1. Introduction
Hyperlipidemia is a status of an elevated lipid profile in the blood due to lipid metabolic disorders [1]. The WHO announced that hyperlipidemia and high blood pressure, along with alcohol consumption and smoking, are the major causes of fatality in recent years [2]. The disease is generally treated with dietary intervention and hypolipidemic agents by a clinical practitioner according to the lipid profiles of the patient [3]. The clinical features of hyperlipidemia are elevated lipids in the bloodstream, including fat, fatty acids, cholesterol, phospholipids, and triglycerides [4]. The reported environmental factors of hyperlipidemia were obesity, excessive alcohol intake, BMI, and genetic factors include several genes that impact lipid metabolism including LPL (lipoprotein lipase), LCAT (lecithin cholesterol acyltransferase), PPARA (peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor α), apolipoprotein member gene family, and variants in multiple loci [5,6]. Dietary patterns fundamentally impact increased LDL cholesterol levels which lead to progression of acquired dyslipidemia, while genetic factors determine inherited familial hyperlipidemia [6,7]. The elevated LDL cholesterol is a significant clinical marker of patients with atherosclerosis or several cardiovascular diseases because it describes disorders in lipid profiles [8]. The significant complications of hyperlipidemia include atherosclerosis, coronary artery disease, myocardial infarction, and ischemic stroke [9]. Reducing LDL cholesterol is considered the first goal in treating hyperlipidemia to lower the risk of cardiovascular disease [3].
The first-line medication for hyperlipidemia includes statins, whose mechanism is the inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase, which is the rate-limiting enzyme of cholesterol synthesis [9]. Studies have reported rhabdomyolysis, muscle pain, and myositis as side effects of statin drugs [10]. Increased serum statin concentration or decreased body muscle mass increases the risk of statin-associated muscle symptoms [10]. Statin treatment has been associated with new-onset diabetes, but the exact mechanisms are unknown [11,12].
The recent trend in studying mechanisms of herbal medicine adopts network pharmacology as a feasible tool for mapping the known interactions and analyzing networks between natural drugs and target genes to identify potential targets based on multi-compound and multi-target theory [13]. This approach, based on a widely existing database, can form an initial understanding of the mechanism of action of many polyherbal prescriptions [14]. One study showed that the Network Pharmacology techniques presented significant results for hyperlipidemia [15]. The characteristics of symptoms from hyperlipidemia and chronic metabolic disorders can be recognized as ‘phlegm’, which is a pathological byproduct in oriental medicine, and differentiated or treated as ‘damp-phlegm’ phenotype (or pattern) patient by practitioners [16]. Banxia Baizhu Tianma Decoction (BBTD) is a representative prescription that treats phlegm pattern patients in oriental medicine [17]. In addition, there are reports that BBTD attenuated high blood pressure [17]. Yijin-tang is a traditional prescription for hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis in oriental medicine [18]. In addition, Yijin-tang improved systemic inflammation caused by obesity, which can cause hyperlipidemia, and improved insulin resistance [19]. The common medicinal herbs of these prescriptions are Pinelliae Tuber (Arum ternata, AT), Poria Sclerotium (Poria cocos, PC), and Zingiberis Rhizoma (Zingiber officinale, ZO). These three herbs were also enlisted as the top five most frequently found in phlegm-eliminating herbal prescriptions according to a recent study [20]. ZO inhibited lipid peroxidation using a high-cholesterol-fed rat model by scavenging radicals. PC was proven effective in a high-fat-diet-induced hyperlipidemia rat model by modulating the metabolic pathways [21,22]. In addition, AT lowered the blood triglyceride and free fatty acid levels when administered for six weeks using an obese mouse model [23].
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is one of the most common metabolic liver disorders worldwide and is closely associated with metabolic syndromes, such as dyslipidemia and obesity [24]. The main characteristic of NAFLD is too much fat stored in the liver [25]. Evidence suggests that NAFLD causes dyslipidemia, such as hyperlipidemia [26]. Decreased LDLR expression on the cell surface of NAFLD may discourage the removal of LDL cholesterol from the sera [27]. Therefore, targeting NAFLD is a potential strategy for attenuating hyperlipidemia [26].
The phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT) pathway is an intracellular signal transduction pathway that plays a pivotal role in glucose, lipid, and protein metabolism [28]. The level of AKT phosphorylation decreased in the muscle, liver, and visceral adipose tissues in obese patients with NAFLD [29]. In NAFLD, the phosphorylation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) decreases fatty acid and cholesterol synthesis by regulating the expression of adipogenesis genes (Acetyl-CoA carboxylase, ACC; Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma, PPARG; CCAAT Enhancer Binding Protein Alpha, CEBPA; and 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA Reductase, HMGCR), and increases the expression of fatty acid oxidation and lipolysis genes, such as serine/threonine kinase 1 (CPT1) [30-32]. AMPK directly impacts lipid metabolism as a regulator of energy expenditure, but FFAs directly impair hepatic glucose and lipid homeostasis [33].
Using the latest network pharmacology technique and online pharmacological database, this study analyzed the components and target information of three herbal medicines to find targets and mechanisms that can modulate hyperlipidemia. In addition, an in vitro study was performed to verify the mechanism of these herbs estimated by network pharmacology using a fatty acid-induced hepatic steatosis model. Finally, an analysis of the efficacy and mechanism of the three medicinal herbs that can be used in the prescription of hyperlipidemia highlights their potential for treating hyperlipidemia.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data preparation
2.1.1. Data acquisition of herbs from the online database
The TCMSP (
https://tcmsp-e.com accessed on 22/08/12) [34], which is a pharmacology database of Traditional Chinese Medicine, was used to collect the compounds and targets of the herbal combination. The oral bioavailability (OB) and drug-likeness (DL) were used [18]. OB represents the rate and extent of an active ingredient or active moiety that is absorbed into the blood circulation and becomes available at the site of action [35]. DL can describe the molecular properties affecting the pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics [36]. The threshold values of the two indices were ≥ 30% (OB) and ≥ 0.18 (DL) [37]. The results from the TCMSP database were reinforced using the OASIS database to sum the additional bioactive compounds with proper literature-based evidence for their activity (
https://oasis.kiom.re.kr/ accessed on 22/08/12).
2.2. Hyperlipidemia-associated targets prediction
Information on hyperlipidemia-associated target genes was collected from the DisGeNET(
https://www.disgenet.org/, accessed on 22/08/17) and genecards (
https://www.genecards.org/, accessed on 22/08/17) [38,39]. “Hyperlipidemia” was used for the search, and only Homo sapien proteins were selected. The distributional results of targets and compounds from herbs were presented as Venn diagrams using bioinformatics and evolutionary genomics website (
http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/Venn/) [40].
2.3. Protein-protein interaction (PPI) network construction
A PPI network with STRING was produced using a query list of target genes and exported to Cytoscape software (version 3.9.1), a free software package for visualizing, modeling, and analyzing molecular and genetic interaction networks [41]. The total PPI network was clustered functionally using MCODE and analyzed further with ClueGO and CluePedia, which are Cytoscape plugins [41-43]. The STRING database aims to provide a critical assessment and integration of protein-protein interactions, including direct [44]. A protein-chemical network was then screened using the STITCH database (version 5.0) by submitting a target gene list [45].
2.4. Gene ontology (GO) terms and KEGG pathway enrichment analysis
The enrichment of GO terms of BP was analyzed in the DAVID database. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) signaling-pathway enrichment analysis was performed using the Database for Annotation, Visualization, and Integrated Discovery (DAVID) v.6.8 (
https://david.ncifcrf.gov/, accessed on 22/08/29) [46]. A list of target genes was submitted, and the gene identifier was set to ‘official gene symbol’.
The false discovery rate (FDR) was used as a statistical test method of the enrichment analysis in the DAVID database, which is based on fisher’s exact test [47]. The data of relative gene ratio, adjusted p-value, and gene counts of each GO term and KEGG were processed and presented as bubble plots using the R package (ggplot2) and public script in R studio [48].
2.5. Chemicals and Antibodies
Dulbecco’s from Modified Eagle’s Medium (DMEM) was purchased from Hyclone (Logan, UT, USA), and Fetal bovine serum (FBS) and penicillin/streptomycin solution were from Invitrogen (Carlsbad, CA, USA). The EZ-cytox assay kit was used to measure cell viability was obtained from Daeil Lab Service (Chungcheongkuk-do, South Korea). The phosphorylation form or non-phosphorylation form primary antibodies of ACC (Acetyl-CoA carboxylase), AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase), AKT (Protein kinase B), CPT-1 (Carnitine palmitoyltransferase-1) were purchased from Cell signaling Technology (Berkeley, CA, USA), and β-actin was obtained from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Santa Cruz, CA, USA). Santa Cruz Biotechnology supplied the secondary antibodies. The oligonucleotide primers for real-time qPCR were produced by Macrogen (Seoul, South Korea).
2.6. Preparation of Samples
Dried herbs of A. ternata (AT), P. cocos (PC), and Z. officinale (ZO) were purchased from Herbmaul (Chungcheongbuk-do, South Korea). To prepare the extract, dried herbs (100 g) were ground to a powder and extracted with 500 mL in distilled water at 100°C for 15 min. In addition, the mixed sample was blended with equal weights of AT, PC, and ZO (33 g each). The hot water extracts were filtered twice through 8 μm-pore-size Whatman filter paper, concentrated by rotary evaporation (Buchi, Flawil, Switzerland), and freeze-dried to obtain lyophilized extracts of AT, PC, and ZO. These were then eluted with DPBS and filtered through a 0.22 μm syringe filter before cell treatment.
2.7. Cell culture and treatment
HepG2 cells (a human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line) were purchased from the Korean Cell Bank (no. 88065, Seoul, South Korea) and cultured in DMEM supplemented with a 1 % penicillin/streptomycin and 10 % FBS at 37°C in humidified 5 % CO2 environment. To evaluate anti-intracellular lipid accumulation effects, The FFAs (oleic acid and palmitic acid, 2:1, v/v, respectively) were dissolved in DMSO at 1 mM concentrations. The HepG2 cells were serum-starved for 12 h, cultured with serum-free DMEM containing 1% bovine serum albumin (BSA), and exposed to 1 mM FFAs [49]. Each sample was co-treated during incubation in FFAs-BSA complex media for 24–48 h for further analysis.
