Submitted:
13 January 2023
Posted:
17 January 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Structural Evaluation and Optimization of COVID-19 Main Protease Complex
2.2. Molecular docking of COVID-19 main protease complex with a modified and derivative form of 2-Deoxy-Glucose
2.3. ADMET prediction of 2-Deoxy-Glucose ligands for toxicity assessment
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. The target PDB Structure Selection and Validation
3.2. Active Site Prediction
3.3. Ligand Files Preparation and Optimization
3.4. Molecular Docking
3.5. Prediction of ADMET Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Ethics approval (include appropriate permissions or waivers)
Consent to participate (include relevant statements)
Consent for publication
Availability of data and material (data transparency)
Code availability (software application or custom code)
Conflicts of interest/Competing interests
References
- Cimolai, N. The Complexity of Co-Infections in the Era of COVID-19. SN Compr. Clin. Med. 2021, 3, 1502–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandala, E.R.; Kruger, B.R.; Cesarino, I.; Leao, A.L.; Wijesiri, B.; Goonetilleke, A. Impacts of COVID-19 Pandemic on the Wastewater Pathway into Surface Water: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 774, 145586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aygün, İ.; Kaya, M.; Alhajj, R. Identifying Side Effects of Commonly Used Drugs in the Treatment of Covid 19. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barlow, A.; Landolf, K.M.; Barlow, B.; Yeung, S.Y.A.; Heavner, J.J.; Claassen, C.W.; Heavner, M.S. Review of Emerging Pharmacotherapy for the Treatment of Coronavirus Disease 2019. Pharmacotherapy 2020, 40, 416–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathinavel, T.; Aroulmoji, V. Hyaluronic Acid - 2-Deoxy-D-Glucose Conjugate Act as a Promising Targeted Drug Delivery Option for the Treatment of COVID-19. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, Q.; Ma, Y.; Gao, X.; Liu, R.; Liu, P.; Mi, Y.; Fu, X.; Gao, Q. 2-Deoxyglucose Conjugated Platinum (II) Complexes for Targeted Therapy: Design, Synthesis, and Antitumor Activity. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2016, 34, 2339–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, A.; Adhikary, A.; Woloschak, G.; Dwarakanath, B.S.; Papineni, R.V.L. A Combinatorial Approach of a Polypharmacological Adjuvant 2-Deoxy-D-Glucose with Low Dose Radiation Therapy to Quell the Cytokine Storm in COVID-19 Management. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2020, 96, 1323–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwarakanath, B.S. Cytotoxicity, Radiosensitization, and Chemosensitization of Tumor Cells by 2-Deoxy-D-Glucose in Vitro. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2009, 5 Suppl 1, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passalacqua, K.D.; Lu, J.; Goodfellow, I.; Kolawole, A.O.; Arche, J.R.; Maddox, R.J.; Carnahan, K.E.; O’riordan, M.X.D.; Wobus, C.E. Glycolysis Is an Intrinsic Factor for Optimal Replication of a Norovirus. MBio 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokt, I.; Ziemniak, M.; Ja, A. 2-Deoxy- d -Glucose and Its Analogs : From Diagnostic to Therapeutic Agents. 2020.
- Laussel, C.; Léon, S. Cellular Toxicity of the Metabolic Inhibitor 2-Deoxyglucose and Associated Resistance Mechanisms. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Du, C.; Shan, L.; Zhu, H.; Xue, B.; Qian, Z.; Achilefu, S.; Gu, Y. Comparison of Near-Infrared Fluorescent Deoxyglucose Probes with Different Dyes for Tumor Diagnosis in Vivo. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2012, 7, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Bloch, S.; Kao, J.; Achilefu, S. Multivalent Carbocyanine Molecular Probes: Synthesis and Applications. Bioconjug. Chem. 2005, 16, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Du, X.; Xu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Liu, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, B.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Peng, C.; et al. Structure of Mpro from SARS-CoV-2 and Discovery of Its Inhibitors. Nature 2020, 582, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, K.B.; Guedes, I.A.; Karl, A.L.M.; Dardenne, L.E. Highly Flexible Ligand Docking: Benchmarking of the DockThor Program on the LEADS-PEP Protein-Peptide Data Set. