1. Introduction
Terrain or topography is one of the most important factors in many application areas like agriculture influencing soil characteristics, water flow patterns, sediment and contaminant transport, hydrological behaviour, and irrigation methods [
1]. Other applications of terrain modelling include Earth science and hydrological applications [
2], landform analysis [
3], volcanic hazards [
4], etc. Digital Elevation Model (DEM) is a 3-D representation of the bare earth surface excluding trees, buildings, and any other surface objects. It is the ideal and most widely used method for the representation of Earth’s topography. DEMs in diverse resolutions, height accuracy, and coverages are routinely produced by different techniques for various applications in different fields, such as navigation, geographical studies of the environment, or the ortho-rectification of remote sensing imagery [
5]. It is an indispensable source of data in many applications, such as flood modeling, infrastructure design, and land management. DEM data at high spatial resolution and high elevation data accuracy are costly, time-consuming to acquire, and often confidential [
6].
Interpolation is the process of estimating the value of attributes at unsampled sites from measurements made at point locations within the same area or region [
7]. Machine learning algorithms are widely being used to extract patterns and spatial extent in geographic data. Many researchers have studied the implementation of Machine Learning for the interpolation of DEMs. A. Setiyoko et al. (2019) implemented a semi-variogram-based Kriging interpolation technique using machine learning algorithms like SVM (Support Vector Machine) and GPR (Gaussian Process Regressor) to generate DEM from known height points of Cartosat-1 stereo imagery [
7]. The results showed that both SVM and GPR performed better than the traditional interpolation technique in terms of error prediction and accuracy of DEM. Venkatesh Kasi et al. (2020) attempted to improve the vertical accuracy of Casrtosat DEM by fusing its elevation data with SRTM DEM using Artificial Neural Networks and Genetic Programming. The achieved results showed an improvement of 47 and 35% respectively [
8]. Yifan Zhang et al. (2022). The vertical accuracy of DEMs has been focused on in research for a long time. Many studies have been conducted for the assessment of vertical accuracies of various openly accessible DEMs. G.Sun et al. (2003) validated the accuracy of SRTM 90m resolution DEM. Z. Hu et al. (2017) evaluated the vertical accuracy of SRTM 3, SRTM 1, ASTER GDEM and AW3D30 with a 1:50,000 reference DEM. Scot A. Kulp et al. (2018) implemented a neural network which was trained using the ICESat-2 as a reference and samples from SRTM DEM to improve the vertical accuracy of SRTM CosatalDEMs of the regions of the USA and Australia [
9]. Sandip Mukherjee et al. (2013) derived the accuracy of Cartosat DEM with 11 GCPs (Ground Control Points) which came out to be 1.11m [
10]. Cartosat DEM is proven to have reasonably good vertical accuracy which can further be improved by integrating ICESat-2 data. CARTOSAT DEM V3 R1 is a product of an Indian satellite Cartosat, which is also openly available at a resolution of 30m. The vertical accuracy provided by the Cartosat DEM is of the order of 8m [