2.8. Cell viability assay
The cell viability of HepG2 cells was determined using the EZ-Cytox cell viability assay kit according to the manufacturer’s instructions with slight modifications [50]. Briefly, HepG2 cells were plated at a density of 4 × 104 cells/well in 96-well plates. After 24 h incubation, the medium was changed to FBS-free DMEM containing a serially diluted sample (0–50 µg/ml) and treated with different concentrations, was incubated at 37°C in a humidified containing 5 % CO2 for 24 h. Since then, 10 µl of EZ-Cytox reagent was added to each well, and cells were incubated for 1 h. Optical densities (ODs) were measured at 450 nm using a microplate reader (Versamax, Molecular Devices, CA, USA).
2.9. Western blot analysis
The protein levels related to hepatic steatosis were measured by western blot. The whole protein was isolated using RIPA buffer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Rockford, IL, USA) containing a protease and phosphatase inhibitor cocktail (Gendepot, Barker, TX, USA) after the cells were washed with Dulbecco’s phosphate-buffered saline (DPBS). The protein concentrations were determined using a BCA kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Rockford, IL, USA). Equal amounts of protein sample (40 µg/ml) were mixed with the 5× Lane Marker Reducing sample buffer (BioRad, Hercules, CA, USA) and denatured at 95°C for 10min. The protein lysates were loaded into 7.5% SDS-PAGE gels, electrophoresed, and transferred to PVDF membranes activated by methanol at 100 V for 60 min using an electrophoretic transfer cell (Bio-rad, Hercules, CA, USA). The membranes were blocked with 5% BSA in TBS/T (TBS containing 0.1% Tween 20) for 2 h at room temperature. The blots were incubated with primary antibodies (diluted at 1:1500 in TBS/T containing 3% BSA) overnight at 4℃ with gentle shaking. After washing with TBS/T, the membranes were incubated with secondary antibodies (diluted at 1:3000 in TBS/T containing 1% BSA) at room temperature for 3 h. The membrane was detected using a Western blot imaging system (Fusion Solo chemiluminescence system, Vilber Lourmat, Collegien, France), and proteins were visualized using a Super Signal West Pico ECL buffer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Rockford, IL, USA) [51].
2.10. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction
The expression levels related to hepatic steatosis were determined using a quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qPCR). The total RNA was isolated from HepG2 cells using a TRIzol reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Rockford, IL, USA). According to the manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly, reverse transcription was performed using AccuPower RT PreMix (Bioneer, Daejeon, South Korea) and oligo deoxythymine (dt) 18 primers (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). Primer-specific binding cDNA was amplified on a Light Cycler 480 PCR system (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) using 10 µl of SYBR green fluorescence dye Mastermix (Roche, Basel, Switzerland), 8 µl of ultrapure water, 1 pmol/µl of primer, and 1 µl of template cDNA. At least 45 amplification cycles consisting of denaturation at 95°C for 10 min, annealing at 55–58°C for 15 s, and extension at 72°C for 15 s. The following primers were used: CEBPA-forward, 5’-GCGCAAGAGCCGAGATAAAG-3’, reverse, 5’-CACGGCTCAGCTGTTCCA-3’; PPARG-forward, 5’- ATGCCAAAAATATCCCTGGTTTC-3’, reverse, 5’-GGAGGCCAGCATGGTGTAGA-3’; ACC-forward, 5’- TGGCGTCCGCTCTGTGATA-3’, reverse, 5’-CATGGCGACTTCTGGGTTG-3’; HMGCR-forward, 5’-TGATTGACCTTTCCAGAGCAAG-3’, reverse, 5’-CTAAAATTGCCATTCCACGAGC-3’; and β-actin-forward, 5’-GACGGCCAGGTCATCACTATTG-3’, reverse, 5’-CCACAGGATTCCATACCCAAGA-3’; used as the internal control. Ct results with a melting curve were checked using Roche LightCycler 480 software (Roche Applied Science, USA). The Ct values for the expression of each gene were normalized using the Ct values of β-actin gene expression [52].
2.11. Oil Red O staining
The lipid accumulation was estimated by staining the intracellular lipid droplets with the Oil Red O reagent. HepG2 cells were plated at a density of 4 × 105 cells/well in six-well plates. After 24 hours, the cells were incubated with the samples (25, 50 µg/ml) and FFAs (1 mM) for 48 hours. The cells were washed with DPBS and then fixed with 10% formalin for one hour at room temperature. After fixation, the cells were washed with 60% isopropanol and stained with a prepared working solution of Oil Red O for 15 min. The stained cells were washed three times with ultrapure water and dried. The cells were examined under an inverted microscope system with the camera (DMI 6000, Leica, Wetzlar, Germany), and the stains were re-dissolved in pure isopropanol to measure OD at 520 nm wavelength [53].
2.12. Statistical analysis
The analysis was conducted using One-Way ANOVA in Graph Pad Prism version 5.0 software (Graph Pad, La Jolla, CA, USA). The standard curves were constructed using Excel and PowerPoint (Microsoft, Redmond, WA, USA). The significance of the differences between the untreated controls and the FFAs-treated cells and between the FFAs-treated and the samples-treated cells were determined. The results are presented as means ± SDs, and p-values of <0.05 were considered significant.
3. Results
3.1. Selection of potential compounds from AT, PC, and ZO
The data of AT, PC, and ZO compound and target were retrieved from TCMSP and OASIS.
Table 1 lists the compounds studied, and
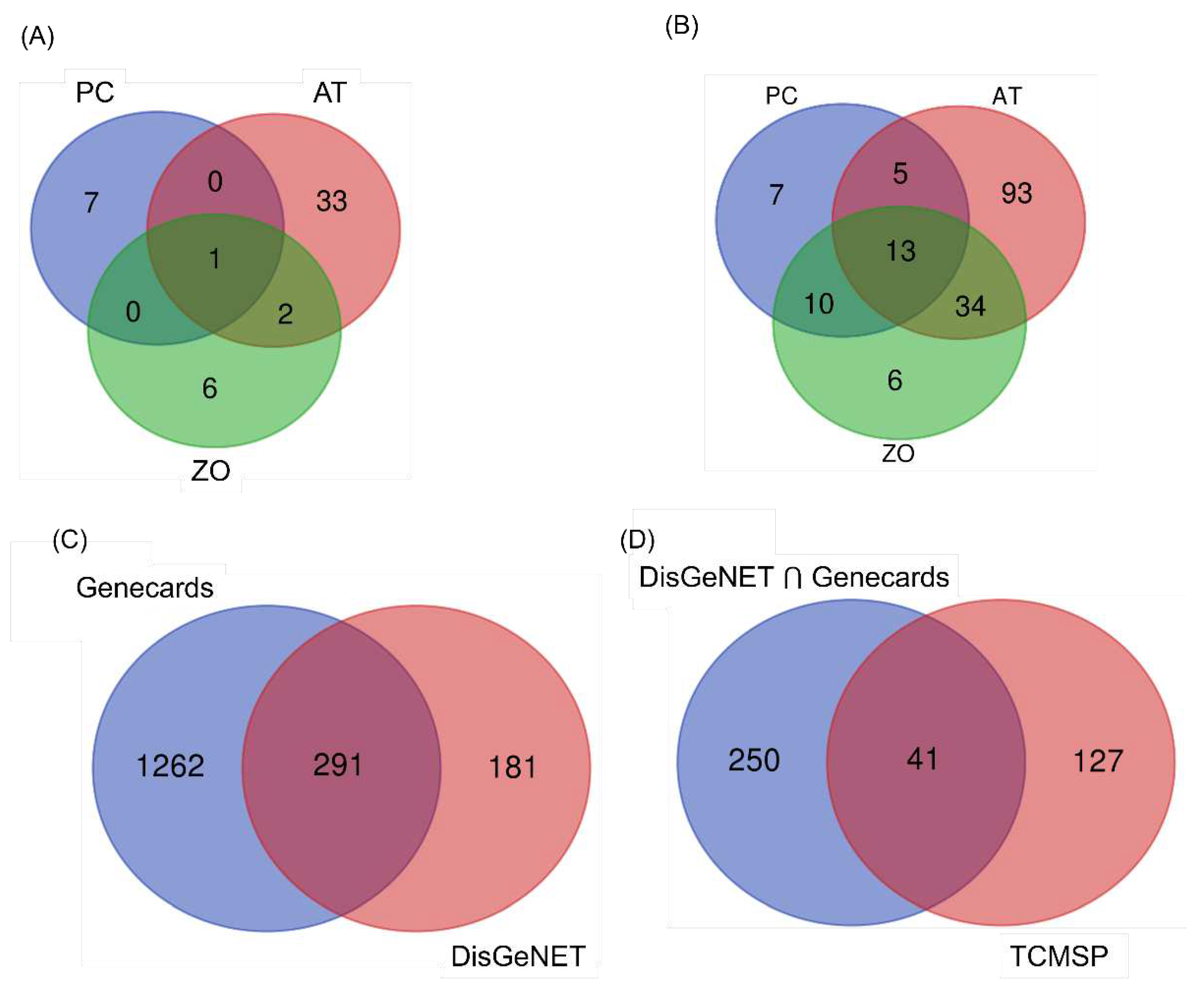
Figure 1A presents a data plot. ZO, PC, and AT have 6, 7, and 33 compounds; all three herbs commonly share one compound (palmitic acid).
3.2. Target prediction
One hundred and sixty-eight targets were screened for three herbs from TCMSP and 291 targets for hyperlipidemia from disease databases (
Figure 1B,C). As a result, forty-one common targets assumed to be involved with hyperlipidemia were obtained between the target lists of the disease database and TCMSP (
Figure 1D). The distributions of targets were visualized using a Venn diagram.
