Submitted:
07 March 2023
Posted:
08 March 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
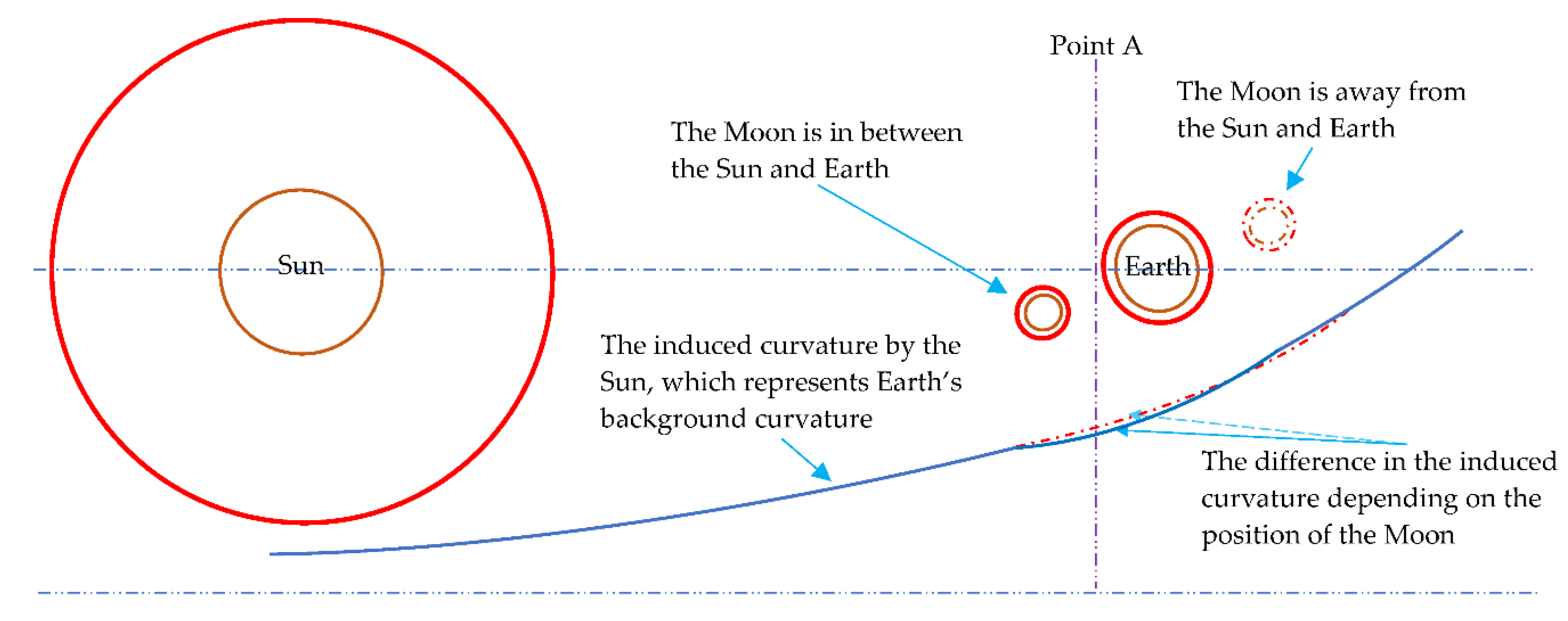
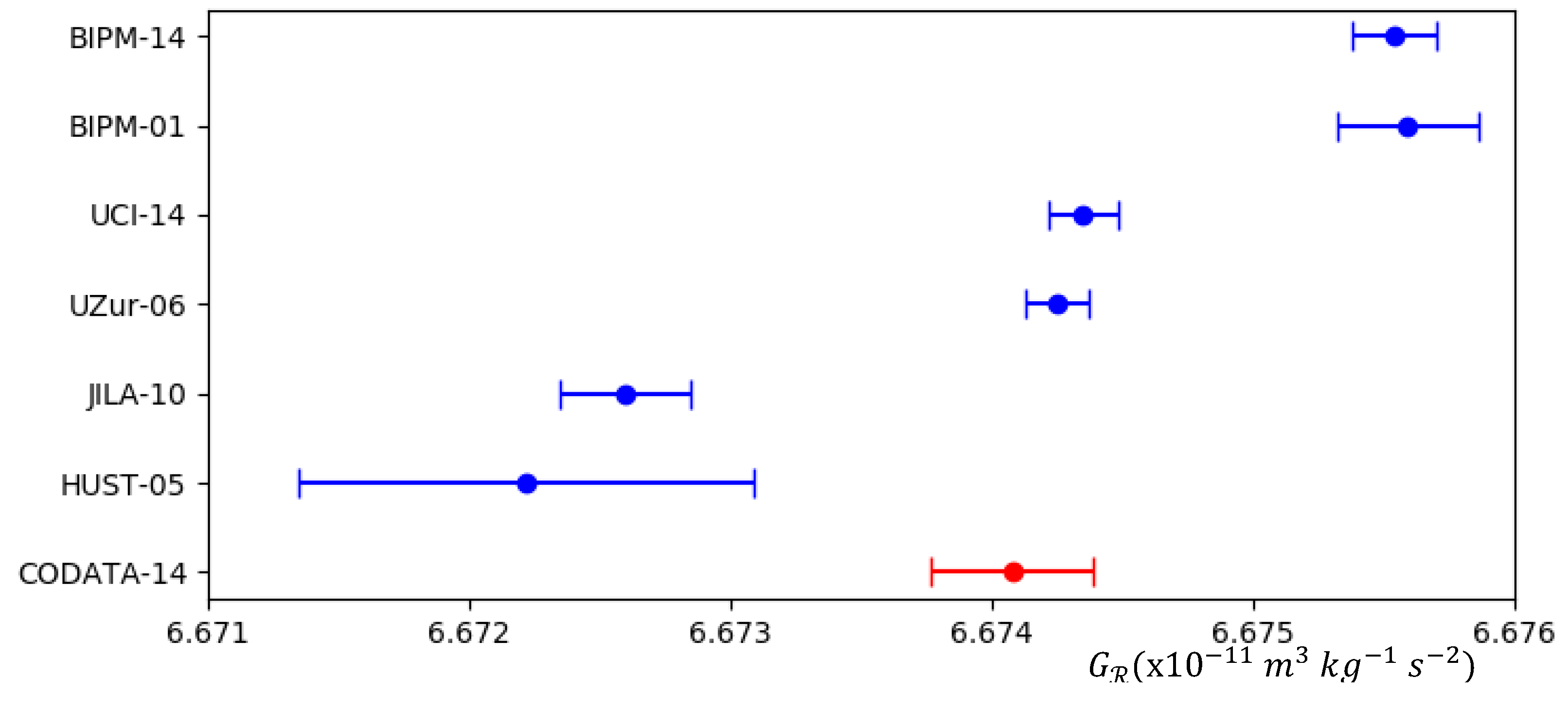
2. Newtonian Gravitational Parameter
3. Emergence of Mass
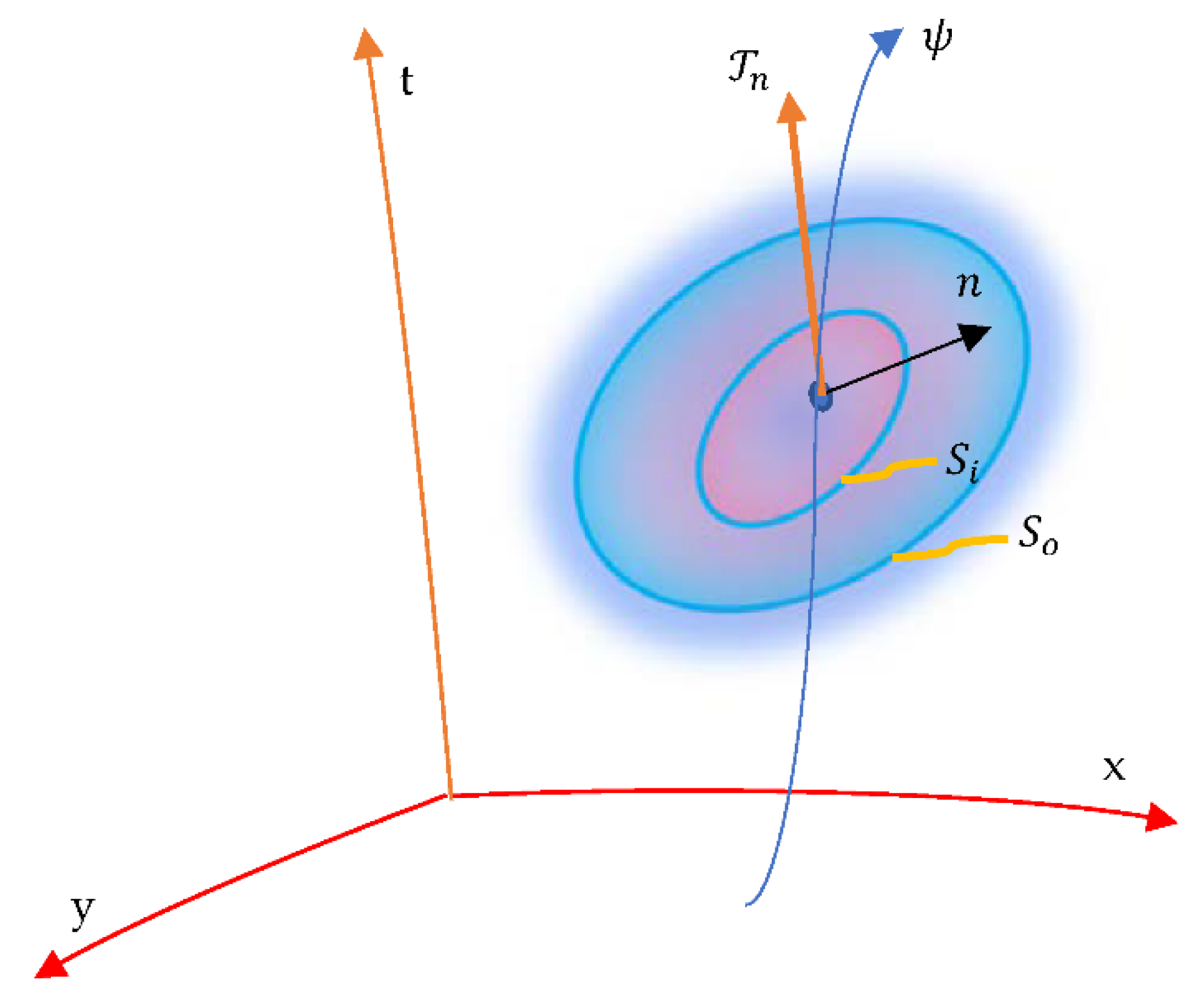
4. Geometric-Abstraction Reduction
5. Conclusions and Future Experiment Recommendations
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xue, C.; Liu, J.P.; Li, Q.; Wu, J.F.; Yang, S.Q.; Liu, Q.; Shao, C.G.; Tu, L.C.; Hu, Z.K.; Luo, J. Precision measurement of the Newtonian gravitational constant. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 7, 1803–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosi, G.; Sorrentino, F.; Cacciapuoti, L.; Prevedelli, M.; Tino, G.M. Precision measurement of the Newtonian gravitational constant using cold atoms. Nature 2014, 510, 518–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlamminger, S. Gravity measured with record precision. Nature 2018, 562–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibney, E. Rivals join forces to nail down