11].
ICESat-2
NASA’s Ice, Cloud, and land Elevation Satellite launched as a part of its Earth Observing System. ICESat-2 data records ground surface elevation and the canopy height information, providing more intensive and sufficient reference data for the quality analysis of different DEMs. In the previous research, Neuenschwander et al. (2019) presented a quantitative assessment of the terrain height of ICESat-2 ATL-08 product as compared to airborne LiDAR data [
12]. The initial result of the best-fit terrain height validation over Finland indicates that the terrain residual has a mean absolute error of 0.5 m, while the Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) is 0.82 m. Thus, it is suitable to be used to assess the DEM accuracy. In this study, the altimetry data acquired by ICESat-2 in the first few months were selected to further assess the vertical accuracies of different DEMs, to help us understand the DEM accuracy and the corresponding error characteristics [
13]. Abdalati et al. (2010), pre-tested the performance of ICESat-2 and the results showed that under complex terrain conditions, there is a mean deviation of less than 14 cm with root mean squared error values between 22 and 46 cm compared by OIB data [
14]. Brunt et al. (2019), validated the ATL06 product using GNSS data, and the results showed that the elevation bias of ATL06 is less than 3 cm [
15]; Li et al. (2021), obtained the ATL06 datasets elevation accuracy of 1.5 cm compared by coordinated multi-sensor observations [
16]. As it is providing quality and sufficient reference data, it is suitable for the accurate analysis of different DEMs [
17]. Various studies have concluded that the vertical accuracy of ICESat-2 elevation data is of the order of centimetres, which significantly improves over conventionally obtained DEMs. Machine Learning is a well-established technology which enables computers to determine the trend in data and henceforth, predict or estimate the absent values. To obtain an improved DEM with a resolution of an openly accessible DEM, interpolation of the ICESat-2 data points is attempted in this study with the help of Cartosat DEM.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study area
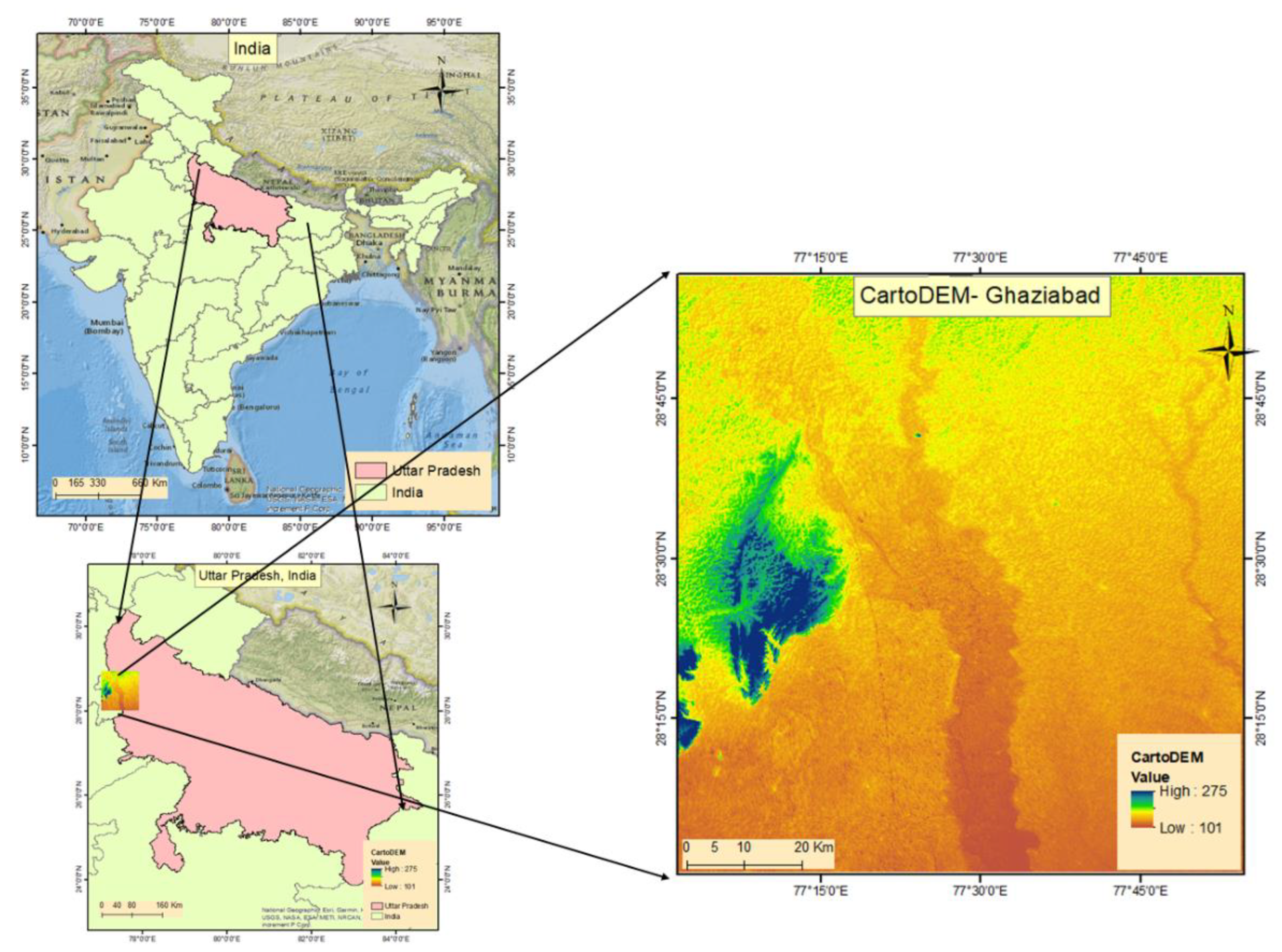
This study has been conducted on the Delhi-NCR region with Ghaziabad district and surrounding regions (
Figure 1) having central coordinates of 77.3689⁰ E, 29.6055⁰ N. The area is predominantly plain region with minor variations in the elevation values.
2.2. Datasets
1. CartoDEM Version 3 Release 1
CARTOSAT–1 is the first Indian Remote Sensing Satellite capable of providing in-orbit stereo images. The Cartosat–1 provided stereo pairs required for generating Digital Elevation Models (
Figure 1), Ortho Image products, and Value added products for various applications of Geographical Information System (GIS) [
18]. CartoDEM V3 R1 comes with a spatial resolution of 1 arc-second (30 m) with 16 bits per pixel and WGS84 datum [
19]. The CartoDEM V3 R1 product can be openly accessed via the NRSCs (National Remote Sensing Centre) Bhuvan portal.