3.3. PPI networks construction and analysis
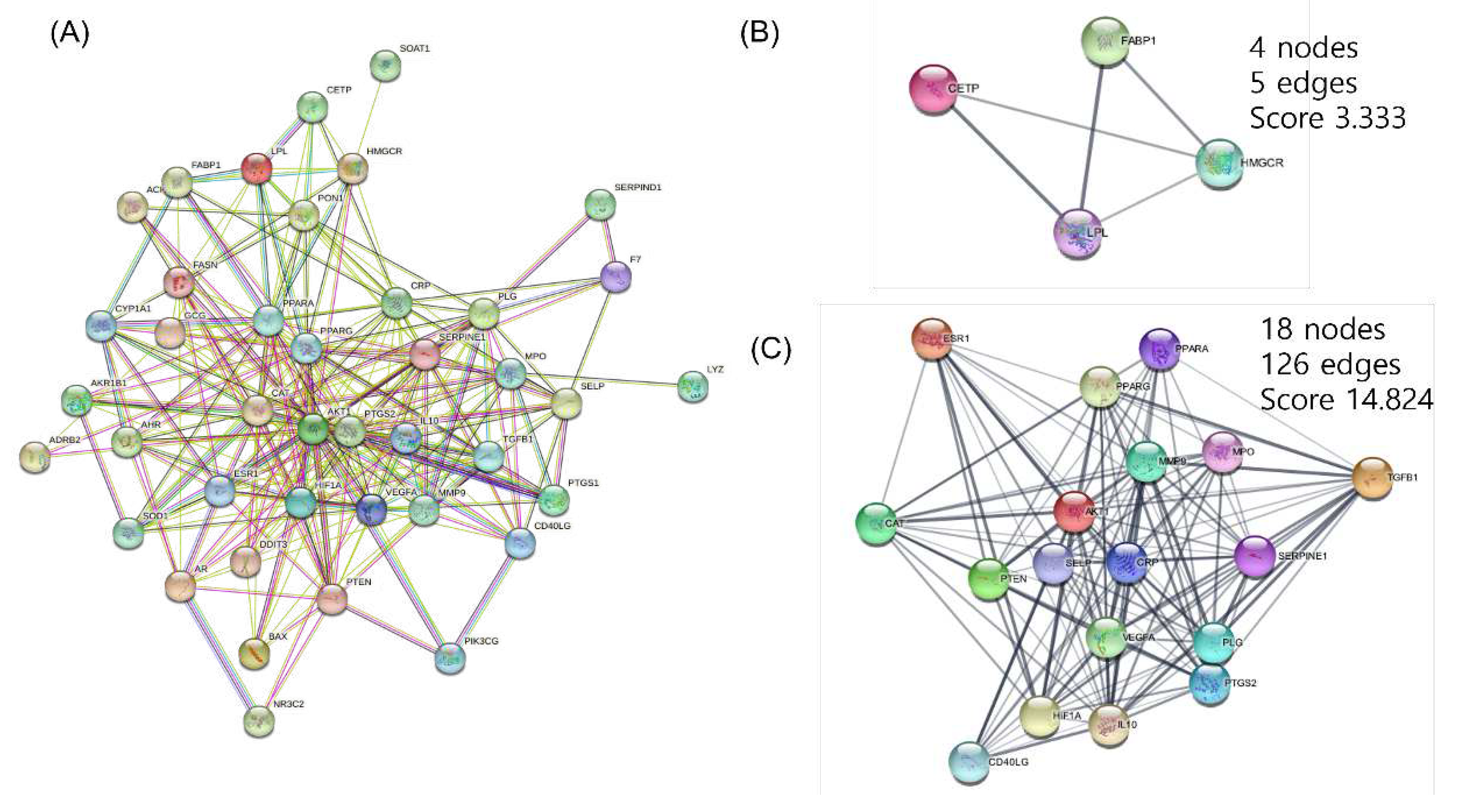
The PPI Network was built for 41 targets that are expected to be significant for hyperlipidemia using the STRING Database. The full network consisted of 41 nodes and can be divided into two clusters using the MCODE of Cytoscape (
Figure 2). The targets were arranged in order of importance of network parameters of degree, betweenness centrality, and stress. AKT Serine/Threonine Kinase 1(AKT1), peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ), and prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2 (PTGS2) act as important targets (Table 3).
Table 2.
Network parameters analyzed from the total PPI network.
Table 2.
Network parameters analyzed from the total PPI network.
| |
Degree |
stress |
Betweenness centrality |
| AKT1 |
31 |
894 |
0.131579 |
| PPARG |
27 |
682 |
0.092949 |
| PTGS2 |
26 |
494 |
0.049889 |
| CAT |
26 |
484 |
0.049086 |
| VEGFA |
25 |
454 |
0.042859 |
| PPARA |
23 |
448 |
0.049087 |
| CRP |
23 |
542 |
0.066034 |
| IL10 |
22 |
238 |
0.018832 |
| SERPINE1 |
21 |
476 |
0.049813 |
| MMP9 |
19 |
164 |
0.011888 |
| HIF1A |
19 |
178 |
0.012385 |
| PLG |
18 |
472 |
0.057540 |
| ESR1 |
17 |
154 |
0.010555 |
| PTEN |
16 |
228 |
0.023134 |
| MPO |
15 |
314 |
0.053684 |
| TGFB1 |
14 |
26 |
0.001131 |
| SELP |
12 |
98 |
0.007016 |
| FASN |
12 |
104 |
0.011726 |
| PON1 |
11 |
100 |
0.012281 |
| LPL |
11 |
72 |
0.006200 |
| CD40LG |
11 |
42 |
0.004880 |
| AR |
11 |
94 |
0.010259 |
| GCG |
11 |
42 |
0.005491 |
| AHR |
11 |
30 |
0.001772 |
| SOD1 |
10 |
12 |
0.000844 |
| HMGCR |
9 |
256 |
0.051766 |
| DDIT3 |
9 |
26 |
0.001189 |
| CYP1A1 |
9 |
50 |
0.005523 |
| BAX |
8 |
8 |
0.000513 |
| PTGS1 |
8 |
4 |
0.000256 |
| AKR1B1 |
7 |
2 |
0.000056 |
| FABP1 |
7 |
18 |
0.001893 |
| CETP |
6 |
6 |
0.000569 |
| F7 |
5 |
32 |
0.005104 |
| PIK3CG |
4 |
2 |
0.000214 |
| ACHE |
4 |
6 |
0.000341 |
| ADRB2 |
3 |
0 |
0.000000 |
| NR3C2 |
3 |
8 |
0.000383 |
| SERPIND1 |
2 |
0 |
0.000000 |
| LYZ |
1 |
0 |
0.000000 |
| SOAT1 |
1 |
0 |
0.000000 |
3.4. CTP visualization of Cytoscape
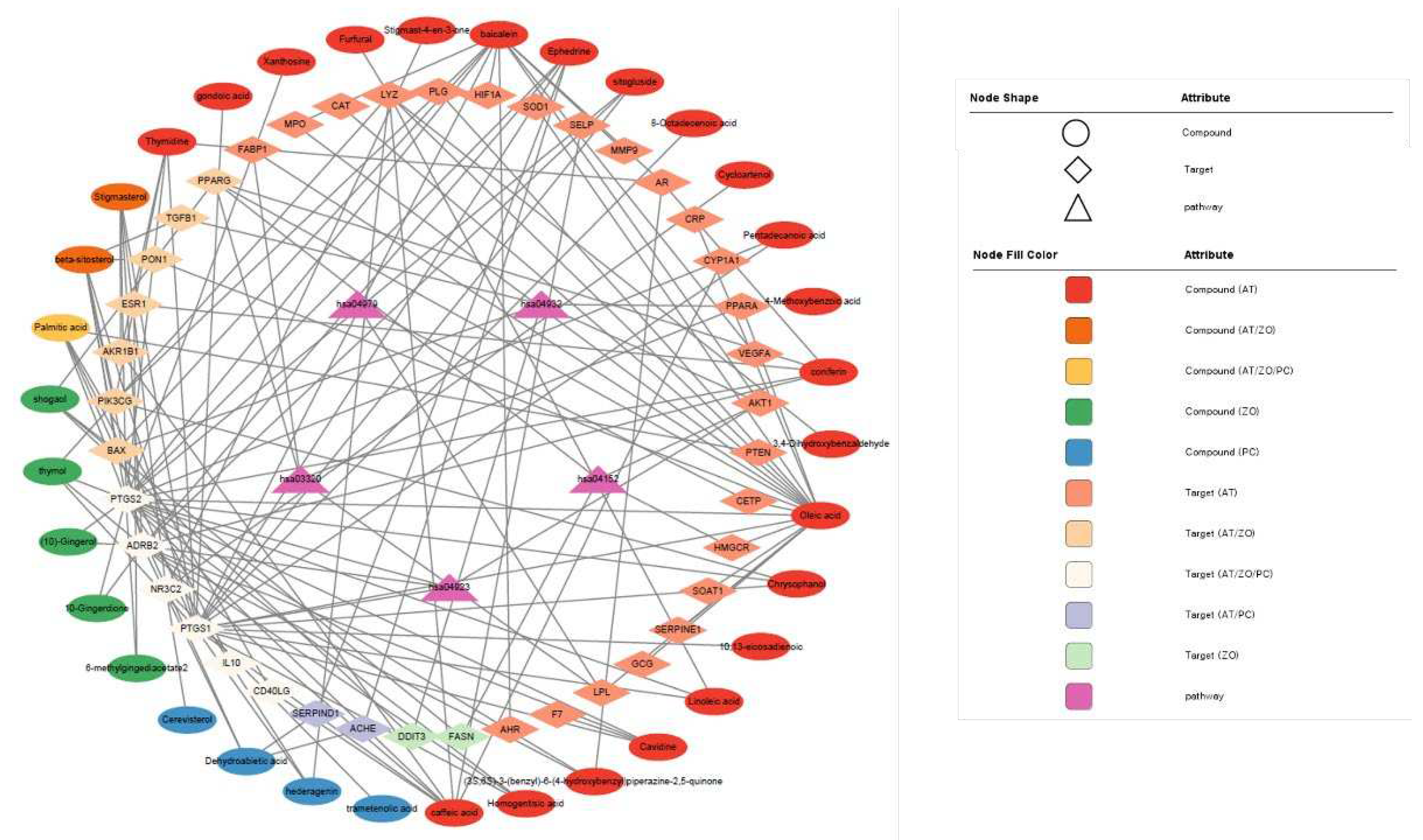
Forty-one targets were analyzed through the KEGG pathway. Based on this, the Compound-Target-Pathway network was visualized in Cytoscape (
Figure 3). The top five pathways expected to be effective for hyperlipidemia were identified by importing 41 targets into the DAVID database. Each node was connected to the edges of the Compound, target, and pathways that are expected to be correlated with each other. Table 3 lists the top enriched KEGG pathways related to lipid metabolism analyzed using the target gene list.
Table 3.
Enriched KEGG Pathway result obtained from DAVID database.
Table 3.
