Submitted:
08 January 2023
Posted:
09 January 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
I. Introduction
II. Literature Review
III. Contributions
IV. Dataset
| Ref. | Data type | Train/Test | Method | Performance (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liu et al. [19] | MRI, PET | 10- fold | stacked sparse auto-encoders and a softmax regression layer | Accuracy 87.76 |
| Liu et al. [21] | MRI, PET | 10- fold | stacked autoencoders and a softmax logistic regressor | Accuracy 82.59 |
| Korolev et al. [22] | MRI | 5 -fold | VoxCNN and ResNet | Accuracy 80.00 |
| Aderghal et al. [23] | sMRI, FuseMe (Method Name) | NA | 2D CNN | Accuracy 85.90 |
| Liu et al. [24] | FDG-PET | 10- fold | 2D CNN and RNNs | Accuracy 91.20 |
| Choi et al. [25] | FDG-PET, AV-45 PET /V | 10- fold | 3D CNN | Accuracy 96.00 |
| Cheng et al. [26] | T1-weighted MR and FDG-PET | 10- fold | 3D CNN | Accuracy 89.64 |
| Wang et al. [27] | MRI | 50% -50% | 2D CNN | Accuracy 97.65 |
| Shi et al. [28] | MRI, PET, MMSDN | 10- fold | Multi-modal stacked DPN + SVM | Accuracy 97.13 |
| Suk et al. [29] | MRI, PET | 10- fold | Multi-modal DBM + SVM | Accuracy 95.35 |
| Suk et al. [30] | MRI, PET, CSF | 10- fold | Stacked AEs + multi-kernel SVM | Accuracy 98.80 |
| Payan et al. [31] | MRI | 5- fold | Sparse AEs + 3D CNN | Accuracy 95.39 |
| Hosseini-Asl et al. [32] | MRI | 10- fold | 3D CNN | Accuracy 99.30 |
| Lu et al. [33] | FDG-PET, sMRI | 10- fold | Multimodal and multiscale DNNs | Accuracy 84.60 |
| Sarraf et al. [34] | MRI and fMRI | 5- fold | GoogLeNet + LeNet-5 | Accuracy 100 |
| Gupta et al. [35] | MRI | 75%-25% | Sparse AE + CNN | Accuracy 94.74 |
| Liu et al. [36] | MRI, LDMIL (method) | 5- fold | 3D CNN | Accuracy 91.09 |
| Vu et al. [37] | MRI, PET | 80%-20% | Sparse Autoencoder + 3D CNN | Accuracy 91.14 |
| Bi et al. [38] | MRI | 10- fold | 3D CNN+ K means clustering | Accuracy 95.52 |
| Puente-Castro et al. [39] | Sagittal MRI | 80%-20% | ANN ResNet + Transfer Learning + SVM | Accuracy 86.81 |
| Feng et al. [40] | MRI+PET | 10- fold | fully stacked bidirectional, long short-term memory | Accuracy 94.82 |
| Bi et al. [18] | EEG spectral images | 50%-50% | Deep Boltzmann Machine + SVM | Accuracy 95.04 |
| Islam et al. [41] | MRI | 80%-20% | Inception-v4 + ResNet | F1 Score 90.00 |
| Maqsood et al. [43] | MRI | 60%-40% | AlexNet | Accuracy 89.66 |
| Previtali et al. [44] | MRI (ORB Method) | 10- fold | SVM | Accuracy 97.00 |
| Hon et al. [45] | MRI | 5- fold | InceptionV4, VGG16 | Accuracy 96.25 |
| Ji et al. [46] | MRI | 60%-40% | ResNet50, NASNet, and MobileNet | Accuracy 88.37 |
| Zhu et al. [47] | sMRI, DA-MIDL (method) | 5 -fold | Patch-level features, Attention + multi- instance learning | Accuracy 89.50 |