2. ICESat-2 (ATL08)
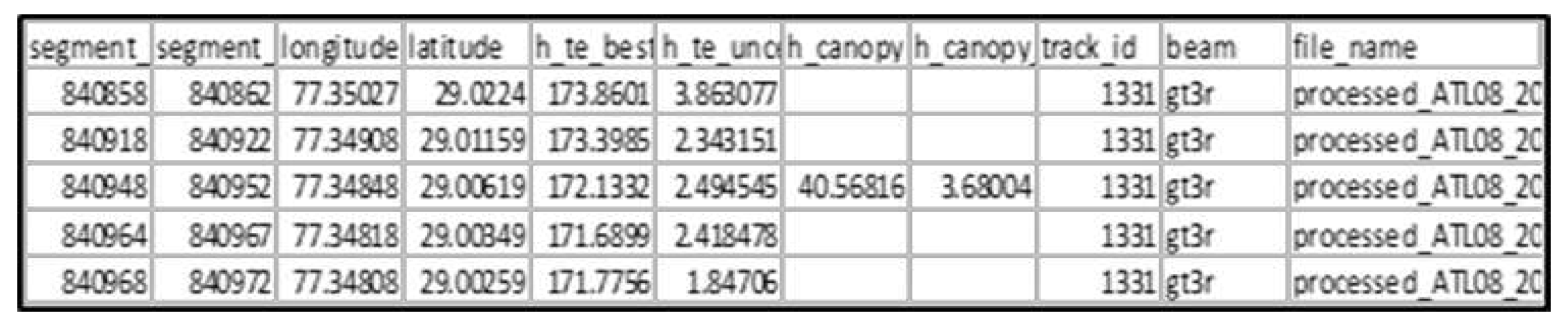
ICESat-2, part of NASA’s Earth Observation System, is a space borne LiDAR satellite which monitors the changes in the thickness of Polar ice sheets and clouds, canopy heights and surface elevation. The instrument on board ICESat-2 is ATLAS (Advanced Topographic Laser Altimetry System) which is responsible for providing all the topographic information. A laser light pulse of 532 nm is emitted at the rate of 10,000 Hz which gets split into 6 beams by ATLAS with unequal energies. There are 3 relatively strong and 3 relatively weak beams [
20]. ICESat-2 takes measurement both along track and across track in a single pass. The ATLAS instrument is aimed to measure changes in polar ice and land ice thickness but it also gathers elevation data for all surfaces by the distribution of signal photons, and the ATL08 algorithm produces Land Water Vegetation Elevation, which consists of elevation heights and canopy surface. This data set (ATL08) contains along-track heights above the WGS84 ellipsoid (ITRF2014 reference frame) for the ground and canopy surfaces. The canopy and ground surfaces are processed in fixed 100 m data segments, which typically contain more than 100 signal photons [
21]. As it is providing quality and sufficient reference data, it is suitable for accurate analysis of different DEMs [
17].
Figure 3.
Dataset format of ICESat-2.
Figure 3.
Dataset format of ICESat-2.
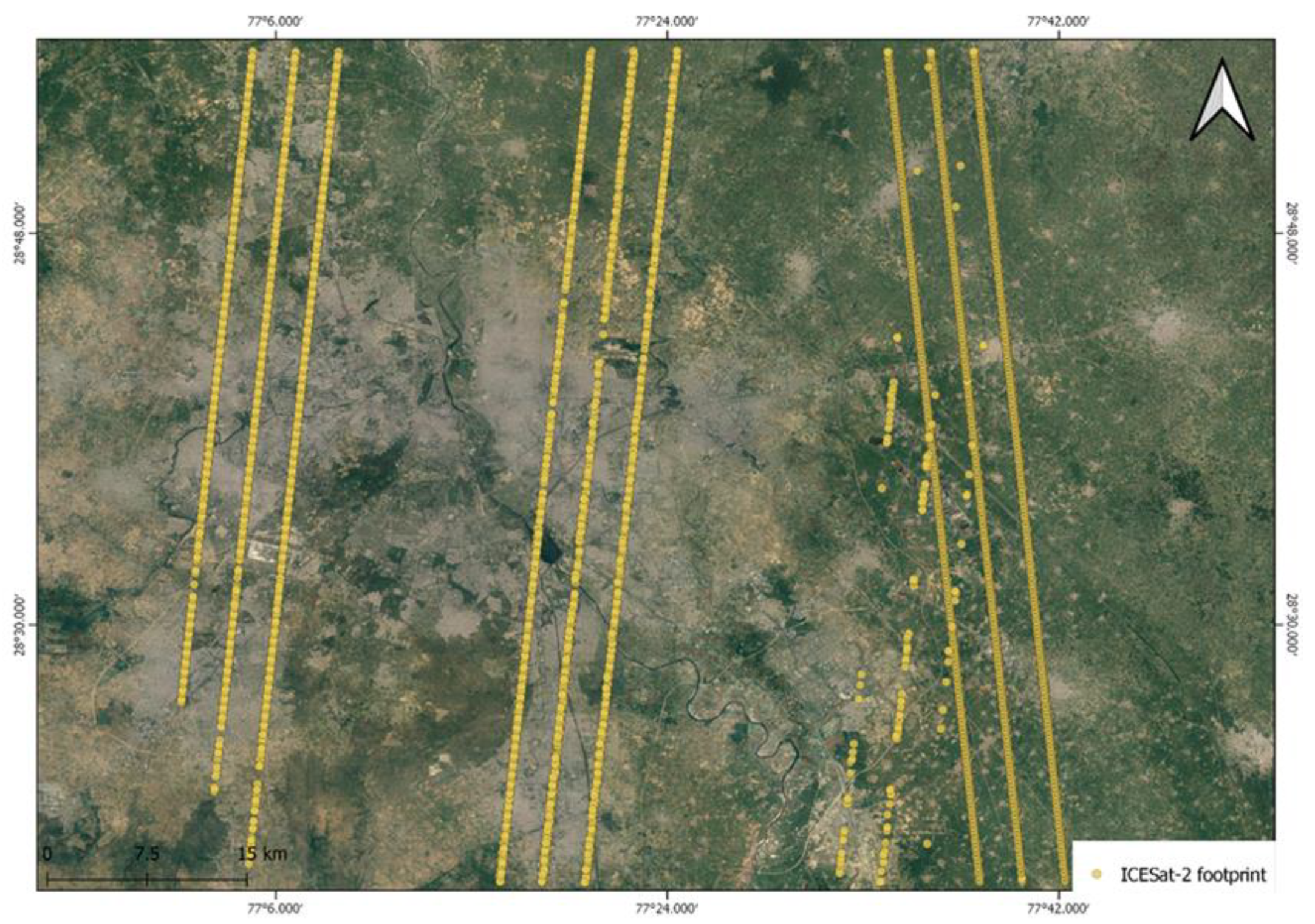
Figure 4.
ICESat-2 data points overlaid on the study area.
Figure 4.
ICESat-2 data points overlaid on the study area.
3. TanDEM-X 90m DEM
TanDEM-X (TerraSAR-X add-on for Digital Elevation Measurements) is an Earth observation radar mission of the DLR (German Aerospace Centre) that consists of a SAR interferometer built by two almost identical satellites flying in close formation. With a typical separation between the satellites of 120m to 500m, a global Digital Elevation Model (DEM) has been generated [
22]. The global accuracy goal for TanDEM-X is below 10m. The TanDEM-X 90m product can be freely downloaded for the entire globe from the EOC GEO service. The better performance of TanDEM-X in plain regions makes it a vital dataset for evaluation of the simulated output DEM.
2.3. Models
The four advanced machine learning models namely, Decision Tree, Random Forest, Gradient Boosting, and Artificial Neural Network are used in the study to synthesise the DEM.
- 1.
Decision Tree Model
The decision tree model is a powerful measure for addressing classification and regression issues, which has its roots in machine learning theory [
23]. It is based on a multilevel or hierarchical decision strategy or a tree-like structure, in contrast to other classification methods that use a collection of characteristics (or bands) together to accomplish classification/regression in a single decision step [
