Submitted:
30 December 2022
Posted:
04 January 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
| SHAME | GUILT | |
|---|---|---|
| Target | What we are: related to the entire self. ”I’m bad” |
What we do: related to specific behaviours “What I did has been bad” |
| Level | Interpersonal – it occurs only with others | Intrapsychic – it occurs alone |
| Emotional activation | Painful | Less painful |
| Emotional perception | Difficult to recognize | Easy to recognize |
| Action tendency | Motivates hiding and inhibition | Motivates reparation to the situation |
| Relation with aggression, hostility, violence, externalization | Increased for shame-proneness individuals | Decreased for guilt- proneness individuals |
| Scapegoat | Blame mainly others | Blame myself |
| Responsibility | Deflected outward | Accepted |
2. Materials and Methods
- 1)
- paper originally published in English;
- 2)
- fMRI or PET studies including task-related whole brain analyses. Studies reporting region of interest (ROI analyses, resting-state fMRI analyses, diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) or voxel-based morphometry (VBM) were excluded;
- 3)
- participants were healthy adults: In case of studies involving neurological or psychiatric patients, children or adolescents, we considered only contrasts involving healthy controls, if reported;
- 4)
- Studies investigating the neural underpinnings of shame and guilt were included into two different sets, for two distinct meta-analyses. Specifically, we included studies contrasting shame/embarrassment vs. neutral or other emotional conditions and guilt vs. neutral or other emotional conditions. Studies failing to distinguish embarrassment/shame and guilt were excluded.
| Subset | Authors | Paradigm | Stimulus type | Contrasts | Foci | Subjects (Females) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shame/ | Bas-Hoogendam et al. 2017 | Induction | Verbal scripts | Unintentional violations > neutral | 5 | 21(15) |
| embarrassment | Berthoz et al. 2002 | Induction | Verbal scripts | Unintentional violations > normal | 15 | 12(0) |
| Finger et al. 2006 | Induction | Verbal scripts | Moral and social with audience > social and neutral without audience | 2 | 16(-) | |
| Krach et al. 2011 | Induction | Vignettes | Vicarious embarrassment > neutral | 9 | 32(17) | |
| Krach et al. 2015 | Induction | Vignettes | Social pain > social neutral | 17 | 16(0) | |
| Laneri et al. 2017 | Induction | Vignettes | Empathic embarrassment > neutral | 14 | 51(21) | |
| Melchers et al. 2015 | Induction | Pictures | Vicarious embarrassment > neutral | 6 | 60(39) | |
| Michl et al. 2012 | Induction | Verbal scripts | Shame > neutral | 10 | 14(7) | |
| Morita et al. 2008 | Induction | self- and other-faces | Self-face > other-face | 9 | 19(10) | |
| Morita et al. 2012 | Induction | self- and other-faces | Self-face > other-face | 29 | 15(2) | |
