Introduction
Endothelial dysfunction is a hall marker of systemic disease resulting from SARS-CoV2 infection [
1]. Endothelium is a dynamic cell layer involved in multitude of physiologic functions, including control of vasomotor tone, trafficking of cells and nutrients, maintenance of blood fluidity, and growth of new blood vessels [
2]. Once endothelial layer is disrupted following infection [
3], released toxin [
4], trauma [
5], irradiation [
6], and ischemia [
7], etc., an endotheliopathy develops. Endotheliopathy is marked by an increased level of plasma von Willebrand factor (VWF), E-selectin, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1), soluble thrombomodulin (sTM), and syndecan-1 [
8], which is strongly associated with a poor outcome in patients with severe COVID-19 [
9,
10].
Syndecan-1 is a core backbone of vascular glycocalyx proteoglycans [
11] that play an important role in regulating hemostasis, inflammation, trans-capillary flux, and microvascular permeability [
12,
13,
14]. Plasma or serum levels of syndecan-1 on admission were found to be significantly elevated in patients with severe and critical COVID-19, which appears to be associated with mortality, intensive care unit (ICU) admission, and multiple organ damage [
11,
15,
16,
17,
18,
19]. However, the data published to date remains inconclusive owing to small sample sizes and in most cases a single time measurement. Thus, the role of assessing plasma syndecan-1 in hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV2 infection in classifying disease severity and predicting outcome is still not clear. Here, we report a longitudinal assessment of plasma levels of syndecan-1 in these patients and its association with the disease severity and long-term outcomes.
Methods
Patients and sample collection. Institutional Review Boards of the University of Kansas Medical Center (KUMC) has approved the study (IRB #00148313). The study was conducted according to the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. One hundred and twenty-four consecutive hospitalized patients between January and March 2022 at the University of Kansas Hospital with a polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection and 20 healthy individuals were prospectively enrolled into the study. Venous blood was collected on admission (T1), 3-4 days following treatment (T2), and 1-2 days prior to discharge or death (T3) and anticoagulated with ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA). Of 124 patients, 62 had more than 3 longitudinal blood samples and 72 patients had at least 2 samples collected. The exclusion criteria include those who were under 18 years old, patients who underwent a surgical procedure before the initial sample collection or those with the initial sample collected 48 hours after hospital admission. Patient demographic, clinical, and laboratory data were collected from electronic medical record at the time of blood collection. All patients were assessed for in-hospital adverse events and followed up to 60 days for obtaining all-cause survival information. Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) criteria were used to define acute kidney injury (AKI).
Plasma from healthy controls. Age-, sex-matched healthy individuals who do not have acute and chronic inflammatory and thrombotic diseases or cancer were selected for the healthy controls.
Assay for plasma levels of syndecan-1. Plasma syndecan-1 was determined using a commercially available enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Abcam, Waltham, MA). The intra- and inter-assay coefficient of variations are 6.2% and 10.2%, respectively.
Statistical Analysis. Continuous variables are expressed as the means ± standard deviations (SD) or the medians ± interquartile ranges (IQR) as appropriate. Mann-Whitney, Wilcoxon, or Kruskal-Wallis tests were used for paired and unpaired continuous variables, respectively. All categorical variables were described as numbers and percentages, and Fisher’s exact test (or χ2 test) was used for data analysis. Furthermore, Cox proportional hazard ratio regressions were employed to determine the most valuable predictor for 60-day mortality of COVID-19. To evaluate how variables can predict COVID-19 prognoses, the Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) and Kaplan-Meier survival curves were calculated. All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS statistics version 26.0 (IBM) and Prism 8.0.
Results
Demographic, clinical and laboratory characteristics of the patients
A total of 124 consecutive hospitalized patients with PCR-positive SARS-CoV-2 were included in our study. These patients were categorized to asymptomatic, moderate, severe, and critical groups according to the updated World Health Organization guideline (WHO/2019-CoV/clinical/2021.2).