24]. It comprises a root node, internal nodes and leaves. Each node of a decision tree performs binary classification differentiating one or more classes from the rest utilising a top-down approach by moving down the tree unless the leaf node is reached[
25]. Basically, the decision tree splits a complex problem statement into simpler problems and simpler decisions are made which leads to the complex decision. Decision tree model is selected in the study as it efficiently solves both problems containing linear relationships and non-linear relationships.
- 2.
Random Forest Model
Random forest model is an ensemble machine learning model that contains two or more decision trees that finally yield a ‘decision forest’ [
26]. The outcome of the random forest model is obtained by finding the majority through voting of the results of the individual decision trees [
27]. The performance of Random Forest depends on the design of each decision tree which constitutes the forest. This procedure has two steps that include random selection. To build each decision tree, the initial phase employs a bootstrap technique to randomly select around two-third of the training dataset. The remaining one-third of the dataset is called out-of-bag (OOB) data, which are used for inner cross-validation to evaluate the accuracy of the mode [
28].
- 3.
Gradient Boosting Machine Model
Gradient boosting is also an ensemble machine learning algorithm that relies on the power of boosting on a decision tree to predict the output. It contains multiple decision trees built sequentially which are ‘weak’ learners and these subsequent learners learn from the mistakes of the previous model to make the final model a ‘strong’ one [
29]. The first model is initialised with some constant values which are obtained by taking the average of all the target values. The difference between the actual target values and the predicted value is calculated and is termed as residuals. These residuals r1 are given as the target values to the next decision tree and the residuals r2 is calculated from the predicted value and r1. This continues till all the decision trees are trained [
30].
- 4.
Artificial Neural Network Model
Artificial Neural Network is a nonlinear nonparametric framework that models human brain receptors and information processing by using neural network propagation across layers based on gradient learning methods. [
31] It is composed of three layers: input layer, hidden layer and output layer. The input layer receives the input and transfers them to hidden layers through synapses, and similarly the hidden layers transfer the data to output layer. The synapses contain values referred as weights that control the flow of information from one layer to the other. Mathematically, a neuron in the hidden layer or output layer is described in Equation (1).
and
where w is the synaptic weights, x is the input to the neurons, y is the output from the neuron, u is the linear combiner of input signals, b is the bias and
() is the activation function used to limit the range of the inputs.