| Morita et al. 2014 | Induction | self- and other-faces | Self-face > other-face | 17 | 32(16) | |
| Morita et al. 2016 | Induction | self- and other-faces | Self-face > other-face | 13 | 18(0) | |
| Paulus et al. 2015 | Induction | Vignettes | Positive correlation of vicarious embarrassment | 11 | 32(17) | |
| Paulus et al. 2018 | Induction | Vignettes | Fremdscham > neutral | 15 | 34(0) | |
| Takahashi et al. 2004 | Induction | Verbal scripts | Embarrassment > neutral | 10 | 19(9) | |
| Wagner et al. 2011 | Recollection | Verbal scripts | Shame > neutral | 10 | 15(15) | |
| Zhu et al. 2018 | Interpersonal game | Pictorial stimuli (dots) | Shame > happiness | 2 | 30(17) | |
| Guilt | Basile B et al. 2011 | Induction | Verbal and facial stimuli | Guilt > anger and sadness | 3 | 22(13) |
| Finger et al. 2006 | Induction | Verbal scripts | Moral > social and neutral | 5 | 16(-) | |
| Fourie et al. 2014 | implicit association task | verbal and facial stimuli | Prejudice feedback > neutral feedback | 5 | 22(22) | |
| Gilead et al. 2016 | Induction | Verbal scripts | Guilt > anger, joy, pride | 10 | 19(14) | |
| Gradin et al. 2016 | Interpersonal game | Verbal | Defection > cooperation | 6 | 25(17) | |
| Green et al. 2012 | Induction | Verbal scripts | Guilt > indignation (Within HC) | 7 | 22(18) | |
| Kédia et al. 2008 | Induction | Verbal scripts | Guilt > self-anger | 4 | 29(14) | |
| Michl et al. 2012 | Induction | Verbal scripts | Guilt > neutral | 19 | 14(7) | |
| Molenberghs et al. 2015 | Induction | Video | Civilians > Soldiers | 3 | 48(24) | |
| Morey et al. 2012 | Induction | Verbal scripts | Positive correlation of guilt | 6 | 16(0) | |
| Peth et al. 2015 | Recollection | Verbal | Guilty action > neutral | 10 | 20(6) | |
| Shin et al. 2000 | Recollection | Verbal scripts | Guilt > neutral | 8 | 8(0) | |
| Takahashi et al. 2004 | Induction | Verbal scripts | Guilt > neutral | 5 | 19(9) | |
| Ty et al. 2017 | Induction | Verbal and pictorial stimuli | Restitution > harm | 1 | 18(9) | |
| Wagner et al. 2011 | Recollection | Verbal scripts | Guilt > neutral | 24 | 15(15) | |
| Yu et al. 2014 | Interpersonal game | Pictorial stimuli (dots) | Self-incorrect > both incorrect | 1 | 24(11) | |
| Zhu et al. 2018 | Interpersonal game | Pictorial stimuli (dots) | Guilt > happiness | 5 | 30(17) |
2.1. Statistical Analysis
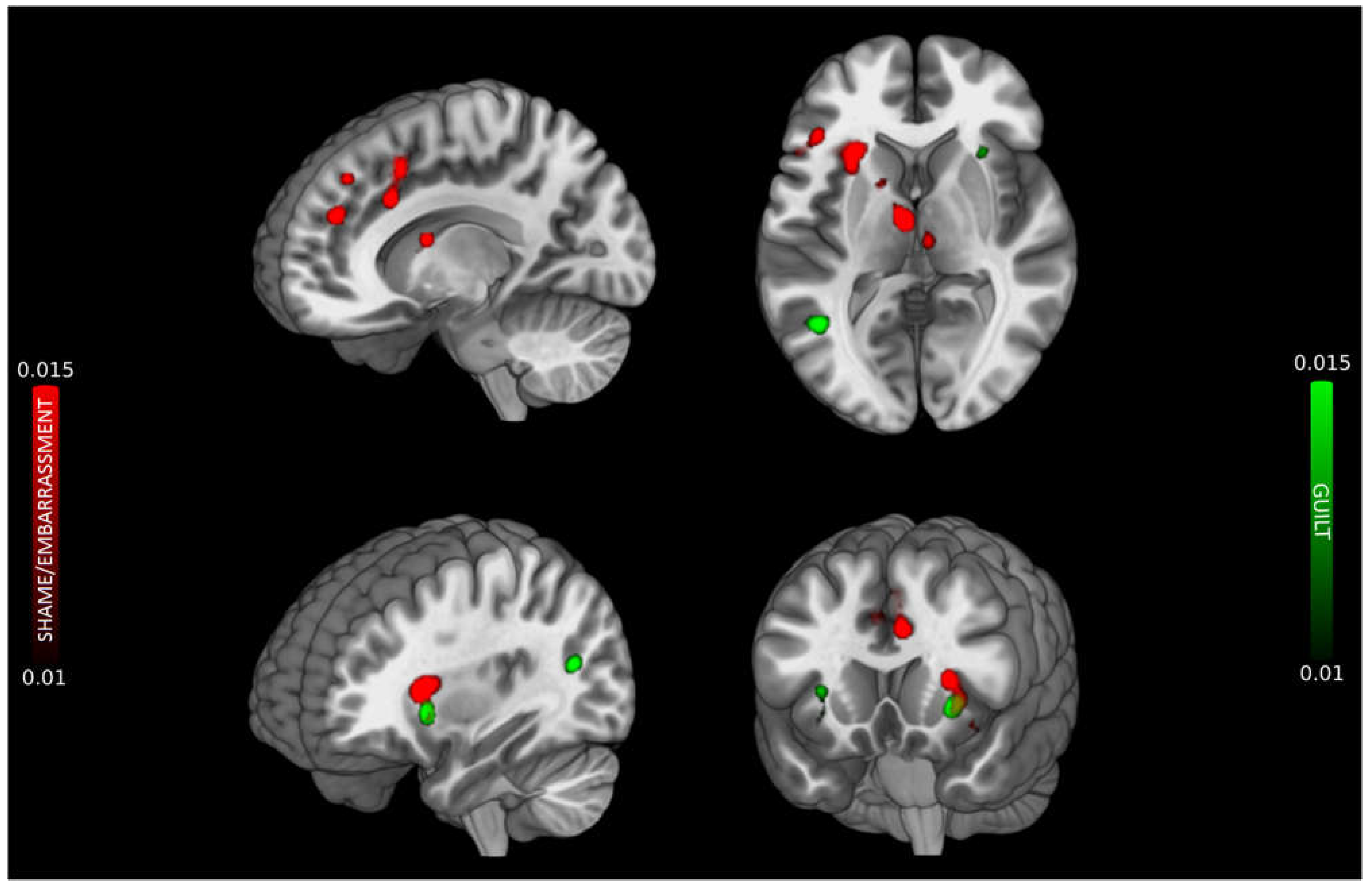
3. Results
3.1. Shame/Embarrassment
3.2. Guilt
3.3. Conjunction and subtraction analyses
4. Discussion
4.1. Common areas
4.2. The Shame network
4.3. The Guilt network
5. Conclusions
6. Limitations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alexander, W. H., & Brown, J. W. (2011). Medial prefrontal cortex as an action-outcome predictor. Nature neuroscience, 14(10), 1338. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (DSM-5®). American Psychiatric Pub.