Table 1 showed that there was no statistically significant difference in demographic features including gender, age, body mass index, and race among various groups. Additionally, a similar comorbidity rate including diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, hyperlipoidemia, chronic kidney insufficiency, and history of malignancy and thrombotic events, except for hypertension in which more patients exhibited hypertension in the critical group (
p=0.03). Of 124 patients, 14 (11.3%) were in the status of post organ transplantation and immunosuppression, 44 (35.4%) were admitted to intensive care unit (ICU) with the critical group having the highest rate of ICU admission (93.5%). There was a significantly higher incidence of sepsis or septic shock, AKI, and thrombotic events in patients with severe and critical COVID-19 than those with mild to moderate disease. 14 patients were intubated for mechanical ventilation and 15 died within 60 days following admission. Asymptomatic patients were those hospitalized for reasons other than COVID-19, including depression, coronary artery disease, alcoholism with alcohol withdrawal, hypothyroidism, trauma, post-operative infection, diabetic foot, burns, stroke, cirrhosis, end stage of renal diseases on hemodialysis, etc.
Table 2 summarizes the baseline laboratory data collected from COVID-19 patients within 24 hours following admission. The results showed that the median levels of neutrophil proportion, lymphocyte count, serum protein, and D-dimers were significantly different in patients with severe and critical disease from those with asymptomatic and moderate diseases. However, no statistically significant difference was detected in the baseline white blood cell count, neutrophil granulocyte and platelet counts, creatinine, or lactate dehydrogenase levels among all the groups.
