1. Introduction
Biological processes operating within and between intracellular compartments are coordinated, in part, via metabolic enzymes that act as key regulators of cellular metabolism. Certain metabolic enzymes coordinate metabolite sensing and signaling mechanisms to maintain energy homeostasis, including glucose, lipid and amino acid metabolism, energy storage and utilization, and responses to injury and the environment [1, 2]. In addition, some of these metabolic enzymes actively shuttle between the cytoplasm and the nucleus enabling them to act as multifunctional regulatory proteins [3, 4]. They execute discrete biochemical and signaling roles in the cytoplasm and the nucleus depending upon the needs of cells under varying conditions. Further, these regulatory metabolic enzymes can modulate gene expression through direct or indirect mechanisms whereby they can behave as transcription factors, regulators of transcription factors, or post-translational modifiers of protein function.
Acyl-coenzyme A synthetase short-chain family member 2 (Acss2, also known as acetyl-CoA synthetase-1) is an evolutionarily conserved, lipogenic enzyme [5, 6]. It was first identified in rat liver as a cytosolic enzyme that participated in the synthesis of fatty acids and sterols [7, 8]. Acss2 catalyzes a reaction that consumes acetate, coenzyme A (CoA) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to generate acetyl-CoA, adenosine monophosphate (AMP) and pyrophosphate (enzyme classification; EC 6.2.1.1) [
5]. These findings implicate Acss2 as an additional route to cytoplasmic acetyl-CoA generation, parallel to ATP-citrate lyase (Acly). It has been also documented that the expression of Acss2 mRNA is regulated by sterol regulatory element-binding proteins, further substantiating its role in lipid synthesis [9-12]. Acss2-deficient (Acss2
-/-) mice reproduce well and their young develop normally, indicating that Acss2 is nonessential under normal conditions with adequate food [
13]. Thus, Acss2 acts as a parallel pathway to extramitochondrial acetyl-CoA synthesis that is not critical for survival under favorable conditions. Nonetheless, the evolutionary conservation of Acss2 indicates that it provides significant selective advantages.
Despite its clear role in providing acetyl-CoA for lipid synthesis in the cytoplasm, strong Acss2 expression has been observed in the nucleus of most cell types, delineating it as a nucleocytosolic enzyme [14-16]. Importantly, Acss2 has been shown to translocate from the cytoplasm to the nucleus in response to nutrient deprivation, stress or injury [17-19]. In the nucleus, Acss2 facilitates acetylation reactions for numerous proteins including histones [20, 21]. Acss2 also facilitates acetylation of transcription factors, for example, hypoxia-inducible factor-2 alpha (Hif-2α) [17, 22], transcription factor EB (Tfeb) [
19] and interferon regulatory factor 4 (Irf4) [
23]. The phosphorylation status of Acss2 determines its subcellular localization, with the unphosphorylated form being retained in the cytoplasm and the phosphorylated form being translocated to the nucleus [
19]. These studies demonstrate additional regulatory roles of Acss2 in gene transcription, metabolic reprogramming, cell cycle progression, lysosomal biogenesis and autophagy. The importance of these cellular biological processes in maintaining cellular energy balance, homeostasis and cell survival is well-known, therefore, not surprisingly the dysregulation of Acss2 has been linked to various human diseases including cardiovascular diseases, cancer, diabetes, and obesity [reviewed in 24, 25].
We performed genome-wide transcriptome profiling (microarray) in normally fed (non-fasted) adult (15 to 16 weeks old) Acss2-/- mice and age-matched wild-type (WT) mice. We examined differentially expressed genes (DEGs) associated with the deletion of Acss2 in metabolically disparate organ systems involved in extensive lipid synthesis, deposition, and mobilization including the liver, brain, and mesenteric adipose tissue. The liver is a site of lipid and ketone body synthesis while adipose tissue is a site of lipid storage and mobilization. The brain is also a site of extensive lipid metabolism and deposition. The data reveal distinct patterns of gene expression in the 3 organ systems examined. Further, analyses of DEGs show that loss of Acss2 leads to dysregulation of numerous canonical signaling pathways, upstream transcriptional regulatory molecules, cellular processes, and biological functions, which were also distinct in the liver, brain, and adipose tissue. Despite such alterations in transcriptional states, and cellular pathways and processes, the analysis of global fatty acid content demonstrated that the loss of Acss2 resulted in few changes in fatty acid constitution in all three organ systems. Our results reveal dynamic reprogramming of gene expression patterns and associated cellular pathways and processes between Acss2-/- and wild-type mice, which were distinct in the liver, brain, and adipose tissue. These findings contribute to the growing knowledge base linking metabolic enzymes such as Acss2 with dynamic reprogramming of signaling and metabolic pathways necessary to adapt to changing internal and external conditions.
2. Results
2.1. Fatty Acid Quantification
To determine the effect of loss of Acss2 on fatty acid constitution, we performed liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) fatty acid analysis in liver, brain, and mesenteric adipose tissues from normally fed (non-fasted) adult (15 to 16 weeks old) Acss2
-/- (knockout mice, KO) and age-matched control wild-type (WT) mice of the same strain. Acss2 deletion did not result in broad alternations in FA levels, but rather there were several specific, significant differences in key fatty acids in a tissue-specific context. Liver eicosanoic acid (a saturated fatty acid; 20:0) was slightly elevated in the knockout mice (KO = 1.55 μg/ml
+ 0.18, WT = 1.31 μg/ml
+ 0.15, p = 0.054). In the brain, oleic acid (a monounsaturated omega-9 fatty acid; 18:1 cis-9) was significantly lower in the KO mice (KO = 1084 μg/ml
+ 121, WT = 1401 μg/ml
+ 268, p =0.043). Brain stearic acid (a saturated fatty acid; 18:0) also was significantly lower in the KO mice (KO = 773 μg/ml
+ 38, WT = 884 μg/ml
+ 66, p = 0.012). In adipose tissue myristic acid (C14:0) was significantly higher in the KO mice (KO = 22.2 μg/ml
+ 3.1, WT = 15.5 μg/ml
+ 4.4, p = 0.024). No other significant differences were noted (Data in
Supplementary Table 1). These results indicate that the role of Acss2 in lipogenesis can be mostly compensated for by Acly in normally fed mice, and argues against a strong, selective role for Acss2 in the synthesis of specific fatty acids.