Enriched KEGG Pathway result obtained from DAVID database.
| |
KEGG Pathway |
| Entry |
Pathway |
FDR |
Genes |
| hsa04923 |
Regulation of lipolysis in adipocytes |
0.00039 |
AKT1, PTGS1, PTGS2, ADRB2 |
| hsa04932 |
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
0.00054 |
AKT1, BAX, DDIT3, PPARA, TGFB1 |
| hsa03320 |
PPAR signaling pathway |
0.00062 |
FABP1, LPL, PPARA, PPARG |
| hsa04152 |
AMPK signaling pathway |
0.0019 |
AKT1, FASN, HMGCR, PPARG |
| hsa04979 |
Cholesterol metabolism |
0.0023 |
CETP, LPL, SOAT1 |
3.5. Network analysis using ClueGO, CluePedia
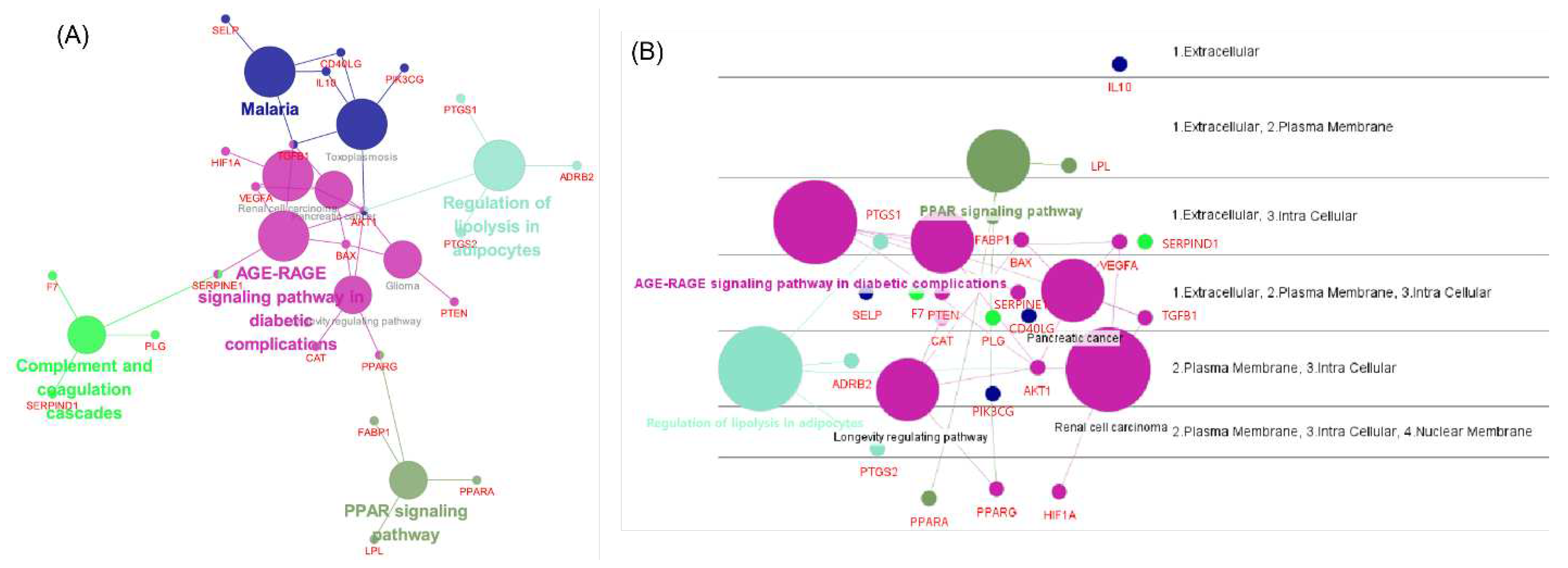
Using the full target list of the herbal combination, the network of major pathways and its component targets was visualized using ClueGO and CluePedia in Cytoscape (Figure.4). The ClueGO network could identify and visualize the interaction of pathways and consisting targets. As a result, the pathway of the ‘AGE-RAGE signaling pathway in diabetic complication’ was interconnecting two other significant pathways in lipid disorders, such as ‘regulation of lipolysis in adipocytes’ and ‘PPAR signaling pathway’, with the core target of AKT1 or PPARG (
Figure 4A). In addition, CluePedia illustrated the layout of the disposition of major pathways and their component genes according to their cellular layer of localization (
Figure 4B).
3.6. BP and KEGG enrichment analysis
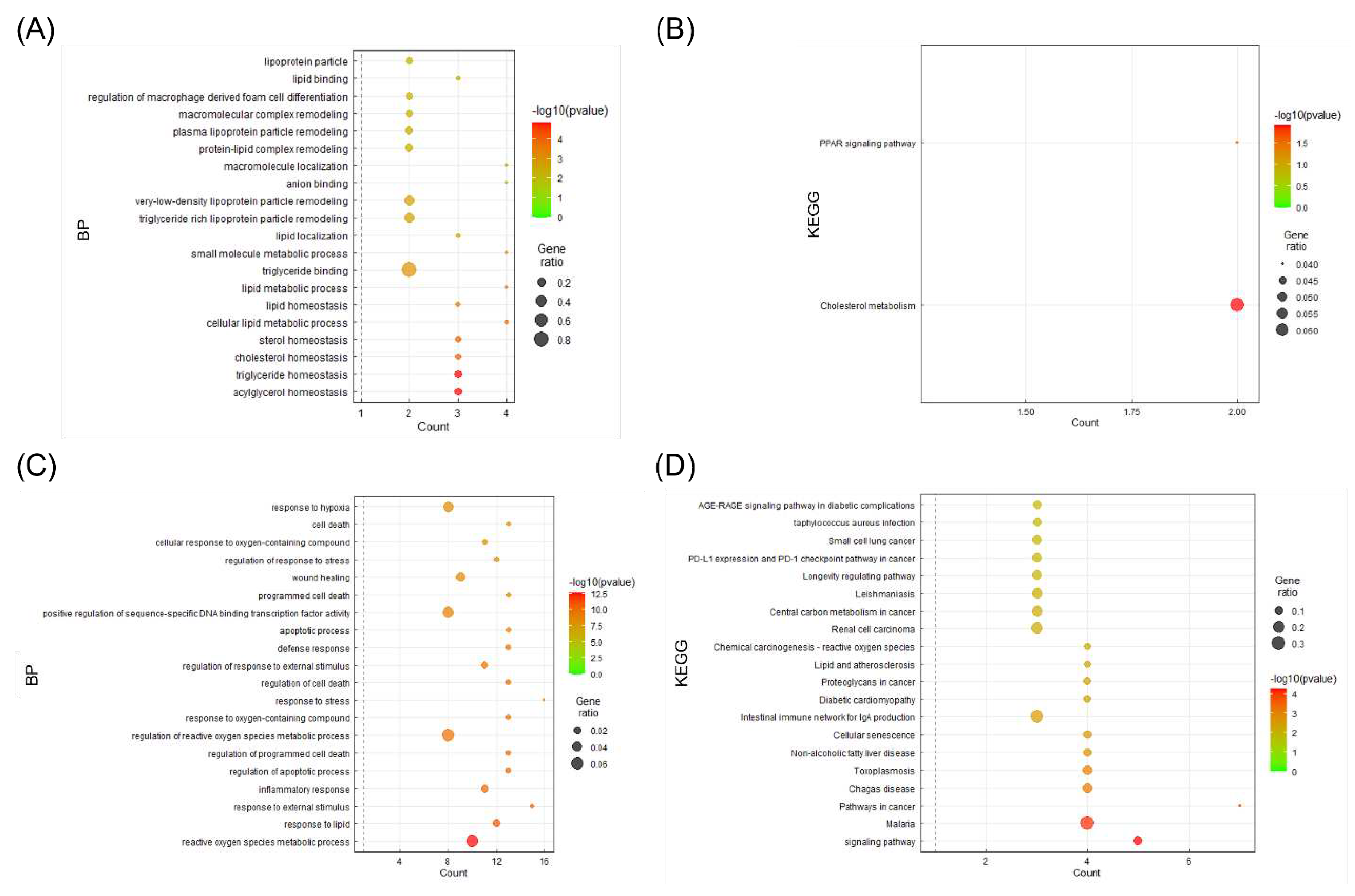
For detailed analysis among the 41 targets, two clusters divided through Cytoscape’s MCODE app were analyzed to obtain information on the pathways of the candidate targets through the KEGG pathway analysis in the DAVID Database, and each cluster was represented using the bubble plot of the GGPlot2 package (
Figure 5). A and B are the results of cluster 1, confirming that they had significant results on cholesterol, triglyceride, PPAR signaling pathway, and cholesterol metabolism. C and D are the results of cluster 2. Significant results were confirmed for lipid response, non-alcoholic fatty liver, and atherosclerotic disease.
3.7. Visualization of the target-chemical interaction using STITCH
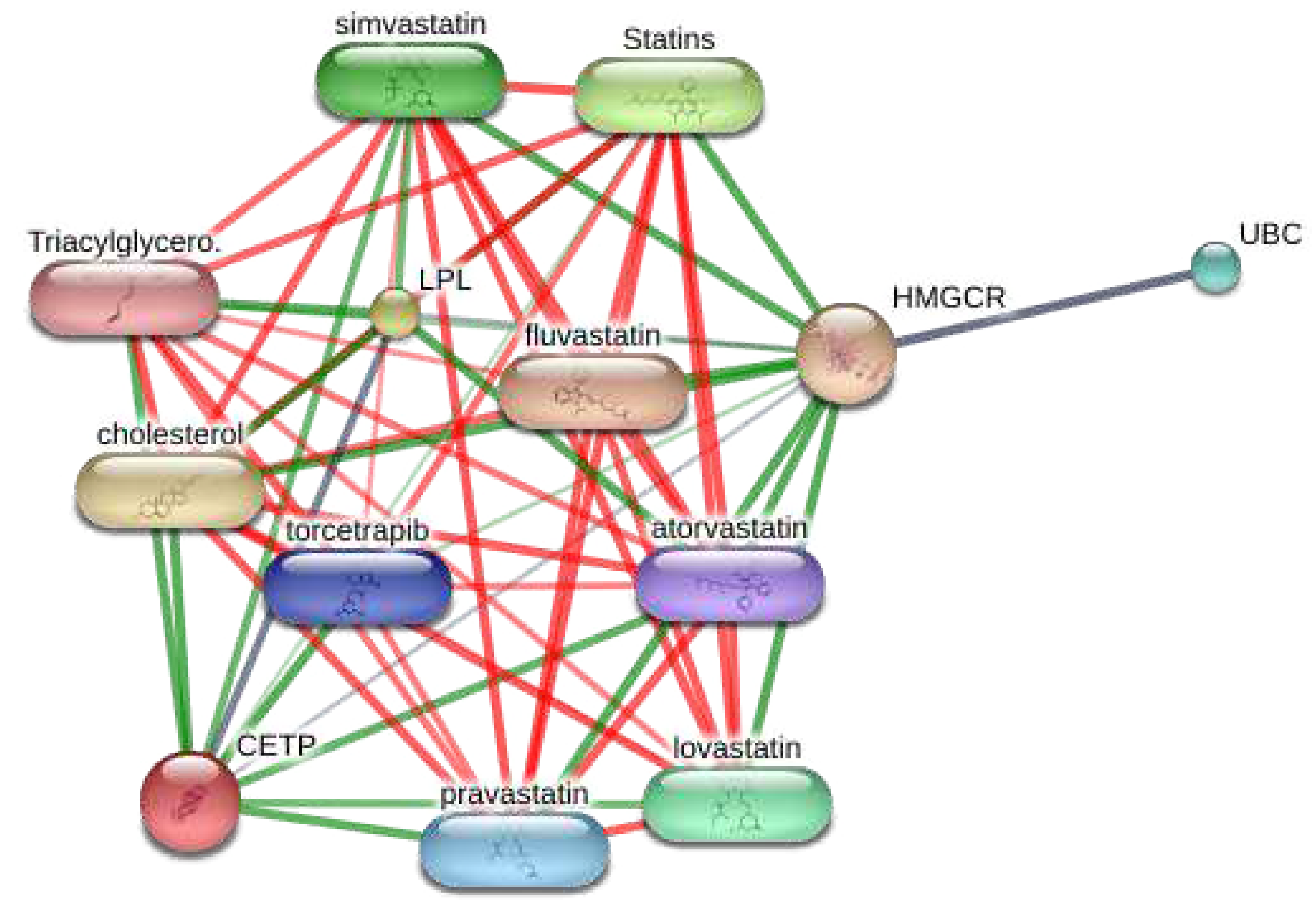
As the enrichment analysis results from the functional cluster indicated the significant potential of targets on lipid disorders, this study investigated the chemical-target network in the STITCH database (
Figure 6). As a result, the targets from cluster 1 harbor strong interactions with various statins currently used.