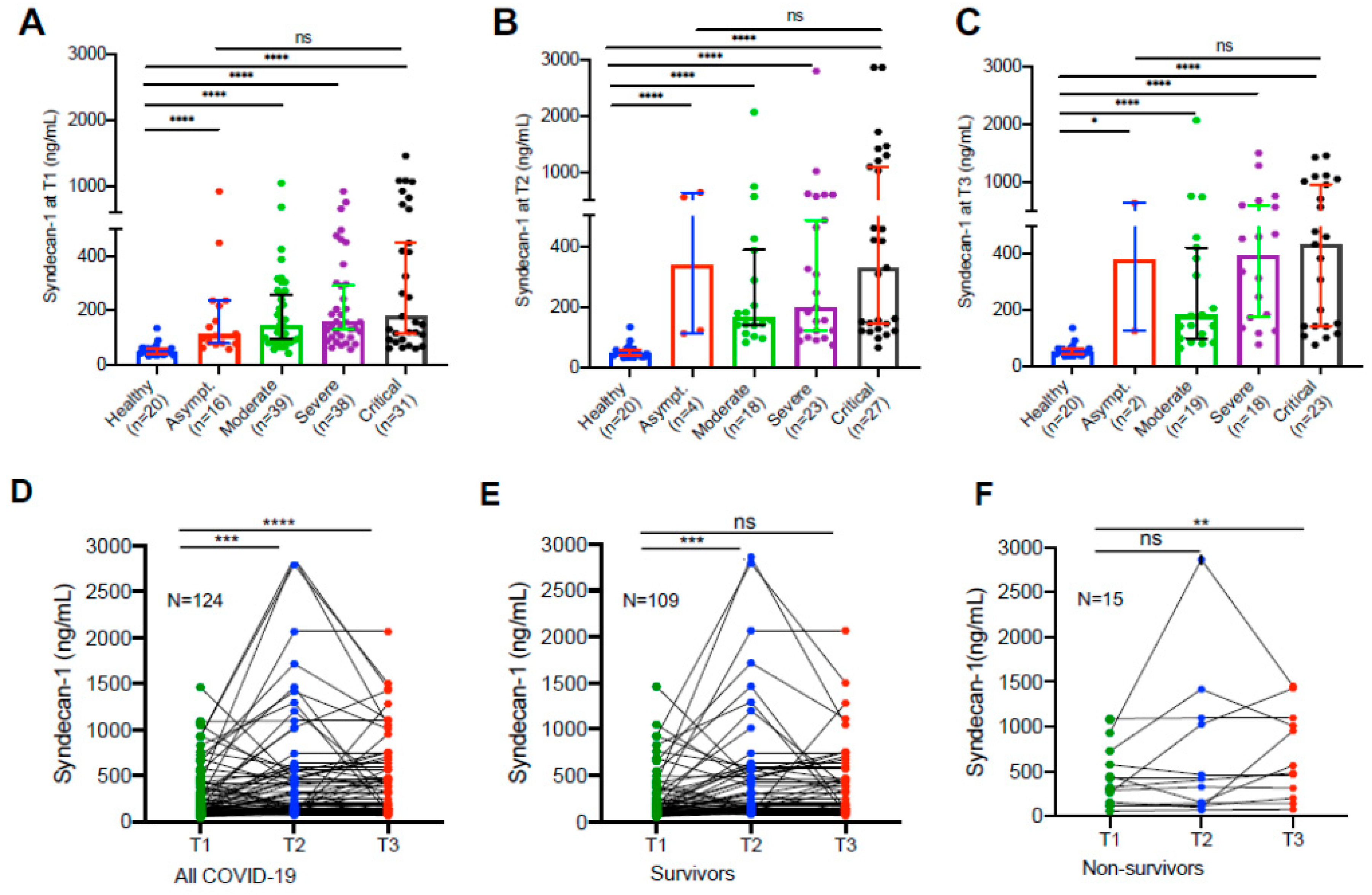
Hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV2 infection exhibited significantly elevated plasma levels of syndecan-1
Compared with the levels (median, IQR) in the healthy controls (49.5, 38.1-62.1 ng/mL), plasma syndecan-1 levels in hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV2 infection on admission (156.8, 92.4-321.4 ng/mL) were significantly increased (
p<0.0001). Statistically significant difference in plasma sydecan-1 levels was found in patients with moderate to critical disease compared with those in the healthy controls (
p<0.0001) at all three time points (
Figure 1A–C). These results suggest that endothelial damage appears to occur in all hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV2 infection, regardless of their disease severity.
Longitudinal changes of plasma syndecan-1 in hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV2 infection
Longitudinal blood samples were collected and assayed for plasma syndecan-1 levels in patients following
SARS-CoV2 infection during hospitalization. We found that in all hospitalized patients their plasma levels (median 156.8, IQR 92.4-321.4 ng/mL) of syndecan-1 tended to increase initially (2-3 days) following treatments (median 191.7, IQR 124.2-567.0 ng/mL) (
p=0.003) (
Figure 1D), then either slowly increased to reach a certain extent in those who survived (median 226.5, IQR 125.0-485.6 ng/mL) (
p=0.052) (
Figure 1D &
Figure 1E) or persistently elevated in those who died (median 523.3, IQR 228.8-1,074.0 ng/mL) (
p=0.007) (
Figure 1D &
Figure 1F). These results suggest that endotheliopathy, indicated by an elevation of plasma syndecan-1, persists in patients with severe and critical COVID-19.