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2020, 60, 667–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yang, M.; Ding, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lou, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Sun, L.; Mo, L.; Ye, S.; Pang, H.; et al. The Crystal Structures of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Virus Main Protease and Its Complex with an Inhibitor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2003, 100, 13190–13195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, K.; Palm, G.J.; Mesters, J.R.; Siddell, S.G.; Ziebuhr, J.; Hilgenfeld, R. Structure of Coronavirus Main Proteinase Reveals Combination of a Chymotrypsin Fold with an Extra α-Helical Domain. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 3213–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colovos, C.; Yeates, T.O. Verification of Protein Structures: Patterns of Nonbonded Atomic Interactions. Protein Sci. 1993, 2, 1511–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messaoudi, A.; Belguith, H.; Ben Hamida, J. Homology Modeling and Virtual Screening Approaches to Identify Potent Inhibitors of VEB-1 β-Lactamase. Theor. Biol. Med. Model. 2013, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskowski, R.A.; MacArthur, M.W.; Moss, D.S.; Thornton, J.M. PROCHECK: A Program to Check the Stereochemical Quality of Protein Structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1993, 26, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisakht, M.; Mahmoodzadeh, A.; Darabian, M. Plant-Derived Chemicals as Potential Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease (6LU7), a Virtual Screening Study. Phyther. Res. 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatada, R.; Okuwaki, K.; Mochizuki, Y.; Handa, Y.; Fukuzawa, K.; Komeiji, Y.; Okiyama, Y.; Tanaka, S. Fragment Molecular Orbital Based Interaction Analyses on COVID-19 Main Protease - Inhibitor N3 Complex (PDB ID: 6LU7). J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2020, 60, 3593–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stank, A.; Kokh, D.B.; Fuller, J.C.; Wade, R.C. Protein Binding Pocket Dynamics. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guedes, I.A.; Barreto, A.M.S.; Marinho, D.; Krempser, E.; Kuenemann, M.A.; Sperandio, O.; Dardenne, L.E.; Miteva, M.A. New Machine Learning and Physics-Based Scoring Functions for Drug Discovery. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.G.; Jin Xu, X.; Hua Li, C.; Chen, W.Z.; Wang, C.X. Identification of Key Residues for Protein Conformational Transition Using Elastic Network Model. J. Chem. Phys. 2011, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, M.I.; Shaikh, M. ; Atia-Tul-Wahab; Atta-Ur-Rahman In Silico Identification of Potential Inhibitors of Key SARS-CoV-2 3CL Hydrolase (Mpro) via Molecular Docking, MMGBSA Predictive Binding Energy Calculations, and Molecular Dynamics Simulation. PLoS One 2020, 15, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, E.; Khan, R.J.; Jha, R.K.; Amera, G.M.; Jain, M.; Singh, R.P.; Muthukumaran, J.; Singh, A.K. A Comprehensive Review on Promising Anti-Viral Therapeutic Candidates Identified against Main Protease from SARS-CoV-2 through Various Computational Methods. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2020, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keretsu, S.; Bhujbal, S.P.; Cho, S.J. Rational Approach toward COVID-19 Main Protease Inhibitors via Molecular Docking, Molecular Dynamics Simulation and Free Energy Calculation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.K.; Mahanta, S.; Tanti, B.; Tag, H.; Hui, P.K. Identification of Phytocompounds from Houttuynia Cordata Thunb. as Potential Inhibitors for SARS-CoV-2 Replication Proteins through GC–MS/LC–MS Characterization, Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Mol. Divers. 2021,. [CrossRef]
- El-Demerdash, A.; Metwaly, A.M.; Hassan, A.; El-Aziz, T.M.A.; Elkaeed, E.B.; Eissa, I.H.; Arafa, R.K.; Stockand, J.D. Comprehensive Virtual Screening of the Antiviral Potentialities of Marine Polycyclic Guanidine Alkaloids against Sars-Cov-2 (Covid-19). Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ya’u Ibrahim, Z.; Uzairu, A.; Shallangwa, G.; Abechi, S. Molecular Docking Studies, Drug-Likeness and in-Silico ADMET Prediction of Some Novel β-Amino Alcohol Grafted 1,4,5-Trisubstituted 1,2,3-Triazoles Derivatives as Elevators of P53 Protein Levels. Sci. African 2020, 10, e00570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, M.; Humphries, M.M.; Kiang, A.S.; Nguyen, A.T.H.; Gobbo, O.L.; Tam, L.C.S.; Suzuki, M.; Hanrahan, F.; Ozaki, E.; Farrar, G.J.; et al. Systemic Low-Molecular Weight Drug Delivery to Pre-Selected Neuronal Regions. EMBO Mol. Med. 2011, 3, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, G. Prediction of Drug-Like Properties The “ Drug-Likeness ” Concept. 2000, 1–34.