2.2. Transcriptional Analysis of Acss2 Deletion
To further investigate the roles of Acss2 we performed microarray analysis on liver, brain and adipose tissues from the same mice described above. Despite the lack of broad differential fatty acid composition of the tissues, a high proportion of genes associated with glycolysis and lipid synthesis were upregulated specifically in adipose tissue of Acss2
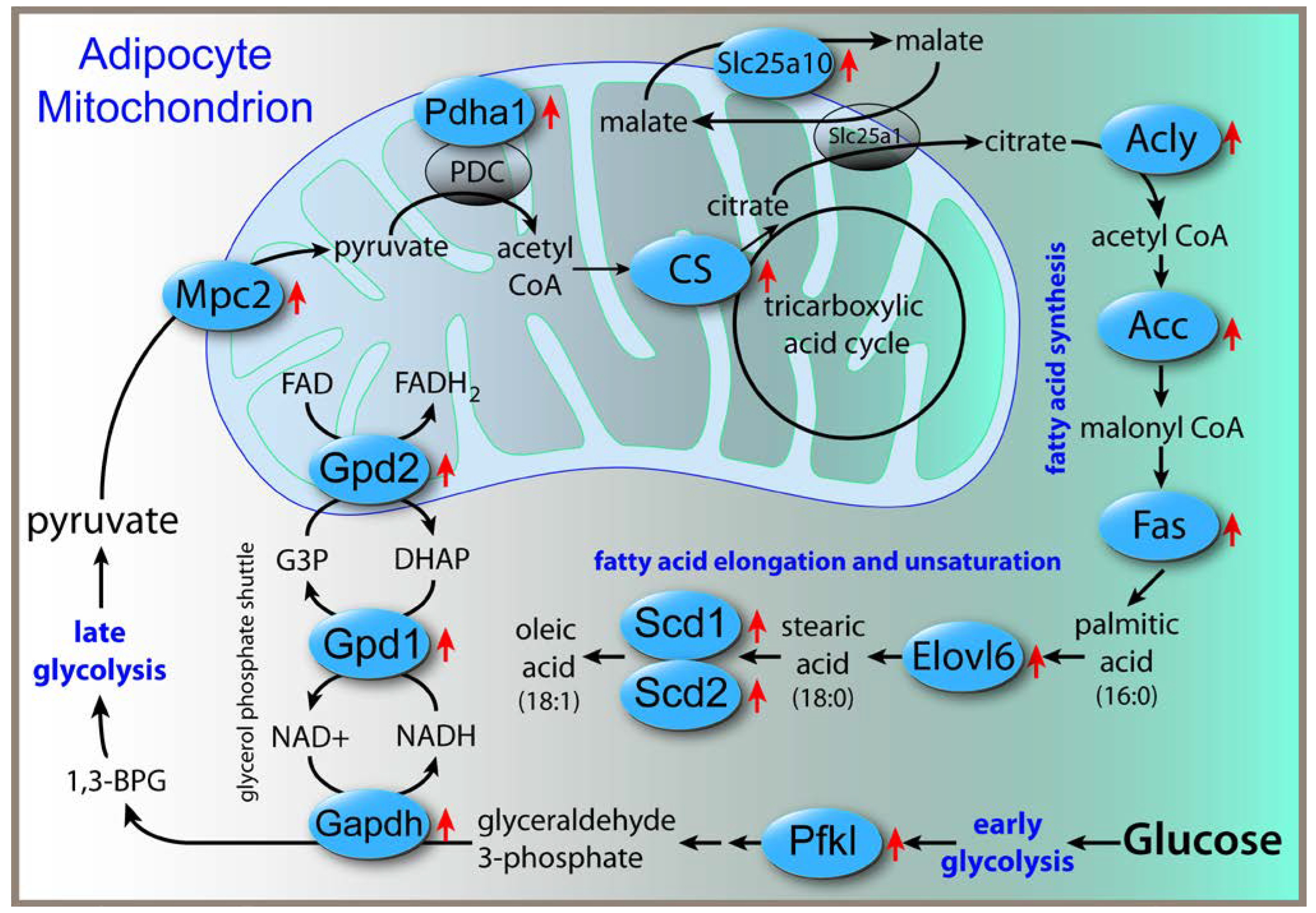
-/- mice. Similar changes were not observed in either liver or brain, highlighting the tissue-specific effects of Acss2 deletion. In adipose tissue, the lipogenic genes with increased expression included ATP citrate lyase (Acly), fatty acid synthase (Fasn) and fatty acid elongase 6 (Elovl6). In fact, Elovl6 (log2 fold change +3.59) and Acly (log2 fold change +2.59) were the two most upregulated genes in adipose tissue. The biochemical relationships between the upregulated genes associated with glycolysis and lipogenesis in adipose tissue are shown in
Figure 1. Loss of Acss2 acted to upregulate expression of all of these genes, possibly indicating that these changes acted to compensate for the lack of Acss2 activity. Gene upregulation was observed for glycolytic enzymes as well as enzymes of the glycerol-phosphate shunt, which assists the malate-aspartate mitochondrial shuttle in moving reducing equivalents into the mitochondrial matrix. A mitochondrial pyruvate transporter was upregulated, and a catalytic unit of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, which acts to convert intramitochondrial pyruvate to acetyl CoA, was also upregulated. A malate transporter that assists the main mitochondrial malate-citrate antiporter was upregulated, along with ATP citrate lyase, which converts citrate into acetyl CoA in the cytoplasm and nucleus. Upregulation was also seen in key enzymes for fatty acid synthesis including fatty acid synthase, a fatty acid elongase and two fatty acid desaturases. Overall, these results suggest increased throughput from glucose to unsaturated fatty acids in adipose tissue of Acss2
-/- mice relative to wild-type mice.
This increased expression pattern for lipogenic genes in adipose tissue could reflect a compensation for the loss of Acss2 activity in Acss2
-/- mice, and yet similar changes were not observed in the liver, which is a major site of fatty acid synthesis. In contrast to adipose tissue, Huang et al. also found no expression changes in fatty acid associated genes in the livers of Acss2
-/- mice fed a normal chow diet [
13]. Interestingly, even though expression of lipogenic genes was not significantly affected in the brain, two key fatty acids were lower in the brain; stearic acid (18:0) and oleic acid (18:1 cis9). Genes for enzymes involved in the synthesis of stearic and oleic acids were upregulated in adipose tissue (
Figure 1), but those genes were not altered in the brain, so the cause of the lower levels of these two fatty acids in the brain remains to be determined. Because Acly was strongly upregulated in adipose tissue of Acss2
-/- mice, but not in the liver, it is likely that Acss2 has more a pronounced lipogenic role in adipocytes than in hepatocytes. These results are in agreement with the findings of Huang et al. [
13].
2.3. Acss2 Loss Institutes Organ-Specific Changes in the Transcriptome and Canonical Signaling Pathways in Liver, Brain and Adipose Tissue
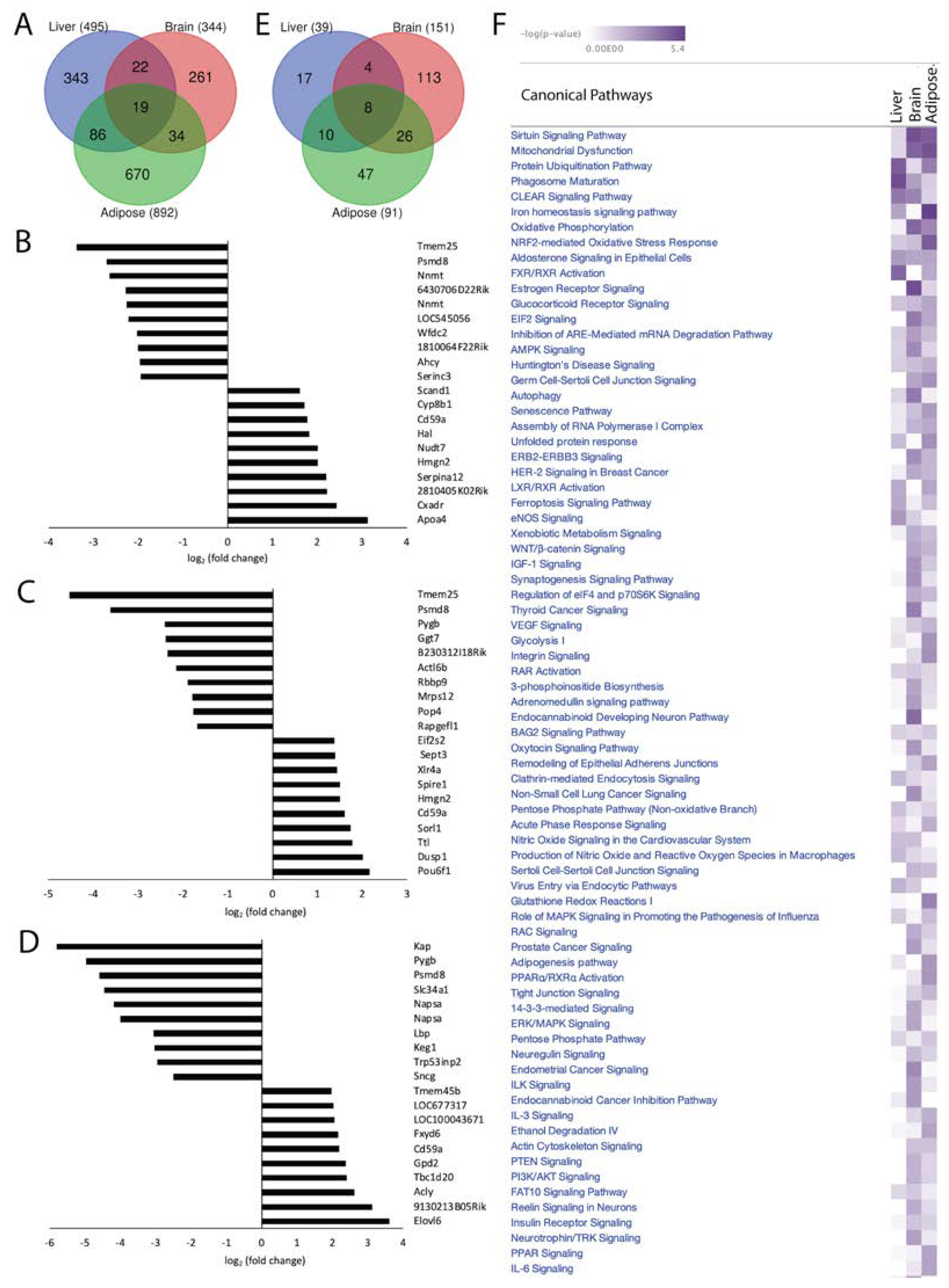
Loss of Acss2 in normally fed mice was associated with 1731 statistically significant DEGs in the three organ systems (p-value < 0.05, log2 fold change > 1, z-score > 2). We found 495 significant DEGs in liver, 344 in brain and 892 in adipose tissue (
Figure 2A). Out of 495 DEGs in the liver, 347 transcripts (70.10%) were downregulated and 148 (29.90%) were upregulated in response to Acss2 deletion. Among 344 DEGs observed in brain, 94 (27.33%) were downregulated and 250 (72.67%) were upregulated in Acss2