| Salvatore et al. [48] | MRI | 20- fold | voxel-level features, Principal Components Analysis | Accuracy 76.00 |
| Eskildsen et al. [49] | MRI | LOOCV | ROI-level features, minimal-redundancy-maximal-relevance | Accuracy 86.70 |
| Cao et al. [50] | MRI | 10- fold | ROI-level features, multi-kernel + KNN | Accuracy 88.60 |
| Tong et al. [51] | MRI | 10- fold | Patch-level Features, multipleinstance-Grap+ SVM | Accuracy 90.0 |
| Singh et al. [52] | FDG-PET | 10- fold | PCA+MLP+SVM | Accuracy 72.47 |
| Dolph et al. [53] | MRI | 10- fold | stacked AE (SAE) and DNN | Accuracy 56.80 |
| Raju et al. [55] | sMRI | 10- fold | 3DCNN with MLP | Accuracy 96.66 |
| Cheng et al. [56] | MRI-PET | 10- fold | SAE with elastic net | Accuracy 47.00 |
| Karasawa et al. [57] | MRI | 90%-10% | 3D CNN | Accuracy 87.00 |
| Ba¨ckstro¨m et al. [58] | MRI | 60%-40% | 3D CNN | Accuracy 98.74 |
| Shakeri et al. [59] | MRI | 80%-20% | VAE, MLP | Accuracy 84.00 |
| Faturrahman et al. [60] | MRI | 10- fold | DBN | Accuracy 91.00 |
| Li et al. [61] | MRI | 10- fold | LSTM-RNN | NA |
| Murugan et al. [62] | MRI, DEMNET(method) | 80%-20% | CNN | Accuracy 95.23 |
V. Prerequisite and Proposed Method
A. Background
B. Bayesian network (BN)
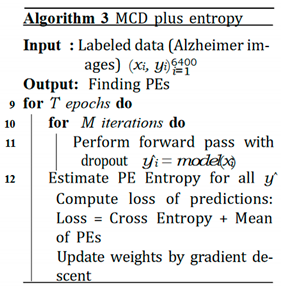
C. MCD
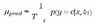
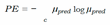
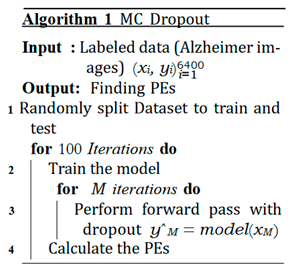
D. Ensemble Networks
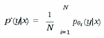
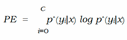
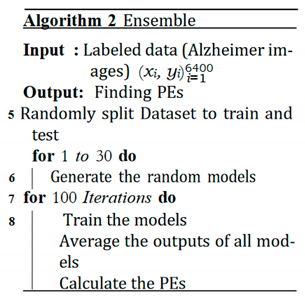
E. Expected Calibration Error (ECE)
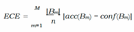
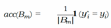

F. The Essence of Knowing Uncertainty
G. Proposed Method
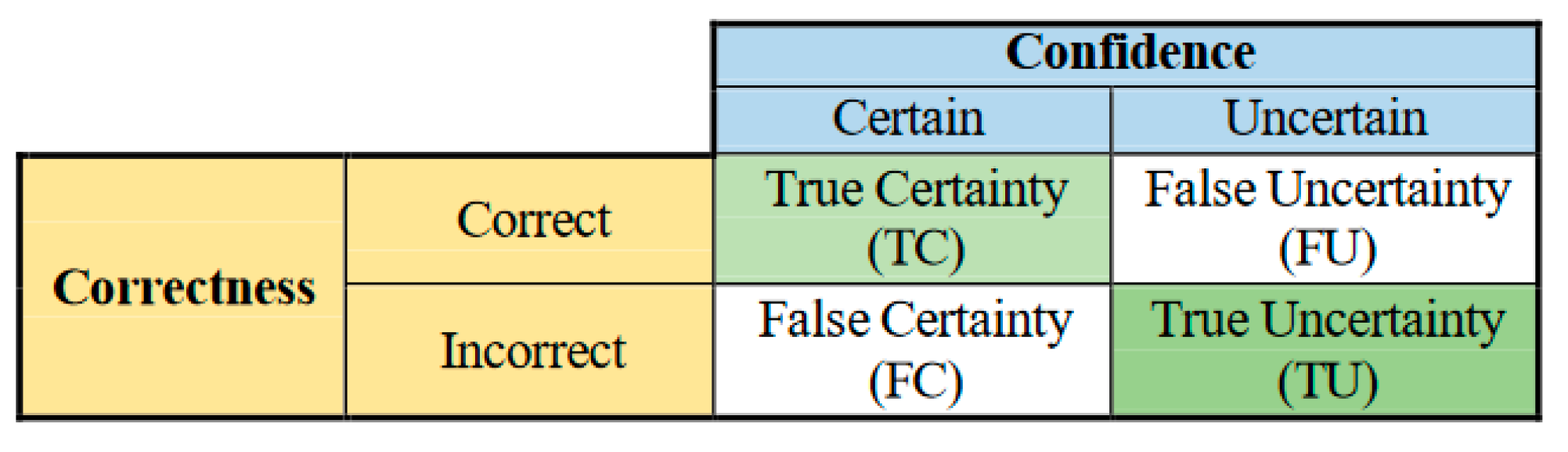
- − Uncertainty sensitivity (USen) which could be estimated by dividing the the number of predictions which are in- correct and uncertain by the all the incorrect predictions:
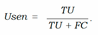
- − Uncertainty Specificity (USpe) which could be obtained by dividing the number of correct and certain predictions by the all number of correct predictions:
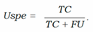
- − Uncertainty precision (Upre) that relates to the predic- tions which are incorrect and uncertain dividing by the total number of uncertain prediction:
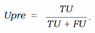
- − Uncertainty accuracy (Uacc) which is defines as the sum of the predictions located diagonally divided by the total number of predictions:
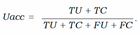
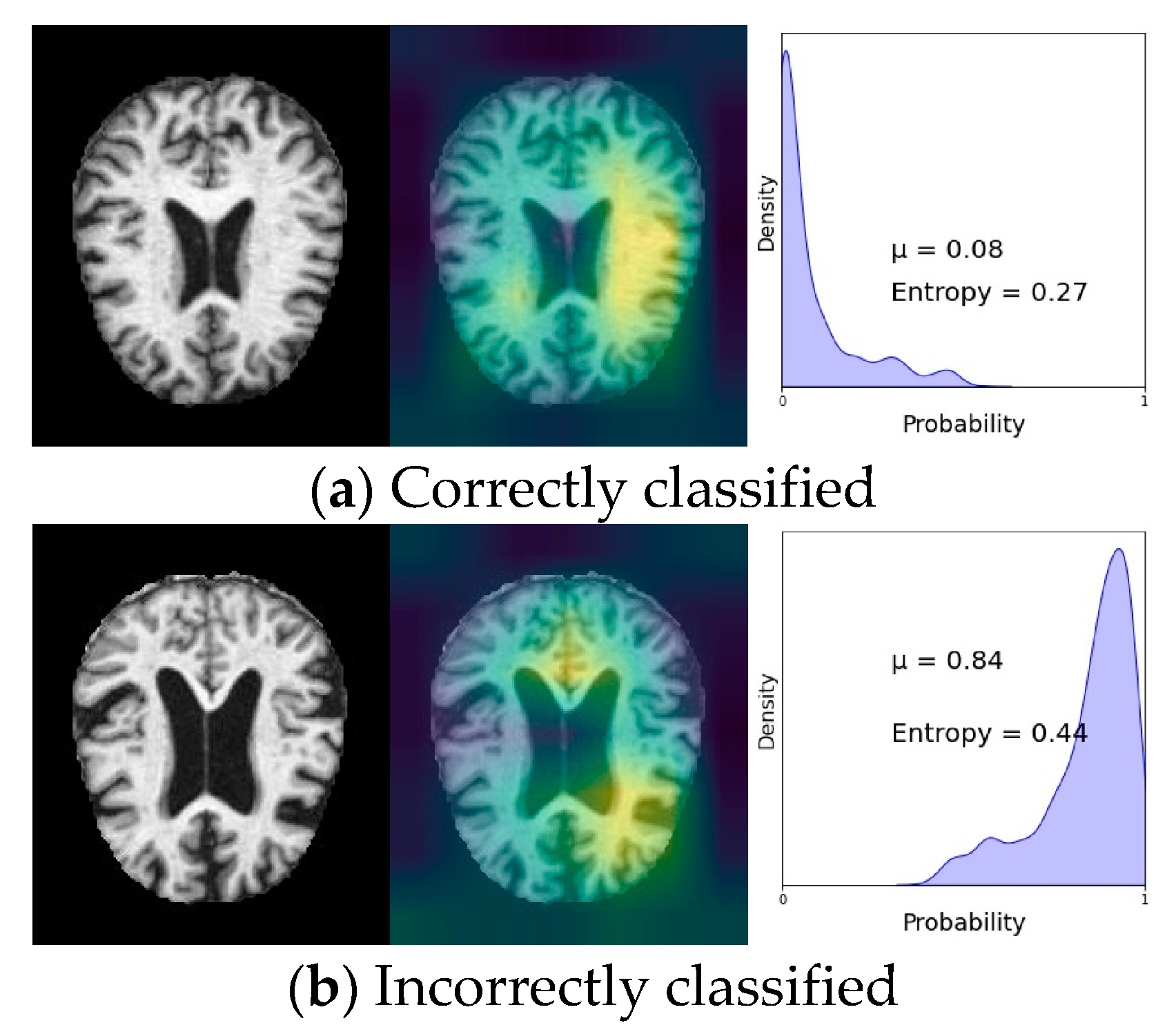
VI. Experimental Results
A. Discussion
VII. Conclusion
Appendices
References
- S. Afzal, M. S. Afzal, M. Maqsood, U. Khan, I. Mehmood, H. Nawaz, F. Aadil, O.-Y. Song, and N. Yunyoung, “Alzheimer disease detection techniques and methods: a review,” 2021.