- Amodio, D. M., & Frith, C. D. (2006). Meeting of minds: the medial frontal cortex and social cognition. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 7(4), 268. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, S. W., Bechara, A., Damasio, H., Tranel, D., & Damasio, A. R. (1999). Impairment of social and moral behavior related to early damage in human prefrontal cortex. Nature neuroscience, 2(11), 1032. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asendorpf, J. B. Evidence for situational specificity and a two-factor model. (1990). Development of inhibition during childhood.
- Aydede, M. (Ed.). (2005). Pain: new essays on its nature and the methodology of its study. MIT Press.
- Bas-Hoogendam, J. M., van Steenbergen, H., Kreuk, T., van der Wee, N. J., & Westenberg, P. M. (2017). How embarrassing! The behavioral and neural correlates of processing social norm violations. PloS one, 12(4), e0176326. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basile, B. Mancini, F., Macaluso, E., Caltagirone, C., Frackowiak, R. S., & Bozzali, M. (2011). Deontological and altruistic guilt: evidence for distinct neurobiological substrates. Human Brain Mapping, 32(2), 229-239. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastin, C., Harrison, B. J., Davey, C. G., Moll, J., & Whittle, S. (2016). Feelings of shame, embarrassment and guilt and their neural correlates: A systematic review. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 71, 455-471. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumeister, R. F., & Leary, M. R. (1995). The need to belong: desire for interpersonal attachments as a fundamental human motivation. Psychological bulletin, 117(3), 497.
- Berntson, G. G., Norman, G. J., Bechara, A., Bruss, J., Tranel, D., & Cacioppo, J. T. (2011). The insula and evaluative processes. Psychological science, 22(1), 80-86. [CrossRef]
- Berthier, M., Starkstein, S., & Leiguarda, R. (1988). Asymbolia for pain: A sensory-limbic disconnection syndrome. Annals of neurology, 24(1), 41-49. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthoz, S., Armony, J. L., Blair, R. J. R., & Dolan, R. J. (2002). An fMRI study of intentional and unintentional (embarrassing) violations of social norms. Brain, 125(8), 1696-1708. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, R. J. R. (1995). A cognitive developmental approach to morality: Investigating the psychopath. Cognition, 57(1), 1-29. [CrossRef]
- Buss, A. (2001). Psychological dimensions of the self. Thousand Oaks, CA, US: Sage Publications, Inc.
- Carretié, L., Albert, J., López-Martín, S., & Tapia, M. (2009). Negative brain: an integrative review on the neural processes activated by unpleasant stimuli. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 71(1), 57-63. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, A. D., & Craig, A. D. (2009). How do you feel--now? The anterior insula and human awareness. Nature reviews neuroscience, 10(1). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crozier, W. R. (2014). Differentiating shame from embarrassment. Emotion Review, 6(3), 269-276. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dadomo, H., Salvato, G., Lapomarda, G., Ciftci, Z., Messina, I., Grecucci, A. (2022). Structural features predict sexual trauma and interpersonal problems in Borderline personality disorder but not in controls: a Multi-voxel pattern analysis. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 23.
- Decety, J., & Lamm, C. (2007). The role of the right temporoparietal junction in social interaction: how low-level computational processes contribute to meta-cognition. The Neuroscientist, 13(6), 580-593. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Panfilis, C., Schito, G., Generali, I., Gozzi, L., Ossola, P., Marchesi, C., Grecucci, A. (2019). Emotions at the border: Increased punishment behavior during fair interpersonal exchanges in Borderline Personality Disorder. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 128(2), 162-172.
- Eickhoff, S. B., Bzdok, D., Laird, A. R., Kurth, F., & Fox, P. T. (2012). Activation likelihood estimation meta-analysis revisited. Neuroimage, 59(3), 2349-2361. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eickhoff, S. B., Laird, A. R., Grefkes, C., Wang, L. E., Zilles, K., & Fox, P. T. (2009). Coordinate-based activation likelihood estimation meta-analysis of neuroimaging data: A random-effects approach based on empirical estimates of spatial uncertainty. Human brain mapping, 30(9), 2907-2926.
- Eickhoff, S. B., Nichols, T. E., Laird, A. R., Hoffstaedter, F., Amunts, K., Fox, P. T.,... & Eickhoff, C. R. (2016). Behavior, sensitivity, and power of activation likelihood estimation characterized by massive empirical simulation. Neuroimage, 137, 70-85. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenberger, N. I. (2012). The pain of social disconnection: examining the shared neural underpinnings of physical and social pain. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 13(6), 421. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekman, P. (1992). An argument for basic emotions. Cognition & emotion, 6(3-4), 169-200. [CrossRef]
- Etkin, A., Büchel, C., & Gross, J. J. (2015). The neural bases of emotion regulation. Nature reviews neuroscience, 16(11), 693. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finger, E. C., Marsh, A. A., Kamel, N., Mitchell, D. G., & Blair, J. R. (2006). Caught in the act: The impact of audience on the neural response to morally and socially inappropriate behavior. NeuroImage, 33(1), 414-421. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiske, A. P. (1991). Structures of social life: The four elementary forms of human relations: Communal sharing, authority ranking, equality matching, market pricing. New York, NY, US: Free Press.