3.8. AT, PC, ZO, and mixed extract (MIX) improved the energy metabolism-related proteins in the hepatic steatosis model.
The HepG2 cells did not show any significant decrease in viability at <50 µg/ml (93.96%, 96.37%, 95.84%, and 95.42% at 50 µg/ml of AT, PC, ZO, and MIX, respectively) (
Figure 7A). The influence on the protein expression of ACC, AMPK, AKT, and CPT-1 was investigated in the steatosis model. At 50 µg/ml, AT and PC stimulated the phosphorylation of ACC, AMPK, and AKT and increased CPT-1 expression related to fatty acid oxidation. In addition, ZO promoted the phosphorylation of AMPK and AKT, and the expression of CPT-1. In particular, MIX strongly upregulated AKT, AMPK, and CPT-1, comparable to their effects of AT, PC, and ZO at 50 µg/ml (
Figure 7B).
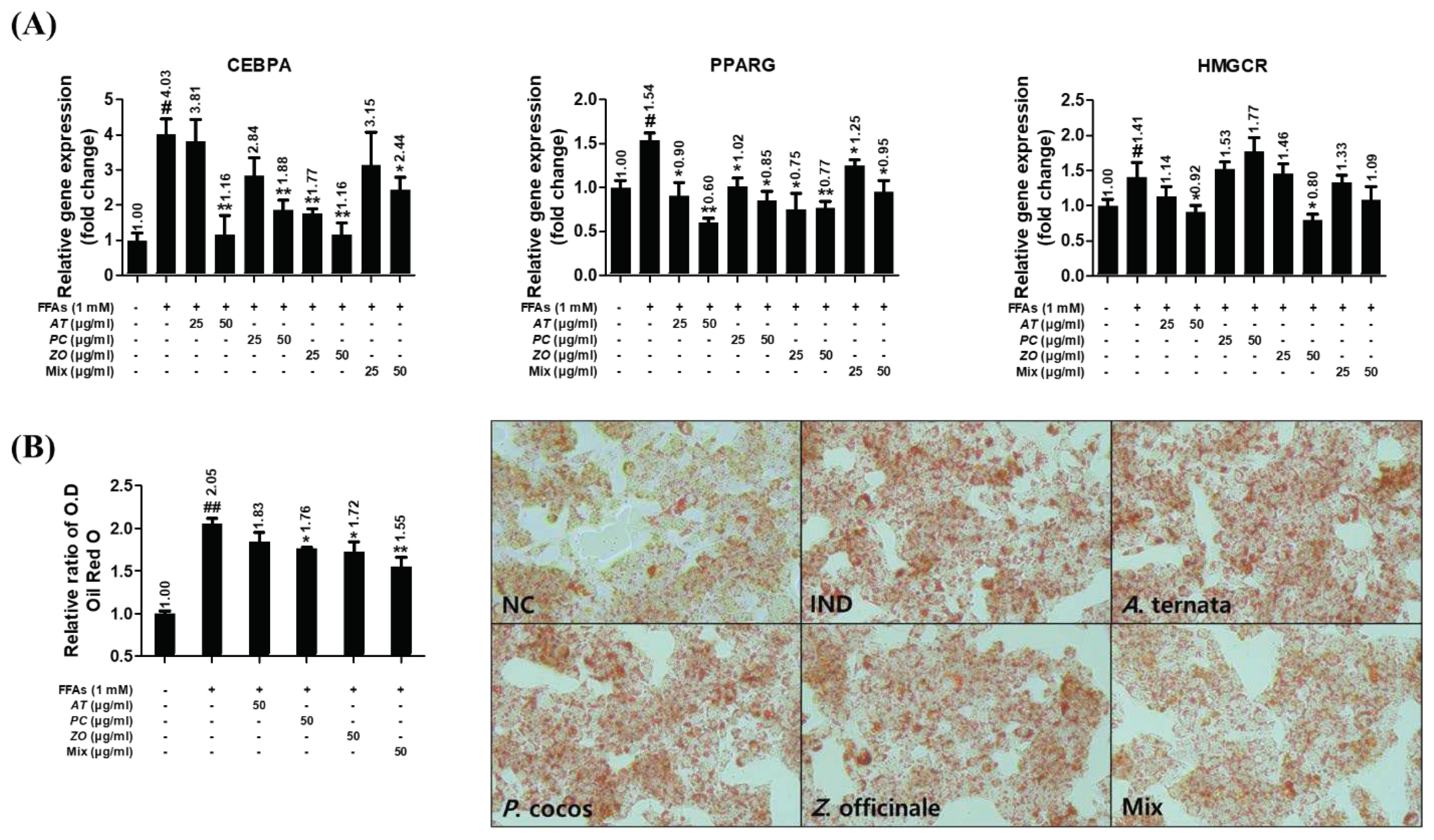
3.9. AT, PC, and ZO regulated the expression of genes related to lipogenesis and reduced FFAs-induced intracellular lipid accumulation.
The influence of herbal extracts on the gene expressions of CEBPA, PPARG, and HMGCR was investigated in FFAs-induced HepG2 cells incubated with various concentrations of AT, PC, ZO, and MIX for 6 h or 48 h. HepG2 cells stimulated with 1 mM FFAs showed increased CEBPA, PPARG, and HMGCR mRNA expression. AT and ZO prevented these upregulations. The mixture of AT, PC, and ZO regulated these, excluding the mRNA expression of HMGCR (
Figure 8A). Furthermore, the Oil Red O staining result showed superior efficacy of MIX in reducing lipid accumulation both in optical density and microscopic analysis (
Figure 8B).
4. Discussion
The holistic effects of herbal medicines were difficult to analyze because of their complex multi-components in extracts [54]. As the therapeutic efficacy is based on the combined effects of mixed compounds, it was necessary to understand the complex interaction between multi-compounds from the herbal medicines and multi-targets of its compounds [55]. On the other hand, drug discovery is challenging and time-consuming using conventional experiment-based screening methodologies [56].
In recent studies of oriental medicine, the network pharmacological approach allowed an examination of the complex mechanisms of activity exerted by multiple compounds and to predict the pharmacological activity [13]. In recent studies of oriental medicine, however, the network pharmacological approach allowed an understanding of the complex mechanisms of activity exerted by multiple compounds and an ability to predict the pharmacological activity [57,58]. Several studies investigated the impact of natural products on hyperlipidemia using network pharmacology [15,59,60], but studies investigating herbal prescriptions (or combination) are relatively rare. This study deduced the targets, estimated to have a significant impact on hyperlipidemia based on the in silico study using network pharmacology analysis, and validated the real impact by performing an in vitro study. In the present study, herbal combination exerted stronger activity than single herbs on hyperlipidemia and their related metabolic disorders, at least in certain aspects. Therefore, this result will arouse the interest of peer researchers to promote investigations on other herbal prescriptions on hyperlipidemia.
Three major herbs with potential use in hyperlipidemia and its backgrounding metabolic disorders were deduced by analyzing the composition of the prescription based on the empirical knowledge databases of oriental medicine. Network pharmacology analysis revealed the key compounds from the herb combination that can modulate multiple targets critical to certain phenotype differentiation in oriental medicine for hyperlipidemia. In detail, a seemingly complex target network (PPI network) was divided into two different functional clusters of targets (
Figure 2). Many common genes, which are closely related to the pathologic mechanisms of hyperlipidemia were shared by two KEGG pathways ‘regulation of lipolysis in adipocytes’ and ‘PPAR signaling pathway’, as investigated by ClueGO.
The lipolysis process can be defined as the hydrolysis of triacylglycerol into fatty acids and glycerol to be used as an energy source [61]. This result might explain the observation of decreased neural lipid accumulation by three herbal extracts in the hepatic steatosis model, as demonstrated by the Oil red O staining assay (
Figure 7B).
The PPAR signaling pathway plays a key role in treating dyslipidemia by modulating the lipoprotein metabolism, which is targeted by fibrates [62,63]. Furthermore, KEGG enrichment analysis of the functional clusters demonstrated its relationship with cholesterol metabolism and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (
Figure 4B,D). The enriched BP term results of these clusters are limited to cholesterol-related terms as well as triglycerides, sterol, and lipid homeostasis (
Figure 4A). This appears to be relative merit of the herbal combination to current statin treatment, of which its primary drug mechanism is to inhibit the rate-limiting enzyme for cholesterol synthesis [64]. In addition, five significantly enriched KEGG pathways (p<0.05), which are strongly involved in lipid metabolism within the rank of the top 20, were found (
Table 2).