-/- mice. Out of 892 DEGs in adipose, 584 (65.47%) were downregulated and 308 (34.53%) were upregulated in Acss2
-/- mice. The transcripts with the largest differential expression are shown in Figures 2B, C and D. Only 19 significant DEGs were common to all 3 organ systems examined, strongly indicating that Acss2 has very tissue-specific functions. In the brain, almost ¾ of the DEGs were upregulated, whereas in the liver and adipose tissue, approximately 2/3 of the DEGs were downregulated. Further, the effects of Acss2 deletion on transcription factor (TF) expression in the liver and brain were opposite (see
Supplementary Online Figure 2). In the liver of Acss2
-/- mice, no TF were upregulated, but 193 were downregulated. In the brain, 68 TF were upregulated in response to Acss2 deletion, but none were downregulated. Adipose tissue had a somewhat mixed reaction to Acss2 deletion, with 98 TF upregulated and 235 downregulated. Summarizing, while about 73% of DEGs in the brain were upregulated, 100% of all TF-related DEGs were upregulated in the brain. In contrast, whereas about 65% of DEGs in the liver were downregulated, all TF-related DEGs there were downregulated. These findings further substantiate the tissue-specific regulatory roles of Acss2 and raise the possibility that Acss2 may act primarily as a transcriptional repressor in the brain, and a transcriptional activator in the liver, while having a mixed role in the regulation of transcription factor expression in adipose tissue. The dichotomous effect of Acss2 deletion on TF expression in the brain and liver warrants further attention.
To further investigate the system-wide functional significance of the transcriptomic changes seen in these 3 organ systems we applied in silico analyses using Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) and performed core analysis. The obtained DEGs in Acss2
-/- compared with WT mice were overlaid with the global molecular network in the Ingenuity Pathway Knowledge Base (IPKB). Comparing Acss2
-/- to WT mice revealed the association of 39 statistically significant (-log (p-value) > 1.3) canonical signaling pathways in the liver, 151 in the brain and 91 in adipose (
Figure 2E). There was minimal overlap between altered signaling pathways in the organ systems studied, with only 8 canonical signaling pathways common to all three. It is notable that the liver showed the lowest number of significantly altered signaling pathways in response to loss of Acss2. A heatmap of the affected canonical signal transduction pathways (-log (p-value) in response to loss of Acss2 function among the 3 organ systems is shown in
Figure 2F. Significantly altered signaling pathways, associated diseases and gene networks for each organ system are discussed briefly below. IPA canonical signaling pathways, disease and cellular function and regulatory biological relationships are highlighted in the text using quotation marks.
2.4. Liver
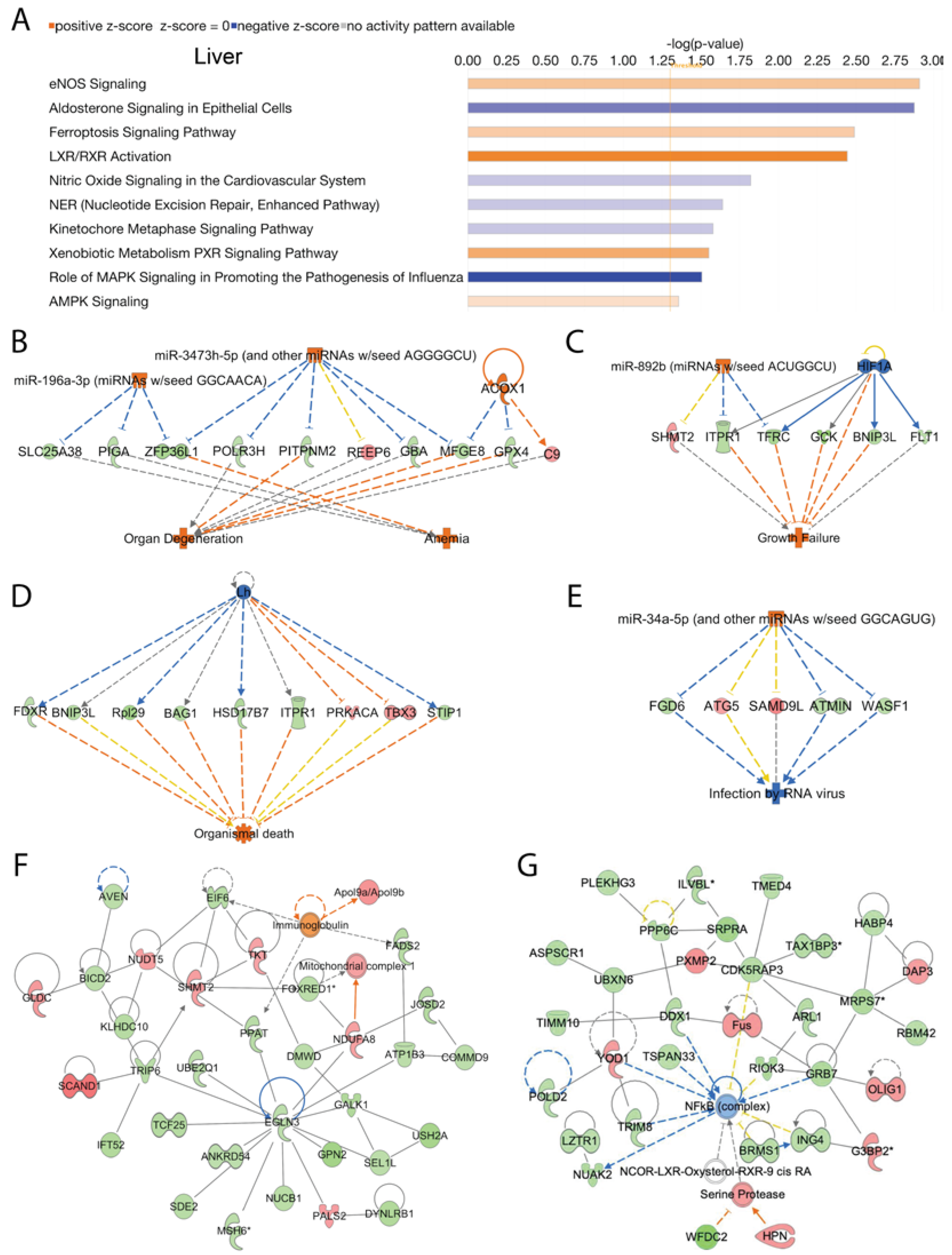
We analyzed activated and inhibited canonical signal transduction pathways in the liver associated with the loss of Acss2 using IPA. The analysis revealed numerous differentially upregulated and downregulated canonical signaling pathways responsive to Acss2 loss. The top 10 statistically significant (-log (p-value) > 1.3) and differentially regulated canonical pathways are shown in
Figure 3A. Among them, “eNOS signaling”, “ferroptosis signaling pathway”, “LXR/RXR activation”, “xenobiotic metabolism PXR signaling pathway”, and “AMPK signaling” were activated in response to loss of Acss2 function. Downregulated signaling pathways in the liver of Acss2
-/- mice included “aldosterone signaling in epithelial cells”, “nitric oxide signaling in the cardiovascular system”, “nucleotide excision repair enhanced pathway”, “kinetochore metaphase signaling pathway” and “the role of MAPK signaling in promoting the pathogenesis of influenza” (
Figure 3A). The -log (p-values) and z-scores of these canonical signaling pathways are given in
Supplementary Data Table 2A.