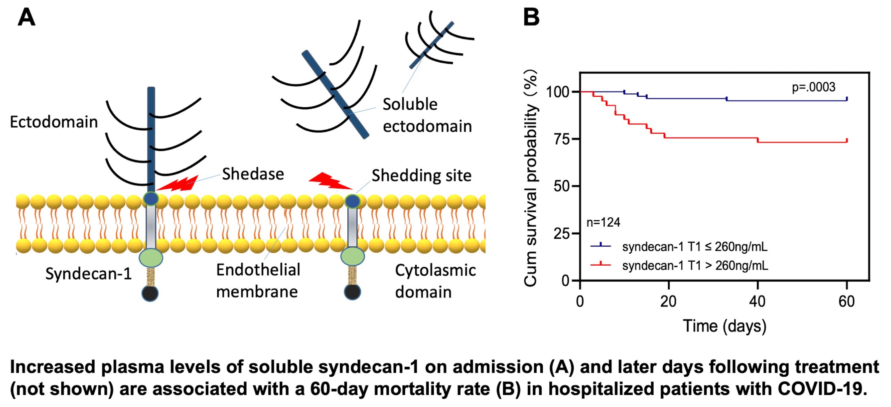
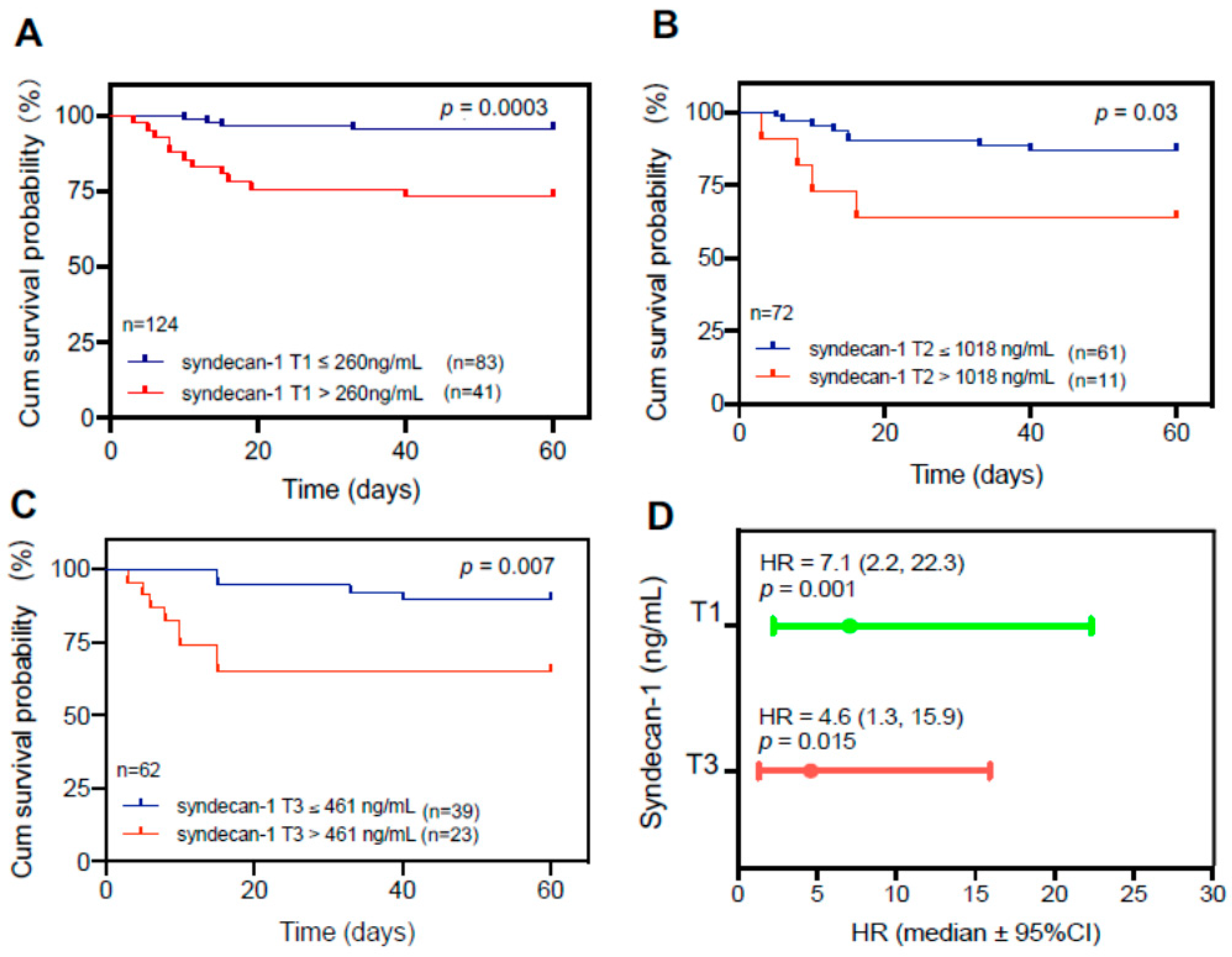
Elevated plasma levels of syndecan-1 are associated with mortality in patients with COVID-19
To determine the clinical relevance of elevated plasma levels of syndecan-1, we performed the receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) analysis, Cox proportional hazard risk assessment, and Kaplan-Meier survival analyses. ROC analysis demonstrated the cut-off value based on performance characteristic of sensitivity and 1-specificity using the cut-off. We found that plasma levels of syndecan-1 at T1 (>260 ng/mL) (
p=0.003) (
Figure 2A), at T2 (>1,018 ng/mL) (
p=0.03) (
Figure 2B), and at T3 (>461 ng/mL) (p=0.007) (
Figure 2C) were associated with an increased 60-day mortality rate in patients with COVID-19. Cox proportional hazard risk analysis revealed that plasma syndecan-1 at T1 (>260 ng/mL) and T3 (>461 ng/mL) were strongly associated with the 60-day mortality rate in patients with COVID-19 with a hazard ratio (HR) of 7.1 (95% CI, 2.2-22.3) (
p=0.001) and 4.6 (95%CI, 1.3-15.9) (
p=0.015), respectively (
Figure 2D). These results indicate that the plasma levels of syndecan-1 are predictive for an adverse outcome in hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV2 infection.
Discussion
The present study demonstrates the role of longitudinal assessment of plasma levels of syndecan-1 in predicting the 60-day mortality in patients with COVID-19. These novel findings are important but come to us with little surprise. The study addressed hard clinical endpoints including ICU admission, acute renal insufficiency (data not shown) and 60-day all-cause mortality rate. Only one patient died on 26 days after discharge (40 days after admission). This patient was re-admitted after recovery from SARS-Cov2 infection, although he died of end-stage lung and heart failure eventually. All other patients died of COVID-19 disease or COVID-19-related complications during hospitalization.