- Veber, D.F.; Johnson, S.R.; Cheng, H.Y.; Smith, B.R.; Ward, K.W.; Kopple, K.D. Molecular Properties That Influence the Oral Bioavailability of Drug Candidates. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 2615–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, A.; Wang, Z.; Cai, Z. Prediction of Human Intestinal Absorption by GA Feature Selection and Support Vector Machine Regression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2008, 9, 1961–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Wang, N.N.; Yao, Z.J.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, Y.; Ouyang, D.; Lu, A.P.; Cao, D.S. Admetlab: A Platform for Systematic ADMET Evaluation Based on a Comprehensively Collected ADMET Database. J. Cheminform. 2018, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, R.; Esaki, T.; Kawashima, H.; Natsume-Kitatani, Y.; Nagao, C.; Ohashi, R.; Mizuguchi, K. Predicting Fraction Unbound in Human Plasma from Chemical Structure: Improved Accuracy in the Low Value Ranges. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 5302–5311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helsen, N.; Vervoort, T.; Vandenbossche, J.; Lenz, O.; Monshouwer, M.; Pauwels, F.; Snoeys, J. Effect of Plasma Protein Binding on the Anti-Hepatitis B Virus Activity and Pharmacokinetic Properties of NVR 3-778. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, G.; Wu, Z.; Yi, J.; Fu, L.; Yang, Z.; Hsieh, C.; Yin, M.; Zeng, X.; Wu, C.; Lu, A.; et al. ADMETlab 2.0: An Integrated Online Platform for Accurate and Comprehensive Predictions of ADMET Properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, P.A.; Ryder, S.; Lavado, A.; Dilworth, C.; Riley, R.J. The Evolution of Strategies to Minimise the Risk of Human Drug-Induced Liver Injury (DILI) in Drug Discovery and Development. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 2559–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Suzuki, A.; Borlak, J.; Andrade, R.J.; Lucena, M.I. Drug-Induced Liver Injury: Interactions between Drug Properties and Host Factors. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