Subsequently, we performed disease and cellular function analysis using IPA to determine upstream regulator, cellular processes, and biological functions in the liver that are modulated by deletion of Acss2. Our analysis showed Acss2 loss activated upstream regulators Acox1, miR-196a-3p (miRNAs w/seed GGCAACA), and miR-3473h-5p (and other miRNAs w/seed AGGGGCU), which lead to alterations in expression of several genes (listed in
Supplementary Table 3A) associated with disease and cellular functions linked to activation of “anemia” and “organ degeneration” (consistency score = 1.897) (
Figure 2C). Similarly, activation of upstream regulator miR-892b (miRNAs w/seed ACUGGCU) and inhibition of upstream regulator HIF1A, which lead to altered expression of several genes (listed in
Supplementary Table 3B) was associated with activation of “growth failure” (consistency score = 1.633) (
Figure 3C). Further analyses of the DEGs in liver tissue from Acss2
-/- mice indicated possible inhibition of upstream regulator Lh and activation of upstream regulator miR-34a-5p (and other miRNAs w/seed GGCAGUG), as inferred by alterations in the expression of several genes (listed in
Supplementary Table 3C and 3D) and these were associated with activation of “organismal death” (consistency score = -8.667) and inhibition of “infection by RNA virus” (consistency score = -5.367) respectively (
Figure 3D and 3E).
We further analyzed DEGs to determine regulatory biological relationships mediated by the Acss2 in the liver. The top two enriched networks were “amino acid metabolism, carbohydrate metabolism, small molecule biochemistry” (Network 1: score = 62, focus molecules = 33) (
Figure 3F), and “cellular development, cellular growth and proliferation, connective tissue development and function” (Network 2: score = 59, focus molecules = 32) (
Figure 3G). The corresponding genes and their expression are listed in
Supplementary Table 4A and 4B. Overall, these findings indicate regulatory roles for Acss2 in the liver, but do not support a strong role for Acss2 in lipid synthesis or processing in the liver under well-fed conditions. Further, we did observe decreased expression of two enzymes associated with protein and metabolite methylation, namely nicotinamide N-methyltransferase (Nnmt) and adenosylhomocysteinase (Ahcy) (
Figure 2B). S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) is the sole methyl donor for SAM-dependent methyltransferases (SDMs), and Nnmt competes with SDMs for availability of SAM. Decreased Nnmt expression can increase SAM availability for protein and DNA methylation reactions. SDMs transfer the methyl group from SAM to protein and DNA targets, generating S-adenosylhomocysteine (SAH) in the process. Increased concentrations of SAH act to inhibit SDMs, and therefore it is important to catabolize SAH, which is accomplished by Ahcy. These results suggest that Acss2 may have some regulatory actions over protein and metabolite methylation in the liver.
2.5. Brain
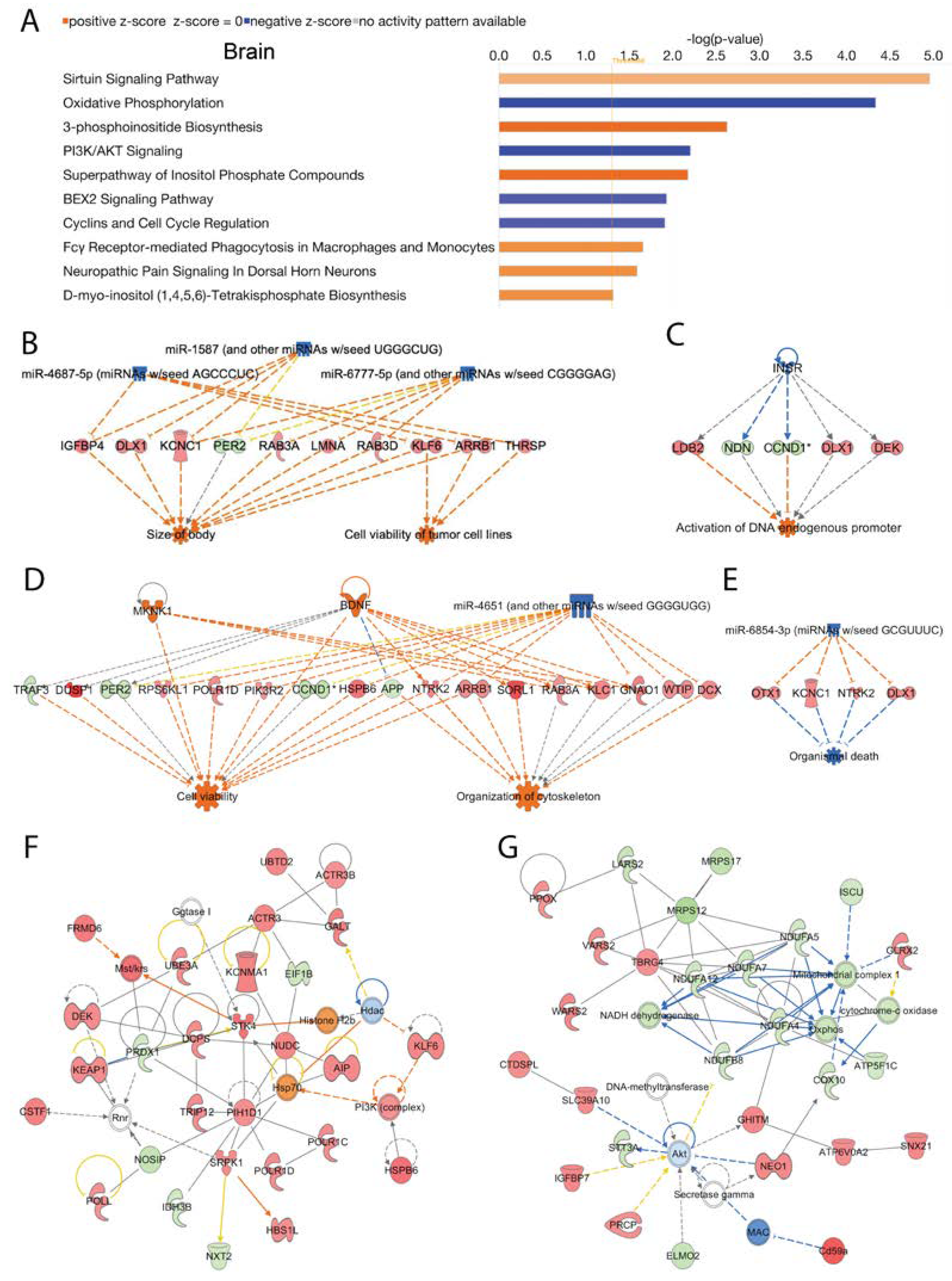
Several canonical signaling pathways were modulated by loss of Acss2 in the brain. The top 10 statistically significant (-log (p-value) > 1.3) and differentially regulated canonical pathways are shown in
Figure 4A. Signaling pathways in the brain that were increased in response to loss of Acss2 function were the “sirtuin signaling pathway”, “3-phosphoinositide biosynthesis”, “superpathway of inositol phosphate compounds”, “Fcγ receptor-mediated phagocytosis in macrophages and monocytes”, “neuropathic pain signaling in dorsal horn neurons”, “D-myo-inositol (1,4,5,6)-tetrakisphosphate biosynthesis in neurons” and D-myo-inositol (3,4,5,6)-tetrakisphosphate biosynthesis”. Downregulated signaling pathways in the brain included “oxidative phosphorylation”, “PI3K/AKT signaling”, “BEX2 signaling pathway” and “cyclins and cell cycle regulation”. The -log (p-values) and z-scores of these canonical signaling pathways are given in
Supplementary Table 2B.
