0. Introduction
In recent decades, the concepts of fractional calculus and the related techniques have been gaining momentum in circuit system fields [1–3]. It has been confirmed that, exploring the potential fractional-order characteristics of electronic components is helpful for both the condition monitoring of components and the reliability design of circuit systems [7–11]. An increasing body of evidence suggests that fractional-order characteristic is widely distributed in electronic components [4–6], such as ultracapacitors (UCs), lithium batteries, and non-solid electrolytic capacitors. Moreover, introducing fractional-order elements (or constant phase elements, CPEs) to traditional circuit and control systems can enhance the design flexibility [12–14].
In order to better describe the characteristics of circuit systems with fractional-order components, it is of necessity to develop a set of reliable calculation and analysis methods. Basically, the lumped parameter model with fractional-order differential equations is a well-established approach to quantify the characteristics of fractional-order circuit systems, and a number of calculation and analysis works have been proposed for such systems, definition-based methods [15], rational approximation methods [16–18], and numerical methods [19–21], to name but a few. The methods listed above have been applied to the modeling and analysis of a wide variety of fractional-order circuit systems [22–24].
However, to the best of the authors’ knowledge, most existing calculation and analysis methods are applied only to continuous fractional-order circuit systems, but rarely to piecewise smooth ones [25–27]. In practice, the piecewise-smooth characteristic is common in circuit systems, especially for those with semiconductor switching devices, and such characteristic may bring in effects on the accuracy of numerical methods. Therefore, it is worthwhile to compare and evaluate the effectiveness of existing methods in analyzing piecewise smooth fractional-order systems.
In allusion to state-of-the-art, this work tries to unfold the applicability of three typical calculation methods for piecewise smooth fractional-order circuit systems. The rest of the work is organized as follows: test scenarios are established in
Section 1, in which a non-solid aluminum electrolytic capacitor is employed in the test bench, since this kind of components have been confirmed to have frequency-related fractional-order characteristics in a wide frequency band [6]. Section III deduces the solutions of the test scenarios by different approaches. Section IV compares and discusses the results of different approaches, while section V concludes the work.
1. Test Bench Settings and Mathematical Model
1.1. Test Bench Settings
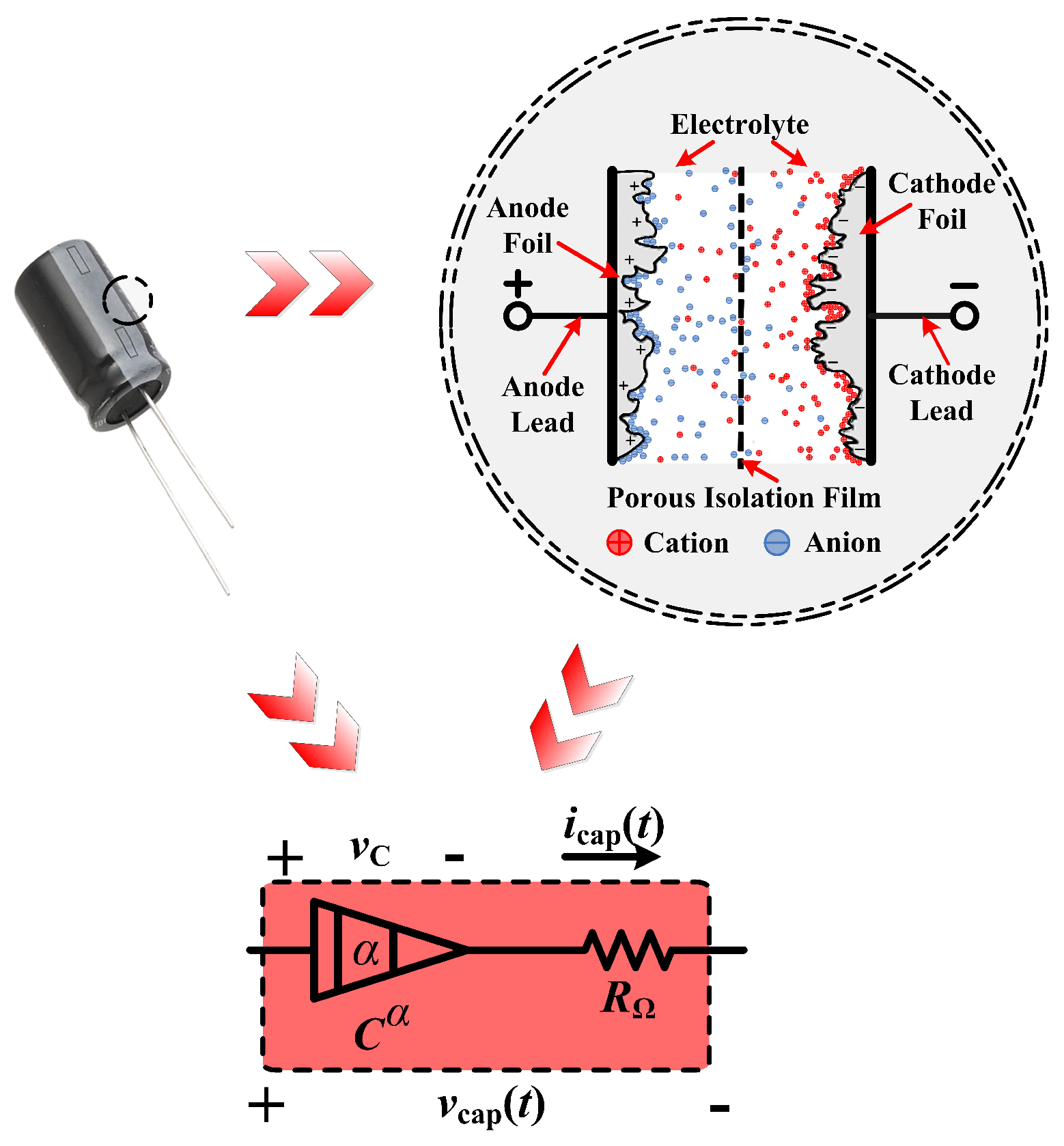
In a previous work, it has been confirm that, the electrode surface in the capacitor has an infinite self-similar structure, and the particle distribution law in it has a long-tail effect under the electric field, which is suitable to be described by the fractional equivalent impedance model [6]. The internal structure and fractional-order equivalent impedance circuit in
Figure 1:
In the above figure, the symbol
C is the nominal capacitance of the capacitor, while the symbol
is an estimated fractional order of 0 to 1, and the symbol
is the equivalent series resistance of the capacitor. Then, a test bench is established in this section, which contains such a capacitor. The schematic of this test bench is displayed is depicted in
Figure 2.
