Submitted:
31 December 2022
Posted:
04 January 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Highlights
- Craters might be produced by electric currents both in laboratory conditions and on celestial bodies
- An extremely large solar outburst or a nearby supernova may cause cratering of Solar System bodies
- Laboratory electric discharge machining is a useful tool for studying larger scale craters
- Piezoelectricity may play a major role even in impact cratering
- Electrically induced cratering may solve some problems of impact crater hypothesis
1. Introduction
1.1. Impact Crater Formation
1.1.1. Contact
1.1.2. Compression
1.1.3. Excavation
1.1.4. Modification
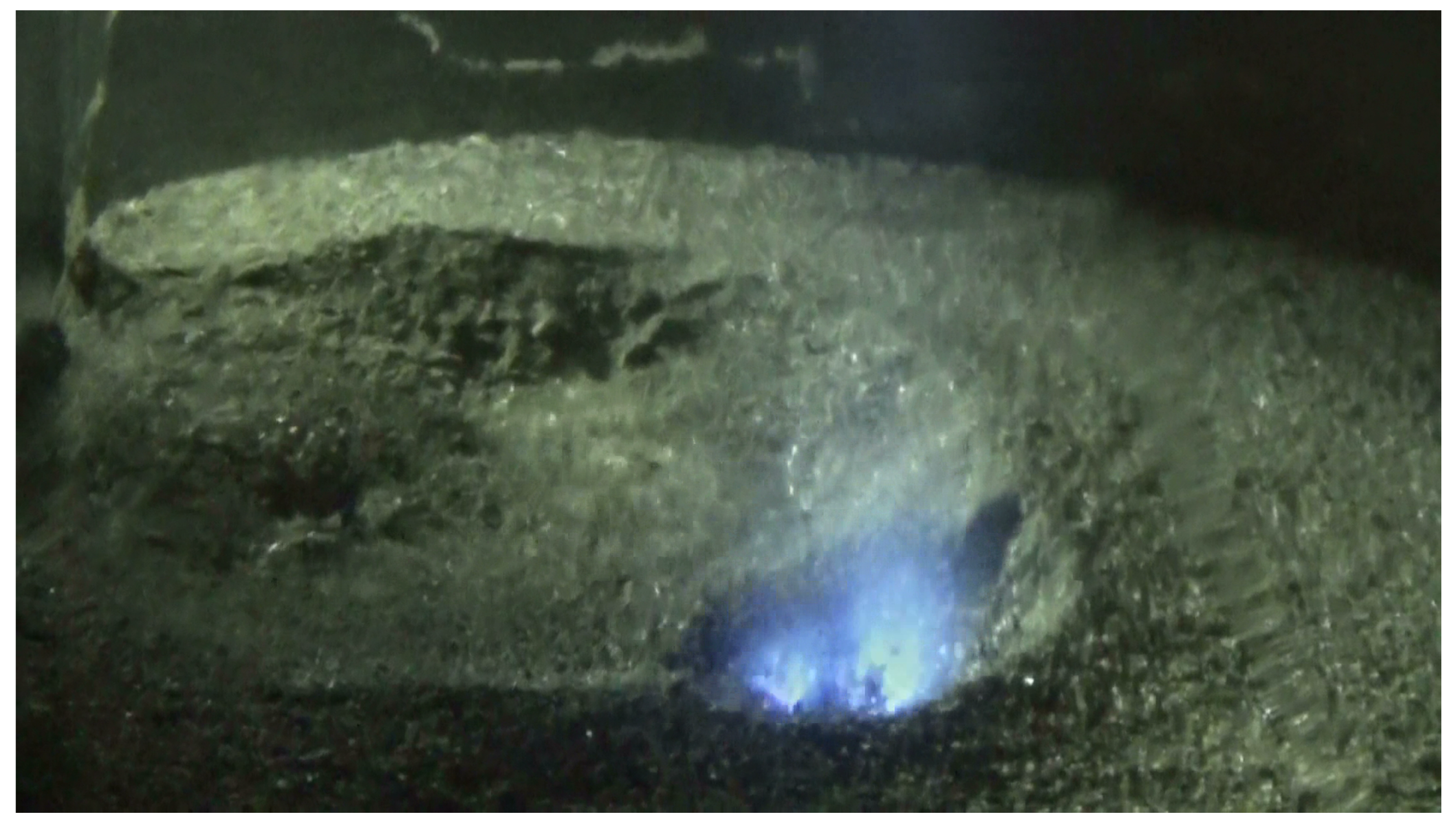
1.2. EDM as an Alternative
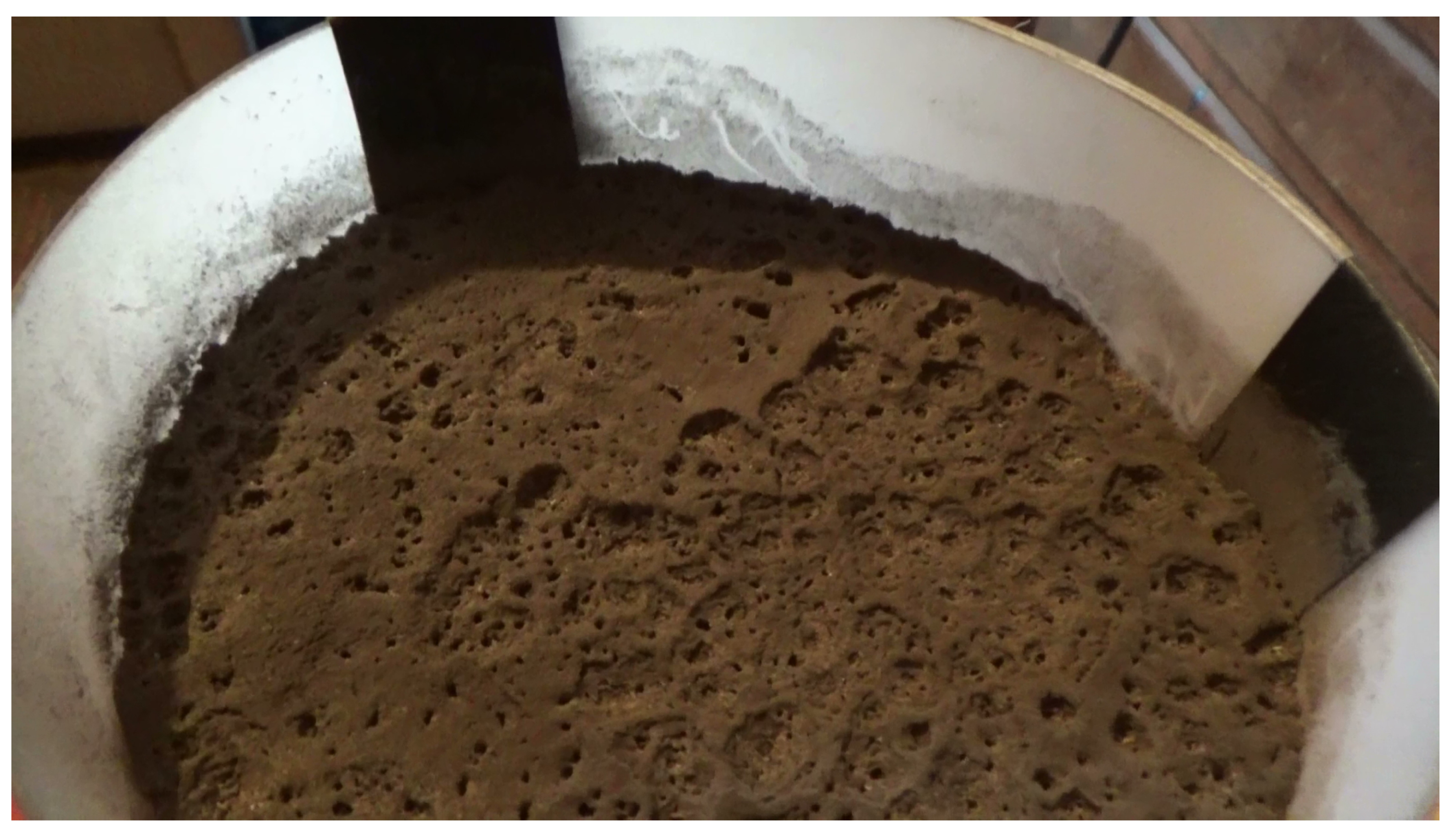
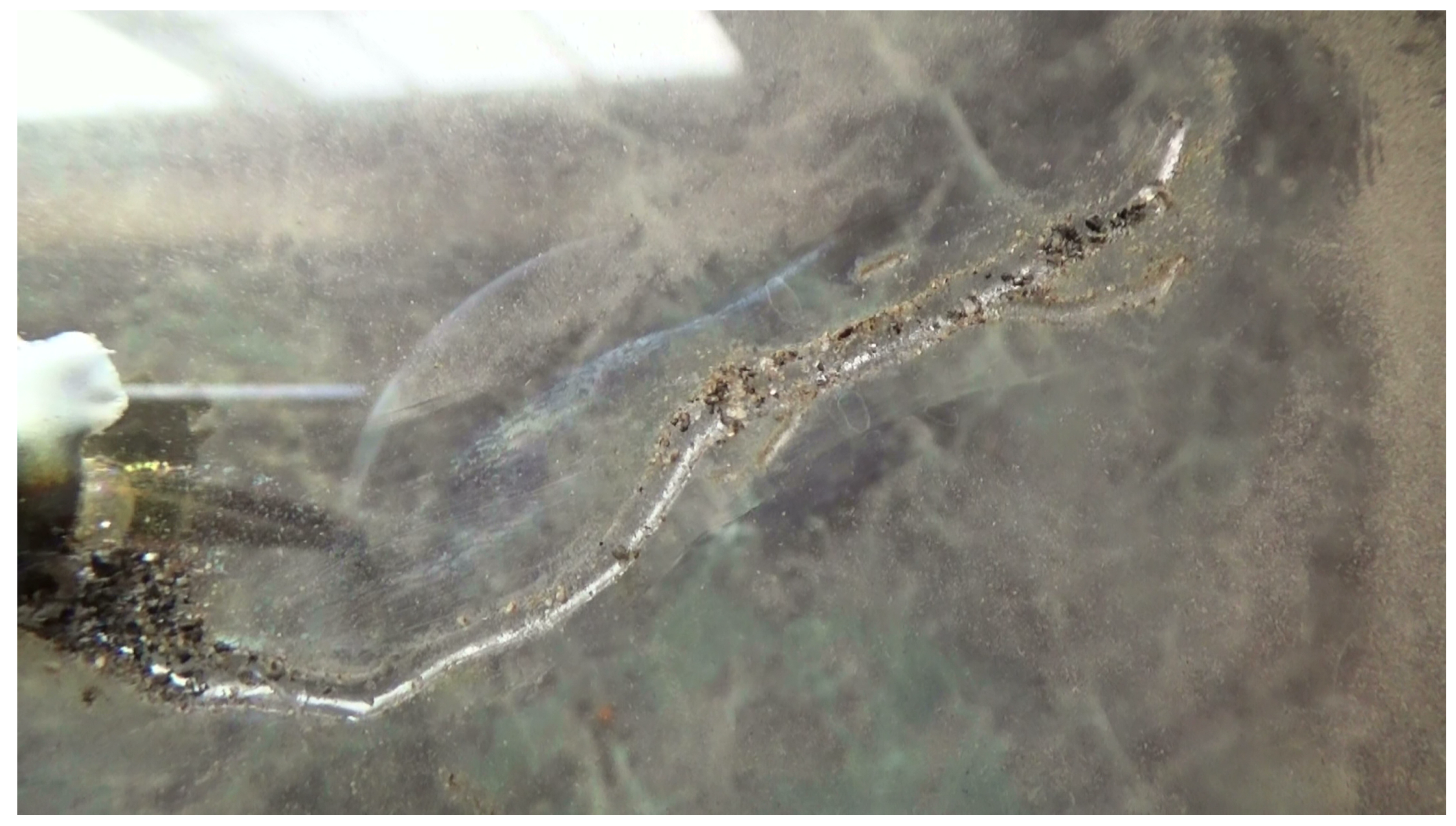
2. Material and Methods
3. Theory
3.1. Basic Model
3.2. Experimental Case
4. Results
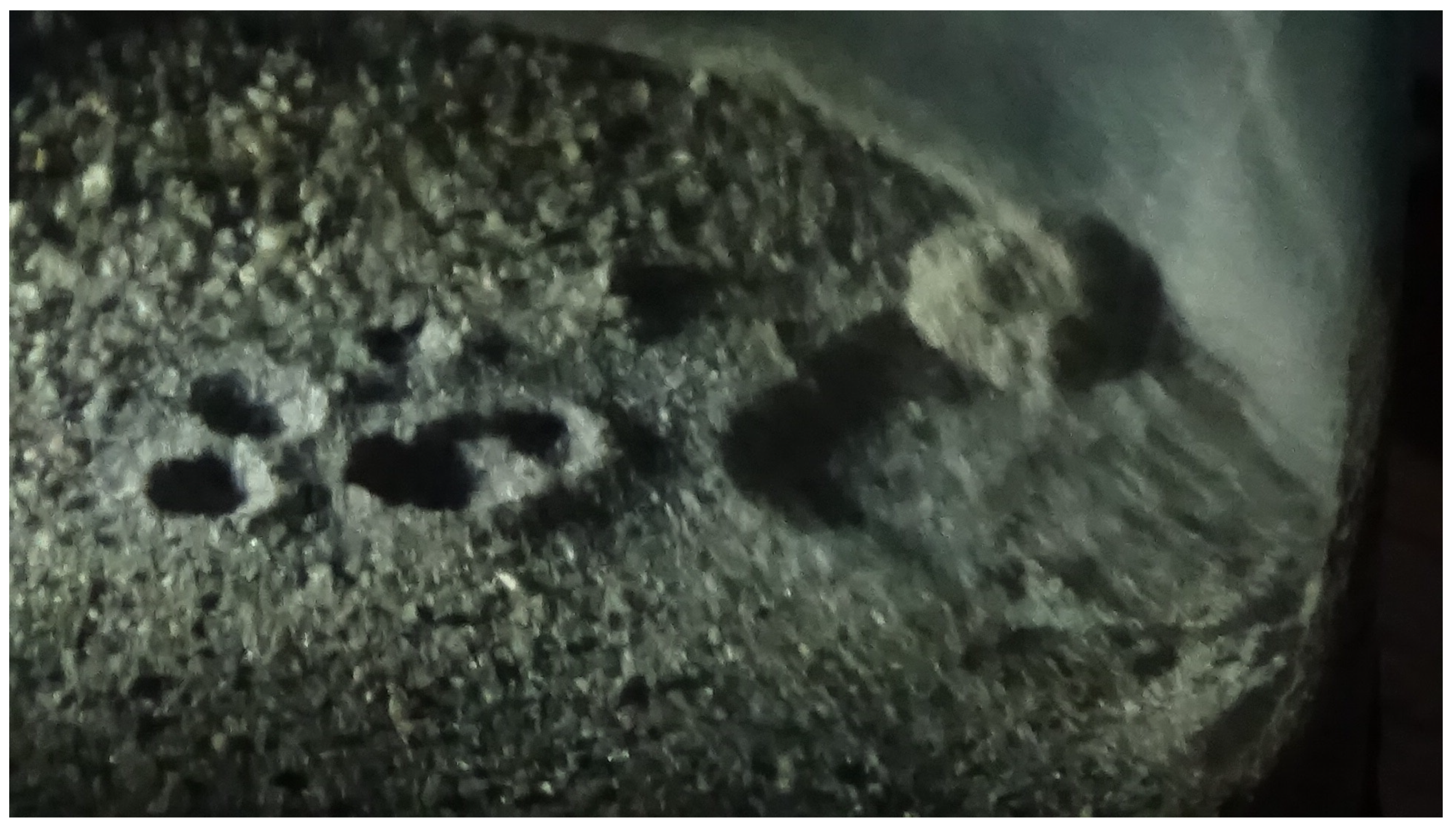
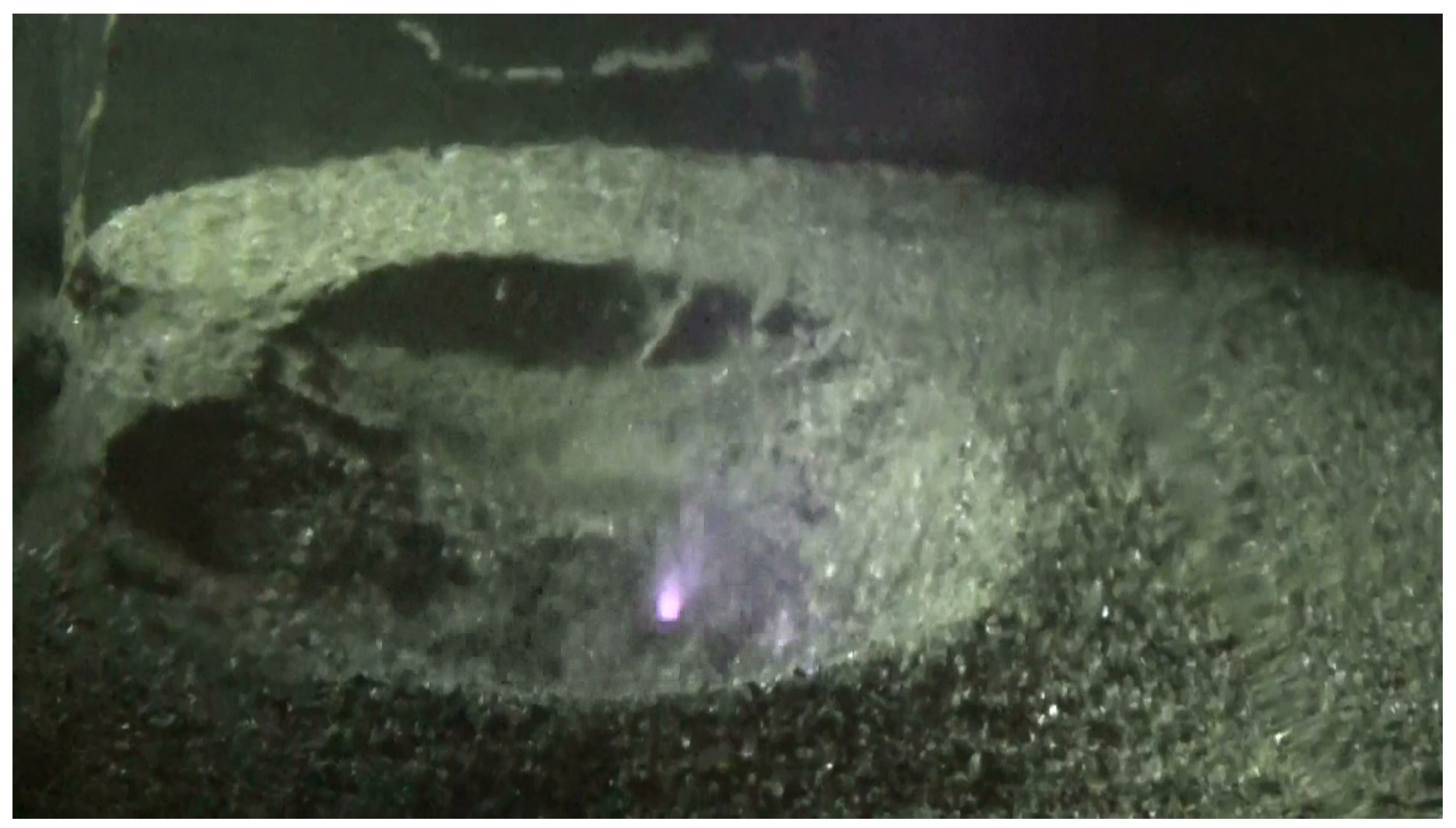
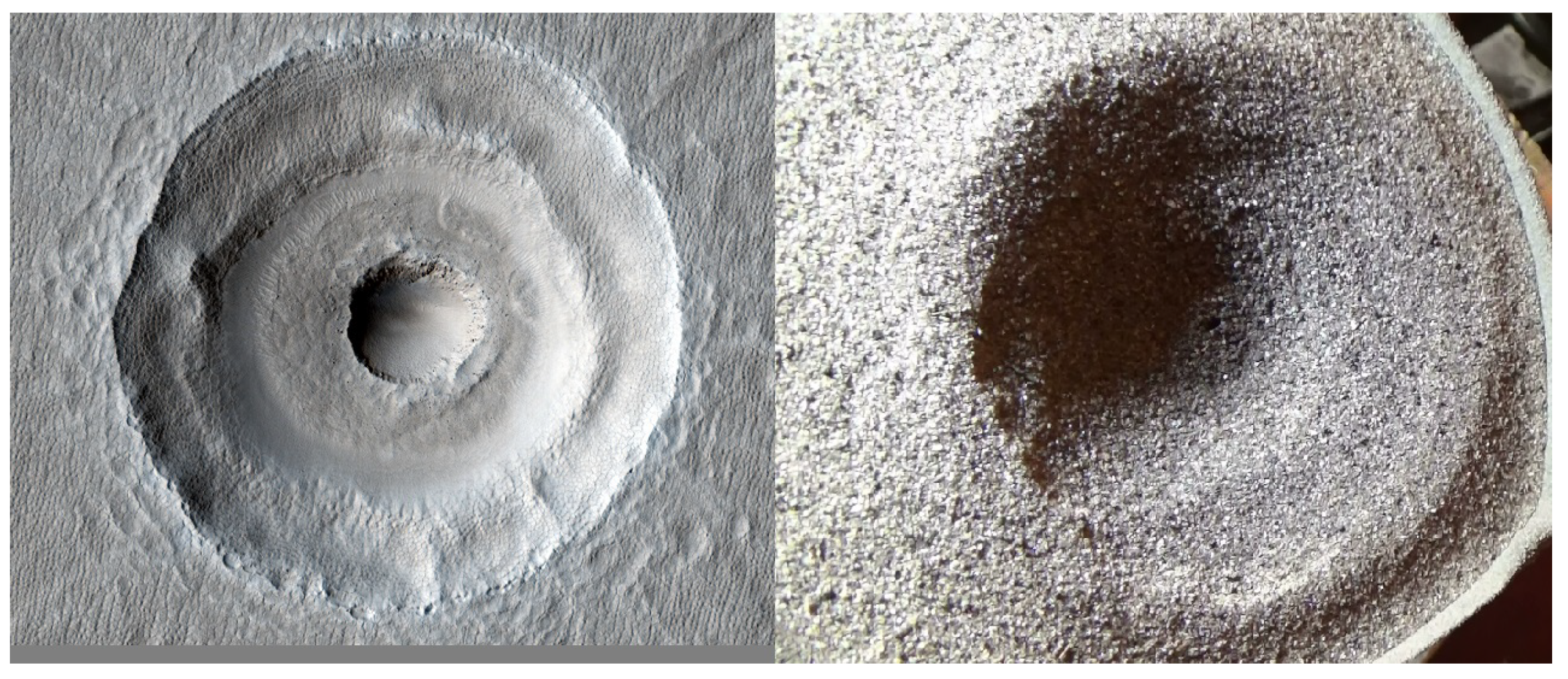
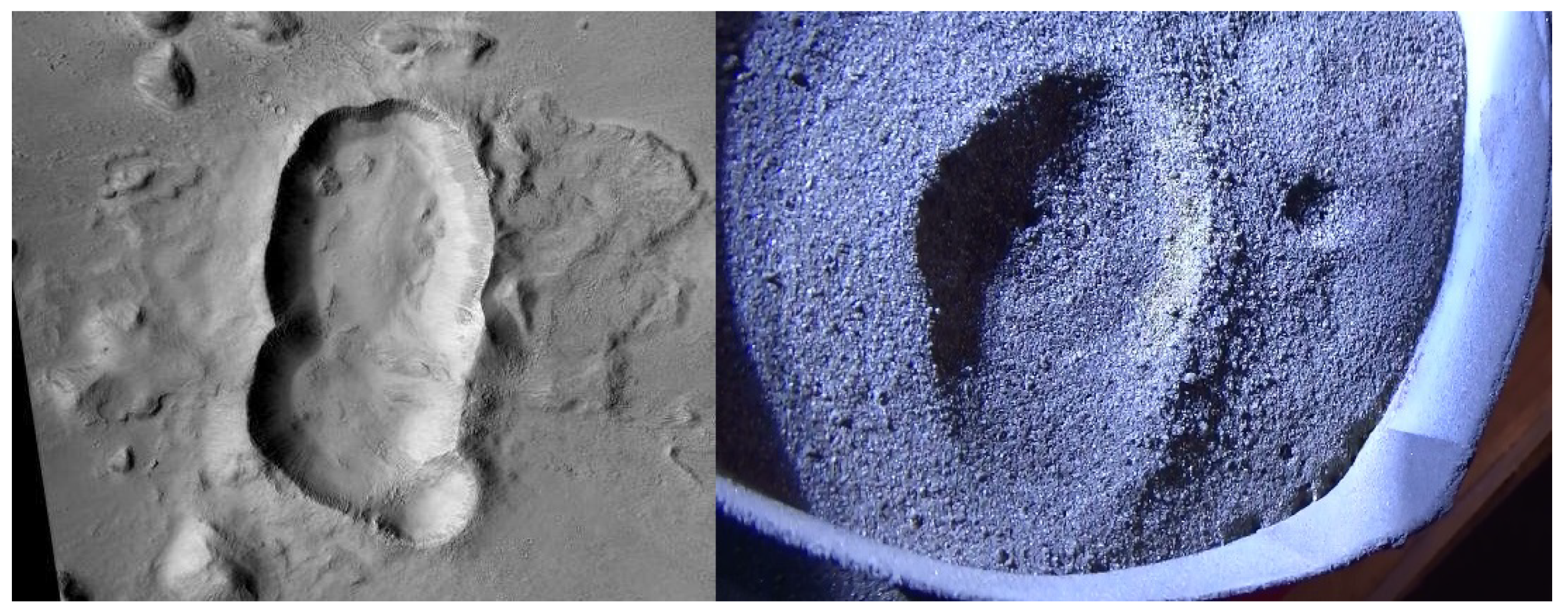
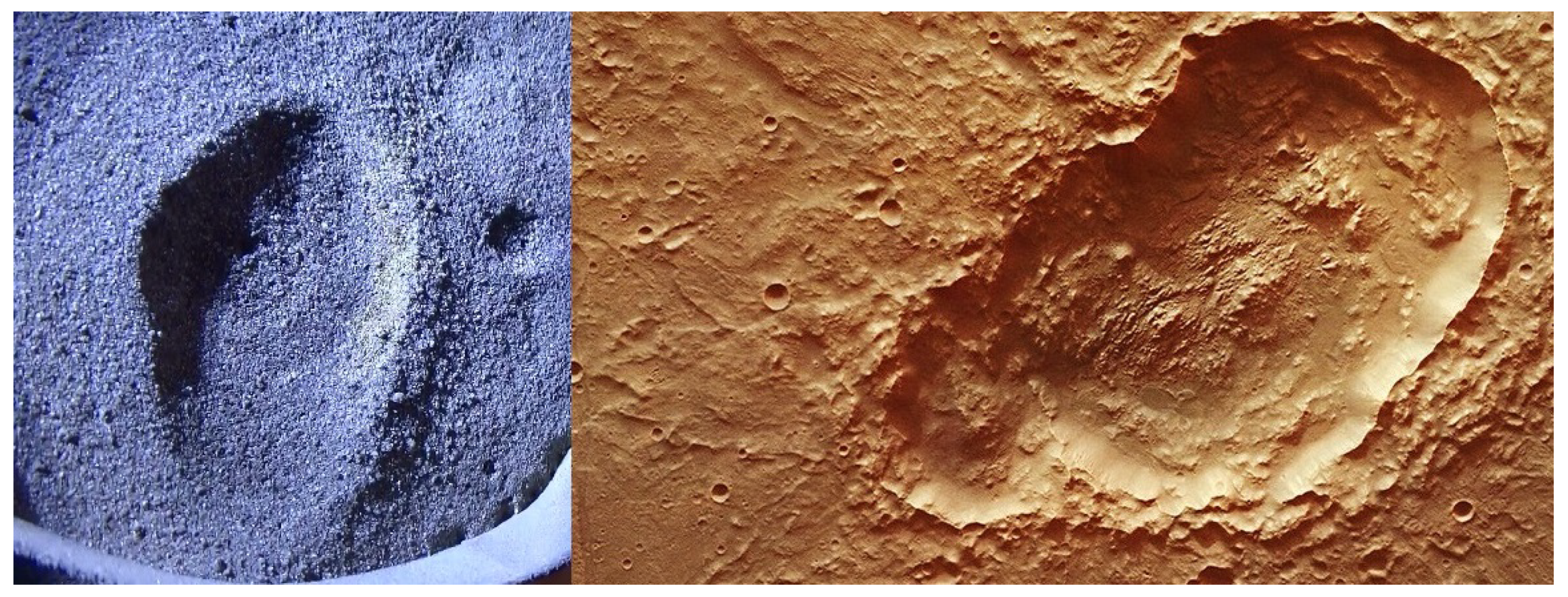
4.1. Analogues
5. Discussion
5.1. Mineralogical Evidence
5.2. Comets and Asteroids
5.3. Piezoelectricity
5.4. Large Scale Craters
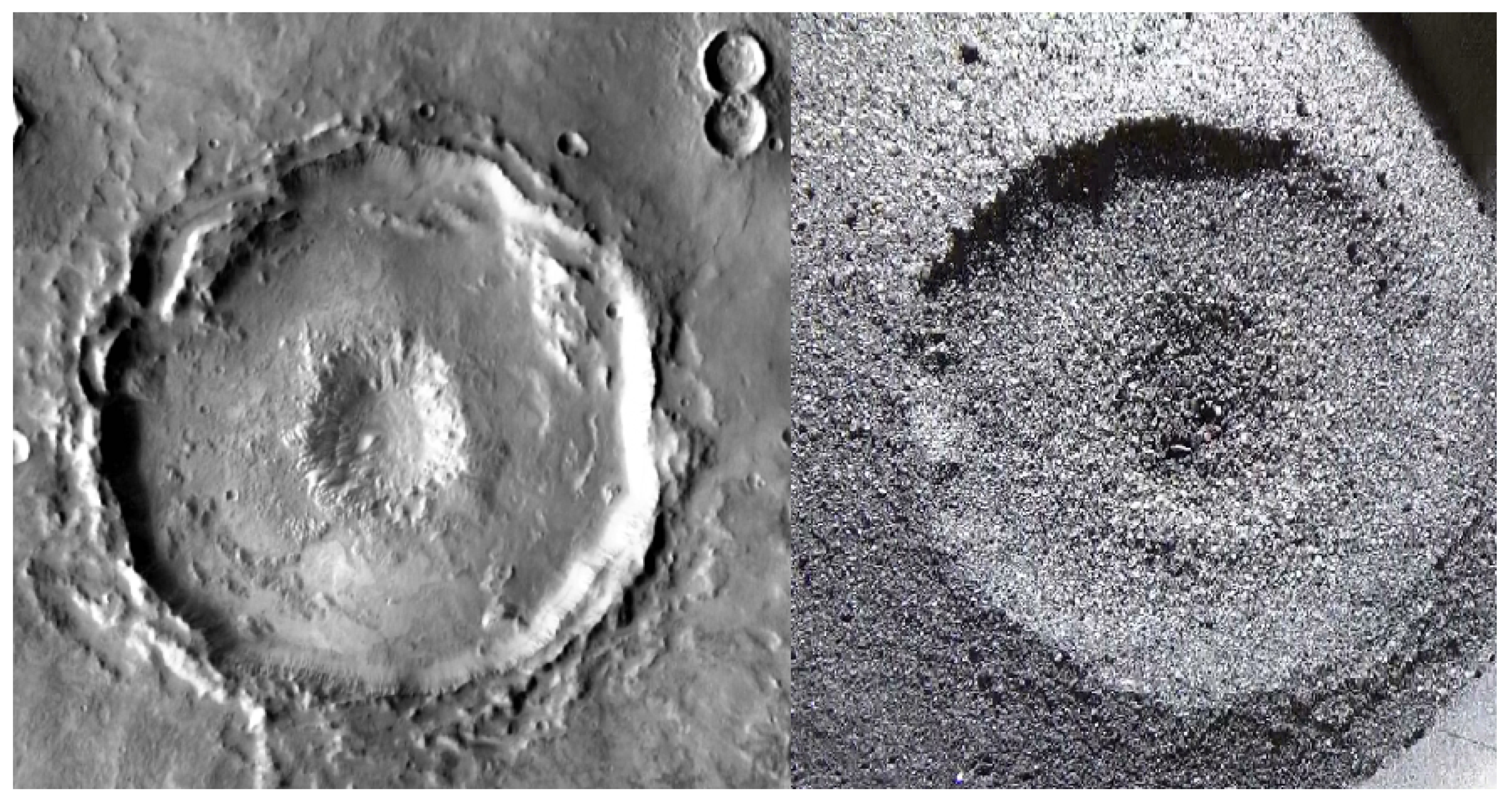
5.5. General Features
- horizontal rim strata;
- vertical walls coupled with a large completely flat floor;
- an ejecta blanket system;
- a central peak ring.
- overturned rim layers;
- a ray system or radiating ridges;
- nickel-iron bodies embedded under the rim and shocked quartz in the crater;
- a mascon associated with it.
6. Conclusions
Data Availability Statement
References
- Bland, P. Crater counting. Astronomy & Geophysics 2003, 44, 4.21–4.21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melosh, H.J. Planetary Surface Processes, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, 2011; p. 534. [Google Scholar]
- Gifford, A.C. The mountains of the Moon. New Zealand Journal of Science and Technology 1924, 7, 129–142. [Google Scholar]
- Gifford, A.C. The Origin of the Surface Features of the Moon. New Zealand Journal of Science and Technology 1930, 11, 319–327. [Google Scholar]