- https://www.healthline.com/health/alzheimers-disease/ difference-dementia-alzheimers.
- R. N. Bryan, “Machine learning applied to alzheimer disease,” 2016.
- S. Kumar, I. S. Kumar, I. Oh, S. Schindler, A. M. Lai, P. R. Payne, and A. Gupta, “Machine learning for modeling the progression of alzheimer disease dementia using clinical data: a systematic literature review,” JAMIA open, vol. 4, no. 3, p. ooab052, 2021.
- M. Tanveer, B. M. Tanveer, B. Richhariya, R. U. Khan, A. H. Rashid, P. Khanna, M. Prasad, and C. Lin, “Machine learning techniques for the diagnosis of alzheimer’s disease: A review,” ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications, and Applications (TOMM), vol. 16, no. 1s, pp. 1–35, 2020.
- E. Pellegrini, L. E. Pellegrini, L. Ballerini, M. d. C. V. Hernandez, F. M. Chappell, V. Gonza´lez-Castro, D. Anblagan, S. Danso, S. Mun˜oz-Maniega, D. Job, C. Pernet, et al., “Machine learning of neuroimaging for assisted diagnosis of cognitive impairment and dementia: a systematic review,” Alzheimer’s & Dementia: Diagnosis, Assessment & Disease Monitoring, vol. 10, pp. 519–535, 2018.
- W. P. dos Santos, R. E. W. P. dos Santos, R. E. de Souza, and P. B. dos Santos Filho, “Evaluation of alzheimer’s disease by analysis of mr images using multilayer perceptrons and kohonen som classifiers as an alternative to the adc maps,” in 2007 29th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, pp. 2118–2121, IEEE, 2007.
- V. Jayanthi, B. C. V. Jayanthi, B. C. Simon, and D. Baskar, “Alzheimer’s disease clas- sification using deep learning,” in Computational Intelligence and Its Applications in Healthcare, pp. 157–173, Elsevier, 2020.
- M. Sethi, S. M. Sethi, S. Ahuja, S. Rani, D. Koundal, A. Zaguia, and W. Enbeyle, “An exploration: Alzheimer’s disease classification based on convolutional neural network,” BioMed Research International, vol. 2022, 2022.
- Y. Wang, X. Y. Wang, X. Liu, and C. Yu, “Assisted diagnosis of alzheimer’s disease based on deep learning and multimodal feature fusion,” Complexity, vol. 2021, 2021.
- P. M. Raees and V. Thomas, “Automated detection of alzheimer’s disease using deep learning in mri,” in Journal of Physics: Conference Series, vol. 1921, p. 012024, IOP Publishing, 2021.
- B. Lu, H.-X. B. Lu, H.-X. Li, Z.-K. Chang, L. Li, N.-X. Chen, Z.-C. Zhu, H.-X. Zhou, X.-Y. Li, Y.-W. Wang, S.-X. Cui, et al., “A practical alzheimer’s disease classifier via brain imaging-based deep learning on 85,721 samples,” Journal of Big Data, vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 1–22, 2022.
- M. Odusami, R. M. Odusami, R. Maskeliu¯nas, and R. Damasˇevicˇius, “An intelligent system for early recognition of alzheimer’s disease using neuroimaging,” Sensors, vol. 22, no. 3, p. 740, 2022.
- Y. Ding, J. H. Y. Ding, J. H. Sohn, M. G. Kawczynski, H. Trivedi, R. Harnish, N. W. Jenkins, D. Lituiev, T. P. Copeland, M. S. Aboian, C. Mari Aparici, et al., “A deep learning model to predict a diagnosis of alzheimer disease by using 18f-fdg pet of the brain,” Radiology, vol. 290, no. 2, pp. 456–464, 2019.
- N. Goenka and S. Tiwari, “Deep learning for alzheimer prediction using brain biomarkers,” Artificial Intelligence Review, vol. 54, no. 7, pp. 4827–4871, 2021.
- D. Zhang, D. D. Zhang, D. Shen, A. D. N. Initiative, et al., “Multi-modal multi-task learning for joint prediction of multiple regression and classification variables in alzheimer’s disease,” NeuroImage, vol. 59, no. 2, pp. 895– 907, 2012.
- G. Battineni, N. G. Battineni, N. Chintalapudi, F. Amenta, and E. Traini, “Deep learning type convolution neural network architecture for multiclass classification of alzheimer’s disease.,” in BIOIMAGING, pp. 209–215, 2021.