The design of the test bench refers to the previous work [28], in which a type GPS-3303C 3-channel isolated dc power supply is adopted to provide power, and an oscilloscope is employed to record the data. In the platform, a type STP80NF70 power MOSFET
is adopted, the gate-source voltage of which is controlled by a driving circuit. As a result, the test bench will work in charging and discharging cycle working mode, so the circuit can be deem as a piecewise smooth circuit system. On the right side of the red dash line in
Figure 3, the resistor
provides a discharging path for the capacitor, while
is mainly used as the current sensing and limiting resistor. The circuit in the box with red background is the fractional-order equivalent circuit of a
Rubycon PX series non-solid aluminum electrolytic capacitor. The voltage and the current of the capacitor are
and
, respectively, and two probes of the oscillascope are used to observe them. In addition, the voltage of the equivalent CPE is assumed to be
. A glimpse of the experimental scene is as
Figure 3.
1.2. Mathematical Model
The test platform can be regarded as a charge-discharge circuit for the non-solid aluminum electrolytic capacitor. One can find that, there is only one energy-storage component in the platform, so the interferences and errors are minimized compared with the schemes with rational approximation methods or those with magnetic elements. In the following parts, the test platform will be operated in two test scenarios to verify the applicability of different calculation and analysis methods.
According to the fractional-order equivalent impedance circuit of the capacitor in
Figure 1, the current
and the voltage
of the capacitor satisfy the following relationships,
It is noteworthy that the nominal capacitance C is in this work, while and the fractional order relate to the fractional-order characteristics of the capacitor can be identified by using the method proposed in a previous work [6], and in this work, their values are , , respectively.
In order to validate different methods, we established two groups of test scenarios, the basic and the advanced. In basic test group, we consider two operating modes, the first one is sinusoidal mode, where the power supply is a single phase AC power supply with a pre-determined frequency. The second one is step mode, where a DC power supply is employed as the source and the power MOSFET is turned on at time with a constant forward voltage drop .
The state of the sinusoidal mode can be governed by:
where
is a sinusoidal function.
K is the predetermined magnitude of the signal,
is the angular frequency, and
is the frequency of the sinusoidal function.
The state of the step mode can be governed by:
in which
is a predetermined constant value.
In the first group of test scenarios, the text bench works under continuous mode or step response mode. This group are used to assess the feasibility of different calculation methods.
In the second group of test scenario, the power MOSFET is controlled by a periodic square waveform with a duty ratio and a variable frequency from to . The performances of the circuit under test in one steady-state cycle can be governed by:
Charge performance in
is:
where
k is the
k-th switching cycle,
is the switching period, and
Discharge performance in
is:
and
In the second group of test scenarios, the capacitor of the test bench will be charged and discharged cycle by cycle, thus the circuit under test is a typical piecewise smooth circuit system.
One can find that, to reveal the time-domain performances of these two scenarios, the voltage
should be calculated. However, this voltage is an equivalent quantity of the CPE, thus one cannot probe it directly and has to solve fractional-order differential equations
2 to
7, which are all fractional-order differential equations with constant coefficients. Rewrite these equations to the following generalized form:
where
,
is the only state variable of the circuit, and the coefficients are:
,
,
,
,
, and
.
All the coefficients are predetermined in their own time intervals. Meanwhile, the initial conditions of Equation
8 are continuous in their own domains of definition, hence according to theorem 3.2 of literature [29], fractional-order differential Equation
8 have uniqueness solutions. At this time, the initial values problem of fractional-order differential equations arises.
2. Computation Approaches
In this section, the principles of some related techniques are introduced first. Then three different approaches will be applied to calculate equations
2 to
7, and the results will be adopted for validation and comparison. The first calculation method is a numerical calculation method, that is the fractional Adams-Bashforth-Moulton typed method (F-ABM) [21]. The second calculation method is based on Gr
nwald-Letnikov (G-L) definition [15]. To obtain solutions by using the first and the second methods, the stroboscopic map technique should be applied [30]. The third calculation method is Oustaloup’s rational approximation method [16], which will be conducted by using the state-space averaging (SSA) technique [31].