2.4. Methods
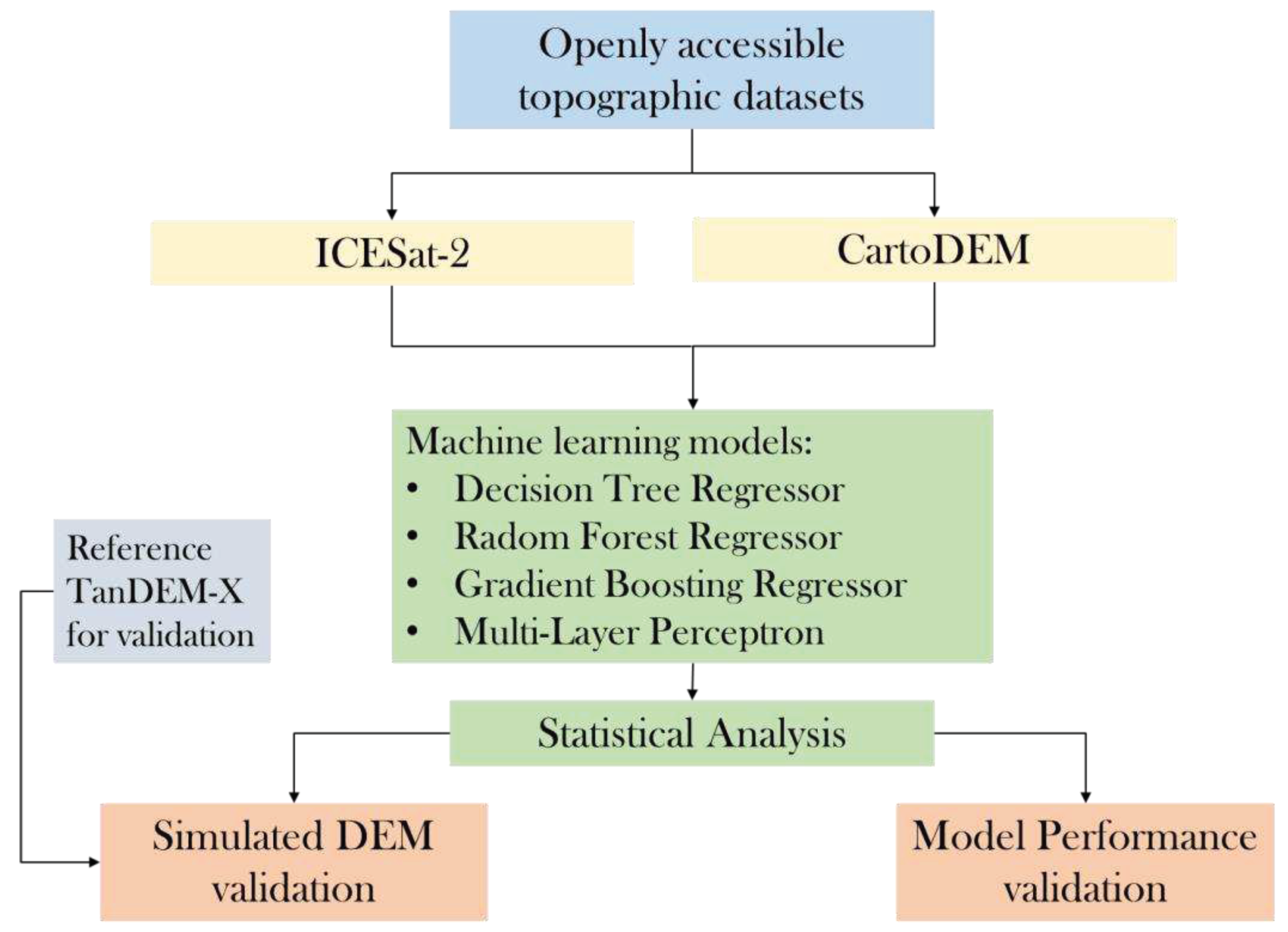
The methodology followed for the proposed approach is shown in
Figure 4. The machine learning models- Gradient Boosting Regressor, Random Forest, Support Vector Machine (SVM) and Decision Tree Regressor were first trained using the CartoDEM data and the corresponding ICESat-2 elevation points. The highly accurate ICESat-2 points act as the target variable, and the relatively less accurate CartoDEM acts as the predictor variable.
The machine learning models employed in the study aims to find the relationship between the elevation values of CartoDEM and ICESat-2 and to predict the values of ICESat-2 in the areas which are not covered by the satellite to yield a DEM based on ICESat-2. The statistical analysis of the machine learning models was performed using coefficient of determination (R
2), Root Mean Square Error (RMSE), and Mean Absolute Error (MAE) [
32] on comparison with the simulated DEM and TanDEM. R
2 was used to find the goodness of fit of the model, whereas RMSE and MAE was used to assess the accuracy. RMSE was used to compare the performances of different models used in the study. In general, the performances of regression models are assessed using R
2 and RMSE of the predicted and actual values. Higher values of R
2 and lower values of MAE and RMSE corresponds to higher precision and accuracy respectively for predicting the elevation values of an area.