- X. Bi and H. Wang, “Early alzheimer’s disease diagnosis based on eeg spectral images using deep learning,” Neural Networks, vol. 114, pp. 119–135, 2019.
- S. Liu, S. S. Liu, S. Liu, W. Cai, S. Pujol, R. Kikinis, and D. Feng, “Early diagnosis of alzheimer’s disease with deep learning,” in 2014 IEEE 11th international symposium on biomedical imaging (ISBI), pp. 1015–1018, IEEE, 2014.
- “Adni alzheimer‘s disease neuroimaging initiative.” https://adni.loni.usc. edu/.
- S. Liu, S. S. Liu, S. Liu, W. Cai, H. Che, S. Pujol, R. Kikinis, D. Feng, M. J. Fulham, et al., “Multimodal neuroimaging feature learning for multiclass diagnosis of alzheimer’s disease,” IEEE transactions on biomedical engineering, vol. 62, no. 4, pp. 1132–1140, 2014.
- S. Korolev, A. S. Korolev, A. Safiullin, M. Belyaev, and Y. Dodonova, “Residual and plain convolutional neural networks for 3d brain mri classification,” in 2017 IEEE 14th international symposium on biomedical imaging (ISBI 2017), pp. 835–838, IEEE, 2017.
- K. Aderghal, J. K. Aderghal, J. Benois-Pineau, K. Afdel, and C. Gwenae¨lle, “Fuseme: Classification of smri images by fusion of deep cnns in 2d+ ε projec- tions,” in Proceedings of the 15th International Workshop on Content- Based Multimedia Indexing, pp. 1–7, 2017.
- M. Liu, D. M. Liu, D. Cheng, W. Yan, and A. D. N. Initiative, “Classification of alzheimer’s disease by combination of convolutional and recurrent neural networks using fdg-pet images,” Frontiers in neuroinformatics, vol. 12, p. 35, 2018.
- H. Choi, K. H. H. Choi, K. H. Jin, A. D. N. Initiative, et al., “Predicting cognitive decline with deep learning of brain metabolism and amyloid imaging,” Behavioural brain research, vol. 344, pp. 103–109, 2018.
- D. Cheng and M. Liu, “Cnns based multi-modality classification for ad diagnosis,” in 2017 10th international congress on image and sig- nal processing, biomedical engineering and informatics (CISP-BMEI), pp. 1–5, IEEE, 2017.
- S.-H. Wang, P. S.-H. Wang, P. Phillips, Y. Sui, B. Liu, M. Yang, and H. Cheng, “Classification of alzheimer’s disease based on eight-layer convolutional neural network with leaky rectified linear unit and max pooling,” Journal of medical systems, vol. 42, no. 5, pp. 1–11, 2018.
- J. Shi, X. J. Shi, X. Zheng, Y. Li, Q. Zhang, and S. Ying, “Multimodal neuroimag- ing feature learning with multimodal stacked deep polynomial networks for diagnosis of alzheimer’s disease,” IEEE journal of biomedical and health informatics, vol. 22, no. 1, pp. 173–183, 2017.
- H.-I. Suk, S.-W. H.-I. Suk, S.-W. Lee, D. Shen, A. D. N. Initiative, et al., “Hierarchical feature representation and multimodal fusion with deep learning for ad/mci diagnosis,” NeuroImage, vol. 101, pp. 569–582, 2014.
- H.-I. Suk and D. Shen, “Deep learning-based feature representation for ad/mci classification,” in International conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention, pp. 583–590, Springer, 2013.
- A. Payan and G. a: Montana, “Predicting alzheimer’s disease; arXiv:1502.02506, 2015.
- E. Hosseini-Asl, R. E. Hosseini-Asl, R. Keynton, and A. El-Baz, “Alzheimer’s disease diagnostics by adaptation of 3d convolutional network,” in 2016 IEEE international conference on image processing (ICIP), pp. 126–130, IEEE, 2016.
- D. Lu, K. D. Lu, K. Popuri, G. W. Ding, R. Balachandar, and M. F. Beg, “Multimodal and multiscale deep neural networks for the early diagnosis of alzheimer’s disease using structural mr and fdg-pet images,” Scientific reports, vol. 8, no. 1, pp. 1–13, 2018.
- S. Sarraf, D. D. S. Sarraf, D. D. DeSouza, J. Anderson, G. Tofighi, et al., “Deepad: Alzheimer’s disease classification via deep convolutional neural net- works using mri and fmri,” BioRxiv, p. 070441, 2017.
- A. Gupta, M. A. Gupta, M. Ayhan, and A. Maida, “Natural image bases to represent neuroimaging data,” in International conference on machine learning, pp. 987–994, PMLR, 2013.
- M. Liu, J. M. Liu, J. Zhang, E. Adeli, and D. Shen, “Landmark-based deep multi- instance learning for brain disease diagnosis,” Medical image analysis, vol. 43, pp. 157–168, 2018.
- T. D. Vu, H.-J. T. D. Vu, H.-J. Yang, V. Q. Nguyen, A.-R. Oh, and M.-S. Kim, “Multimodal learning using convolution neural network and sparse autoencoder,” in 2017 IEEE International Conference on Big Data and Smart Computing (BigComp), pp. 309–312, IEEE, 2017.
- X. Bi, S. X. Bi, S. Li, B. Xiao, Y. Li, G. Wang, and X. Ma, “Computer aided alzheimer’s disease diagnosis by an unsupervised deep learning technology,” Neurocomputing, vol. 392, pp. 296–304, 2020.
- A. Puente-Castro, E. A. Puente-Castro, E. Fernandez-Blanco, A. Pazos, and C. R. Munteanu, “Automatic assessment of alzheimer’s disease diagnosis based on deep learning techniques,” Computers in Biology and Medicine, vol. 120, p. 103764, 2020.
- C. Feng, A. C. Feng, A. Elazab, P. Yang, T. Wang, F. Zhou, H. Hu, X. Xiao, and B. Lei, “Deep learning framework for alzheimer’s disease diagnosis via 3d-cnn and fsbi-lstm,” IEEE Access, vol. 7, pp. 63605–63618, 2019.