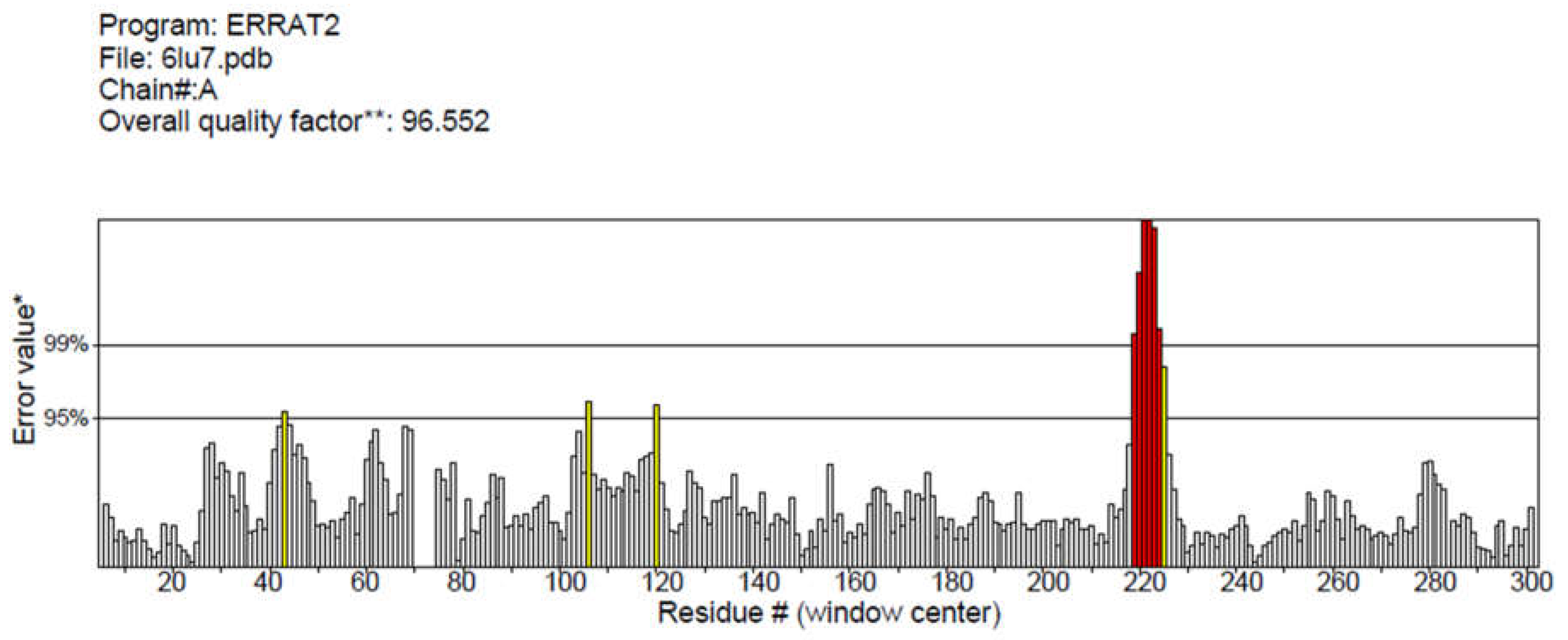
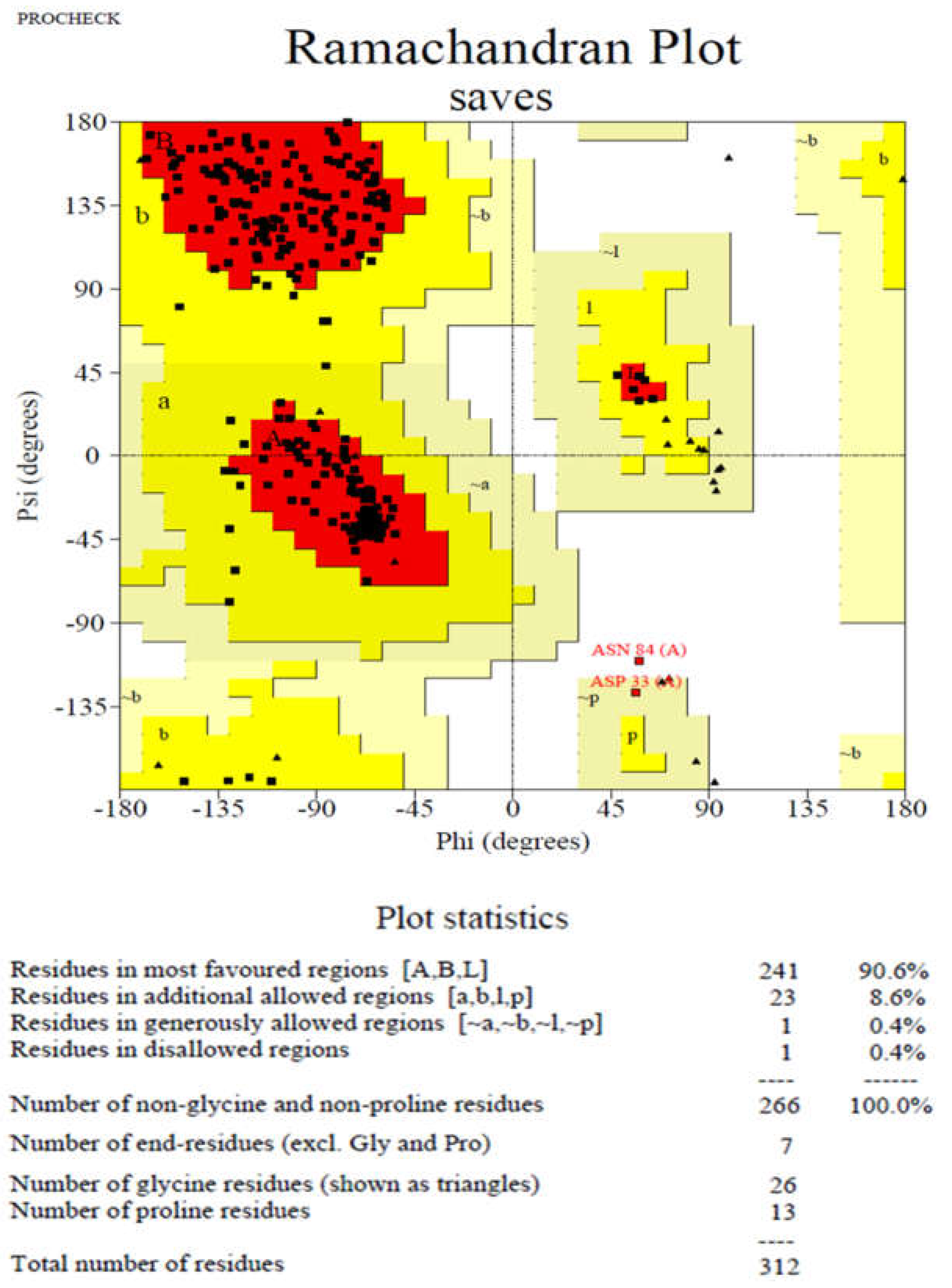
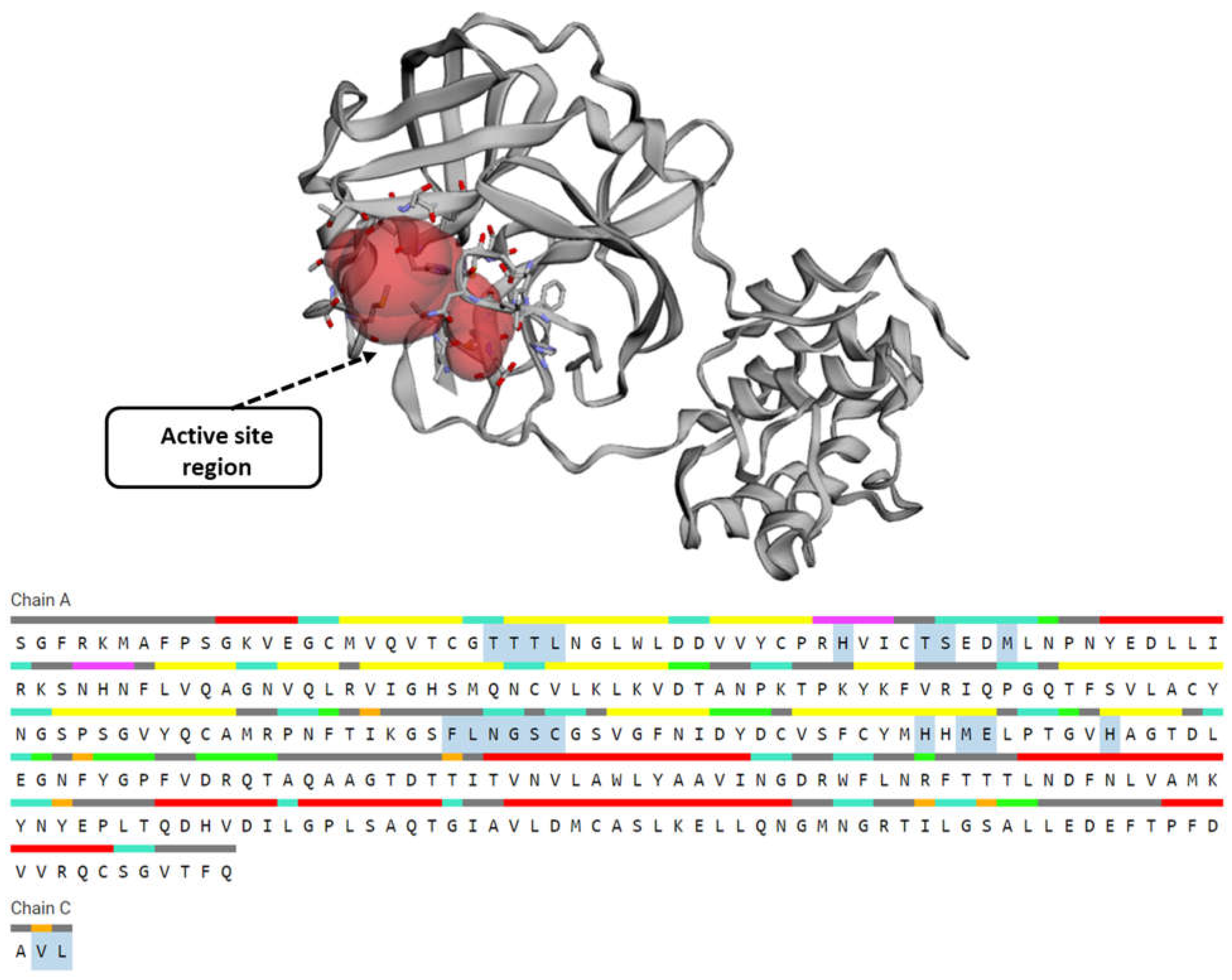
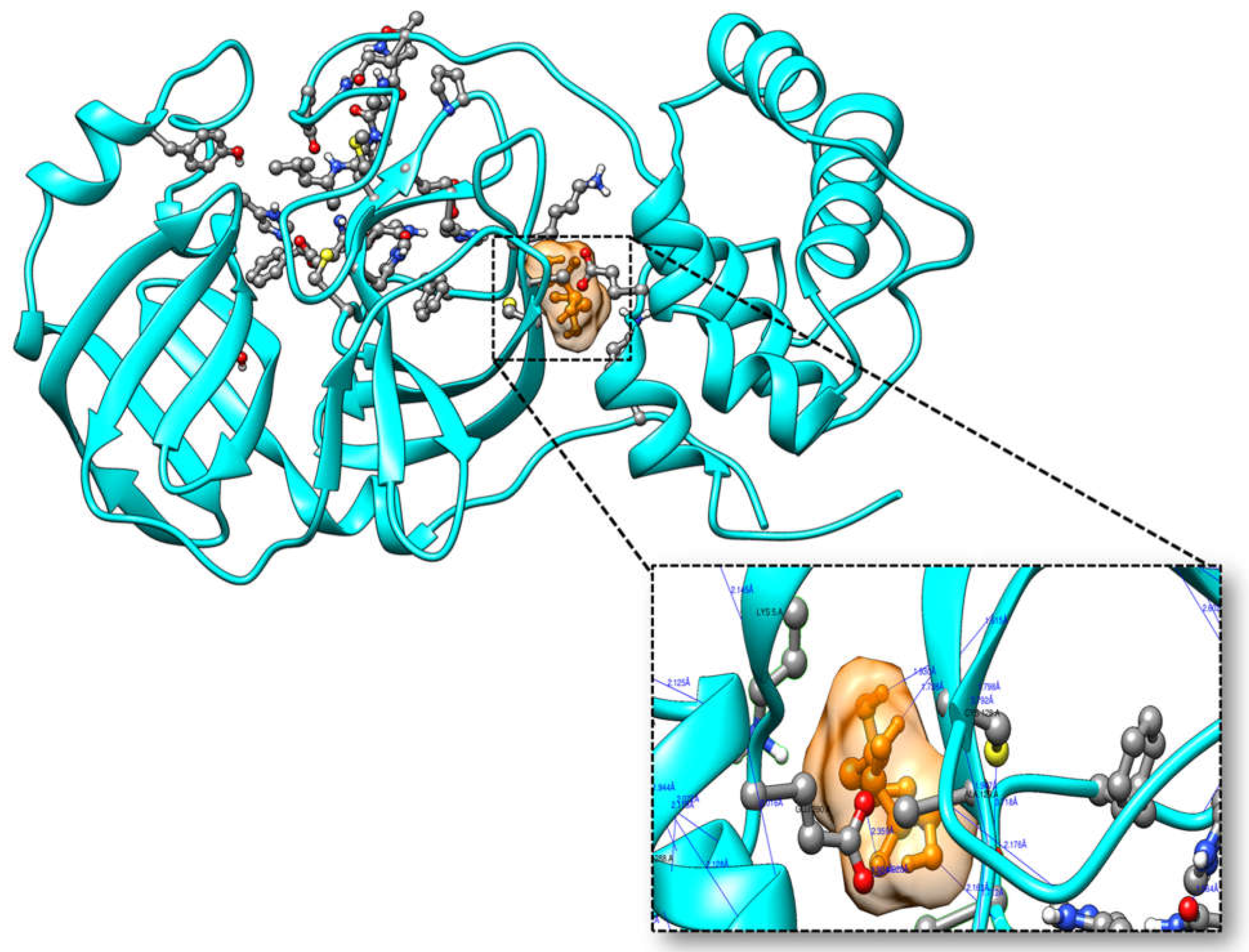
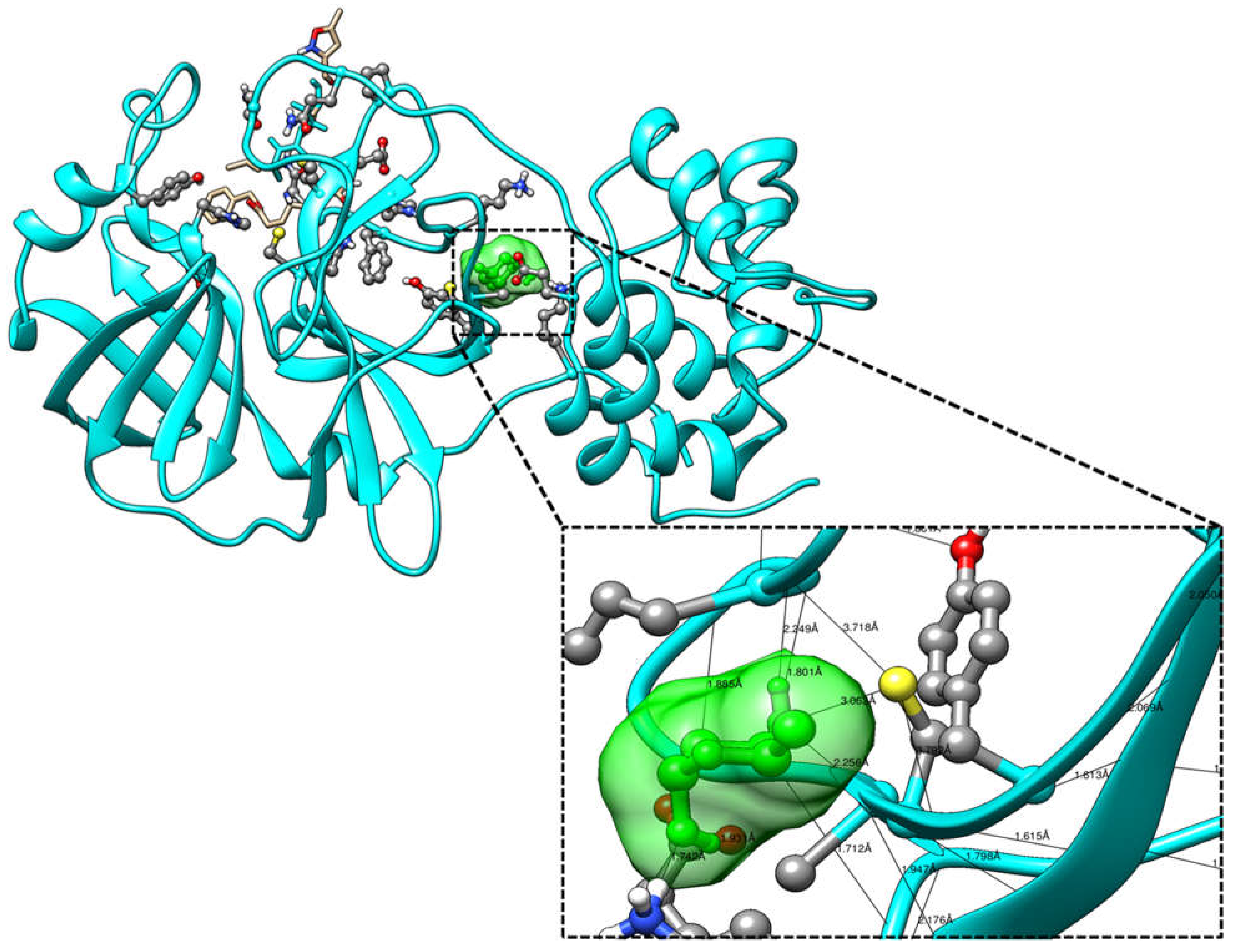

| Ligands | Affinity(kcal/mol) | VDW Energy(kcal/mol) | Electrostatic Energy(kcal/mol) | Binding Energy(kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2-Deoxy-D-glucose | -5.683 | 0.760 | -34.78 | -2.065 |
| Modified 2-Deoxy-D-glucose | -5.821 | -2.622 | -19.69 | -39.263 |
| Cypate 2-Deoxy-D-glucose | -9.18 | -29.34 | -25.43 | -8.01 |
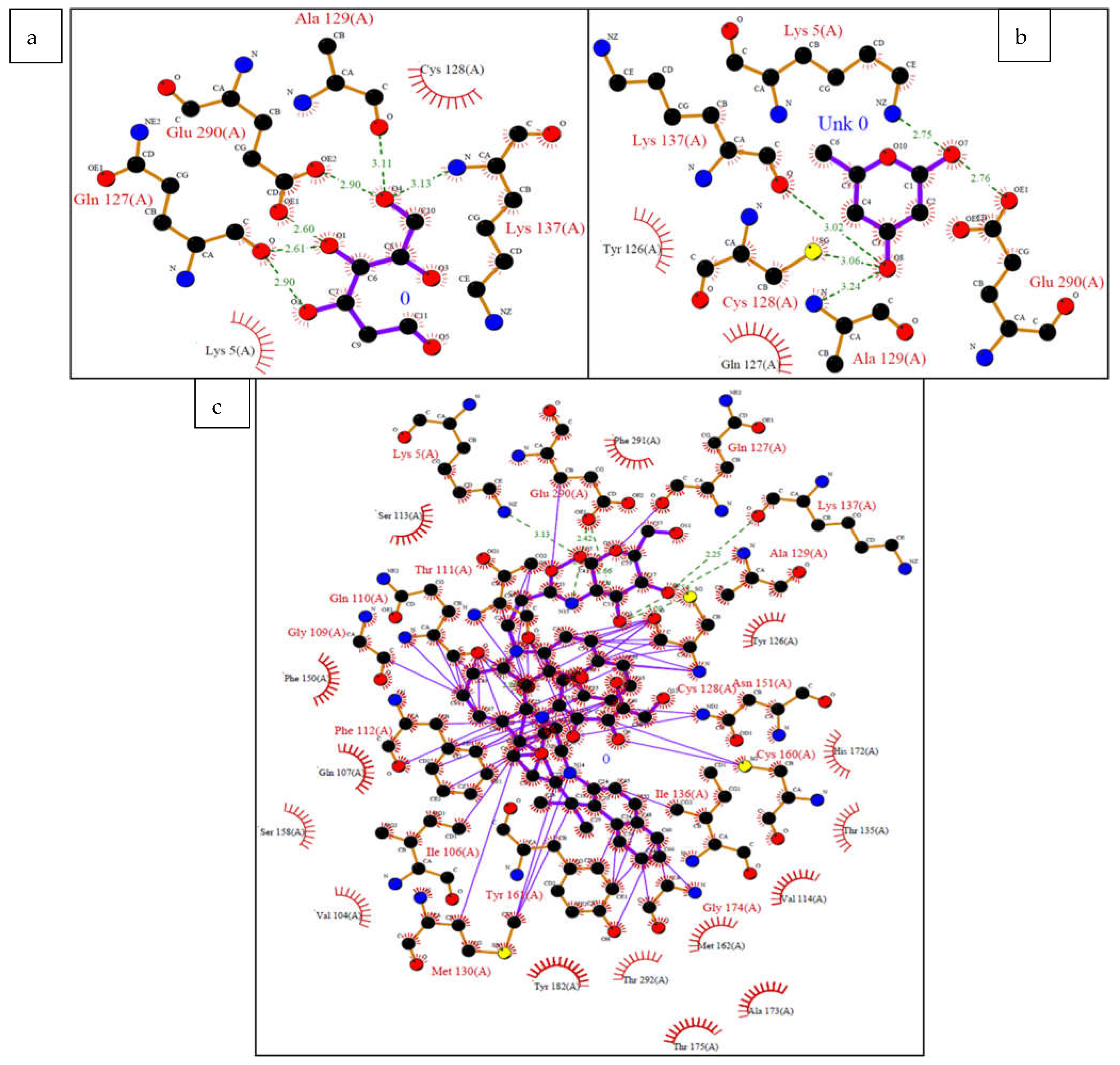