2.1. Preliminaries: Principles of Some Related Techniques
2.1.1. Stroboscopic map technique
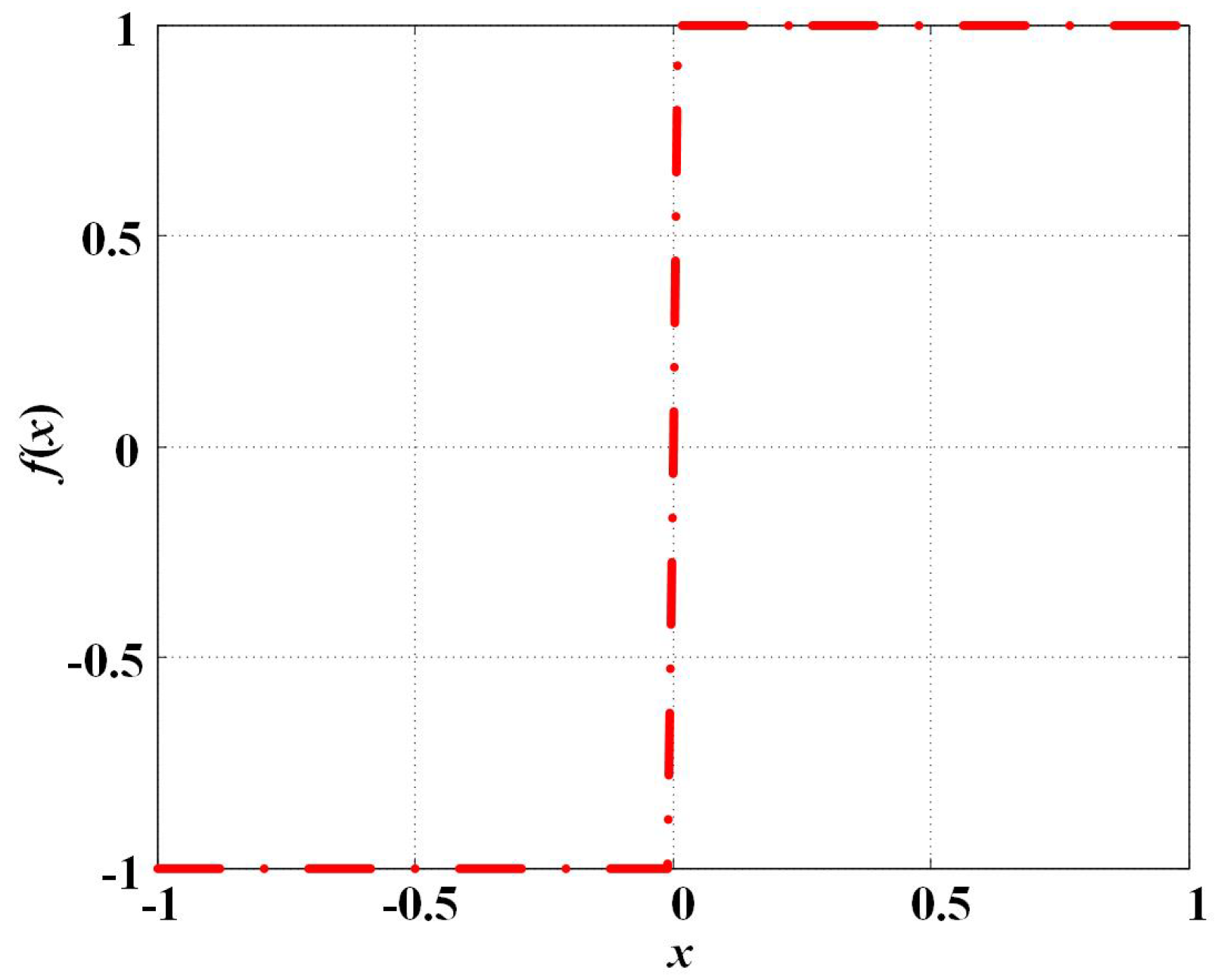
One can always apply most calculation approaches to calculate fractional-order differential equations in continuous cases directly. But in discontinuous cases, or the piecewise smooth case discussed in this work, one may have to face a different situation. For example, the sign function of , which has the value of 1 for all and the value of for all .
Figure 4.
A graph of typical function.
Figure 4.
A graph of typical function.
The sign function of appears in a variety of piecewise smooth fractional systems, which creates the initial value problem at the discontinuous point , and one needs physically interpret initial conditions at this point.
In the step mode of the basic test scenario, the proposed test bench also experiences a similar situation like the sign function. In addition, in the advanced test scenario, the the capacitor experiences a recurrence of charging and discharging behaviors in each switching cycle, thus the test bench will be in continuous state switching. Along with the on- and off operations of the power MOSFET
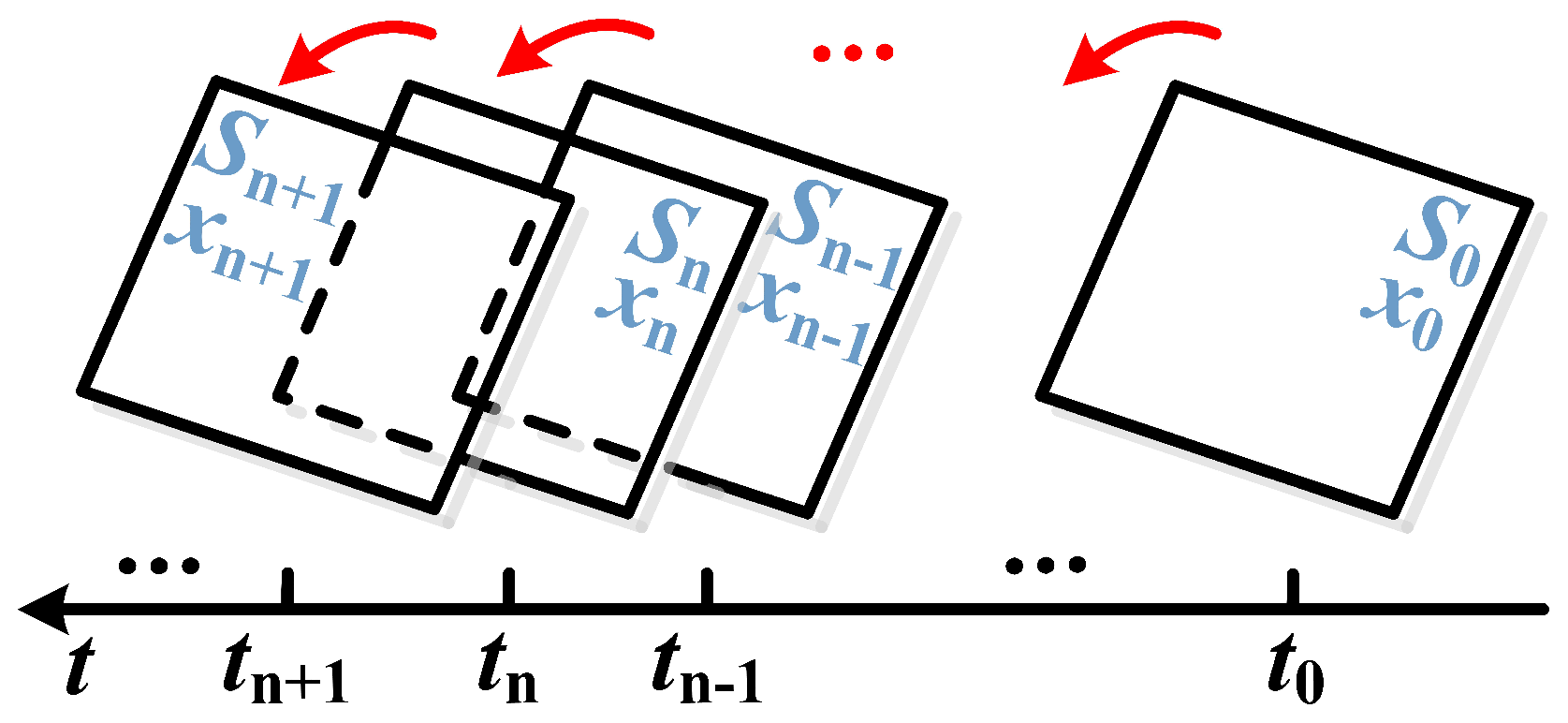
, there are a set of discontinuous points. Accordingly, a technique called stroboscopic map should be employed in both analytical and numerical calculations. This technique has been widely adopted in the dynamic analysis of piecewise-smooth systems and switching power converters. By this technique, the dynamic behavior of the test circuit at each switching state
will be collected in one switching cycle, that is, the solution
of the previous switching state at time
will be employed as the initial value of the next switching state, thus a cycle-by-cycle calculation can be carried out. The principle of is stroboscopic map technique depicted in
Figure 5.