Several upstream regulator miRNAs in the brain were reduced with the loss of Acss2 including miR-1587 (and other miRNAs w/seed UGGGCUG), miR-4687-5p (miRNAs w/seed AGCCCUC), and miR-6777-5p (and other miRNAs w/seed CGGGGAG). These miRNA act to alter the expression of several genes (listed in
Supplementary Table 5A) associated with disease and cellular functions including activation of “cell viability of tumor cell lines” and “size of body” (consistency score = 4.111) (
Figure 4B). A number of upstream regulating systems were affected including “inhibition of the insulin receptor INSR” (z-score = -2.8), as inferred by alterations in the expression of several downstream genes (listed in
Supplementary Table 5B) potentially associating Acss2 with “activation of DNA endogenous promoter” (consistency score = 0.447) (
Figure 4C). IPA analysis also indicated activated upstream regulators BDNF and MKNK1, and inhibited upstream regulator miR-4651 (and other miRNAs w/seed GGGGUGG), based on alterations in the expression of several genes (listed in
Supplementary Table 5C). These expression changes are linked to activation of “cell viability” and “organization of cytoskeleton” (consistency score = 3.395) (
Figure 4D). Further analyses in brain tissue from Acss2 deficient mice demonstrated suppression of the upstream regulator miR-6854-3p (miRNAs w/seed GCGUUUC), associated with alterations in expression of several genes (listed in
Supplementary Table 5D) linked to “inhibition of organismal death” (consistency score = 2) (
Figure 4E).
Subsequently, using IPA network analysis we found the top two enriched networks in the brain were 1) “connective tissue disorders, developmental disorder, hereditary disorder” (Network 1: score = 53, focus molecules = 28), and 2) “metabolic disease, neurological disease, organismal injury and abnormalities” (Network 2: score = 50, focus molecules = 27) (
Figure 4F and 4G). The corresponding genes and their expression changes are listed in
Supplementary Table 6A and 6B. Overall, these findings support the conclusion that Acss2 has regulatory actions on numerous signaling pathways in the brain, many of which are unrelated to fatty acid synthesis.
2.6. Adipose
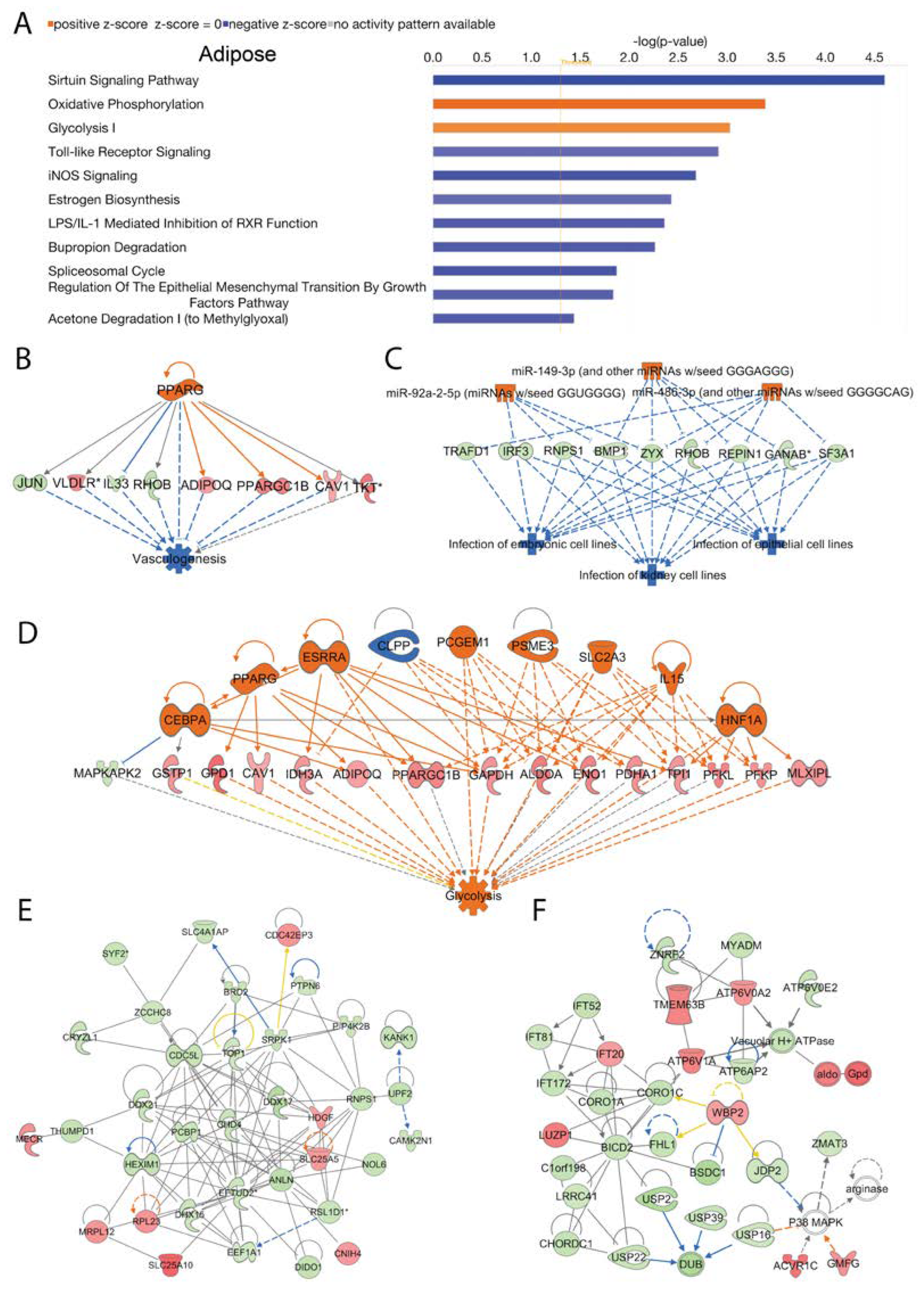
In adipose tissue we analyzed activated and inhibited canonical signal transduction pathways associated with the loss of Acss2. The data revealed numerous differentially regulated (activated or inhibited) canonical signaling pathways that were modulated by Acss2. The top 10 statistically significant (-log (p-value) > 1.3) and differentially regulated canonical pathways are shown in
Figure 5A. Among them, “oxidative phosphorylation” and “glycolysis I” were activated in response to loss of Acss2 function in adipose tissue. In contrast, the inhibited canonical signaling pathways in adipose tissue of Acss2
-/- mice included the “sirtuin signaling pathway”, “toll-like receptor signaling”, “iNOS signaling”, “LPS/IL-1 mediated inhibition of RXR function”, “bupropion degradation”, “spliceosomal cycle regulation of the epithelial mesenchymal transition by growth factors pathway” and “acetone degradation” (
Figure 5A). The -log (p-values) and z-scores of these canonical signaling pathways are given in
Supplementary Data Table 2C. It is noteworthy that the sirtuin signaling pathway was inhibited as sirtuins act to regulate Acss2 activity through acetylation [
26].
IPA disease and cellular function analysis revealed activated upstream regulator PPARG, as inferred by alterations in the expression of several genes (listed in
Supplementary Table 7A) associated with “inhibition of vasculogenesis” (consistency score = 2.739) (
Figure 5B). Similarly, activation of upstream regulators miR-149-3p (and other miRNAs w/seed GGGAGGG), miR-486-3p (and other miRNAs w/seed GGGGCAG), and miR-92a-2-5p (miRNAs w/seed GGUGGGG), inferred by alterations in expression of several genes (listed in
Supplementary Table 7B) were associated with “inhibited infection” of several different cell lines (consistency score = 13.333) (
Figure 5C). Additionally, we found activation of upstream regulators Cebpa, Esrra, Hnf1a, IL15, Pcgem1, Psme3 and Slc2a3 as well as inhibition of upstream regulator Clpp linked to alterations in the expression of several genes (listed in
Supplementary Table 7C) associated with “activation of glycolysis” (consistency score = 4.906) (
Figure 5D).