- French, B.M. Traces of Catastrophe : A Handbook of Shock-Metamorphic Effects in Terrestrial Meteorite Impact Structures, 1st ed.; Lunar and Planetary Institute: Houston TX, 1998; p. 120. [Google Scholar]
- Ford, B.J. Origin of the lunar craters. Spaceflight 1965, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Ransom, C.J.; Thornhill, W. Plasma-Generated Craters and Spherules. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science 2007, 35, 828–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velázquez, V.F.; Gomes, C.B.; Mansueto, M.; de Moraes, L.A.; Sobrinho, J.M.A.; Lucena, R.F.; Sallun, A.E.; Sallun Filho, W. Morphological aspects, textural features and chemical composition of spherules from the Colônia impact crater, São Paulo, Brazil. Solid Earth Sciences 2021, 6, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawthorne Jr., R. Electric Discharge - Not an Impact Caused Formation of Upheaval Dome, Canyonlands National Park, Utah. Journal on Systemics, Cybernetics and Informatics 2020, 18, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumm, S.A.; Simons, D.B. Lunar Rivers or Coalesced Chain Craters? Science 1969, 165, 201–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juergens, R.E. OF THE Moon AND MARS part I: The Origins Of The Lunar Sinuous Rilles. Pensée 1974, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Lakatos, S.; Heymann, D.; Yaniv, A. Green spherules from Apollo 15: Inferences about their origin from inert gas measurements. The Moon 1973, 7, 132–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denevi, B.W.; Robinson, M.S.; Boyd, A.K.; Blewett, D.T.; Klima, R.L. The distribution and extent of lunar swirls. Icarus 2016, 273, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemingway, D.J.; Tikoo, S.M. Lunar Swirl Morphology Constrains the Geometry, Magnetization, and Origins of Lunar Magnetic Anomalies. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets 2018, 123, 2223–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H.; Mann, I.; Biesecker, D.A. Olivine and Pyroxene Dust Aggregates in Sungrazing Comets. Meteoritics & Planetary Science 2001, 36, A99. [Google Scholar]