2.1.2. State-space averaging (SSA) technique
In practice, some methods are difficult to be directly used in the advanced test scenario of this work. In allusion to this, the SSA technique can be exploited, by which the steady-state characteristic analysis can be achieved. By this technology, the average value of
in one switching cycle can be expressed by:
Accordingly, in steady-state, when the low-frequency hypothesis and the small ripple hypothesis are satisfied, the test platform in discontinuous case can be governed by the following SSA model:
in which the terms
and
can be decomposed into DC terms
and
D, AC terms
and
like follows:
2.2. Solutions of the Test Bench
2.2.1. Solutions obtained by G-L definition
According to G-L definition, the fractional-order derivative of state variable
can be written in the following discrete form [15]:
where
h is the predetermined discrete step size and
can be deduced by
Introducing Equation
13 into Equation
12 leads to the following recurrence form solution:
Then one can obtain G-L based solutions of Equation
8 by point-by-point iteration of Equation
14. In addition, the numerical solutions of charging and discharging state in the advanced test scenario will be collected in each switching cycle by the aforementioned stroboscopic map technique.
2.2.2. Solutions obtained by F-ABM method
In case of
, according to the definition of F-ABM method [19], the initial value problem of the fractional-order system of Equation
8 can be determined by:
where the term
n is any integer and
is
The predictor
in Equation
15 is
in which the term
is
Then the numerical solutions of Equation
8 can be obtained by Equation
15. Additionally, the numerical solutions of charging and discharging state in the advanced test scenario will be collected in each switching cycle by the aforementioned stroboscopic map technique.
2.2.3. Solutions obtained by Oustaloup’s rational approximation method
By Oustaloup’s rational approximation method, a continuous filter can be designed in frequency domain to achieve fractional-order calculus operations approximately. More specifically, by Laplace transform, the fractional-order operation
can be transformed to an s-domain term
, then the frequency domain characteristics of
can be approximated in the pre-defined frequency interval
by an s-domain rational fraction function
where the gain
K, zeros
, and poles
are
respectively. The coefficient
is
Then the numerical solutions of Equation
8 can be obtained by encapsulating Equation
19 to a module in MATLAB/Simulink, like those introduced in literature [16–18]. In addition, the Equation
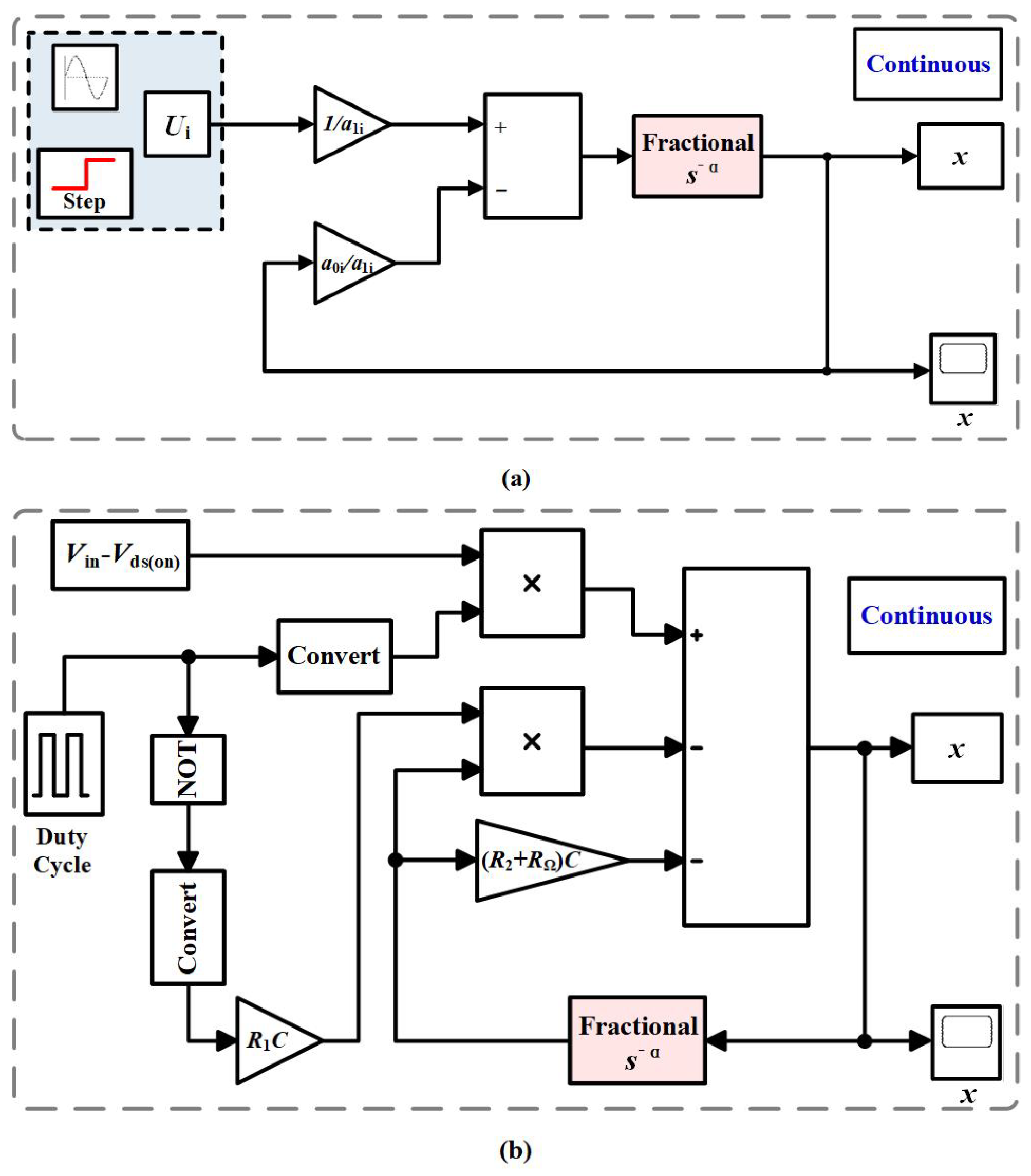
10 of SSA technique should be applied. The block diagrams of the basic test scenario and the advanced test scenario are provided in
Figure 6, where the block
with red background is encapsulated according to equation
18.