- J. Islam and Y. Zhang, “Early diagnosis of alzheimer’s disease: A neuroimaging study with deep learning architectures,” in Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops, pp. 1881–1883, 2018.
- T. Brosch, R. T. Brosch, R. Tam, A. D. N. Initiative, et al., “Manifold learning of brain mris by deep learning,” in International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, pp. 633–640, Springer, 2013.
- M. Maqsood, F. M. Maqsood, F. Nazir, U. Khan, F. Aadil, H. Jamal, I. Mehmood, and O.-y. Song, “Transfer learning assisted classification and detection of alzheimer’s disease stages using 3d mri scans,” Sensors, vol. 19, no. 11, p. 2645, 2019.
- F. Previtali, P. F. Previtali, P. Bertolazzi, G. Felici, and E. Weitschek, “A novel method and software for automatically classifying alzheimer’s disease patients by magnetic resonance imaging analysis,” Computer methods and programs in biomedicine, vol. 143, pp. 89–95, 2017.
- M. Hon and N. M. Khan, “Towards alzheimer’s disease classification through transfer learning,” in 2017 IEEE International conference on bioinformatics and biomedicine (BIBM), pp. 1166–1169, IEEE, 2017.
- H. Ji, Z. H. Ji, Z. Liu, W. Q. Yan, and R. Klette, “Early diagnosis of alzheimer’s disease using deep learning,” in Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Control and Computer Vision, pp. 87–91, 2019.
- W. Zhu, L. W. Zhu, L. Sun, J. Huang, L. Han, and D. Zhang, “Dual attention multi- instance deep learning for alzheimer’s disease diagnosis with structural mri,” IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, vol. 40, no. 9, pp. 2354– 2366, 2021.
- R. Cuingnet, E. R. Cuingnet, E. Gerardin, J. Tessieras, G. Auzias, S. Lehe´ricy, M.-O. Habert, M. Chupin, H. Benali, O. Colliot, A. D. N. Initiative, et al., “Automatic classification of patients with alzheimer’s disease from structural mri: a comparison of ten methods using the adni database,” neuroimage, vol. 56, no. 2, pp. 766–781, 2011.
- S. F. Eskildsen, P. S. F. Eskildsen, P. Coupe´, D. Garc´ıa-Lorenzo, V. Fonov, J. C. Pruessner, D. L. Collins, A. D. N. Initiative, et al., “Prediction of alzheimer’s disease in subjects with mild cognitive impairment from the adni cohort using patterns of cortical thinning,” Neuroimage, vol. 65, pp. 511–521, 2013.
- P. Cao, X. P. Cao, X. Liu, J. Yang, D. Zhao, M. Huang, J. Zhang, and O. Zaiane, “Nonlinearity-aware based dimensionality reduction and over-sampling for ad/mci classification from mri measures,” Computers in biology and medicine, vol. 91, pp. 21–37, 2017.
- T. Tong, R. T. Tong, R. Wolz, Q. Gao, R. Guerrero, J. V. Hajnal, D. Rueckert, A. D. N. Initiative, et al., “Multiple instance learning for classification of dementia in brain mri,” Medical image analysis, vol. 18, no. 5, pp. 808– 818, 2014.
- S. Singh, A. S. Singh, A. Srivastava, L. Mi, R. J. Caselli, K. Chen, D. Goradia, E. M. Reiman, and Y. Wang, “Deep-learning-based classification of fdg- pet data for alzheimer’s disease categories,” in 13th International Con- ference on Medical Information Processing and Analysis, vol. 10572, pp. 143–158, SPIE, 2017.
- C. V. Dolph, M. C. V. Dolph, M. Alam, Z. Shboul, M. D. Samad, and K. M. Iftekharud- din, “Deep learning of texture and structural features for multiclass alzheimer’s disease classification,” in 2017 International Joint Confer- ence on Neural Networks (IJCNN), pp. 2259–2266, IEEE, 2017.
- “Caddementia mri dataset.” https://caddementia.grand-challenge.org/.
- M. Raju, V. P. M. Raju, V. P. Gopi, and V. Anitha, “Multi-class classification of alzheimer’s disease using 3dcnn features and multilayer perceptron,” in 2021 Sixth International Conference on Wireless Communications, Signal Processing and Networking (WiSPNET), pp. 368–373, IEEE, 2021.
- B. Cheng, M. B. Cheng, M. Liu, H.-I. Suk, D. Shen, and D. Zhang, “Multimodal manifold-regularized transfer learning for mci conversion prediction,” Brain imaging and behavior, vol. 9, no. 4, pp. 913–926, 2015.
- H. Karasawa, C.-L. H. Karasawa, C.-L. Liu, and H. Ohwada, “Deep 3d convolutional neural network architectures for alzheimer’s disease diagnosis,” in Asian conference on intelligent information and database systems, pp. 287– 296, Springer, 2018.
- K. Ba¨ckstro¨m, M. K. Ba¨ckstro¨m, M. Nazari, I. Y.-H. Gu, and A. S. Jakola, “An efficient 3d deep convolutional network for alzheimer’s disease diagnosis using mr images,” in 2018 IEEE 15th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2018), pp. 149–153, IEEE, 2018.
- M. Shakeri, H. M. Shakeri, H. Lombaert, S. Tripathi, S. Kadoury, A. D. N. Initiative, et al., “Deep spectral-based shape features for alzheimer’s disease clas- sification,” in International Workshop on Spectral and Shape Analysis in Medical Imaging, pp. 15–24, Springer, 2016.
- M. Faturrahman, I. M. Faturrahman, I. Wasito, N. Hanifah, and R. Mufidah, “Structural mri classification for alzheimer’s disease detection using deep belief network,” in 2017 11th International Conference on Information & Communication Technology and System (ICTS), pp. 37–42, IEEE, 2017.
- H. Li and Y. Fan, “Early prediction of alzheimer’s disease dementia based on baseline hippocampal mri and 1-year follow-up cognitive measures using deep recurrent neural networks,” in 2019 IEEE 16th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2019), pp. 368– 371, IEEE, 2019.
- S. Murugan, C. S. Murugan, C. Venkatesan, M. Sumithra, X.-Z. Gao, B. Elakkiya, M. Akila, and S. Manoharan, “Demnet: a deep learning model for early diagnosis of alzheimer diseases and dementia from mr images,” IEEE Access, vol. 9, pp. 90319–90329, 2021.