- Schultze, D.S.; Jourdan, F.; Hecht, L.; Reimold, W.U.; Schmitt, R.T. Tenoumer impact crater, Mauritania: Impact melt genesis from a lithologically diverse target. Meteoritics & Planetary Science 2016, 51, 323–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfvén, H. Cosmic Plasma, 1st ed.; D. Reidel Publishing Company: Dordrecht, 1981; p. 164. [Google Scholar]
- Peratt, A.L. Physics of the Plasma Universe, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, 2015; p. 430. [Google Scholar]
- Kenkmann, T.; von Dalwigk, I. Radial transpression ridges: A new structural feature of complex impact craters. Meteoritics & Planetary Science 2000, 35, 1189–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, J.W. On the relationships between impact crater diameters and projectile kinetic energy. The Moon and the Planets 1982, 26, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, S.; Sheffer, A.; McCanta, M.; Dyar, M.; Sklute, E. Oxidation state of iron in fulgurites and Trinitite: Implications for redox changes during abrupt high-temperature and pressure events. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 2019, 266, 332–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ende, M.; Schorr, S.; Kloess, G.; Franz, A.; Tovar, M. Shocked quartz in Sahara fulgurite. European Journal of Mineralogy 2012, 24, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, S.E.; Sheffer, A.A.; McCanta, M.C.; Dyar, M.D.; Sklute, E.C. Investigating Redox Change During Impacts. 50th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference 2019 (LPI Contrib. No. 2132), 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gieré, R.; Wimmenauer, W.; Müller-Sigmund, H.; Wirth, R.; Lumpkin, G.R.; Smith, K.L. Lightning-induced shock lamellae in quartz. American Mineralogist 2015, 100, 1645–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, H.; Yonezawa, K.; Kouno, Y.; Shindo, T. Propagation of Lightning Current Studied by Remanent Magnetization. IEEJ Transactions on Power and Energy 2013, 133, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begnini, G.S.; Tohver, E.; Schmieder, M. Fulgurites: a rock magnetic study of mineralogical changes caused by lightning. American Geophysical Union, Spring Meeting 