3. Results Comparison and Evaluation
According to the scenario settings and the related derivation, comparative works are carried out in this section, numerical results are obtained by F-ABM method, G-L definition, and Oustaloup’s method and are collected in groups. In addition, experiment waveforms are provided as reference.
3.1. Results of Calculation and Simulation
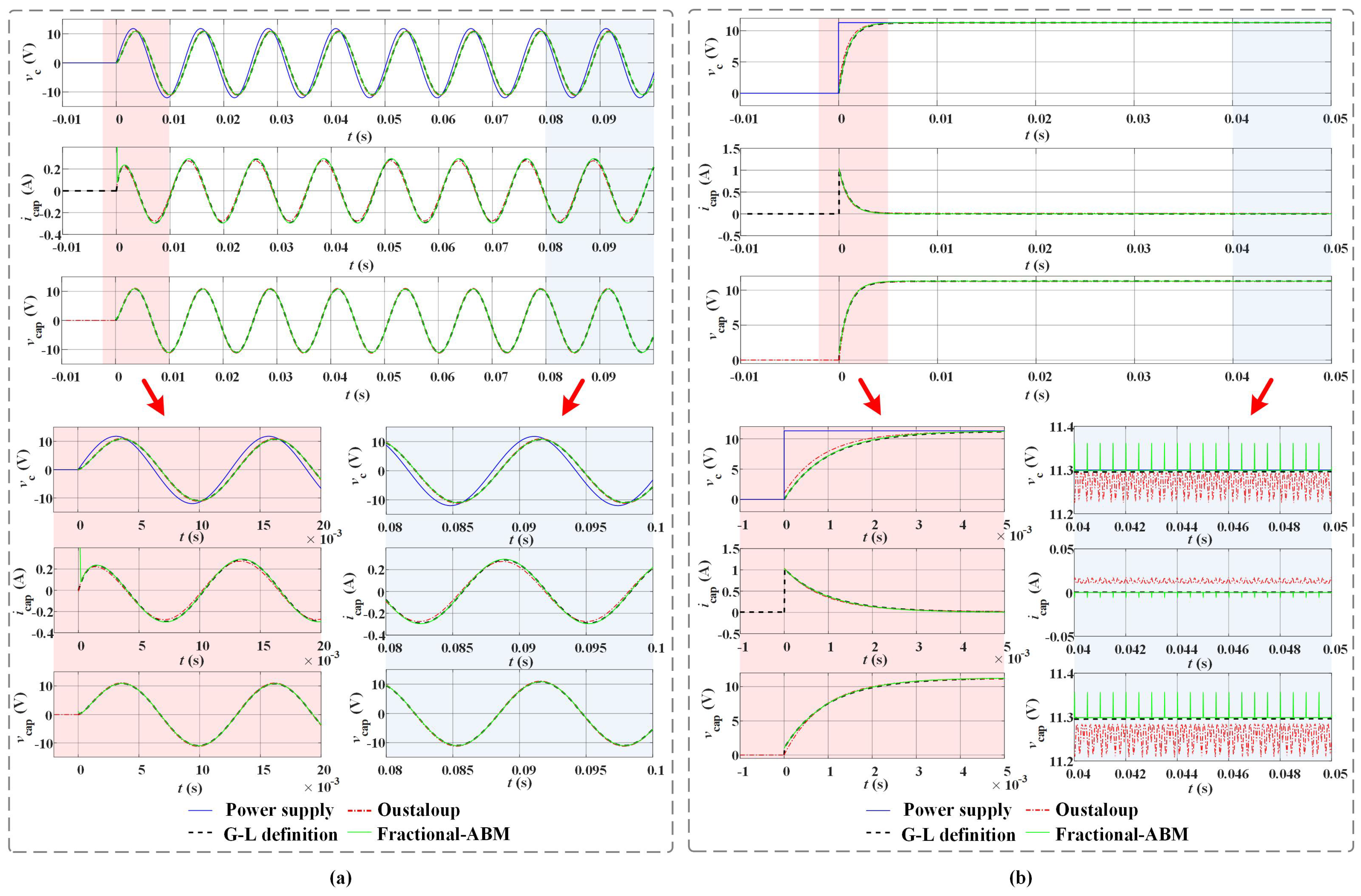
The first group of results are from the basic test scenario, by using the aforementioned three approaches, one can obtain numerical simulation results, as depicted in
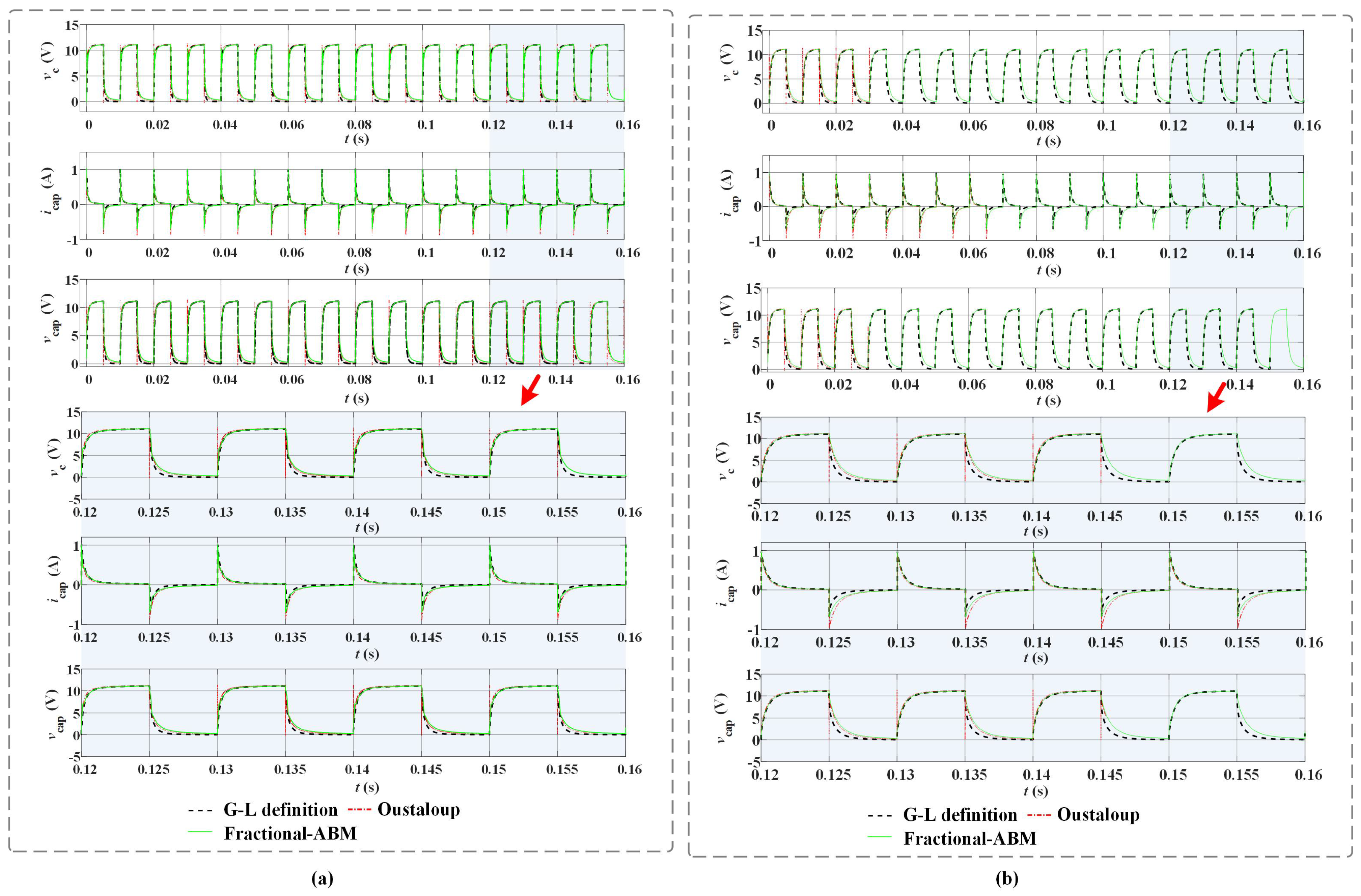
Figure 7. The second group of results are from the advanced test scenario, simulation results are as
Figure 8, In both cases, the blue solid line represents the voltage of power supply, while the red dash-and-dot line corresponds to the results of Oustaloup’s rational approximation method, the black dash line corresponds to the results of G-L definition, and the green solid line corresponds to the results of the F-ABM method.
In the above two figures, the sub-graphs with red and blue backgrounds refer to the enlarged parts.
In sinusoidal case, It can be seen that, the results of three methods mesh well with each other in steady-state. There is a lag of around between the voltage and the voltage of power supply, which is determined by the capacitance and the fractional order of the equivalent impedance model of the capacitor.