- Foltz, E. L., & White Jr, L. E. (1962). Pain “relief” by frontal cingulumotomy. Journal of neurosurgery, 19(2), 89-100. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fourie, M. M., Thomas, K. G., Amodio, D. M., Warton, C. M., & Meintjes, E. M. (2014). Neural correlates of experienced moral emotion: an fMRI investigation of emotion in response to prejudice feedback. Social neuroscience, 9(2), 203-218. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frith, C. D., & Frith, U. (2006). The neural basis of mentalizing. Neuron, 50(4), 531-534.
- Garrigan, B., Adlam, A. L., & Langdon, P. E. (2016). The neural correlates of moral decision-making: A systematic review and meta-analysis of moral evaluations and response decision judgements. Brain and cognition, 108, 88-97. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giammarco, E. A., & Vernon, P. A. (2015). Interpersonal guilt and the dark triad. Personality and Individual Differences, 81, 96-101. [CrossRef]
- Gibson, M. (2015). Shame and guilt in child protection social work: new interpretations and opportunities for practice. Child & Family Social Work, 20(3), 333-343. [CrossRef]
- Gifuni, A. J., Kendal, A., & Jollant, F. (2017). Neural mapping of guilt: a quantitative meta-analysis of functional imaging studies. Brain imaging and behavior, 11(4), 1164-1178. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilead, M., Katzir, M., Eyal, T., & Liberman, N. (2016). Neural correlates of processing “self-conscious” vs.“basic” emotions. Neuropsychologia, 81, 207-218. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glahn, D. C., Laird, A. R., Ellison-Wright, I., Thelen, S. M., Robinson, J. L., Lancaster, J. L.,... & Fox, P. T. (2008). Meta-analysis of gray matter anomalies in schizophrenia: application of anatomic likelihood estimation and network analysis. Biological psychiatry, 64(9), 774-781. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goss, K., & Allan, S. (2009). Shame, pride and eating disorders. Clinical psychology & psychotherapy, 16(4), 303-316. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gradin, V. B., Pérez, A., Macfarlane, J. A., Cavin, I., Waiter, G., Tone, E. B.,... & Steele, J. D. (2016). Neural correlates of social exchanges during the Prisoner’s Dilemma game in depression. Psychological medicine, 46(6), 1289-1300. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grecucci, A., Frederickson, J., Job, R. (2017). Editorial: Advances in Emotion Regulation: from neuroscience to psychotherapy. Frontiers in Psychology, Special issue.
- Grecucci, A., Giorgetta, C., Van’t Wout, M., Bonini, N., & Sanfey, A. G. (2013). Reappraising the ultimatum: an fMRI study of emotion regulation and decision making. Cerebral Cortex, 23(2), 399-410. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grecucci, A., Lapomarda, G., Messina I., Monachesi, B., Sorella, S., Siugzdaite, R (2022). Structural features related to affective instability correctly classify the diagnosis of Borderline Personality Disorder. A Supervised Machine Learning approach. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 2022.
- Grecucci, A., Neresini, A., Job, R. (2021). The moral algorithm. Toward a neuropsychological model of shame. In Giacomoni, P., Valentini, N., Dellantonio, S. Eds. The Dark Side: Philosophical Reflections on the “Negative Emotions”.
- Green, S., Ralph, M. A. L., Moll, J., Deakin, J. F., & Zahn, R. (2012). Guilt-selective functional disconnection of anterior temporal and subgenual cortices in major depressive disorder. Archives of General Psychiatry, 69(10), 1014-1021. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, S., Simmons, A., Kumari, V., Howard, M., Hodgins, S., & Blackwood, N. (2012). The antisocial brain: psychopathy matters: a structural MRI investigation of antisocial male violent offenders. Archives of general psychiatry, 69(9), 962-972. [CrossRef]
- Grieve, S. M., Korgaonkar, M. S., Koslow, S. H., Gordon, E., & Williams, L. M. (2013). Widespread reductions in gray matter volume in depression. NeuroImage: Clinical, 3, 332-339. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haidt, J. (2003). The moral emotions. Handbook of affective sciences, 11(2003), 852-870.
- Harman, R., & Lee, D. (2010). The role of shame and self-critical thinking in the development and maintenance of current threat in post-traumatic stress disorder. Clinical psychology & psychotherapy, 17(1), 13-24. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedman, E., Ström, P., Stünkel, A., & Mörtberg, E. (2013). Shame and guilt in social anxiety disorder: effects of cognitive behavior therapy and association with social anxiety and depressive symptoms. PloS One, 8(4), e61713. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodgins, S., De Brito, S. A., Chhabra, P., & Côté, G. (2010). Anxiety disorders among offenders with antisocial personality disorders: a distinct subtype?. The Canadian Journal of Psychiatry, 55(12), 784-791. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, M. L. (1982). Development of prosocial motivation: Empathy and guilt. In The development of prosocial behavior (pp. 281-313).