2013, abstract ID: GP33A-07, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wasilewski, P.J. Shock remagnetization associated with meteorite impact at planetary surfaces. The Moon 1973, 6, 264–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gattacceca, J.; Boustie, M.; Lima, E.; Weiss, B.; de Resseguier, T.; Cuq-Lelandais, J. Unraveling the simultaneous shock magnetization and demagnetization of rocks. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors 2010, 182, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikoo, S.M.; Gattacceca, J.; Swanson-Hysell, N.L.; Weiss, B.P.; Suavet, C.; Cournède, C. Preservation and detectability of shock-induced magnetization. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets 2015, 120, 1461–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasek, M.; Pasek, V. The forensics of fulgurite formation. Mineralogy and Petrology 2018, 112, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrière, L.; Koeberl, C.; Libowitzky, E.; Reimold, W.U.; Greshake, A.; Brandstätter, F. Ballen quartz and cristobalite in impactites: New investigations. In Large Meteorite Impacts and Planetary Evolution IV; Geological Society of America: 2010. [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Chen, M.; Sharp, T. A TEM Investigation of Formation Process of Coesite From the Xiuyan Impact Crater. 82nd Annual Meeting of The Meteoritical Society 2019 (LPI Contrib. No. 2157), 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Plescia, J.B.; Cintala, M.J. Impact melt in small lunar highland craters. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Chen, M. Microtextures of Coesites with Different Occurrences from the Xiuyan Crater. 50th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference 2019 (LPI Contrib. No. 2132), 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Trepmann, C.A.; Dellefant, F.; Kaliwoda, M.; Hess, K.U.; Schmahl, W.W.; Hölzl, S. Quartz and cristobalite ballen in impact melt rocks from the Ries impact structure, Germany, formed by dehydration of shock-generated amorphous phases. Meteoritics & Planetary Science 2020, 55, 