In step case, it can be seen that at the discontinuous point, the peak currents obtained by three methods are almost the same, the value is around . But note that, the results obtained by three methods are slightly different at steady state. In specific, the steady-state voltage calculated by Oustaloup’s method is about lower than the results obtained by G-L definition and F-ABM method. In addition, the steady-state current calculated by Oustaloup’s method is about higher than the results obtained by G-L definition and F-ABM method.
In advanced test scenarios, it can be seen that, the results of three methods mesh well with each other. But note that, there are spikes of the voltages and at discontinuous points if one uses Oustaloup’s method. With the acceleration frequency of charge-discharge state transition, this spike phenomenon becomes obvious. In addition, the steady-state current and the voltage calculated by the three methods are slightly different. With the acceleration frequency of charge-discharge state transition, this difference becomes obvious.
3.2. Evaluation and discussion
In order to further validate the calculation results, experiment waveforms are provided in
Figure 9 and
Figure 10.
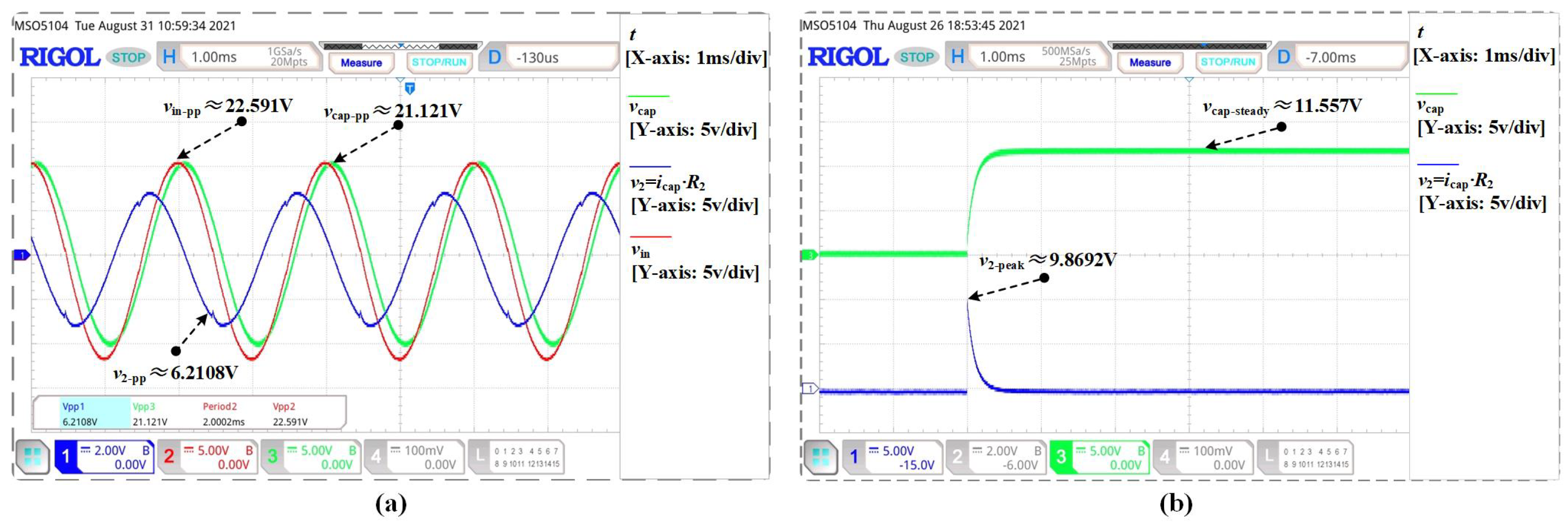
In
Figure 9, the blue solid lines are the voltage
of the resistor
. It can be regarded as the sampling for the current
flowing through the capacitor. The red solid lines correspond to the voltage of power supply, the green solid line corresponds to the voltage
of the capacitor.