| Ligands | Atom Name of Ligands | Residue Name of Receptor | Distance in Å |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2-Deoxy-D-glucose | O2 | Gln127 | 2.9 |
| O1 | Gln127 | 2.6 | |
| O4 | Ala129 | 3.11 | |
| O4 | Lys137 | 3.13 | |
| O1 | Glu290 | 2.6 | |
| O4 | Glu290 | 2.9 | |
| Modified 2-Deoxy-D-glucose | O7 | Lys5 | 2.75 |
| O8 | Cys128 | 3.06 | |
| O8 | Ala129 | 3.24 | |
| O8 | Lys137 | 3.02 | |
| O7 | Glu290 | 2.76 | |
| Cypate 2-Deoxy-D-glucose | O7 | Lys5 | 3.13 |
| N16 | Gln110 | 2.86 | |
| O4 | Thr111 | 1.43 | |
| O3 | Cys128 | 3.20 | |
| O3 | Ala129 | 2.54 | |
| O5 | Lys137 | 2.25 | |
| O4 | Asn151 | 1.89 | |
| O6 | Cys160 | 1.48 | |
| N15 | Glu290 | 2.03 | |
| O3 | Glu290 | 2.66 | |
| O7 | Glu290 | 2.42 |
| Parameters | 2-Deoxy-D-glucose | Modified 2-Deoxy-D-glucose | Cypate 2-Deoxy-D-glucose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | 164.07 | 132.08 | 948.45 |
| logP | -2.035 | 0.029 | 3.383 |
| logS | -0.071 | 0.44 | -3.999 |
| H-Acceptors | 5 | 3 | 16 |
| H-Donors | 4 | 2 | 10 |
| Polar Surface Area | 97.99 | 49.69 | 244.98 |
| HIA | 0.392 | 0.005 | 0.948 |
| F30% | 0.911 | 0.513 | 0.981 |
| Fu | 82.05% | 85.23% | 0.680% |
| PPB | 22.54% | 6.58% | 97.58% |
| CL | 1.954 | 8.07 | 1.13 |
| T1/2 | 0.703 | 0.756 | 0.268 |
| DILI | 0.02 | 0.047 | 0.552 |
| Mutagenic | none | none | 4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