3. Results and Discussion
The model performances were compared using R
2 scores. Gradient Boosting Regressor performs the best among the 4 models followed by Decision Tree, Random Forest and Multi-Layer Perceptron.
Table 1 shows the obtained statistical scores for each model.
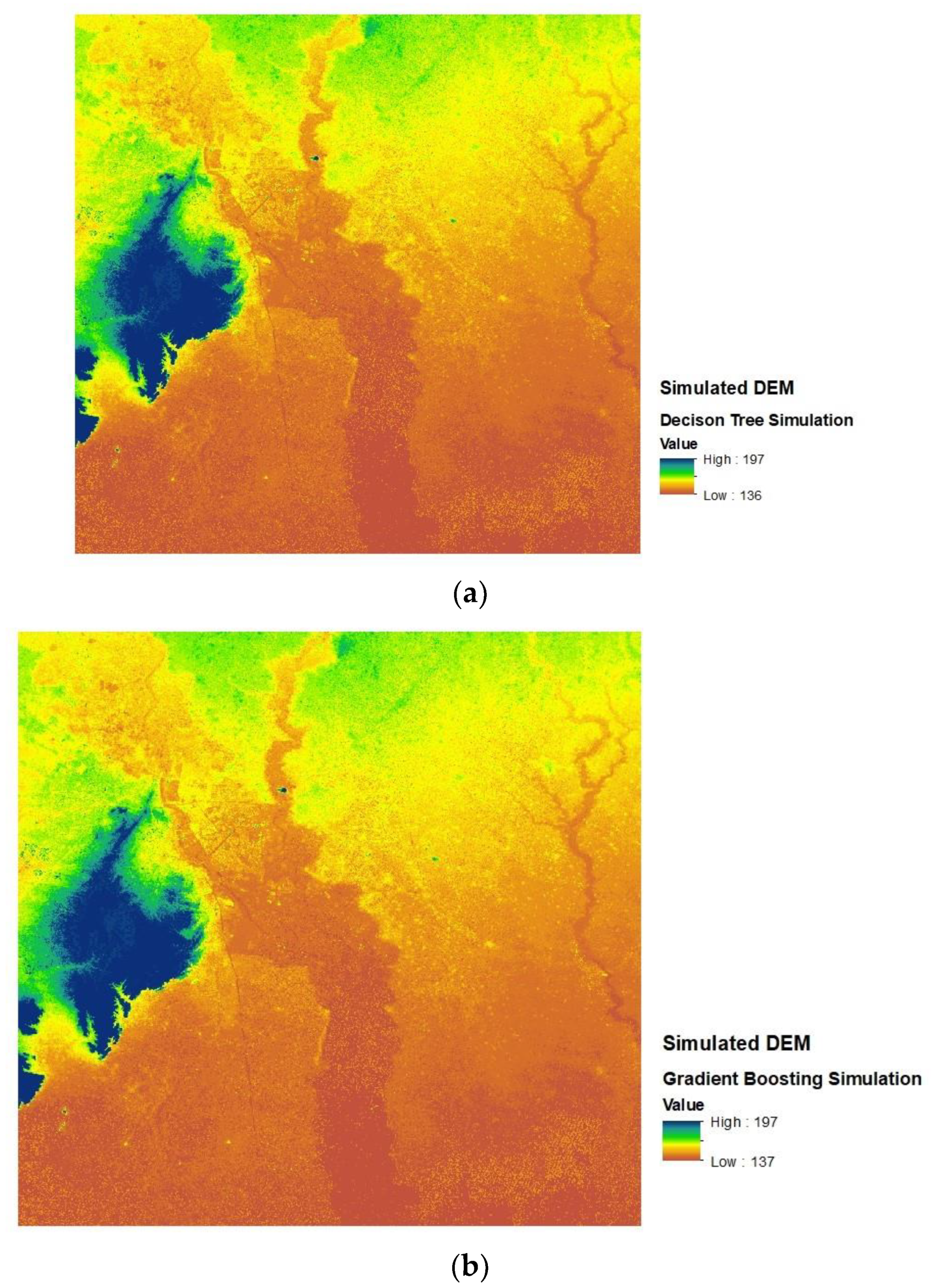
The simulated DEMs generated from different models are shown in
Figure 5. The accuracy assessment of the existing CartoDEM was done using Mobile GNSS which came out to have MAE of the order of 3.26m and RMSE of the order of 4.13m.