Syndecan-1 is released from the degradation of endothelial glycocalyx. It may be caused by direct infection of endothelial cells with SARS-CoV2 following binding to outer membrane angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE-2) receptor [
20,
21]. It may also be the result of acute inflammation following viral infection [
22]. Our correlation analysis provided evidence that an elevated plasma level of syndecan-1 was positively and moderately associated with inflammation biomarkers, including white blood cell count, C-reactive protein, D-dimer, and lactate dehydrogenase (data not shown). More recently, Lambadiari et al. [
23] have demonstrated that when comparing with the healthy control, the thickness of glycocalyx in convalescent COVID-19 patients without hypertension and hypertensive patients decreases significantly, although the reduction of endothelial glycocalyx in these groups was not related to disease severity. These findings are consistent with ours, suggesting overlapping contributing factors to hypertension and SARS-CoV2 infection.
Other potential mechanisms contributing to the elevation of plasmas syndecan-1 levels include prolonged and overactive immune response with abnormality in cytotoxic T cells and monocytes [
24]. Glycocalyx degradation may be mediated by reactive oxygen/nitrogen species, matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), hyaluronidase, and deficiency of heparanase [
25]. MMP-2, MMP-9, MT1-MMP, and ADAM-17 were shown to be capable of releasing syndecan-1 from endothelial surface [
26]. Stahl et al. have demonstrated that in patients with critical COVID-19 an acquired deficiency of heparanase-2 might contribute to an increased degradation of endothelial glycocalyx [
27]. Overexpression of heparanase-2 or addition of heparin appears to prevent endothelial glycocalyx degradation
in vitro [
28,
29,
30], suggesting a therapeutic potential of targeting endothelial glycocalyx.