- Johnson, S. C., Schmitz, T. W., Kawahara-Baccus, T. N., Rowley, H. A., Alexander, A. L., Lee, J., & Davidson, R. J. (2005). The cerebral response during subjective choice with and without self-reference. Journal of cognitive neuroscience, 17(12), 1897-1906. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufman, G. (1989). The psychology of shame: Theory and treatment of shame-based syndromes. New York, NY, US: Springer Publishing Co.
- Kédia, G., Berthoz, S., Wessa, M., Hilton, D., & Martinot, J. L. (2008). An agent harms a victim: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study on specific moral emotions. Journal of cognitive neuroscience, 20(10), 1788-1798. [CrossRef]
- Keltner, D., & Buswell, B. N. (1996). Evidence for the distinctness of embarrassment, shame, and guilt: A study of recalled antecedents and facial expressions of emotion. Cognition and Emotion, 10, 155-171. [CrossRef]
- Keltner, D., & Buswell, B. N. (1997). Embarrassment: its distinct form and appeasement functions. Psychological bulletin, 122(3), 250.
- Krach, S., Cohrs, J. C., de Echeverría Loebell, N. C., Kircher, T., Sommer, J., Jansen, A., & Paulus, F. M. (2011). Your flaws are my pain: Linking empathy to vicarious embarrassment. PLoS One, 6(4), e18675. [CrossRef]
- Krach, S., Kamp-Becker, I., Einhäuser, W., Sommer, J., Frässle, S., Jansen, A.,... & Paulus, F. M. (2015). Evidence from pupillometry and fMRI indicates reduced neural response during vicarious social pain but not physical pain in autism. Human Brain Mapping, 36(11), 4730-4744. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroll, J., & Egan, E. (2004). Psychiatry, moral worry, and the moral emotions. Journal of Psychiatric Practice®, 10(6), 352-360.
- Kurczek, J., Wechsler, E., Ahuja, S., Jensen, U., Cohen, N. J., Tranel, D., & Duff, M. (2015). Differential contributions of hippocampus and medial prefrontal cortex to self-projection and self-referential processing. Neuropsychologia, 73, 116-126. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laird, A. R., Fox, P. M., Price, C. J., Glahn, D. C., Uecker, A. M., Lancaster, J. L.,... & Fox, P. T. (2005). ALE meta-analysis: Controlling the false discovery rate and performing statistical contrasts. Human brain mapping, 25(1), 155-164. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laneri, D., Krach, S., Paulus, F. M., Kanske, P., Schuster, V., Sommer, J., & Müller-Pinzler, L. (2017). Mindfulness meditation regulates anterior insula activity during empathy for social pain. Human brain mapping, 38(8), 4034-4046. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leith, K. P., & Baumeister, R. F. (1998). Empathy, shame, guilt, and narratives of interpersonal conflicts: Guilt-prone people are better at perspective taking. Journal of personality, 66(1), 1-37. [CrossRef]
- Lewis, H. B. (1971). Shame and guilt in neurosis. Psychoanalytic review, 58(3), 419.
- Lewis, M., Haviland-Jones, J. M., & Feldman Barrett, L. (1993). Handbook of Emotions. New York.
- Lewis, P. A., Critchley, H. D., Rotshtein, P., & Dolan, R. J. (2006). Neural correlates of processing valence and arousal in affective words. Cerebral cortex, 17(3), 742-748. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L., Wu, M., Liao, Y., Ouyang, L., Du, M., Lei, D.,... & Gong, Q. (2014). Grey matter reduction associated with posttraumatic stress disorder and traumatic stress. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 43, 163-172. [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, A. W., Cohen, J. D., Stenger, V. A., & Carter, C. S. (2000). Dissociating the role of the dorsolateral prefrontal and anterior cingulate cortex in cognitive control. Science, 288(5472), 1835-1838. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDonald, G., & Leary, M. R. (2005). Why does social exclusion hurt? The relationship between social and physical pain. Psychological bulletin, 131(2), 202. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melchers, M., Markett, S., Montag, C., Trautner, P., Weber, B., Lachmann, B.,... & Reuter, M. (2015). Reality TV and vicarious embarrassment: An fMRI study. NeuroImage, 109, 109-117. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michl, P., Meindl, T., Meister, F., Born, C., Engel, R. R., Reiser, M., & Hennig-Fast, K. (2012). Neurobiological underpinnings of shame and guilt: a pilot fMRI study. Social cognitive and affective neuroscience, 9(2), 150-157. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, R., & Mason, S. E. (2005). Shame and guilt in first-episode schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorders. Journal of Contemporary Psychotherapy, 35(2), 211-221.
