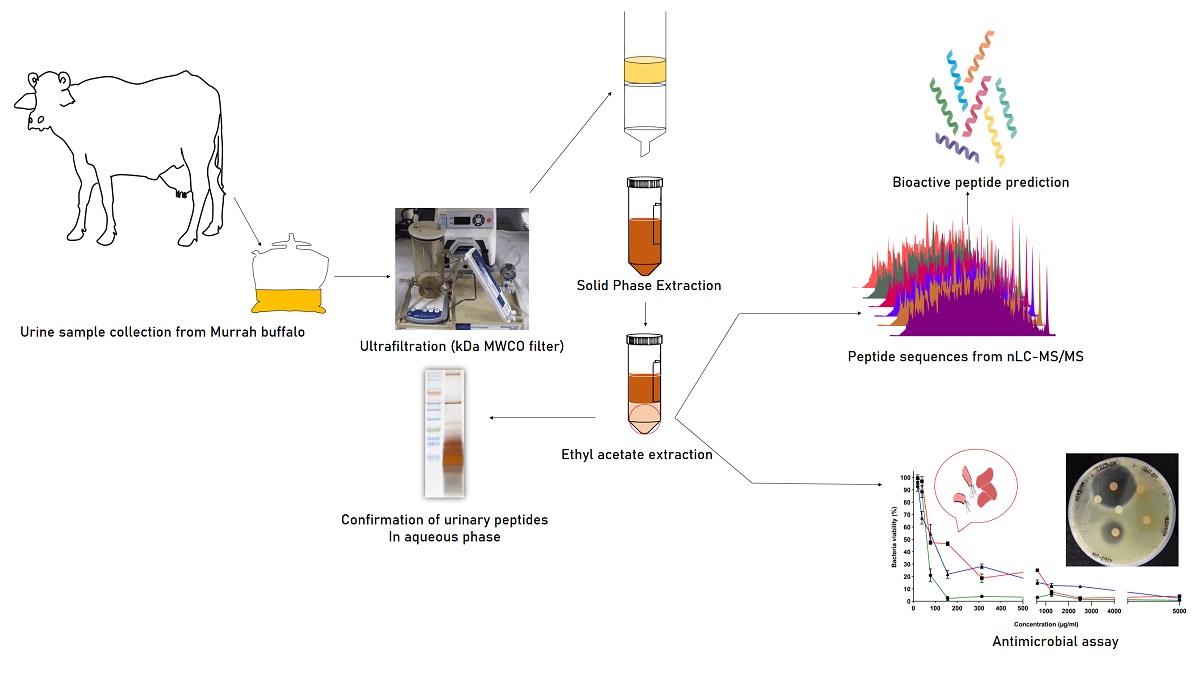
Urinary peptides are the products of systemic protein turn over which are excreted out of the body and hence can serve as an important biomarker for various pathophysiology. These peptides in other species of bovine have been reported to possess several bioactive properties. To investigate the potential of urinary peptides we generated a peptidome profile from the urine of Murrah Buffaloes (n=10). Urine samples were processed using <10 kDa MWCO filter, filtrate obtained was used for peptide extraction using Solid Phase Extraction (SPE). Eluate, obtained after SPE was extracted using ethyl acetate and the peptide-containing aqueous phase was collected. We extensively assessed the antimicrobial properties of the urinary aqueous phase. The nLC-MS/MS of the aqueous phase from 10 animals resulted in the identification of 8165 peptides originating from 6041 parent proteins. 76 Proteases responsible for the release of these sequences from precursor proteins were also identified. We further analyzed these peptide sequences to identify bioactive peptides and classify them into anti-cancerous, anti-hypertensive, anti-microbial, and anti-inflammatory groups with a special emphasis on antimicrobial properties. With this in mind, we simultaneously conducted experiments to evaluate antimicrobial properties of urinary aqueous extract on three pathogenic bacterial strains S. aureus, E. coli, & S. agalactiae.