- “Kaggle.” https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/tourist55/ alzheimers-dataset-4-class-of-images.
- “Aibl australian imaging, biomarkers and lifestyle.” http://aibl.csiro.au.
- “Oasis open access series of imaging studies.” http://oasis-brains.org.
- “Miriad minimal interval resonance imaging in alzheimer’s disease.” http://ucl.ac.uk/drc/research/methods/ minimalinterval-resonance-imaging-alzheimers-disease-miriad.
- A. Shamsi, H. A. Shamsi, H. Asgharnezhad, M. Abdar, A. Tajally, A. Khosravi, S. Nahavandi, and H. arXiv:2110.03260, 2021.
- R. Alizadehsani, M. R. Alizadehsani, M. Roshanzamir, M. Abdar, A. Beykikhoshk, M. H. Zangooei, A. Khosravi, S. Nahavandi, R. S. Tan, and U. R. Acharya, “Model uncertainty quantification for diagnosis of each main coronary artery stenosis,” Soft Computing, vol. 24, no. 13, pp. 10149–10160, 2020.
- R. Alizadehsani, M. R. Alizadehsani, M. Roshanzamir, M. Abdar, A. Beykikhoshk, A. Khos- ravi, S. Nahavandi, P. Plawiak, R. S. Tan, and U. R. Acharya, “Hybrid genetic-discretized algorithm to handle data uncertainty in diagnosing stenosis of coronary arteries,” Expert Systems, vol. 39, no. 7, p. e12573, 2022.
- H. D. Kabir, S. H. D. Kabir, S. Khanam, F. Khozeimeh, A. Khosravi, S. K. Mondal, S. Nahavandi, and U. R. Acharya, “Aleatory-aware deep uncertainty quantification for transfer learning,” Computers in Biology and Medicine, vol. 143, p. 105246, 2022.
- H. D. Kabir, A. H. D. Kabir, A. Khosravi, A. Kavousi-Fard, S. Nahavandi, and D. Srini- vasan, “Optimal uncertainty-guided neural network training,” Applied Soft Computing, vol. 99, p. 106878, 2021.
- N. Ye and Z. Zhu, “Functional bayesian neural networks for model uncertainty quantification,” 2018.
- T. A. Stephenson, “An introduction to bayesian network theory and usage,” tech. rep., Idiap, 2000.
- Y. Gal and Z. Ghahramani, “Dropout as a bayesian approximation: Representing model uncertainty in deep learning,” in international conference on machine learning, pp. 1050–1059, PMLR, 2016.
- B. Lakshminarayanan, A. B. Lakshminarayanan, A. Pritzel, and C. Blundell, “Simple and scalable predictive uncertainty estimation using deep ensembles,” Advances in neural information processing systems, vol. 30, 2017.
- C. Guo, G. C. Guo, G. Pleiss, Y. Sun, and K. Q. Weinberger, “On calibration of modern neural networks,” in International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 1321–1330, PMLR, 2017.
- R. Alizadehsani, M. R. Alizadehsani, M. Roshanzamir, S. Hussain, A. Khosravi, A. Koohes- tani, M. H. Zangooei, M. Abdar, A. Beykikhoshk, A. Shoeibi, A. Zare, et al., “Handling of uncertainty in medical data using machine learning and probability theory techniques: A review of 30 years (1991–2020),” Annals of Operations Research, pp. 1–42, 2021.
- M. Raghu, K. M. Raghu, K. Blumer, R. Sayres, Z. Obermeyer, B. Kleinberg, S. Mul- lainathan, and J. Kleinberg, “Direct uncertainty prediction for medical second opinions,” in International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 5281–5290, PMLR, 2019.
- A. Shamsi, H. A. Shamsi, H. Asgharnezhad, S. S. Jokandan, A. Khosravi, P. M. Kebria, D. Nahavandi, S. Nahavandi, and D. Srinivasan, “An uncertainty- aware transfer learning-based framework for covid-19 diagnosis,” IEEE transactions on neural networks and learning systems, vol. 32, no. 4, pp. 1408–1417, 2021.
- H. Asgharnezhad, A. H. Asgharnezhad, A. Shamsi, R. Alizadehsani, A. Khosravi, S. Na- havandi, Z. A. Sani, D. Srinivasan, and S. M. S. Islam, “Objective evaluation of deep uncertainty predictions for covid-19 detection,” Scientific Reports, vol. 12, no. 1, pp. 1–11, 2022.
- R.Z. Nasab, M.R.E. R.Z. Nasab, M.R.E. Ghamsari, A. Argha, C. Macphillamy, A. Beheshti, R. Alizadehsani, N. Lovell, (2022). Deep Learning in Spatially Resolved Transcriptomics: A Comprehensive Technical View. arXiv:2210.04453.
- A. Shoeibi, M. A. Shoeibi, M. Khodatars, M. Jafari, N. Ghassemi, P. Moridian, R. Alizadesani, J.M Gorriz, (2022). Diagnosis of Brain Diseases in Fusion of Neuroimaging Modalities Using Deep Learning: A Review. Information Fusion, 94: 85-113.
- H. Alinejad-Rokny, R. H. Alinejad-Rokny, R. Ghavami Modegh, H.R. Rabiee, E. Ramezani Sarbandi, N. Rezaie, K.T. Tam, A.R. Forrest, (2022). MaxHiC: A robust background correction model to identify biologically relevant chromatin interactions in Hi-C and capture Hi-C experiments. PLOS Computational Biology, 18(6): e1010241.
- M. Labani, A. M. Labani, A. Afrasiabi, A. Beheshti, N.H. Lovell, (2022). PeakCNV: A multi-feature ranking algorithm-based tool for genome-wide copy number variation-association study. Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal, 20: 4975-4983.
- H. Dashti, I. H. Dashti, I. Dehzangi, M. Bayati, J. Breen, A. Beheshti, N. Lovell, (2022). Integrative analysis of mutated genes and mutational processes reveals novel mutational biomarkers in colorectal cancer. BMC bioinformatics, 23(1): 1-24.