- Mitchell, J. P., Heatherton, T. F., & Macrae, C. N. (2002). Distinct neural systems subserve person and object knowledge. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 99(23), 15238-15243. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modinos, G., Ormel, J., & Aleman, A. (2009). Activation of anterior insula during self-reflection. PloS one, 4(2), e4618. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molenberghs, P., Ogilvie, C., Louis, W. R., Decety, J., Bagnall, J., & Bain, P. G. (2015). The neural correlates of justified and unjustified killing: an fMRI study. Social cognitive and affective neuroscience, 10(10), 1397-1404. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moll, J., De Oliveira-Souza, R., & Zahn, R. (2008). The neural basis of moral cognition. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1124(1), 161-180. [CrossRef]
- Morey, R. A., McCarthy, G., Selgrade, E. S., Seth, S., Nasser, J. D., & LaBar, K. S. (2012). Neural systems for guilt from actions affecting self versus others. Neuroimage, 60(1), 683-692. [CrossRef]
- Morita, T., Itakura, S., Saito, D. N., Nakashita, S., Harada, T., Kochiyama, T., & Sadato, N. (2008). The role of the right prefrontal cortex in self-evaluation of the face: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 20(2), 342-355. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, T., Kosaka, H., Saito, D. N., Fujii, T., Ishitobi, M., Munesue, T.,... & Sadato, N. (2016). Neural correlates of emotion processing during observed self-face recognition in individuals with autism spectrum disorders. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 26, 16-32. [CrossRef]
- Morita, T., Kosaka, H., Saito, D. N., Ishitobi, M., Munesue, T., Itakura, S.,... & Sadato, N. (2012). Emotional responses associated with self-face processing in individuals with autism spectrum disorders: An fMRI study. Social Neuroscience, 7(3), 223-239. [CrossRef]
- Morita, T., Tanabe, H. C., Sasaki, A. T., Shimada, K., Kakigi, R., & Sadato, N. (2013). The anterior insular and anterior cingulate cortices in emotional processing for self-face recognition. Social cognitive and affective neuroscience, 9(5), 570-579. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orth, U., Berking, M., & Burkhardt, S. (2006). Self-conscious emotions and depression: Rumination explains why shame but not guilt is maladaptive. Personality and social psychology bulletin, 32(12), 1608-1619. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulus, F. M., Müller-Pinzler, L., Jansen, A., Gazzola, V., & Krach, S. (2014). Mentalizing and the role of the posterior superior temporal sulcus in sharing others’ embarrassment. Cerebral cortex, 25(8), 2065-2075. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulus, F. M., Müller-Pinzler, L., Stolz, D. S., Mayer, A. V., Rademacher, L., & Krach, S. (2018). Laugh or cringe? Common and distinct processes of reward-based schadenfreude and empathy-based fremdscham. Neuropsychologia, 116, 52-60. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peth, J., Sommer, T., Hebart, M. N., Vossel, G., Büchel, C., & Gamer, M. (2015). Memory detection using fMRI—Does the encoding context matter?. NeuroImage, 113, 164-174. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philippi, C. L., Duff, M. C., Denburg, N. L., Tranel, D., & Rudrauf, D. (2012). Medial PFC damage abolishes the self-reference effect. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 24(2), 475-481. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piretti, L., Pappaianni, E., Lunardelli, A., Zorzenon, I., Ukmar, M., Pesavento, V., Rumiati, R.I., Job, R., Grecucci, A. (2020). The role of amygdala in self-conscious emotions in a patient with acquired bilateral damage. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 14, 677.
- Piretti, L., Pappaianni, E., Rumiati, R., Job, R., Grecucci, A. (2021). Dissociating the role of dlPFC and dACC/dmPFC in emotional processing using tDCS. Cognitive, Affective Behavioral Neuroscience.
- Price, D. D. (2000). Psychological and neural mechanisms of the affective dimension of pain. Science, 288(5472), 1769-1772. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Probyn, E. (2005). Blush: Faces of shame. U of Minnesota Press.
- Ridley, M., & Waal, F. B. D. (1996). The origins of virtue. Nature, 383(6603), 785-785.
- Ritter, K., Vater, A., Rüsch, N., Schröder-Abé, M., Schütz, A., Fydrich, T.,... & Roepke, S. (2014). Shame in patients with narcissistic personality disorder. Psychiatry research, 215(2), 429-437. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochat, P. (2009). Others in mind: Social origins of self-consciousness. Cambridge University Press.
- Rotge, J. Y., Langbour, N., Guehl, D., Bioulac, B., Jaafari, N., Allard, M.,... & Burbaud, P. (2010). Gray matter alterations in obsessive–compulsive disorder: an anatomic likelihood estimation meta-analysis. Neuropsychopharmacology, 35(3), 686. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, M., Shohamy, D., & Wager, T. D. (2012). Ventromedial prefrontal-subcortical systems and the generation of affective meaning. Trends in cognitive sciences, 16(3), 147-156. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabini, J., & Silver, M. (2005). Why emotion names and experiences don’t neatly pair. Psychological inquiry, 16(1), 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, A., Vaitl, D., & Schienle, A. (2010). Regional grey matter volume abnormalities in bulimia nervosa and binge-eating disorder. Neuroimage, 50(2), 639-643. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheff, T. J. (1994). Microsociology: Discourse, emotion, and social structure. University of Chicago Press.