The combinational effect was evaluated by comparing the efficacy of single extracts and mixed extract. As shown in the
in vitro data, a mixed extract of three herbs and single herb extracts against FFAs-induced hepatic steatosis had a notable effect on the lipid biosynthesis genes (
Figure 7). Moreover, as a complex mixture of bioactive compounds, it had several additional benefits on energy expenditure (by phosphorylating AMPK) or lipid catabolism (by increasing CPT1a expression) in the aspects of treating dyslipidemia-related complications (
Figure 6). On these markers, even more favorably, the mixed extract exerted enhanced efficacy than the single herb extracts. That is more advantageous when patients with hyperlipidemia usually have comorbidities of other metabolic disorders related to obesity [65,66]. In addition, the STITCH result suggested that the targets of the herbal combination have a close interaction with several statins that might imply a similar drug mechanism. Therefore, the herbal mixture might provide an option to treat hyperlipidemia with new molecular targets and mechanisms that can ameliorate metabolic disorders and ultimately alternate statins.
However, this study presented limited evidence of the possibility of the herbal combination on hyperlipidemia and other metabolic disorders. The 41 key target genes do not include the core targets related to the lipid metabolism, such as SREBF1 and SCD1 (
Table 2). Moreover, not all the targets could be validated in the experiments deduced from network pharmacology. The herbal combination sample might show efficacy in the steatosis model but not in hyperlipidemia because it could not be determined that the reduced accumulation of lipid droplets was not caused by decreased fatty acid uptake in media.
The hypolipidemic efficacy of the herbal combination needs to be validated in vivo studies. In particular, a comparative study to evaluate the overall efficacy of the herbal combination on metabolic disorders, not only for dyslipidemia, should be conducted in comparison with the current statin doses.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D-W L. and T-H K and G-R Y.; methodology, D-W L. and T-H K. and G-R Y; software, D-W L. and T-H K.; validation, D-W L. and W-H P.; formal analysis, T-H K and G-R Y.; investigation, D-W L and T-H K.; resources, W-H P. and J-E K; data curation, D-W L. and T-H K.; writing-original draft preparation, D-W L. and T-H K. and G-R Y.; writing-review and editing, J-E K. and H K.; visualization, T-H K.; supervision, D-W L. and W-H P.; project administration, D-W L. and W-H P. and H K.; funding acquisition, W-H P.; T-H K and G-R Y equally contributed to the study. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), grant number 2022R1A2C1010265.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea by the ministry of education (Grant no.: 2022R1A2C1010265).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- He, N.; Ye, H. Exercise and hyperlipidemia. Physical Exercise for Human Health 2020, 79-90.
- Organization, W.H. The world health report 2002: reducing risks, promoting healthy life; World Health Organization: 2002.
- Song, D.-x.; Jiang, J.-g. Hypolipidemic components from medicine food homology species used in China: pharmacological and health effects. Archives of Medical Research 2017, 48, 569-581. [CrossRef]
- Jain, K.S.; Kathiravan, M.; Somani, R.S.; Shishoo, C.J. The biology and chemistry of hyperlipidemia. Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry 2007, 15, 4674-4699. [CrossRef]
- Ruixing, Y.; Jinzhen, W.; Weixiong, L.; Yuming, C.; Dezhai, Y.; Shangling, P. The environmental and genetic evidence for the association of hyperlipidemia and hypertension. Journal of hypertension 2009, 27, 251-258. [CrossRef]
- Naukkarinen, J.; Ehnholm, C.; Peltonen, L. Genetics of familial combined hyperlipidemia. Current opinion in lipidology 2006, 17, 285-290. [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Hoang, T.; Lee, S.; Kim, J. Association Between Dietary Patterns and Dyslipidemia in Korean Women. Frontiers in Nutrition 2021, 8. [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, D.; Qureshi, A.; Ghosh, S.; Ashish, K.; Heise, L.R.; Hajra, A.; Ghosh, R.K. Safety and efficacy of extremely low LDL-cholesterol levels and its prospects in hyperlipidemia management. Journal of lipids 2018, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Shattat, G.F. A review article on hyperlipidemia: types, treatments and new drug targets. Biomedical and Pharmacology Journal 2015, 7, 399-409. [CrossRef]
- Thompson, P.D.; Panza, G.; Zaleski, A.; Taylor, B. Statin-associated side effects. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 2016, 67, 2395-2410.
- Brault, M.; Ray, J.; Gomez, Y.-H.; Mantzoros, C.S.; Daskalopoulou, S.S. Statin treatment and new-onset diabetes: a review of proposed mechanisms. Metabolism 2014, 63, 735-745. [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Xu, C.-B. Statins and new-onset diabetes mellitus: LDL receptor may provide a key link. Frontiers in Pharmacology 2017, 8, 372. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhu, X.; Bai, H.; Ning, K. Network pharmacology databases for traditional Chinese medicine: review and assessment. Frontiers in pharmacology 2019, 10, 123. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Li, S. Network-based relating pharmacological and genomic spaces for drug target identification. PloS one 2010, 5, e11764. [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Bhattacharjee, P.; Kar, A.; Mukherjee, P.K. LC–MS/MS analysis and network pharmacology of Trigonella foenum-graecum–A plant from Ayurveda against hyperlipidemia and hyperglycemia with combination synergy. Phytomedicine 2019, 60, 152944. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Guo, S.; Yang, J.; Tang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Ren, S. An Objective Diagnosis Model with Integrated Metabolic and Immunity Parameters for Phlegm-Dampness Constitution. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2022, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.-H.; Zhang, P.; Tao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cao, G.; Zhou, L.; Yang, C.-H. Banxia Baizhu Tianma decoction attenuates obesity-related hypertension. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 2021, 266, 113453. [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.Y.; Park, W.; Kang, T.-W.; Cha, M.H.; Chun, J.M. Network pharmacology-based prediction of active compounds and molecular targets in Yijin-Tang acting on hyperlipidaemia and atherosclerosis. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 2018, 221, 151-159. [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.M.; Lee, J.; Kang, E.; Kim, H.-L.; Hwang, G.-S.; Jung, J. Lipidomic analysis reveals therapeutic effects of Yijin-Tang on high-fat/high-cholesterol diet-induced obese mice. Phytomedicine 2020, 74, 152936. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Tong, H.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, T. Potential mechanisms for traditional Chinese medicine in treating airway mucus hypersecretion associated with coronavirus disease 2019. Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences 2020, 7, 577285.
- Liu, N.; Huo, G.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X. Effect of Zingiber OfficinaleRosc on lipid peroxidation in hyperlipidemia rats. Wei sheng yan jiu= Journal of Hygiene Research 2003, 32, 22-23.
- Chen, H.; Chen, L.; Tang, D.-D.; Chen, D.-Q.; Miao, H.; Zhao, Y.-Y.; Ma, S.-C. Metabolomics reveals hyperlipidemic biomarkers and antihyperlipidemic effect of Poria cocos. Current Metabolomics 2016, 4, 104-115. [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-J.; Shin, Y.-O.; Ha, Y.-W.; Lee, S.; Oh, J.-K.; Kim, Y.S. Anti-obesity effect of Pinellia ternata extract in Zucker rats. Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 2006, 29, 1278-1281. [CrossRef]
- Nemes, K.; Åberg, F. Interpreting lipoproteins in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Current opinion in lipidology 2017, 28, 355-360. [CrossRef]
- Hydes, T.; Alam, U.; Cuthbertson, D.J. The impact of macronutrient intake on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): too much fat, too much carbohydrate, or just too many calories? Frontiers in nutrition 2021, 8, 640557. [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Guo, W.-L.; Li, Q.-Y.; Xu, J.-X.; Cao, Y.-J.; Liu, B.; Yu, X.-D.; Rao, P.-F.; Ni, L.; Lv, X.-C. The protective mechanism of Lactobacillus plantarum FZU3013 against non-alcoholic fatty liver associated with hyperlipidemia in mice fed a high-fat diet. Food & function 2020, 11, 3316-3331. [CrossRef]
- Deprince, A.; Haas, J.T.; Staels, B. Dysregulated lipid metabolism links NAFLD to cardiovascular disease. Molecular metabolism 2020, 42, 101092. [CrossRef]
- Świderska, E.; Strycharz, J.; Wróblewski, A.; Szemraj, J.; Drzewoski, J.; Śliwińska, A. Role of PI3K/AKT pathway in insulin-mediated glucose uptake. Blood Glucose Levels 2018, 1, 1-18.
- Ferreira, D.; Castro, R.; Machado, M.; Evangelista, T.; Silvestre, A.; Costa, A.; Coutinho, J.; Carepa, F.; Cortez-Pinto, H.; Rodrigues, C. Apoptosis and insulin resistance in liver and peripheral tissues of morbidly obese patients is associated with different stages of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Diabetologia 2011, 54, 1788-1798. [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Li, S.; Na, L.; Feng, R.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Sun, C. Mangiferin decreases plasma free fatty acids through promoting its catabolism in liver by activation of AMPK. PLoS one 2012, 7, e30782. [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.H.; Kim, S.G. AMPK-dependent metabolic regulation by PPAR agonists. PPAR research 2010, 2010. [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Jing, F.; Yu, C.; Gao, L.; Qin, Y.; Zhao, J. AICAR-induced activation of AMPK inhibits TSH/SREBP-2/HMGCR pathway in liver. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0124951.
- Vecchione, G.; Grasselli, E.; Compalati, A.D.; Ragazzoni, M.; Cortese, K.; Gallo, G.; Voci, A.; Vergani, L. Ethanol and fatty acids impair lipid homeostasis in an in vitro model of hepatic steatosis. Food and Chemical Toxicology 2016, 90, 84-94. [CrossRef]
- Ru, J.; Li, P.; Wang, J.; Zhou, W.; Li, B.; Huang, C.; Li, P.; Guo, Z.; Tao, W.; Yang, Y. TCMSP: a database of systems pharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines. Journal of cheminformatics 2014, 6, 1-6.