Elevated plasma syndecan-1 may not only serve as a biomarker for endothelial dysfunction and damage [
31], but also contribute to a variety of pathophysiological functions [
32]. Studies have shown that plasma syndecan-1 may attribute to inflammation [
11,
17] and thrombosis [
33]. Plasma levels of syndecan-1 are associated with neutrophil activation and may reflect the degree of endothelial damage in patients with sepsis [
34]. Syndecan-1 protein is found to be the major component of thrombi and plays a role of thrombus formation in a mouse model of anthrax [
33]. In another animal study, shedding of proteoglycans may result in diminished thickness of the glycocalyx layer, leading to rapid adhesion and migration of leukocytes through injured endothelium [
32].
Our study has some limitations. First, we did not have data from all follow-up samples due to early discharge, which makes comparison of longitudinal results less powerful; second, we did not recruit asymptomatic individuals who are not hospitalized as controls, or compared the plasma syndecan-1 levels with other patients who have sepsis and ICU admission for other reasons than severe/critical COVID-19 disease, although such a comparison has been extensively performed in other previous studies and interpretation for the results would be complicated. Third, this is a single-center study, although our sample size is larger than those previously published in the biomarker studies [
11,
35]. Thus, a much larger and multi-center study with a longer follow-up should be conducted to confirm our findings. A more recent study demonstrates that prolonged endotheliopathy may be present even in patients with mid-to-moderate COVID-19 convalescents [
36].
We conclude that significantly elevated plasma levels of syndecan-1 on admission and other time points in patients with severe to critical COVID-19 compared with the healthy controls. The elevated admission levels of plasma syndecan-1 may predict the all-cause 60-day mortality in patients with severe and critical COVID-19 disease. Our findings support the needs for additional therapeutic strategies to improve endothelial health, thus reducing disease-related mortality in these patients.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: QZ and XLZ; Methodology: QZ and XLZ; Software: QZ and XLZ; Validation: YZ, AB, and XLZ; Formal Analysis: QZ; Investigation: QZ and XLZ; Resources: YZ, AB, and XLZ; Data Curation: YZ and XLZ; Original Drafting: QZ; Review & Editing: YZ, AY and XLZ; Visualization: YZ, AB and XLZ; Supervision: XLZ; Project Administration: QZ, XLZ; Funding Acquisition: QZ and XLZ. All authors have read and agreed to the final version of the manuscript for publication.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Boards of the University of Kansas Medical Center (KUMC) (protocol code 00148313, February 10, 2022) for studies involving humans.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author at request.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported in part by grants from NHLBI R01HL144552 and R01HL157975-01A1 to X.L.Z and Central South University, Changsha, China for Ph.D. scholarship to study abroad to Q.Z.
Conflicts of Interest
X.L.Z. is a consultant for Alexion, Sanofi, and Takeda, as well as the founder of Clotsolution. Other authors have nothing to declare.