2360–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, H.H.; DellaGiustina, D.N.; Simon, A.A.; Hamilton, V.E.; Poggiali, G.; Barucci, M.A.; Reuter, D.C.; Lauretta, D.S. Detection of Pyroxenes on Bennu with the OSIRIS-REx Visible and InfraRed Spectrometer. Asteroid Science in the Age of Hayabusa2 and OSIRIS-REx, held 5–7 November, 2019 in Tucson, Arizona. LPI Contribution No. 2189, id.2056, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, H.H.; Lauretta, D.S.; Simon, A.A.; Hamilton, V.E.; DellaGiustina, D.N.; Golish, D.R.; Reuter, D.C.; Bennett, C.A.; Burke, K.N.; Campins, H.; Connolly, H.C.; Dworkin, J.P.; Emery, J.P.; Glavin, D.P.; Glotch, T.D.; Hanna, R.; Ishimaru, K.; Jawin, E.R.; McCoy, T.J.; Porter, N.; Sandford, S.A.; Ferrone, S.; Clark, B.E.; Li, J.Y.; Zou, X.D.; Daly, M.G.; Barnouin, O.S.; Seabrook, J.A.; Enos, H.L. Bright carbonate veins on asteroid (101955) Bennu: Implications for aqueous alteration history. Science 2020, 370, eabc3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flynn, G.J.; Leroux, H.; Tomeoka, K.; Tomioka, N.; Ohnishi, I.; Mikouchi, T.; Wirick, S.; Keller, L.P.; Jacobsen, C.; Sandford, S.A. Carbonate in Comets: A Comparison of Comets 1P/Halley, 9P/Temple 1, and 81P/Wild 2. 39th Lunar Planetary Science Conference (League City, TX), 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Carrozzo, F.G.; Sanctis, M.C.D.; Raponi, A.; Ammannito, E.; Castillo-Rogez, J.; Ehlmann, B.L.; Marchi, S.; Stein, N.; Ciarniello, M.; Tosi, F.; Capaccioni, F.; Capria, M.T.; Fonte, S.; Formisano, M.; Frigeri, A.; Giardino, M.; Longobardo, A.; Magni, G.; Palomba, E.; Zambon, F.; Raymond, C.A.; Russell, C.T. Nature, formation, and distribution of carbonates on Ceres. Science Advances 2018, 4, e1701645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacomini, L.; Massironi, M.; El-Maarry, M.R.; Penasa, L.; Pajola, M.; Thomas, N.; Lowry, S.C.; Barbieri, C.; Cremonese, G.; Ferri, F.; Naletto, G.; Bertini, I.; La Forgia, F.; Lazzarin, M.; Marzari, F.; Sierks, H.; Lamy, P.L.; Rodrigo, R.; Rickman, H.; Koschny, D.; Keller, H.U.; Agarwal, J.; A’Hearn, M.F.; Auger, A.T.; Barucci, M.A.; Bertaux, J.L.; Besse, S.; Bodewits, D.; Da Deppo, V.; Davidsson, B.; De