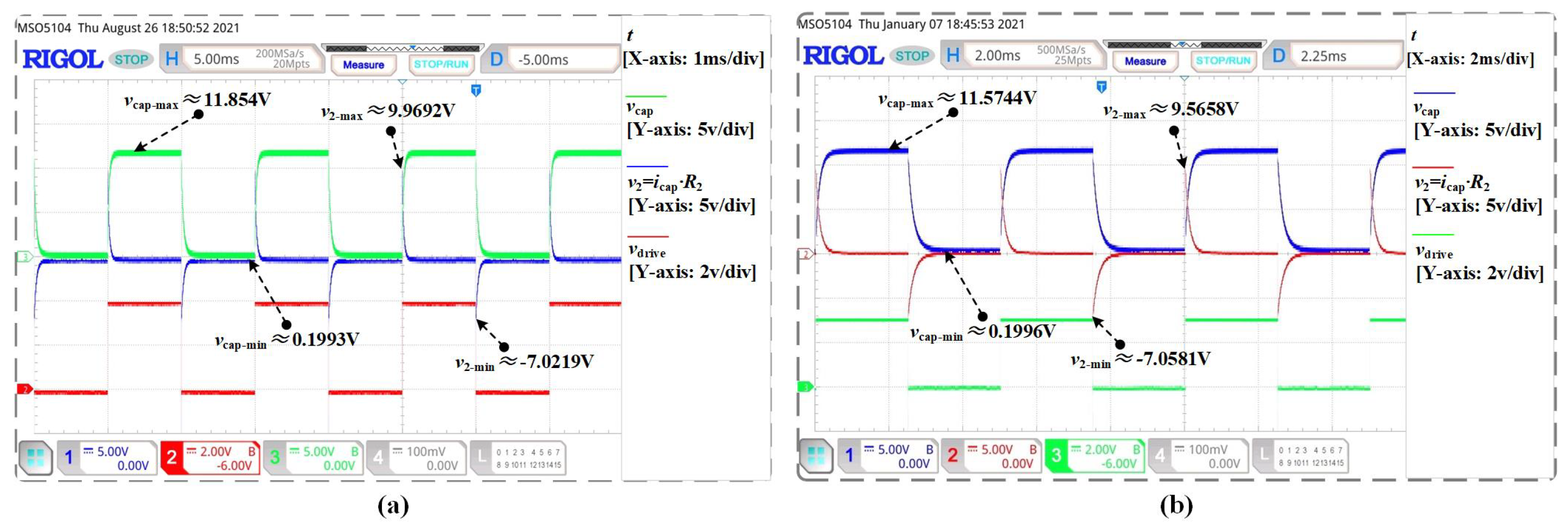
It can be found that experimental waveforms are very similar to the theoretical calculation and simulation results. In order to assess the results of calculation, statistical analysis was used to qualify different methods.
First of all, we compare the spike current
, the averaged steady-state capacitor voltage
, and the averaged steady-state capacitor current
in step case in
Table 1.
From
Table 1, it can be seen that the most calculation results of three methods have little deviation from experimental results in step case. However, compared with other results, the averaged current
obtained by Oustaloup’s method is too large. This current value is unreasonable, because in both theory and practice, if the electric field applied to the capacitor is constant, the current of the capacitor should be in a trickle state.
Then, we compare the calculations results in sinusoidal case and advanced scenarios, and list the peak-to-peak values obtained by different ways in
Table 2.
From
Table 2, it can be seen that the calculation results of three methods have little deviation from experimental results in sinusoidal case, it means that three methods are applicable for continuous situations.
However, compared with other results, the peak-to-peak current
obtained by Oustaloup’s method is larger in advanced scenarios. In addition, one can observe pulse voltage signals at some edge time points in the simulation results obtained by Oustaloup’s method, which cannot be observed in both experiments and the results of other two methods. In principle, this pulse voltage phenomenon mainly occur at on- and off operation edges of the power MOSFET
. At these time points, the test circuit switches between charging and discharging states, just like the high-level and low-level signals of the sign function in
Figure 6 undergo periodic switching. As a result, the state equation of the test circuit switches between Equation
5 and Equation
7, and the test bench is a typical piecewise smooth circuit system.
Basically, the expressions of most frequency-domain rational approximation methods are the approximation of the amplitude-frequency or phase-frequency characteristics of ideal fractional calculus operators in a predetermined frequency band, and usually considering the situation of continuously differentiable. However, at the boundary points of piecewise smooth scenarios, the state equation of the test bench is discontinuous and non-derivable. Therefore, the approximation results of rational approximation method are not that effective. This pulse-voltage phenomena can also be explained by the Fourier transform of a step function.
4. Conclusions
This paper compares the effectiveness of G-L definition based method, F-ABM method, and Oustaloup’s rational approximation method for fractional-order piecewise smooth circuit systems. A test platform for verification is developed, in which a fractional-order component, a non-solid electrolytic capacitor, is adopted. The test platform can be operated under basic and advanced test scenarios. The basic scenario contains a continuous sinusoidal case and a step case, while the advanced scenario is the periodic charging and discharging operation of the capacitor.