Big G. Metrologists meet to design the ultimate gravitational-constant experiment. Nature 2014, 514, 150–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlamminger, S. Fundamental constants: a cool way to measure big G. Nature 2014, 510, 478–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Fadhli, M.B. Celestial and Quantum Propagation, Spinning, and Interaction as 4D Relativistic Cloud-Worlds Embedded in a 4D Conformal Bulk: From String to Cloud Theory. Preprints 2022, 2020100320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozameh, C.; Newman, E.; gravitation, K. T-G relativity 1985 Conformal Einstein spaces. Springer.
- Quinn, T.; Parks, H.; Speake, C.; Davis, R. Improved determination of G using two methods. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 111, 101102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, T.J.; Speake, C.C.; Richman, S.J.; Davis, R.S.; Picard, A. A New Determination of G Using Two Methods. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 87, 111101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, R.; Bantel, M.; Berg, E.; Cross, W. A measurement of G with a cryogenic torsion pendulum. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2014, 372, 20140025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlamminger, S.; Holzschuh, E.; Kündig, W.; Nolting, F.; Pixley, R.E.; Schurr, J.; Straumann, U. Measurement of Newton’s gravitational constant. Phys. Rev. D Part. Fields Gravit. Cosmol. 2006, 74, 082001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, H.V.; Faller, J.E. Simple pendulum determination of the gravitational constant. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 110801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.K.; Guo, J.Q.; Luo, J. Correction of source mass effects in the HUST-99 measurement of G. Phys. Rev. D Part. Fields Gravit. Cosmol. 2005, 71, 127505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, P.J.; Newell, D.B.; Taylor, B.N. CODATA recommended values of the fundamental physical constants: 2014. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2016, 88, 035009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