- Xu, X.; Zhang, W.; Huang, C.; Li, Y.; Yu, H.; Wang, Y.; Duan, J.; Ling, Y. A novel chemometric method for the prediction of human oral bioavailability. International journal of molecular sciences 2012, 13, 6964-6982. [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.; Xu, X.; Wang, X.; Li, B.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, L. Network pharmacology-based prediction of the active ingredients and potential targets of Chinese herbal Radix Curcumae formula for application to cardiovascular disease. Journal of ethnopharmacology 2013, 145, 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Yue, S.-J.; Liu, J.; Feng, W.-W.; Zhang, F.-L.; Chen, J.-X.; Xin, L.-T.; Peng, C.; Guan, H.-S.; Wang, C.-Y.; Yan, D. System pharmacology-based dissection of the synergistic mechanism of Huangqi and Huanglian for diabetes mellitus. Frontiers in Pharmacology 2017, 8, 694. [CrossRef]
- Safran, M.; Dalah, I.; Alexander, J.; Rosen, N.; Iny Stein, T.; Shmoish, M.; Nativ, N.; Bahir, I.; Doniger, T.; Krug, H. GeneCards Version 3: the human gene integrator. Database 2010, 2010. [CrossRef]
- Piñero, J.; Queralt-Rosinach, N.; Bravo, A.; Deu-Pons, J.; Bauer-Mehren, A.; Baron, M.; Sanz, F.; Furlong, L.I. DisGeNET: a discovery platform for the dynamical exploration of human diseases and their genes. Database 2015, 2015. [CrossRef]
- Bardou, P.; Mariette, J.; Escudié, F.; Djemiel, C.; Klopp, C. jvenn: an interactive Venn diagram viewer. BMC bioinformatics 2014, 15, 1-7. [CrossRef]
- Cline, M.S.; Smoot, M.; Cerami, E.; Kuchinsky, A.; Landys, N.; Workman, C.; Christmas, R.; Avila-Campilo, I.; Creech, M.; Gross, B. Integration of biological networks and gene expression data using Cytoscape. Nature protocols 2007, 2, 2366-2382. [CrossRef]
- Bindea, G.; Galon, J.; Mlecnik, B. CluePedia Cytoscape plugin: pathway insights using integrated experimental and in silico data. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 661-663. [CrossRef]
- Bindea, G.; Mlecnik, B.; Hackl, H.; Charoentong, P.; Tosolini, M.; Kirilovsky, A.; Fridman, W.-H.; Pagès, F.; Trajanoski, Z.; Galon, J. ClueGO: a Cytoscape plug-in to decipher functionally grouped gene ontology and pathway annotation networks. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1091-1093. [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Lyon, D.; Junge, A.; Wyder, S.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Doncheva, N.T.; Morris, J.H.; Bork, P. STRING v11: protein–protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets. Nucleic acids research 2019, 47, D607-D613.
- Szklarczyk, D.; Santos, A.; Von Mering, C.; Jensen, L.J.; Bork, P.; Kuhn, M. STITCH 5: augmenting protein–chemical interaction networks with tissue and affinity data. Nucleic acids research 2016, 44, D380-D384.
- Dennis, G.; Sherman, B.T.; Hosack, D.A.; Yang, J.; Gao, W.; Lane, H.C.; Lempicki, R.A. DAVID: database for annotation, visualization, and integrated discovery. Genome biology 2003, 4, 1-11.
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of the Royal statistical society: series B (Methodological) 1995, 57, 289-300. [CrossRef]
- Bonnot, T.; Gillard, M.B.; Nagel, D.H. A simple protocol for informative visualization of enriched gene ontology terms. Bio-protocol 2019, e3429-e3429. [CrossRef]
- Lim, D.-W.; Kim, H.; Lee, S.-J.; Yu, G.-R.; Kim, J.-E.; Park, W.-H. Jwa Kum Whan attenuates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by modulating glucose metabolism and the insulin signaling pathway. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2019, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.R.; Lim, D.W.; Karunarathne, W.A.H.M.; Kim, G.Y.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.E.; Park, W.H. A non-polar fraction of Saponaria officinalis L. acted as a TLR4/MD2 complex antagonist and inhibited TLR4/MyD88 signaling in vitro and in vivo. The FASEB Journal 2022, 36, e22387.
- Yu, G.-R.; Lee, S.-J.; Kim, D.-H.; Lim, D.-W.; Kim, H.; Park, W.-H.; Kim, J.-E. Literature-based drug repurposing in traditional Chinese medicine: Reduced inflammatory M1 macrophage polarization by Jisil Haebaek Gyeji-Tang alleviates cardiovascular disease in vitro and ex vivo. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2020, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Ren, N.; Li, S.; Chen, M.; Pu, P. Novel anti-obesity effect of scutellarein and potential underlying mechanism of actions. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2019, 117, 109042. [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.-R.; Liu, J.; Plumeri, D.; Cao, Y.-B.; He, T.; Lin, L.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Y.-Y.; Li, J.; Shang, J. Lipotoxicity in HepG2 cells triggered by free fatty acids. American journal of translational research 2011, 3, 284.
- Long, F.; Yang, H.; Xu, Y.; Hao, H.; Li, P. A strategy for the identification of combinatorial bioactive compounds contributing to the holistic effect of herbal medicines. Scientific reports 2015, 5, 1-11. [CrossRef]
- Efferth, T.; Koch, E. Complex interactions between phytochemicals. The multi-target therapeutic concept of phytotherapy. Current drug targets 2011, 12, 122-132. [CrossRef]
- Lahlou, M. Screening of natural products for drug discovery. Expert opinion on drug discovery 2007, 2, 697-705. [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X.; Jin, X.; Ma, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Liang, L.; Liu, R.; Li, Z. A comprehensive application: molecular docking and network pharmacology for the prediction of bioactive constituents and elucidation of mechanisms of action in component-based Chinese medicine. Computational Biology and Chemistry 2021, 90, 107402. [CrossRef]
- Poornima, P.; Kumar, J.D.; Zhao, Q.; Blunder, M.; Efferth, T. Network pharmacology of cancer: From understanding of complex interactomes to the design of multi-target specific therapeutics from nature. Pharmacological Research 2016, 111, 290-302. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.-t.; Liu, S.-y.; Kuang, Y.-j.; Jiang, Z.-m.; Lin, Y.; Xie, Z.-s.; Liu, E.-H. Network pharmacology analysis and experimental validation to explore the mechanism of sea buckthorn flavonoids on hyperlipidemia. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 2021, 264, 113380. [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Li, L.; Hu, Z. Exploring the molecular mechanism of action of Yinchen Wuling powder for the treatment of hyperlipidemia, using network pharmacology, molecular docking, and molecular dynamics simulation. BioMed research international 2021, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Duncan, R.E.; Ahmadian, M.; Jaworski, K.; Sarkadi-Nagy, E.; Sul, H.S. Regulation of lipolysis in adipocytes. Annual review of nutrition 2007, 27, 79. [CrossRef]
- Kersten, S. Peroxisome proliferator activated receptors and lipoprotein metabolism. PPAR research 2008, 2008. [CrossRef]
- Grundy, S.M.; Vega, G.L. Fibric acids: effects on lipids and lipoprotein metabolism. The American journal of medicine 1987, 83, 9-20. [CrossRef]
- Ginsberg, H.N. Effects of statins on triglyceride metabolism. The American journal of cardiology 1998, 81, 32B-35B. [CrossRef]
- Bozkurt, B.; Aguilar, D.; Deswal, A.; Dunbar, S.B.; Francis, G.S.; Horwich, T.; Jessup, M.; Kosiborod, M.; Pritchett, A.M.; Ramasubbu, K. Contributory risk and management of comorbidities of hypertension, obesity, diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, and metabolic syndrome in chronic heart failure: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2016, 134, e535-e578. [CrossRef]
- Ul-Haq, Z.; Mackay, D.F.; Fenwick, E.; Pell, J.P. Impact of metabolic comorbidity on the association between body mass index and health-related quality of life: a Scotland-wide cross-sectional study of 5,608 participants. BMC Public Health 2012, 12, 1-7. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Venn diagrams of the compounds and target genes from the herbal combination. (A) Distribution of potential compounds from PC, AT, and ZO. (B) Target of potential form PC, AT, and ZO (C) Hyperlipidemia-related target genes from two web databases. (D) Dyslipidemia-related common target genes from both web databases and TCMSP.
Figure 1.
Venn diagrams of the compounds and target genes from the herbal combination. (A) Distribution of potential compounds from PC, AT, and ZO. (B) Target of potential form PC, AT, and ZO (C) Hyperlipidemia-related target genes from two web databases. (D) Dyslipidemia-related common target genes from both web databases and TCMSP.
Figure 2.
(A) Full protein-protein interaction network of 41 hyperlipidemia-related target genes from the herbal combination. (B), (C) Functional cluster of full PPI network created from MCODE of Cytoscape.
Figure 2.
(A) Full protein-protein interaction network of 41 hyperlipidemia-related target genes from the herbal combination. (B), (C) Functional cluster of full PPI network created from MCODE of Cytoscape.
Figure 3.
Visualization of the compounds-targets-pathways network constructed with the components of the herbal combination.
Figure 3.
Visualization of the compounds-targets-pathways network constructed with the components of the herbal combination.
Figure 4.
Visualization of the KEGG pathways and targets of the herbal combination analyzed by ClueGO and CluePedia. (A) Visualization of significantly enriched KEGG pathways and their consisting genes (created with ClueGO) (B) Cerebral layout of significant KEGG pathways and their consisting genes by their cellular compartment (created with CluePedia).
Figure 4.
Visualization of the KEGG pathways and targets of the herbal combination analyzed by ClueGO and CluePedia. (A) Visualization of significantly enriched KEGG pathways and their consisting genes (created with ClueGO) (B) Cerebral layout of significant KEGG pathways and their consisting genes by their cellular compartment (created with CluePedia).
Figure 5.
Bubble plot visualization of enrichment analysis (BP terms and KEGG pathways) from two target clusters from the herbal combination. Significant (A) BP terms and (B) KEGG pathways of target cluster 1. Significant (C) BP terms and (D) KEGG pathways of target cluster 2.
Figure 5.
Bubble plot visualization of enrichment analysis (BP terms and KEGG pathways) from two target clusters from the herbal combination. Significant (A) BP terms and (B) KEGG pathways of target cluster 1. Significant (C) BP terms and (D) KEGG pathways of target cluster 2.
Figure 6.
Visualization of the target-chemical interaction of targets from cluster 1 using the STITCH database.
Figure 6.
Visualization of the target-chemical interaction of targets from cluster 1 using the STITCH database.
Figure 7.
AT, PC, ZO, and MIX stimulate ACC, AMPK, and AKT phosphorylation in FFAs-induced hepatic steatosis and activate CPT-1 related to fatty acid oxidation. HepG2 cells were incubated in the absence or presence of FFAs (1 mM) with AT, PC, ZO, and MIX for 24 hours. (A) HepG2 cells were treated with various concentrations (0–50 µg/ml) of AT, PC, ZO, and MIX for 24 h. The results are presented as means ± SDs of the percentages determined by three independent experiments versus the non-treated controls. (B) HepG2 cells were co-treated with each sample and FFAs for 24 h. Western blot analysis showing the effect on the phosphorylation of ACC and AMPK and AKT protein expression related to the energy metabolism and lipogenesis in FFAs-induced hepatic steatosis HepG2 cells. The band intensities were measured by densitometry and normalized versus the intensities of the total forms and β-actin. The results are presented as the means ± SDs of three independent experiments. #p < .05 versus FFAs-treated controls, and *p < .05, **p < .01 versus FFAs-treated HepG2 cells.
