450 nm at 37 °C.
Figure 4.
Ratiometric measurements of fluorescence signals of I662/I570 of DCM-HBU (10 µM) over time in the presence of different related enzymes at the same concentration (5 µg mL−1) by excitation at 450 nm at 37 °C.
Figure 5.
(a) R:G ratio maps of live MEL1 cell line at different time points after adding DCM-HBU (5 μM) without (upper panel) and with (lower panel) the TYR inhibitor quercetin (100 μM) (λex = 453 nm). The scale bars represent 10 μm; (b) Representation of the R:G ratios from microscopy images in absence (circles) and presence (square) of quercetin. Error bars represent the standard deviation (SD).
Figure 5.
(a) R:G ratio maps of live MEL1 cell line at different time points after adding DCM-HBU (5 μM) without (upper panel) and with (lower panel) the TYR inhibitor quercetin (100 μM) (λex = 453 nm). The scale bars represent 10 μm; (b) Representation of the R:G ratios from microscopy images in absence (circles) and presence (square) of quercetin. Error bars represent the standard deviation (SD).
Figure 6.
(a) Fluorescence microscopy R:G ratio maps of live A-375 cell line at different time points after adding DCM-HBU, obtained by two-photon excitation at 800 nm (G: 520/35, R: 685/70). Scale bar represents 10 µm; (b) Representation of the R:G ratios from microscopy images. Error bars represent the SD; (c) FLIM of live A-375 cell line after adding DCM−NH2 5 µM by excitation with two 800 nm photons.
Figure 6.
(a) Fluorescence microscopy R:G ratio maps of live A-375 cell line at different time points after adding DCM-HBU, obtained by two-photon excitation at 800 nm (G: 520/35, R: 685/70). Scale bar represents 10 µm; (b) Representation of the R:G ratios from microscopy images. Error bars represent the SD; (c) FLIM of live A-375 cell line after adding DCM−NH2 5 µM by excitation with two 800 nm photons.
Figure 7.
(a) Ratiometric images of A-375 tumours after adding DCM-HBU (5 μM) over time using two-photon microscopy with excitation at 800 nm. Scale bars are 10 µm. (b) 3D ratiometric images of A-375 tumours using two-photon microscopy with excitation at 800 nm. (c) Representation of the R:G ratio values from microscopy images. Boxes represent the 25th, 50th and 75th percentiles. Whiskers represent the SE.
Figure 7.
(a) Ratiometric images of A-375 tumours after adding DCM-HBU (5 μM) over time using two-photon microscopy with excitation at 800 nm. Scale bars are 10 µm. (b) 3D ratiometric images of A-375 tumours using two-photon microscopy with excitation at 800 nm. (c) Representation of the R:G ratio values from microscopy images. Boxes represent the 25th, 50th and 75th percentiles. Whiskers represent the SE.
Figure 8.
(a) Living zebrafish embryos and larvae incubated with DCM-HBU (10 μM) for 3 h at different developmental stages (1, 3, 5 and 7 dpf); red fluorescent (left), brightfield (centre), and merge (right) images were taken by a stereo microscope (λex = 458 nm, λem = 680 nm). Detail (head with central nervous system) of a living zebrafish larva at 5 dpf is also shown. Scale bars: 1 dpf: 250 µm, 3-7 dpf: 500 µm, detail: 200 µm. (b) Living zebrafish embryos and larvae at the same dpf preincubated for 3 h with 200 μM quercetin and incubated with 10 μM DCM-HBU for 3 h. (c) Intensity values of NIR emission of zebrafish at different dpf, incubated with 10 μM DCM-HBU in presence or absence of the inhibitor quercetin. Boxes represent the 25th, 50th and 75th percentiles. Whiskers represent the SE.
Figure 8.
(a) Living zebrafish embryos and larvae incubated with DCM-HBU (10 μM) for 3 h at different developmental stages (1, 3, 5 and 7 dpf); red fluorescent (left), brightfield (centre), and merge (right) images were taken by a stereo microscope (λex = 458 nm, λem = 680 nm). Detail (head with central nervous system) of a living zebrafish larva at 5 dpf is also shown. Scale bars: 1 dpf: 250 µm, 3-7 dpf: 500 µm, detail: 200 µm. (b) Living zebrafish embryos and larvae at the same dpf preincubated for 3 h with 200 μM quercetin and incubated with 10 μM DCM-HBU for 3 h. (c) Intensity values of NIR emission of zebrafish at different dpf, incubated with 10 μM DCM-HBU in presence or absence of the inhibitor quercetin. Boxes represent the 25th, 50th and 75th percentiles. Whiskers represent the SE.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).