Subsequently, using IPA network analysis we found the top enriched networks in adipose tissue were “cellular assembly and organization”, “RNA damage and repair”, “RNA post-transcriptional modification” (Network 1, score = 60, focus molecules = 35), and “connective tissue disorders, developmental disorder, hereditary disorder” (Network 2, score = 44, focus molecules = 29) associated with the loss of Acss2 activity (
Figure 5E and 5F). The corresponding genes and their expression changes are listed in
Supplementary Table 8A and 8B. It is noteworthy that the most enriched network in adipose tissue included RNA post-transcriptional modification, indicating that Acss2 has regulatory actions at both the pre- and post-transcriptional levels.
2.7. Karyoplot Analysis
Karyoplots were constructed to show the chromosomal distribution of DEGs in liver, brain and adipose tissue. Upregulated and downregulated DEGs were plotted separately for each tissue (
Figure 6). Loss of Acss2 resulted in widespread expression changes distributed in a tissue-specific manner across all autosomes. A modest number of expression changes were also observed on X chromosomes in all 3 organ systems. In contrast, no expression changes were seen on the Y chromosome in any tissue.
3. Discussion
We examined the effects of Acss2 deletion in 3 organ systems with distinct lipid metabolism behaviors. The liver is involved in many aspects of lipid physiology including being a major site of lipid and lipoprotein synthesis processing and release. The brain is a major site of lipid metabolism required to generate and maintain the myelin sheathing of neuronal axons and support membrane lipid turnover necessary for neurotransmission. Adipose tissue is associated with lipid synthesis, deposition, storage and release, depending on nutritional availability. The results we obtained in response to Acss2 deletion in these 3 organ systems demonstrate a strong effect on cellular signaling pathways, but relatively minimal effects on fatty acid content. In adipose tissue, a number of genes associated with glycolysis and fatty acid synthesis were upregulated in Acss2
-/- mice (
Figure 1), but among fatty acids, only myristic acid was elevated in adipose tissue. Huang and colleagues studied lipid metabolism in Acss2
-/- mice and found that loss of Acss2 had opposing effects under fed and fasted conditions [
13]. They noted that Acss2 acted in a transcription factor-like way to promote the storage of fats when food was abundant, but in turn Acss2 enhances the metabolism of fats during fasting through the selective regulation of genes involved in lipid metabolism.
In general, the effects of Acss2 deletion on signaling pathways were mostly specific for each organ system, with relatively limited overlap. However, in brain and adipose tissue two canonical signaling pathways were strongly perturbed, including “sirtuin signaling pathway” and “oxidative phosphorylation” (
Figure 4A and
Figure 5A). However, the effects of Acss2 deletion in the two tissues were opposite, with the sirtuin pathway being activated in the brain, but inhibited in adipose tissue. Oxidative phosphorylation, on the other hand, was inhibited in the brain but was stimulated in adipose tissue. This indicates that the regulatory effects of Acss2 reflect the physiological roles of different organ systems. Adipose tissue is a net exporter of energy substrates, especially when food is limiting, whereas brain is a net consumer, and Acss2 clearly plays complementary roles in the regulation of energy distribution and utilization in these tissues. Sirtuins are NAD+ dependent deacetylases that regulate metabolism. For example, sirtuin-1 (Sirt1) acts to deacetylate and thereby activate Acss2, and increase fatty acid synthesis from acetate [
26]. The effects of Acss2 deletion on signaling pathways are consistent with the observation that Acss2 can translocate to the cell nucleus where it can regulate transcription [13, 18, 19, 27]. Earlier studies in the brain demonstrated a predominant localization of Acss2 in the nuclei of neurons, astrocytes and oligodendrocytes, with greatly increased expression 24 hours following traumatic brain injury [
16]. The substantially increased nuclear expression of Acss2 after brain injury indicated that the enzyme is likely involved in stress responses and possibly tissue repair.
While the gene expression differences in the current study were mostly distinct for each tissue, it is noteworthy that we observed large expression changes for transmembrane protein-25 (Tmem25) in the liver and the brain. Tmem25 was the most downregulated gene observed in both tissues (
Figure 2B and C). Tmem25 has been associated with lysosomal acidification and accelerated protein degradation in neurons [
28]. Because the loss of Acss2 substantially reduced expression of Tmem25, it is possible that Acss2 acts to enhance Tmem25 transcription during autophagic responses to increase lysosomal acidification and facilitate protein turnover. Further, proteasome 26S subunit, non-ATPase-8 (Psmd8) was downregulated in all three tissues (
Figure 2, B, C and D). PSMD8 (proteasome 26S Subunit, Non-ATPase 8) is also called regulatory particle of non-ATPase-12 (Rpn12), and is part of the 19S regulatory proteasome subunit. It is therefore possible that Acss2 upregulates the expression of proteasome subunits during autophagic responses. Our results are in agreement with previous studies on Acss2 and autophagy [18, 19, 29].
3.1. Acss2 as an Epigenetic Regulator and Metabolic Integrator
Chromatin can assume multiple distinct configurations that modulate gene expression by making transcription sites accessible or inaccessible. Specific chromatin states induced by post-translational modifications of nucleosome proteins are brought about in part by enzymes that also play roles in energy metabolism [1, 2]. The role of metabolic enzymes acting in the cell nucleus is an emerging theme in transcriptional regulation. Acss2 acts as one of these epigenetic regulatory enzymes involved in chromatin remodeling that also plays a role in central acetyl-CoA metabolism [reviewed in 24]. Acss2 regulates the transcription of specific gene suites by at least two mechanisms, the acetylation of histones acting to open specific nucleosome sites, and by the acetylation of specific transcription factors [reviewed in 25]. By interacting with transcription factor complexes, Acss2 provides acetyl-CoA on-demand to histone acetyltransferases (HAT) that utilize acetyl-CoA to open chromatin and allow access of transcriptional enzyme complexes. A third way for Acss2 to facilitate transcription is the local production of AMP near nascent transcription sites, which could increase nuclear AMPK activity to phosphorylate and activate targets such as histone acetyltransferase-1 [
30]. Acss2 also interacts with p300 and CREB binding protein (CBP), which are transcriptional coactivators with acetyltransferase activity that target histones and other transcription-associated proteins for acetylation [
31]. In this role Acss2 provides on-demand acetyl-CoA for the activity of p300 and CBP. For example, in certain cancer cells exposed either to hypoxia or glucose deprivation, hypoxia inducible factor 2-alpha (HIF-2α) binds to an erythropoietin promoter region and enhances erythropoietin expression. HIF-2α acetylation requires Acss2 and CBP, and Acss2 is required for stable CBP/HIF-2α complex formation [
17]. In this manner, HIF-2α acetylation by the sequential activity of Acss2 and CBP improves the response to low oxygen tension. Further, Acss2 expression is increased in the nuclei of differentiating neurons [
16] and localizes to chromatin regions of increased histone acetylation and transcriptional activity [
32]. Acetate, acting through Acss2, activates transcriptional programs in the brain linked to learning and memory, and loss of Acss2 reduces nuclear acetyl-CoA levels, histone acetylation and expression of associated genes [32, 33]. These investigators examined transcription factor binding motifs for Acss2 and found an association with the acetyltransferases p300 and CBP, as in the case of enhanced erythropoietin expression noted above.
Autophagy is associated with nutrient deprivation and cellular stress responses, and here again Acss2 plays a regulatory role. Nutrient deprivation leads to AMPK activation, which in turn phosphorylates Acss2, resulting in Acss2 translocation to the cell nucleus. In conjunction with transcription factor EB (Tfeb), Acss2 associates with lysosomal and autophagosomal gene promoter regions, and utilizes acetate derived from histone deacetylation to locally produce acetyl-CoA for acetylation of histone H3, thereby promoting autophagic gene expression [18, 19]. As such, Acss2 is at the hub of interactions between acetyl-CoA metabolism and transcriptional regulation of genes associated with numerous cellular functions ranging from lipid metabolism to autophagy to memory formation. In this capacity Acss2 acts to augment or enhance distinct regimens of transcriptional activity in different tissues during development and under various stressors including nutrient deprivation and injury.