Even though, the models show high accuracy metrics, the models except Multi-Layer Perceptron are not able to address the extreme values in the terrain; and are not a true representation of the elevation. The lowest elevation points in the synthesized DEM using Gradient Boosting Model is 137m, Random Forest is 138m, Decision Tree is 136m, and Multi-Layer Perceptron is 90m, but that of the CartoDEM is 99m. Similarly, the highest elevation value of Synthesized DEM using Gradient Boosting Model, Random Forest, and Decision Tree is 136m, and Multi-Layer Perceptron is 90m, but that of the CartoDEM is 273 m. This is due to the uneven distribution of ICESat-2 footprints across different elevation levels in the study area. While the lowest value of CartoDEM is 99m, the lowest value of ICESat-2 points used in the study is 133.4m. Similarly, the highest value of CartoDEM in the study area is 273m, but that of the available ICESat-2 point is 211m. So, the models learn from the available ICESat-2 points from 133.4m to 211m and represents the elevation values in between this range in an efficient manner compared to the elevation outside this range. But Multi-Layer Perceptron model is a better representation of the elevation of the study area even though the accuracy metrics of the model is the lowest among the four.
Hence, accuracy metrics of the models are not sufficient to assess the accuracy of the models as the sampling of data is not even across the elevation levels. An external DEM that is not seen by the models that covers the entire study area is used to find the real accuracy of the models used in the study. TanDEM-X is used as the external DEM for the validation of the models and to find out the real accuracy metrics.
The statistical measures of simulated DEM in comparison with TanDEM-X are given in
Table 2. It was observed that the MLP Regressor model outperforms the other models considered in this study. The accuracy assessment of the simulated DEMs was done using TanDEM-X data and MLP Regressor provided with the best accuracy of all the four models. The accuracy of the Gradient Boosting, Random Forest, and the Decision Tree models are less compared to the Multi-Layer Perceptron model because the first three models are not the true representation of the elevation on the ground. The extreme values of elevation is not captured by the models as the training data lacked these extreme points in the study area. But Multi-Layer Perceptron was able to generate a true representation of the elevation values when compared to TanDEM-X with good accuracy metric scores in the form of R
2, RMSE, and MAE. The results show the robust nature of Multi-Layer Perceptron as it was able to produce promising results when dealing with datapoints that is unseen during the training of the model while other models are unable to.
In future, this study can be extended by using analyzing the possibilities of other models that is not used in the current study for synthesizing DEM.
4. Conclusions
This study is done to examine the scope and application of machine learning in the domain of elevation data. Four machine learning models- Random Forest, Gradient Boosting Machine, Multilayer Perceptron, and Decision Tree was used in the study to synthesize DEM from ICESat-2 points scattered across the study area in the plains of Ghaziabad. CartoDEM was used as the feature and TanDEM-X was used to validate the synthesized ICESat-2 DEM. MLP model produced the best results with an R2 score of 0.95 followed by Random Forest, Gradient Boosting Machine, and Decision Tree with R2 scores of 0.84. The outcomes of this study prove it to be a useful asset by generating accurate DEM derived from ICESat-2. The future scope of the study includes the usage of other machine learning models and deep learning models for synthesizing DEM from ICESat-2.
References
- C. Okolie, J. Mills, and J. Smit, “Fusion of Copernicus and ALOS World 3D DEMs for Watershed and Stream Network Delineation.” EasyChair, May 21, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Pipaud, D. Loibl, and F. Lehmkuhl, “Evaluation of TanDEM-X elevation data for geomorphological mapping and interpretation in high mountain environments - A case study from SE Tibet, China,” Geomorphology, vol. 246, pp. 232–254, Oct. 2015. [CrossRef]
- R. Weibel and M. Heller, “A framework for digital terrain modeling,” in Fourth International Symposium on Spatial Data Handling, Zurich, Switzerland, 1990, pp. 219–229.
- S. Vassilopoulou et al., “Orthophoto generation using IKONOS imagery and high-resolution DEM: a case study on volcanic hazard monitoring of Nisyros Island (Greece),” ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens., vol. 57, no. 1–2, pp. 24–38, Nov. 2002. [CrossRef]
- H. Bagheri, M. Schmitt, and X. X. Zhu, “Fusion of TanDEM-X and Cartosat-1 elevation data supported by neural network-predicted weight maps,” ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens., vol. 144, pp. 285–297, Oct. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Nelson, H. I. Reuter, and P. Gessler, “Chapter 3 DEM Production Methods and Sources,” Dev. Soil Sci., vol. 33, no. C, pp. 65–85, Jan. 2009. [CrossRef]
- Y. Zhang et al., “Semivariogram fitting based on SVM and GPR for DEM interpolation,” IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci., vol. 311, no. 1, p. 012076, Aug. 2019. [CrossRef]
- V. Kasi et al., “A novel method to improve vertical accuracy of CARTOSAT DEM using machine learning models,” Earth Sci. Informatics, vol. 13, no. 4, pp. 1139–1150, Dec. 2020. [CrossRef]
- S. A. Kulp and B. H. Strauss, “CoastalDEM: A global coastal digital elevation model improved from SRTM using a neural network,” Remote Sens. Environ., vol. 206, pp. 231–239, Mar. 2018. [CrossRef]
- S. Mukherjee, P. K. Joshi, S. Mukherjee, A. Ghosh, R. D. Garg, and A. Mukhopadhyay, “Evaluation of vertical accuracy of open source Digital Elevation Model (DEM),” Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf., vol. 21, no. 1, pp. 205–217, 2012. [CrossRef]
- “Evaluation of Indian National DEM from Cartosat-1 Data Summary Report (Ver.1),” 2011.