- A. Ghareyazi, A. A. Ghareyazi, A. Mohseni, H. Dashti, A. Beheshti, I. Dehzangi, H.R. Rabiee, (2021). Whole-genome analysis of de novo somatic point mutations reveals novel mutational biomarkers in pancreatic cancer. Cancers, 13(17): 4376.
- M. Bayati, H.R. M. Bayati, H.R. Rabiee, M. Mehrbod, F. Vafaee, D. Ebrahimi, A.R. Forrest, (2020). CANCERSIGN: a user-friendly and robust tool for identification and classification of mutational signatures and patterns in cancer genomes. Scientific reports, 10(1): 1-11.
- M. Hosseinpoor, H. M. Hosseinpoor, H. Parvin, S. Nejatian, V. Rezaie, K. Bagherifard, A. Dehzangi, (2020). Proposing a novel community detection approach to identify cointeracting genomic regions. Mathematical Biosciences and Engineering, 17(3): 2193-2217.
- H. Alinejad-Rokny, E. H. Alinejad-Rokny, E. Sadroddiny, V. Scaria, (2018). Machine learning and data mining techniques for medical complex data analysis. Neurocomputing, 276(1).
- A. Argha, B.G. A. Argha, B.G. Celler, N.H. Lovell, (2022). Blood Pressure Estimation from Korotkoff Sound Signals Using an End-to-End Deep-Learning-Based Algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 71: 1-10.
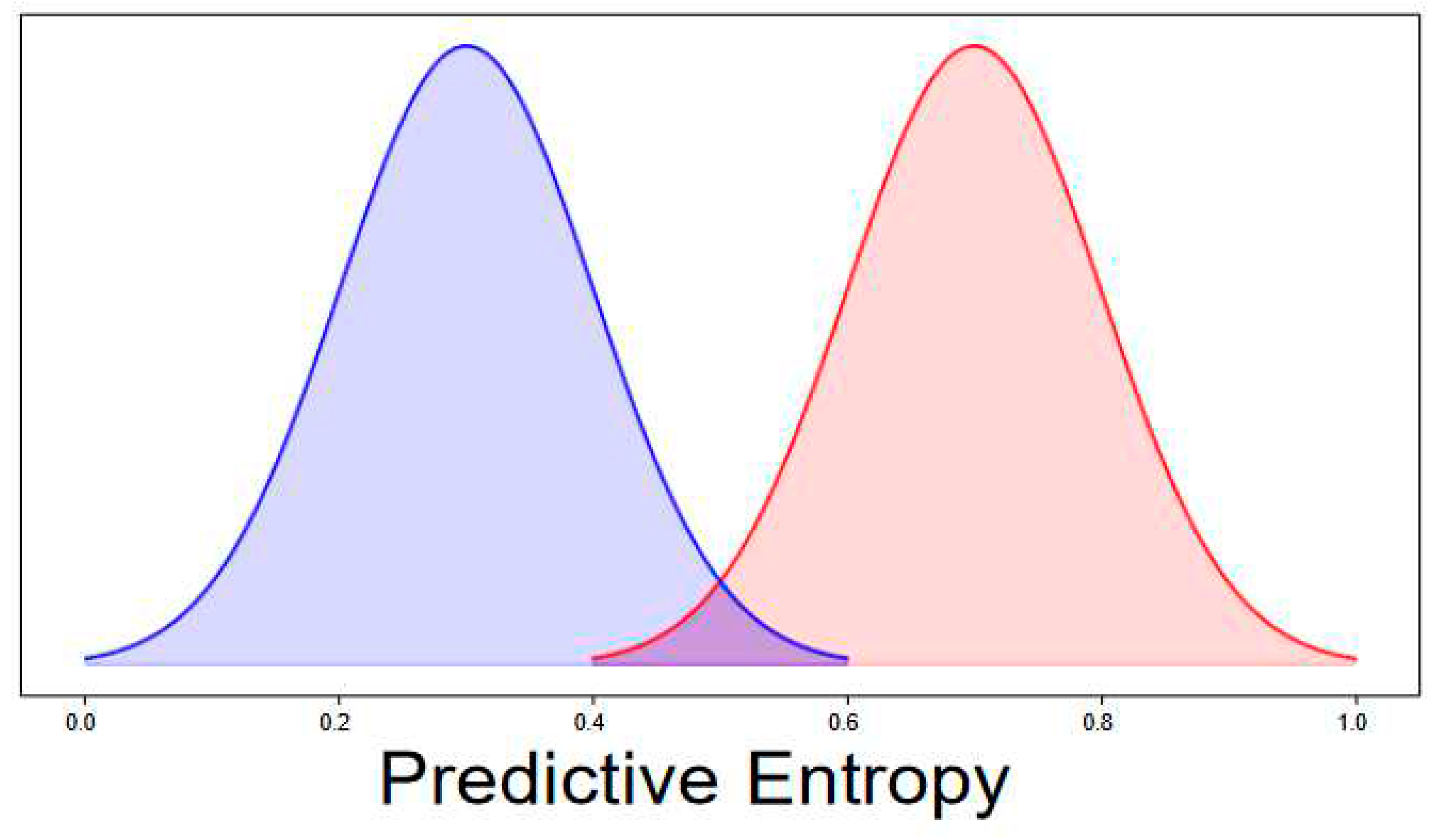
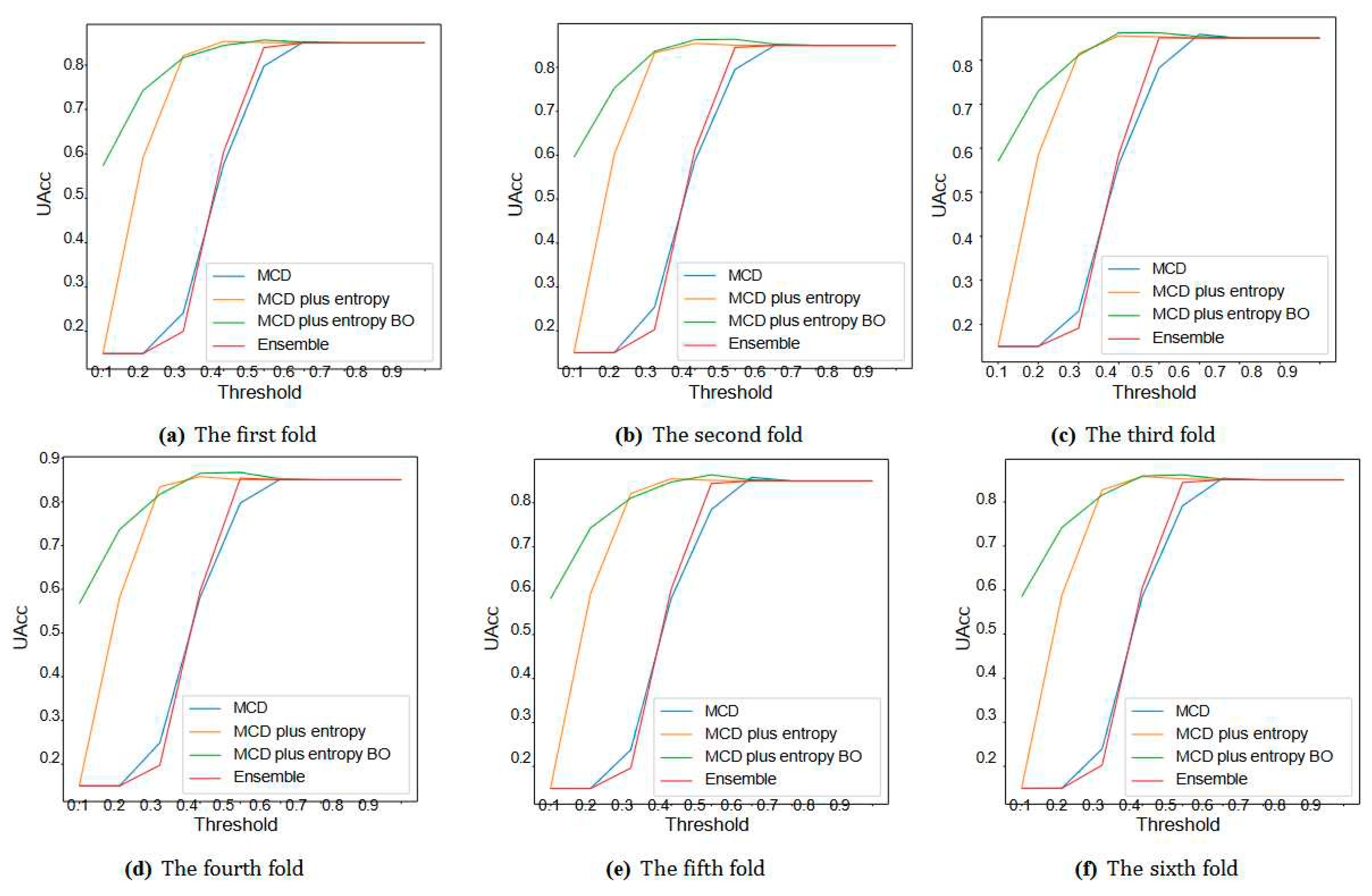
| UQ Method | Fold = 1 | Fold = 2 | Fold = 3 | Fold = 4 | Fold=5 | Fold = 6 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Uacc | ECE | Uacc | ECE | Uacc | ECE | Uacc | ECE | Uacc | ECE | Uacc | ECE | |
| MCD | 78.3 | 12.1 | 80.4 | 9.71 | 79.3 | 9.5 | 78.1 | 9.6 | 78.4 | 9.74 | 79.5 | 9.9 |