Figure 7.
AT, PC, ZO, and MIX stimulate ACC, AMPK, and AKT phosphorylation in FFAs-induced hepatic steatosis and activate CPT-1 related to fatty acid oxidation. HepG2 cells were incubated in the absence or presence of FFAs (1 mM) with AT, PC, ZO, and MIX for 24 hours. (A) HepG2 cells were treated with various concentrations (0–50 µg/ml) of AT, PC, ZO, and MIX for 24 h. The results are presented as means ± SDs of the percentages determined by three independent experiments versus the non-treated controls. (B) HepG2 cells were co-treated with each sample and FFAs for 24 h. Western blot analysis showing the effect on the phosphorylation of ACC and AMPK and AKT protein expression related to the energy metabolism and lipogenesis in FFAs-induced hepatic steatosis HepG2 cells. The band intensities were measured by densitometry and normalized versus the intensities of the total forms and β-actin. The results are presented as the means ± SDs of three independent experiments. #p < .05 versus FFAs-treated controls, and *p < .05, **p < .01 versus FFAs-treated HepG2 cells.
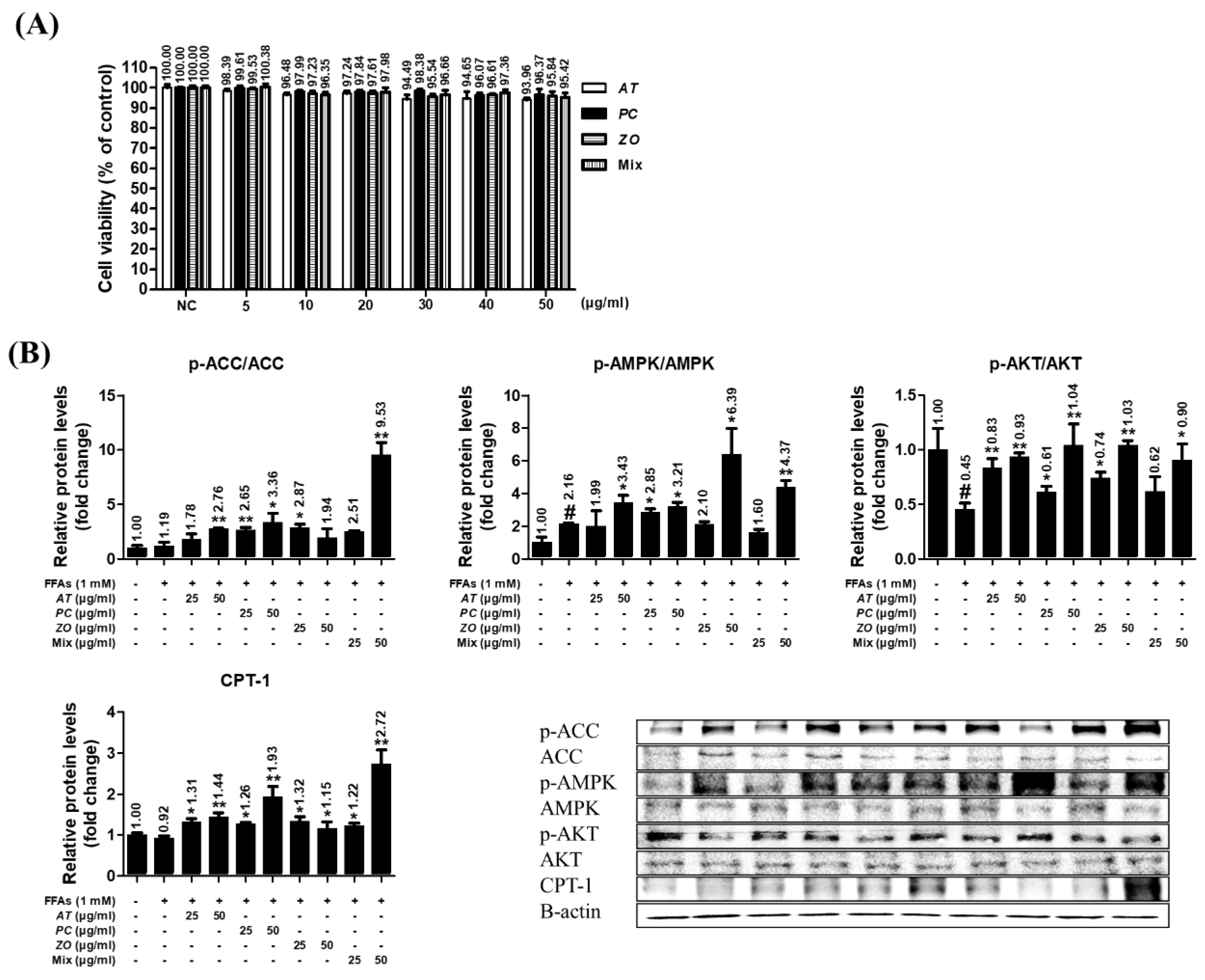
Figure 8.
AT, PC, ZO, and MIX ameliorate lipogenesis in FFAs-induced hepatic steatosis HepG2 cells. HepG2 cells were incubated in the absence or presence of FFAs (1 mM) with AT, PC, ZO, and MIX for six or 48 hours. (A) Relative expressions of CEBPA, PPARγ, ACC, and HMGCR genes were determined by qPCR. (B) The impact on lipid accumulation was evaluated by measuring the Oil Red O stain and comparing the microscopic images. Representative images (100×) of lipid accumulation by Oil Red O staining in HepG2 cells under different conditions. The results are presented as the means ± SDs of three independent experiments. #p < .05, ##p < .01 versus the FFAs-treated controls, and *p < .05, **p < .01 versus FFAs-treated HepG2 cells.
Figure 8.
AT, PC, ZO, and MIX ameliorate lipogenesis in FFAs-induced hepatic steatosis HepG2 cells. HepG2 cells were incubated in the absence or presence of FFAs (1 mM) with AT, PC, ZO, and MIX for six or 48 hours. (A) Relative expressions of CEBPA, PPARγ, ACC, and HMGCR genes were determined by qPCR. (B) The impact on lipid accumulation was evaluated by measuring the Oil Red O stain and comparing the microscopic images. Representative images (100×) of lipid accumulation by Oil Red O staining in HepG2 cells under different conditions. The results are presented as the means ± SDs of three independent experiments. #p < .05, ##p < .01 versus the FFAs-treated controls, and *p < .05, **p < .01 versus FFAs-treated HepG2 cells.
Table 1.
Compounds of Zingiber officinale, Poria cocos and Arum ternata.
Table 1.
Compounds of Zingiber officinale, Poria cocos and Arum ternata.
| Compound List |
| Herb |
Name |
CID |
OB |
DL |
Zingiber officinale
(ZO) |
(10)-Gingerol |
168115 |
19.14 |
0.28 |
| 10-Gingerdione |
5317591 |
21.42 |
0.29 |
| 6-methylgingediacetate2 |
53179662 |
48.73 |
0.32 |
| shogaol |
5281794 |
31.00 |
0.14 |
| poriferast-5-en-3beta-ol |
457801 |
36.91 |
0.75 |
| thymol |
6989 |
41.47 |
0.03 |
Poria cocos
(PC) |
Cerevisterol |
10181133 |
37.96 |
0.77 |
| Dehydroabietic acid |
94391 |
14.93 |
0.28 |
| (2R)-2-[(3S,5R,10S,13R,14R,16R,17R)-3,16-dihydroxy-4,4,10,13,14-pentamethyl-2,3,5,6,12,15,16,17-octahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]-6-methylhept-5-enoic acid |
10743008 |
30.93 |
0.81 |
| Ergosterol peroxide |
5351516 |
40.36 |
0.81 |
| ergosta-7,22E-dien-3beta-ol |
5283628 |
43.51 |
0.72 |
| hederagenin |
73299 |
22.42 |
0.74 |
| trametenolic acid |
12309443 |
38.71 |
0.80 |
| Arum ternata (AT) |
(3S,6S)-3-(benzyl)-6-(4-hydroxybenzyl)piperazine-2,5-quinone |
11438306 |
46.89 |
0.27 |
| 10,13-eicosadienoic |
549062 |
39.99 |
0.20 |
| 3,4-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde |
8768 |
38.35 |
0.03 |
| 4-Methoxybenzoic acid |
7478 |
29.69 |
0.03 |
| 8-Octadecenoic acid |
5282758 |
33.13 |
0.14 |
| Baicalein |
5281605 |
33.52 |
0.21 |
| Xanthosine |
64959 |
44.72 |
0.21 |
| caffeic acid |
689043 |
25.76 |
0.05 |
| oct-1-ene |
8125 |
39.25 |
0.01 |
| Baicalin |
64982 |
40.12 |
0.75 |
| Choline |
305 |
0.47 |
0.01 |
| 9-oxononanoic acid |
75704 |
19.60 |
0.03 |
| docosanoic acid |
8125 |
15.69 |
0.26 |
| 9-Heptadecanol |
136435 |
14.24 |
0.09 |
| Palmitic acid |
985 |
19.30 |
0.10 |
| Baicalein |
5281605 |
33.52 |
0.21 |
| Hydroquinone |
785 |
29.26 |
0.02 |
| Anethole |
637563 |
32.49 |
0.03 |
| Adenine |
190 |
62.81 |
0.03 |
| Cavidine |
193148 |
35.64 |
0.81 |
| Chrysophanol |
10208 |
18.64 |
0.21 |
| Coniferin |
5280372 |
10.28 |
0.27 |
| Cycloartenol |
92110 |
38.69 |
0.78 |
| Ephedrine |
9294 |
43.35 |
0.03 |
| Furfural |
7362 |
34.35 |
0.01 |
| gondoic acid |
5282768 |
30.70 |
0.20 |
| Homogentisic acid |
780 |
92.44 |
0.04 |
| Linoleic acid |
5280450 |
41.90 |
0.14 |
| Oleic acid |
445639 |
33.13 |
0.14 |
| Pentadecanoic acid |
13849 |
20.18 |
0.08 |
| Sitogluside |
5742590 |
20.63 |
0.62 |
| Stigmast-4-en-3-one |
5484202 |
36.08 |
0.76 |
| Thymidine |
5789 |
11.34 |
0.11 |
| AT∩ZO |
beta-sitosterol |
222284 |
15.00 |
0.81 |
| Stigmasterol |
5280794 |
43.83 |
0.76 |
| AT∩ZO∩PC |
Palmitic acid |
985 |
19.30 |
0.10 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).