- L. Neuenschwander and L. A. Magruder, “Canopy and Terrain Height Retrievals with ICESat-2: A First Look,” Remote Sens. 2019, Vol. 11, Page 1721, vol. 11, no. 14, p. 1721, Jul. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Z. Liu, J. Zhu, H. Fu, C. Zhou, and T. Zuo, “Evaluation of the vertical accuracy of open global dems over steep terrain regions using icesat data: A case study over hunan province, china,” Sensors (Switzerland), vol. 20, no. 17, pp. 1–16, Sep. 2020. [CrossRef]
- W. Abdalati et al., “The ICESat-2 laser altimetry mission,” Proc. IEEE, vol. 98, no. 5, pp. 735–751, 2010. [CrossRef]
- K. M. Brunt, T. A. Neumann, and B. E. Smith, “Assessment of ICESat-2 Ice Sheet Surface Heights, Based on Comparisons Over the Interior of the Antarctic Ice Sheet,” Geophys. Res. Lett., vol. 46, no. 22, pp. 13072–13078, Nov. 2019. [CrossRef]
- R. Li et al., “Assessment of ICESat-2 ice surface elevations over the Chinese Antarctic Research Expedition (CHINARE) route, East Antarctica, based on coordinated multi-sensor observations,” Cryosphere, vol. 15, no. 7, pp. 3083–3099, Jul. 2021. [CrossRef]
- S. Mariani, G. Pavan, S. Goud, and A. Bhardwaj, “Estimation of Building Heights and DEM Accuracy Assessment Using ICESat-2 Data Products,” Eng. Proc. 2021, Vol. 10, Page 37, vol. 10, no. 1, p. 37, Nov. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Indian Space Research Organisation, “CARTOSAT-1 - ISRO,” 2005. https://www.isro.gov.in/Spacecraft/cartosat-1 (accessed Jul. 31, 2022).
- U. Yadav and A. Bhardwaj, “Accuracy Assessment of TanDEM-X 90 and CartoDEM Using ICESat-2 Datasets for Plain Regions of Ratlam City and Surroundings,” no. November 2021, p. 59, 2022. [CrossRef]
- T. A. Neumann et al., “The Ice, Cloud, and Land Elevation Satellite – 2 mission: A global geolocated photon product derived from the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System,” Remote Sens. Environ., vol. 233, p. 111325, Nov. 2019. [CrossRef]
- “ATLAS/ICESat-2 L3A Land and Vegetation Height, Version 4 | National Snow and Ice Data Center.” https://nsidc.org/data/atl08/versions/4 (accessed Jul. 30, 2022).
- “TanDEM-X - Digital Elevation Model (DEM) - Global, 90m.” https://geoservice.dlr.de/data-assets/ju28hc7pui09.html (accessed Jul. 30, 2022).
- S. B. Kotsiantis, “Decision trees: a recent overview,” Artif. Intell. Rev. 2011 394, vol. 39, no. 4, pp. 261–283, Jun. 2011. [CrossRef]
- C. Kingsford and S. L. Salzberg, “What are decision trees?,” Nat. Biotechnol. 2008 269, vol. 26, no. 9, pp. 1011–1013, Sep. 2008. [CrossRef]
- L. Rokach and O. Maimon, “Decision Trees,” Data Min. Knowl. Discov. Handb., pp. 165–192, May 2005. [CrossRef]
- Cutler, D. R. Cutler, and J. R. Stevens, “Random Forests,” Ensemble Mach. Learn., pp. 157–175, 2012. [CrossRef]
- L. Breiman, “Random Forests,” Mach. Learn. 2001 451, vol. 45, no. 1, pp. 5–32, Oct. 2001. [CrossRef]
- M. Pal, “Random forest classifier for remote sensing classification,” vol. 26, no. 1, pp. 217–222. [CrossRef]
- V. K. Ayyadevara, “Gradient Boosting Machine,” Pro Mach. Learn. Algorithms, pp. 117–134, 2018. [CrossRef]
- R. Lawrence, A. Bunn, S. Powell, and M. Zambon, “Classification of remotely sensed imagery using stochastic gradient boosting as a refinement of classification tree analysis,” Remote Sens. Environ., vol. 90, no. 3, pp. 331–336, Apr. 2004. [CrossRef]
- N. A. Mahmon and N. Ya’Acob, “A review on classification of satellite image using Artificial Neural Network (ANN),” Proc. - 2014 5th IEEE Control Syst. Grad. Res. Colloquium, ICSGRC 2014, pp. 153–157, Sep. 2014. [CrossRef]
- L. Wang, X. Zhou, X. Zhu, Z. Dong, and W. Guo, “Estimation of biomass in wheat using random forest regression algorithm and remote sensing data,” Crop J., vol. 4, no. 3, pp. 212–219, Jun. 2016. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).