Cecco, M.; Debei, S.; Fornasier, S.; Fulle, M.; Groussin, O.; Gutierrez, P.J.; Güttler, C.; Hviid, S.F.; Ip, W.H.; Jorda, L.; Knollenberg, J.; Kovacs, G.; Kramm, J.R.; Kührt, E.; Küppers, M.; Lara, L.M.; Moreno, J.J.L.; Magrin, S.; Michalik, H.; Oklay, N.; Pommerol, A.; Preusker, F.; Scholten, F.; Tubiana, C.; Vincent, J.B. Geologic mapping of the Comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko’s Northern hemisphere. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 2016, 462, 352–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garimella, R.C.; Sastry, V.; Mohiuddin, M.S. Piezo-Gen - An Approach to Generate Electricity from Vibrations. Procedia Earth and Planetary Science 2015, 11, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hough, R.M.; Langenhorst, F.; Stoffler, D.; Pillinger, C.; Gilmour, I. Suevites from the Rochechouart Impact Crater, France, and the Lake Mien Impact Crater, Sweden: The Search for Robust Carbon Minerals. Meteoritics 1995, 30, 521. [Google Scholar]
- Hess, B.L.; Piazolo, S.; Harvey, J. Lightning strikes as a major facilitator of prebiotic phosphorus reduction on early Earth. Nature Communications 2021, 12, 1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Dwyer, J.J. The theory of dielectric breakdown of solids, 1st ed.; Clarendon Press: Oxford, 1964; p. 142. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P. Coronal Mass Ejections: Models and Their Observational Basis. Living Reviews in Solar Physics 2011, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, J.J.; Cohen, O.; Yashiro, S.; Gopalswamy, N. IMPLICATIONS OF MASS AND ENERGY LOSS DUE TO CORONAL MASS EJECTIONS ON MAGNETICALLY ACTIVE STARS. The Astrophysical Journal 2013, 764, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namekata, K.; Maehara, H.; Honda, S.; Notsu, Y.; Okamoto, S.; Takahashi, J.; Takayama, M.; Ohshima, T.; Saito, T.; Katoh, N.; Tozuka, M.; Murata, K.L.; Ogawa, F.; Niwano, M.; Adachi, R.; Oeda, M.; Shiraishi, K.; Isogai, K.; Seki, D.; Ishii, T.T.; Ichimoto, K.; Nogami, D.; Shibata, K. Probable detection of an eruptive filament from a superflare on a solar-type star. Nature Astronomy 2022, 6, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrodera, C.; Nikitina, L.; Cid, C. Estimation of the Solar Wind Extreme Events. Space Weather 2021, 19, e2021SW002902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, T. Large solar outbursts in the past. Pontificiae Academiae Scientiarum Scripta Varia 1962, 25, 159–174. [Google Scholar]