| MCD plus entropy | 85 | 1.3 | 85.25 | 5.9 | 85 | 6.3 | 85.2 | 4.85 | 85.2 | 4.9 | 85 | 5 |
| MCD plus entropy BO | 85.2 | 1.04 | 86.3 | 3.06 | 86.4 | 3.31 | 85.7 | 3.09 | 86.2 | 2.9 | 85.9 | 3.2 |
| ensemble | 84.6 | 9.2 | 84.68 | 5.9 | 84 | 8.9 | 84.5 | 8.9 | 84.5 | 8.9 | 83.9 | 9.3 |
| UQ Method | Fold = 1 | Fold = 2 | Fold = 3 | Fold = 4 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| µ1 | µ2 | Dist | Acc | µ1 | µ2 | Dist | Acc | µ1 | µ2 | Dist | Acc | µ1 | µ2 | Dist | Acc | |
| MCD | 0.417 | 0.470 | 0.053 | 85.06 | 0.400 | 0.503 | 0.103 | 85 | 0.404 | 0.506 | 0.102 | 85 | 0.405 | 0.503 | 0.097 | 85 |
| MCD plus entropy | 0.190 | 0.231 | 0.041 | 85.06 | 0.207 | 0.296 | 0.089 | 85 | 0.209 | 0.301 | 0.092 | 85 | 0.208 | 0.295 | 0.087 | 85 |
| MCD plus entropy BO | 0.103 | 0.180 | 0.077 | 85.06 | 0.147 | 0.340 | 0.192 | 85 | 0.149 | 0.352 | 0.203 | 85 | 0.147 | 0.339 | 0.191 | 85 |
| ensemble | 0.404 | 0.441 | 0.037 | 85.06 | 0.390 | 0.454 | 0.064 | 85 | 0.391 | 0.453 | 0.063 | 85 | 0.393 | 0.453 | 0.060 | 85 |
| UQ Method | Fold = 5 | Fold = 6 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| µ1 | µ2 | Dist | Acc | µ1 | µ2 | Dist | Acc | |
| MCD | 0.404 | 0.496 | 0.092 | 85.02 | 0.404 | 0.494 | 0.090 | 85 |
| MCD plus entropy | 0.208 | 0.287 | 0.079 | 85.02 | 0.209 | 0.282 | 0.073 | 85 |
| MCD plus entropy BO | 0.148 | 0.329 | 0.181 | 85.02 | 0.149 | 0.316 | 0.167 | 85 |
| ensemble | 0.392 | 0.450 | 0.058 | 85.02 | 0.391 | 0.448 | 0.057 | 85 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