References
- Xu, S.W.; Ilyas, I., Weng, J.P. Endothelial dysfunction in COVID-19: an overview of evidence, biomarkers, mechanisms and potential therapies. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2022:1-15. [CrossRef]
- Aird, W.C. Endothelium as an organ system. Crit Care Med. 2004;32:S271-279. [CrossRef]
- Hellenthal, K.E.M.; Brabenec, L., Wagner, N.M. Regulation and Dysregulation of Endothelial Permeability during Systemic Inflammation. Cells. 2022;1: 1935. [CrossRef]
- Petruzziello-Pellegrini, T.N.; Moslemi-Naeini, M., Marsden, P.A. New insights into Shiga toxin-mediated endothelial dysfunction in hemolytic uremic syndrome. Virulence. [CrossRef]
- Russell, R.T.; McDaniel, J.K.; Cao, W.; Shroyer, M., et al. Low Plasma ADAMTS13 Activity Is Associated with Coagulopathy, Endothelial Cell Damage and Mortality after Severe Paediatric Trauma. Thromb Haemost. 2018;118:676-687. [CrossRef]
- Paris, F.; Fuks, Z.; Kang, A.; Capodieci, P., et al. Endothelial apoptosis as the primary lesion initiating intestinal radiation damage in mice. Science. 2001;293:293-297. [CrossRef]
- van Ierssel, S.H.; Conraads, V.M.; Van Craenenbroeck, E.M.; Liu, Y., et al. Endothelial dysfunction in acute brain injury and the development of cerebral ischemia. J Neurosci Res. 2015;93:866-872. [CrossRef]
- Gorog, D.A.; Storey, R.F.; Gurbel, P.A.; Tantry, U.S., et al. Current and novel biomarkers of thrombotic risk in COVID-19: a Consensus Statement from the International COVID-19 Thrombosis Biomarkers Colloquium. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2022;19:475-495. [CrossRef]
- Orea-Tejada, A.; Sanchez-Moreno, C.; Aztatzi-Aguilar, O.G.; Sierra-Vargas, M.P., et al. Plasma Endothelial and Oxidative Stress Biomarkers Associated with Late Mortality in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients. J Clin Med. 2022;11. [CrossRef]
- Andrianto; Al-Farabi, M.J.; Nugraha, R.A.; Marsudi, B.A., et al. Biomarkers of endothelial dysfunction and outcomes in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Microvasc Res. 2021;138:104224. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Li, L.; Chen, Y.; Ma, J., et al. Syndecan-1, an indicator of endothelial glycocalyx degradation, predicts outcome of patients admitted to an ICU with COVID-19. Mol Med. 2021;27:151. [CrossRef]
- Betteridge, K.B.; Arkill, K.P.; Neal, C.R.; Harper, S.J., et al. Sialic acids regulate microvessel permeability, revealed by novel in vivo studies of endothelial glycocalyx structure and function. J Physiol. 2017;595:5015-5035. [CrossRef]
- Butler, M.J.; Ramnath, R.; Kadoya, H.; Desposito, D., et al. Aldosterone induces albuminuria via matrix metalloproteinase-dependent damage of the endothelial glycocalyx. Kidney Int. 2019;95:94-107. [CrossRef]
- Teng, Y.H.; Aquino, R.S., Park, P.W. Molecular functions of syndecan-1 in disease. Matrix Biol. 2012;31:3-16. [CrossRef]
- Mobayen, G.; Dhutia, A.; Clarke, C.; Prendecki, M., et al. Severe COVID-19 is associated with endothelial activation and abnormal glycosylation of von Willebrand factor in patients undergoing hemodialysis. Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2021;5:e12582. [CrossRef]
- Beurskens, D.M.; Bol, M.E.; Delhaas, T.; van de Poll, M.C., et al. Decreased endothelial glycocalyx thickness is an early predictor of mortality in sepsis. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2020;48:221-228. [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, F.; Oi, Y.; Nakajima, K.; Matsumura, R., et al. Temporal change in Syndecan-1 as a therapeutic target and a biomarker for the severity classification of COVID-19. Thromb J. 2021;19:55. [CrossRef]