Our current results support the conclusion that Acss2, while predominantly redundant to Acly in lipid synthesis, is unique in its metabolic regulation and signaling roles. The observed changes occurred in well-fed, non-stressed mice, and therefore reflect only a subset of expression changes that would be expected under stressed conditions or in response to injury. Our results can be explained by Acss2 acting as a transcriptional regulator through selective on-demand acetyl-CoA synthesis at sites of enhanced transcriptional activity. As such, Acss2 provides acetyl-CoA not only for histone acetylation, but also for acetylation of transcription factors and associated protein targets that act to modulate transcription. Because the differential expression patterns mapped to transcription factors in an organ-specific manner, Acss2 is binding to various transcription factor complexes and assisting in regulating the transcriptional expression of specific genes during various cellular stress responses. In conclusion, Acss2 can be considered a task-switching metabolic effector that transitions from roles in cytoplasmic acetyl-CoA formation and lipid synthesis to a nuclear transcriptional regulator through its targeted actions on histone and transcription factor acetylation and other actions in the cell nucleus, e.g., locally increased levels of AMP at sites of high Acss2 activity. Future research on the underlying mechanisms whereby Acss2 acts to institute various metabolic programs in different organ systems will shed light on the pathophysiology of diseases ranging from metabolic disorder to cancer.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Acss2 Gene Knockout:
Breeding pairs of Acss2 gene (NM-019811) knockout mice were obtained from Lexicon Pharmaceuticals via Taconic Farms, New York, and they were bred in our animal facility on a C57BL background. The Acss2 gene knockout involved standard procedures using embryonic stem cells with the 129S5 genetic background. The deleted region included approximately 3.6 kb beginning at the transcription start site. Deletion of Acss2 was confirmed using RT-PCR (Transnetyx, Inc.).
4.2. Animal Breeding:
Animal care and experimental procedures were carried out in accordance with NIH guidelines and approved by the Uniformed Services University Animal Care and Use Committee. Animals were housed in an environmentally controlled room (20-23°C, ~44% humidity, 12 hours light/dark cycle, 350-400 lux, lights on at 6:00 am), with food and water available continuously. Animal handling was minimized to reduce animal stress. The homozygous Acss2-/- mice reproduced normally, and therefore wild-type mice and homozygous mice were bred separately for the experiments. Before use in experiments, individual genotypes were confirmed via PCR using probes designed by Lexicon Pharmaceuticals.
4.3. Fatty Acid Analysis:
For tissue fatty acid determinations, 5 male mice were used per group. Liver, brain, and mesenteric fat were rapidly collected, immediately homogenized in Trizol and the homogenates were frozen rapidly on dry ice. Tissue homogenates were thawed, and 10 μl aliquots were mixed with 50 μl of 1M NaOH and left for 60 min at room temperature in the dark. The mixtures were then acidified with 1 M HCl to pH 3-4, 10 ng of the fatty acid internal standard mix was added, and the solutions were saturated with NaCl. The mixtures were extracted with isooctane-ethyl acetate (9:1) four times and the extracts from each sample were pooled. Samples were then dried and dissolved in 65 μl of solvent B (methanol-water-ammonium acetate; 95:5:0.1%, pH 7.6). To each sample, 35 μl of solvent A was added (methanol-acetonitrile-water-ammonium acetate; 5:5:85:0.1%, pH 7.6). An aminopropyl-Strata column was conditioned with di-isopropyl ether followed by hexane, and the samples loaded. Columns were eluted with 3 ml di-isopropyl ether-formic acid (98:2). Eluates were dried and dissolved in a mixture of solvents A and B (35:65%). LC-MS was performed as previously described [
34].
4.4. Gene Array:
Gene array analysis was done on tissues from normally fed (non-fasted) adult male Acss2-/- and age-matched wild-type mice of the same strain (15 to 16 weeks old). Liver, Brain and mesenteric fat were rapidly collected, immediately homogenized in Trizol and the homogenates were frozen rapidly on dry ice. RNA was extracted, frozen and processed at the University of Chicago Genomics Facility. RNA quality and quantity were checked using an Agilent Bioanalyzer. RNA was processed into biotinylated cRNA using the Ambion Illumina® TotalPrep™ RNA Amplification Kit and the biotinylated cRNA was hybridized to Illumina microarray using an Illumina provided protocol. Staining of the arrays and scanning on an Illumina HiScan were also performed using Illumina provided protocols. Tissues examined included liver (n = 5 Acss2-/- and 4 wild-type), brain (n = 3 Acss2-/- and 3 wild-type) and adipose tissue (n = 4 Acss2-/- and 3 wild-type).
4.5. Gene Alignment and Counts:
Reads were aligned to the Mus musculus genome version mm10 [
35] using Star Aligner [
36] and the RSEM software package to quantify transcripts [
37]. Resulting TPM/FPKM counts were used in the differential expression analysis using the limma R software package [
38]. Samples were grouped according to treatment and tissue type. DEG lists were arranged according to the foldchange and associated p-value. These DEG lists were used for further enrichment analysis as described below.
4.6. Pathway Analyses:
In silico analyses of DEGs, (p-value < 0.05, log2 fold change > 1) of Acss2
-/- (knockout mice, KO) compared to wild-type (WT) control groups in the liver, brain, and mesenteric adipose tissue were performed using Qiagen’s Ingenuity Pathway Analyses (IPA, QIAGEN Inc.,
https://www.qiagenbioinformatics.com/products/ingenuity-pathway-analysis) system. The analyses were based on experimentally observed and predicted data from the Ingenuity Knowledge Base data sources using Benjamini Hochberg-corrected right-tailed Fisher’s exact test.
4.7. Karyoplot Analysis:
Karyoplots were done using KaryoploteR in the R programming language [
39]. DEG lists were used to map the expression patterns onto mouse chromosomal positions. All statistically significant DEGs (p < 0.05) were included. The log fold change was mapped to the size of the dots on the karyoplots.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at:
www.mdpi.com/xxx/s1, Supplementary data.docx.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and Methodology: AMN, RB, JRM, Investigation: JKSK, APA, AMN and SG, Formal Analysis: NPV, DKS and JRM, Writing: NPV, DKS, JRM, PA, RB and AMN, Visualization: NPV, DKS and JRM, Review and editing: NPV, DKS, JRM, JMD, APA, PA, RB and AMN, Supervision and Project Administration: AMN, RB, Funding Acquisition: AMN, TF.
Funding
This work was supported by NIH grant NS 084206 and USUHS CHIRP internal grant APG-70-3917 to AMN.
Institutional Review Board Statement
All animal protocols were reviewed by the USUHS IACUC and adhere to the NIH guidelines on animal use.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available upon request.
Disclosure statement
JMD is a cofounder of Galilei Biosciences and a consultant for Evrys Bio.
Disclaimer
The opinions and assertions expressed herein are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of the Uniformed Services University or the Department of Defense.