- Scherer, K. R., Schorr, A., & Johnstone, T. (Eds.). (2001). Appraisal processes in emotion: Theory, methods, research. Oxford University Press.
- Schmitz, T. W., Rowley, H. A., Kawahara, T. N., & Johnson, S. C. (2006). Neural correlates of self-evaluative accuracy after traumatic brain injury. Neuropsychologia, 44(5), 762-773. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, L. M., Dougherty, D. D., Orr, S. P., Pitman, R. K., Lasko, M., Macklin, M. L.,... & Rauch, S. L. (2000). Activation of anterior paralimbic structures during guilt-related script-driven imagery. Biological psychiatry, 48(1), 43-50. [CrossRef]
- Simmonds, D. J., Pekar, J. J., & Mostofsky, S. H. (2008). Meta-analysis of Go/No-go tasks demonstrating that fMRI activation associated with response inhibition is task-dependent. Neuropsychologia, 46(1), 224-232. [CrossRef]
- Sober, E., & Wilson, D. S. (1998). Unto others: The evolution and psychology of unselfish behavior. Cambridge/Mass.
- Street, A. E., & Arias, I. (2001). Psychological abuse and posttraumatic stress disorder in battered women: Examining the roles of shame and guilt. Violence and victims, 16(1), 65. [CrossRef]
- Sznycer, D. (2018). Forms and Functions of the Self-Conscious Emotions. Trends in cognitive sciences, 23(2), 143-157. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, H., Yahata, N., Koeda, M., Matsuda, T., Asai, K., & Okubo, Y. (2004). Brain activation associated with evaluative processes of guilt and embarrassment: an fMRI study. Neuroimage, 23(3), 967-974. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tangney, J. P. (2003). Self-relevant emotions. In M. R. Leary & J. P. Tangney (Eds.), Handbook of self and identity (pp. 384-400). New York, NY, US: Guilford Press.
- Tangney, J. P., Miller, R. S., Flicker, L., & Barlow, D. H. (1996). Are shame, guilt and embarrassment distinct emotions? Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 70, 1256-1267. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tangney, J. P., Stuewig, J., & Martinez, A. G. (2014). Two faces of shame: the roles of shame and guilt in predicting recidivism. Psych. Sci. 2014 Mar;25(3):799-805. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tangney, J. P., Stuewig, J., & Mashek, D. J. (2007). Moral emotions and moral behavior. Annu. Rev. Psychol., 58, 345-372. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tangney, J. P., Wagner, P., & Gramzow, R. (1992). Proneness to shame, proneness to guilt, and psychopathology. Journal of abnormal psychology, 101(3), 469. [CrossRef]
- Tow, P. M., & Whitty, C. W. M. (1953). Personality changes after operations on the cingulate gyrus in man. Journal of neurology, neurosurgery, and psychiatry, 16(3), 186.
- Troop, N. A., Allan, S., Serpell, L., & Treasure, J. L. (2008). Shame in women with a history of eating disorders. European Eating Disorders Review, 16(6), 480-488. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turkeltaub, P. E., Eickhoff, S. B., Laird, A. R., Fox, M., Wiener, M., & Fox, P. (2012). Minimizing within-experiment and within-group effects in activation likelihood estimation meta-analyses. Human brain mapping, 33(1), 1-13. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ty, A., Mitchell, D. G., & Finger, E. (2017). Making amends: Neural systems supporting donation decisions prompting guilt and restitution. Personality and Individual Differences, 107, 28-36. [CrossRef]
- van der Meer, L., Costafreda, S., Aleman, A., & David, A. S. (2010). Self-reflection and the brain: a theoretical review and meta-analysis of neuroimaging studies with implications for schizophrenia. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 34(6), 935-946. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vytal, K., & Hamann, S. (2010). Neuroimaging support for discrete neural correlates of basic emotions: a voxel-based meta-analysis. Journal of cognitive neuroscience, 22(12), 2864-2885. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, U., N’diaye, K., Ethofer, T., & Vuilleumier, P. (2011). Guilt-specific processing in the prefrontal cortex. Cerebral cortex, 21(11), 2461-2470. [CrossRef]
- Weingarden, H., & Renshaw, K. D. (2015). Shame in the obsessive compulsive related disorders: a conceptual review. Journal of affective disorders, 171, 74-84. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, Y., & Tsai, J. (2007). Cultural models of shame and guilt. The self-conscious emotions: Theory and research, 209-223.