- Fränz, M.; Dubinin, E.; Maes, L. Electric current systems at Mars and Venus. Europlanet Science Congress 2020, online, 21 September–9 Oct 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paleari, C.I.; Mekhaldi, F.; Adolphi, F.; Christl, M.; Vockenhuber, C.; Gautschi, P.; Beer, J.; Brehm, N.; Erhardt, T.; Synal, H.A.; Wacker, L.; Wilhelms, F.; Muscheler, R. Cosmogenic radionuclides reveal an extreme solar particle storm near a solar minimum 9125 years BP. Nature Communications 2015, 13, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pryor, W.R.; Rymer, A.M.; Mitchell, D.G.; Hill, T.W.; Young, D.T.; Saur, J.; Jones, G.H.; Jacobsen, S.; Cowley, S.W.H.; Mauk, B.H.; Coates, A.J.; Gustin, J.; Grodent, D.; Gérard, J.C.; Lamy, L.; Nichols, J.D.; Krimigis, S.M.; Esposito, L.W.; Dougherty, M.K.; Jouchoux, A.J.; Stewart, A.I.F.; McClintock, W.E.; Holsclaw, G.M.; Ajello, J.M.; Colwell, J.E.; Hendrix, A.R.; Crary, F.J.; Clarke, J.T.; Zhou, X. The auroral footprint of Enceladus on Saturn. Nature 2011, 472, 331–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peratt, A.L.; Dessler, A.J. Filamentation of volcanic plumes on the Jovian satellite Io. Astrophysics and Space Science 1988, 144, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R. Massive Solar Euptions and Their Contribution to the Causes of Tectonic Uplift. New Concepts in Global Tectonics 2014, 2, 16–36. [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer, B.E.; King, J.R.; Deliyannis, C.P. Superflares on Ordinary Solar-Type Stars. The Astrophysical Journal 2000, 529, 1026–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.S.; Scalo, J. Solar X-ray flare hazards on the surface of Mars. Planetary and Space Science 2007, 55, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfvén, H. Cosmical Electrodynamics, 1st ed.; Clarendon Press: Oxford, 1950; p. 244. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, C.; Chi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, M.; Wang, S. Statistical comparison of the ICME’s geoeffectiveness of different types and different solar phases from 1995 to 2014. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics 2017, 122, 5931–5948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsurutani, B.T.; Lakhina, G.S.; Echer, E.; Hajra, R.; Nayak, C.; Mannucci, A.J.; Meng, X. Comment on “Modeling Extreme “Carrington-Type” Space Weather Events Using Three-Dimensional Global MHD Simulations” by C. M. Ngwira, A. Pulkkinen, M. M. Kuznetsova, and A. Glocer. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics 2018, 123, 1388–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, A.P.; Stubbs, T.J.; Wilson, J.K.; Schwadron, N.A.; Spence, H.E.; Joyce, C.J. Deep dielectric charging of regolith within the Moon’s permanently shadowed regions. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets 2014, 119, 1806–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burn, W. Polygonal crater formation by electrical discharges. New Concepts in Global Tectonics 2015, 3, 158–186. [Google Scholar]
- Kuznetsova, N.; Zhgun, D.; Golovanevskiy, V. Plasma blasting of rocks and rocks-like materials: An analytical model. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences 2022, 150, 104986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nature Journal. A NEW CRATER ON THE LUNAR SURFACE. Nature 1878, 18, 197–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speyerer, E.J.; Povilaitis, R.Z.; Robinson, M.S.; Thomas, P.C.; Wagner, R.V. Quantifying crater production and regolith overturn on the Moon with temporal imaging. Nature 2016, 538, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, D.W. Transient lunar phenomena. Nature 1980, 285, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehnke, P.; Harrison, T.M. Illusory Late Heavy Bombardments. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA 2016, 113, 10802–10806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| 1 | perhaps, one could call it a sub-nova, as it’s – times weaker than a typical nova in terms of the fraction of ejected |












Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