References
- van der Knaap, J.A.; Verrijzer, C.P. Undercover: gene control by metabolites and metabolic enzymes. Genes Dev 2016, 30, 2345–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Egervari, G.; Wang, Y.; Berger, S.L.; Lu, Z. Regulation of chromatin and gene expression by metabolic enzymes and metabolites. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2018, 19, 563–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boukouris, A.E.; Zervopoulos, S.D.; Michelakis, E.D. Metabolic Enzymes Moonlighting in the Nucleus: Metabolic Regulation of Gene Transcription. Trends Biochem Sci 2016, 41, 712–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egervari, G.; Glastad, K.M.; Berger, S.L. Food for thought. Science 2020, 370, 660–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, R.P.; Brunengraber, H. Contributions of cytosolic and mitochondrial acetyl-CoA syntheses to the activation of lipogenic acetate in rat liver. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1980, 132, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ingram-Smith, C.; Smith, K.S. AMP-forming acetyl-CoA synthetases in Archaea show unexpected diversity in substrate utilization. Archaea 2007, 2, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imesch, E.; Rous, S. Partial purification of rat liver cytoplasmic acetyl-CoA synthetase; characterization of some properties. Int. J. Biochem. 1984, 16, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodnutt, G.; Parker, D.S. Rabbit liver acetyl-CoA synthetase. Biochem. J. 1978, 175, 757–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, Y.; Yamamoto, J.; Okamura, M.; Fujino, T.; Takahashi, S.; Takeuchi, K.; Osborne, T.F.; Yamamoto, T. T.; Ito, S.; Sakai, J. Transcriptional regulation of the murine acetyl-CoA synthetase 1 gene through multiple clustered binding sites for sterol regulatory element-binding proteins and a single neighboring site for Sp1. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2001, 276, 34259–34269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luong, A.; Hannah, V.C.; Brown, M.S.; Goldstein, J.L. Molecular characterization of human acetyl-CoA synthetase, an enzyme regulated by sterol regulatory element-binding proteins. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2000, 275, 26458–26466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sone, H.; Shimano, H.; Sakakura, Y.; Inoue, N.; Amemiya-Kudo, M.; Yahagi, N.; Osawa, M.; Suzuki, H.; Yokoo, T.; Takahashi, A.; et al. Acetyl-coenzyme A synthetase is a lipogenic enzyme controlled by SREBP-1 and energy status. Am. J. Physiol Endocrinol. Metab 2002, 282, E222–E230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Luo, J.; Ma, G.; Zhang, X.; Yao, D.; Li, M.; Loor, J.J. Acyl-CoA synthetase short-chain family member 2 (ACSS2) is regulated by SREBP-1 and plays a role in fatty acid synthesis in caprine mammary epithelial cells. Journal of Cellular Physiology 2017. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Plec, A.A.; Estill, S.J.; Cai, L.; Repa, J.J.; McKnight, S.L.; Tu, B.P. ACSS2 promotes systemic fat storage and utilization through selective regulation of genes involved in lipid metabolism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E9499–E9506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; McCaffery, J.M.; Irizarry, R.A.; Boeke, J.D. Nucleocytosolic acetyl-coenzyme a synthetase is required for histone acetylation and global transcription. Mol. Cell 2006, 23, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wellen, K.E.; Hatzivassiliou, G.; Sachdeva, U.M.; Bui, T.V.; Cross, J.R.; Thompson, C.B. ATP-citrate lyase links cellular metabolism to histone acetylation. Science 2009, 324, 1076–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ariyannur, P.S.; Moffett, J.R.; Madhavarao, C.N.; Arun, P.; Vishnu, N.; Jacobowitz, D.; Hallows, W.C.; Denu, J.M.; Namboodiri, A.M. Nuclear-cytoplasmic localization of acetyl coenzyme A synthetase-1 in the rat brain. J. Comp Neurol. 2010, 518, 2952–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Xu, M.; Nagati, J.; Garcia, J.A. Coordinate regulation of stress signaling and epigenetic events by Acss2 and HIF-2 in cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0190241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Qian, X.; Lu, Z. Local histone acetylation by ACSS2 promotes gene transcription for lysosomal biogenesis and autophagy. Autophagy 2017, 13, 1790–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yu, W.; Qian, X.; Xia, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Lee, J.H.; Li, W.; Lyu, J.; Rao, G.; Zhang, X.; et al. Nucleus-translocated ACSS2 promotes gene transcription for lysosomal biogenesis and autophagy. Mol. Cell 2017, 66, 684–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashimo, T.; Pichumani, K.; Vemireddy, V.; Hatanpaa, K.J.; Singh, D.K.; Sirasanagandla, S.; Nannepaga, S.; Piccirillo, S.G.; Kovacs, Z.; Foong, C.; et al. Acetate is a bioenergetic substrate for human glioblastoma and brain metastases. Cell 2014, 159, 1603–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulusu, V.; Tumanov, S.; Michalopoulou, E.; van den Broek, N.J.; Mackay, G.; Nixon, C.; Dhayade, S.; Schug, Z.T.; Vande, V.J.; Blyth, K.; et al. Acetate Recapturing by Nuclear Acetyl-CoA Synthetase 2 Prevents Loss of Histone Acetylation during Oxygen and Serum Limitation. Cell Rep. 2017, 18, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagati, J.S.; Xu, M.; Garcia, T.; Comerford, S.A.; Hammer, R.E.; Garcia, J.A. A substitution mutation in a conserved domain of mammalian acetate-dependent acetyl CoA synthetase 2 results in destabilized protein and impaired HIF-2 signaling. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Liu, H.; He, J.; Wang, Z.; Yin, Z.; You, G.; Wang, Z.; Davis, R.E.; Lin, P.; Bergsagel, P.L.; et al. Acetyl-CoA Synthetase 2: A Critical Linkage in Obesity-Induced Tumorigenesis in Myeloma. Cell Metab 2021, 33, 78–93 e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moffett, J.R.; Puthillathu, N.; Vengilote, R.; Jaworski, D.M.; Namboodiri, A.M. Acetate Revisited: A Key Biomolecule at the Nexus of Metabolism, Epigenetics and Oncogenesis: Part 1: Acetyl-CoA, Acetogenesis and Acyl-CoA Short-Chain Synthetases. Frontiers in Physiology 2020, 11, 1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moffett, J.R.; Puthillathu, N.; Vengilote, R.; Jaworski, D.M.; Namboodiri, A.M. Acetate Revisited: A Key Biomolecule at the Nexus of Metabolism, Epigenetics, and Oncogenesis: Part 2: Acetate and ACSS2 in Health and Disease. Frontiers in Physiology 2020, 11, 1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallows, W.C.; Lee, S.; Denu, J.M. Sirtuins deacetylate and activate mammalian acetyl-CoA synthetases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 10230–10235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Xu, M.; Nagati, J.S.; Hogg, R.T.; Das, A.; Gerard, R.D.; Garcia, J.A. The Acetate/ACSS2 Switch Regulates HIF-2 Stress Signaling in the Tumor Cell Microenvironment. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Tian, X.; Lu, X.; Xu, D.; Guo, Y.; Dong, Z.; Li, Y.; Ma, Y.; Chen, C.; Yang, Y.; et al. TMEM25 modulates neuronal excitability and NMDA receptor subunit NR2B degradation. J Clin. Invest. 2019, 129, 3864–3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Zhou, X.; Wu, Q.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Deng, C.; Zhang, X. Acetyl CoA synthase 2 potentiates ATG5-induced autophagy against neuronal apoptosis after subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Mol Histol 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, T.L.; Gongol, B.; Zhang, F.; Martin, M.; Johnson, D.A.; Xiao, H.; Wang, Y.; Subramaniam, S.; Chien, S.; Shyy, J.Y. AMPK promotes mitochondrial biogenesis and function by phosphorylating the epigenetic factors DNMT1, RBBP7, and HAT1. Sci Signal 2017, 10, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogryzko, V.V.; Schiltz, R.L.; Russanova, V.; Howard, B.H.; Nakatani, Y. The transcriptional coactivators p300 and CBP are histone acetyltransferases. Cell 1996, 87, 953–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mews, P.; Donahue, G.; Drake, A.M.; Luczak, V.; Abel, T.; Berger, S.L. Acetyl-CoA synthetase regulates histone acetylation and hippocampal memory. Nature 2017, 546, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mews, P.; Egervari, G.; Nativio, R.; Sidoli, S.; Donahue, G.; Lombroso, S.I.; Alexander, D.C.; Riesche, S.L.; Heller, E.A.; Nestler, E.J.; et al. Alcohol metabolism contributes to brain histone acetylation. Nature 2019, 574, 717–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellmuth, C.; Weber, M.; Koletzko, B.; Peissner, W. Nonesterified fatty acid determination for functional lipidomics: comprehensive ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry quantitation, qualification, and parameter prediction. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 1483–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Church, D.M.; Goodstadt, L.; Hillier, L.W.; Zody, M.C.; Goldstein, S.; She, X.; Bult, C.J.; Agarwala, R.; Cherry, J.L.; DiCuccio, M.; et al. Lineage-specific biology revealed by a finished genome assembly of the mouse. PLoS Biol 2009, 7, e1000112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Dewey, C.N. RSEM: accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinformatics 2011, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, M.E.; Phipson, B.; Wu, D.; Hu, Y.; Law, C.W.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res 2015, 43, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gel, B.; Serra, E. karyoploteR: an R/Bioconductor package to plot customizable genomes displaying arbitrary data. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 3088–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).