- Xue, G., Aron, A. R., & Poldrack, R. A. (2008). Common neural substrates for inhibition of spoken and manual responses. Cerebral Cortex, 18(8), 1923-1932. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, C. P., Kung, S. S., Su, Y. F., Lin, W. C., Howng, S. L., & Kwan, A. L. (2005). Stereotactic bilateral anterior cingulotomy for intractable pain. Journal of clinical neuroscience, 12(8), 886-890. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H., Hu, J., Hu, L., & Zhou, X. (2013). The voice of conscience: neural bases of interpersonal guilt and compensation. Social cognitive and affective neuroscience, 9(8), 1150-1158. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, R., Feng, C., Zhang, S., Mai, X., & Liu, C. (2019). Differentiating guilt and shame in an interpersonal context with univariate activation and multivariate pattern analyses. NeuroImage, 186, 476-486. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zmigrod, L., Garrison, J. R., Carr, J., & Simons, J. S. (2016). The neural mechanisms of hallucinations: a quantitative meta-analysis of neuroimaging studies. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 69, 113-123. [CrossRef]

| Cluster # | Volume (mm^3) | Extrema Value | Coordinate | Side | Anatomical Label | BA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | y | z | ||||||
| 1 | 3896 | 27.37 | -28 | 22 | 8 | Left | Anterior Insula | |
| 17.81 | -36 | 20 | -8 | IFGorb | 47 | |||
| 2 | 2064 | 21.19 | -10 | 44 | 26 | Left | Medial frontal gyrus | 9 |
| 19.53 | -20 | 36 | 36 | Superior frontal gyrus | 9 | |||
| 17.05 | -6 | 38 | 42 | Medial frontal gyrus | 8 | |||
| 3 | 1976 | 29.51 | -6 | -10 | 10 | Left | Thalamus | |
| 18.24 | -14 | 4 | 14 | Left | Caudate | |||
| 15.41 | 6 | -20 | 6 | Right | Thalamus | |||
| 4 | 1688 | 22.70 | -6 | 14 | 44 | Left | Pre-SMA | 6 |
| 22.57 | -6 | 14 | 48 | Pre-SMA | 8 | |||
| 20.21 | -8 | 18 | 32 | dACC | 32 | |||
| 5† | 1016 | 16.64 | 4 | -2 | 34 | Right | dACC | 24 |
| 16.45 | 4 | 16 | 36 | dACC | 32 | |||
| 6† | 976 | 17.42 | -42 | 28 | 16 | Left | Middle frontal gyrus | 46 |
| 13.98 | -52 | 20 | 12 | IFGtri | 45 | |||
| 7† | 960 | 25.41 | 42 | 30 | 14 | Right | Middle frontal gyrus | 46 |
| 8† | 832 | 21.25 | 44 | 2 | 30 | Right | Precentral gyrus/IFGop | 9 |
| Cluster # | Volume (mm3) |
ALE value (*103) |
Coordinates | Side | Anatomical label | BA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | y | z | ||||||
| 1 | 1528 | 23.42 | -32 | 18 | -2 | Left | Anterior insula/IFGorb | 47 |
| 2 | 1080 | 20.34 | -44 | -58 | 16 | Left | Superior temporal gyrus | 22 |
| 3† | 848 | 14.65 | 30 | 20 | 4 | Right | Anterior insula | |
| 11.04 | 32 | 16 | -10 | |||||
| 10.81 | 28 | 16 | -6 | |||||
| Shame/embarrassment and Guilt | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cluster # | Volume (mm3) | ALE value (*103) | Coordinates | Side | Anatomical label | BA | ||
| x | y | z | ||||||
| 1 | 1160 | 18.76 | -34 | 18 | 0 | Left | Anterior insula/IFGorb | 47 |
| Shame/embarrassment vs. Guilt | ||||||||
| Cluster # | Volume (mm3) | Z-scores | Coordinates | Side | Anatomical label | BA | ||
| x | y | z | ||||||
| 1 | 1280 | 2.56 | 0 | -10 | 12 | Left | Thalamus | |
| 2.14 | -10 | 2 | 14 | Caudate | ||||
| 2 | 1280 | 3.06 | -30 | 20 | 14 | Left | Anterior insula | |
| 3 | 1200 | 2.56 | -8 | 17 | 43 | Left | dACC | 32 |
| 1.98 | -10 | 14 | 48 | Pre-SMA | 6 | |||
| 4 | 1000 | 3.06 | 0 | 4 | 36 | Right | dACC | 24 |
| 5 | 960 | 2.36 | 40 | 28 | 18 | Right | Middle frontal gyrus | 46 |
| 2.07 | 44 | 32 | 8 | IFGorb | 46 | |||
| 6 | 688 | 3.24 | -39 | 28 | 17 | Left | Middle frontal gyrus | 46 |
| 7 | 672 | 2.44 | -18 | 32 | 36 | Left | Middle frontal gyrus | 8 |
| 2.18 | -14 | 38 | 34 | Superior frontal gyrus | 9 | |||
| 2.13 | -20 | 40 | 36 | Superior frontal gyrus | 9 | |||
| 8 | 536 | 2.12 | 48 | 1 | 29 | Right | Precentral gyrus | 6 |
| 1.89 | 46 | 3 | 36 | Precentral gyrus | 6 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