Three computational methods work well in basic test scenarios, especially in sinusoidal case, which indicates that these methods are effective in continuous situations. However, in step case, the averaged current obtained by Oustaloup’s method is too large. In advanced scenarios, the waveforms obtained by three methods are similar to experimental results. Two iterative numerical calculation methods, G-L definition method and F-ABM method, perform well in and advanced scenarios, the deviation between their calculation results and the experimental results is small. However, applying Oustaloup’s method in advanced scenarios leads to large calculation deviations. Moreover, if one employs Oustaloup’s method in advanced scenarios, there is pulse-voltage phenomenon when the circuit changes from charging state to discharging state, which cannot be observed in both experiments and the results of two iterative numerical calculation methods. The comparison and experimental verification results show that, G-L definition based method and F-ABM method are effective for fractional-order piecewise smooth circuit systems. The results provided by this research will provide more confidence for understanding the dynamics of real-world systems governed by fractional calculus.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, writing—original draft preparation, and supervision, X.C.; validation, formal analysis, and data curation, F.Z.; writing—review and editing, and project administration, Y.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Hubei Provincial Natural Science Foundation, China, grant number 2020CFB248.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Elwakil, A. Fractional-Order Circuits and Systems: An Emerging Interdisciplinary Research Area. IEEE Circuits and Systems Magazines 2010, 10, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Shu, X. Fractional-Order Electrical Circuit Theory (CPSS Power Electronics Series), 1st ed.; Springer: Singapore, Singapore, 2022; pp. 39–54. [Google Scholar]
- Petráš, I. Fractional-Order Nonlinear Systems; Springer-Verlag: Berlin Heidelberg, 2011; pp. 43–54. [Google Scholar]
- Mondal, D.; Biswas, K. Packaging of Single-Component Fractional Order Element. IEEE Transactions on Device and Materials Reliability 2013, 13, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allagui, A.; Freeborn T., J.; Elwakil A., S.; et al. Review of fractional-order electrical characterization of supercapacitors. Journal of Power Sources 2018, 400, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xi, L.; et al. Fractional techniques to characterize non-solid aluminum electrolytic capacitors for power electronic applications. Nonlinear Dynamics 2019, 98, 3125–3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Zhang, L.; et al. A review of fractional-order techniques applied to lithium-ion batteries, lead-acid batteries, and supercapacitors. Journal of Power Sources 2018, 390, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Kartci, A.; et al. Fractional-Order Inductor: Design, Simulation, and Implementation. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 73695–73702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allagui, A.; Elwakil, A.S.; Fouda M., E. Revisiting the Time-Domain and Frequency-Domain Definitions of Capacitance. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices 2021, 68, 2912–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, X. A fractional-order equivalent model for characterizing the interelectrode capacitance of MOSFETs. IEEE COMPEL - The international journal for computation and mathematics in electrical and electronic engineering 2022, 41, 1660–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, M.; Chen, X. Enhancing parameter identification of electrochemical double layer capacitors by fractional-order equivalent impedance models and Levy flight strategy. International Journal of Circuit Theory and Applications 2022. online. [Google Scholar]
- Freeborn, T.J. A Survey of Fractional-Order Circuit Models for Biology and Biomedicine. IEEE Journal on Emerging and Selected Topics in Circuits and Systems 2013, 3, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, M.C.; Mondal, D.; et al. Experimental studies on realization of fractional inductors and fractional-order bandpass filters. International Journal of Circuit Theory and Applications 2015, 43, 1183–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhang, B.; et al. Fractional-order autonomous circuits with order larger than one. Journal of Advanced Research 2020, 25, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherer, R.; Kalla, S.L.; et al. The Grünwald–Letnikov method for fractional differential equations. Computers & Mathematics with Applications 2011, 62, 902–917. [Google Scholar]
- Oustaloup, A.; Levron, F.; et al. Frequency-band complex noninteger differentiator: Characterization and synthesis. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I-Fundamental Theory and Applications 2000, 47, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malti, R.; Victor, S.; et al. CRONE Toolbox for system identification using fractional differentiation models. IFAC-Papers OnLine 2015, 48, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, D.; Chen, Y. System Simulation Techniques with MATLAB® and Simulink®, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons: West Sussex, United Kingdom, 2013; pp. 85–90. [Google Scholar]
- Diethelm, K. The Analysis of Fractional Differential Equations: An Application-Oriented Exposition Using Differential Operators of Caputo Type; Springer-Verlag: Berlin Heidelberg, 2010; pp. 195–225. [Google Scholar]
- Momani, S.; Odibat, Z. Numerical approach to differential equations of fractional order. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics 2007, 1, 96–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owolabi, K.M.; Atangana, A. Numerical Methods for Fractional Differentiation; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2019; pp. 203–208. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Chen, Y. A Modeling and Analysis Method for Fractional-order DC-DC Converters. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics 2017, 32, 7034–7044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, Y. Analysis and Modeling of Fractional-Order Buck Converter Based on Riemann-Liouville Derivative. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 162768–162777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Lehman, B. Averaging Theory for Fractional Differential Equations. Fractional Calculus and Applied Analysis 2021, 24, 621–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danca, M.F. Synchronization of piecewise continuous systems of fractional order. Nonlinear Dynamics 2014, 78, 2065–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hong, L.; et al. Crises in a fractional-order piecewise system. Nonlinear Dynamics 2021, 103, 2855–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alazman, I.; Alkahtani, B.S.T. Investigation of Novel Piecewise Fractional Mathematical Model for COVID-19. Fractal and Fractional 2022, 6, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Xi, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X. An Online Parameter Identification Method for Non-solid Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitors. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs 2022, 69, 3475–3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podlubny, I. Fractional Differential Equations: An Introduction to Fractional Derivatives, Fractional Differential Equations, to Methods of their Solution and some of their Applications; Academic Press: London, UK, 1998; pp. 124–125. [Google Scholar]
- Tse, C.K.; Xi, L.; Bernardo, M.D. Complex Behavior in Switching Power Converters. Proceedings of the IEEE 2002, 90, 768–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, R.W.; Maksimovic, D. Fundamentals of Power Electronics, 2nd ed.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Massachusetts, US, 2001; pp. 213–246. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).