- Panigada, M.; Bottino, N.; Tagliabue, P.; Grasselli, G., et al. Hypercoagulability of COVID-19 patients in intensive care unit: A report of thromboelastography findings and other parameters of hemostasis. J Thromb Haemost. 2020;18:1738-1742. [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Sui, J., Zheng, X.L. Elevated plasma levels of syndecan-1 and soluble thrombomodulin predict adverse outcomes in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood Adv. 2020;4:5378-5388. [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Liu, F.; Blair, R.; Wang, C., et al. Endothelial cell infection and dysfunction, immune activation in severe COVID-19. Theranostics. 2021;11:8076-8091. [CrossRef]
- Varga, Z.; Flammer, A.J.; Steiger, P.; Haberecker, M., et al. Endothelial cell infection and endotheliitis in COVID-19. Lancet. 2020;395:1417-1418. [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Lei, T.; Patel, P.S.; Lee, C.H., et al. Direct Activation of Endothelial Cells by SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein Is Blocked by Simvastatin. J Virol. 2021;95:e0139621. [CrossRef]
- Lambadiari, V.; Mitrakou, A.; Kountouri, A.; Thymis, J., et al. Association of COVID-19 with impaired endothelial glycocalyx, vascular function and myocardial deformation 4 months after infection. Eur J Heart Fail. 2021;23:1916-1926. [CrossRef]
- Chioh, F.W.; Fong, S.W.; Young, B.E.; Wu, K.X., et al. Convalescent COVID-19 patients are susceptible to endothelial dysfunction due to persistent immune activation. Elife. 2021;10. [CrossRef]
- Masola, V.; Zaza, G.; Arduini, A.; Onisto, M., et al. Endothelial Glycocalyx as a Regulator of Fibrotic Processes. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22: 2996. [CrossRef]
- Dreyfuss, J.L.; Regatieri, C.V.; Jarrouge, T.R.; Cavalheiro, R.P., et al. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans: structure, protein interactions and cell signaling. An Acad Bras Cienc. 2009;81:409-429. [CrossRef]
- Stahl, K.; Gronski, P.A.; Kiyan, Y.; Seeliger, B., et al. Injury to the Endothelial Glycocalyx in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020;202:1178-1181. [CrossRef]
- Potje, S.R.; Costa, T.J.; Fraga-Silva, T.F.C.; Martins, R.B., et al. Heparin prevents in vitro glycocalyx shedding induced by plasma from COVID-19 patients. Life Sci. 2021;276:119376. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Cheng, S.; Sol, W.; van der Velden, A.I.M., et al. Heparan sulfate mimetic fucoidan restores the endothelial glycocalyx and protects against dysfunction induced by serum of COVID-19 patients in the intensive care unit. ERJ Open Res. 2022;8:00652-2021. [CrossRef]
- Drost, C.C.; Rovas, A.; Osiaevi, I.; Rauen, M., et al. Heparanase Is a Putative Mediator of Endothelial Glycocalyx Damage in COVID-19 - A Proof-of-Concept Study. Front Immunol. 2022;13:916512. [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez Rodriguez, E.; Ostrowski, S.R.; Cardenas, J.C.; Baer, L.A., et al. Syndecan-1: A Quantitative Marker for the Endotheliopathy of Trauma. J Am Coll Surg. 2017;225:419-427. [CrossRef]
- Lipowsky, H.H.; Sah, R., Lescanic, A. Relative roles of doxycycline and cation chelation in endothelial glycan shedding and adhesion of leukocytes. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011;300:H415-422. [CrossRef]
- Popova, T.G.; Millis, B.; Bailey, C., Popov, S.G. Platelets, inflammatory cells, von Willebrand factor, syndecan-1, fibrin, fibronectin, and bacteria co-localize in the liver thrombi of Bacillus anthracis-infected mice. Microb Pathog. 2012;52:1-9. [CrossRef]
- Smart, L.; Bosio, E.; Macdonald, S.P.J.; Dull, R., et al. Glycocalyx biomarker syndecan-1 is a stronger predictor of respiratory failure in patients with sepsis due to pneumonia, compared to endocan. J Crit Care. 2018;47:93-98. [CrossRef]
- Karampoor, S.; Zahednasab, H.; Farahmand, M.; Mirzaei, R., et al. A possible pathogenic role of Syndecan-1 in the pathogenesis of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;97:107684. [CrossRef]
- Kozlowski, P.; Smiarowski, M.; Przyborska, W.; Zemlik, K., et al. Mild-to-Moderate COVID-19 Convalescents May Present Pro-Longed Endothelium Injury. J Clin Med. 2022;11: 6461. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).